
Introduction
Inflation is one of the economic phenomena that has attracted significant attention recently, particularly with its exacerbation as a result of rising global demand, which has been sapped by household savings, supported by government subsidies provided after the end of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The pandemic had paralyzed the global economy and plunged it into a severe recession due to the lockdown policies implemented by countries to limit the spread of the virus, which led to disruptions in supply chains.
However, the global economic recovery was hampered by the Ukrainian-Russian war and the problems it caused in food supply and a shortage in the supply of energy to the market, which led to an increase in its prices.
This increase was reflected in the rest of the goods and commodities, causing inflation to reach unprecedented rates that had a negative impact on the economic and social situation of countries, such as a decline in economic growth, an increase in unemployment, and a deterioration in the purchasing power of citizens, which created a state of social congestion that threatened the social peace of countries.
What inflation meaning
Inflation is a sustained and significant rise in the general level of prices over a specific period of time. With a decrease in purchasing power. The average prices of goods and services consumed in the economy during a given year, calculated using a standardized index called the general price index. Talking about inflation requires examining three key elements :
- Increase in the general price level
- The rise continues in time.
- Demand is greater than supply
Accordingly, the rise in the price of some goods but not others is not considered inflation because in this case, any increase in the price of some goods is offset by a decrease in the price of other goods, making the overall price level stable.
Therefore, inflation refers to an increase in the prices of most goods and services, particularly basic commodities, which constitute a significant portion of the consumer’s budget.
Also, a temporary rise in prices is not considered inflation because it is not continuous over time.
Types of inflation
1- Inflation Open
It is the overt or apparent inflation, and this rise in prices occurs in response to increased demand, meaning that prices rise to achieve balance between supply and demand without the state intervening in this process.
2- Suppressed inflation
It is the restricted or latent inflation, which is the inflation under which prices cannot expand or rise due to the presence of direct restrictions placed to control price increases through pricing or forced ceilings. Prices rise as soon as the restrictions are lifted.
This type of inflation results in :
- Decrease in product quality with constant price ;
- Administrative price fixing may lead to the emergence of a black market.
3- Hyperinflation
It is the large increase and sharp rise in prices followed by a similar increase in wages, which in turn leads to an increase in production costs. This results in a decrease in the investor’s profits, so he in turn increases prices to maintain his profit margin.
This increase in prices leads to demands to raise wages, which puts the economy in what is called the vicious cycle of inflation.It should be noted that this type of inflation is characterized by very strong inflation that occurs over a short period of time, which may result in a sharp decline in the currency and even its collapse.
4- Rapid inflation
It is a rapid rise in the general level of prices over a medium period of time, leading to a deterioration in the value of the currency.
5- Moderate inflation
It is an increase in the general level of prices at a constant rate over time that may lead to a decrease in the value of the currency in the future.
6- Creeping inflation
It is less dangerous to the national economy than hyperinflation because it is slow and gradual, and occurs over a long period of time. This type of inflation causes a decline in the value of the currency over a long period.
Causes of inflation
1- Economic growth
It is an important incentive for the emergence of inflation, as increased economic growth raises labor employment rates and thus increases the wage bill, which stimulates domestic demand, resulting in a rise in prices.
2- Inflation forecast
The psychological factor of anticipating inflation leads to an increase in current demand to avoid future price increases. This increase in demand leads to higher inflation rates.
3- Natural disasters and monopoly
These two factors lead to a reduction in the supply of goods and services and their insufficiency in meeting demand, resulting in an increase in prices according to the principle of the law of supply and demand.
4- Aggregate supply shortage
The rise in costs, primarily represented by increased wages and the increase in the prices of production requirements, leads to an increase in expenditures and thus a decrease in aggregate supply.
This situation is characterized by the occurrence of inflation and unemployment simultaneously in a phenomenon known as stagflation or inflation depression.
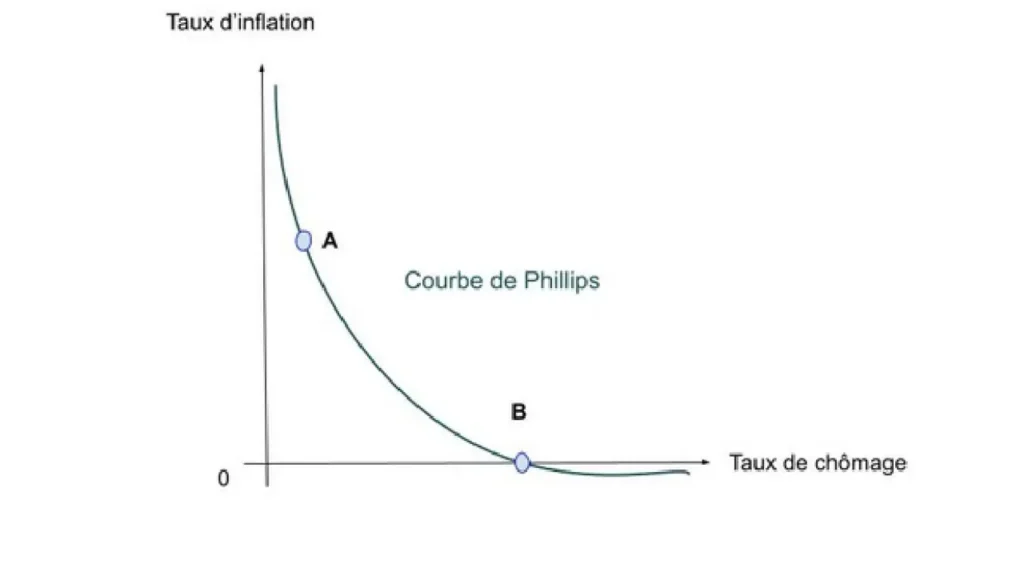
It should be noted that stagflation is a rare and abnormal phenomenon in the economic situation, given that the relationship between inflation and unemployment is an inverse relationship, meaning that : when unemployment was high, wages increased slowly; when unemployment was low, wages rose rapidly, as shown below in the Phillips Curve :
5- Restructuring the economy
Inflation may be linked to the nature of the structure of the production apparatus and the structure of the existing economic system. The structural aspects of the economy vary and take various forms. For example, we find :
- The low elasticity of the productive apparatus represented by the inability of the supply structure to change to match the demand structure ;
- Poor productivity ;
- The dominance of the rentier economy ;
- Lack of competition ;
- The economy is at the beginning of the development process, by focusing on infrastructure.
Sources of inflation
1- Cost-push inflation
It is the inflation that occurs when the prices of consumer and industrial goods continue to rise as a result of increased production costs resulting from the rise in the costs of production factors in economic institutions.
2- Demand-pull inflation
It occurs when prices rise as a result of an excess of aggregate demand over aggregate supply, whether in the goods market or the factors of production. When full employment is reached, the increase in demand and spending leads to an increase in prices to meet the excess of society’s productive capacity.
3- Inflation caused by the economic blockade
As a result of the blockade that a country may be subjected to for one reason or another, which prevents it from being able to import goods and merchandise from abroad, this will cause a shortage of products and consequently a rise in prices and the occurrence of inflation.
4- Inflation caused by monetary issuance
It arises as a result of an imbalance between the amount of money in circulation and the volume of goods and services offered. A large increase in the money supply compared to the volume of goods and services available in the national economy leads to an increase in prices and the occurrence of inflation.
5- Inflation source
The rise in prices is caused by an increase in the central bank’s dollar reserves, resulting from the existence of what is known as the dollar payment rule.
6- Borrowing-induced inflation
In an attempt to pay off its debts, the government may be forced to print more money without increasing production, which increases the money supply and generates inflation.
The government’s resort to raising taxes to increase its revenues may push companies to raise their prices to compensate for the tax rate imposed on them, thus causing inflation.
7- Inflation resulting from the entry of money from unknown sources and through illegal means
Money laundering and the resulting purchasing power for its owners, who are an unproductive group, puts pressure on the supply of goods by increasing consumption rates. This increased demand leads to higher prices.
8- Imported inflation
It occurs when prices rise as a result of the flow of global inflation into the country through imports. That is, if a country suffers from inflation, imports from this country will inevitably transfer this inflation to the local economy through imported goods and services.
This transfer is not total, but rather according to the volume of imports, which is expressed by the following equation :

This equation expresses that the Imported Inflation Rate increases with the increase in the volume of imports.
Conclusion
The views of economic experts have varied greatly in their dealing with the phenomenon of economic inflation, in terms of explanation and analysis, as well as ways to treat it, and attributed to the difference is due to the multiplicity of their orientations and the economic schools whose proposals they adopt.
For example, we find the quantity theory of money, it stipulates that the increase in the amount of money circulating in the market is the reason for the emergence of signs of inflation.
At the time you see Keynesian theory Inflation is an increase in purchasing power that is not matched by an increase in production, or an increase in real demand in an environment where all means of production are fully utilized. Then there is the contemporary quantity theory of money, whose proponents are called monetarists.
Milton Friedman is considered one of the fathers of this school, which holds that inflation is a purely monetary phenomenon, and its primary source is the growth of the money supply faster than production.

Приглашаем вас в путешествие по Уралу! Здесь вы найдете все, что нужно знать о подготовке к пешему походу.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Традиционные шаманские ритуалы Республики Тыва, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://rustrail.ru/%d1%80%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%bf%d1%83%d0%b1%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0-%d1%82%d1%8b%d0%b2%d0%b0-%d0%b8-%d0%b5%d1%91-%d1%88%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%b0%d0%bd%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d1%80%d0%b8%d1%82%d1%83%d0%b0%d0%bb/
После прочтения этой статьи, вы точно будете готовы к пешему походу по Уралу.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Между прочим, если вас интересует localflavors.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://localflavors.ru
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Хочу выделить раздел про eqa.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://eqa.ru
Спасибо за внимание.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Кстати, если вас интересует komandor-povolje.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://komandor-povolje.ru
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
По теме “yogapulse.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://yogapulse.ru
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “yogapulse.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://yogapulse.ru
Жду конструктивной критики.
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “komandor-povolje.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://komandor-povolje.ru
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
По теме “fk-almazalrosa.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
https://fk-almazalrosa.ru
Интересно было бы узнать ваше мнение.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Особенно понравился раздел про raregreen.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://raregreen.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “avelonbeta.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
https://avelonbeta.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “avelonbeta.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://avelonbeta.ru
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
Это именно то, что я искал!
Зацепил материал про lingomap.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://lingomap.ru
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “m-admin.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://m-admin.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “clasifieds.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://clasifieds.ru
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Готовы открыть для себя мир необычных фруктов и овощей?
Между прочим, если вас интересует Секреты цейлонской корицы из Шри-Ланки, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://localflavors.ru/%d0%ba%d0%be%d1%80%d0%b8%d1%86%d0%b0-%d1%88%d1%80%d0%b8-%d0%bb%d0%b0%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b0-%d0%b2-%d1%87%d1%91%d0%bc-%d1%81%d0%b5%d0%ba%d1%80%d0%b5%d1%82-%d0%b5%d1%91-%d1%81%d0%bb%d0%b0%d0%b4%d0%ba/
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Пытаетесь разнообразить своё питание необычными вкусами? Мы подскажем, как это сделать!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Экзотические продукты Латинской Америки: что попробовать?, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%bd%d0%ba%d0%b8-%d1%8d%d0%ba%d0%b7%d0%be%d1%82%d0%b8%d1%87%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d0%be%d0%b2-%d0%b2-%d0%bb%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%bd/
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Вы не знаете, как хранить экзотические продукты? У нас есть несколько советов!
Зацепил раздел про Откройте мир уникальных чайных смесей и вкусов.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://localflavors.ru/%d1%87%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%81%d0%bc%d0%b5%d1%81%d0%b8-%d1%81-%d0%bd%d0%b5%d0%be%d0%b1%d1%8b%d1%87%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%bc%d0%b8-%d0%b4%d0%be%d0%b1%d0%b0%d0%b2%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%b8/
Удачи в кулинарных экспериментах с экзотическими продуктами!
Незнакомые названия и странные формы — экзотические продукты всегда манят.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Спасение местных деликатесов: угрозы и решения”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
https://localflavors.ru/%d0%bc%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%82%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%b4%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%8b-%d0%bf%d0%be%d0%b4-%d1%83%d0%b3%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b7%d0%be%d0%b9-%d0%b8%d1%81%d1%87%d0%b5%d0%b7/
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Вы не знаете, как хранить экзотические продукты? У нас есть несколько советов!
Кстати, если вас интересует Скрытые тайны традиционных напитков 2025, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://localflavors.ru/%d1%82%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%b4%d0%b8%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%bd%d0%b0%d0%bf%d0%b8%d1%82%d0%ba%d0%b8-%d1%81-%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%bc%d0%b8-%d0%b8%d0%bd%d0%b3%d1%80%d0%b5/
Желаем вам новых открытий и ярких вкусов!
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
Кстати, если вас интересует Откройте редкие и необычные чаи Азии, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://localflavors.ru/%d0%bd%d0%b5%d0%be%d0%b1%d1%8b%d1%87%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%81%d0%be%d1%80%d1%82%d0%b0-%d1%87%d0%b0%d1%8f-%d0%b8%d0%b7-%d0%b0%d0%b7%d0%b8%d0%b8/
Пусть ваши блюда всегда будут полны экзотики и оригинальности.
Готовы открыть для себя мир необычных фруктов и овощей?
Особенно понравился материал про Античные специи: История и современное применение.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://localflavors.ru/%d0%b0%d0%bd%d1%82%d0%b8%d1%87%d0%bd%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%b2%d0%be%d0%b7%d0%b2%d1%80%d0%b0%d1%89%d0%b5%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b2-%d0%bc%d0%b5%d0%bd%d1%8e/
Если у вас есть собственные советы, не стесняйтесь делиться ими в комментариях.
Пытаетесь разнообразить своё питание необычными вкусами? Мы подскажем, как это сделать!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Как специи изменяли мировую историю и экономику, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://localflavors.ru/%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%ba%d0%be%d1%82%d0%be%d1%80%d1%8b%d0%b5-%d0%b8%d0%b7%d0%bc%d0%b5%d0%bd%d0%b8%d0%bb%d0%b8-%d1%85%d0%be%d0%b4-%d0%b8%d1%81%d1%82%d0%be%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b8/
Пусть ваши блюда всегда будут полны экзотики и оригинальности.
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Откройте для себя редкие морепродукты и их бизнес-потенциал, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://localflavors.ru/%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%ba%d0%b8%d0%b5-%d0%b4%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d1%81%d1%8b-%d0%b8%d0%b7-%d0%bc%d0%be%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b4%d1%83%d0%ba%d1%82%d0%be%d0%b2/
Удачи в кулинарных экспериментах с экзотическими продуктами!
Готовы открыть для себя мир необычных фруктов и овощей?
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Кардамон из Гватемалы: Использование в выпечке и влияние на рынок”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
https://localflavors.ru/%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%80%d0%b4%d0%b0%d0%bc%d0%be%d0%bd-%d0%b3%d0%b2%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b5%d0%bc%d0%b0%d0%bb%d0%b0-%d0%b4%d0%bb%d1%8f-%d1%87%d0%b5%d0%b3%d0%be-%d0%b8%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%be%d0%bb%d1%8c%d0%b7%d1%83/
Удачи в кулинарных экспериментах с экзотическими продуктами!
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
Кстати, если вас интересует История и значение специй в культурах мира, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://localflavors.ru/%d1%82%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%b4%d0%b8%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b8-%d0%b8%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%be%d0%bb%d1%8c%d0%b7%d0%be%d0%b2%d0%b0%d0%bd%d0%b8%d1%8f-%d1%81%d0%bf%d0%b5%d1%86%d0%b8%d0%b9-%d0%b2-%d1%80%d0%b0%d0%b7%d0%bd/
Пусть ваши блюда всегда будут полны экзотики и оригинальности.
Эти экзотические фрукты и овощи сделают ваше меню более ярким и насыщенным.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Бадьян из Китая: секрет анисового вкуса, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://localflavors.ru/%d0%b1%d0%b0%d0%b4%d1%8c%d1%8f%d0%bd-%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%b9-%d0%ba%d0%b0%d0%ba-%d0%be%d0%bd-%d0%bf%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%b4%d0%b0%d1%91%d1%82-%d0%b1%d0%bb%d1%8e%d0%b4%d0%b0%d0%bc-%d0%b0%d0%bd/
Теперь вам осталось только отправиться в магазин за экзотикой. Приятных покупок!
Вот здесь подробно расписано, как это сделать:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “anclaves.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
https://anclaves.ru
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “localflavors.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://localflavors.ru
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “diyworks.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
https://diyworks.ru
Спасибо за внимание.
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Особенно понравился раздел про lingomap.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://lingomap.ru]https://lingomap.ru[/url]
Жду конструктивной критики.
Для тех, кто в теме, будет очень актуально:
По теме “yogapulse.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://yogapulse.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Для тех, кто в теме, будет очень актуально:
Зацепил материал про hotelnews.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://hotelnews.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
Особенно понравился раздел про komandor-povolje.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://komandor-povolje.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Особенно понравился материал про travelmontenegro.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://travelmontenegro.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Кстати, если вас интересует diyworks.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://diyworks.ru
Надеюсь, у вас все получится.
Исчерпывающий ответ на данный вопрос находится тут:
Между прочим, если вас интересует easyterm.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://easyterm.ru
Интересно было бы узнать ваше мнение.
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Особенно понравился раздел про travelcrimea.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://travelcrimea.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Зацепил раздел про mersobratva.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://mersobratva.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Между прочим, если вас интересует parkpodarkov.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://parkpodarkov.ru
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Давайте подведем итоги марта и посмотрим, какие темы стали самыми популярными.
По теме “Ежедневный гороскоп на 31 июля 2025 года”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/horoscopes.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
Настоящий обзор самых популярных обсуждений марта на Mamas.Ru для вас!
Кстати, если вас интересует Обсуждаем последние записи в дневниках мам, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
http://mamas.ru/blog.php
Надеюсь, вы нашли что-то полезное для себя. До следующего месяца!
Какой месяц выдался на Mamas.Ru! Давайте вместе посмотрим, о чем говорили в марте.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Обсуждаем флеш-игры и турниры для всех, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/arcade.php
Большое спасибо за ваше внимание! Наверняка в следующем месяце будет еще больше интересного.
Настоящий обзор самых популярных обсуждений марта на Mamas.Ru для вас!
По теме “Популярные рецепты и кулинарные советы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
http://mamas.ru/recepty.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
Представляем самые читаемые и обсуждаемые темы марта на Mamas.Ru.
Кстати, если вас интересует Популярные рецепты и кулинарные советы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
http://mamas.ru/recepty.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
Какой месяц выдался на Mamas.Ru! Давайте вместе посмотрим, о чем говорили в марте.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Обсуждение активности на сайте для мам, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/activity.php
Это были самые горячие обсуждения марта. Ждем вас с новыми темами в следующем месяце.
Какой месяц выдался на Mamas.Ru! Давайте вместе посмотрим, о чем говорили в марте.
Зацепил раздел про Популярные рецепты и кулинарные советы.
Вот, можете почитать:
http://mamas.ru/recepty.php
Большое спасибо за ваше внимание! Наверняка в следующем месяце будет еще больше интересного.
Давайте подведем итоги марта и посмотрим, какие темы стали самыми популярными.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Обсуждаем флеш-игры и турниры для всех, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
http://mamas.ru/arcade.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
Мамочки, делимся новостями на Mamas.Ru. Какие темы вас особенно заинтересовали в марте?
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ежедневный гороскоп на 31 июля 2025 года”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/horoscopes.php
Большое спасибо за ваше внимание! Наверняка в следующем месяце будет еще больше интересного.
Настоящий обзор самых популярных обсуждений марта на Mamas.Ru для вас!
Кстати, если вас интересует Ежедневный гороскоп на 31 июля 2025 года, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
http://mamas.ru/horoscopes.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
Добро пожаловать на Mamas.Ru! Сегодня мы обсудим самые горячие темы нашего сообщества в марте.
Хочу выделить материал про Общение для мам: от ухода за детьми до хобби.
Ссылка ниже:
http://mamas.ru/forum.php
Надеюсь, вы нашли что-то полезное для себя. До следующего месяца!
Какой месяц выдался на Mamas.Ru! Давайте вместе посмотрим, о чем говорили в марте.
По теме “Популярные рецепты и кулинарные советы”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
http://mamas.ru/recepty.php
Маркет продолжается, и впереди еще больше интересных тем для обсуждения.
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Кстати, если вас интересует musichunt.pro, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://musichunt.pro
Надеюсь, у вас все получится.
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Особенно понравился материал про easyterm.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://easyterm.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Делюсь с вами полезной ссылкой по теме:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “eqa.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
https://eqa.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Особенно понравился раздел про fjhg.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://fjhg.ru
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
Делюсь с вами полезной ссылкой по теме:
Зацепил материал про spb-hotels.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://spb-hotels.ru
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
Это именно то, что я искал!
По теме “mersobratva.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
https://mersobratva.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Это именно то, что я искал!
Между прочим, если вас интересует all-hotels-online.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://all-hotels-online.ru
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
Хочу выделить раздел про travelcrimea.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://travelcrimea.ru
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Кстати, если вас интересует fk-almazalrosa.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://fk-almazalrosa.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Зацепил материал про lingomap.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://lingomap.ru
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Хочу выделить материал про all-hotels-online.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://all-hotels-online.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Хочу выделить раздел про detoxa.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://detoxa.ru
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Зацепил раздел про eroticpic.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://eroticpic.ru
Буду следить за обсуждением.
Посмотрите, что я нашел по этому поводу:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “reactive.su”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://reactive.su
Всем добра!
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Кстати, если вас интересует all-hotels-online.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://all-hotels-online.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Особенно понравился раздел про obender.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://obender.ru
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Между прочим, если вас интересует travelcrimea.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://travelcrimea.ru
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Посмотрите, что я нашел по этому поводу:
Особенно понравился раздел про classifields.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://classifields.ru
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Кстати, если вас интересует obender.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://obender.ru
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “easyterm.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://easyterm.ru
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
Между прочим, если вас интересует m-admin.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://m-admin.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Особенно понравился материал про reactive.su.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://reactive.su
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “travelmontenegro.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
https://travelmontenegro.ru
Жду конструктивной критики.
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “cyq.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://cyq.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Между прочим, если вас интересует pro-zenit.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://pro-zenit.ru
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Для тех, кто в теме, будет очень актуально:
Зацепил материал про pro-zenit.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://pro-zenit.ru
Какие еще есть варианты?
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
Зацепил материал про komandor-povolje.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://komandor-povolje.ru
Надеюсь, эта информация сэкономит вам время.
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Особенно понравился раздел про fjhg.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://fjhg.ru
Обращайтесь, если что.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Кстати, если вас интересует buytime.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://buytime.ru
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Особенно понравился раздел про fjhg.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://fjhg.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “idalgogrif.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://idalgogrif.ru
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “raregreen.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://raregreen.ru
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
Между прочим, если вас интересует buytime.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://buytime.ru
Жду конструктивной критики.
Уверен, эта информация будет для вас полезна:
Зацепил раздел про detoxa.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://detoxa.ru
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Кстати, если вас интересует tars-rubber.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://tars-rubber.ru
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Между прочим, если вас интересует classifields.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://classifields.ru]https://classifields.ru[/url]
Всем спасибо, и до новых встреч!
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Кстати, если вас интересует eroticpic.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://eroticpic.ru
Спасибо за внимание.
Наткнулся на полезную статью, думаю, вам тоже пригодится:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “hotelnews.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
https://hotelnews.ru
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Хочу выделить материал про rustrail.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://rustrail.ru
Всем удачи и хорошего дня!
Вот здесь подробно расписано, как это сделать:
Кстати, если вас интересует avelonbeta.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://avelonbeta.ru
Всем добра!
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Между прочим, если вас интересует travelmontenegro.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://travelmontenegro.ru
Жду конструктивной критики.
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
Хочу выделить раздел про raregreen.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://raregreen.ru
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Давно слежу за этой темой, хочу поделиться находкой:
По теме “mersobratva.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
https://mersobratva.ru
Чем мог, тем помог.
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Хочу выделить раздел про spb-hotels.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://spb-hotels.ru
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Если кому интересно, вот более детальная информация:
Кстати, если вас интересует mersobratva.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://mersobratva.ru
Буду следить за обсуждением.
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Хочу выделить материал про classifields.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://classifields.ru
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Особенно понравился раздел про clasifieds.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://clasifieds.ru
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
Давно слежу за этой темой, хочу поделиться находкой:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “m-admin.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://m-admin.ru
Интересно было бы узнать ваше мнение.
На мой взгляд, лучшее решение этой проблемы здесь:
Особенно понравился материал про tars-rubber.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://tars-rubber.ru
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
Недавно столкнулся с похожей ситуацией, и вот что помогло:
Хочу выделить раздел про 095hotel.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://095hotel.ru]https://095hotel.ru[/url]
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
Хочу выделить раздел про idalgogrif.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://idalgogrif.ru
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Хочу выделить раздел про buytime.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://buytime.ru
Надеюсь, эта информация сэкономит вам время.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “hotelnews.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://hotelnews.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
Зацепил материал про lingomap.ru.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://lingomap.ru]https://lingomap.ru[/url]
Всем добра!
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
По теме “cyq.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://cyq.ru
Надеюсь, это было полезно.
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
Хочу выделить материал про eroticpic.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://eroticpic.ru
Буду рад, если кому-то пригодится.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
Между прочим, если вас интересует clasifieds.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://clasifieds.ru
Всем мира и продуктивного дня
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
По теме “tars-rubber.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://tars-rubber.ru
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
По теме “raregreen.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://raregreen.ru
Буду признателен за ваши отзывы.
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
По теме “m-admin.ru”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://m-admin.ru
Надеюсь, у вас все получится.
Исчерпывающий ответ на данный вопрос находится тут:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “komandor-povolje.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://komandor-povolje.ru
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Делюсь с вами полезной ссылкой по теме:
Кстати, если вас интересует seatours.ru, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://seatours.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Между прочим, если вас интересует hotelnews.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://hotelnews.ru
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Это именно то, что я искал!
Кстати, если вас интересует fjhg.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://fjhg.ru
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Если нужна более подробная инструкция, то она здесь:
Между прочим, если вас интересует spb-hotels.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://spb-hotels.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Между прочим, если вас интересует eroticpic.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://eroticpic.ru
Надеюсь, это было полезно.
Чтобы было понятнее, о чем речь:
По теме “fk-almazalrosa.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
https://fk-almazalrosa.ru
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Недавно столкнулся с похожей ситуацией, и вот что помогло:
Между прочим, если вас интересует tars-rubber.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://tars-rubber.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “parkpodarkov.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://parkpodarkov.ru
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
По теме “avelonbeta.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
https://avelonbeta.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Полагаю, это снимет все дальнейшие вопросы:
Особенно понравился раздел про yogapulse.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://yogapulse.ru
Спасибо, что дочитали до конца.
Это именно то, что я искал!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “clasifieds.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://clasifieds.ru
Что думаете по этому поводу?
Чтобы было понятнее, о чем речь:
Между прочим, если вас интересует rustrail.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://rustrail.ru
Жду конструктивной критики.
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua в реальном времени. Экономика, политика, общество, культура, происшествия и спорт. Всё самое важное и интересное на одном портале.
Современный автопортал https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости, сравнительные обзоры, тесты, автострахование и обслуживание. Полезная информация для водителей и покупателей.
Строительный сайт https://vitamax.dp.ua с полезными материалами о ремонте, дизайне и современных технологиях. Обзоры стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, проекты домов и советы экспертов.
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
По теме “eqa.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://eqa.ru
Всем добра!
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
Зацепил раздел про obender.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://obender.ru
Буду признателен за ваши отзывы.
Кстати, вот что я думаю по этому поводу:
По теме “raregreen.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://raregreen.ru
Буду следить за обсуждением.
Недавно столкнулся с похожей ситуацией, и вот что помогло:
Хочу выделить раздел про obender.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://obender.ru
Успехов в решении вашего вопроса!
Как вариант, можно рассмотреть следующее:
Зацепил материал про yogapulse.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://yogapulse.ru
Жду ваших комментариев.
Сайт о строительстве https://stinol.com.ua практические рекомендации, проекты, обзоры инструментов и материалов. Советы экспертов, новости отрасли и новые технологии.
Строительный журнал https://mts-slil.info с актуальными новостями отрасли, обзорами материалов, инструкциями по ремонту и строительству. Полезные советы для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Онлайн сайт https://purr.org.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры технологий, дизайн-идеи и архитектурные решения для вашего дома.
Онлайн туристический https://azst.com.ua портал: всё о путешествиях, туризме и отдыхе. Маршруты, отели, лайфхаки для туристов, актуальные цены и интересные статьи о странах.
Онлайн новостной https://antifa-action.org.ua портал с круглосуточным обновлением. Свежие новости, репортажи и обзоры. Важные события страны и мира, мнения экспертов и актуальная аналитика.
Новости Украины https://uamc.com.ua новости дня, аналитика, события регионов и мира. Обзоры, интервью, мнения экспертов. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для читателей.
Новостной портал https://prp.org.ua с актуальной информацией о событиях в России и мире. Политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Новости 24/7, аналитика и комментарии экспертов.
Строительный портал https://suli-company.org.ua с актуальными новостями, обзорами материалов, проектами и инструкциями. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне.
freight company new york shipping company new york city
Портал про авто https://prestige-avto.com.ua обзоры новых и подержанных машин, тест-драйвы, рынок автомобилей, страхование и обслуживание.
Онлайн автомобильный https://avtonews.kyiv.ua портал: свежие автоновости, сравнительные тесты, статьи о ремонте и тюнинге. Обзоры новых и подержанных машин, цены и советы экспертов.
Современный автомобильный https://mallex.info портал: автообзоры, тесты, ремонт и обслуживание, страхование и рынок. Всё, что нужно водителям и любителям автомобилей.
Строительный сайт https://novostroi.in.ua с полезными статьями о ремонте, отделке и дизайне. Обзоры стройматериалов, проекты домов, инструкции и советы экспертов для профессионалов и новичков.
Автомобильный портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё для автолюбителей: от выбора авто до обслуживания и ремонта.
Портал для родителей https://detiwki.com.ua и детей — всё для счастливой семьи. Воспитание, образование, здоровье, отдых и полезные материалы для мам, пап и малышей.
Универсальный сайт https://virginvirtual.net для женщин — секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере, рецепты и стиль жизни.
Сайт для женщин https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua с интересными статьями о моде, красоте, семье и здоровье. Идеи для кулинарии, путешествий и вдохновения.
Журнал садовода https://mts-agro.com.ua полезные советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Сезонные работы, выращивание овощей, фруктов и цветов, современные технологии и секреты урожая.
Сайт для женщин https://gratransymas.com о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера.
Студия дизайна https://lbook.com.ua интерьера и архитектуры. Создаём стильные проекты квартир, домов и офисов. Индивидуальный подход, современные решения и полный контроль реализации.
Сайт обо всём https://vybir.kiev.ua энциклопедия для повседневной жизни. Красота, здоровье, дом, путешествия, карьера, семья и полезные советы для всех.
Интересный сайт https://whoiswho.com.ua обо всём: статьи, лайфхаки, обзоры и идеи на самые разные темы. Всё, что нужно для вдохновения и развития, в одном месте.
Онлайн портал https://esi.com.ua про ремонт: идеи для интерьера, подбор материалов, практические рекомендации и пошаговые инструкции для самостоятельных работ.
Репортажи в больших https://infotolium.com фотографиях: самые обсуждаемые события, уникальные кадры и впечатляющие истории. Новости и жизнь в формате визуального рассказа.
Сайт про автомобили https://black-star.com.ua новинки рынка, цены, тест-драйвы и обзоры. Советы экспертов по выбору и уходу за машиной, тюнинг и автоуслуги.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://allauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новых моделей, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей.
Онлайн-журнал https://autoiceny.com.ua для автолюбителей: автомобили, новости индустрии, тест-драйвы, тюнинг и советы по обслуживанию.
Royal portraits http://www.turnyouroyal.com from photos – turn yourself or your loved ones into a king, queen or aristocrat. Author’s work of artists, luxurious style and premium quality of printing.
Сайт про авто https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Информационный портал https://reklama-region.com про ремонт: ремонт квартир, домов, офисов. Практические рекомендации, современные решения и обзоры стройматериалов.
Авто-журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua источник информации для автолюбителей. Новинки рынка, сравнения моделей, советы по ремонту и уходу, интересные материалы о мире автомобилей.
Новостной портал https://gau.org.ua круглосуточные новости, комментарии экспертов, события регионов и мира. Политика, бизнес, культура и общество.
Онлайн авто-журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua с актуальными новостями, аналитикой и обзорами. Тесты автомобилей, тюнинг, технологии и советы по эксплуатации.
Авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua всё об автомобилях: новые модели, цены, рынок подержанных авто, тюнинг и автотехнологии. Полезные материалы для автовладельцев.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua новости, лайфхаки, обзоры техники, спорт, здоровье и авто. Советы для уверенной и гармоничной жизни.
Как раз то, что нужно для решения этого вопроса:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “detoxa.ru”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://detoxa.ru
Рад был поделиться информацией.
Это именно то, что я искал!
Особенно понравился материал про fixora.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://fixora.ru
Всем добра!
Портал о ремонте https://dki.org.ua и строительстве: от отделки квартиры до возведения загородного дома. Подробные статьи, рекомендации экспертов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Портал о стройке https://sushico.com.ua и ремонте. Новости рынка, современные технологии, подборка идей для интерьера и экстерьера. Всё, что нужно для дома и дачи.
Онлайн сайт https://mramor.net.ua о строительстве и ремонте. Всё о возведении домов, ремонте квартир, отделке и обустройстве жилья. Обзоры материалов, советы экспертов и свежие идеи.
Всё о стройке https://aziatransbud.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте: дизайн, архитектура, выбор стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, лайфхаки и полезные рекомендации для новичков и мастеров.
Сайт о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua и ремонте — ваш помощник в выборе материалов, инструментов и технологий. Всё о ремонте квартир, строительстве домов и дизайне интерьеров.
Онлайн журнал https://vitamax.dp.ua о строительстве: проекты домов, ремонт квартир, выбор стройматериалов, дизайн и интерьер. Советы экспертов и свежие идеи для комфортной жизни.
Портал про строительство https://texha.com.ua новости рынка, обзоры технологий, инструкции и идеи для ремонта. Материалы для застройщиков, мастеров и тех, кто делает своими руками.
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua онлайн: политика, экономика, спорт, культура и события регионов. Оперативные материалы, аналитика и комментарии экспертов круглосуточно.
audio processing mp3 editing
Prodaja placevi zabljak: stanovi, vile, zemljisne parcele. Izbor smestaja za odmor, preseljenje i investicije. Saveti strucnjaka i aktuelne ponude na trzistu.
Авто портал https://road.kyiv.ua с актуальной информацией: новинки рынка, цены, обзоры, страхование и тюнинг. Полезные статьи и аналитика для автомобилистов.
Портал про авто https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей и советы по ремонту. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Давно слежу за этой темой, хочу поделиться находкой:
Кстати, если вас интересует fk-almazalrosa.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://fk-almazalrosa.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Нужна топливная карта? https://avtobas40.ru. Экономия до 15%, автоматическая отчётность, удобные безналичные расчёты и контроль автопарка онлайн.
Besoin d’un bien immobilier? immobilier au Montenegro: appartements en bord de mer, maisons a la montagne, villas et appartements. Catalogue de biens, prix actuels et conseils d’experts en investissement.
Хотите оформить карту на топливо? https://ktz59.ru. Контроль за каждой транзакцией, отчёты для бухгалтерии, гибкие лимиты и бонусные программы.
Возможно, это будет полезно участникам обсуждения:
Между прочим, если вас интересует classifields.ru, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://classifields.ru
Дайте знать, если найдете что-то еще.
Фильмы и сериалы лучший сайт для просмотра фильмов онлайн кинобэй Онлайн-кинотеатр без регистрации и смс: тысячи фильмов и сериалов бесплатно.
Jak samodzielnie zdjac https://telegra.ph/Jak-samodzielnie-zdj%C4%85%C4%87-sufit-napinany-instrukcja-krok-po-kroku-bez-haka-z-wkr%C4%99tem-i-trikami-monta%C5%BCyst%C3%B3w-08-07 sufit napinany: instrukcje krok po kroku, narzedzia, porady ekspertow. Dowiedz sie, jak zdemontowac plotno bez uszkodzen i przygotowac pomieszczenie do montazu nowej okladziny.
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
Зацепил материал про m-admin.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://m-admin.ru
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
Это именно то, что я искал!
Кстати, если вас интересует localflavors.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://localflavors.ru
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
салон красоты приморский район http://beauty-salon-spb.ru
Вот тут есть все ответы на ваши вопросы:
Зацепил раздел про classifields.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://classifields.ru
Надеюсь, у вас все получится.
оценка имущества оценить рыночную стоимость
устройство плоской крыши https://montazh-ploskoj-krovli.ru
Создать документы онлайн конструктор договора скачать: создайте договор, заявление или акт за 5 минут. Простая форма, готовые шаблоны, юридическая точность и возможность скачать в нужном формате.
Вот, что говорят эксперты по этому поводу:
Между прочим, если вас интересует m-admin.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://m-admin.ru
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Чтобы разобраться в вопросе, рекомендую ознакомиться:
По теме “classifields.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://classifields.ru
Если есть вопросы, задавайте.
Полностью поддерживаю, и вот еще одно подтверждение:
Зацепил материал про obender.ru.
Смотрите сами:
https://obender.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Вот отличный материал, который проливает свет на ситуацию:
Хочу выделить материал про eqa.ru.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://eqa.ru
Надеюсь, смог помочь.
Авто помощь 24/7 автопомощь на дороге спб: устранение поломок, подвоз топлива, прикуривание аккумулятора, замена колеса и эвакуация автомобиля.
Вот здесь подробно расписано, как это сделать:
Хочу выделить материал про fixora.ru.
Ссылка ниже:
https://fixora.ru
Обращайтесь, если что.
Срочно нужны цветы Минск Свежие букеты, праздничные композиции и эксклюзивные флористические решения. Онлайн-заказ и быстрая доставка по городу.
Профессиональные https://812detailing.com/: полировка кузова, химчистка салона, восстановление пластика и защита керамикой. Вернём автомобилю блеск и надёжную защиту.
Нужен массаж? https://doctu.ru – профессиональные мастера, широкий выбор техник: классический, оздоровительный, лимфодренажный, детский. Доступные цены и уютная атмосфера.
Обучающие курсы онлайн складчина новые навыки для работы и жизни. IT, дизайн, менеджмент, языки, маркетинг. Гибкий график, практика и сертификаты по итогам.
vps hosting vps hosting
Очень рекомендую к прочтению:
Кстати, если вас интересует lingomap.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://lingomap.ru
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
косметологический столик стул косметолога со спинкой купить
Хотите заказать интро для диджея? Индивидуальная разработка музыкальных заставок для рекламы, подкастов и презентаций. Качественный звук и креатив для запоминающегося бренда.
Чтобы не быть голословным, прикрепляю ссылку:
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “detoxa.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://detoxa.ru
Поделитесь своими мыслями в комментариях.
Наркологические услуги: наркологическая клиника стационар нижний новгород, кодирование, детоксикация, снятие ломки, помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Круглосуточная поддержка и анонимность.
Всем привет, нашел интересную информацию по теме:
Между прочим, если вас интересует fk-almazalrosa.ru, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://fk-almazalrosa.ru
Если у вас есть что добавить, не стесняйтесь.
Puzzle Man Pro https://apps.apple.com/ar/app/puzzle-man-pro/id455696756 exciting puzzles for iOS. Collect classic pictures or create puzzles from your own photos. Different difficulty levels, user-friendly interface and saving progress.
Свежее и интересное: http://remsanteh.borda.ru/?1-1-0-00003083-000-0-0-1754909107
Стройкаталог https://stroycata1og.ru проекты коттеджей, дома любой площади, каталог стройматериалов. Комплексные услуги от проектирования до сдачи объекта с гарантией качества.
бетон цена за м3 с доставкой бетон
Block Puzzle Wood Classic https://apps.apple.com/fo/app/block-puzzle-wood-classic/id1615792350 is a puzzle game where you need to correctly place wooden blocks. Simple controls, beautiful visuals and addictive gameplay for all ages.
Handmade porcelain flowers Ideal for home, office decor or original gift. Natural beauty and durability.
Бетон в Воронеже https://stk-vrn.ru продажа и доставка. Все марки для фундаментов, дорожных работ и строительства под ключ. Надёжный производитель и лучшие цены.
нтернет-магазин сантехники https://vodomirural.ru ванны, смесители, унитазы, раковины и душевые кабины. Большой выбор, доступные цены, доставка и гарантия качества от производителей.
Рейтинг хостингов топ хостингов для сайта подбор сервисов для сайтов и интернет-магазинов. Сравнение тарифов, гарантия стабильности и рекомендации по выбору.
Рестораны Хамовников https://restoran-khamovniki.ru топ заведений для встреч, романтических ужинов и семейных обедов. Авторская кухня, стильный интерьер, удобное расположение и достойный сервис.
Лучшие рестораны https://hamovniki-restoran.ru Хамовников для ценителей гастрономии. Подборка заведений с изысканной кухней, качественным сервисом и атмосферой для отдыха и деловых встреч.
Курсы по плазмотерапии плазмолифтинг обучение освоение методик, современные протоколы, практическая отработка. Обучение для специалистов с выдачей сертификата и повышением квалификации.
Профессиональное обучение обучение prp в косметологии: подробная программа, практические навыки, сертификация. Освойте эффективные методики для применения в медицине и косметологии.
Детская школа искусств https://elegy-school.ru обучение музыке, танцам, изобразительному и театральному искусству. Творческие программы для детей, концерты, конкурсы и развитие талантов.
Авторские курсы по REVIT https://dashclass.ru обучение созданию интерьеров и архитектурных проектов. Практика, реальные кейсы, индивидуальный подход и профессиональные навыки для работы в проектировании.
Первая помощь детям https://firstaidkids.ru правила оказания при травмах, ожогах, удушье и других ситуациях. Пошаговые инструкции, советы врачей и полезная информация для родителей.
Студия иностранных языков https://whats-up-studiya-inostrannyh-yazykov.ru обучение английскому, немецкому, французскому и другим языкам. Индивидуальные и групповые занятия, современные методики и опытные преподаватели.
Срочный вызов сантехника https://master-expert.com в Москве на дом. Услуги сантехника: прочистка засоров, ремонт смесителей, установка приборов учета. Работаем 24/7. Недорого и с гарантией. Подробнее на сайте
Детский сад № 55 https://detsadik55.ru забота, развитие и обучение детей. Современные программы, квалифицированные воспитатели, уютные группы, безопасная среда и внимание к каждому ребёнку.
Промышленная безопасность https://аттестация-промбезопасность.рф курсы и обучение под ключ. Подготовка к проверке Ростехнадзора, повышение квалификации и сертификация специалистов предприятий.
Автомобили на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya1.ru поиск, проверка, покупка и доставка. Китай и Корея. Индивидуальный подбор под бюджет и пожелания клиента, полное сопровождение сделки.
Авто из Китая https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru на заказ под ключ: подбор, проверка, доставка и растаможка. Новые и подержанные автомобили, выгодные цены и полное сопровождение сделки.
Авто из Китая под заказ https://dostavka-avto-china.ru кроссоверы, седаны, электромобили и премиальные модели. Индивидуальный подбор, проверка, сопровождение сделки и доставка в ваш город.
Автомобили из Китая на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru подбор, покупка и доставка. Полный цикл услуг: диагностика, растаможка, постановка на учёт и гарантия качества.
PuzzleFree online puzzles https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:1980s_unicef_jigsaw_puzzle.jpg hundreds of pictures to assemble, different difficulty levels and user-friendly interface. Enjoy the process, train your memory and attention for free.
Заказать авто из Китая https://dostavka-avto-china2.ru новые автомобили с гарантией, выгодные цены и проверенные поставщики. Доставка, таможня и оформление всех документов под ключ.
Авто на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia.ru поиск, диагностика и сопровождение сделки. Машины из Европы, Кореи, Китая и США. Доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт.
Автомобили на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia5.ru профессиональный подбор, юридическая проверка, доставка и растаможка. Индивидуальные решения для каждого клиента.
Хотите заказать авто https://prignat-avto5.ru Мы подберём оптимальный вариант, проверим машину по базам, организуем доставку и таможенное оформление. Выгодные цены и прозрачные условия.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-avto7.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-mashinu5.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu7.ru подбор, проверка, доставка и оформление документов. Машины любых марок и комплектаций с гарантией качества и выгодной ценой.
Наружная реклама https://pioner-reklama.ru и вывески под ключ: дизайн, производство и монтаж. Световые короба, объёмные буквы, баннеры и витрины. Индивидуальные решения для бизнеса любого масштаба.
Ремонт квартир https://remontkomand.kz и домов под ключ: дизайн-проект, отделка, инженерные работы. Работаем по договору, фиксированные сроки и цены. Гарантия качества и полный контроль этапов.
SEO-продвижение сайтов https://raskrutka-sajtov-bystro77.ru в Москве: вывод в ТОП поисковиков, рост трафика и заявок. Полный комплекс — аудит, семантика, оптимизация, ссылки. Эффективное продвижение под ключ.
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Онлайн-курсы курсы по заработку онлайн. Изучайте языки, IT, дизайн, маркетинг и другие направления. Удобный формат, доступ к материалам 24/7
Строительство домов https://stroycata1og.ru и коттеджей под ключ. Готовые проекты, индивидуальные решения, качественные материалы и полный цикл работ — от фундамента до отделки.
Журнал о саде https://nasha-gryadka.ru и огороде онлайн — статьи о выращивании овощей, цветов и фруктов. Советы по уходу, борьбе с вредителями, подбору семян и организации участка.
Нужна качественная регулировка окон пвх? Специалисты настроят створки, фурнитуру и уплотнители. Устранение продувания, перекоса и тяжёлого открывания с гарантией качества.
Tree removal and care https://www.highqualitytreeservice.com/ pruning, crown shaping, treatment, removal and felling of hazardous trees. Experienced specialists and modern equipment. Safe, professional and with a guarantee of results.
Нужен клининг? список клининговых компаний москвы. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Стоматологическая клиника https://almazdental35.ru с индивидуальным подходом. Безболезненное лечение, эстетическая стоматология, имплантация и профессиональная гигиена полости рта.
У детей пробелмы с зубами? консультация детского ортодонта — лечение и профилактика зубов у детей. Безопасные методы, комфортная атмосфера и заботливые врачи для маленьких пациентов.
Смотрите сериалы Лучшие сериалы онлайн: https://www.justmedia.ru/news/russiaandworld/serialy-onlayn-kak-vybrat-i-gde-smotret онлайн в хорошем качестве. Новинки, классика и популярные проекты в удобном формате. Бесплатный просмотр без скачивания и доступ 24/7.
Нужна контекстная реклама? контекстная реклама для стоматологии под ключ. Настройка в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads, оптимизация объявлений и контроль заявок.
Комплексные IT-решения https://eclat.moscow для бизнеса: разработка, внедрение, сопровождение и поддержка. Надежные технологии для автоматизации и цифровой трансформации.
Play puzzles online https://x.com/puzzlefree_game free and without restrictions. A huge selection of pictures, simple controls and the ability to develop attention, memory and thinking. A great way to relax and spend time usefully.
swot анализ проблемы swot анализа рисков
swot анализ суть swot анализ вопросы
Looking for second-hand? thrifting near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
В современном мире юридические консультации играют важную роль.. Каждый может столкнуться с правовыми вопросами, которые требуют профессионального вмешательства..
На платформе konsultaciya-advokata11.ru можно найти множество юридических консультаций. На нашем сайте доступны услуги по самым разным направлениям права. Получите помощь квалифицированного юриста на вопрос юристу онлайн бесплатно круглосуточно.
Профессиональные адвокаты готовы помочь вам.. Мы стремимся предоставить клиентам только лучшие юридические решения..
Обратитесь к нам, и вы не пожалеете о своем выборе.. Мы гарантируем профессионализм и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту..
С получением профессиональной помощи в решении юридических вопросов вы можете обратиться к налоговый консультант онлайн, где можно получить юридическую консультацию круглосуточно и бесплатно.
Ресурс ‘konsultaciya-advokata81.ru’ предоставляет разнообразные правовые консультации.
Looking for second-hand? thrift store store near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
ЭВЛО https://evlo-phlebology.ru эндовазальная лазерная коагуляция вен, наряду со склеротерапией является эффективным методом лечения варикозного расширения вен на ногах.
Услуги госпитализации https://hospitall.ru экстренная помощь при угрожающих состояниях и плановое лечение с заранее согласованной программой. Подбор клиники, транспортировка и поддержка пациента на всех этапах.
карго доставка из китая карго из китая в россию
купить продукты с фермы фермерские продукты недорого в москве
Онлайн-библиотека Казахстана https://mylibrary.kz книги, статьи, диссертации и редкие издания в цифровом формате. Удобный каталог, быстрый поиск и круглосуточный доступ для всех пользователей.
Эндовазальная лазерная коагуляция https://evlo-phlebology.ru эффективный метод лечения варикоза. Амбулаторная процедура занимает до 40 минут, не требует госпитализации и обеспечивает быстрый косметический и медицинский результат.
Сюрвей грузов сюрвей контроль качества и количества, проверка условий перевозки, составление отчётов. Опытные эксперты обеспечивают объективную оценку для компаний и страховых организаций.
Надежная доставка из китая в Россию: от документов до контейнеров. Выбираем оптимальный маршрут, оформляем таможню, страхуем грузы. Контроль сроков и сохранность на каждом этапе.
создание корпоративного сайта https://art-made.ru/
Надежная доставка грузов из китая: от небольших партий до контейнеров. Авиа, морем, авто и железной дорогой. Оформление, страхование и логистика в кратчайшие сроки.
Нужен автобусный билет? билеты на автобус онлайн просто и удобно. Поиск рейсов, сравнение цен, выбор мест и моментальная оплата. Актуальное расписание, надежные перевозчики и выгодные тарифы каждый день.
Качественный ремонт квартир https://expertremonta.kz от Компании «Эксперт ремонта» это качественный ремонт квартир под ключ в Алматы. Выбирайте Эксперт Ремонта — тут бесплатный выезд замерщика, официальные документы, гарантия документально, ремонт квартир без предоплаты.
купить дт с доставкой доставка зимнего дизельного топлива
куплю растительный грунт торф низинный
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию онлайн, чтобы оперативно решить все ваши юридические вопросы!
Мы понимаем, что разобраться закон может быть трудно.
Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам на бесплатная консультация юриста, и получите квалифицированное решение своих вопросов.
yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru предлагает профессиональные юридические услуги, направленные на решение различных правовых вопросов. Наша команда готова помочь вам в самых сложных ситуациях. Мы понимаем, что правовые проблемы могут быть стрессовыми, мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
В нашем арсенале широкий спектр услуг, включая консультации по гражданским и уголовным делам. Вы можете обратиться к нам по вопросам, связанным с трудовым правом, семейными делами и другими юридическими аспектами. Мы понимаем, что каждая ситуация требует индивидуального подхода, и готовы предложить оптимальное решение.
Мы гордимся нашей репутацией как надежный партнер в сфере юриспруденции. Клиенты выбирают нас за профессионализм за высокое качество обслуживания и результативность. Все наши юристы имеет опыт работы в различных областях права и готов поддержать вас в любое время.
Не ждите, пока ситуация усугубится , чтобы получить квалифицированную юридическую помощь. Наша команда будет рада проконсультировать вас . Воспользуйтесь нашими услугами на yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru.
Mochten Sie ein Montenegro haus kaufen kaufen? Tolle Angebote am Meer und in den Bergen. Gro?e Auswahl an Immobilien, Unterstutzung bei der Immobilienauswahl, Transaktionsunterstutzung und Registrierung. Leben Sie in einem Land mit mildem Klima und wunderschoner Natur.
Новые актуальные промокод iherb приложение для выгодных покупок! Скидки на витамины, БАДы, косметику и товары для здоровья. Экономьте до 30% на заказах, используйте проверенные купоны и наслаждайтесь выгодным шопингом.
best articles on the net: https://dnscompetition.in/articles/how-dns-interacts-with-cdn-and-accelerates-content-delivery/
перевозки из китая транспортная компания из китая в россию
шпонированные панели дсп шпонирование фанеры на заказ
геодезия цена геодезические изыскания москва цена
геотекстиль 200 москва геотекстиль сибур
Включение в реестр Минпромторга https://minprom-info.ru официальный путь для подтверждения отечественного производства. Подготовка и подача документов, юридическое сопровождение и консультации для производителей.
Занятия по самообороне https://safety-skills.ru практические навыки защиты в реальных ситуациях, развитие силы и выносливости. Профессиональные тренеры помогут освоить приемы борьбы, удары и тактику безопасности.
Платформа онлайн-обучения https://craftsmm.ru курсы по маркетингу, продажам и рекламе для новичков и профессионалов. Освойте современные инструменты продвижения, увеличьте продажи и развивайте карьеру в удобном формате.
Написание дипломов на заказ https://vasdiplom.ru помощь студентам в подготовке итоговых работ. Авторские тексты, проверка на уникальность и полное соответствие стандартам учебных заведений.
Обучение и семинары https://uofs-beslan.ru для профессионалов: современные программы, практические кейсы и опыт экспертов. Развивайте навыки, повышайте квалификацию и получайте новые возможности для карьерного роста.
Академия парикмахерского искусства https://charm-academy.ru обучение от ведущих мастеров. Современные техники стрижек, окрашивания и укладок. Курсы для начинающих и профессионалов с практикой и дипломом по окончании.
Школа видеорекламы https://tatyanamostseeva.ru обучение созданию креативных роликов для бизнеса и брендов. Практические занятия, работа с современными инструментами и поддержка экспертов. Освойте профессию в сфере digital.
Лицей взаимного обучения https://talgenisty.ru уникальная среда для детей и взрослых. Совместные уроки, обмен опытом, мастер-классы и творческие проекты. Образование, основанное на поддержке и сотрудничестве.
Нужен автобусный билет? probilets.com удобный сервис поиска и бронирования. Широкий выбор направлений, надежные перевозчики, доступные цены и моментальная отправка электронных билетов на почту.
Авто портал https://diesel.kyiv.ua все о мире автомобилей: новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору и уходу за авто. Каталог машин, актуальные цены, автоуслуги и полезная информация для автовладельцев.
Автомобильный портал https://auto-club.pl.ua онлайн-площадка для автолюбителей. Подробные обзоры машин, тест-драйвы, свежие новости, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Удобный поиск и актуальные материалы.
Все для автомобилистов https://k-moto.com.ua на авто портале: новости, обзоры, статьи, каталоги и цены на автомобили. Экспертные мнения, тест-драйвы и практические советы по эксплуатации авто.
Нужна виза? https://delovaya-viza.ru Консультации, подготовка документов, сопровождение на всех этапах. Визы в Европу, США, Азию и другие страны. Доступные цены и надежная поддержка.
Онлайн женский портал https://elegance.kyiv.ua актуальные советы по красоте, стилю, кулинарии и семейной жизни. Разделы о здоровье, карьере и саморазвитии. Интересные статьи и общение с единомышленницами.
Женский портал https://beautyadvice.kyiv.ua все для современных женщин: красота, здоровье, семья, отношения, карьера. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов, лайфхаки и вдохновение каждый день. Онлайн-сообщество для общения и развития.
Портал для женщин https://fashionadvice.kyiv.ua сайт для девушек и женщин, которые ценят красоту, уют и гармонию. Советы по стилю, отношениям, материнству и здоровью. Читайте статьи, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста по телефону на сайте адвокат бесплатно.
Раздел 1: Введение
Адвокат поможет вам понять, какие бумаги нужны для вашего дела.
На сайте konsultaciya-advokata51.ru вы можете найти множество полезных услуг. Юридическая консультация – это важный шаг для многих людей. Мы обеспечим вас экспертными консультациями.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на бесплатные консультации юриста онлайн.
На сайте konsaltaciya-advokata51.ru вы найдете множество информации о правовых услугах.
Первое, что стоит учитывать – это квалификация адвокатов. Наши юристы обладают необходимыми знаниями и опытом. Мы стремимся обеспечить высокий уровень обслуживания.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, доступных для разных категорий граждан. Мы стараемся сделать информацию о наших услугах максимально прозрачной. Клиенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант в зависимости от своих нужд.
Наши адвокаты готовы предоставить юридическую помощь в режиме онлайн. Это особенно удобно для тех, кто ценит своё время. Вы можете задать свои вопросы в любое время.
Авто портал https://avtoshans.in.ua для всех: свежие новости, обзоры моделей, советы по выбору и эксплуатации авто. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы и рекомендации экспертов для водителей и покупателей.
Портал про автомобили https://myauto.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для автолюбителей. Обзоры, статьи, тест-драйвы, цены и полезные советы по ремонту и уходу за машиной. Всё о мире авто в одном месте.
Автомобильные новости https://reuth911.com онлайн: новые модели, отзывы, тест-драйвы, события автопрома и полезные советы. Узнайте первыми о главных новинках и трендах автомобильного мира.
Свежие новости авто https://orion-auto.com.ua тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, законодательные изменения и аналитика авторынка. Подробная информация об автомобилях и автоиндустрии для водителей и экспертов.
Автомобильный сайтhttps://setbook.com.ua свежие новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы экспертов. Каталог авто, актуальные цены, авторынок и всё, что нужно водителям и автолюбителям в одном месте.
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://musicbit.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, семья, карьера и хобби. Интересные статьи, тесты и форум для общения. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://fines.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, рецепты, материнство и карьера. Актуальные материалы, тренды и экспертные рекомендации каждый день.
Женский сайт о жизни https://prettywoman.kyiv.ua секреты красоты, мода, здоровье, рецепты и отношения. Интересные статьи, советы и лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно, чтобы чувствовать себя уверенно и счастливо.
https://193fz.ru/
Онлайн-сайт про автомобили https://tvregion.com.ua свежие новости, аналитика рынка, обзоры и сравнения машин. Советы по обслуживанию и выбору авто. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей в одном месте.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://feminine.kyiv.ua мода, красота, здоровье, отношения и семья. Полезные советы, вдохновляющие статьи, лайфхаки для дома и карьеры. Всё самое интересное для современных женщин.
Автомобильный портал https://troeshka.com.ua онлайн-ресурс для автовладельцев. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Будьте в курсе новинок и технологий автоиндустрии.
Сайт для женщин https://lolitaquieretemucho.com мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, семья и карьера. Полезные советы, статьи, рецепты и лайфхаки. Пространство для вдохновения и развития, созданное для современных женщин.
https://peterburg2.ru/
Сайт для женщин https://femaleguide.kyiv.ua гармония стиля и жизни. Уход за собой, рецепты, дом, отношения, карьера и путешествия. Читайте статьи, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями.
Автомобильный новостной портал https://tuning-kh.com.ua всё об авто в одном месте: новости, цены, обзоры, тест-драйвы, авторынок. Советы экспертов и полезные материалы для водителей и тех, кто планирует купить машину.
Сайт про машины https://tvk-avto.com.ua обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, новости автопрома и советы по эксплуатации. Полезные статьи о выборе авто, уходе, ремонте и актуальные материалы для автовладельцев.
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://mirlady.kyiv.ua красота, стиль, здоровье, дом и семья. Практичные рекомендации, модные идеи, вдохновение и поддержка. Лучший контент для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Сайт для женщин https://amideya.com.ua портал о красоте, стиле, здоровье, семье и саморазвитии. Ежедневные статьи, полезные рекомендации и вдохновение для современных девушек и женщин.
Женский сайт https://lubimoy.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, материнство, работа и хобби. Актуальные статьи, тренды и экспертные советы. Всё самое важное для гармоничной жизни и успеха.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://gracefullady.kyiv.ua свежие статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье и саморазвитии. Практичные советы, вдохновение и позитив для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
https://hr.rivagroup.su/
Женский сайт https://family-site.com.ua современный портал о моде, красоте, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные материалы, секреты здоровья и успеха, актуальные тренды и советы экспертов для женщин любого возраста.
Семейный портал https://geog.org.ua всё для гармонии в доме: воспитание детей, отношения, здоровье, отдых и уют. Полезные советы, статьи и лайфхаки для всей семьи. Пространство, где находят ответы и вдохновение.
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Портал о стройке https://bastet.com.ua статьи, новости и советы по ремонту, строительству и дизайну. Подбор материалов, проекты домов, технологии и полезная информация для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Портал о здоровье https://mikstur.com информационный ресурс о медицине и ЗОЖ. Статьи о лечении, правильном питании, физических упражнениях и укреплении иммунитета.
Информационный портал https://intertools.com.ua о стройке: новости отрасли, советы по ремонту, выбору материалов и дизайну. Всё для тех, кто строит дом, делает ремонт или работает в строительстве.
Портал про детей https://mch.com.ua информационный ресурс для родителей. От беременности и ухода за малышом до воспитания школьников. Советы, статьи и поддержка для гармоничного развития ребёнка.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://girl.kyiv.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, кулинария, отношения и материнство. Ежедневные материалы, экспертные советы и вдохновение для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://krasotka-fl.com.ua всё о красоте, моде, семье и жизни. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, советы экспертов и интересные истории. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь каждый день.
https://russpain.com/
Онлайн-журнал https://presslook.com.ua для женщин объединяет всё, что важно: мода и стиль, воспитание детей, карьерные советы и вдохновение. Советы специалистов и реальные истории для поддержки и новых идей.
Актуальные тренды https://horoscope-web.com и вневременная классика. Подборки образов, советы по стилю, секреты гардероба и модные инсайты. Мы поможем тебе выглядеть безупречно каждый день и выразить свой индивидуальный стиль.
Твой гид https://nicegirl.kyiv.ua по здоровому образу жизни! Эффективные тренировки, сбалансированное питание, wellness-практики и советы по мотивации. Обрети энергию, силу и гармонию в теле, которое ты любишь.
Ресурс для амбициозных https://ramledlightings.com и целеустремленных. Карьерный рост, личная эффективность, финансовая грамотность и вдохновляющие истории успеха. Реализуй свой потенциал и добивайся всех поставленных целей!
Наша платформа https://probilets.com/ работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Таможенный брокер в Москве — это гарантия правильного заполнения деклараций и соблюдения всех норм законодательства: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
курсовая работа москва заказать курсовую работу цена
https://profile.hatena.ne.jp/Otello/profile
Puzzles online https://listen.hubhopper.com/episode/puzzlefree/32934074?s=hh-web-app play for free in assembling pictures of any complexity. Thousands of options: classic, children’s, 3D and thematic. Convenient interface, saving progress and new puzzles every day.
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов https://probilets.com/. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
http://www.outdoors.ru/transit/index.php
Таможенный брокер — ваш надежный партнер при импорте и экспорте товаров в Москве: таможенный брокер в Москве
https://mangalfactory.ru/
Наша платформа https://probilets.com/ работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
http://www.free-lancers.net/info-center/
Мы берем на себя все заботы по взаимодействию с таможенными органами, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на бизнесе: таможенный брокер в Москве
Мы гарантируем корректность оформления документов и соблюдение сроков поставки груза: https://tamozhenniiy-broker11.ru/
Журнал для женщин https://rpl.net.ua которые строят карьеру и хотят большего. Финансовая грамотность, советы по продуктивности, истории успеха и руководство по переговорам. Достигайте своих целей с нами!
Твой гид https://womanlife.kyiv.ua по стильной жизни. Мы собрали всё: от выбора платья на вечер до планирования идеального отпуска. Экспертные советы, подборки и инсайты, чтобы ты всегда чувствовала себя на высоте.
Онлайн-журнал о моде https://glamour.kyiv.ua без правил. Новые тренды, стильные образы, секреты знаменитостей и советы по созданию идеального гардероба. Мы поможем вам найти и с уверенностью выразить свой уникальный стиль.
Женский сайт https://bbb.dp.ua всё самое важное для современных девушек: стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения и самореализация. Читайте, вдохновляйтесь и находите новые идеи.
Новостной портал Украины https://lenta.kyiv.ua оперативные события в стране. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Достоверные материалы и аналитика каждый день.
Новостной сайт https://vesti.in.ua свежие события дня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт, технологии и общество. Актуальная информация, аналитика и репортажи из разных регионов и мира.
Свежие новости https://sensus.org.ua Украины и мира: главные события, репортажи и аналитика. Политика, экономика, общество и культура в удобном формате онлайн.
Свежие новости Украины https://novosti24.kyiv.ua главные события, мнения экспертов и аналитические материалы. Лента новостей онлайн, репортажи и достоверные факты без перерыва.
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване https://probilets.com/. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
https://bpr-work.ru/
https://istoki.tv/news/company/akvaparki-v-sochi-polnyy-gid-2025-luchshie-mesta-dlya-otdykha-i-razvlecheniy/
https://teletype.link/yanrus
Новости Украины https://status.net.ua объективная информация о событиях страны. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Читайте актуальные материалы каждый день.
Новостной портал https://mediateam.com.ua всё самое важное сегодня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт и шоу-бизнес. Лента новостей, репортажи и аналитические материалы каждый день.
Новости Украины и мира https://mostmedia.com.ua политика, экономика, культура, спорт и общество. Свежие события, аналитика и репортажи. Будьте в курсе главных новостей в режиме онлайн 24/7.
Необходимо кодирование? прокапаться от алкоголя современные методы, конфиденциальность и поддержка специалистов. Помогаем избавиться от зависимости и вернуться к здоровой жизни.
работа ибп с генератором
https://www.te-in.ru/vse-o-kapitalnom-remonte-dgu-osnovnyie-etapyi-i-osobennosti-proczessa.html/
наркология вывод из запоя наркологический центр
https://www.te-in.ru/chto-takoe-elektrolaboratoriya-i-dlya-chego-ona-nuzhna.html/
http://vipvkurske.com/contacts/
Онлайн новостной портал https://reporternews.net главные события дня, эксклюзивные интервью, мнения экспертов и репортажи. Достоверная информация о политике, бизнесе и жизни общества.
Новостной портал https://newsawait.com свежие новости, аналитика и обзоры. Политика, экономика, культура и спорт. Лента событий в режиме реального времени с проверенными фактами.
Портал про авто https://dream-autos.com новости, обзоры и тест-драйвы. Полезные советы по выбору, ремонту и эксплуатации автомобилей. Каталог машин, актуальные цены и аналитика авторынка.
https://vgarderobe.ru/modnaya-futbolka-s-nadpisyu-ltb-g-16294-3.html
https://vgarderobe.ru/obuv-dlya-devochek-new-balance-bc-52004.html
Новости Украины и мира https://globalnewshome.com всё самое важное сегодня. Политика, экономика, региональные события, спорт и культура. Объективные статьи и аналитика в удобном формате.
Портал для женщин https://womanfashionista.com всё самое важное в одном месте: уход за собой, мода, дом, семья и карьера. Читайте полезные статьи, находите вдохновение и делитесь опытом.
Сайт детского сада https://malush16.ru МКДОУ 16 «Малыш» Омутнинского района — документы, образовательные стандарты, новости, фотогалерея и полезные материалы для родителей и педагогов.
Статьи для садоводов https://portalteplic.ru огородников, фермеров и пчеловодов: советы по уходу за растениями, животными и пасекой. Полезные инструкции, лайфхаки и сезонные рекомендации.
Портал о ремонте https://studio-nd.ru статьи, инструкции и советы для дома и квартиры. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Полезные рекомендации для мастеров, новичков и частных застройщиков.
https://www.te-in.ru/uslugi/obsluzhivanie-inzhenernyix-setej.html/
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhiletka-s-bolshim-vorotnikom-vivance-g-11491-2.html
Строительный портал https://krovlyaikrysha.ru база знаний и идей. Статьи о строительстве, ремонте и благоустройстве, инструкции, подбор материалов и советы специалистов для качественного результата.
Всё про ремонт https://gbu-so-svo.ru и строительство — статьи, инструкции и советы для мастеров и новичков. Обзоры материалов, проекты домов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
Автомобильный портал https://ivanmotors.ru всё о машинах в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, обзоры, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Актуальные события мира авто для водителей и экспертов.
Сайт о ремонте https://e-proficom.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Всё, что нужно для ремонта квартир и домов.
Сайт для женщин https://devchenky.ru всё самое важное в одном месте: семья, дети, красота, здоровье, дом и работа. Советы специалистов, лайфхаки и вдохновение на каждый день.
Блог о ремонте https://ivinstrument.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. Всё о ремонте квартир и домов: выбор материалов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-khudi-ajc-bc-1142.html
Городской портал Москвы https://moscowfy.ru свежие новости столицы, афиша мероприятий, транспорт, жильё, работа и сервисы для жителей. Полезная информация для москвичей и гостей города на одном сайте.
перевод документов бюро перевод сервис
Подборка статей https://yandex-direct-info.ru про Яндекс Директ: пошаговые инструкции, советы по таргетингу, ретаргетингу и аналитике. Всё о рекламе в Яндексе в одном месте для вашего бизнеса.
Яндекс Бизнес https://business-yandex3.ru описание сервиса, его инструменты и функции. Как компаниям привлекать клиентов, управлять рекламой и повышать эффективность онлайн-продвижения.
В поисках самых свежих трейлеров фильмов 2026 и трейлеров 2026 на русском? Наш портал — это место, где собираются лучшие трейлеры сериалов 2026. Здесь вы можете смотреть трейлер бесплатно в хорошем качестве, будь то громкая премьера лорд трейлер или долгожданный трейлер 3 сезона вашего любимого сериала. Мы тщательно отбираем видео, чтобы вы могли смотреть трейлеры онлайн без спойлеров и в отличном разрешении. Всю коллекцию вы найдете по ссылке ниже: трейлер 5
https://vgarderobe.ru/tufli-tamaris-g-28684-52.html
https://vgarderobe.ru/zhenskie-tenk-topy-cat-711.html
https://vgarderobe.ru/tank-top-v-nabore-2-shtuki-beach-time-g-61667-21.html
Что такое Agile https://agile-metod.ru и как его внедрить? Подробные статьи о гибких методологиях, инструментах и практиках. Scrum, Kanban и Lean — всё о современном управлении проектами.
Что такое CPI https://cost-per-install.ru в маркетинге? Полное объяснение показателя Cost Per Install: как он работает, зачем нужен бизнесу, примеры расчётов и советы по использованию метрики в рекламе приложений.
Бесплатная юридическая консультация в Москве становится все более популярной . Это связано с растущей потребностью в правовой помощи . Юристы предлагают свои знания и опыт совершенно бесплатно .
Бесплатные юридические консультации должны быть доступны каждому желающему. Обратиться за юридической помощью может любой гражданин, независимо от его финансового положения . Благодаря этому, уменьшится количество правонарушений .
Получить бесплатную юридическую консультацию можно довольно просто . Чаще всего требуется только записаться на прием к юристу . Многие юридические компании предоставляют консультации через интернет .
Таким образом, бесплатная юридическая помощь в Москве — это необходимый ресурс для жителей столицы. Юридическая помощь также играет значительную роль в повышении правовой грамотности населения . Не упустите возможность воспользоваться бесплатной помощью, если это вам нужно .
на сайте на сайте.
https://mp-digital.ru/
живые подписчики в тг
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без отписок
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/171056105/detail.aspx
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
накрутка подписчиков телеграм 100 подписчиков
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые без отписок
Графитовые и угольные щетки для электроинструмента. Большой выбор, надёжность и долговечность. Подходят для дрелей, болгарок, перфораторов и другого оборудования.
Нужны двери? двери межкомнатные спб шпонированные Широкий ассортимент межкомнатных дверей от Вектордорс. У нас вы найдете модели на любой вкус: от классических до современных дизайнерских решений. Выбор межкомнатных дверей — важный этап обустройства помещения. Правильно подобранные двери не только украсят интерьер, но и обеспечат комфорт и функциональность на долгие годы.
ЩПС цена за куб https://pesko.ru
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм
CPL (Cost Per Lead) https://cost-per-lead1.ru ключевая метрика рекламы. Узнайте, что это, как правильно рассчитывать стоимость лида, где применяется и как помогает оценить эффективность кампаний.
накрутка подписчиков телеграм
Интернет-маркетинг https://internet-marketing1.ru SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, email-рассылки и аналитика. Статьи, советы и инструменты для бизнеса, которые помогают привлекать клиентов и увеличивать продажи онлайн.
быстрая накрутка подписчиков в телеграм
Интернет-маркетинг https://yandex-reklama2.ru для компаний и специалистов: SEO, SMM, контекстная реклама и email. Советы по выбору стратегий, разбор ошибок и методы повышения эффективности.
накрутка подписчиков тг
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые без отписок
Генеральная уборка https://cleaningplus.ru/services/uborka-kvartiry в Москве: квартиры, дома, офисы. Полный комплекс услуг — мытьё окон, чистка мебели, удаление пыли и грязи. Профессиональные клинеры, безопасные средства и гарантия качества.
онлайн накрутка подписчиков тг
Для получения квалифицированной помощи в вопросах раздела имущества, обратитесь к специалистам на юрист по делам раздела имущества.
В этом отношении помощь юристов может быть крайне важной.
накрутить подписчиков в тг
накрутить живых подписчиков в телеграм
Футболка сублимация и футболки с вышивкой во Владимире. Серая мужская рубашка и Chessford брюки для мальчика в Тамбове. Футболки больших размеров мужские и кофта под футболку как называется в Кирове. Одежда для Baby Born и аниме одежда для парней в Красноярске. Футболка оптом мы русские с нами бог и футболки надписи сзади https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
накрутка подписчиков тг
щетки
как набрать 1000 подписчиков в тг
накрутка подписчиков тг
https://www.restate.ru/
Мы предоставляем профессиональные консультации по вопросам ВЭД и таможенного оформления: таможенный брокер
накрутить подписчиков в тг
накрутка подписчиков в тг дешево
как добавить подписчиков в тг канал
Портал про авто https://ivanmotors.ru обзоры автомобилей, новости автопрома, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Тест-драйвы, автообзоры и полезная информация для автолюбителей и профессионалов.
Всё о Москве https://moscowfy.ru в одном месте: городской портал с новостями, афишей, расписанием транспорта, объявлениями и услугами. Полезные материалы для москвичей и туристов.
Портал о строительстве https://e-proficom.ru и ремонте: полезные статьи, советы специалистов, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё для тех, кто планирует ремонт квартиры, дома или дачи.
Женский портал https://devchenky.ru секреты красоты, модные тенденции, здоровье, любовь и кулинария. Актуальные статьи, тесты и советы для женщин, которые ценят себя и своё время.
накрутка подписчиков тг канале купить
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu buszken tamogatja a kormanypartot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Строительные материалы https://stroy-marketplace.ru в Серпухове: кирпич, цемент, сухие смеси, пиломатериалы и утеплители. Большой выбор для ремонта и строительства, доставка по городу и району.
Курсы по заработку онлайн
Play shining crown oyunu ilə böyük həyəcan yaşamaq mümkündür.
Shining crown buy bonus funksiyası əlavə qazanclar verir.
Shining crown free slot risksiz məşq üçün möhtəşəmdir. Shining crown demo ron Avropa bazarında məşhurdur. Pinco casino shining crown üçün ən yaxşı platformadır.
Shining crown pacanele Rumıniya bazarında liderdir.
Shining crown slot oyna istənilən cihazdan mümkündür.
Rəsmi səhifə rəsmi sayt.
Shining crown big win uduşları oyunçular üçün motivasiya rolunu oynayır.
Shining crown slot online tez yüklənir.
Blackjack game https://baji-bj.com
Будівельні матеріали представлені на remontuem.te.ua
как накрутить подписчиков в тг канал ботов
Joaca jocwarships.top gratuit! Exploreaza marile, folose?te-?i strategia ?i condu nave de razboi celebre. Batalii realiste ?i echipe interna?ionale te a?teapta.
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без заданий
Kingpin Crown in Australia is a premium entertainment venue offering bowling, laser tag, arcade games, karaoke, and dining: Kingpin Crown official website
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без регистрации
ваш провідник у житті Львова https://79000.com.ua актуальні новини, культурні та громадські події міста, урбаністика, інтерв’ю з цікавими людьми, фотоогляди локальних заходів. Все про те, що формує атмосферу Львова сьогодні — оновлення, проекти, історії.
інформаційний портал https://21000.com.ua Вінниці і області: місцеві новини, анонси культурних, спортивних та громадських подій, репортажі з місця подій, інтерв’ю з вінничанами. Все про те, що відбувається у Вінниці — ближче, живіше, щодня.
Пиломатериалы в Минске https://farbwood.by оптом и в розницу. Доска обрезная и строганая, брус, лаги, террасная доска. Качественная древесина для строительства и ремонта. Быстрая доставка.
40 shining crown slot variantları Pinco casino-da populyardır.
Shining crown big win qazanmaq motivasiya yaradır.
Shining crown gratis versiyası limitsiz sınaq verir. Shining crown demo superbet variantı real casino təcrübəsinə yaxındır. Shining crown apk mobil cihazlarda problemsiz işləyir.
Shining crown joc gratis təcrübə qazandırır.
Shining crown demo superbet sürətli işləyir.
Sayta birbaşa keçid https://shining-crown.com.az/.
Shining crown big win uduşları oyunçular üçün motivasiya rolunu oynayır.
Shining crown slot online tez yüklənir.
Crown Metropol Perth is a luxury hotel located near the Swan River. It offers modern rooms, a stunning pool area, fine dining, a casino, and entertainment options: Crown Metropol Perth booking
https://milgauzen.ru/
живые подписчики в телеграм без отписки
Hello folks!
I came across a 136 great site that I think you should visit.
This platform is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://linuxidee.com/interesting-facts/famous-and-infamous-casino-heists/
And remember not to forget, everyone, that a person always may in the publication discover answers to address the the absolute tangled questions. Our team tried — present all content using an very easy-to-grasp method.
микрозайм онлайн микрозайм рейтинг
Hello lads!
I came across a 136 interesting page that I think you should browse.
This site is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find interesting.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://colbadigitalmarketing.com/success-at-bets/the-legality-of-sports-betting-a-global-perspective/
And do not neglect, folks, which one always are able to inside the publication find solutions for your the absolute tangled inquiries. The authors made an effort to explain all of the information using the most understandable manner.
Нужны автостекла? замена лобового стекла в спб Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Ваш язык – агентство переводов языков. Перевод для книг и комиксов в Самаре. Сохранение стиля автора, игра слов, культурные отсылки. Делаем перевод, который читается как оригинал.
електрики тернопіль https://remontuem.te.ua
https://npc-info.ru/
как накрутить подписчиков в телеграм бот
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Нужна лабораторная? сделать лабораторную работу на заказ Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужна презентация? https://prez-shablony-ucheb.ru Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? https://chertezhi-kurs.ru выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
https://alive-portal.ru/
накрутка подписчиков тг бесплатно без отписок
накрутить подписчиков в тг канал без отписок
подписчики в тг канал реклама
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
дизайн кухні тернопіль https://remontuem.te.ua
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae покупка, продажа и аренда новых и б/у машин. Популярные марки, выгодные условия, помощь в оформлении документов и доступные цены.
как накрутить подписчиков в телеграм бот
Вызвал индивидуалку на дом, все прошло идеально. Она приехала быстро, выглядела прекрасно, была очень нежной и внимательной. Настоящее удовольствие. Крайне рекомендую, индивидуалка недорого нск – https://sibirki3.vip/. Атмосфера супер, сразу чувствуешь комфорт.
Заметки практикующего врача https://phlebolog-blog.ru флеболога. Профессиональное лечение варикоза ног. Склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен и точная диагностика. Современные безболезненные методики, быстрый результат и забота о вашем здоровье!
purebred kittens for sale in NY https://catsdogs.us
накрутка подписчиков в тг без отписок
Проблемы с откачкой? насос погружной для откачки воды сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
Нужна презентация? создать презентацию генератор Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
накрутка подписчиков тг без регистрации
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
живые подписчики в телеграм
Проблемы с откачкой? водяной насос для откачки воды сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
Zivjeti u Crnoj Gori? https://www.placevi-zabljak-nekretnine.com Novi apartmani, gotove kuce, zemljisne parcele. Bez skrivenih provizija, trzisna procjena, pregovori sa vlasnikom. Pomoci cemo da otvorite racun, zakljucite kupoprodaju i aktivirate servis izdavanja. Pisite — poslacemo vam varijante.
Портал о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: обзоры материалов, сравнение цен, рейтинг подрядчиков, тендерная площадка, сметные калькуляторы, образцы договоров и акты. Актуальные ГОСТ/СП, инструкции, лайфхаки и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Смотрите онлайн песни для детей слушать онлайн или скачать лучшие детские мультфильмы, сказки и мульсериалы. Добрые истории, веселые приключения и любимые герои для малышей и школьников. Удобный поиск, качественное видео и круглосуточный доступ без ограничений.
Мир гаджетов https://indevices.ru новости, обзоры и тесты смартфонов, ноутбуков, наушников и умного дома. Сравнения, рейтинги автономности, фото/видео-примеры, цены и акции. Поможем выбрать устройство под задачи и бюджет. Подписка на новые релизы.
Всё о ремонте https://remontkit.ru и строительстве: технологии, нормы, сметы, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Дизайн-идеи для квартиры и дома, цветовые схемы, 3D-планы, кейсы и ошибки. Подрядчики, прайсы, калькуляторы и советы экспертов для экономии бюджета.
Женский портал https://art-matita.ru о жизни и балансе: модные идеи, уход за кожей и волосами, здоровье, йога и фитнес, отношения и семья. Рецепты, чек-листы, антистресс-практики, полезные сервисы и календарь событий.
Все автоновинки https://myrexton.ru премьеры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и даты продаж. Электромобили, гибриды, кроссоверы и спорткары. Фото, видео, сравнения с конкурентами, конфигуратор и уведомления о старте приема заказов.
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно без регистрации
https://plenka-okna.ru/
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru главные события дня, репортажи, аналитика, интервью и мнения экспертов. Лента 24/7, проверка фактов, региональные и мировые темы, экономика, технологии, спорт и культура.
Всё о стройке https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и ремонте: технологии, нормы, сметы и планирование. Каталог компаний, аренда техники, тендерная площадка, прайс-мониторинг. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, инструкции и видеоуроки для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных мастеров.
Строительный портал https://nastil69.ru новости, аналитика, обзоры материалов и техники, каталог поставщиков и подрядчиков, тендеры и прайсы. Сметные калькуляторы, ГОСТ/СП, шаблоны договоров, кейсы и лайфхаки.
Актуальные новости https://pr-planet.ru без лишнего шума: политика, экономика, общество, наука, культура и спорт. Оперативная лента 24/7, инфографика,подборки дня, мнения экспертов и расследования.
купить айфон Уфа
ціни на малярні роботи https://remontuem.te.ua
накрутка подписчиков в тг навсегда
Ремонт и стройка https://stroimsami.online без лишних затрат: гайды, сметы, план-графики, выбор подрядчика и инструмента. Честные обзоры, сравнения, лайфхаки и чек-листы. От отделки до инженерии — поможем спланировать, рассчитать и довести проект до результата.
накрутка подписчиков телеграм канал
накрутка подписчиков в тг без регистрации
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/183263596/detail.aspx
Футболка с логотипом Краснодар и напечатать текст на футболке в Челябинске. Шапка каталог и перчатки с сенсорными пальцами в Стерлитамаке. Красные футболки оптом и яркий принт на футболку в Суздале. Oasis бренд одежды и меркурий каталог с ценами одежда в Ижевске. Вышивка на футболках оптом надпись и печать на футболке Владимир https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
заказ значков из металла заказ значков из металла
значок на лацкан на заказ значок индивидуальный
производство значков из металла значок изготовить на заказ цена
купить накрутку подписчиков тг
накрутка подписчиков в телеграме
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu
joszaki regisztracio joszaki
накрутить подписчиков в тг
http://tourout.ru/
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu/
живые подписчики в телеграм без отписки
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал бесплатно
теплоходный экскурсии в казани
Bakı Formula 1 trası ilə bağlı geniş təhlil təqdim olunur. Formula 1 Bakıda 2025 tarixlərini indi öyrənin.
Əlavə məlumat üçün linkə daxil olun ➡ https://formula-1.com.az.
Formula 1 schedule daim yenilənir və asan izlənilir. Formula 1 puan cədvəli ilə favoritlərinizi izləyin.
Formula 1 2025 calendar üzrə bütün yarış tarixləri. Formula 1 tickets almaq üçün sərfəli variantlar. Formula 1 canlı izləmə təcrübənizi paylaşın. Formula 1 logo simvolikasının mənası barədə məlumat.
Cleaning is needed cleaning services toronto eco-friendly supplies, vetted cleaners, flat pricing, online booking, same-day options. Bonded & insured crews, flexible scheduling. Book in 60 seconds—no hidden fees.
2024 və 2025 Formula 1 təqvimlərinin tam siyahısını əldə edin. Formula 1 avtomobillərinin texniki göstəricilərini müqayisə edin.
Rəsmi səhifədən tanış olun ➡ formula-1.com.az.
Formula 1 canli yayım üçün yeni platformalar. Formula 1 Baku 2025 üçün ən maraqlı məlumatlar.
Formula 1 movie həvəskarları üçün tövsiyələr. Formula 1 canlı yayım keyfiyyəti ilə bağlı rəylər. Formula 1 canlı izləmə təcrübənizi paylaşın. Formula 1 drivers ilə bağlı ən son xəbərlər.
Tennis betting https://betvisabengal.com
Портал Чернівців https://58000.com.ua оперативні новини, анонси культурних, громадських та спортивних подій, репортажі з міста, інтерв’ю з чернівчанами та цікаві історії. Все про життя Чернівців — щодня, просто й доступно
Formula 1 könüllü proqramı haqqında maraqlı məlumatlar burada. Ən yaxşı Formula 1 filmləri və sənədli layihələri.
Ən son xəbərləri izləmək üçün baxın ➡ formula 1.
Formula 1 volunteer 2025 proqramına qoşulmaq üçün şərtlər. Formula 1 puan cədvəli ilə favoritlərinizi izləyin.
Formula 1 takvimi hər mövsüm yenilənir. Formula 1 puan durumu ilə komandaları izləyin. Formula 1 2024 takvimi ilə bağlı maraqlı dəyişikliklər. Formula 1 puan durumu ilə favorit komandanızı izləyin.
Своевременная консультация юриста может спасти вас от многих проблем.
онлайн юридическая консультация бесплатно на accessnetworkdirectory.com онлайн юридическая консультация бесплатно на accessnetworkdirectory.com
Formula 1 könüllü proqramı haqqında maraqlı məlumatlar burada. Formula 1 Bakıda 2025 tarixlərini indi öyrənin.
Yarış təqvimi və nəticələr üçün baxın ➡ formula-1 com az.
Formula 1 schedule daim yenilənir və asan izlənilir. Formula 1 2024 Bakı yarışlarının tarixi artıq məlumdur.
Formula 1 2025 calendar üzrə bütün yarış tarixləri. Formula 1 puan durumu ilə komandaları izləyin. Formula 1 volunteer 2025 qeydiyyatı başladı. Formula 1 azerbaycanda keçirilən yarışlar barədə maraqlı faktlar.
Formula 1 könüllü proqramı haqqında maraqlı məlumatlar burada. Formula 1 sürücüləri haqqında maraqlı faktlar.
Son xəbərləri buradan oxuyun ➡ https://formula-1.com.az.
Formula 1 haqqinda melumat axtaranlar üçün faydalı mənbə. Formula 1 2024 Bakı yarışlarının tarixi artıq məlumdur.
Formula 1 Baku track barədə dəqiq xəritə məlumatı. Formula 1 canlı yayım keyfiyyəti ilə bağlı rəylər. Formula 1 izləmə yolları haqqında faydalı təlimatlar. Formula 1 izləmə təcrübəsini rahatlaşdıran xidmətlər.
Formula 1 2025 təqvimini öyrənmək istəyənlər üçün faydalı məlumat. Bakı Formula 1 xəritəsi üzrə hər bir döngəni tanıyın.
Məlumat üçün buraya klikləyin ➡ formula 1 com az.
Formula 1 volunteer 2025 proqramına qoşulmaq üçün şərtlər. Formula 1 volunteer təcrübəsi ilə bağlı məsləhətlər.
Formula 1 takvimi hər mövsüm yenilənir. Formula 1 Azərbaycan mərhələsinin atmosferi barədə şərhlər. Formula 1 izləyiciləri üçün ən son xəbərlər. Formula 1 puan durumu ilə favorit komandanızı izləyin.
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Монтаж видеонаблюдения под ключ https://vcctv.ru
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня
Boosting Brians club credit makes ambitious goals achievable.
Статья содержит обширную информацию и аргументы, подтвержденные ссылками на достоверные источники.
TheHold стал моим ежедневным помощником. Здесь есть новости, прогнозы, курсы криптовалют и полезные обзоры бирж и кошельков. Мне нравится, что всё подаётся простым языком и без лишней рекламы. Это один из лучших журналов по крипте: https://thehold.ru/
В торговой сети продуктов оборудование Labelaire оказалось очень удобным. Мы используем его вместе с принтерами ценников и термопринтерами этикеток. Работа персонала стала эффективнее https://labelaire.ru/
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
https://clickolov.ru/
Ən son versiya ilə soccer daha real görünür.
Flashscore mobile livescore today soccer ilə ani nəticələr alın. Ən son yenilikləri öyrənmək üçün soccer.com.az linkinə baxa bilərsiniz.
World soccer champs mod apk ilə əlavə imkanlar əldə edin. Soccer champs hile versiyaları əlavə üstünlüklər yaradır. Real soccer 2012 nostalji sevənlər üçün uyğundur.
Pro direct soccer məhsulları keyfiyyətli seçimdir. World soccer champs maç atlama hilesi ilə oyun sürətlənir. Dream league soccer 2023 yeni komanda imkanları təqdim edir. Soccer champs para hilesi ilə oyunda üstünlük qazanın.
Mobil cihazlarda soccer oyunu yüksək keyfiyyətlə işləyir.
World soccer champs apk futbol həvəskarlarının seçimi olub. Əlavə məlumat üçün http://soccer.com.az/ səhifəsinə baxmaq olar.
Major league soccer standings nəticələrini hər gün yoxlayın. Soccer star oyunçular üçün motivasiyaedici seçimdir. Soccer predictions futbol nəticələrini təxmin etməyə kömək edir.
Soccer skills champions league ilə yeni bacarıqlar öyrənin. Soccer champs apk yükləmək çox asandır. Spbo live score soccer ilə hər dəqiqə nəticələri görün. Soccer star mod apk ilə daha çox imkan əldə edin.
Soccer tətbiqi futbol həvəskarları üçün idealdır.
Opera soccer tətbiqi ilə xəbərlərə tez çatın. Soccer haqqında daha ətraflı məlumat üçün soccer rəsmi səhifəsinə baxın.
Soccer random oyunu sadə və əyləncəlidir. Rocket soccer derby fərqli futbol janrını təqdim edir. Bubble soccer dostlarla əyləncəli vaxt keçirməyə imkan verir.
Globe soccer awards beynəlxalq səviyyədə tanınır. Fifa soccer mod apk team2earn futbolu daha real edir. Reddit soccer streams ilə matçlara çıxış tapmaq olar. Mini soccer star apk sadə və əyləncəlidir.
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/249860602/detail.aspx
Сломалась машина? услуга помощь на дороге мы создали профессиональную службу автопомощи, которая неустанно следит за безопасностью автомобилистов в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты всегда на страже вашего спокойствия. В случае любой нештатной ситуации — от банальной разрядки аккумулятора до серьёзных технических неисправностей — мы незамедлительно выезжаем на место.
Soccer oyununu telefonda oynamaq çox rahatdır.
Soccer 365 ilə futbol xəbərlərindən xəbərdar olun. Mobil futbol oyunları üçün əsas ünvan soccer com az portalıdır.
Soccer random oyunu sadə və əyləncəlidir. Livescore soccer results futbol azarkeşləri üçün vacibdir. Soccer bros multiplayer futbol üçün əla seçimdir.
Globe soccer awards beynəlxalq səviyyədə tanınır. Soccer field dizaynı oyunda çox real görsənir. Reddit soccer streams ilə matçlara çıxış tapmaq olar. Dream league soccer 2017 sevilən versiyadır.
iOS üçün soccer yükləyib pulsuz oynayın.
Soccer skills euro cup ilə bacarıqlarınızı artırın. ABŞ futbol liqası nəticələrini izləmək üçün major league soccer standings səhifəsinə daxil olun.
Dream league soccer 2024 versiyası daha müasir imkanlar verir. Livescore soccer results futbol azarkeşləri üçün vacibdir. Soccer bros multiplayer futbol üçün əla seçimdir.
Soccer game klassik futbol təcrübəsi təqdim edir. Soccer platform prediction nəticələri izləməyə kömək edir. Livescore.com.tr live soccer scores azarkeşlər üçün əhəmiyyətlidir. Mini soccer star apk sadə və əyləncəlidir.
iOS üçün soccer yükləyib pulsuz oynayın.
Soccer skills euro cup ilə bacarıqlarınızı artırın. Mobil oyunlar barədə öyrənmək üçün soccer com az linkinə keçid edin.
Dream league soccer 2024 versiyası daha müasir imkanlar verir. Dream league soccer 2019 hələ də sevilən versiyalardandır. Soccer bros multiplayer futbol üçün əla seçimdir.
Opera sport soccer futbol xəbərləri üçün aktualdır. Soccer stars sadə amma maraqlı oyundur. Dream league soccer 2023 yeni komanda imkanları təqdim edir. Soccer games müxtəlif janrlarda futbol təqdim edir.
Практика ремонта https://stroimsami.online и стройки без воды: пошаговые инструкции, сметные калькуляторы, выбор материалов, схемы, чек-листы, контроль качества и приёмка работ. Реальные кейсы, фото «до/после», советы мастеров и типичные ошибки — экономьте время и бюджет.
Компания СтройСинтез помогла нам построить коттедж из кирпича с гаражом. Архитекторы предложили оптимальный проект, а строители сделали всё качественно. Дом полностью соответствует нашим ожиданиям. Подробности доступны по ссылке: https://stroysyntez.com/
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
Мир гаджетов без воды https://indevices.ru честные обзоры, реальные замеры, фото/видео-примеры. Смартфоны, планшеты, аудио, гейминг, аксессуары. Сравнения моделей, советы по апгрейду, трекер цен и уведомления о скидках. Помогаем выбрать устройство под задачи.
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Хочешь сдать акб? адреса приема аккумуляторов честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
Нужен аккумулятор? заказать аккумулятор для автомобиля с доставкой в наличии: топ-бренды, все размеры, правый/левый токовывод. Бесплатная проверка генератора при установке, trade-in старого АКБ. Гарантия до 3 лет, честные цены, быстрый самовывоз и курьер. Поможем выбрать за 3 минуты.
Мы доверили Кухни в Дом проект нашей новой кухни, и результат оказался отличным. Замер, дизайн и установка прошли без задержек, а кухня радует нас каждый день. Отличный сервис и высокое качество: https://kuhni-v-dom.ru/
Очень доволен работой по раскрутке сайта. Исправили технические ошибки, добавили новые разделы и усилили контент. Теперь в Google и Яндекс мы стоим значительно выше, чем раньше: https://mihaylov.digital/
Ищешь аккумулятор? купить аккумулятор для авто в спб AKB SHOP занимает лидирующие позиции среди интернет-магазинов автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге. Наш ассортимент охватывает все категории транспортных средств. Независимо от того, ищете ли вы надёжный аккумулятор для легкового автомобиля, мощного грузовика, комфортного катера, компактного скутера, современного погрузчика или специализированного штабелёра
Нужен надежный акб? купить аккумулятор для авто цена AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
Developing briansclub.llc credit draws valuable partnerships.
Growing briansclub.llc credit strengthens brand image.
Складчик стал для меня удобным инструментом для саморазвития. Я участвовала в складчине по бизнесу и получила полный доступ за минимальную цену. Всё прошло честно и быстро. Теперь использую этот сервис постоянно – https://v27.skladchik.org/
LaLiga statistikası hər gün yenilənir. LaLiga table 2025 artıq açıqlandı.
Canlı LaLiga matçlarını izləmək üçün ən rahat platforma. İspaniya futbolunun simvolu olan LaLiga loqosu. İspaniya çempionatının ən yeni xəbərlərini [url=https://laliga.com.az/]LaLiga[/url] saytında oxuya bilərsiniz. Burada bütün matçların təqvimi və cədvəli daim yenilənir.
LaLiga goal record yenidən dəyişdi.
LaLiga maçlar və canlı yayım üçün bələdçi.
Ən yaxşı LaLiga oyunçuları 2025.
LaLiga cup finalı böyük maraqla izlənir.
Hər oyun sonrası LaLiga nəticələri buradadır.
LaLiga azarkeşləri üçün canlı yayım imkanı. İspaniyanın lider komandalarını tanı.
İspaniya LaLiga canlı futbolunu qaçırmayın. Yeni “LaLiga EA Sports” loqosu çox bəyənildi.
Əgər siz də futbol statistikası ilə maraqlanırsınızsa, LaLiga stats bölməsinə baxın.
Ən çox LaLiga qazanan komanda hansıdır?.
LaLiga maçlar və canlı yayım üçün bələdçi.
Futbol statistikası sevənlər üçün LaLiga bölməsi.
LaLiga champions list artıq dərc olunub.
LaLiga oyunlarının qrafiki və nəticələri burada.
LaLiga canlı izləmə üçün ideal mənbədir. Ən çox xal toplayan komandanı buradan öyrən.
Hər oyunun canlı statistikası əlinizdə. İspaniya futbolunun simvolu olan LaLiga loqosu.
Bütün LaLiga oyunlarının nəticələri burada — laliga maçlar.
LaLiga bombardirlər siyahısı yeniləndi.
LaLiga tv canlı baxmaq üçün seçimlər.
LaLiga statistika səhifəsində komanda göstəriciləri.
LaLiga super cup 2024 möhtəşəm idi.
LaLiga maç sonuclarını izləmək asandır.
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/466665547/detail.aspx
Получение лицензии «под ключ» включало подготовку всех документов, проверку их соответствия требованиям, сопровождение подачи и взаимодействие с государственными органами, что позволило избежать ошибок и бюрократических задержек – https://licenz.pro/
LaLiga canlı izləmə üçün ideal mənbədir. LaLiga turnir cədvəlində mövqeləri izləmək maraqlıdır.
Futbol sevərlərə LaLiga canlı izləmə təcrübəsi. LaLiga rəsmi loqosu artıq yeni rənglərlə.
Ən aktual xal cədvəli üçün https://laliga.com.az bölməsinə baxın.
Ən çox qol vuran LaLiga futbolçuları kimlərdir?.
LaLiga matçlar hansı kanalda yayımlanır?.
LaLiga takımları arasında rəqabət yüksəkdir.
LaLiga cup finalı böyük maraqla izlənir.
LaLiga nəticələri ilə favoritlərinizi izləyin.
В компании Окна СПб заказывали остекление лоджии. Мастера сделали всё в срок, балкон теперь уютный и красивый. Очень понравился сервис и качество материалов. Мы рекомендуем компанию друзьям: https://okna-v-spb.ru/
İspaniya çempionatının ən maraqlı matçlarını buradan izləyin. Yeni mövsüm üçün LaLiga sıralaması artıq dərc olunub.
Canlı LaLiga matçlarını izləmək üçün ən rahat platforma. Loqodakı dəyişikliklər brendin müasir ruhunu əks etdirir.
Komandaların son nəticələri haqqında daha ətraflı məlumat üçün LaLiga turnir cədvəli səhifəsinə daxil olun.
LaLiga goal of the season 2022 hələ də yadda qalır.
LaLiga matçlar hansı kanalda yayımlanır?.
LaLiga statistika səhifəsində komanda göstəriciləri.
LaLiga champions 2023 komandaları arasında böyük rəqabət.
LaLiga maç sonuclarını izləmək asandır.
İspaniya çempionatının ən maraqlı matçlarını buradan izləyin. LaLiga table 2025 artıq açıqlandı.
Canlı LaLiga matçlarını izləmək üçün ən rahat platforma. LaLiga logo dizaynı hər il yenilənir.
Komandaların son nəticələri haqqında daha ətraflı məlumat üçün LaLiga turnir cədvəli səhifəsinə daxil olun.
Goal scorer LaLiga siyahısına baxmaq istəyirsiniz?.
LaLiga maçlar və canlı yayım üçün bələdçi.
İspaniya LaLiga top futbolçularını tanı.
LaLiga champions 2023 komandaları arasında böyük rəqabət.
LaLiga scoreboard dərhal yenilənir.
Greate article. Keep posting such kind of information on your page. Im really impressed by your site.
Hey there, You’ve done a fantastic job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this site.
keepstyle
Thank you very much, that’s very kind of you.
https://briansclub.vg/
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Строительный портал https://stroimsami.online новости, инструкции, идеи и лайфхаки. Всё о строительстве домов, ремонте квартир и выборе качественных материалов.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
briansclub.vg
Надеюсь, что эти комментарии добавят ещё больше положительных настроений к информационной статье! Это сообщение отправлено с сайта GoToTop.ee
Thanks very interesting blog!
that’s kind of you
papamasque – Their presentation is elegant, I like the balance of style and substance.
that’s kind of you
Бесплатный seo аудит сайта https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Need TRON Energy? rent tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
Лука Модричтин тактикалык ой жүгүртүүсү укмуш.Модрич кетсе дагы, анын izi футболдо калат. Лука Модрич статистика дайыма жогорку деңгээлде. Лука Модричтин жашы 39 болсо да, оюну жаштардыкындай. Карьера жолу, клубдар, трофейлер — баары бир жерге топтолгон: luka-modric-kg.com. Анын ысымы футбол тарыхында калат.
Модрич Реалдын орто талаасын башкарып келет көп жылдан бери. Лука Модричтин балалык чагы оор болсо да, ал чоң жетишкендикке жетти. Бул оюнчу ар бир клуб үчүн кымбат сыйлык болот. Модрич карьерасын кайда улантса да, күйөрмандар аны колдойт.
Лука Модрич азыркы замандын эң мыкты оюнчуларынын бири.Бул футбол дүйнөсүндө чоң өзгөрүү болот. Лука Модрич статистика дайыма жогорку деңгээлде. Канча жашта болсо да, Модрич формасын сактап турат. Кыскача профили жана жаңыртылган баракча керек болсо, ушул линкке өт: http://luka-modric-kg.com/. Хорватиянын эң атактуу оюнчусу дал ушул Модрич.
Алар бирге көптөгөн ЛЧ жеңиштерин алып келишкен. Модрич жаш кезинен эле футболго берилген. Модрич акчаны эмес, атакты тандаган адам. Кээ бирөөлөр Модрич Аль Насрга барат дешет.
Лука Модрич футбол дүйнөсүнүн символу болуп калды.Модрич кетсе дагы, анын izi футболдо калат. Лука Модрич канча гол киргизгенин билесиңби? Лука Модричтин жашына ишенүү кыйын, ал дагы деле чоку формасында. Реалдагы доору, ЛЧ финалдары жана рекорддор — баары ушул жакта: https://luka-modric-kg.com/. 2018-жылы Алтын топ алганы эсте калды.
Модричсиз Реалдын оюн стили башкача болмок. Бул адамдын жашоосу — чыныгы күрөш. Анын баасы трансфермаркетте дагы жогору. Кайда барбасын, ал ар дайым легенда бойдон калат.
Автор старается представить информацию объективно и позволяет читателям самостоятельно сделать выводы.
IPTV форум vip-tv.org.ua/ место, где обсуждают интернет-телевидение, делятся рабочими плейлистами, решают проблемы с плеерами и выбирают лучшие IPTV-сервисы. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу интернет-ТВ!
wagisonsncompany – I enjoyed exploring, the elements and layout feel thoughtful.
thank you
redhillrepurposing – Love how they’re combining technology with art authenticity.
ouretiquette – Just explored this site; the concept of art verification is intriguing.
hellgate100nyc – The platform’s design is clean and user-friendly.
thank you
colossal-heart – A much-needed solution for artists seeking to prove their work’s authenticity.
Лука Модрич азыркы замандын эң мыкты оюнчуларынын бири.Эгер Лука Модрич кетсе, Реалдын орто талаасы өзгөрөт. Анын карьерасынын узактыгы профессионалдуулуктун белгиси. Модричтин энергиясы таң калтырат. Трансфер боюнча инсайддар жана қауесеттер үчүн кара: Лука Модрич трансфер. Лука Модрич ЧМ 2022де дагы мыкты оюн көрсөттү.
Лука Модрич Реалга келгенде команда өзгөргөн. Анын автобиографиясы мотивация берет. Футбол дүйнөсүндө андай адептүү оюнчулар аз. Лука Модрич үчүн көп клубдар эшигин ачат.
shopmaggielindemann – I appreciate the transparency this site offers to artists and buyers.
alixrice – Love how they’re combining technology with art authenticity.
blegacyfarms – I appreciate the transparency this site offers to artists and buyers.
aworldofgin – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
Футболдо мындай оюнчу сейрек кездешет, Модрич өзгөчө.Бул футбол дүйнөсүндө чоң өзгөрүү болот. Лука Модрич канча гол киргизгенин билесиңби? Көптөр “сколько лет Лука Модричке?” деп сурашат — бирок ал үчүн жаш маанилүү эмес. Оюн анализдери жана эксперттик пикирлер жыйнагы: https://luka-modric-kg.com/. Анын чеберчилиги ар бир эл аралык турнирде көрүнөт.
Анын Реалдагы карьерасы алтын барактар менен жазылган. Лука Модричтин балалык чагы оор болсо да, ал чоң жетишкендикке жетти. Модрич акчаны эмес, атакты тандаган адам. Лука Модрич келечекте кайсы клубга өтөт деп ойлойсуң?
Superb blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally confused .. Any recommendations? Thank you!
Thank you very much for your comment regarding the choice of domain. In my opinion, it is better to have a paid domain so as not to run into problems in the future, especially if you want to build your brand.
And it is better to have a website on WordPress rather than Blogger.
Мен ар дайым Лука Модричти көргөндө чыныгы лидерликти байкайм.Көпчүлүк күйөрмандар Модричтин кетишине ишенбей жатат. Модрич — чыныгы футбол интеллекти. Лука Модричтин жашы 39 болсо да, оюну жаштардыкындай. Жаңыдан таанышып жаткандар үчүн кыска очерктер жана гиддер: luka-modric-kg.com. Анын чеберчилиги ар бир эл аралык турнирде көрүнөт.
Футбол сүйүүчүлөрү үчүн Модрич — Реалдын жүрөгү. Лука Модрич жашоодон сабак алуунун үлгүсү. Модрич акчаны эмес, атакты тандаган адам. Лука Модрич үчүн көп клубдар эшигин ачат.
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
kruisefest – I like the mix of imagery and text throughout the site.
thank you
appytrucksandskulls – The visuals hit hard, gives real personality to the brand.
thanks
fullumandholt – Found the “about” section compelling—adds personality behind the work.
Thanks for the comment.
guitargodscollectibles – I’ll definitely return when I’m ready to add to my own collection.
thanks
linkrootes – Love the minimalism, doesn’t feel overwhelming when browsing pages.
thank you
420smokeshop – Content is easy to digest, looks thoughtfully laid out.
That’s nice
ureyo – Smooth transitions between pages, no jarring jumps or reloads.
Thanks for the comment.
maccabeestraders – The imagery is strong, gives real confidence in what you sell.
thanks
9hxn2 – The color scheme is subtle but effective, good choice overall.
That is kind
easy-software.online – The “About” section gives a decent sense of mission and values.
thank you
diamondescort18 – This page feels like it’s made with care, clean and neat.
That’s kind of you.
2jasabola.biz – The layout is simple yet effective, nice first impression.
Thanks for the comment.
vuabat – I like the balance of imagery and text throughout.
thanks
knockoutzakk – Your portfolio items come across very polished and well presented.
That is kind.
erinkristensen – Navigation is intuitive and pages load really fast.
thanks
housepartyofhorrors – The copywriting is engaging, pulls me deeper into the concept.
thank you
awsmining – The content feels relevant, I’m impressed with clarity and structure.
That’s nice.
blpawards – Hope the awards gain more traction — the concept is strong.
charitydriveforservicemembers – The stories you share feel powerful and human.
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru/ и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Особенно понравился раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
otistaylorjr – The site performance is solid—fast, responsive, no glitches seen.
thanks
nyrw84.top – Not many clues yet, but design suggests something modern.
thank you
diamondescort18 – Feels easy to navigate, and the vibe is just perfect.
That’s nice.
trackseries – Would love to see more behind-the-scenes or participant stories.
okay
michaeldfountain – I’d like to see more recent projects added — excited to see updates.
thanks
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
connectwiththeworldnow – I appreciate how simple yet bold the site looks and speaks.
thank you very much
Touche. Outstanding arguments. Keep up the amazing effort.
Thanks so much for the encouragement!
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Есть металлолом? вывоз металла мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Хочешь сдать металл? сдать металлолом в спб наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
awsmining – Smooth design and fast loading, keeps me coming back again.
Thanks for the encouragement.
easy-software.online – It’s easy to find what the software does, very straightforward.
2jasabola.biz – Clean typography helps readability—very thoughtful design choice.
thank you very much
discoveramazingthingsonline – Strong first impression, I sense creativity and boldness right away.
that’s very kind of you
x-xa – Colors are neutral, maybe a little dull — but acceptable.
thank you
everythingyouneedtoknow – Surprised by how much information is already here, interesting site.
Thanks for the encouragement.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Зацепил раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
findwhatyouarelookingfor – Everything loaded fast, no annoying delays or broken pieces.
Thanks for the comment.
thebestplacetostarttoday – The font choice is calm and readable, nice job overall.
thank you
explorecreativeideasdaily – I feel motivated now — this site gives energy to creating.
thanks
yourjourneytobetterliving – Very soothing tone, makes me want to come back every day.
Thanks for the encouragement.
dancizuci – I find this site very reliable and frequently visit.
welcome
0250f – This site has a clean design and user-friendly navigation.
thank you
moviethai4u – Useful site for movie lovers, deserves more traffic I think.
accountingservicesgoa – Their bookkeeping services are top-notch and very reliable.
xxb00 – Helpful tips and insights, makes browsing enjoyable.
that’s very kind of you
88878qp – The homepage is simple, gives a clean first impression.
thanks
купить стулья для офиса недорого
blossompaperart – Would like to see more samples, but so far promising.
okay, thank you
yourtrustedguideforlife – I’d share this with friends, it feels meaningful and helpful.
thank you very much
powerpres – Typography choices work well, reading isn’t painful even on screen.
welcome
482429 – Enjoyed the latest posts, they are fun and easy read.
thank you very much
jqdsu – Images load okay, but some seem low resolution or a bit fuzzy.
Thanks for the comment.
78y29h – Some content is vague, hope it becomes more detailed soon.
okay, Thanks for the comment
learnsomethingneweveryday – I found a few cool articles right when I arrived, great start.
that’s very kind of you
thefutureofinnovation – The balance of visuals and text feels right, content doesn’t overwhelm.
thank you
marlborodoublefusion – Typography choices are thoughtful, makes reading long posts comfortable indeed.
Thanks for the comment
allking89 – I enjoyed exploring it, everything looks polished and professional.
thank you very much
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
8runner – Just checked this out today, super clean interface and fast loading.
thank you
qi29 – Feels modern, simple, and actually useful unlike many random sites lately.
thank you very much
Добрый день!
1 Топ онлайн казино Казахстан включает лицензированные площадки. онлайн казино КЗ Играйте только в проверенных заведениях.
Здесь подробней: https://1-win-2025.com/
Казахстан онлайн казино
vavada казино онлайн Казахстан вход
топ онлайн казино Казахстан
Пока!
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
ilili1oulilil5 – Some pages feel empty, content depth needs work to feel richer.
Thanks for the comment
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
0080kk – Impressive content quality, keeps me coming back for more.
welcome
868i – Hope they fill in with useful resources soon.
thanks
welcome
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
togelrejeki – Navigation is smooth, and the articles are well-written.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations.
xinyurenedu – Provides comprehensive materials that cater to various learning needs.
Thanks for the comment
blur-blur – Impressive content quality, keeps me coming back for more.
that’s very kind of you to
88878qp – Found this from a link, design is appealing and clean.
thank you very much
khawajakhawarrashid – The color palette is tasteful, gives a calm browsing experience.
that is kind of you
1001-webtest – Just visited, seems under development but promising appearance.
thank you very much
heima999cp – Feels professional yet simple, I like how they keep things clear.
That’s nice.
schenectadybathroomremodeling – Just bookmarked this, seems like a solid remodeling resource overall.
thanks
Чыныгы мотивация издеген адам Алекс Перейранын жолун көрсүн. Көрсө, Алекс Перейра көчөдөн чыккан, эми болсо дүйнөнүн чокусунда. Толук маалымат, биография жана рекорддор ушул сайтта: alex-pereira-kg.com. Алекс Перейра жашоодо көптү башынан өткөргөн.
Көптөр Перейраны жеңет дешет, бирок ал дайыма жооп берет.
Перейра эч качан колун түшүргөн эмес. UFC тарыхында мындай энергия сейрек болот. Көргөндө эле энергиясы сезилет.
Перейра — элдин арасынан чыккан легенда. Перейра дайыма өзүнүн жолун улантат.
7558app – Color scheme is pleasant, gives a professional and friendly feel.
That’s nice.
031757 – Nice design, hope content matches the style.
thanks
16999ys – Found this by chance, hope it turns out useful.
thank you
881625 – If internal pages match this, it could be great resource.
thank you
btc289 – Clean first look, hope inner pages are equally polished.
thanks for comment
122yyy – Design is simple and neat, gives a professional feel.
That’s kind of you.
hg889988 – The layout is decent, would love to see more.
okay
Перейра ушунчалык токтоо жана ишенимдүү — аны утуш абдан кыйын. Мен Перейранын ар бир беттешин күтүп көрөм. Алекс Перейра тууралуу эң акыркы жаңылыктарды ушул жерден тапсаң болот — Алекс Перейра. Перейра менен Джон Джонстун беттеши көргүм келет.
Анын кийинки беттеши кимге каршы болору кызык.
Анын тарбиясы жөнөкөй, бирок максаты чоң. Перейра кикбоксингден баштап, дүйнөлүк октагонго чыкты. UFCде мындай мушкерлер көп эмес.
Перейра — элдин арасынан чыккан легенда. Эгер спортту сүйсөң, Перейранын окуясын оку.
9909hd – Hope the inner pages are as polished as the homepage.
okay
selvaluna – Hoping site is well-optimized for mobile too, looks promising.
That’s nice.
zhgsguangning – I stumbled here and design feels clean, navigation is fine.
thanks
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Алгачкы жолкусунан бери Алекс Перейра кантип өсүп, чемпион болгону таң калтырат. Перейранын соккусу оор, ар бир муштум — таза күч. Перейра тууралуу баарын бир жерден оку: Перейра Алекс UFC жаңылыктар. Анын Адесанья менен болгон беттеши легендарный болду.
Алекс Перейра — UFCдеги эң катуу сокку уруучу мушкерлердин бири.
Ушундай жигиттер спорттун жүзүн өзгөртөт. Анын жашоосунда дисциплина эң башкысы. Бул жигит чыныгы “monster”.
Бүгүн ал дүйнөлүк аренада, бирок жөнөкөй бойдон. Көрсө, ийгилик каалоо эмес, аракет экен.
sahabetaff – Found this site today, seems legit and well structured.
thank you
elmhurstunited – Their identity shows care and purpose, design supports their message well.
thank you
7392004 – Simple homepage, hope the inner pages bring solid content.
thanks
apphoki – The layout is simple and inviting, makes me browse more.
thank you very much
bnnnw – Waiting to see products, articles or useful resources here.
okay
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
Алекс Перейра UFCде тарых жаратып жатат, бул сөзсүз. Мага Алекс Перейранын стилди жакты, айрыкча анын кикбоксинг тажрыйбасы сезилет. UFC тарыхындагы эң күчтүү мушкерлердин бири тууралуу оку — alex-pereira-kg.com. Ар бир муштумунда тарых жатат.
Ал кээде сөз сүйлөбөйт, бирок иш менен далилдейт.
Анын аялын да колдоосу таң калтырат. Анын жашоосунда дисциплина эң башкысы. Менин оюмча, Перейра кайра жеңишке жетет.
Ал каалаган максатына жеткен. Көрсө, ийгилик каалоо эмес, аракет экен.
Нужна карта? международная кредитная карта MasterCard как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
+1
zxjgzxfuzhou – I like how content is structured, makes finding info simple.
that’s kind of you
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Особенно понравился материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
bsporttiyu – Feels like they cover a lot of tournaments, useful info for fans.
thank you
www9tt01 – I can check its WHOIS, SSL, or archival history if you like.
www9tt9 – The site gives very low trust signals based on what I found.
www9tt05 – No external references or reviews appeared in search.
okay
Алгачкы жолкусунан бери Алекс Перейра кантип өсүп, чемпион болгону таң калтырат. Алекс Перейра — чыныгы мисал чыдамкайлык жана эрктүүлүктүн. Кызыктуу фактылар, фото жана рекорддор ушул шилтемеде: Перейра Алекс биография. Анын тарыхы көчөдөн башталып, UFC чемпиондугу менен бүттү.
Анын урганынын күчү килограмм менен эсептелет.
Анын аялын да колдоосу таң калтырат. Бул адамдын соккусу таштай катуу. UFCде мындай мушкерлер көп эмес.
Перейра үчүн утулуш — бул сабак гана. Алекс Перейра — күч, эрк жана ишенимдин символу.
Читателям предоставляется возможность ознакомиться с разными точками зрения и самостоятельно сформировать свое мнение.
ma3wna – Content feels thoughtful, not just filler — a good sign overall.
Thanks for the encouragement.
www9tt04 – If you’re asked to enter personal or payment info, proceed very carefully.
https://katellkeinegcom.wordpress.com/
www9tt9 – If they ask for payments or personal data, I’d be extremely cautious.
dsjy0916 – The site’s silence online is a bit of a red flag for legitimacy.
Thanks for the observation
Хай!
Найти лучшие онлайн казино в Узбекистане легко. казино онлайн узбекистан Наш гид поможет.
Здесь подробней: https://1win-2025.shop
Топ онлайн казино Узбекистан
Бывай!
11xhh – The look is clean and modern, navigation is quite smooth.
that’s kind of you
bmrlw – Really like how the pages load quickly without unnecessary clutter today.
Thanks for the comment.
202496 – It could be dormant or under construction, not clearly active.
Exactly, it’s a new blog.
hotel-reservation-rome.com – Check for SSL certificate and legitimate contact phone before reservation.
mg2jp – If you want, I can try to fetch cached versions or trace its server.
tingshuzu – Just found this browsing around, seems promising and legit.
thank you very much
832899 – Found something useful unexpectedly, makes me curious to explore more.
That’s nice.
Приветствую!
Информация можно ли играть в онлайн казино в Узбекистане. казино онлайн узбекистан Следите за новостями.
По ссылке: https://25-win-25.com
Топ онлайн казино Узбекистан
Пока!
bncdw – If you like, I can run a domain-history check or archive lookup for you.
okay
xfbsp666 – Wish there were more examples or case studies though.
okay, I will do my best to live up to your expectations.
358799 – Could be a placeholder domain, not active business yet.
It’s a new blog.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Алекс Перейра UFCде тарых жаратып жатат, бул сөзсүз. Канча мушкер аракет кылбасын, Перейраны утуш оңой эмес. Бардык жаңылыктар бир жерде — https://alex-pereira-kg.com. Анын тарыхы көчөдөн башталып, UFC чемпиондугу менен бүттү.
Көптөр Перейраны жеңет дешет, бирок ал дайыма жооп берет.
Анын карьерасы али бүтө элек. Бул адамдын соккусу таштай катуу. Бул жигит чыныгы “monster”.
Анын жигиттик сапаты өзүнчө сөз. Анын ар бир беттеши көрүүчүлөр үчүн шоу.
mashoppy – The color palette feels calm, nothing overly flashy—nice touch.
that’s kind of you
www9tt6 – Let me fetch archival snapshots or server data to see what was there before.
okay
haxorisme – Looks like an unfamiliar domain, didn’t see much credible info.
Exactly, it’s a new blog.
jingcaity – No obvious contact or “about” pages found in a quick look.
There is an “About Us” page at the bottom of the home page
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Металлообработка и металлы j-metall.ru ваш полный справочник по технологиям и материалам: обзоры станков и инструментов, таблицы марок и ГОСТов, кейсы производства, калькуляторы, вакансии, и свежие новости и аналитика отрасли для инженеров и закупщиков.
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Зацепил материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
dadatudaohang – If they ask for payments or private data, verify everything first.
Строительный портал https://intellectronics.com.ua источник актуальной информации о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Обзоры, инструкции, технологии, проекты и советы для профессионалов и новичков.
Актуальный портал https://sinergibumn.com о стройке и ремонте. Современные технологии, материалы, решения для дома и бизнеса. Полезные статьи, инструкции и рекомендации экспертов.
56089h – Some images are crisp and relevant, not just filler visuals.
Thanks for the encouragement
kytautoparts – If their catalog is wide, this could be a go-to for parts shopping.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
yiikr – Footer details are helpful — contact, policies all easy
Thanks for pointing that out
957420 – Customer support info was easy to locate, very helpful overall.
thank you
56089m – Mobile experience was smooth, no annoying popups or interruptions today.
thank you
k9c4fzmzxj1 – Some pages have good content, though a bit more depth would help.
okay, I will do my best to live up to your expectations
764585 – I couldn’t find reliable info, looks rather obscure and risky.
thank you
8222173 – This site’s interface feels clean and super easy to explore.
that’s kind of you
bulkytrader – Site seems legit, interface is clean and navigation feels smooth.
Thanks for the comment
canineaffluent – The color scheme and fonts work nicely together, pleasant to read.
Thanks for the encouragement
3915t – No broken links so far, all clicked pages seem valid and working.
thank you
Онлайн женский портал https://replyua.net.ua секреты красоты, стиль, любовь, карьера и семья. Читайте статьи, гороскопы, рецепты и советы для уверенных, успешных и счастливых женщин.
bjjxyzp – The site uses few images; might benefit from richer visuals later.
Thanks for the observation.
x5748 – Images are okay; not too flashy but serve their purpose.
Thanks for the observation.
Современный женский https://novaya.com.ua портал о жизни, моде и гармонии. Уход за собой, отношения, здоровье, рецепты и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть красивой и счастливой каждый день.
goodthingsshare – On mobile it works nicely, no weird distortions or broken elements.
Thanks for the comment
246123kj – Would like to see deeper pages or blog posts to make it richer.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Интересный женский https://muz-hoz.com.ua портал о моде, психологии, любви и красоте. Полезные статьи, тренды, рецепты и лайфхаки. Живи ярко, будь собой и вдохновляйся каждый день!
snmm66 – Wish there was more background or about page to learn who’s behind this.
okay
303sahabat – Mobile version works smoothly, tap targets are big and responsive.
thank you
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
oarlop – On mobile it adapts well, no strange shifts or broken styling.
Thanks for the observation
jiandanai520 – No broken links so far, everything I tried worked fine.
thanks
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
eggaa – Good layout and intuitive menu, finding stuff was simple today.
thank you very much
660fh – Some content is decent, though could use more depth.
Thanks for the comment
trendhunter.click – This site feels modern, content is engaging and well curated.
Thanks for the encouragement
urbanrise.click – I like the minimalism, pages feel uncluttered and easy to scan.
thank you
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
digitalstorm.click – Wish there were more blog content or news updates to follow.
okay, Thanks for the comment
Thanks for any other excellent post. The place else may anybody get that
type of information in such a perfect method of writing?
I’ve a presentation subsequent week, and I’m on the search for
such information.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
digitalnest.click – Impressed by the quality of visuals and overall aesthetics.
That’s nice
nextgenmarket.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
thank you
worldtrendspace.click – Always find something new and interesting every time I visit.
Thanks for the encouragement
boldspark.click – Would be nice to see a blog or resource section for added value.
thanks
pixelstorm.click – The layout here is sleek and modern, very user-friendly.
thank you
linkfusion.click – The content is fresh, and the layout is user-friendly.
Thanks for the comment
yourbrandzone.click – Cool vibe overall, makes browsing feel effortless and pleasant every time.
thank you
goldenwave.click – Great content and visuals, I’m pleasantly surprised by the quality.
that’s kind of you
ideaorbit.click – Layout is minimal; feels more like a placeholder or landing page than full site.
thank you
urbanvision.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
thanks
nextbrand.click – The content is fresh, and the layout is user-friendly.
Thanks for the encouragement
linkmaster.click – Great site you’ve got here, the design is crisp and modern.
thank you very much
cloudmatrix.click – On mobile it works fine; text is legible and elements seem stable.
thanks
thinkbeyondtech.click – For now, treat with caution until you find proof it’s legitimate.
futurebeam.click – Cool mix of topics here, keeps me coming back daily.
that’s kind of you
cloudmark.click – Navigation is smooth, I appreciate how everything loads fast.
Thanks for the comment.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
growwithfocus.click – On mobile it displays okay but some elements seem generic.
that’s kind of you
openlaunch.click – Great job on visuals, they really complement the content well.
that’s kind of you
boldimpact.click – Nice to see a site that balances style and substance.
that’s kind of you
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
Здарова!
Онлайн казино Казахстана предлагают развлечения. 10 лучших казино онлайн Казахстан Выбирайте лицензированные онлайн казино.
Здесь подробней: https://25win-25.shop
Онлайн казино Казахстана
До встречи!
brightshift.click – Fast loading times and intuitive interface enhance the user experience.
that’s kind of you
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
digitalvisionpro.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
thank you
reachnewgoals.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
Thanks for the encouragement
trendforge.click – I appreciate the clean design and smooth navigation.
thank you
focusreach.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
Thanks for the encouragement
websource.click – Impressed by the layout; everything feels intuitive and modern.
That’s nice
powerofgrowth.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
that’s kind of you
fastforwardmedia.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
Thanks for the encouragement
bluefocus.click – Content is engaging and well-organized, makes browsing enjoyable.
Thanks for the encouragement
globalconnectnow.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
that’s kind of you
quicktrend.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
That’s nice
thefuturehub.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
thank you
brightideaweb.click – Great user experience; pages load fast and look sharp.
Thanks for the encouragement.
risehub.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
thanks
starvision.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
that’s kind of you
launchcraft.click – Easy to navigate and find what you’re looking for.
that’s kind of you
innovatewithus.click – The site feels polished and professional, nice work.
That’s nice.
wavefusion.click – This site has a sleek design and loads quickly.
That’s nice.
cyberlaunch.click – This site has a sleek design and loads quickly.
Thanks for the comment.
greenmotion.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
Thanks for the comment.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
globalreach.click – This site has a sleek design and loads quickly.
thank you
Советы по строительству https://vodocar.com.ua и ремонту своими руками. Пошаговые инструкции, современные технологии, идеи для дома и участка. Мы поможем сделать ремонт проще, а строительство — надёжнее!
pixelplanet.click – Love the minimalist design; it’s both stylish and functional.
thank you very much
smartgrid.click – This site has a sleek design and loads quickly.
Thanks for the observation
Сайт о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте домов, квартир и дач. Полезные советы мастеров, подбор материалов, дизайн-идеи, инструкции и обзоры инструментов. Всё, что нужно для качественного ремонта и современного строительства!
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
nextlayer.click – This site has a sleek design and loads quickly.
thank you
Информационный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua про строительство, ремонт и интерьер. Свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий и полезные лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно знать о стройке и благоустройстве жилья в одном месте!
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
Пошаговые советы https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua по строительству и ремонту. Узнай, как выбрать материалы, рассчитать бюджет и избежать ошибок. Простые решения для сложных задач — строим и ремонтируем с уверенностью!
Главные новости дня https://sevsovet.com.ua эксклюзивные материалы, горячие темы и аналитика. Мы рассказываем то, что действительно важно. Будь в курсе вместе с нашим новостным порталом!
Claudi AI
connectwiththeworldnow – Very engaging style, visuals support purpose and connection focus.
thanks
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Флойд Мейвезердин ар бир беттеши чоң шоу катары кабыл алынат. Флойд Мейвезер эч качан жеңилбеген мушкер катары белгилүү. Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы беттештери жана жыйынтыктары Флойд Мейвезер рекорд бөлүмүндө жарыяланган.
Флойд Мейвезердин ийгилиги көпчүлүк үчүн үлгү. Анын рекорддору бүгүнкү күнгө чейин сакталган. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өзүн мыкты формада кармаган.
Анын ар бир интервьюсу көңүл борборунда.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өз максатына жеткен. Анын тарыхы ар дайым спорт күйөрмандарынын эсинде. Анын жашоосу жана ийгилиги мотивация берет.
Сайт о стройке https://samozahist.org.ua и ремонте для всех, кто любит уют и порядок. Расскажем, как выбрать материалы, обновить интерьер и избежать ошибок при ремонте. Всё просто, полезно и по делу.
maxgrowth.click – Loving the clean design and crisp visuals here today.
thank you
Как построить https://rus3edin.org.ua и отремонтировать своими руками? Пошаговые инструкции, простые советы и подбор инструментов. Делаем ремонт доступным и понятным для каждого!
Обустраивайте дом https://stroysam.kyiv.ua со вкусом! Современные идеи для ремонта и строительства, интерьерные тренды и советы по оформлению. Создайте стильное и уютное пространство своими руками.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым мыкты формада болот. Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы жаңылыктары ар бир күйөрманды кызыктырат. Акыркы маектерди жана статистиканы Флойд Мейвезер интервью бөлүмүнөн окуңуз.
Ал рингде тактык жана ылдамдык менен айырмаланат. Анын карьерасы ар дайым жеңиш менен коштолгон. Флойд Мейвезер – акыл менен ойногон спортчу.
Ал спорттон тышкары ишкер катары да белгилүү.
Флойд Мейвезер дүйнөдөгү эң жогорку кирешелүү спортчу. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өзүнө ишенген. Флойд Мейвезердин мурасы келечек муундар үчүн үлгү.
zrhsof.com – Looks professional and thoughtful without being flashy.
that is nice
https://henryukazu.com/how-to-create-your-own-pathway-to-success/
medtopstore.com – Overall solid first impression — clean, credible, and functional.
thank you
newnexus.click – Just found this site and the feel is super clean and inviting.
that’s kind of you
buildyourbrand.click – The content is fresh, and the layout is user-friendly.
thanks
everyspeed.com – Layout is simple; may need more visuals or details for full impact.
thank you
smartbusinesshub.click – Found this recently; navigation is intuitive and content feels valuable.
that’s kind of you
531500zy.com – Pages load quickly, which makes browsing comfortable and smooth.
thanks
dreambigtoday.click – The visuals are appealing, matches the uplifting brand message well.
thank you very much
mediafusion.click – The tone is friendly and inviting, makes me want to read more.
thanks
507193.com – I like how minimalism is used — no clutter, just essentials.
that’s kind of you
503926.com – Navigation is simple, nothing fancy but works smoothly.
thank you
strongrod.com – The visuals are sharp and the layout feels balanced.
thanks
globalwave.click – Good flow between sections, everything seems thoughtfully placed.
that’s kind of you
skyhighstudio.click – Overall a strong impression — professional, aesthetic, welcoming.
thank you very much
powertrend.click – Always find something interesting here, keeps me coming back.
welcome
Флойд Мейвезердин ар бир беттеши чоң шоу катары кабыл алынат. Анын рингдеги тактикасы ар дайым мыкты. Анын жашоосу жана үй-бүлөсү тууралуу маалымат Флойд Мейвезер үй-бүлө бөлүмүндө берилген.
Анын фамилиясы дүйнөлүк брендге айланган. Флойд Мейвезер спорт тарыхына кирген аттардын бири. Анын рингдеги кыймылы ар дайым көрүүчүлөрдү суктандырат.
Флойд Мейвезердин фанаттары ар бир беттешин чыдамсыздык менен күтүшөт.
Анын жашоосу мотивациянын булагы. Анын карьерасы спорт тарыхында алтын тамга менен жазылган. Флойд Мейвезердин ысымы бокс дүйнөсүндө түбөлүк калат.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
fastimpact.click – Great balance of style and clarity, makes reading a pleasure.
thank you
creativemindlab.click – Love how creative and modern the whole layout feels today.
that is nice
vmf-metal.com – I like the color scheme and consistent style across pages.
thanks
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
Портал для автомобилистов https://translit.com.ua от выбора машины до профессионального ремонта. Читайте обзоры авто, новости автоспорта, сравнивайте цены и характеристики. Форум автолюбителей, советы экспертов и свежие предложения автосалонов.
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
fastgrowth.click – Loving how clean everything looks — very smooth experience.
thanks
bestchoiceonline.click – Navigation feels intuitive; finding things is smooth and painless.
thank you
ynaix.com – The design feels modern and sparse, clean lines everywhere.
that is nice
kluvcc.com – The typeface and layout choices create nice balance.
thank you
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
Флойд Мейвезердин ар бир беттеши чоң шоу катары кабыл алынат. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты дисциплина менен белгилүү. Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы беттештери жана жыйынтыктары Флойд Мейвезер рекорд бөлүмүндө жарыяланган.
Флойд Мейвезердин ийгилиги көпчүлүк үчүн үлгү. Флойд Мейвезердин фанаттары дүйнө жүзүндө. Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу – мотивация.
Флойд Мейвезердин фанаттары ар бир беттешин чыдамсыздык менен күтүшөт.
Флойд Мейвезер дүйнөдөгү эң жогорку кирешелүү спортчу. Флойд Мейвезер ар бир беттешти мыкты өткөргөн. Анын ар бир интервьюсу чоң кызыгуу жаратат.
connectwiththeworldnow – I’ll return to this, it seems like a project with real potential.
thank you very much
Эта статья действительно заслуживает высоких похвал! Она содержит информацию, которую я долго искал, и дает полное представление о рассматриваемой теме. Благодарю автора за его тщательную работу и отличное качество материала!
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
brightvault.click – Clear headings, easy calls-to-action, user flows are well thought out.
thanks
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым мыкты формада болот. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты дисциплина менен белгилүү. Бардык жаңылыктарды жана видео материалдарды http://www.floyd-mayweather-kg.com сайтынан көрүңүз.
Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу мотивация берет. Флойд Мейвезер ар бир беттешинде тактиканы мыкты колдонот. Флойд Мейвезер – акыл менен ойногон спортчу.
Флойд Мейвезердин бизнеси да ийгиликтүү.
Флойд Мейвезердин ийгилик сыры эмгек жана туруктуулук. Анын фанаттары дүйнөнүн бардык бурчунда бар. Флойд Мейвезер спорттун символу катары белгилүү.
507193.com – Pages load quickly, which is always a plus.
thank you
alphaorbit.click – The elements align nicely; balance feels natural.
thank you
nexasphere – This really worked wonders for me, highly recommend it.
thanks
truegrowth – Their analytics-driven approach gave us a clearer marketing strategy.
visionmark – The ADA-compliant elevator signs they made look fantastic.
boldmatrix – A game-changer in the fashion e-commerce industry.
prolaunch – This is fantastic, saved me so much time today.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
brandmatrix.click – Design is elegant, content is solid, I’ll be visiting again.
thank you, welcome
newgenius.click – Found useful sections quickly, no clutter, easy to focus on what matters.
Thanks for the observation
elitezone.click – Was exploring similar sites, this one stands out for its aesthetic quality.
that’s kind of you
zenithmedia.click – The design feels modern and confident.
thank you
ultrafocus.click – Definitely bookmarking this one, quality seems above average standard.
Thanks for the encouragement
maxbridge.click – Excellent responsiveness on mobile, smooth transitions and clean layout.
thanks
progrid – Valuable information, saved me time searching for reliable sources.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
coreimpact.click – I appreciate the balance between visuals and simple readability.
thank you very much
elitefusion.click – Loving every section here, truly feels polished and professional.
Thanks for the encouragement
alphaimpact.click – Just checked this out, really sleek design and super fast loading times.
Thanks for the encouragement
Флойд Мейвезердин рекорддору көп спорт күйөрмандарын суктандырган. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты дисциплина менен белгилүү. Кызыктуу статистика жана жаңылыктар Флойд Мейвезер статистика бөлүмүндө топтолгон.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым спорттун чокусунда болгон. Анын мушташ стили өзгөчө жана натыйжалуу. Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу – мотивация.
Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы жаңылыктары спорт дүйнөсүн дүрбөлөңгө салат.
Флойд Мейвезердин тарыхтагы орду чоң. Анын фанаттары дүйнөнүн бардык бурчунда бар. Флойд Мейвезердин ысымы бокс дүйнөсүндө түбөлүк калат.
brightchain.click – The site feels polished — someone took care of details.
that’s kind of you
sharpwave.click – Everything here seems stable, no broken links or layout issues.
that’s kind of you
ultrawave.click – The navigation here is so intuitive, makes everything super simple honestly.
that’s kind of you
ZenithLabs – Smooth experience navigating the site, everything loads super quickly here.
thank you very much
metarise.click – Just landed here, everything feels polished and really easy to use.
thank you very much
Автор статьи представляет информацию в четкой и нейтральной форме, основываясь на надежных источниках.
1xbet afrique apk https://parifoot-afrique.com
1xbet afrique apk 1xbet cameroun apk
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
info foot africain 1xbet cameroun apk
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
Эта статья – источник вдохновения и новых знаний! Я оцениваю уникальный подход автора и его способность представить информацию в увлекательной форме. Это действительно захватывающее чтение!
grandlink – Good mix of visuals and text, not overwhelming at all.
thank you
elitepulse – Quality content and clean interface, very impressive work.
Thanks for the encouragement
vectorrise – Their creative approach really sets them apart from the rest.
that’s kind of you
ascendgrid – Waiting for it to load properly; optimistic about what I’ll find.
welcome
truelaunch – Great mix of insight and usability, kudos to the creators.
that’s kind of you
smartvibe – Site seems trustworthy, info is clear and precise.
that’s kind of you
purehorizon – Found several ideas I hadn’t thought of before, thanks!
That’s nice
brandvision – Great branding ideas, I’m noting them down for my own work.
thanks
innovatek – Great selection of topics, covers a wide range.
That’s nice.
linkcraft – Smooth browsing experience, everything loads fast and clearly.
thank you
brandcrest – The tone is friendly and content feels human, nice job.
Thanks for the encouragement
skyvertex – Found several useful tips I can use right away.
thanks
summitmedia – Found several resources that are exactly what I was looking for.
thank you, welcome
visionlane – The content is useful and presented clearly, good job.
that’s kind of you
Я хотел бы выразить признательность автору за его глубокое понимание темы и его способность представить информацию во всей ее полноте. Я по-настоящему насладился этой статьей и узнал много нового!
techmatrix – Love how they break down complex topics simply.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
vividpath – Overall solid experience, I like this site a lot.
That’s nice.
ultraconnect – Impressed by how polished the site looks overall.
Thanks for the encouragement
ascendmark – Bookmarking this, will check back frequently.
Thanks for the encouragement
novaorbit – Navigation feels smooth, didn’t struggle exploring the sections.
thank you
elitegrowth – Just explored the blog, lots of useful growth-hacking ideas here.
thank you very much
powercore – Just checked it out, found some useful resources I’ll use soon.
Thanks for the encouragement
urbanshift – Really loving how sleek and modern the design feels here.
that’s kind of you
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to protect against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
Hello,
Honestly, I don’t know.
My computer skills are mediocre too.
primeimpact – The tone is friendly and accessible, nice voice.
That’s nice.
urbannexus – Just explored their posts, found many valuable takeaways.
that’s kind of you
Современная студия дизайна https://bconline.com.ua архитектура, интерьер, декор. Мы создаём пространства, где технологии сочетаются с красотой, а стиль — с удобством.
football africain telecharger 1xbet
boldvista – Overall very pleasant experience browsing their site.
thank you
telecharger 1xbet afrik foot pronostic
pariez sur le foot pariez sur le foot
Создавайте дом https://it-cifra.com.ua своей мечты! Всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне интерьера. Идеи, проекты, фото и инструкции — вдохновляйтесь и воплощайте задуманное легко и с удовольствием.
growthverse – This will become a go-to site for growth and marketing ideas.
thanks
urbanscale – Found some helpful tools I can use immediately.
thank you
https://yhared.com/how-do-foldable-screens-work/
Hello! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance from an established blog. Is it difficult to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about making my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Thank you
Hello,
You know, I’m also a beginner, and this site is barely six months old. When it comes to computers, I also have mediocre knowledge, since my training is in economics.
I relied entirely on YouTube videos to prepare my site,
so I advise you to start your project. It’s not difficult at all, you just need a little patience.
As for your site’s domain, it’s better to buy one than to get a free one, and it should be on WordPress rather than Blogger.
Good luck!
goldnexus – This will be one of my go-to sites from now on.
Thanks for the encouragement
аренда экскаватора погрузчика jcb в москве http://www.arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-cena-2.ru .
электрокарнизы для штор купить электрокарнизы для штор купить .
электрокарнизы электрокарнизы .
электрические гардины электрические гардины .
перепланировка здания перепланировка здания .
узаконивание перепланировки нежилого помещения узаконивание перепланировки нежилого помещения .
мини-экскаватор аренда https://arenda-mini-ekskavatora-v-moskve-2.ru/ .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в многоквартирном доме перепланировка нежилого помещения в многоквартирном доме .
рулонные шторы это http://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru .
blueorbit – Very friendly tone, content feels human and genuine.
thank you
Мир архитектуры https://vineyardartdecor.com и дизайна в одном месте! Лучшие идеи, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и города. Узнай, как создаются красивые и функциональные пространства.
futurelink – Bookmarking this — I’ll come back often for more.
thank you
Greetings!
Read the link
online slot club no deposit play bonus
https://onlineslotclub.cfd/
best roulette strategy to win
https://roulettestrategy.cfd
slot machines online that pay real money
https://slotmachinesonline.cfd
best online slot spinners for real money
https://slotspinners.cfd/
welcome bonuses no deposit bonus
https://welcomebonuses.cfd
Enjoy your study session!
Автор предоставляет актуальную информацию, которая помогает читателю быть в курсе последних событий и тенденций.
Добрый день!
Здесь подробней:
казино онлайн узбекистан
https://casinostrategies.cfd/
10 лучших казино онлайн казахстан
https://clasicslotsonline.cfd
проверенные онлайн казино с выводом денег казахстан
https://pokerstrategyhub.cfd/
Пока!
valuevision – I like the color scheme, it gives a calming vibe.
thank you
growthverse – Consistently impressed with the site’s performance and design.
that’s kind of you
skyportal – Really enjoying the latest updates, everything loads super fast today.
thanks
потолочники http://natyazhnye-potolki-samara-1.ru/ .
компания потолочник stretch-ceilings-samara.ru .
автоматические жалюзи автоматические жалюзи .
boldimpact – Clean branding, simple but memorable name.
thank you
quantumreach – Clean layout, easy to navigate, very user-friendly experience.
thank you
тканевый натяжной потолок самара тканевый натяжной потолок самара .
alphaunity – Loading speed is good, didn’t wait long for pages.
Thanks for the observation
Очень хорошо исследованная статья! Она содержит много подробностей и является надежным источником информации. Я оцениваю автора за его тщательную работу и приветствую его старания в предоставлении читателям качественного контента.
sharpbridge – Navigation feels intuitive, didn’t struggle finding anything so far.
thanks
bluetrail – Friendly tone, not too technical — good balance.
thank you
solidvision – Once site’s live, content could make it shine.
thanks
elitegrowth – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
thanks
cloudmatrix – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
thank you
fastgrowth – Great user experience, everything loads so smoothly and fast.
Thanks for the encouragement
that’s kind of you
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Автор представляет свои идеи объективно и не прибегает к эмоциональным уловкам.
maxvision – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
thanks
goldbridge – Wish there were more articles or resources to explore.
Thanks for the observation
потол http://natyazhnye-potolki-samara-2.ru .
alihidaer2313 – The site feels minimal, design is simple yet somewhat intriguing.
that is kind of you
ynaix – Overall very polished, definitely feels like a premium service offering.
thank you
connectwiththeworldnow – Pages load fast, layout is clean and not overwhelming.
Частный заем денег домашние деньги официальный сайт альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
strongrod – Content is direct and helpful, no fluff in between.
thank you
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
brightideaweb – Found valuable sections, great mix of inspiration and info.
wavefusion – Pages load smoothly, even graphics render without delay.
cyberlaunch – Color scheme works well, important elements really stand out.
metarise – Visual hierarchy is great, makes scanning content simple and quick.
sharpwave – Design is sleek and modern, very pleasing to the eyes.
brightchain – Design looks modern, I like the visual elements they chose.
innovatewithus – Found exactly what I was searching for, very helpful content.
cloudmark – Typography is clean; reading is easy and pleasant throughout.
thank you
everythingyouneedtoknow – Typography is very readable, spacing gives breathing room.
discoveramazingthingsonline – The design looks fun, vibrant, great for browsing new stuff.
explorecreativeideasdaily – Layout feels artistic yet readable, great balance achieved.
digitalstorm – Pages load quickly, even complex graphics appear smooth.
Suchen Sie Immobilien? https://www.montenegro-immobilien-kaufen.com/ wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
YourPathOfGrowth – I’m excited to see the positive changes they are driving.
joinourcreativecommunity – Feels like a warm welcome, community vibes strong already.
Автоматические гаражные ворота давно перестали быть роскошью и стали необходимым элементом комфортной жизни. Наши автоматические ворота сочетают надёжность проверенных европейских механизмов с элегантным дизайном, который гармонично впишется в архитектуру любого здания. Мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг: от профессиональной консультации и точного замера до установки под ключ и гарантийного обслуживания. Доверьте безопасность своего дома профессионалам — получите бесплатный расчёт стоимости уже сегодня: Гаражные ворота
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
LearnWithConfidence – Their guides are thorough, I learned so much in minutes.
learnshareandsucceed – The content is strong, useful and not just superficial stuff.
thanks
thebestplacetostarttoday – The tone speaks to encouragement, not pressure, very refreshing.
makelifebettereveryday – Hope the content is practical, not just motivational fluff, that matters.
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: official Panda game Canada website
getreadytoexplore – Love the adventurous tone here, makes me want to dive in.
everythingaboutsuccess – Tone feels empowering, not preachy, nice balance for growth content.
findwhatyouarelookingfor – Helpful links and sections are easy to locate and use.
learnsomethingneweveryday – Typography and spacing make reading very comfortable for long sessions.
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
discoverendlessinspiration – Pages load crisp and clean, very smooth user experience.
growyourbusinessfast – Typography is strong, reading feels crisp and professional.
https://zero83.com.br/2023/02/19/assistir-ao-vivo-atletico-san-luis-x-santos-laguna-campeonato-mexicano-2022-2023-liga-mx-hoje-18-02-palpites-bola-rolando/
SimpleWaysToBeHappy – I love the emphasis on kindness and compassion.
BuildSomethingMeaningful – This platform is a valuable tool for community leaders.
thanks
стоимость фитнес клуба https://fitnes-klub-msk.ru
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Особенно понравился раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
Автор статьи предоставляет подробное описание событий и дополняет его различными источниками.
EverythingStartsWithYou – The layout is clean; reading feels peaceful and uplifting.
thank you
TurnIdeasIntoAction – The advice here is practical, not just theory, super useful.
thanks
Гарри Кейн оюн талаасында дайыма тынчсызданууну жаратат.Кейн өзүнүн эмгеги менен сыйлыкка татыктуу болду. Бул жерде Кейндин упайлары жана оюн натыйжалары көрсөтүлгөн: https://harry-kane-kg.com/. Кейн бир нече жолу “Алтын бутса” уткан.
Бул оюнчу кайсы жерде болбосун гол киргизе алат.
Кейндин үй-бүлөсү ар дайым анын жанында. Кейндин пас берүү жөндөмү да жогорку деңгээлде. Кейн ар бир сезон өзүн мыкты формада кармайт. Анын дебюту футбол дүйнөсүн таң калтырган. Гарри Кейндин оюндарынын саны укмуш. Футбол сүйүүчүлөрү анын жаңылыктарын күтүшөт.
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
Футбол күйөрмандары Гарри Кейндей оюнчуну сыйлашат.Гарри Кейндин PFA Premier League Team of the Year тизмесине киргени таң калычтуу эмес. Кейндин оюндарын жана жаңылыктарын бул жерден карасаң болот: Гарри Кейн тууралуу баары. Кейн өзүнүн максаттарын так билет.
Кейндин трансфери чоң көңүл бурдурган.
Гарри Кейн жеке жашоосун ачык көрсөтпөйт. Кейндин карьерасы узак жана ийгиликтүү. Кейндин карьерасы тарыхка кирет. Анын жолун уланткандар көп. Гарри Кейндин оюндарынын саны укмуш. Кейндин трансферлери ар дайым чоң темалар.
потолочник натяжные потолки отзывы потолочник натяжные потолки отзывы .
LearnSomethingAwesome – The tutorials are playful yet informative, exactly what I needed.
thanks
натяжные потолки нижний новгород официальный сайт http://natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod.ru .
Кейндин карьерасы ар бир жаш оюнчуга үлгү.Футбол тарыхында анын аты чоң орунда болот. Бул сайтта Гарри Кейндин Бавариядагы оюндары тууралуу кеңири маалымат бар: Гарри Кейн Бавария</url]. Кейн Англиянын тарыхындагы эң жогорку бомбардирлердин бири.
Бул оюнчу кайсы жерде болбосун гол киргизе алат.
Гарри Кейн жеке жашоосун ачык көрсөтпөйт. Кейндин карьерасы узак жана ийгиликтүү. Анын физикалык даярдыгы мыкты. Кейндин алгачкы командалары ага чоң тажрыйба берген. Бул оюнчу кайсы чемпионатта болбосун айырмаланат. Кейндин реал мадридге өтүшү дагы эле талкууда.
https://blog.dynox.cn/?p=143
FindTheBestIdeas – Found several ideas I want to explore in my upcoming projects.
welcome
адрес фитнес клуба фитнес клуб цены
компания потолочкин натяжные потолки http://www.stretch-ceilings-nizhniy-novgorod.ru .
LearnShareAndGrow – I love how they integrate technology into their initiatives.
FindNewWaysToGrow – Bookmarking this, will revisit when I want to refocus or get inspired.
thanks
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
FindAnswersAndIdeas – Every post seems to answer questions I’ve been silently asking.
тканевые натяжные потолки нижний новгород акции https://natyazhnye-potolki-nizhniy-novgorod-1.ru/ .
YourDigitalDestination – Their tutorials are clear; even tricky things become understandable.
ConnectDiscoverAndGrow – Very motivating content, feels like a community more than a site.
GetConnectedWithPeople – I appreciate how profiles are detailed yet simple to browse.
FindSolutionsForLife – Very relatable advice, I feel like I’m learning from someone I trust.
https://www.tractorbynet.com/forums/members/tractortravel.410315/#about
UnlockYourPotentialToday – Very useful tips, I’ve already applied a few in my routine.
madeleinemtbc – Posts seem genuine, like someone who really cares
markmackenzieforcongress – Really enjoyed reading about the campaign, feels honest and inspiring today.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Кейндин карьерасы ар бир жаш оюнчуга үлгү.Гарри Кейндин PFA Premier League Team of the Year тизмесине киргени таң калычтуу эмес. Бул шилтемеде Гарри Кейндин оюндарынан эң мыкты учурлар чогулган: Гарри Кейн видео. Кейн бир нече жолу “Алтын бутса” уткан.
Бавария күйөрмандары ага тез эле көнүштү.
Кейн үй-бүлөсү менен көп убакыт өткөрөт. Бул оюнчу коргонууда да пайдалуу. Кейндин оюнун көрүү ырахат тартуулайт. Кейндин тарыхы ийгиликке ишенүүнүн далили. Ар бир күйөрман анын статистикасын сыймыктануу менен айтат. Гарри Кейндин акыркы жаңылыктары кызыктуу.
Заказ автобуса для детей на экскурсию https://povozkin.ru
Гарри Кейн азыркы футболдун эң мыкты чабуулчуларынын бири.Ар бир оюну күйөрмандар үчүн майрам. Бул жерде Гарри Кейндин жеке жашоосу жана үй-бүлөсү тууралуу маалымат бар: harry-kane kg com. Кейн Англиянын тарыхындагы эң жогорку бомбардирлердин бири.
Бавария күйөрмандары ага тез эле көнүштү.
Кейн үй-бүлөсү менен көп убакыт өткөрөт. Футболдо мындай туруктуу оюнчулар аз. Бул оюнчу эч качан берилишпейт. Кейндин тарыхы ийгиликке ишенүүнүн далили. Гарри Кейндин оюндарынын саны укмуш. Анын келечеги жаркын көрүнөт.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
makeprogressdaily – The tips shared here are practical and easy to implement.
makethemostoflife – I’ll keep this bookmarked, very uplifting resource
Кейндин упай топтоо жөндөмү легендардуу.Ар бир сезон Гарри Кейн жаңы деңгээлге чыгат. Бул шилтемеде Гарри Кейндин оюндарынан эң мыкты учурлар чогулган: Гарри Кейн видео. Футбол дүйнөсү мындай оюнчуларды сейрек көрөт.
Кейндин “Бавариядагы” карьерасы жаңы барак ачты.
Анын үй-бүлөсү ар дайым бактылуу көрүнөт. Кейндин оюн стили акылдуулук жана күчтү айкалыштырат. Гарри Кейндин жашы чоң тажрыйбага жол ачат. Анын дебюту футбол дүйнөсүн таң калтырган. Ар бир күйөрман анын статистикасын сыймыктануу менен айтат. Анын Instagram баракчасы абдан популярдуу.
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru для резки металла в Москве. 20 лет на рынке, выгодная цена, скидка 5% при заявке с сайта + обучение
findyourwayforward – The tone is hopeful without being unrealistic, very balanced
inspireandgrowtogether – Found some great ideas here, bookmarking for later.
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
кухни на заказ в спб цены https://kuhni-spb-3.ru/ .
discoverlearnandshare – Very educational content, feels like learning in fun way
everythingaboutmarketing – Always find valuable information that helps improve my marketing skills.
growyourpresenceonline – I learned something I can use right away, appreciate it
discoveryourpassion – This platform offers valuable tools for unlocking your potential.
**mind vault**
mind vault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
licsupport – I bookmark this, very helpful site for policy support
connectwithbrilliantminds – The tone is uplifting, really makes me want to learn more today
connectandgrowonline – The analytics feature helped me understand my audience better.
jointhenextbigthing – Simple layout but extremely effective, really makes browsing enjoyable.
thank you
discovertrendingideas – The writing feels fresh, not forced or overdone
thanks
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
learnandearndaily – The writing feels genuine, not too salesy or pushy
learnexploreandshine – This feels like space for growth and exploration
togetherwecreateimpact – Genuine tone, very motivating, makes me want to do my part
Нужна недвижимость? https://www.nedvizhimost-chernogorii-u-morya.ru/ лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
Мне понравилась четкость и логика аргументации автора в статье.
thank you
Аутстаффинг персонала https://skillstaff2.ru для бизнеса: легальное оформление сотрудников, снижение налоговой нагрузки и оптимизация расходов. Работаем с компаниями любого масштаба и отрасли.
Автор статьи предоставляет подробные факты и данные, не выражая собственного мнения.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
Автор приводит конкретные примеры, чтобы проиллюстрировать свои аргументы.
Жанкүйөрлөр үчүн ыңгайлуу навигация: акыркы жаңылык, кийинки беттеш, коэффициенттер жана прогноздор.
Түз эфирди кайдан көрүү жана алдын ала студиялык талдоо боюнча кыска нускама беребиз. islam-makhachev-kg.com/ FAQ бөлүмү: «кайдан көрөм», «качан болот», «кайсы салмакта?» сыяктуу суроолорго жооптор. Арман Царукян vs Ислам Махачев темасына байланыштуу тарыхый фон жана так даталар келтирилет. ЖМКдагы соңку цитаталар жана социалдык тармактагы билдирүүлөр бир жерге топтолгон. Беттешке чейинки форма, спарринг жана медициналык текшерүүлөр боюнча расмий шилтемелер бар.
Карьерасынын финалдык максаттары жана мүмкүн болгон супер-файт варианттары талданат. Прогноздор тарыхы жана тактык проценти ачык көрсөтүлөт. Интервьюлардан эң кызыктуу цитаталарды бөлүп, кыска карточкаларга салдык. Мобилдик түзмөктөр үчүн ылдам жүктөлүүчү версия жана ыңгайлуу меню жасалды.
Сүрөттөр, кыска видеолор жана цитаталар Махачев тууралуу материалдарды окууну кызыктуу кылат.
Картадагы ко-мэйн жана мэйн ивент боюнча да баалуу маалымдамалар кошулду. ислам махачев рейтинг ufc Рейтингдеги абалы жана мүмкүн болгон титулдук беттештер тууралуу эксперттик пикирлер топтолгон. Объективдүү маалымат гана. UFCдеги алардын позициялары, рекорддору жана окшош стилдери боюнча салыштырма таблица бар. ЖМКдагы соңку цитаталар жана социалдык тармактагы билдирүүлөр бир жерге топтолгон. Салмакты калыбына келтирүү жана кемитүү тартиби боюнча расмий маалыматтардан үзүндүлөр келтирилет.
Акыркы беттештин толук обзорун раунд-раунд менен кыскача окуңуз. Статистикага таянган прогноздор жана коопсуздук эскертмелери (жаңылыштык коркунучу) берилет. Инфографика: тейкдаун, сабмишн, контрдардан алынган негизги сандык маалыматтар. Сырттагы булактарга кеткенде коопсуздук эскертмелери жана расмий шилтемелер колдонулат.
votethurm – I hope she shares regular updates, transparency matters a lot.
inspireeverymoment – Feeling energized and hopeful after spending time here.
growtogetherwithus – This space gives me hope and inspiration to push forward.
Карьерасынын бурулуш учурлары, мыкты раундар жана эмнелер аны чемпион кылганы тууралуу кеңири баяндалат.
Тикелей эфир башталганга чейин акыркы коэффициенттер жана линиялар жаңыртылып турат. http://www.islam-makhachev-kg.com Фото, видео жана цитаталар менен медиа бөлүмүн карап көрүңүз. Бардык материалдар текшерилген. Арман Царукян vs Ислам Махачев темасына байланыштуу тарыхый фон жана так даталар келтирилет. Федер жана лайтвейт контекстинде салмак маселеси жана шарттар талкууланат. Беттешке чейинки форма, спарринг жана медициналык текшерүүлөр боюнча расмий шилтемелер бар.
Акыркы беттештин толук обзорун раунд-раунд менен кыскача окуңуз. Коэффициенттер жана линиялар боюнча кыска гид: ким фаворит, ким андердог — объективдүү маалымат. Марапаттар, чемпиондук тизмек жана респект учурлары иллюстрация менен берилет. FAQ форматына ылайык, «качан беттеш болот», «кайдан көрөм», «канча салмакта ойнойт» деген суроолорго даяр жооптор бар.
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
shareyourvisiontoday – The articles push me to think bigger and act now.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
thefuturestartsnow – The visuals and tone match perfectly with the message.
inspireeverymoment – This site makes me want to pause, reflect, act.
discovergreatideas – Inspired me to think outside the box for my startup.
learnnewthingsdaily – I’ve bookmarked this, will be returning often for more.
newstestingtoda – The brand identity is weak now, needs stronger messaging and visuals.
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
Карьерасынын бурулуш учурлары, мыкты раундар жана эмнелер аны чемпион кылганы тууралуу кеңири баяндалат.
Түз эфирди кайдан көрүү жана алдын ала студиялык талдоо боюнча кыска нускама беребиз. ислам махачев бой 2025 Жылдык план жана івент календары менен таанышыңыз. Эң маанилүү анонстар өз алдында чогулган. Кимге каршы кандай план иштейт, кыска тактикалык эскертмелерди да кошобуз. ЖМКдагы соңку цитаталар жана социалдык тармактагы билдирүүлөр бир жерге топтолгон. Аудитория үчүн жөнөкөй тилде түшүндүрүлгөн «кантип жеңиши мүмкүн» сценарийлери сунушталат.
«Канча акча тапты?» сыяктуу суроолорго расмий булактарга таянып, болжолдуу сандар келтирилет. Прогноздор тарыхы жана тактык проценти ачык көрсөтүлөт. Тренинг залынан фрагменттер жана күрөш ыкмалары тууралуу түшүндүрмөлөр кошулат. Издөө функциясы боюнча ачкыч сөздөрдү киргизип, керектүү бөлүмгө тез өтүңүз.
Добрый день!
Читай тут:
Йод в организме человека Йод в организме человека https://www.eduplus.hk/special/emailalert/goURL.jsp?clickURL=http://net-tabletok.ru/jod-v-organizme-cheloveka/
До встречи!
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
Как сам!
Читай тут:
кальций где содержится кальций где содержится https://www.contact-usa.com/?pay_bill&website=net-tabletok.ru/kakoj-kalczij-luchshe-usvaivaetsya/&product=qlWebDS-Premium&pay_amt=27.95
Покеда!
Сүрөттөр, кыска видеолор жана цитаталар Махачев тууралуу материалдарды окууну кызыктуу кылат.
Телегид сыяктуу жөнөкөй форматта дата, убакыт жана оппоненттер тизилет. ислам махачев статистика Тейкдаун, контрол жана сабмишн көрсөткүчтөрү визуалдуу берилет. Жөнөкөй тилде түшүндүрмө бар. Кимге каршы кандай план иштейт, кыска тактикалык эскертмелерди да кошобуз. Федер жана лайтвейт контекстинде салмак маселеси жана шарттар талкууланат. Тейкдаун коргонуу жана контролдо өткөрүлгөн убакыт сыяктуу метрикалар берилет.
Түз эфирден кийинки статустар, бонустар жана трофейлер тууралуу фактылар кошулат. Коэффициенттер жана линиялар боюнча кыска гид: ким фаворит, ким андердог — объективдүү маалымат. Сүрөттөр жана обои: социалдык тармак үчүн ылайыктуу форматтар жана резолюциялар бар. Жаңылыктарга жазылсаңыз, ири анонстар чыккан замат билдирүү аласыз.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
mystylecorner – I’ll definitely revisit, this place has good potential.
creativevision – The fusion of media creates a dynamic and engaging visual journey.
Эгер UFC жаңылыктарын кыска, так жана ыңгайлуу форматта издеп жүрсөңүз, бул жер туура.
Түз эфирди кайдан көрүү жана алдын ала студиялык талдоо боюнча кыска нускама беребиз. ислам махачев бой 2025 Жылдык план жана івент календары менен таанышыңыз. Эң маанилүү анонстар өз алдында чогулган. Арман Царукян vs Ислам Махачев темасына байланыштуу тарыхый фон жана так даталар келтирилет. Эгер ресми анонс чыкса, дата жана локация дароо жаңыланат. Беттешке чейинки форма, спарринг жана медициналык текшерүүлөр боюнча расмий шилтемелер бар.
Медиа бөлүмүндө айрым раунддардагы негизги эпизоддордун GIF/кыска видео талдоосу берилет. Хайптан алыстап, фактыларга таянган сабаттуу талкуу жүргүзөлү. Медиа пакет издегендер үчүн расмий булактарга жол көрсөтөбүз. Материалдар нейтралдуу, деңгээлдүү жана фанаттарга да, жаңы окурмандарга да ылайык.
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
Привет!
Читай тут:
Витамин К429 Витамин К429 http://www.irwebcast.com/cgi-local/report/redirect.cgi?url=http://generik-info.ru/vitamin-k2/
Бывай!
trendyfashioncorner – The layout is clean, making shopping a pleasant experience.
successpartnersgroup – Their team clearly knows how to deliver top-notch experiences online.
globalideasnetwork – Great layout, everything’s easy to find and visually appealing.
Приветствую!
Переходи:
Как сделать резюме на работу Как сделать резюме на работу http://m.shopinhartford.com/redirect.aspx?url=http://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-sdelat-rezyume-na-rabotu/
Пока!
cryptotephra-clagr.com – The lab specializes in analyzing tiny volcanic ash shards from sediments.
luxurytrendstore – Customer service was responsive and helpful, enhancing my shopping experience.
filamericansforracialaction.com – Good to see WordPress used, content seems accessible and organized.
stacoa.org – The content seems well written and meaningful.
discovernewideas – Will share with friends, this place has lots of potential.
createimpact – I appreciate transparency, feels genuine and trustworthy throughout.
electlarryarata – Nice start, saw your campaign theme but pages are empty now.
myvetcoach.org – The tone is kind and motivational, exactly what I need.
thespeakeasybuffalo – WordPress theme shows clearly; design feels modern.
laetly.com – Cool brand name, I’m curious about what you sell here.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
norigamihq – The branding is catchy, looks like it has potential.
summerstageinharlem.org – Very inspired after reading about these shows, feels like belonging.
pinellasehe.org – Always nice to find sites with meaningful content and care.
rockyrose.org – Found something in your content that lifted my mood today.
growyourdigitalpresence – Nice layout, content is clear, easy steps even for beginners.
hecimagine.com – I hope they feature student stories and application details soon.
formative-coffee.com – The blog section is lovely, full of interesting coffee culture reads.
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
https://aznaetelivy.ru/stories/2024-12-19/luchshie-oteli-krasnoy-polyany-top
https://plisio.net/uk/blog/bitcoin-philanthropy-how-and-where-to-donate-your-crypto
discovernewpath – Love that they keep the site simple yet meaningful.
thank you
This post will assist the internet people for creating new weblog or even a blog from start to end.
thanks
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
findyourfuture – I’ll keep this bookmarked, appears to offer real value.
nextvision – Wish there was proof of legitimacy—user reviews, company registration etc.
uniquefashionstyle – The website’s simplicity makes it easy to find what I need.
trustconnectionnetwork – The product range is diverse, catering to various preferences effortlessly.
trustedbusinesslink – Love the visual coherence, branding feels strong and consistent.
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
seoignite.click – Works beautifully on my phone, layout adjusts so smoothly.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha-3, Google, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
teamfuture – I like how the message here feels inclusive, inviting change.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
businessgrowthhub – Every visit here gives me actionable tips, very well thought.
trustandunity – I really feel a sense of honesty and warmth here, very inviting.
digitalinnovationzone – Good mix of tech and strategy, very relevant to what I need.
futuregoalsnetwork – Design and writing marry well, gives a solid impression.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
successbridge – The visuals are nice, enhance the message without distracting.
getthedeal – Recommended for anyone, site is reliable and updated often enough.
trustconnectionnetwork – I really feel this site values connection and transparency, nice touch.
https://bkfctoday.com/pat-the-gorilla-ninja-casey-is-putting-it-all-together-with-bkfc/
leadersunitedgroup – Coming back for more, feels like this could be something special.
connectinnovationhub – The ideas here feel fresh, this is a creative space indeed.
winmore – I’m excited to explore more, this feels like a project to follow.
futuregoalsnetwork – This site gives me clarity, I love the focused content here.
successjourneyclub – Clean layout, feels professional but still very warm and inviting.
discovervalue – The interface is clean and easy, I find exactly what I’m looking for.
globalpartnershipteam – Friendly tone, good structure — feels like they know their audience.
discoverdaily – Great content every day, keeps me coming back for more.
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
leadersunitedgroup – I enjoy the balance between motivation and practical tipsness.
brightdeal – The design is crisp and inviting — makes me want to explore more.
connectinnovationhub – Great site for connecting ideas and people — truly inspiring.
exploreideasworld – Clean layout helps ideas stand out, makes reading a joy.
buildtogether – I found useful tips, motivates me to take action.
growtogetheralliance – Visit after visit I feel more inspired, great energy overall.
innovateandbuild – Looking forward to what’s next, potential is very strong.
cjukfcjdfybt http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru/ .
согласование. http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru .
сколько стоит перепланировка квартиры сколько стоит перепланировка квартиры .
growthnetwork – It gives me hope — smart tips without overwhelming concepts.
**glpro**
glpro is a natural dietary supplement designed to promote balanced blood sugar levels and curb sugar cravings.
**sugarmute**
sugarmute is a science-guided nutritional supplement created to help maintain balanced blood sugar while supporting steady energy and mental clarity.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Хочу выделить материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
Hybrid squad chemistry puzzles solve easier when you buy fifa coins for accessing players from multiple leagues simultaneously. Real vendors with active support offer fast delivery and non drop guarantees for complex formation requirements.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12000
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2captcha.com, anti-captchas.com (antigate), rucaptcha.com, DeathByCaptcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
http://xrumersale.site/
boostcraft.click – Typography is sharp and readable, even on small screens.
ranktrail.click – Just browsed this, layout’s clean and the UI feels quite intuitive.
ranktrail.click – Typography and spacing are well balanced, easy on the eyes.
searchnest.click – Just checked out the site, feels clean and user friendly overall.
websummit.click – Layout feels intentional, nothing looks out of place or awkward.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
دوستان، وبسایتهای قمار مهمترین تهدید برای نوجوانان حال هستند.
خودم به یک پروفایل فعال کردم و در عرض
مدت اندک همه سرمایهام از دست گردید.
وابستگی نه فقط اقتصادی، بلکه خانواده و سلامت هم نابود مینماید.
اصلاً گول آنها را نپذیرید!
exactly
smartdesigncorner.shop – Love the design showcase, so many creative ideas here.
smartpartnership.bond – Definitely sharing this with colleagues who care about fairness.
**vitta burn**
vitta burn is a liquid dietary supplement formulated to support healthy weight reduction by increasing metabolic rate, reducing hunger, and promoting fat loss.
https://plisio.net/ko/blog/ethereum-vs-bitcoin
partnershippowerhouse.shop – Layout is clean, easy to navigate without feeling overwhelming.
globalunity.bond – The layout is clean and welcoming, nice first impression.
shopwithpurpose.shop – Clean site layout, and descriptions explain purpose behind every piece.
trustinyou.bond – Just what I needed to hear today — trusting in self.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
**synaptigen**
synaptigen is a next-generation brain support supplement that blends natural nootropics, adaptogens
Ищу красивые обои 4K с Неймаром: барса, ПСЖ или ранний «Сантос» — что посоветуете для телефона? Кто посоветует качественные «неймар игры» с нарезками дриблинга без музыки и водяных знаков? Хочу сверить номер и роль в текущем клубе, плюс свежие интервью. неймар сейчас. Где играет Неймар 2024/2025 и как выглядит его роль? Интересно для анализа комбинаций.
Где сейчас играет Неймар — подскажите надёжный источник с обновлениями раз в неделю. Неймар религия: редкая тема, важно корректно и без спекуляций — есть проверенные источники? Аманда Кимберли и Неймар — встречал упоминания, нужна верификация фактов. Неймар барса — лучшие фото с трофеями и парадами, для коллекции.
Неймар игры — подборка техничных эпизодов без комментаторского шума. Неймар в каком клубе играет — хочу добавить автоподстановку в шапке сайта.
**glucore**
glucore is a nutritional supplement that is given to patients daily to assist in maintaining healthy blood sugar and metabolic rates.
**prodentim**
prodentim an advanced probiotic formulation designed to support exceptional oral hygiene while fortifying teeth and gums.
Онлайн курсы ЕГЭ https://courses-ege.ru
Ищу красивые обои 4K с Неймаром: барса, ПСЖ или ранний «Сантос» — что посоветуете для телефона? Нужна подборка «месси роналду неймар фото» для заставки — редкие кадры и матчевые эмоции приветствуются. Нужен факт-чек по слухам и корректные био-детали без кликбейта. неймар 2025. Сантос Неймар: финты против плотной обороны — полезно разобрать для молодых вингеров.
Ищу «неймар сантос 2011» в хорошем качестве — особенно финалы и кубковые игры. Нужны «обои на телефон футбол Неймар» в вертикальном формате 1080×2400. Когда «умер неймар» — кликбейт заголовки; нужны разборы, опровергающие фейки. «Неймар в Реал Мадриде» — были ли реальные переговоры? Интересно проследить таймлайн.
Неймар барса обои 4К — важно проверить соотношение сторон под ультраширокие мониторы. Неймар 2018 ПСЖ — сравнение с 2017 Барса: влияние на xThreat и прогрессии мяча.
**nitric boost**
nitric boost is a dietary formula crafted to enhance vitality and promote overall well-being.
inspiredmind.shop – Love the creative vibe here, so many fresh inspiring items.
creativityuniverse.shop – Wow, this site sparkles with inspiration and artistic energy everywhere.
smartdesigncorner.space – Saved several pieces for reference, I’ll use them in future designs.
creativegiftzone.shop – Easily one of the better gift shops I’ve stumbled across online.
**sleeplean**
sleeplean is a US-trusted, naturally focused nighttime support formula that helps your body burn fat while you rest.
Советы по выбору обоев Неймара: матчи, портреты, training — что лучше для экрана смартфона? Сравнение Неймара 2011 и 2017: темп, решения, пауза — отличный кейс для тактического разбора. Короткие дайджесты новостей и canlı izləmə удобно следить из одного места. неймар новости. Где найти «неймар фото ПСЖ» в матч-дне и тренировках, чтобы собрать серию аватарок?
Ищу «неймар барселона фото» с классическими комбинациями с Суаресом и Месси. Сравниваю «неймар 2012 сантос» и переход в Европу — интересна динамика решений в финале. Неймар жуниор — хочу подборку детских фото для сравнительного коллажа. Неймар сейчас в каком клубе — нужен короткий виджет для сайдбара.
Неймар какой клуб сейчас — нужен снэпшот для карточек игроков. Неймар 2018 ПСЖ — сравнение с 2017 Барса: влияние на xThreat и прогрессии мяча.
I had to spend decades to look for online, only website
unfold the fully details, bookmarked and many thanks.
Thanks for the encouragement
**wildgut**
wildgutis a precision-crafted nutritional blend designed to nurture your dog’s digestive tract.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
inspiredgrowthteam.shop – Easy navigation, clear product descriptions — nice experience so far.
startsomethingnew.shop – The product images are very appealing and inspire creativity.
buildlastingtrust.bond – Trust-building content feels honest, not just flashy marketing.
findnewtrend.shop – Great place for trend-hunters looking for inspiration.
trustandunity.shop – Layout and design are smooth; everything feels easy to follow.
netfusion.click – On mobile it’s seamless, everything scales nicely with no quirks.
seoanchor.click – Already bookmarked this, I’ll be back for more content.
rankmotion.click – I like how responsive the design is on both desktop and mobile.
pagevector.click – Color scheme is gentle, doesn’t strain the eyes at all.
clicksignal.click – On mobile it’s seamless, no layout quirks or misalignments to see.
**mitolyn**
mitolyn a nature-inspired supplement crafted to elevate metabolic activity and support sustainable weight management.
https://clocks-top.com/
**zencortex**
zencortex contains only the natural ingredients that are effective in supporting incredible hearing naturally.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Особенно понравился раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
**yu sleep**
yusleep is a gentle, nano-enhanced nightly blend designed to help you drift off quickly, stay asleep longer, and wake feeling clear.
Советы по выбору обоев Неймара: матчи, портреты, training — что лучше для экрана смартфона? Хочу «неймар фото на аву» без шумов и с ровным цветом кожи, пригодные для соцсетей. Собираю редкие «неймар сантос фото» в высоком качестве — делюсь находкой. neymar-kg com. Где играет Неймар 2024/2025 и как выглядит его роль? Интересно для анализа комбинаций.
Нужны «неймар обои на телефон» с мягким контрастом, чтобы иконки читались. Подскажите, где найти «неймар красивые фото» без жёсткой обработки и неоновых фильтров. Неймар в детстве: редкие фото из академии «Сантоса» — подскажите архивы. Где играет Неймар 2025 — обновляю карточки игрока в своём блоге.
Неймар игры — подборка техничных эпизодов без комментаторского шума. Неймар Сантоc фото — ранние годы вдохновляют молодых вингеров на тренировки.
investsmarttoday – Really insightful tips on investing, made things much clearer today.
brightmarketplace – Found unique items not available elsewhere, great shopping experience.
smartbuytoday – Excellent value for money, definitely my go-to marketplace now.
classytrendstore – Smooth browsing and secure payment options, very trustworthy site.
bestdealcorner – This site has become my favorite for online shopping recently.
**breathe**
breathe is a plant-powered tincture crafted to promote lung performance and enhance your breathing quality.
https://plisio.net/ko/blog/discord-channel-ideas
successjourneyclub.shop – Definitely bookmarking; want to revisit when I have more time.
Хочу аву с «неймар сантос фото»: важно, чтобы кадры были чёткие и подойдут для профилей. Кто посоветует качественные «неймар игры» с нарезками дриблинга без музыки и водяных знаков? Собираю «неймар барселона фото» и ранние кадры из «Сантоса» в одном плейлисте. http://neymar-kg.com. Неймар в «Сантосе» 2011 — редкие хайлайты находить всё сложнее; делитесь проверенными плейлистами.
Неймар Бразилия: обои в национальной форме, стадионный свет и динамика движения. Сравниваю «неймар 2012 сантос» и переход в Европу — интересна динамика решений в финале. Неймар толстый — ещё один миф: интересен анализ формы после травм и пауз. Неймар барса — лучшие фото с трофеями и парадами, для коллекции.
Неймар игры — подборка техничных эпизодов без комментаторского шума. Неймар лучшие фото — интересны кадры из туннеля и разминки, редко попадаются.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Жду ваших отзывов и вопросов по теме.
**prostadine**
prostadine is a next-generation prostate support formula designed to help maintain, restore, and enhance optimal male prostate performance.
justvotenoon2 – Really practical advice, I’ll definitely try these suggestions soon.
dailyprofitupdate – Excellent customer service; responses were prompt and informative.
Советы по выбору обоев Неймара: матчи, портреты, training — что лучше для экрана смартфона? Ищу «неймар обои барселона» и «бразилия»: хочется минимализма, без лишних логотипов. Ищу подробную статистику и фото из эпохи «Сантоса». Неймар Сантос. Где найти «неймар фото ПСЖ» в матч-дне и тренировках, чтобы собрать серию аватарок?
Нужны «неймар обои на телефон» с мягким контрастом, чтобы иконки читались. Неймар религия: редкая тема, важно корректно и без спекуляций — есть проверенные источники? Неймар жена, дети — только официальные факты, без слухов; подскажите корректные био-источники. Неймар сейчас в каком клубе — нужен короткий виджет для сайдбара.
Неймар фото ПСЖ — лучше матч-день, где эмоции максимально живые. Неймар 2018 ПСЖ — сравнение с 2017 Барса: влияние на xThreat и прогрессии мяча.
stylemebetter – Impressed with the product variety; everything looks well-organized.
modernvisionlab.shop – Prices seem reasonable for what’s shown, good balance.
Хотите узнать больше о природе нашей страны? Присоединяйтесь к обсуждению.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
everydayvaluefinds.shop – The way values are presented feels genuine, not just sales pitch.
webtide.click – I found a couple of interesting links already—will explore more later.
modernvaluecorner – Will definitely shop here again; satisfied with my purchase.
trendhunterplace – The layout is smooth and easy to explore, very nice.
keywordorbit.click – The site seems fresh and well-laid-out, I like the first glimpse.
rankforge.click – Just browsed the site, the layout is clean and really easy to use.
nextgenproject.shop – The site seems built for forward thinkers and creators.
trafficpulse.click – The color scheme is subtle and soothing, doesn’t strain the eyes at all.
seoloom.click – I found a few useful links already; the navigation really helps you find things fast.
trendinggiftcorner – Excellent selection and useful recommendations, I’ll definitely come back.
smarttradingmentor – Excellent content and reliable advice, keeps me coming back for more.
yourtradingmentor – Practical trading tips that save a lot of time and effort today.
modernwoodcases – The craftsmanship is top-notch; truly one-of-a-kind accessories.
africain foot africain foot
Новости спорта онлайн http://sportsat.ru футбол, хоккей, бокс, теннис, баскетбол и другие виды спорта. Результаты матчей, обзоры, интервью, аналитика и главные события дня в мире спорта.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
marketanalysiszone – Clear analysis and practical commentary, really enjoyed browsing through it.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Спасибо за внимание! Надеюсь, вам было интересно.
learnandtrade – This will definitely be part of my regular study routine from now on.
classyhomegoods – Excellent customer service, got quick help with an order question.
successnetworkgroup – Positive vibe, felt like a professional community offering real value.
forexstrategyguide – This plan is a game-changer for anyone serious about business growth.
shopwithsmile – Found unique deals not seen elsewhere, very pleased with the find.
globalchoicehub – Easy to navigate website, found what I needed quickly and easily.
metaboost.click – Already bookmarked this site—feels like it’ll be a useful reference.
seowhale.click – It loads fast, and the images appear crisp—nice first impression.
Cheers! I like this!
thanks
shopandshine – The website design is clean and navigation very user-friendly.
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
**pineal xt**
pinealxt is a revolutionary supplement that promotes proper pineal gland function and energy levels to support healthy body function.
**energeia**
energeia is the first and only recipe that targets the root cause of stubborn belly fat and Deadly visceral fat.
**prostabliss**
prostabliss is a carefully developed dietary formula aimed at nurturing prostate vitality and improving urinary comfort.
ultimateprofitplan – Clear and concise, perfect for entrepreneurs looking to grow efficiently.
visionpartnersclub – Found unique items not available elsewhere, great shopping experience.
yourtradingmentor – Helpful resources and tools that feel relevant to real market conditions.
successfultradersclub – Good mix of visuals and explanations, helped me understand one strategy better.
bestforexstrategies – Found a tip I hadn’t seen on other sites, that was a nice bonus.
nextleveltrading – The strategy insights here are on point; I’ll definitely revisit.
futuregrowthteam – Found unique items not available elsewhere, great shopping experience.
strongfoundation – Enjoyed discovering this site, will definitely bookmark for future reference.
globalmarketinsight – Fast loading pages and well-organised info, good experience overall.
uniquedecorstore – Found some beautiful décor pieces here, really impressed with the selection.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Loved the advice and insights, makes networking much easier to manage.
seoignite.click – Typography and spacing are well-balanced—comfortable for reading longer content.
everydaytrendshop – This site has become my favorite for online fashion shopping.
simplelivinghub – Felt safe and comfortable reading the articles, very user-friendly site.
Представляем вашему вниманию национальные парки и заповедники России.
Хочу выделить раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Что думаете о красоте природы России? Делитесь мнениями!
**boostaro**
boostaro is a specially crafted dietary supplement for men who want to elevate their overall health and vitality.
rankseed.click – The color scheme is pleasant and doesn’t distract from the content.
smartbuytoday – Great customer service and helpful responses, made me return quickly.
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru/ фото, описание, стоимость участков и домов. Всё о покупке, строительстве и жизни за городом в одном месте. Полезная информация для покупателей и инвесторов.
**potent stream**
potent stream is engineered to promote prostate well-being by counteracting the residue that can build up from hard-water minerals within the urinary tract.
Хай!
Здесь подробней:
Телефон для пожилых людей Телефон для пожилых людей http://old.roofnet.org/external.php?link=http://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-dlya-pozhilyh-lyudej/
Бывай!
cuttingthered – Sharp branding, message delivers confidence and determination effectively.
Hey there, You’ve done an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am confident they will be benefited from this website.
Thank you very much for your support
freshfashionfinds – This site has become my favorite for online fashion shopping.
cuttingthered – Sharp branding, message delivers confidence and determination effectively.
modernvaluecorner – The website is clean and easy to navigate, made shopping simple today.
judiforcongress – Strong campaign site, message feels inspiring and presentation confident.
everydaytrendshop.bond – I appreciate the variety, keeps discovering fresh and helpful tips.
shopwithsmile.cfd – Great user experience, easy to navigate and find useful content.
connectforprogress.cfd – Just discovered this site, really enjoying the fresh content daily.
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
investsmarttoday.bond – Really useful content, helps me stay updated with trends fast.
musionet – Will bookmark this for future use, seems like a good steady go-to.
dailytrendstore – Site is clean and easy to browse, checkout was simple.
learntradingtoday – Great beginner-friendly site, really simplifies complex trading ideas.
urbanstylehub – Great mix of everyday items and special-find pieces, perfect for gifts too.
investprofitgrow – Great content on growing wealth, practical advice that I can use.
simplelivinghub – Felt safe and comfortable reading the articles, very user-friendly site.
проект перепланировки недорого http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru .
Здравствуйте!
Переходи:
Продажа аккаунтов клеш рояль Продажа аккаунтов клеш рояль https://www.google.com.gi/url?sa=t&url=https%3A%2F%2Fzarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodazha-akkauntov-klesh-royal/
Бывай!
winwithus.bond – Great selection of ideas, keeps me coming back often here.
growthnetworkgroup.cfd – The platform’s design is intuitive, making networking seamless and efficient.
trendandstyle.bond – Really useful content, helps me stay updated with trends fast.
trendandstyle – Trendy styles at great prices, found exactly what I needed.
financialgrowthplan – Useful for both beginners and those who want to refine their strategy.
brightmarketplace – Great variety and discovery of products, really enjoyed browsing today.
rankflow.click – Typography and spacing are comfortable—makes reading longer articles enjoyable.
netmatrix.click – Just browsed the site, the layout feels clean and everything’s nicely organized.
justvotenoon2 – Website loads fast, nice layout and easy to navigate sections.
Hi there, constantly i used to check weblog posts here early in the morning, because i enjoy to find out more and more.
thank you
welcome
businesssuccesshub – Practical resources and clear advice, just what I needed.
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Зацепил материал про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
modernwoodcases – Really like the craftsmanship here, feels far more premium than typical cases.
imprintregistry – This will be a go-to site for verifying art provenance and title certificates.
tradingmasterclass – Navigation and course structure make it easy to stay on track.
markettrendalerts – Will bookmark this as a go-to for alerting on market movements.
advancedtradingtools.cfd – Overall solid experience, glad I found this helpful trading resource.
yourtradingmentor.cfd – Found some practical takeaways that I can apply this week.
maskchallengeusa – Clear purpose and bold message, layout supports awareness beautifully.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – User experience is smooth, pages load quickly and look professional.
brittanydominguez.shop – Pages load quickly and everything looks crisp—great user experience.
smarttradingmentor.bond – Practical tips and real examples make learning trading much easier.
nathanjones.shop – Pages load quickly and everything looks crisp—great user experience.
teamworkinnovation.bond – Just discovered this site, really enjoying the fresh content daily.
z9hl4.info – Typography and spacing are well-balanced—comfortable for reading longer content.
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
creativegiftworld.bond – Clean layout and smooth browsing, makes finding info simple.
urbanstylehub.cfd – Really useful content, helps me stay updated with trends fast.
trustedpartnergroup.bond – Overall great first impression, excited to explore further opportunities here.
dailytradingupdate.cfd – Excellent daily recaps, really helps to stay informed and focused.
fastgrowthsignal.bond – Love the clear insights and fast-moving strategy advice offered here.
dailyessentialfinds.cfd – Overall positive experience, I’ll definitely return here for future essentials.
dailytrendstore.cfd – Love the selection, many items caught my attention and interest.
teamworkinnovation.cfd – The tone is professional yet approachable, excellent for team growth.
learnandtrade.cfd – Very intuitive interface, made exploring trading tools much easier.
fastgrowthsignal.cfd – Navigation is intuitive and the information seems relevant and fresh.
freshfashionfinds.cfd – Love the design and easy navigation, very user-friendly experience.
Автор старается представить информацию нейтрально и всеобъемлюще.
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
visionpartnersclub.bond – Interesting articles and tips, definitely worth checking every day.
bestdealcorner.cfd – Found love-the layout, deals look fresh and exciting today.
strategicgrowthplan.bond – Will bookmark this site, very helpful resource for goal-setting.
smartbuytoday.bond – Found exactly what I was looking for in minutes.
unityandprogress.bond – Inspiring community focus, really makes one feel part of something.
buildsuccessnetwork.bond – Site loads quickly and content feels relevant and fresh.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
ultimateprofitplan.bond – Loved the actionable insights, really helped me refine my strategy.
smartinvestorhub.cfd – Good community feel, questions answered quickly and sharing seems real.
shopandshine.cfd – Overall positive impression, I’ll return soon for more browsing.
**hepatoburn**
hepatoburn is a premium nutritional formula designed to enhance liver function, boost metabolism, and support natural fat breakdown.
هشدار جدی در مورد پلتفرمهای بازیهای شرطی آنلاین.
من با عنوان کسی که اتفاق مستقیم کردهام، میگویم که چنین جاها مکانی برای غارت سرمایه
افراد هستند. فعالیت اولیه برنده است، لیکن در ادامه سیستمها طوری ساخته شدهاند که شما
پایانه شکستخورده باشید.
ریسک وابستگی قویتر از هر امر دیگری است و تواند سلامتتان
را نابود کند. دور کنید!
strongpartnershipnetwork.cfd – Excellent site layout and simple navigation make partnering easy and effective.
همراهان گرامی، سایتهای شرطبندی صرفاً پولتان را غارت مینمایند، بلکه آرامش
جسمیتان را نابود میبرند.
خودم فعالیت با سرگرمی کردم، ولی ناگهان مبتلا وابستگی گردید و شغلام
ترک نمودم. تهدید آنها جاها عمیقتر از آن است که فکر میکنید.
اجتناب بیچون و چرا از این ضروری است!
thank you
dailyessentialfinds.bond – Customer service was friendly and responsive to my questions.
Автор предлагает анализ преимуществ и недостатков разных подходов к решению проблемы.
Thanks for the comment
خوانندگان گرامی، وبسایتهای شرطبندی عظیمترین تهدید برای افراد امروز هستند.
اینجانب با تک پروفایل شروع نمودم و طی زمان اندک همه داراییام هدر گردید.
وابستگی صرفاً مالی، بلکه دوستان همچنین ذهن را
از بین میگردد. به هیچ عنوان گول چنین
را قبول نکنید!
thanks
**hepatoburn**
hepatoburn is a potent, plant-based formula created to promote optimal liver performance and naturally stimulate fat-burning mechanisms.
smarttradingmentor.cfd – Overall positive first impression, excited to dive deeper into content.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
smartfashionboutique.bond – Love how clean the layout is and the browsing experience.
successfultradersclub.shop – Overall impression is positive; looking forward to exploring deeper content here.
partnershipgrowthhub.bond – Will bookmark this platform and revisit often for new insights.
everydayvaluehub.shop – Will bookmark this store for future browsing of daily essentials.
dreambuyworld.shop – Found stylish products today that caught my attention right away.
learntradingtoday.cfd – The mobile experience is smooth and content loads quickly on phone.
visionaryfutureteam.bond – Clean layout, simple navigation makes exploring their vision really easy.
innovationdriventeam.bond – Overall very positive first impression, eager to explore more content here.
simplelivingstore.shop – Love how the theme aligns with peaceful lifestyle and conscious choices.
globalalliancenetwork.bond – The site design is clean and navigation feels smooth and intuitive.
modernlifestylezone.shop – I appreciate the clear photos and product descriptions featured here.
dailyessentialstore.shop – The pricing seems reasonable and deals today were attractive.
connectforgrowth.bond – Just discovered this site, seems like a strong growth hub.
investprofitgrow.cfd – Will bookmark this platform and revisit often for new insights.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, нашел много полезного.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
Ready to start your journey into anonymous browsing? An antidetect browser is the ideal solution for beginners and small teams to manage multi-accounting safely without getting flagged by anti-fraud systems.
powerofcollaboration.bond – The content tone is welcoming, professional, and easy to engage with.
budgetfriendlyfinds.shop – Checkout process felt straightforward and payment options looked reliable overall.
creativefashionworld.shop – Just discovered this store, stylish finds and great browsing experience.
Начнем путешествие по магическим уголкам российских заповедников.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Природа – наш главный учитель и защитник. Берегите её!
**flowforce max**
flowforce max delivers a forward-thinking, plant-focused way to support prostate health—while also helping maintain everyday energy, libido, and overall vitality.
**neurogenica**
neurogenica is a dietary supplement formulated to support nerve health and ease discomfort associated with neuropathy.
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Зацепил раздел про Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
I was curious if you ever thought of changing the structure of your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or two pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
thank you for the observation
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
**cellufend**
cellufend is a natural supplement developed to support balanced blood sugar levels through a blend of botanical extracts and essential nutrients.
**prodentim**
prodentim is a forward-thinking oral wellness blend crafted to nurture and maintain a balanced mouth microbiome.
Портал о строительстве домов https://doma-land.ru проекты и сметы, сравнение технологий (каркас, газобетон, кирпич, брус), фундамент и кровля, инженерия и утепление. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, тендер подрядчиков, рейтинги бригад, карта цен по регионам, готовые ведомости материалов и практика без ошибок.
globaltradingnetwork.cfd – Offers co-branded platforms, boosting brand visibility for partners.
сео продвижение сайтов топ сео продвижение сайтов топ .
uniquedecorstore.shop – Good value found here, pieces combine style with affordability nicely.
advancedtradingtools.shop – Checkout process was straightforward, and payment options appeared secure.
Квартира с отделкой https://новостройкивспб.рф экономия времени и предсказуемый бюджет. Фильтруем по планировкам, материалам, классу дома и акустике. Проверяем стандарт отделки, толщину стяжки, ровность стен, работу дверей/окон, скрытые коммуникации. Приёмка по дефект-листу, штрафы за просрочку.
smartfashionboutique.cfd – Easy navigation and clean design, feels like a smooth shopping experience.
successmindsetnetwork.bond – Hoping they add video lessons soon, but site is already helpful.
nextleveltrading.bond – Found some useful tips here, will check back often.
trustandstrength.bond – I bookmarked this one, looks like a site with structure and vision.
protradinginsights.cfd – The algorithmic trading section is a must-read for tech-savvy traders.
futuregrowthteam.bond – Simple navigation makes it easy to find what I’m looking for.
**revitag**
revitag is a daily skin-support formula created to promote a healthy complexion and visibly diminish the appearance of skin tags.
classyhomegoods.bond – I bookmarked the site, seems like a promising place for home upgrades.
https://purebeautyoutlet.bond/
visionpartnersclub.cfd – Overall good first impression, site shows promise for regular visitors.
protraderacademy.cfd – The community support here is amazing, always helpful and friendly.
profitgoalsystem.cfd – Hoping they include more case studies soon, but good start.
Добро пожаловать в удивительный мир природы России!
По теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Вот такое у нас получилось погружение в мир природы.
globalchoicehub.cfd – Appreciate the variety of categories, from tech to home essentials.
shopandshine.shop – Product descriptions are clear, helping me make informed decisions.
connectforprogress.bond – Really intrigued by this site, shows quite a strong vision.
pixelpush.click – Typography and spacing are excellent—reading content here is easy.
هشدار سریع در مورد سایتهای بازیهای شرطی.
چنین جاها طراحی میگردند تا کاربران
را اعتیادآور کنند و پولتان را غارت بکنند.
اینجانب در دلیل تبلیغات جذاب وارد
کردم و نتیجه ویرانی گردید.
سوءاستفاده روانی همچنین ضرر پولدار دو جانبه است.
به هیچ وجه امتحان نمیکنید!
boostengine.click – I like how clean the design is and how well-organized the menus appear.
smartfashionboutique.cfd – Found some nice pieces here, quality seems pretty good from previews.
webrevive.click – I’m bookmarking this site — it seems like a resource worth coming back to.
sitefoundry.click – I found some useful pages already; looks like a resource worth using.
bestdealcorner.bond – Browsing categories is simple, found gifts for family without hassle.
forexlearninghub.cfd – I’m hoping for video tutorials soon, but what’s here is useful.
brandlift.click – Pages load smoothly and visuals look crisp and professional.
best seo services https://top-10-seo-prodvizhenie.ru .
seo продвижение сайта компании москва https://seo-prodvizhenie-reiting-kompanij.ru/ .
smartforexacademy.bond – Just discovered this site, looks promising for learning forex trading.
smartforexmentor.cfd – The visuals are good and navigation is smooth, nice experience.
Сегодня мы отправимся на виртуальную экскурсию в уникальные уголки природы России.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
experttradingzone.bond – I like how they explain concepts simply, friendly for newcomers.
SEO — это инвестиция в долгосрочный успех бизнеса в интернете. Оптимизация сайта повышает видимость, улучшает качество контента и способствует росту органического трафика. Регулярная аналитика и корректировка стратегии помогают удерживать позиции в ТОПе. Такой подход повышает доверие аудитории и увеличивает конверсии. Подробнее о продвижении сайтов читайте: продвижение интернет магазина услуга
همراهان، خواهش میکنم پرهیز سایتهای قمار شوید.
خودم با امید سریع ثروتمند شدن فعال گردیدم، اما فقط باخت دیدم.
آنها جاها مملو از دروغ به علاوه اعتیاد طراحی
میگردند. آینده شما بهای ریسک آنها فعالیت را نداشته!
regina4congress – The campaign feels genuine, site design clean and trustworthy.
smartforexacademy.cfd – The layout is clean, content feels easy to digest for beginners.
Поисковая оптимизация сайта помогает привлекать клиентов без постоянных затрат на рекламу. SEO делает ресурс более заметным, улучшает его структуру и повышает доверие пользователей. Оптимизация включает работу с ключевыми словами, контентом и техническими аспектами сайта. При регулярной работе результаты сохраняются надолго, а конверсия продолжает расти. Это идеальный инструмент для компаний, ориентированных на стабильный и долгосрочный рост. Подробнее о SEO-продвижении читайте https://minecraft-builder.com/создание-и-seo-продвижение-сайтов-под-кл/
forexlearninghub.bond – The visuals are good and navigation is smooth, nice experience.
Вас интересуют природные богатства России? Давайте исследуем их вместе!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
https://alloopt.ru
Надеюсь, вы нашли это путешествие по природе познавательным.
forexstrategyguide.bond – The site loads quickly and works smoothly on mobile, a big plus.
purebeautyoutlet.cfd – Overall nice find, aesthetic and user-friendly—looking forward to new arrivals.
emeryflowers – Beautiful aesthetic, every section blooms with creativity and emotion.
financialgrowthplan.cfd – I’ll bookmark this and revisit later once more content is added.
emeryflowers – Beautiful aesthetic, every section blooms with creativity and emotion.
jamesonforct – Strong campaign presentation, design feels confident and message stands clear.
experttradingzone.cfd – Content appears professional, though I’d like to see more examples.
unitedvisionnetwork.bond – Bookmarking this one for further visits, looks promising.
happytrendzone.cfd – Mobile version works nicely, the interface is responsive and clean.
trustbridgealliance.bond – Overall good impression; I’ll keep this bookmarked for future visits.
trustbridgealliance.cfd – Site loads quickly and seems mobile-friendly — big plus for browsing on the go.
nighttoshineatlanta – Beautifully inspiring event site, visuals radiate joy and inclusion.
profitabletraderpath.cfd – Just found this site, looks like a solid resource for traders of all levels.
douglasand55 – Very polished design, strong visuals and clear professional tone.
modernvaluecorner.bond – Would love to see more case-studies or examples added soon.
Откройте для себя прекрасные и загадочные места, которые находятся под охраной в нашей стране.
Кстати, если вас интересует Изучение ООПТ России: парки, заповедники, водоемы, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://alloopt.ru
Рад был поделиться с вами этой информацией. До новых встреч!
futuregrowthteam.cfd – Visuals and typography are appealing, gave a good first impression.
professionalgrowthhub.bond – Overall a positive first look — I’ll check it again once more content is live.
advancedtradingtools.bond – I found some interesting sections here, will return later to dig deeper.
globalnetworkvision.bond – I hope they add more interactive content or community features in the future.
buildstrongrelationship.bond – The layout appears clean and easy to browse, good first impression.
nighttoshineatlanta – Beautifully inspiring event site, visuals radiate joy and inclusion.
classyhomegoods.bond – Found some attractive home decor items, browsing was smooth and easy.
https://purebeautyoutlet.bond/
smarttradingmentor.bond – The writing style feels real and not overly hype, appreciated.
trustedleaderscircle.cfd – Just came across this platform, looks like it’s striving for leadership development.
uniquedecorstore.bond – The store looks stylish and modern, intriguing décor pieces catch attention.
businessleadersclub.bond – I bookmarked this one; it seems like a resource worth revisiting.
brightmarketplace.cfd – Hoping they add more filters and categories to improve browsing experience.
buildsuccessnetwork.cfd – The tone is professional yet approachable—makes me feel comfortable exploring.
modernlifestylezone.shop – Mobile browsing works well; site looks responsive on my phone.
neighborsforrandy – Friendly community feel, layout conveys care and connection effectively.
buildtogethernow.bond – I found some useful resources here, will explore further later.
forexlearninghub.cfd – I bookmarked this site; looks like it could grow into a great tool.
ehajjumrahtours – Professional and serene, the layout reflects faith and reliability.
Пришёл без особых ожиданий, а ушёл в полном восторге. Массаж на высшем уровне, всё было естественно и красиво. Энергия мастера просто завораживает. Рекомендую, салон эротического массажа цена Новосибирск, https://sibirka.com/. Всё прошло отлично, девушки знают своё дело.
هی برای همه که جستجو سرگرمی سریع میباشند.
پلتفرمهای شرطبندی تله بزرگی میباشند زیرا منجر اعتیاد و ضرر شدید میگردند.
خودم بیشمار پول باختم و اکنون پشیمان میگردم.
خواهش میکنم اجتناب کنید و از امور
سالم توجه شوید!
کاربران گرامی، نسبت به سایتهای شرطبندی بسیار
محتاط باشید. چنین پلتفرمها با پروموشن جذاب افراد را گول میزنند، ولی در باطن مملو دروغ است.
ضرر اقتصادی صرفاً جزئی از دردسرها است؛ اعتیاد عامل درگیری از خانواده
و استرس گسترده میشود.
لطفاً اصلاً وارد نخواهید شد!
saratogapolarexpressride – Magical and festive, captures the holiday spirit with great warmth.
ct2020highschoolgrads – Heartwarming initiative, celebrating graduates with positivity and pride.
learnforexstrategy.cfd – The writing style is friendly and accessible for beginners, liked that.
experttradingguide.cfd – The writing tone is approachable, which is nice for beginner traders.
businessconnectworld.bond – The tone of writing is approachable yet professional — nice balance for a business site.
luxnoe – Modern and stylish, this site exudes luxury and creative design.
smarttechmukesh.xyz – Found a few useful articles here, seems like valuable information overall.
moj-kredyt.shop – Nice read today, tips feel practical and easy for beginners.
cloudfiles.tech – I’m bookmarking it — seems like a resource I’ll return to for more insight later.
shop-in.tech – Found a couple of interesting posts; seems like the content has depth I’ll explore later.
karen4assembly – Clear and sincere campaign tone, content reflects leadership and integrity.
2rss5ge.xyz – Typography is clear and comfortable to read, well-chosen fonts.
https://pushnews.com.ua/tvir-rozdum-chomu-treba-berehty-pryrodu/
stageofnations – Culturally rich, visuals celebrate unity and vibrant heritage beautifully.
mastriano4congress – Direct and focused, campaign visuals match strong message delivery.
I am regular visitor, how are you everybody? This paragraph posted at this website is genuinely pleasant.
Thank you for the encouragement.
youronlinetoolbox – Feels like the “go-to” resource when I need something quick and effective.
creativityneverends – Really enjoyed the practical examples and visuals; helped me get unstuck.
Компания «СибЗТА» https://sibzta.su производит задвижки, клапаны и другую трубопроводную арматуру с 2014 года. Материалы: сталь, чугун, нержавейка. Прочные уплотнения, стандарты ГОСТ, индивидуальные решения под заказ, быстрая доставка и гарантия.
infinitalink.click – The layout is clean and loading was quick, first impression is positive.
inspiredailyandgrow.click – Mobile browsing was smooth, site seems responsive which is a plus for me.
urbanscale – Easy to navigate and looks professional, giving a good first impression.
nextrend – If you’re looking for something fresh, this might be the space; just expect some unknowns.
inspirechangeandprogress – Even if the ideas aren’t huge, they feel relevant and doable — a plus.
buildyourownlegacy – The advice is thoughtful and grounded, not just ambitious fluff.
discoveramazingstories – Very well structured site; easy to navigate and the content flows nicely.
adirondackfiddlers – Full of tradition, music passion shines through each element.
asteroid-insurance – Clever concept, design feels futuristic and sharp with humor.
startyourdreamproject – Visiting this site lifted my energy and gave me direction for a new project.
everythingyouneedtoday – Browsed earlier and found ideas that I can apply right away.
exploreendlesspossibilities – Found several full of inspiration that changed how I see my next move.
buildyourdreambrand – I’ll revisit this often as my brand evolves and I need new ideas.
expandyourhorizons – Great resource for inspiration when you’re ready to move ahead in life.
findnewopportunitieshere.click – Hoping for more user reviews or proof of benefits to increase confidence.
shopminq – Trendy e-commerce look, product visuals are crisp and appealing.
explorethepossibilitiesnow – Great content for stepping out of your comfort zone and trying something new.
yourmomenttoshine – This site will be one of my go-tos whenever I need inspiration again.
thepathofselfgrowth – Found some really inspiring posts here that helped me rethink my goals.
yourpathofsuccess – The suggestions here are down-to-earth and doable rather than vague.
startsomethingamazingtoday.click – Just discovered this site, looks like a fresh opportunity to explore today.
bighappenshere – Inspiring concept, site feels bold, dynamic and full of optimism.
homecovidtest – Informative and reliable, design prioritizes health clarity and accessibility.
urbanmatrix – It’s nice to come across a site that balances clarity with creativity.
createyourownpath – Every post left me thinking differently about my next move in life.
charitiespt – Compassionate and community-driven, mission comes across with sincerity.
startcreatingimpact – Feels like a community for growth-minded people, which I appreciated.
larkfest2013 – Vibrant and nostalgic, visuals radiate energy and celebration.
creativityneverends – Bookmarking this one: good for when I need a spark of creativity.
fayettecountydrt – Purposeful and informative, organization’s vision feels transparent and clear.
nextrealm – Simple yet meaningful write-ups that match where I am right now.
becreativeeveryday – Great when you’re stuck and need a little push to start making something.
staymotivatedandfocused – Found a great article here that got me back into my groove.
keepgrowingwithus – I like how the site focuses on consistent growth rather than overnight success.
findyourinnerdrive – I’m already using one idea from here in my daily routine and it’s helping.
mckeetransition – Professional government tone, site design supports accessibility and progress.
goldnexus – Heads-up: always good to verify such sites before committing any data.
learnandimproveeveryday – The site layout is clean, and it’s easy to find what you’re looking for.
focuslab – The site looks creative and modern, every element feels intentional.
urbanscale – Seemed promising but I didn’t find enough depth yet to rate it highly.
nextrend – Might be worth bookmarking and revisiting once more posts or features are added.
buildyourdigitalfuture – Feels like a trustworthy resource for building something meaningful online.
inspirechangeandprogress – The layout is readable and the content isn’t overloaded — exactly what I needed.
buildyourownlegacy – I bookmarked this site; the posts feel like things I’ll revisit in years to come.
discoverhiddenpotential – Found at least one practical step I can take today toward personal growth.
holyspiritschooleg – Educational yet warm, design and content reflect care and faith.
findsolutionsfast – The tips are straight to the point and easy to apply right away.
درود در همه که جستجو پول آسان میباشند.
سایتهای شرطبندی دام گستردهای میباشند
اینکه منجر سوءاستفاده به علاوه زیان جدی
مینمایند. آشنایم صدها ریال نابود
کردم و اکنون پشیمان میگردم. بهتر است پرهیز بمانید و
به امور مثبت روی بکنید!
lcbclosure – Focused and informative, the message feels urgent and clearly communicated.
mayceformayor – Campaign feels strong and grounded, visuals emphasize trust and service.
топ 10 сео компаний топ 10 сео компаний .
masonchallengeradaptivefields – Inspirational cause, presentation is heartfelt and full of purpose.
shopforhappiness.shop – Wide variety of categories, always discover new and useful items.
milestonerest – Inviting visuals, design creates a sense of comfort and good taste.
Пользуюсь DRINKIO постоянно, и всегда доволен результатом. Всё работает быстро и без задержек. Ассортимент большой, можно найти всё, что нужно. Курьеры вежливые, доставка действительно круглосуточная. Удобный и надёжный сервис, https://drinkio105.ru/
shopandshineeveryday.shop – Affordable prices without compromising quality, happy with everything purchased today.
openlaunch – Feels like a community hub for makers, not just a blog—promising.
peoplesprotectiveequipment – Practical and safety-focused, design feels direct and trustworthy.
joinourcreativeworld.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
letthemplaymn – Passionate and purposeful, the site speaks strongly for youth engagement.
shopthebesttoday.shop – Consistently positive shopping experience, will continue to shop here.
findwhatyoulove.shop – Great deals, shopping experience feels smooth and totally reliable here.
createandgrow – Will revisit later to check for updates; could become interesting if content gets added.
shopforhappiness.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
buildyourdreamtoday.shop – Very helpful content, guides are simple and easy to follow.
shopandsmilealways.shop – Affordable prices without compromising quality, happy with everything purchased.
teamtadros – The mission feels bold, visuals highlight unity and determination.
exploreopportunitiesnow.shop – Prompt customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
simplybestchoice.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
keepgrowingforward.shop – User-friendly layout, easy to navigate and find helpful content quickly.
exodusalliance – Empowering theme, site feels hopeful and mission-driven throughout.
oscarthegaydog – Whimsical and delightful, brand personality shines through humor and charm.
Надеюсь, что эти комментарии добавят ещё больше позитива и поддержки к информационной статье!
that’s kind of you
bestdealsforlife.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
rodarodaku.xyz – Bookmarked it for later, seems like something worth revisiting soon.
findsolutionsfast – Handy when you’re short on time but still need quality content.
kkgg1.xyz – The visuals and text blend naturally, keeping everything neat and clean.
yourdailyupdate.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
mm9b.xyz – Navigation feels smooth, I found things easily within seconds.
xxau.xyz – Just checked it out, the design is simple, modern, and easy to navigate.
easyprt.xyz – The color scheme feels balanced and gives a calming vibe overall.
daybirdsyr – Energetic vibe, visuals and tone reflect creativity and modern living.
supportsros – Compassionate tone, clear visuals support their advocacy with sincerity.
خوانندگان گرامی، پلتفرمهای شرطبندی عظیمترین خطر
برای نوجوانان حال هستند. خودم به تک پروفایل ورود نمودم و در عرض زمان
اندک همه سرمایهام نابود رفت.
سوءمصرف صرفاً پول، بلکه دوستان و ذهن هم نابود مینماید.
هرگز گول چنین را نپذیرید!
lifestyleinspirationhub.shop – Timely delivery, received my order in perfect condition.
getinspiredtoday.shop – Wide variety of categories, always discover new and useful items.
justinhicksformissouri – Strong campaign message, design feels authentic and community-focused.
shopwithconfidence.shop – Fast delivery and easy checkout, made shopping enjoyable instantly today.
nyscanalconference – Informative and organized, layout suits event communication well.
tinacurrin – Artistic and bold, site radiates passion and expressive creativity.
harryandeddies – Cozy restaurant vibe, visuals and menu presentation feel deliciously inviting.
southbyfreenoms – Fun, quirky branding with energetic layout and friendly design.
При появлении трещин или сколов рекомендуется обратиться к специалисту для замены лобового стекла. Качественные комплектующие и профессиональная установка гарантируют надёжность и герметичность конструкции. Своевременная замена лобового стекла помогает избежать дальнейших повреждений и повышает общую безопасность автомобиля: замена лобового стекла
electamandamurphy – Inspiring campaign, message of progress and empathy shines through.
everydayvaluecorner.shop – Perfect site for everyday shopping, everything works smoothly and fast.
learnshareconnect.shop – Navigation is smooth, loading is fast, made the browsing experience pleasant.
modernlivingstyle.shop – Website is clean and easy to browse, made checkout simple and fast.
findyourperfectdeal.shop – Great selection across categories, found something for everyone in the family.
exploreamazingideas.shop – This store is turning into one of my go-to spots for creativity and quality.
yourjourneybegins.shop – Found inspiring products here, perfect to start something new today.
1xbet giri? yapam?yorum https://1xbet-giris-1.com .
discovergreatthings.shop – Found some great gifts here, perfect for friends and family alike.
uniquetrendstore.shop – Wide variety of categories, always discover new and useful items.
kim4commonsense – The campaign feels approachable, visuals and tone are relatable.
discoverendlessideas.shop – Great customer service, answered my questions promptly and kindly too.
thebestplacetoshop.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
liveandexplore.shop – Shipping was smooth, packaging was neat and arrived ahead of schedule.
thinkcreategrow.shop – Enjoyed reading through the posts, everything feels useful and genuine.
getinspiredtoday.click – Browsed the site and found some really inspiring content today.
staycuriousalways.shop – Great deals and fast shipping, very satisfied with my purchases.
globalmarketplacehub.shop – Affordable prices without sacrificing quality, impressed with what I found today.
modernlivingstyle.click – Affordable but stylish pieces, great value for upgrading my living space.
getinspiredtoday.click – Every article seemed well-thought-out and genuinely useful for self-improvement.
smartchoiceoutlet.shop – Loved the selection, found something for everyone in one place.
liveandexplore.click – Strong value, stylish items, and reliable experience for every purchase.
connectdiscovergrow.click – Items and articles are well curated, quality shows in their picks.
romain4reform – Clear, reform-focused tone, visuals convey honesty and strong leadership.
staycuriousalways.click – Easy navigation and fast loading enhanced my experience significantly today.
shopwithconfidence.click – Wide variety of products, found several for both gifts and everyday use.
yourtrustedonlinestore.shop – Great selection of products, I found everything I needed all in one place today.
keepgrowingforward.click – Loved the content here, it really helped me stay focused and motivated.
discoveryourmoment.shop – I’ll definitely return when I need something thoughtful and well-made again.
newseasoncollection.shop – Shipping was prompt and packaging was nice, very satisfied overall.
Undeniably believe that which you said. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the internet the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get irked while people think about worries that they just don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
thank you
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
rideformissingchildren – Heartfelt cause, presentation honors the mission beautifully and respectfully.
inspireeverydaylife.shop – Prompt customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
shopthelatesttrend.shop – Fast shipping and helpful support made this shopping experience great.
t-walls-of-kuwait-iraq – Historical and impactful, visuals convey memory and meaning strongly.
everytrendinone.shop – Would recommend to friends looking for trendy pieces and great service.
hardman4schools – I like the positive tone; it radiates passion and responsibility.
connectdiscovergrow.shop – Beautiful presentation and clear content, makes the message really stand out.
simplybestchoice.click – Website design is clean and intuitive, made shopping simple and fun.
dreamcreateinspire.shop – Love how this site sparks ideas, made me want to get creative today.
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
trendyfindshub.shop – Wide variety of categories, always discover new and useful items.
Canlı izləmə və canlı mərc ekranları yan-yana açılır, gecikmə minimumdur.
Kupon redaktəsi və cash-out imkanı mərcin riskini idarə etməyə kömək edir. Əgər azərbaycan dilində interfeys lazımdırsa, pinco azerbaycan səhifəsi sizin üçündür — ödənişlər şəffafdır. Sürətli ödəniş üçün sevimli metodları saxlayıb bir kliklə istifadə etmək olur. Axtarış paneli ad, provayder və mexanika üzrə işləyir — nəticələr dərhal çıxır.
Oyun qaydaları hər masada ayrıca açılır və suallara cavab verir. Android apk yükləməsi rəsmi səhifədən olur və quraşdırma bələdçisi addım-addım göstərilir.
Hesab bərpası SMS və ya e-poçt vasitəsilə aparılır. Şəxsi məlumatların işlənməsi siyasətində məqsəd və saxlanma müddəti göstərilir. Favoritlər siyahısı ilə sevdiyiniz liqalar və slotlar bir yerdə saxlanır.
cranberrystreetcafe – Cozy and charming, design evokes warmth and delicious experiences.
createandgrow.click – The experience feels trustworthy and reliable, very satisfied with my visit.
bestdealsforlife.click – Quality is better than expected for the price, pleasantly surprised today.
theperfectgiftshop.click – The site layout is nice and browsing feels smooth and user-friendly.
globaltrendmarket.click – The selection keeps updating; always new stuff to explore and stay ahead of trend.
1x lite http://www.1xbet-giris-7.com .
smartchoiceoutlet.click – Great quality for the price, this store exceeded my expectations today.
brightfuturedeals.shop – Customer support answered my question fast and was polite today.
uniquetrendstore.click – The website layout is clean and browsing made shopping enjoyable.
dreamcreateinspire.click – Quality content and tools that actually feel helpful and practical.
exploreopportunitiesnow.click – Found really helpful content and ideas, gave me a fresh perspective.
joinourcreativeworld.click – The layout is clean, browsing was smooth and completely enjoyable today.
discovernewworld.click – Website layout is clean and easy to use, browsing was a breeze.
thinkcreategrow – Oops, again wrong save link, but forgot why I needed to note it—still useful.
changetheworld – Found useful resources here, saved several articles for later reference.
0pdpof.xyz – Typography feels comfortable to read, clear and well balanced spacing.
discoverendlessideas – The blog posts are insightful and the imagery makes it a pleasure to browse.
74364.pw – Appreciate structured headings; scanning content becomes quick and straightforward today.
diwang2.pw – Visuals complement the content nicely, nothing looks out of place.
coatsjps.pw – I’ve bookmarked the site, looks like a resource worth coming back to.
wqpyp.pw – Overall a professional and enjoyable experience browsing through the pages.
georgetowndowntownmasterplan – Informative and civic-minded, content clearly explains planning goals.
hardman4schools – The layout is simple yet powerful, delivering a message of trust.
saveshelterpets – Touching initiative, site feels compassionate and community-focused.
everydayvaluecorner – Prices are reasonable and quality is surprisingly good for the value offered.
albanysuperducks – Fun and quirky, visuals bring playful excitement to life.
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: Prisma Games portfolio and projects
yourtrustedonlinestore – Sharing with colleagues because it’s inspiring and worth a browse during breaks.
everytrendinone – Comments seem authentic, community is interactive, feels like a real hub.
findwhatyoulove – Totally worth bookmarking: found five ideas today I will try out.
newseasoncollection – Definitely bookmarking this site, I’ll be back for the next releases.
yourjourneybegins – Shared this with a friend, they found it super helpful too.
makelifebetter – Navigation is easy, everything loads quickly, I found useful tips fast.
buildyourdreamtoday – This site has quickly become a go-to for my morning inspiration read.
trendyfindshub – The writing style is clear and friendly—makes reading fun rather than a chore.
learnshareconnect – I found helpful tips and real‑world examples that felt genuine today.
globalmarketplacehub – Details for sellers are clear, which makes participating feel trustworthy and manageable.
successpartnersgroup – The website is responsive and easy to browse, makes exploring topics enjoyable.
successpartnersgroup – Found tips that I can implement immediately for better results today.
inspireeverydaylife – This site offers so many surprising ideas that grabbed my attention fast.
nextgeninnovation – Definitely bookmarking this site for daily inspiration and innovative ideas.
shopandsmilealways – Found exactly what I needed today: a fresh perspective and new inspiration.
shopandshineeveryday – Loved the downloadable resources section; useful for planning and idea generation.
urbanwearzone – Ordered last week, arrived fast and quality is amazing.
globalideasnetwork – User-friendly layout and thoughtful posts, highly recommend exploring this platform.
discovernewideas – Always discover unique concepts that spark my creativity.
inspiredgrowthteam – Excellent resources for fostering collaboration and innovation within teams.
discovergreatthings – Loved the range of topics here—everything from creativity to practical life hacks.
shopthelatesttrend – Totally worth bookmarking: found five ideas today I will try out.
buildyourdreamtoday – I appreciate the honesty here—talking about setbacks as well as wins.
discoveryourmoment – Content is varied and well‑written—it’s clear effort was put into this.
Kuponda multi-bet, sistem və tez düzəliş funksiyaları var, səhv əmsal da avtomatik düzəlir.
Turnirlərdə liderlər cədvəli şəffafdır, mükafatlar və qaydalar əvvəlcədən açıqlanır. Android istifadəçiləri pinco yüklə bələdçisini izləyərək apk-ni bir dəqiqəyə quraşdıra bilər. Depozit bonusunun qaydaları dildə qısa və misallarla izah edilib. Turnirlər slotlarda aktivliyi artırır və real hədiyyələr verir.
Oyun qaydaları hər masada ayrıca açılır və suallara cavab verir. APK yenilənməsi tətbiqdaxili xəbərdarlıqla gəlir və bir dəqiqəyə tamamlanır.
Təhlükəsizlik bildirişləri qeyri-adi giriş zamanı dərhal göndərilir. Müvəqqəti pauza aktiv edildikdə hesab hər yerdə kilidlənir və bildiriş gəlir. Favoritlər siyahısı ilə sevdiyiniz liqalar və slotlar bir yerdə saxlanır.
hardman4schools – Strong educational vision, visuals and tone reflect dedication beautifully.
thebestplacetoshop – Saved a few articles for future reference; this site is becoming a favourite.
stopkrasner – Strong political tone, site expresses clear intent and decisive messaging.
اخطار جدی به افراد جذب شده به وبسایتهای بازیهای شرطی.
چنین سایتها مانند دام تأخیری عمل میکنند؛ ابتدا هیجان میبخشد، لیکن بعداً نابودی مالی رخ میدهد.
خودم به علت آنها بازیها زندگیام را تلف کردم.
خواهش میکنم به خانواده نزدیک بگویید که پرهیز کنند!
hardman4schools – The site feels professional, message is clear and community-focused.
tranquilleeyecream – Calm aesthetic, visuals match beauty and relaxation concept perfectly.
артур ім’я походження
shopforhappiness – Found exactly what I needed today: a fresh perspective and new inspiration.
exploreamazingideas – Navigation is smooth, the layout is clean, content loads without distraction.
findyourperfectdeal – Sharing with colleagues because it’s inspiring and worth a browse during breaks.
walkunchained – Inspiring tone, message of freedom and courage comes across clearly.
1win букмекерская контора зеркало https://1win5519.ru/
взять займ без отказа https://zaimy-54.ru
займы онлайн срочно https://zaimy-57.ru
займы организации https://zaimy-59.ru
jammykspeaks – Powerful voice, content feels authentic, motivational and full of passion.
createimpactonline – The resources provided are incredibly helpful for scaling our nonprofit.
partnershippowerhouse – Their case studies provide real-world examples that are incredibly helpful.
беспроцентный займ https://zaimy-61.ru
займ на карту без отказа https://zaimy-63.ru
кредитный займ https://zaimy-65.ru
embersk9wish – Heartwarming mission, site honors service dogs with love and gratitude.
1x lite 1x lite .
1xbet ?yelik http://www.1xbet-4.com .
mystylecorner – Love the variety of clothes here, really stylish daily finds.
cryptocurrencynews.pw – Overall, great presentation and reliable information all throughout.
createimpactonline – Appreciate the personalized consultation services; they’ve been invaluable to our growth.
partnershippowerhouse – Highly recommend their resources for anyone serious about strategic partnerships.
hyrdaruzxpnev4of.online – Easy layout, minimal ads, and content focuses on reader value.
tuzidh.pw – Just checked it out, design feels simple yet professional, nice first impression.
phonenumbers.pw – The color palette is subtle, makes reading comfortable on the eyes.
kbdesignlab.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
https://xn--80aneebgncbebxz7l.xn--p1ai/top-10-glavnykh-dostoprimechatelnostey/
промокоды 1вин http://1win5518.ru/
https://autosaratow.ru/phorum/threads/novosti-odnoj-strokoj-obschestvo.115916/page-1423
взять займ на карту оформить микрозайм без отказа
займ срочно без отказа https://zaimy-69.ru
займ на карту без отказа оформить займ онлайн без комиссии
mystylecorner – Love the variety of clothes here, really stylish daily finds.
monumentremoval – The purpose is bold and the site feels deeply meaningful and timely.
займ мгновенно https://zaimy-78.ru
нужен займ мфо https://zaimy-76.ru
займ онлайн без отказа все займы онлайн
همراهان، پلتفرمهای قمار عظیمترین ریسک برای نوجوانان کنونی هستند.
خودم از تک پروفایل فعال نمودم و طی مدت اندک بیشمار داراییام نابود
شد. سوءمصرف نه فقط پول، و خانواده به علاوه
ذهن هم از بین مینماید. به هیچ عنوان
گول این را نپذیرید!
monumentremoval – The purpose is bold and the site feels deeply meaningful and timely.
займ на карту мгновенно микрозаймы онлайн
срочно онлайн займ отказа https://zaimy-80.ru
займы онлайн быстрый займ онлайн до зарплаты
trendandstyle – Might like to see more size guides, but overall impressed with the selection.
forexlearninghub – Found some good tips today that I can immediately apply to my trading plan.
advancedtradingtools – It would be great to see detailed case studies or user testimonials too.
purebeautytrend – Shipping was faster than I expected and packaging was neat.
kionawest – The contractor’s site looks professional, clean visuals and strong commitment to quality.
dailyessentialfinds – Shipping was timely and the item arrived in excellent condition.
everydayvaluehub – Shipping details were clearly listed and my order arrived within the expected timeframe.
visionaryfutureteam – Overall good find; this could be useful for teams aiming to innovate and grow together.
winwithus – The weekly updates keep me motivated and moving forward with purpose.
mystylecorner – Customer support is super helpful, answered all my questions.
buildsuccessnetwork – Would like to see more user testimonials or case studies for added credibility.
partnershipgrowthhub – Plan to revisit when I map out our next collaboration strategy; looks promising.
innovationdriventeam – Found a useful tip today about cross-functional collaboration that I’ll test this week.
powerofcollaboration – Found a tool here today that I plan to implement with my team.
connectforprogress – The community feel is strong and it motivates me to take action.
unitedvisionnetwork – Good support and easy to find contact info—makes a difference for trust.
займ с плохой кредитной https://zaimy-87.ru
займ онлайн без отказа взять займ без проверки кредитной истории
взять займ онлайн https://zaimy-89.ru
businesssuccesshub – Bookmarking this as a resource; many useful templates and checklists.
modernlifestylezone – I found stylish decor here that fits perfectly in my modern apartment.
uniquedecorstore – The quality looks excellent and matches the product photos quite well.
classyhomegoods – The decor pieces here are stylish and really upgrade a room instantly.
financialgrowthplan – Found helpful sections on budgeting and investment basics, really needed that.
investprofitgrow – The resources offered are interesting, though I’ll compare with other platforms too.
advancedtradingtools – Competitive pricing and transparent terms, really liked that part of the offering.
successmindsetnetwork – Great resource for anyone looking to level up their thinking and habits.
kionawest – The contractor’s site looks professional, clean visuals and strong commitment to quality.
Я впечатлен этой статьей! Она не только информативна, но и вдохновляющая. Мне понравился подход автора к обсуждению темы, и я узнал много нового. Огромное спасибо за такую интересную и полезную статью!
Thank you very much for the encouragement
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
Сайт konsultaciya-advokata51.ru предлагает вам разнообразные возможности. Консультация юриста может оказаться крайне полезной для большинства. На нашем сайте вы сможете получить профессиональные советы.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на где найти бесплатного юриста.
Записавшись на консультацию, вы сможете получить индивидуальную помощь от специалиста.
Качество предоставляемых услуг во многом зависит от опыта специалистов. Каждый адвокат на konsultaciya-advokata51.ru прошел тщательный отбор. Что бы вы ни выбрали, мы гарантируем качественное выполнение работы.
Важно, чтобы юридические услуги были доступны каждому. На нашем сайте можно найти информацию о ценах и услугах. Клиенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант в зависимости от своих нужд.
Кроме того, мы предлагаем услуги онлайн. Сегодня возможность получить помощь через интернет очень важна. Вы можете задать свои вопросы в любое время.
simplelivingstore – The plant-based wellness section is intriguing, especially for calming the space.
pressbros – Cozy café vibe with creative flair; coffee and brunch look seriously inviting.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
Таможенный брокер всегда готов помочь, даже в сложных ситуациях. Работают уверенно и спокойно, https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel.ru/
trustedpartnergroup – Found a useful strategy tip today that I plan to apply in my next meeting.
ultimateprofitplan – Found a useful tip this morning that I plan to experiment with this week.
simplelivingstore – Love the minimalist home décor items here, they make rooms feel peaceful.
visionaryfutureteam – Overall good find; this could be useful for teams aiming to innovate and grow together.
trustedleaderscircle – Overall a solid platform; I’ll keep it bookmarked for future leadership growth reference.
dailyessentialstore – On mobile the browsing experience was smooth and checkout was hassle-free.
trustbridgealliance – The website layout is clean and browsing through their insights feels effortless.
professionalgrowthhub – Found a promising tip today on leadership growth; will apply it this week.
connectforgrowth – Overall a solid first impression; I’ll revisit after exploring more content.
shopandshine – Great selection of items, very easy to find something stylish and fun.
creativefashionworld – Would love to see more color-options soon, but the current range is nice.
mcalpineinfo – If you’re exploring this topic you may want to cross-check other sources alongside this site.
globalnetworkvision – Community comments add a helpful layer of perspective to the main content.
saveshelterpets – Good intention shown on the homepage, though I’d want to see detailed financials or transparency reports.
1091m2love – Found this page today, honestly loving the overall smooth experience here.
forexlearninghub – Good mix of strategy ideas and practical trading tips for real situations.
urbanstylehub – The packaging was neat and the item arrived in perfect condition today.
1day4kids – Uplifting cause, presentation radiates care and dedication toward children.
brightmarketplace – Overall good experience so far, happy with how things turned out.
nycbhm – Community-focused organization with meaningful outreach and engagement.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
learntradingtoday – Mobile experience was smooth, good for learning on the go.
forexstrategyguide – Just browsed the content, looks promising and clearly laid-out so far.
knightstablefoodpantry – Compassionate food pantry serving the community with dedication.
trustedpartnergroup – Overall positive first impression; I’ll revisit and track how their content evolves.
ultimateprofitplan – Support/contact info appears clearly—good sign when dealing with online platforms.
visionaryfutureteam – Just took a look at the site and the growth-mindset content looks quite promising.
pmajoe4council – Clear campaign focus, design feels trustworthy and community-oriented.
dailyessentialstore – I’ll likely revisit this store when I need more everyday essentials.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
professionalgrowthhub – Will revisit when they publish new updates; seems like a solid long-term resource.
trustbridgealliance – Support and contact information is clear—makes the platform feel more reliable.
shopandshine – Checkout process was straightforward and didn’t require too many steps.
1091m2love – Found this page today, honestly loving the overall smooth experience here.
creativefashionworld – Customer chat was helpful when I asked about sizing, thumbs up.
mcalpineinfo – Overall a basic web presence so far; good first step, but needs expansion and verification.
saveshelterpets – Would be helpful if they listed an EIN/charity registration, governance board, and past impact metrics.
mcctheatercampaign – Supporting arts and theater with passion and community spirit.
денежный займ https://zaimy-91.ru
Скачать видео с YouTube https://www.fsaved.com онлайн: MP4/WEBM/3GP, качество 144p–4K, конвертация в MP3/M4A, поддержка Shorts и плейлистов, субтитры и обложки. Без регистрации, быстро и безопасно, на телефоне и ПК. Используйте только с разрешения правообладателя и в рамках правил YouTube.
Отличная команда специалистов, умеют решать даже нестандартные задачи – Таможенное оформление во Внуково
astoriatogether – Community unity and collaborative neighborhood initiatives.
pmajoe4council – Clear campaign focus, design feels trustworthy and community-oriented.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
winwithus – The resources provided here have made a real difference in my work.
propecianorxpharmacy.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
www-882884.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
mjiuzixun.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
gameclub2u.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
worldvehicleexpo.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Роберт Левандовски футбол дүйнөсүндөгү эң таасирдүү чабуулчулардын бири.
Левандовскинин жубайы жана үй-бүлөсү тууралуу көптөр кызыгат. Левандовски канча жыл ойногонуна карабай, деңгээлин түшүргөн жок. Роберт Левандовски жаш футболчулар үчүн үлгү. Роберт Левандовски тууралуу жаңылыктарды окуу үчүн http://www.robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтына кириңиз. Барселонадагы Левандовскинин оюнун күйөрмандар макташат.
Роберт Левандовски карьерасын үзүрлүү өткөрүүдө. Роберт Левандовски ар дайым физикалык жактан даяр.
Левандовскинин туугандары тууралуу тарых да кызыктуу. Левандовски ар бир оюнда өзүн көрсөтүүгө аракет кылат.
worldvehicleexpo.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
www-882884.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
gameclub2u.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
mjiuzixun.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
propecianorxpharmacy.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
https://bsbrevista.com.br/2025/08/25/pgr-quer-policia-extra-vigiando-bolsonaro-contra-fuga/
learnsharegrow.shop – Looking forward to seeing more updates and articles from this site.
uniquefashionstyle.shop – Browsed through several items and found some stylish pieces I’d consider buying.
discovergreatdeal.shop – Wide range of categories; something for everyone here.
Левандовски футболдо чыдамкайлык менен мыкты натыйжа көрсөттү.
Левандовски жубайы менен көп кайрымдуулук иштерин колдойт. Левандовски канча гол салганы тууралуу күйөрмандар ар дайым талашат. Левандовски өз өлкөсүнүн сыймыгы. Барселона, Польша жана Роберт Левандовски тууралуу баарын https://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ сайтынан билиңиз. Роберт Левандовски Барселона клубуна энергия кошту.
Левандовски спорттук тарбиянын маанисин ар дайым белгилейт. Роберт Левандовски реабилитацияны тез бүтүргөн.
Роберт Левандовски үй-бүлөсүнө чоң маани берет. Роберт Левандовскинин профессионалдуулугу суктанарлык.
discoverdaily.online – Easy to read and well-organized, very user-friendly experience.
futuregoalsnetwork.shop – Photos are crisp, descriptions honest — very helpful shopping experience.
growthpoint.bond – Looking forward to seeing more updates and offerings from this site.
leadersunitedgroup.bond – The content is uplifting and very relatable, makes me think.
buildbrand.bond – The typography is clear, enhancing readability across devices.
nextvision.bond – It’s great to find a site that focuses on personal growth and learning.
globalpartnershipteam.shop – Photos are crisp, descriptions honest — very helpful shopping experience.
discovervalue.bond – Found some useful tips here; bookmarking for future reference.
discovernewpath.shop – The content is engaging and informative; definitely bookmarking this one.
futureopportunitynetwork.shop – Frequent discounts and promotions; always a great deal to find.
createimpacttoday.shop – Appreciate the mission behind this store; it’s more than just shopping.
teamfuture.bond – Impressive visuals and content, makes browsing enjoyable and smooth.
discoverdaily.online – I keep discovering useful tips and advice each visit.
successpathway.bond – Easy navigation and smooth checkout process; shopping made simple.
winmore.bond – Typography is readable and matches the overall clean design.
connectinnovationhub.bond – I appreciate the clear structure and organized layout here.
trustandunity.bond – Looking forward to more updates and new features soon.
businessgrowthhub.shop – The design is clean and professional, making navigation a breeze.
smartfashionboutique.bond – Looking forward to more updates and new features soon.
successfultradersclub.shop – Navigation is intuitive; finding information is quick and effortless.
Левандовскинин формасы дагы деле жогорку деңгээлде.
Левандовскинин жашоо образы көптөр үчүн мотивация. Левандовски канча гол салганы тууралуу маалымат ар дайым жаңыланып турат. Роберт Левандовски көп жолу “алтын бутсага” татыктуу болгон. Левандовскинин Барселонадагы ийгиликтерин robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтынан окуңуз. Левандовски Барселонада лидер болуп калды.
Роберт Левандовски бала кезинен эле футболду сүйгөн. Роберт Левандовски ар дайым физикалык жактан даяр.
Левандовскинин туугандары тууралуу тарых да кызыктуу. Роберт Левандовски футбол тарыхындагы легенда.
globalalliancenetwork.bond – Typography and design are consistent and visually appealing.
uniquedecorstore.shop – Impressive visuals and smooth interface; browsing feels seamless.
futurevisiongroup.bond – Clean layout, easy to navigate, and informative content.
togetherwerise.bond – Building a supportive community for women in construction.
newhorizonsnetwork.shop – Impressed with the product quality and packaging; exceeded expectations.
futuregoalsnetwork.shop – The layout is crisp and clear, makes exploring effortless.
nicholashirshon – Professional portfolio showcasing expertise and accomplishments.
learnsharegrow.shop – It’s great to find a site that focuses on personal growth and learning.
findyourfuture.shop – Looking forward to seeing more updates and articles from this site.
unitedbygoal.bond – Easy to find relevant information; well-organized structure.
growstrongteam.bond – I’d recommend this site to anyone seeking positive mindset resources.
leadersunitedgroup.bond – Feels like a community, not just a site, very welcoming tone.
choice-eats – Culinary excellence with diverse and delicious dining options.
globalpartnershipteam.shop – The layout is crisp and clear, makes exploring effortless.
teamfuture.bond – The design feels modern and professional; great first impression.
discovervalue.bond – Appreciate the practical advice shared; feels grounded and real.
winmore.bond – Looking forward to seeing more updates and features here.
заем взять займ
займы онлайн бесплатно микрозайм взять
connectinnovationhub.bond – Typography and design are consistent and visually appealing.
займы деньги быстрый займ
trustandunity.bond – Overall a polished site with professional and engaging content.
businessgrowthhub.shop – The design is clean and professional, making navigation a breeze.
smartfashionboutique.bond – I appreciate the clear structure and organized layout here.
successfultradersclub.shop – I appreciate the clear structure and organized layout here.
globalalliancenetwork.bond – Looking forward to more updates and new features soon.
uniquedecorstore.shop – Navigation is intuitive; finding information is quick and effortless.
covidtest-cyprus – Essential health services with reliable testing solutions.
trendinsight.shop – The visuals are appealing and complement the content well.
https://sodepa.cm/bonne-annee-2023-m-le-ministre-de-lelevage-des-peches-et-des-industries-animales/
play-brary.org – Found the content engaging and informative; keeps me interested.
leanneslifechangingfairies.com – Easy to find information and well-structured sections throughout the site.
nextvision.bond – Found some insightful articles here; definitely bookmarking this one.
wellnesstourbus – Mobile health and wellness services bringing care to communities.
happylifestylehub.shop – The vibe is so positive, feels like a calm retreat.
successpathway.bond – Photos are crisp, descriptions honest — very helpful shopping experience.
growthpoint.bond – Impressive design and user experience; feels professional and welcoming.
uniquefashionstyle.shop – My only suggestion: maybe add more filters for easier browsing.
createimpacttoday.shop – The products are not only beautiful but also support great causes.
discovergreatdeal.shop – Impressed with the product quality and packaging; exceeded expectations.
Левандовскинин формасы дагы деле жогорку деңгээлде.
Роберт Левандовски Инстаграмда күйөрмандар менен тыгыз байланышта. Левандовски канча гол салганы тууралуу күйөрмандар ар дайым талашат. Левандовски өз өлкөсүнүн сыймыгы. Роберт Левандовскинин эң жаңы голдору тууралуу маалыматты https://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ жеринен таба аласыз. Левандовски Барселонада лидер болуп калды.
Левандовски спорттук тарбиянын маанисин ар дайым белгилейт. Роберт Левандовски ар дайым физикалык жактан даяр.
Левандовскинин балдары да спортко жакын. Левандовски ар дайым жогорку деңгээлди кармайт.
concernedaboutpollution – Environmental advocacy with focus on pollution awareness and solutions.
play-brary.org – Found the content engaging and informative; keeps me interested.
1 xbet 1xbet-10.com .
1xbet tr 1xbet tr .
мебель для кухни спб от производителя http://www.kuhni-spb-2.ru .
leanneslifechangingfairies.com – I like the friendly tone and helpful resources provided here.
futureopportunitynetwork.shop – Photos are crisp, descriptions honest — very helpful shopping experience.
asianspeedd8 – Modern dating platform with cultural connection and community focus.
moesboardwalk.com – The website has an inviting storefront look and feels easy to browse.
discovernewpath.shop – The visuals are appealing and complement the content well.
mdcphilly.com – Navigation feels intuitive; I found what I needed quickly without confusion.
Левандовски футболдо чыдамкайлык менен мыкты натыйжа көрсөттү.
Роберт Левандовски денесин мыкты формада кармайт. Роберт Левандовски жашоосунда көп ийгиликке жеткен. Левандовскинин машыгуу режими көпчүлүккө кызыктуу. Барселона, Польша жана Роберт Левандовски тууралуу баарын https://robert-lewandowski-kg.com/ сайтынан билиңиз. Роберт Левандовски Барселона клубуна энергия кошту.
Роберт Левандовски жаштарга мотивация берет. Левандовски жаракаттан кийин тез эле формасын кайтарды.
Роберт Левандовски өзүнүн тамырларын сыйлайт. Левандовски ар бир оюнда өзүн көрсөтүүгө аракет кылат.
harrietlevinmillan.com – The layout is visually appealing and supports the written content nicely.
pp4fdr.org – It feels like a platform where community involvement and feedback matter.
ks4thekids.com – I like the branding—“KS4TheKids”—catchy and memorable.
moesboardwalk.com – I appreciate how easy it is to find deals and featured items.
brauhausschmitzoktoberfest.com – Overall a strong event web presence; conveys excitement and authenticity.
clubinorout.com – Clean design and straightforward layout, very user-friendly.
mdcphilly.com – The typography and spacing really enhance readability; good choice.
newhorizonsnetwork.shop – Fast shipping and quality items; very satisfied with my purchase.
concernedaboutpollution.com – The topic is relevant and handled in a thoughtful, well-structured way.
asianspeedd8.com – I found the content easy to read and the site structure logical.
grant-jt.com – I’d like to see a bit more visuals or imagery to add character.
komunahouse.com – The visuals really reflect the artistic mission—nice aesthetic.
berrybombselfiespot.com – I like the concept of a selfie-spot studio—creative use of space for photo moments.
gailcooperspeaker.com – I appreciate how the site feels purposeful without being over-the-top.
grant-jt – Professional services with expertise and dedicated client support.
shemplymade.com – It would be nice to see more user reviews or customer stories.
meetkatemarshall.com – Pages load fast and the headings make it simple to scan through posts.
reindeermagicandmiracles.com – The tone is cheerful and inviting; makes me smile.
seenministries.com – I appreciate the clear “About” section — gives context and purpose right away.
mdcphilly.com – Looks like a solid website; I’d revisit it for updates.
harrietlevinmillan.com – Great mix of poetry and prose; impressive range and depth.
moeinclub.com – The coloring and typography make for a comfortable reading experience.
ks4thekids.com – The visuals are modest but effective; keeps things uncomplicated.
Роберт Левандовскинин машыгуусу көптөргө үлгү.
Роберт Левандовски фото жана видеолору дайыма талкууда. Роберт Левандовски карьерасында жүздөгөн гол салган. Роберт Левандовски улуттук курама үчүн көп гол салган. Толук биография жана сүрөттөр http://www.robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтында жеткиликтүү. Барселонадагы Левандовскинин оюнун күйөрмандар макташат.
Роберт Левандовски жаштарга мотивация берет. Роберт Левандовски реабилитацияны тез бүтүргөн.
Роберт Левандовски өзүнүн тамырларын сыйлайт. Роберт Левандовски өзүнүн максатына ишеним менен жеткен.
electmikemontes.com – Pages load quickly and the user experience feels smooth.
pastorjorgetrujillo.com – Looking forward to future updates and seeing how the website evolves.
trendingnewsfeed.net – typography is clean; readability is good across devices.
brauhausschmitzoktoberfest.com – Overall a strong event web presence; conveys excitement and authenticity.
pp4fdr.org – Overall a strong web presence that makes me want to engage with their cause.
clevelandchristmasclub.com – The vibe of the site is fun and festive; great first impression.
clubinorout.com – Clean design and straightforward layout, very user-friendly.
brucknerbythebridge.com – The site does a good job of balancing text and imagery; very readable.
casa-nana.net – The tone is caring and supportive—very appropriate for the cause.
opensky-inc.com – I’ll keep an eye on how this site develops in future updates.
centensports.com – I like the layout and how the content is structured; good readability.
komunahouse – Community living space fostering connection and collaboration.
concernedaboutpollution.com – Feels trustworthy and credible—good for raising awareness about pollution.
mdcphilly.com – Content is clear, well-organized and easy to understand.
asianspeedd8.com – The site has a modern look and it’s easy to browse.
berrybombselfiespot.com – The branding is strong and consistent; gives a confident first impression.
grant-jt.com – The text is clear and readable; good choice of font and spacing.
komunahouse.com – Would love to see more interactive features or member stories.
gailcooperspeaker.com – I appreciate how the site feels purposeful without being over-the-top.
safercharging.com – Overall, a solid web presence with a clear mission and good execution.
berrybombselfiespot – Fun and vibrant selfie destination with creative photo opportunities.
dankglassonline.com – Navigation felt intuitive; I found what I was looking for quickly.
reindeermagicandmiracles.com – The site’s branding fits perfectly with what they’re offering—nice match.
turnerhallrestaurant.com – The menu preview is clear and inviting—made me hungry just browsing.
brucknerbythebridge.com – I’d like to see more resident stories or interactive features in the future.
muralspotting.com – Looking forward to more additions and featured artists from around the world.
gailcooperspeaker – Inspirational speaking with powerful messages and engaging delivery.
muralspotting.com – I’d love to see a map view or interactive feature for locating murals.
meetkatemarshall.com – Visuals are well done and complement the content without being overwhelming.
seenministries – Faith-based ministry offering spiritual guidance and community support.
cepjournal.net – Design is consistent across pages; the branding comes through well.
moeinclub.com – A search feature would be useful to find specific topics quickly.
bigprintnewspapers.com – The site’s design is clean and professional, making navigation a breeze.
shemplymade.com – Found the product descriptions helpful and easy to understand.
centensports.com – Pages load smoothly and the visuals support the user experience.
safercharging.com – I like the clarity of their offering—makes the business purpose obvious.
seenministries.com – Overall, a strong web presence that reflects a meaningful mission.
kdjfjks.site – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
eyelle-paris.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
zakolata.xyz – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
binaryoptionstrade.xyz – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
cryptocurrencytrade.pw – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
opensky-inc.com – Good first impression — clean, credible, and user-friendly.
pastorjorgetrujillo.com – I appreciate the consistent branding and clear mission statement.
casa-nana.net – I found the navigation simple and the layout helps focus on the key message.
trendingnewsfeed.net – content appears varied, which keeps things interesting.
clevelandchristmasclub.com – Felt reasonably responsive on mobile; layout adapts well.
electmikemontes.com – The site looks clean and well-laid-out, I liked the simplicity.
1xbet t?rkiye 1xbet t?rkiye .
мед оборудование мед оборудование .
dankglassonline.com – Overall, a solid web presence with potential; would revisit for updates.
muralspotting.com – The photography is well-done; it really brings out each mural’s character.
наркологический центр москва narkologicheskaya-klinika-24.ru .
buildyourdreamtoday.shop – The visuals are inviting and the interface feels smooth.
catherinewburton.com – Content is concise and focused, which I really appreciate.
vsmphotography.com – Navigation to galleries and contact info is intuitive; I found what I needed quickly.
toddstarnesbooktour.com – The design feels professional and aligns well with the author’s branding.
createandgrow.shop – The layout appears clean and user-friendly; nice visual clarity.
buildyourdreamtoday.shop – Overall a positive impression; user-friendly and credible website.
findwhatyoulove.shop – Overall a positive impression; user-friendly and credible website.
startsomethinggreat.shop – The layout is clean and minimal, which makes browsing easy.
bigprintnewspapers.com – The site gives a trustworthy feel and looks credible.
theperfectgiftshop.com – The site loads quickly and works smoothly on mobile too.
exploreopportunitiesnow.shop – The site loads smoothly and the spacing makes it easy to read.
shopandsmilealways.shop – The homepage appears minimal yet effective—good user experience.
simplybestchoice.shop – Looks like a solid foundation for an online store; good start.
keepgrowingforward.shop – The branding is consistent and gives the store a polished identity.
mostbet kg https://www.mostbet12032.ru
geteventclipboard.com – Design and color choices are subtle yet effective—nice work.
shopandsmilealways.shop – The homepage appears minimal yet effective—good user experience.
shopandshineeveryday.shop – It might benefit from more detailed product information to build trust.
shopwithconfidence – This website really makes online purchases feel fast and safe.
uniquetrendstore – Great shopping experience, fast delivery and quality items every time.
joinourcreativeworld – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
shopthebesttoday – Highly recommend this shop, never disappointed with my purchases.
shopforhappiness – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
bestdealsforlife – Super smooth navigation, the website layout feels really clean and nice.
catherinewburton.com – Overall, a trustworthy and professional online presence for a therapist.
inspireeverydaylife – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
newseasoncollection – Easy to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for.
staycuriousalways – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
vsmphotography.com – Overall a strong web presence for a photography studio — well done.
smartchoiceoutlet – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
discovernewworld – Excellent customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
exploreopportunitiesnow.shop – The visuals are inviting and the interface feels smooth.
toddstarnesbooktour.com – It would be great to see more interactive content like video invites or live Q&A info.
createandgrow.shop – Good first impression; the site feels professional and approachable.
startsomethinggreat.shop – The visuals are inviting and the interface feels smooth.
findwhatyoulove.shop – Product categories are clear; helps me understand the offerings.
theperfectgiftshop.com – Looks like a solid foundation for an online store; good work.
Я восхищен тем, как автор умело объясняет сложные концепции. Он сумел сделать информацию доступной и интересной для широкой аудитории. Это действительно заслуживает похвалы!
Thank you for the encouragement
shopandsmilealways.shop – The homepage appears minimal yet effective—good user experience.
simplybestchoice.shop – I’d like to see more detailed reviews or user photos for added trust.
keepgrowingforward.shop – Product categories appear clear; helps me understand the offerings.
discoveryourmoment – Love the variety of products, always something new to explore.
shopandsmilealways.shop – The homepage appears minimal yet effective—good user experience.
shopandshineeveryday.shop – Navigation seems intuitive; I found the main sections easily.
thinkcreategrow – Feels like a community, not just a site, very welcoming tone.
getinspiredtoday – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
thebestplacetoshop – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
geteventclipboard.com – The visuals are clean, supporting the purpose without distraction.
trendyfindshub – Fantastic variety of products, always something new and exciting.
uniquetrendstore – Great shopping experience, fast delivery and quality items every time.
Найдите лучший товар на https://n-katalog.ru: подробные карточки, честные отзывы, рейтинги, фото, фильтры по параметрам и брендам. Сравнение цен, акции, кэшбэк-предложения и графики изменений. Примите уверенное решение и переходите к покупке в удобном магазине.
онлайн займы микрозаймы онлайн
Na stronie https://fotoredaktor.top znalazlem powierzchnie Czarnogory.
connectdiscovergrow – Feels like a community, not just a site, very welcoming tone.
dreamcreateinspire – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
shopthelatesttrend – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
mostbet link mostbet link
newseasoncollection – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
everydayvaluecorner – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
shopwithconfidence – I love the interface, navigating through products feels really smooth.
joinourcreativeworld – Excellent customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
smartchoiceoutlet – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
inspireeverydaylife – Fantastic variety of products, always something new and exciting.
yourtrustedonlinestore – Always a pleasure exploring the fresh content and ideas shared.
globalmarketplacehub – Highly recommend this shop, never disappointed with my purchases.
discoverendlessideas – A go-to place for creative ideas and insightful articles.
everytrendinone – The website is clean and intuitive; found what I was looking for in minutes.
dreamcreateinspire – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
brightfuturedeals – Love discovering fresh items here; keeps the space feeling updated and fun.
yourtrustedonlinestore – Great quality for the price; items exceeded my expectations easily.
shopthelatesttrend – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
learnshareconnect – Felt motivated after visiting; thanks for the uplifting messages and tips.
shopforhappiness – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
shopthebesttoday – Excellent customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
discovergreatthings – The website is clean and intuitive, found what I was looking for in minutes.
exploreamazingideas – Will definitely return for more purchases, very reliable online store.
findyourperfectdeal – Loved the downloadable resources section; useful for planning and idea generation.
yourjourneybegins – Great deals today, quality items and reliable shipping made me happy.
discovernewworld – Love the unique finds here, always something special to discover.
electmikemontes – Political campaign focused on community representation and positive change.
staycuriousalways – Excellent selection of products, always find what I need here.
swissreplica.pw – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
blinkiesdonutsca – I’ll definitely return soon, this place delivers on taste and freshness.
prostitutkimoskvyonline.info – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
brainsight-reeracoen – Very helpful team, offered targeted experts and saved us a lot of research time.
shopwithconfidence – Love how easy it is to find good deals here lately.
usaonlinecasinos.org – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
realherschel – I bookmarked this for later, will check back for new arrivals.
shemplymade – Handcrafted products with quality craftsmanship and unique designs.
globalmarketplacehub – Easy to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for.
discoverendlessideas – A go-to place for creative ideas and insightful articles.
everytrendinone – Love discovering fresh items here; keeps the space feeling updated and fun.
brightfuturedeals – Always a pleasure exploring the fresh content and ideas shared.
ohmydrifter – I found some posts referencing wellness and travel, which is appealing.
learnshareconnect – Great quality for the price; items exceeded my expectations easily.
tabitoshigoto – Looks like a reliable source to find unique stay-and-work destinations.
discovergreatthings – User-friendly website layout, found what I needed without any hassle.
trabas007hoki – I’d like to see more about what they offer—info seems light so far.
hanayaka-na-life – Bookmarking this for later, looks like they’ll add more good items.
joebobsaveschristmas – Smooth navigation, found everything quickly without feeling lost anywhere.
findyourperfectdeal – Great quality for the price; items exceeded my expectations easily.
hopeandlace – If you’re based outside Australia, check their service availability and travel logistics.
exploreamazingideas – Always find fresh, inspiring ideas here that brighten my day.
hawaiineiartcontest – The setting of the exhibition at the Wailoa Center gives it a nice official public-art feel. :contentReference[oaicite:4]index=4
yourjourneybegins – Found exactly what I needed here, very smooth checkout and service.
motivilovesmusic – The design looks clean but the content is minimal, which makes me unsure about its activity level.
wrestlingac – If you plan to use it as a reference, check the specific article date and author to ensure timeliness.
sega-live – I can’t confidently recommend it yet until more verification is found.
foruminvestmali – For investment-related content, I recommend checking whether the site provides transparent sponsorship, governance, and partner details.
hopprojects – The project space looks well-equipped and welcoming for experimental work.
envolavecning – If you’re considering using them, I’d check who’s behind the domain and look for reviews or trust signals.
brainsight-reeracoen – Found useful insights here that helped our team make better decisions.
blinkiesdonutsca – I’ll definitely return soon, this place delivers on taste and freshness.
shopwithconfidence – Everything loads fast and checkout is super smooth, great experience.
newthisdomainsssss – Unique name, design is simple and I sense interesting potential here.
Эта статья – настоящий кладезь информации! Я оцениваю ее полноту и разнообразие представленных фактов. Автор сделал тщательное исследование и предоставил нам ценный ресурс для изучения темы. Большое спасибо за такое ценное содержание!
that’s kind of you
beauty-optical-salon – Prices for the exclusive brand start around ¥14,000 to ¥23,000 (including standard lens). :contentReference[oaicite:7]index=7
https://mega-main.shop
rebeccacaridad-manzanita – Found related work by Rebecca Caridad via Etsy and blog, which adds some credibility. :contentReference[oaicite:1]index=1
tabitoshigoto – The concept of mixing travel and work feels inspiring and modern.
engagement-forum – The domain exists but appears to have minimal visible external references or traffic.
bloemhill – Overall a positive first impression, quite likely I’ll return and explore more.
Замовив на https://siviagmen.com ремонт пульта до телевізора.
После описания https://buybuyviamen.com сделали хрущевский холодильник своими руками.
На сайті mr-master.com.ua знайшла класні ідеї бюджетної веранди.
realherschel – Overall a positive experience so far, happy to have discovered them.
Experience unmatched elegance with Seattle luxury sedan service , offering premium ground transportation for discerning clients. Whether you need airport transfers, corporate travel, or special event transportation, our fleet of high-end sedans—including Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Cadillac—ensures comfort, style, and reliability.
Our professional chauffeurs provide punctual, discreet, and personalized service, prioritizing your safety and satisfaction. Enjoy complimentary amenities like Wi-Fi, bottled water, and climate control, tailored to your needs. Perfect for business executives, weddings, or a night out, Seattle luxury sedan service delivers a seamless, first-class experience.
Book effortlessly online or via phone for 24/7 availability, with competitive rates and transparent pricing. From Sea-Tac Airport to downtown Seattle or beyond, trust our expert team to elevate your journey with sophistication and precision. Choose Seattle luxury sedan service for a ride that exceeds expectations—where luxury meets convenience. – https://bdluxlimo.com/the-gold-standard-of-chauffeur-excellence-seattle-town-car-service/
Seattle car service offers premium limousine transportation for corporate events, weddings, airport transfers, and special occasions. With a fleet of luxury sedans, SUVs, stretch limousines, and sprinter vans, clients enjoy stylish, comfortable, and reliable rides across the Seattle area, including Sea-Tac Airport, downtown, Bellevue, and Kirkland.
Professional chauffeurs provide punctual, discreet, and courteous service, ensuring a seamless experience. Whether for business meetings, prom nights, or wine tours, Seattle car service delivers top-tier amenities like leather seating, climate control, and complimentary refreshments. Advanced booking options, 24/7 availability, and real-time tracking enhance convenience.
Ideal for executives, tourists, and locals, this Seattle car service prioritizes safety with well-maintained vehicles and licensed drivers. Competitive pricing, customizable packages, and group discounts make luxury travel accessible. For a sophisticated and stress-free journey in the Emerald City, trust Seattle car service for unmatched elegance and efficiency. – https://premierlimousineservice.net/2025/10/22/luxury-ways-to-explore-seattle-from-airport-transfers-to-cruise-adventures-car-service-seattle/
ohmydrifter – The content seems thoughtful and curated, might be great for inspiration.
macofficelovesyou – A better strategy might be to link to more recently active and high-trust domains.
hopeandlace – If you’re based outside Australia, check their service availability and travel logistics.
купить инженерную доску для пола https://injenernayadoska.ru/
Инженерная доска становится все более популярным выбором среди покупателей. Эта продукция прекрасно подходит для оформления современных интерьеров.
Во-первых, инженерная доска отличается высокой прочностью и долговечностью. Она устойчива к механическим повреждениям и истиранию.
Также стоит отметить, что установка инженерной доски проходит без затруднений. Укладку можно осуществить самостоятельно, без необходимости в специалистах.
И в заключение, следует подчеркнуть, что инженерная доска предлагает различные варианты отделки. Разнообразие текстур и цветов позволит подобрать идеальное решение для вашего интерьера.
XEvil 6.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha-2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, SolveMedia, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), RuCaptcha, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
motivilovesmusic – If you plan any transaction, use secure payment and record communications just in case.
Современный человек ежедневно сталкивается с ситуациями, которые требуют внутренней устойчивости, эмоционального баланса и понимания собственных реакций. На сайте mypsytest.ru собраны десятки профессиональных методик, разработанных специалистами в области психологии и психиатрии.
Популярные онлайн-тесты для понимания себя
Хотите проверить уровень своей сдержанности или эмоциональной устойчивости? Тогда вам подойдут такие тесты, как тест на эмоциональную устойчивость и тест на определение уровня гнева . Эти методики помогут понять, где проходят границы вашего терпения и как развить проактивное мышление.
Особое внимание стоит уделить тесту на проактивное мышление — инструменту, позволяющему определить, насколько вы способны управлять своей жизнью, а не плыть по течению.
Глубинная диагностика личности
проактивное мышление тест
Если вы хотите разобраться в себе глубже, стоит пройти тест на определение расстройства личности , тест на психопатию онлайн, тест на темную триаду , а также тест на садизм . Эти тесты позволяют выявить скрытые стороны личности, определить уровень эмпатии, моральных ценностей и степень эмоциональной холодности.
Для тех, кто замечает у себя усталость, апатию или эмоциональное выгорание, подойдут тест на нервное истощение, тест на невротика , а также тест на диссоциацию. Они помогут вовремя заметить сигналы организма и психики, требующие внимания.
Не менее популярны тесты, связанные с самоидентификацией и отношениями: тест на гетеросексуальность. Эти методики помогают лучше понять собственные эмоции и мотивацию в отношениях.
Для любителей необычного формата подойдут игровые тесты — тест какая ты фея сегодня. Они не только развлекают, но и тонко показывают особенности восприятия мира и уровень фантазии.
Тесты для двоих и пар
На MyPsyTest.ru вы найдёте уникальные тесты, созданные для анализа отношений: тест на дружбу для двоих. Эти опросы позволяют увидеть истинное состояние общения, понять, не стали ли вы заложником эмоциональной зависимости, и определить, насколько здоровыми являются ваши отношения.
Для мужчин представлен специализированный опрос IPSS для мужчин , который помогает оценить физическое и психологическое состояние организма.
Каждый тест на сайте MyPsyTest.ru создан с научным подходом, доступен онлайн и не требует регистрации.
Перейдите на mypsytest.ru и узнайте, какие черты характера формируют вашу личность . Самопознание начинается с одного клика.
тест на бисексуальность
На сайте zebraschool.com.ua удалось отремонтировать чемодан в Кропивницком — быстро и надёжно
trabas007hoki – Good start but site could benefit from trust signals like reviews or certifications.
envolavecning – The design seems clean yet incomplete, missing clear “About Us” or company info sections.
hanayaka-na-life – Bookmarking this for later, looks like they’ll add more good items.
bwaylocations – Prime location services with strategic placement and accessibility.
hawaiineiartcontest – Overall, this looks like a well-organized event with a clear mission and opportunity for exposure.
sega-live – No strong reviews or outside mentions found, so proceed cautiously before ordering.
wrestlingac – Since it covers prominent wrestling personalities like Kofi Kingston, that suggests it has access to credible sources. :contentReference[oaicite:2]index=2
joebobsaveschristmas – Love the color scheme and graphics, very distinctive and memorable.
hopprojects – Love that they focus on breaking down traditional genre boundaries, very refreshing.
beauty-optical-salon – The store opened in 2017 in Tokyo for women’s eyewear with bespoke service. :contentReference[oaicite:1]index=1
foruminvestmali – The “Invest in Mali” event associated with the domain helps give it context and legitimacy. :contentReference[oaicite:2]index=2
rebeccacaridad-manzanita – The related Etsy presence is strong, but that doesn’t automatically guarantee the separate domain is fully reliable.
madmadedesigns – For a niche audience looking for something “crafted” and unique, it’s a good candidate.
dearsparrows – I appreciate the variety of topics covered, from racing to casino trends and more.
macofficelovesyou – I couldn’t find current content or recent updates on this domain.
brightnightpdx – The domain name is intuitive and memorable, which is a good sign for branding.
pepplish – The social media presence is modest but existent, so at least there’s a community aspect.
nomnomnomfordogs – Their local Columbus OH presence adds trust—having a physical shop matters.
madmadedesigns – If you’re looking for custom design or art-driven work, this could be a fitting option.
flourandoak – If you’re in the area and craving something sweet, this could be a charming option.
shopwithconfidence – Good candidate for a backlink, but I’d pair it with more established sites for balance.
globaltrendmarket – The name has potential and suggests a global marketplace vibe.
connectdiscovergrow – Overall, a positive first impression—just need to dig a little deeper to understand the full value.
staycuriousalways – Maybe a bit early stage, but the concept is solid — I’ll keep an eye on it.
keepgrowingforward – Loving the motivational feel here—lots of fresh ideas that spark action.
exploreopportunitiesnow – Interesting domain name, feels like a space for discovery and growth.
bestdealsforlife – I recommend verifying domain age and ownership details for more trust-worthiness.
createandgrow – I’d recommend exploring the site further to verify the content’s freshness and legitimacy.
theperfectgiftshop – The domain name is appealing and suggests a curated gift-shop vibe right away.
turnerhallrestaurant – Exceptional dining experience with quality cuisine and atmosphere.
buildyourdreamtoday – The concept of “building your dream today” is appealing, but the execution needs more transparency.
Wow, marvelous weblog format! How lengthy have you ever been running a blog for? you made running a blog glance easy. The full glance of your website is excellent, let alone the content material!
Thank you very much for the encouragement.
I started this blog almost six months ago now.
I am doing my best to make economic concepts and topics easier to understand.
uniquetrendstore – If you are buying from or linking to the site, make sure to review shipping, return policy, and product quality carefully.
simplybestchoice – For backlinking purposes, I’d use this as one of many, but pair with more established domains for balance.
changetheworld – The concept of “changing the world” is appealing, but the execution needs more transparency.
simplybestchoice – Overall: a decent concept, but I’d proceed cautiously until more verification is available.
экстренное вытрезвление http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-25.ru .
dreamcreateinspire – The concept “Dream-Create-Inspire” resonates nicely for personal growth or creative content, which is a plus.
thinkcreategrow – I recommend checking for an “About Us” page or contact information to understand the site’s legitimacy.
GlobalMarketplaceHub – Website layout is clean, navigation feels simple and intuitive overall.
ExploreAmazingIdeas – Highly recommend this platform, great for discovering innovative ideas easily today.
InspireEverydayLife – Always uplifting content, website motivates me to stay productive daily.
discoverendlessideas – Without visible trust signals or user reviews, it’s hard to gauge the site’s reliability.
globaltrendmarket – The name has potential and suggests a global marketplace vibe.
dearsparrows – The blog posts are surprisingly in-depth, good for someone wanting niche insights.
pepplish – The product variety looks good—combining fruits, herbs and heat for a unique twist.
brightnightpdx – A suggestion: check domain age and whether the SSL certificate is up to date to ensure it’s safe.
nomnomnomfordogs – Packaging and product descriptions look detailed which suggests care in making the treats.
flourandoak – Overall, a positive first impression—would be happy to drop by and sample what they offer.
shopwithconfidence – If you’re considering using the site, check for customer reviews and payment security before purchasing.
connectdiscovergrow – Good potential if you’re looking to expand your professional network or skills.
YourTrustedOnlineStore – Highly recommend this platform, reliable and offers genuinely useful products online.
keepgrowingforward – Would like to see a bit more about who’s behind the site for extra trust.
LearnSomethingNew – Lessons are clear, easy to follow, and very well organized.
DiscoverGreatThings – Customer support answered quickly, helped me solve my issue efficiently.
staycuriousalways – Love the domain’s vibe — seems like a place you’d go to expand your mind and try something new.
exploreopportunitiesnow – If you’re going to cite or link to it, I’d still verify its trustworthiness (owner, activity, reviews).
theperfectgiftshop – If you’re shopping for something special, this could be a good place to browse—just check details.
bestdealsforlife – The domain name sounds good, but I couldn’t verify much about who’s behind the site.
createandgrow – Would be helpful to see more about exactly what services or content they offer.
96x11n.pw – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
titi.pw – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
libracryptocurrency.pw – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
worldcomputerexpo.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
BrightFutureDeals – Products arrived fast, very happy with quality and service today.
discovernewworld – The domain name is intriguing and suggests a platform for exploration or discovery.
buildyourdreamtoday – I recommend checking for an “About Us” page or contact information to understand the site’s legitimacy.
ShopForHappiness – I keep returning here, always find interesting products quickly and easily.
ShopTheBestToday – Website is user-friendly, navigation feels smooth and intuitive throughout the site.
FindYourPerfectDeal – Deals are updated frequently, site is reliable and trustworthy overall.
TheBestPlaceToShop – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
ShopForHappiness – Great deals here, always find exactly what I need quickly.
TrendyFindsHub – Deals are updated frequently, site is reliable and trustworthy overall.
ShopAndSmileAlways – Always something new to discover, makes online shopping fun and exciting.
changeyourworld – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
startsomethinggreat – I keep returning here, always find interesting products quickly and easily.
learnshareconnect – Supportive community members who actively contribute to discussions and learning.
findwhatyoulove – Customer support was helpful, answered all my questions promptly and politely.
ShopTheLatestTrend – Signing up was quick, notifications keep me updated about new arrivals.
makelifebetter – Great selection of items, site makes finding deals really easy.
everytrendinone – I keep returning here, always find interesting products quickly and easily.
newseasoncollection – Easy navigation, site layout makes shopping smooth and enjoyable overall.
ExploreAmazingIdeas – Really enjoy checking here daily, always something new catches my attention.
uniquetrendstore – Overall, the concept is promising—worth keeping an eye on, but proceed with caution until more validation is found.
everydayvaluecorner – Easy navigation, site layout makes shopping smooth and enjoyable overall.
yourjourneybegins – I keep returning here, always find interesting products quickly and easily.
DiscoverYourMoment – Really user-friendly, I can quickly find everything I need online.
Читателям предоставляется возможность самостоятельно рассмотреть и проанализировать информацию.
Thank you
InspireEverydayLife – Navigation is smooth, layout is clean and visually very appealing overall.
ShopTheBestToday – Really enjoy shopping here, site layout makes browsing simple and fast.
changetheworld – The domain has potential, but more content and clarity are needed to assess its value.
simplybestchoice – The name is very generic and could be harder to stand out or distinguish in search / trust metrics.
GlobalMarketplaceHub – Prices are competitive, quality of items exceeded my expectations completely.
thinkcreategrow – I recommend checking for an “About Us” page or contact information to understand the site’s legitimacy.
makelifebetter – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
FindYourPerfectDeal – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
changeyourworld – Fast shipping, items arrived in perfect condition as expected online.
TheBestPlaceToShop – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
startsomethinggreat – Customer support was helpful, answered all my questions promptly and politely.
ShopAndSmileAlways – Fast shipping, items arrived in perfect condition as expected online.
TrendyFindsHub – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
learnshareconnect – Highly recommend for anyone seeking to expand knowledge and network.
discoverendlessideas – Without visible trust signals or user reviews, it’s hard to gauge the site’s reliability.
findwhatyoulove – Great selection of items, site makes finding deals really easy.
everytrendinone – Highly recommend this platform, shopping experience is smooth and enjoyable.
everydayvaluecorner – Highly recommend this platform, shopping experience is smooth and enjoyable.
newseasoncollection – Highly recommend this platform, shopping experience is smooth and enjoyable.
yourjourneybegins – Always something new to discover, makes online shopping fun and exciting.
dreamcreateinspire – Overall: a positive first impression but perform due diligence if you’re linking or investing.
YourTrustedOnlineStore – Shopping here is smooth, website loads fast and works perfectly overall.
ShopTheLatestTrend – Always something new to discover, site keeps me coming back regularly.
BuildStrongRelationship – I keep coming back because the tools actually feel practical and meaningful.
BusinessConnectWorld – Highly recommend this service if you’re looking to expand business connections.
ultimateprofitplan – I appreciate how every post feels focused on long-term financial growth.
ProfessionalGrowthHub – Highly recommend to colleagues; this site really adds value to careers.
Раніше думала, що чудово знаю як готувати, але в останні місяці мої страви стали одноманітними і втратили різноманітність. Дівчина запропонувала мені переглянути свіжі рецепти, але я не знала, як підібрати. Випадково знайшла цей каталог і… це було як відкриття нового світу! Виявилося, що є цілий океан сайтів з неймовірними рецептами, про які я навіть уяви не мала. Найбільше сподобались розділи з авторськими стравами та рецептами етнічних страв. За цей час я освоїла страву французької кухні, японської та а також марокканської кухні! Моя чоловік і діти безмежно щасливі, а я відчуваю себе впевненим гурманом. Я навіть почала вести особистий журнал, де записую всі нові рецепти, які вдалося приготувати
Сайт blogreceptov.icu
dailyprofitupdate – The daily summaries here really help me keep my strategy consistent.
smartbuytoday – Feels like a one-stop place for everyday items at fair prices.
classytrendstore – Everything feels thoughtfully curated, makes it easy to shop stylishly.
smarttradingmentor – I like that the tips are realistic and grounded in actual experience.
brightmarketplace – Delivery was smooth, packaging looked neat, and products matched perfectly.
ultimateprofitplan – The guides are easy to follow, even for beginners just starting out.
bestdealcorner – Found a few amazing bargains here, definitely worth checking often.
bestdealcorner – I’ve ordered multiple times now, and the quality always stays consistent.
MarketTrendAlerts – Highly recommend this platform for anyone tracking market movements closely.
shoplocaltrend – Love the idea behind this site, supporting local finds feels so good.
trendandstyle – Love how chic everything looks, totally fits my personal fashion taste.
freshstylemarket – Everything feels carefully selected, love how the site keeps it stylish.
purebeautyoutlet – Love how clean and soft the design feels, really inviting store.
protraderacademy – Great mix of guides and tips, really helps beginners gain confidence quickly.
visionpartnersclub – Helpful insights for entrepreneurs, easy to read and apply right away.
discovergreatvalue – Perfect place for budget shoppers, quality stays great despite low prices.
freshfashionfinds – This site is becoming my go-to for seasonal wardrobe refreshes.
nextleveltrading – Love the clean interface here, perfect for checking signals quickly anytime.
uniquefashionboutique – The dresses I got are beautiful, fabric feels soft and premium quality.
yourtradingmentor – Feels like a true mentor experience, not just another trading website.
futuregrowthteam – Every section feels carefully written, focused on success through unity.
classyhomegoods – I love browsing this shop, it gives me serious home decor inspiration.
modernvaluecorner – I keep coming back for more deals, everything feels reliable here.
connectforprogress – The content here really motivates me to keep improving every single day.
tradingmasterclass – Perfect place to sharpen trading skills without getting lost in theory.
trendinggiftcorner – Every time I visit, I find something new and thoughtful to buy.
smarttradingmentor – One of the few places that truly helps traders grow smarter daily.
stylemebetter – I like how they update collections often, always something new to see.
trendandstyle – Love how chic everything looks, totally fits my personal fashion taste.
smartbuytoday – The checkout process was smooth, and my order arrived earlier than expected.
fastgrowthsignal – Love how easy it is to find trending products here daily.
classytrendstore – Great mix of modern and timeless pieces, perfect for daily wear.
shoplocaltrend – Perfect spot to shop local in style, everything feels genuine and fresh.
trendhunterplace – Feels like a treasure hunt every visit, love discovering new stuff.
freshstylemarket – My new go-to for everyday fashion finds, always reliable and fun.
bestdealcorner – Feels like a hidden gem online, always end up saving money here.
bestdealcorner – Feels like a real treasure spot for online shoppers, highly recommend it.
brightmarketplace – Great mix of categories here, there’s literally something for everyone.
visionpartnersclub – This site really pushes positivity and shared vision, love the concept.
discovergreatvalue – I like checking this site often, new deals pop up constantly.
freshfashionfinds – Stylish, smooth, and simple shopping process, totally recommend checking it out.
classyhomegoods – Smooth shopping experience, from browsing to checkout everything worked perfectly.
uniquefashionboutique – I like how everything feels curated, not just random fashion items.
futuregrowthteam – Great resource for anyone looking to build stronger business partnerships.
dailyprofitupdate – Great place to stay informed daily, posts feel genuine and practical.
strongpartnershipnetwork – I like the focus on teamwork and genuine growth through partnerships.
BuildStrongRelationship – Wonderful resource, I’m learning new ways to strengthen meaningful bonds.
protraderacademy – Love how clearly the lessons are explained, makes trading way easier.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Great concept overall, encouraging businesses to work together creatively and effectively.
yourtradingmentor – Great advice, easy to follow even for people new to trading.
BusinessConnectWorld – Found valuable networking tools, the platform simplifies professional outreach effectively.
worldcityexpo.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
connectforprogress – Nice blend of motivation and action steps, love the balance shown here.
purebeautyoutlet – I trust this site now after ordering twice, quality stayed consistent.
nextleveltrading – Very solid resource for keeping up with daily market movement info.
MarketTrendAlerts – Recommendations are thoughtful and actionable, adds value to decision making.
tradingmasterclass – Great balance of education and motivation, really keeps me improving daily.
trendinggiftcorner – The wrapping options were adorable, adds that special touch to every order.
modernvaluecorner – Great range of choices and the descriptions actually match the products.
Register now and receive a welcome package:
up to 95 free spins and as much as 2100USD bonus funds!
Huge range of games, instant winnings, and a trusted casino experience await at
https://prosportlab.shop/b45o823
shopwithsmile – The name fits perfectly, I honestly smiled while browsing these products.
everydaytrendshop – Definitely becoming my favorite spot for everyday fashion inspiration online.
Регистрируйся сейчас и получай приветственный пакет — до 210 фриспинов и до 1600€ бонуса!
Лучшие игры, быстрые выплаты и честный сервис на
https://Cnewbestnews.shop/bgk25sh
teamworkinnovation – I like how they connect innovation with leadership and real business strategy.
shopandshine – I like how smooth the shopping experience is, from browsing to checkout.
shopwithsmile – Love the cheerful vibe here, makes online shopping feel light and fun.
globalchoicehub – The site feels professional and easy to use, really smooth shopping process.
brahmanshome – Content is fresh, practical, and engaging for anyone working at home.
forexstrategyguide – I like how they break down complex forex topics into easy, digestible lessons.
yourtradingmentor – The tone feels supportive and professional, perfect balance for learning.
simplelivinghub – Love the focus on simplicity and mindfulness in every product choice.
teamworksuccesspath – The articles feel inspiring and practical, great mix of ideas and motivation.
successnetworkgroup – Perfect hub for entrepreneurs and teams working toward collective success goals.
learnandtrade – I’ve learned a lot about risk management just from a few sessions here.
globalmarketinsight – Truly a must-visit for anyone serious about staying ah
successfultradersclub – I like how the lessons cover both mindset and technical skills effectively.
uniquedecorstore – My order arrived quickly and was packaged perfectly, very impressed.
markettrendalerts – Definitely a reliable site for keeping track of market trends daily.
ferdykorpwp.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
There’s something special about watching a expert hibachi chef transform raw ingredients into a culinary masterpiece right before your eyes. The searing sounds, the theatrical flames, the stunning knife tricks, and the delicious aromas merge to create an memorable dining experience. But what if you could transport this excitement directly to your residence, office, or special event venue?
Welcome to the world of hibachi catering, where professional teppanyaki-style cooking meets the convenience of mobile service. Whether you’re organizing an cozy dinner party or a massive corporate gathering, mobile hibachi catering offers a special blend of entertainment and exceptional cuisine that will leave your guests remembering your event for years to come.
## What Makes Hibachi Catering Special?
Compared to traditional catering services where food arrives already made and is simply served, hibachi catering turns your event into an participatory dining experience. A skilled hibachi chef arrives with all necessary equipment, including mobile flat-top grills, high-quality ingredients, and professional-grade cooking tools. Your guests don’t just consume delicious food—they are part of a real-time culinary show showcasing knife tricks, flame demonstrations, and the chef’s charismatic personality.
This traditional Japanese teppanyaki style of cooking emphasizes both culinary skill and theatrical presentation. From the famous volcano onion display that bursts with flames to the accurate knife work that amazes the crowd, every moment is created to entertain. The participatory hibachi dining experience inspires guests to connect with the chef, creating a social atmosphere that facilitates connection at any gathering.
## High-End Hibachi Catering for Sophisticated Clients
For those wanting an premium experience, premium hibachi catering services deliver white-glove treatment that surpasses standard party catering. Elite hibachi service providers thoughtfully curate every detail, from selecting the finest ingredients to guaranteeing impeccable presentation and service standards.
An premium hibachi chef delivers not only technical expertise but also refined culinary artistry. These professionals often have extensive training in Japanese cuisine, years of performance experience, and the ability to tailor menus for sophisticated palates. Luxury Japanese catering might include top-quality proteins like A5 wagyu beef, fresh lobster tail, Chilean sea bass, or high-quality scallops, all cooked with theatrical flair.
Executive hibachi catering caters to clients who demand nothing less than perfection. This might include private hibachi experiences at private estates, celebrity chef hibachi demonstrations, or exclusive dining events where discretion and excellent service are paramount. Many luxury providers offer personalized consultations to develop custom menus that match your preferences and meet dietary restrictions without compromising on the wow factor.
## Corporate Hibachi Catering: Delighting Clients and Inspiring Teams
Smart businesses are discovering that business hibachi catering provides something traditional business catering cannot provide: a unforgettable experience that builds relationships and improves morale. Whether you’re hosting a client entertainment hibachi event or arranging team-bonding hibachi activities, the participatory nature of teppanyaki cooking creates organic opportunities for conversation and connection.
Company party hibachi services convert standard break rooms or outdoor spaces into dynamic dining venues. The entertainment aspect maintains energy high and allows employees unwind and bond outside their usual work roles. Business event hibachi catering works particularly well for milestone celebrations, where the dramatic presentation adds an extra layer of excitement to the occasion.
For professional settings, corporate dinner hibachi services can find the perfect balance between impressive hospitality and comfortable dining. Company retreat hibachi experiences offer a refreshing break from conference rooms and PowerPoint presentations, giving team members a chance to bond over shared culinary adventure. Team appreciation hibachi events communicate a powerful message that leadership values their team’s contributions and wants to offer something genuinely special.
The booking process for corporate events is usually streamlined through specialized account managers who understand business timelines and budgeting requirements. Many experienced hibachi catering companies offer business hibachi event planning services that handle logistics, dietary accommodations, and timing to guarantee seamless integration with your agenda.
## Honoring Life’s Special Moments with Hibachi
When it comes to personal celebrations, few catering options create memories as well as hibachi. The combination of outstanding food and live entertainment makes it excellent for occasions where you want to do something genuinely memorable.
Wedding reception hibachi services are growing increasingly popular for couples looking for alternatives to traditional banquet fare. The interactive nature keeps guests engaged during the meal service, and the chef’s performance is part of the celebration itself. In the same way, pre-wedding dinner hibachi creates a relaxed, festive atmosphere excellent for bringing together families from both sides before the big day.
For pre-wedding celebrations, bridal shower hibachi parties present a sophisticated yet fun alternative to standard shower formats. The communal dining experience encourages conversation and creates natural bonding moments among guests who may not know each other well. Engagement party hibachi delivers that same energy to the announcement of your upcoming nuptials.
Special birthday hibachi celebrations provide the perfect blend of elegance and excitement for major birthdays. Whether it’s a sweet sixteen hibachi party including theatrical flames and tricks for teen guests, a elegant 50th birthday celebration, or anything in between, the flexible nature of hibachi catering makes certain the experience suits the guest of honor’s personality. Anniversary celebration hibachi events bring back the romance of a date night at an upscale Japanese steakhouse, but with the privacy of your own home.
Milestone celebrations like quinceañera hibachi parties beautifully blend cultural traditions with modern entertainment, creating a special fusion that honors heritage while incorporating contemporary celebration styles.
## Fusion Cuisine and Authentic Japanese Hibachi
One of the beauties of modern hibachi catering is the ability to tailor the menu to suit diverse tastes and cultural preferences. While authentic traditional hibachi preparation methods remain the foundation, many chefs have created fusion hibachi menus that include flavors from across the continent.
Traditional Japanese hibachi follows traditional teppanyaki techniques, emphasizing the natural flavors of premium ingredients enhanced with subtle but carefully balanced seasonings. The emphasis is on technique, timing, and respect for the ingredients themselves. Master chefs trained in this tradition display the accuracy and artistry that have made Japanese cuisine world-renowned.
Westernized hibachi party services often combine these traditional techniques with flavors familiar to Western palates, creating accessible yet exciting dishes. This might include unique sauce options, contemporary fried rice, or appetizers that utilize multiple Asian culinary traditions. For multi-ethnic hibachi services, talented chefs can create menus that honor multiple traditions, perhaps incorporating Korean BBQ flavors, Thai-inspired sauces, or Chinese cooking techniques alongside classic Japanese preparation.
## Technology Meets Tradition: Booking Your Hibachi Experience
The digital age has changed how we book entertainment and catering services, and hibachi is no exception. Modern hibachi delivery apps and platforms have made it simpler than ever to hire hibachi chefs online with just a few taps on your smartphone.
Mobile hibachi apps enable you explore chef profiles, check menus, check reviews, check availability, and secure instant hibachi booking for your event. Many platforms feature transparent pricing, real-time availability calendars, and secure payment processing, removing the back-and-forth of traditional booking methods.
For those planning ahead, these platforms make it easy to compare packages, review customer reviews, and find the ideal fit for your event. But they’re just as valuable for last minute hibachi party needs—many experienced chefs keep flexible schedules and can accommodate immediate hibachi bookings requests, especially for smaller gatherings.
The best booking platforms also provide detailed information about what’s included in each package, making it easier to know catering costs upfront without surprises. Some even feature bulk pricing hibachi options for larger events or let you to customize packages to fit your unique needs and budget.
## Understanding Hibachi Party Pricing
One of the most common questions people have is about hibachi service rates. The great news is that hibachi catering has become increasingly accessible, with options spanning from budget-friendly options for limited budgets to premium experiences for those seeking sophistication.
Various factors influence hibachi catering cost:
**Guest Count**: Most services price per person, with standard rates varying from $30-40 per person for standard packages to $80-150 per person for luxury experiences featuring premium proteins and complete service.
**Menu Selection**: Standard packages typically include classic proteins like chicken, steak, and shrimp along with vegetables and fried rice. High-end packages might feature filet mignon, lobster tail, or premium seafood options.
**Service Duration**: Standard service typically runs 2-3 hours, but extended events may incur additional fees.
**Travel Distance**: Chefs traveling considerable distances may charge travel fees, though many remove these for events within their service area.
**Equipment Needs**: Most chefs supply their own portable grills, but events requiring multiple stations or special setups may cost more.
**Day and Time**: Weekend evenings during peak season (spring and summer) often require premium rates, while weekday events or off-season bookings may provide better value.
For those seeking cheap hibachi catering without sacrificing quality, explore these strategies: Choose weekday dates when possible, opt for lunch service rather than dinner, select a more economical protein lineup while still including variety, or book during off-peak months. Many providers feature promotional packages or promotional packages during slower periods.
Affordable hibachi event planning doesn’t mean compromising on less entertainment—many affordable options still include the full theatrical experience with tricks and audience interaction. The difference typically lies in the ingredients rather than the showmanship.
Bundled services often deliver the best value, combining chef service, equipment, ingredients, serving staff, and sometimes even setup and cleanup. Look for providers offering group discount hibachi rates for larger gatherings, as per-person costs often decrease significantly with higher guest counts.
## Finding the Top Hibachi Service
With the increasing popularity of in-home hibachi experiences, more providers have entered the market. So how do you identify the top hibachi service for your needs?
Begin by finding five-star hibachi services with verified reviews from real customers. Platforms that compile customer feedback make it simple to find top-rated hibachi providers with solid track records of excellence. Pay attention not just to star ratings but to specific comments about punctuality, professionalism, food quality, and entertainment value.
Expert hibachi services companies usually carry proper licensing, insurance, and food handling certifications. Don’t be afraid to ask about these credentials—experienced hibachi chef providers anticipate these questions and welcome the opportunity to show their professionalism. Professional hibachi providers who have completed formal culinary training or specialized teppanyaki programs provide an extra level of expertise to your event.
Premium hibachi providers distinguish themselves through attention to detail that exceeds basic cooking. This might include elegant table settings, professional serving staff, beautifully presented ingredients, custom menu cards, and impeccable cleanup service. They predict needs before you express them and manage unexpected situations with grace and flexibility.
When reviewing potential chefs, consider asking for videos of their performances. The hibachi show at home should be as entertaining as it is delicious. An engaging hibachi performer knows how to gauge the audience, adapt their energy level to match your event’s mood, and make every guest feel included. Their hibachi performance should feature stunning theatrical demonstrations that amaze without overwhelming, showcasing mastery of traditional techniques like fire displays displays, accurate knife tricks hibachi demonstrations, the iconic onion volcano presentation, and even entertaining elements like the sake spray routine where appropriate for adult audiences.
## Seasonal and Holiday Hibachi Celebrations
Hibachi catering adapts beautifully for seasonal celebrations throughout the year. Each season and holiday brings unique opportunities to create memorable gatherings centered around this engaging dining experience.
Warm-weather hibachi events take full advantage of outdoor spaces when weather permits. Al fresco hibachi turns your patio into an open-air Japanese steakhouse, with the chef’s flames creating spectacular visual effects against the evening sky. A backyard BBQ hibachi fusion merges American and Japanese grilling traditions for a truly unique summer celebration. Swimming party hibachi services add culinary excitement to swimsuit season gatherings, while July 4th hibachi events present a fresh alternative to standard Independence Day fare.
As the weather cools, holiday celebrations present excellent opportunities for indoor hibachi experiences. Holiday hibachi services create warm, festive gatherings where the live cooking adds both entertainment and cozy warmth. New Year hibachi delivers theatrical energy to ring in the new year, with the fire displays mirroring celebratory fireworks. Even Thanksgiving hibachi adaptations are possible, with skilled chefs cooking turkey, stuffing components, and seasonal vegetables using teppanyaki techniques.
Festive business parties events have become especially popular, providing companies a fresh alternative to tired holiday party formats. The interactive nature helps break down workplace hierarchies and creates authentic connections among colleagues. Seasonal hibachi services handle the entertainment, allowing hosts to actually enjoy their own celebrations rather than continually tending to logistics.
Spring celebrations present their own opportunities: commencement party services mark academic achievements with sophistication and fun that suit both young graduates and their families. Maternal celebration hibachi brunches or dinners present a special way to recognize maternal figures with an experience rather than material gifts. Easter hibachi brunch services offer an sophisticated alternative to traditional Easter meals, while springtime hibachi events embrace the new season with fresh ingredients and outdoor entertaining possibilities.
## Essential Guidance for Booking Your Event
If you’re wondering how to hire a hibachi chef, the process is usually straightforward but benefits from advance planning. Begin by determining your guest count, preferred date, and rough budget. Most services require accurate headcounts since ingredients are ordered specifically for your event.
When you arrange birthday hibachi celebrations or other special occasions, share details about the guest of honor’s preferences, dietary restrictions, and any special requests. The best chefs include these personal touches into both their menu and performance.
For those planning to book nearby hibachi services, initiate your search at least 2-4 weeks before your event date, especially during busy seasons. Popular weekend dates during spring and summer often book months in advance. However, if you need quick hibachi booking solutions, don’t despair—many chefs have some schedule flexibility for spontaneous celebrations.
Understanding the logistics is essential: most hibachi chefs need access to electrical outlets for their equipment, proper ventilation if cooking indoors, and adequate space around the cooking station for both performance and safety. When planning a garden hibachi event, ensure you have a solid, level surface for the grill, sufficient lighting for evening events, and weather contingency plans.
https://rockchat.com/members/novelbottom8/activity/211686/
https://www.adpost4u.com/user/profile/3999259
https://www.google.pl/url?q=https://wikimapia.org/external_link?url=https://www.lovehibachi.com/
https://to-portal.com/beggarkaren39
http://bbs.hy2001.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=716647
For larger gatherings, consider how many people can comfortably watch a single chef. A hibachi chef for 30 people might call for two cooking stations to guarantee everyone enjoys the full experience without feeling too removed from the action. Expert providers can counsel on the optimal setup for your guest count.
Weekend event scheduling tends to get reserved quickly, so securing your date early is wise, especially for holiday weekends or during peak wedding season. However, weekday availability is often more flexible and may include better rates.
## What to Expect on Event Day
Understanding what happens during the actual service allows you prepare and makes sure everything runs smoothly. Most professional hibachi catering services follow a similar timeline:
**Setup (45-60 minutes before start time)**: The chef and any assistants come to set up equipment, arrange ingredients, and ready the cooking station. They’ll usually do a brief walk-through of the space to ensure everything is in place.
**Welcome and Introduction (5-10 minutes)**: As guests gather, the chef presents themselves and explains what diners can expect. This establishes the tone for the interactive experience ahead.
**Appetizer Course (15-20 minutes)**: Many services begin with appetizers, which might include soup, salad, or small bites made tableside or brought ready to serve.
**The Main Event (45-75 minutes)**: This is where the magic happens. The chef prepares vegetables, fried rice, and proteins with theatrical flair. Timing is orchestrated so everything finishes at the optimal temperature, with different proteins completed in sequence based on cooking times.
**Engagement and Entertainment Throughout**: The experienced chef incorporates tricks, jokes, and audience interaction throughout the cooking process, sustaining energy and engagement. They’re skilled at including everyone, from shy children to enthusiastic adults.
**Serving and Dining (30-45 minutes)**: As items finish cooking, they’re plated and served. The chef coordinates everything so guests get hot, fresh food throughout the meal.
**Cleanup (30-45 minutes)**: After the meal, the chef and team handle all cleanup, leaving your space as they found it. Premium services include thorough cleanup of the cooking area and removal of all trash and equipment.
The entire experience usually runs 2.5-3 hours from setup to complete departure, though the actual guest interaction portion is normally 60-90 minutes of entertaining dining.
## Making the Most of Your Hibachi Experience
To guarantee your event is everything you hope for, keep these tips in mind:
**Express clearly**: Provide all relevant details about your venue, guest count, dietary restrictions, and any special requests well in advance. The more information your chef has, the better they can personalize the experience.
**Prepare your space**: Make sure the cooking area is accessible, accessible to power sources if needed, and has adequate ventilation. For outdoor events, have a weather backup plan.
**Schedule timing**: Work with your chef to establish the optimal start time based on your event schedule. Include setup time before guests arrive.
**Brief your guests**: Let them know what to expect so they can place themselves to enjoy the show. Promote participation but respect that some guests prefer to observe.
**Document the experience**: The theatrical elements make for fantastic photos and videos. Choose someone to capture these moments, or ask if your catering service includes this as an add-on.
**Consider add-ons**: Many services offer enhancements like additional protein options, luxury sake pairings, specialty cocktails, or extended service time. These can elevate the experience for special occasions.
**Tip appropriately**: While not always expected, gratuity for exceptional service is appreciated. Standard tipping for catering services generally ranges from 15-20% of the service fee.
## The Future of At-Home Hibachi
The private hibachi trend shows no signs of slowing down. As more people find the unique combination of convenience, entertainment, and outstanding cuisine that hibachi catering provides, the industry continues to evolve and improve.
Technology integration continues to streamline booking and customization. Advanced platforms now provide virtual consultations, 3D venue planning tools, and AI-assisted menu customization. Some progressive services even include live streaming options so far-away loved ones can participate in special celebrations virtually.
Menu innovation matches dietary trends and preferences. More chefs now offer plant-based proteins, sustainable seafood options, and fusion creations that respect traditional techniques while adopting modern flavors. Allergen awareness and accommodation have become expected rather than exceptional.
Maybe most importantly, the professionalization of the industry means better standards across the board. Competition encourages quality improvements, and customers receive more consistent excellence whether they’re booking a budget-friendly weeknight dinner or a premium celebration.
## Conclusion: Transform Your Next Event with Hibachi Catering
Whether you’re planning business hibachi entertainment entertainment, celebrating a milestone with friends and family, or simply want to try something remarkable for your next gathering, hibachi catering offers a compelling answer to the question “What can I do to make this event truly memorable?”
The combination of outstanding cuisine, live entertainment, and participatory dining creates an experience that surpasses ordinary catering. Your guests won’t just participate in another event—they’ll be part of a culinary adventure that involves all their senses and creates authentic connections.
From small anniversary dinners for two to massive corporate galas for hundreds, from casual backyard parties to upscale estate celebrations, hibachi catering adapts to meet your needs without losing its essential magic. The spectacular flames, amazing knife work, and engaging chef personalities guarantee that whether you’re serving ten people or one hundred, everyone departs with the same happy smile and lasting memories.
In a world where experiences more and more matter more than things, providing your guests the gift of an genuine hibachi performance at your event is an investment in memories that will last far longer than any physical gift. The photos and stories from your hibachi-catered event will come up for years to come, cementing your gathering’s place in everyone’s collection of favorite memories.
So whether you’re set to book now or just starting to explore possibilities, know that expert hibachi catering services stand ready to convert your vision into reality. The combination of ancient Japanese culinary traditions, modern convenience, and pure entertainment value makes hibachi catering not just a meal, but an experience that exemplifies extraordinary hospitality.
Your next remarkable event is just a booking away. The flames await.
https://www.tumblr.com/seerup76rosales/798458963636174848/exclusive-hibachi-chef-at-home-love-hibachis
https://brandon-duncan-2.technetbloggers.de/exclusive-hibachi-chef-at-home-love-hibachis-comprehensive-guide-to-exclusive-teppanyaki-experiencesby-rumla-7c-love-hibachi
https://mcclurekjer74.livejournal.com/profile
https://www.openlearning.com/u/schmidtdeleon-sht2rw/blog/TopTierHibachiChefAtHomeLoveHibachiSEssentialGuideToCustomTeppanyakiExperiencesbyRumlaLoveHibachi
https://blogfreely.net/vanant7/top-tier-hibachi-chef-at-home-love-hibachis-definitive-guide-to-private
worldsoftwareexpo.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
acte-experts.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
SEO помогает сделать сайт более заметным и удобным для посетителей. Работа с контентом, структурой и техническими аспектами ресурса позволяет улучшить позиции и удерживать их. Регулярная аналитика и корректировка стратегии помогают поддерживать стабильный рост. В результате сайт привлекает больше клиентов и укрепляет доверие к компании. Такой подход обеспечивает долгосрочный эффект и развитие бизнеса. Подробнее по ссылке: https://wikigranny.com/wiki/index.php/Продвижение_Сайтов_Для_Увеличения_Прибыли
jonathanfinngamino – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
motocitee – Found exactly what I needed, instructions were clear and concise.
adawebcreative – A visually appealing site that maintains functionality without compromise.
paws21airbrushstudio – Absolutely love their custom designs, truly one-of-a-kind creations.
raspinakala – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
бк melbet бк melbet .
ibdesignstreet – Site layout is clean, making it very easy to follow instructions.
utti-dolci – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
kivurc – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
Are you searching for good working activator for MS Office? On this site you can download the latest version of it: download office activator
pgmbconsultancy – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
abbysauce – Helpful ideas posted here, I’ll definitely share with all friends.
Доставка пиццы в Туле https://pizzacuba.ru горячо и быстро. Классические и авторские рецепты, несколько размеров и бортики с сыром, добавки по вкусу. Онлайн-меню, акции «2 по цене 1», промокоды. Оплата картой/онлайн, бесконтактная доставка, трекинг заказа.
Продвижение сайта — это не просто набор мероприятий, а комплексная стратегия развития бизнеса. SEO помогает улучшить структуру ресурса, качество контента и технические параметры. Результат — рост органического трафика, увеличение конверсии и укрепление репутации. Регулярная аналитика позволяет корректировать стратегию и удерживать лидирующие позиции. Такой подход эффективен для любого бизнеса. Узнайте больше о SEO-продвижении https://mqbinfo.com/w/Поисковая_Оптимизация_Сайтов_Под_Ключ
forexstrategyguide – The insights here are practical and actually useful for real trading setups.
brahmanshome – Site layout is clean, making it very easy to follow instructions.
Energy Storage Systems https://e7repower.com from E7REPOWER: modular BESS for grid, commercial, and renewable energy applications. LFP batteries, bidirectional inverters, EMS, BMS, fire suppression. 10/20/40 ft containers, scalable to hundreds of MWh. Peak-saving, balancing, and backup. Engineering and service.
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Music FTP 0-DAY https://0daymusic.org
* Reseller1 TakePremium: PayPal, Visa, Bank transfer, Bitcoin, Master Card, Amazon pay, WebMoney…
* Reseller2 Premiumland: Paypal, VISA, Mastercard Apple Pay, Google Pay…
* Reseller3 Premiumkeystore: AltCoins, Webmoney, Perfect Money.
* Software FTPtxt-17 to search for text.
* Software scene MP3 sorter genre, year, group, artist.
* NFO COLLECTION 1997-2021 MUSIC, GAMES, MOVIES, TV, APPS.
* We accept payment method: BitCoin, USDT, ETH, Bank wire, Western Union.
* Server’s capacity: 430 TB MP3, FLAC, Labels, Software, Music Videos.
* Support: FTP, FTPS (File Transfer Protocol Secure), FTPES (Explicit SSL), SFTP.
* Updated on daily: 30GB-100GB, 300-2000 Albums, WEB, Promo, CDM, CDR, CDS, EP, LP, Vinyl…
* Account delivery time: 1 to 48 hours.
* More 16 years Of archives.
* Overal server’s speed: 1 Gb/s.
* Easy to use: Most of genres are sorted by days.
abbysauce – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
everydaytrendshop – Customer support was super responsive and helpful during my checkout.
dividedheartsofamericafilm – Powerful storytelling shedding light on diverse views and experiences.
teamworkinnovation – Every article pushes motivation, teamwork, and forward-thinking solutions.
yourtradingmentor – I really appreciate the real-world examples, they make lessons click instantly.
globalchoicehub – The site offers a nice mix of global brands and local favorites.
conorjmurphy – Really enjoy visiting, articles are short but informative every single time.
simplelivinghub – The site design itself reflects the brand—clean, balanced, and easy to use.
shopandshine – Great mix of trendy products and home favorites, something for everyone.
teamworksuccesspath – Great layout overall, clean design and easy reading experience throughout.
successnetworkgroup – I like how they emphasize teamwork, networking, and long-term achievement.
I recommend this legal remedy to everyone https://gabapentin-garbamaxxx.com
uniquedecorstore – I enjoy browsing the collections, keeps giving me fresh decorating inspiration.
globalmarketinsight – The content feels professional and well-researched, definitely trustworthy information.
successfultradersclub – Every tutorial feels insightful, with examples that make the concepts easy to apply.
markettrendalerts – Every alert feels reliable and easy to understand, even under pressure.
bigjanuarycleanup – Really enjoy visiting, articles are short but informative every single time.
Moldova – rent-auto.md/ro/ – Inchiriere auto Chisinau – arenda masini fara stres, rezervare rapida si cele mai bune preturi.
biotecmedics – Helpful ideas posted here, I’ll definitely share with all friends.
learnandtrade – Love how this site combines trading education with practical real-world examples.
Lezen over https://fotoredaktor.top reisgids Wit-Rusland loonde zich.
dinahshorewexler – Site layout is clean, making it very easy to follow instructions.
Академия Алины Аблязовой https://ablyazovaschool.ru обучение реконструкции волос для мастеров и новичков. Авторские методики, разбор трихологических основ, отработка на моделях, кейсы клиентов. Онлайн и офлайн, сертификат, поддержка кураторов, материалы и чек-листы.
jonathanfinngamino – Helpful ideas posted here, I’ll definitely share with all friends.
Подарок для конкурента https://xrumer.xyz/
В работе несколько програм.
Есть оптовые тарифы
Подарок для конкурента
Проектирование и строительство загородного дома в Санкт-Петербурге – это процесс, требующий внимательности к деталям. Наша строительная компания берет на себя все этапы: от выбора материалов и составления прайса до выполнения работ. Мы предлагаем кладку газоблока https://builder-spb.ru , кирпича и пеноблоков, установку жб-перекрытий, монтаж перегородок, сварочные и отделочные работы. Стоимость рассчитывается за квадратный метр или поштучно. Подрядчики учитывают сорт и уровень прочности блоков, чтобы построить надежный дом. Предлагаем выгодные цены и прозрачные расценки, фиксированные в договоре.
ucbstriketowin – Comprehensive coverage of UC Berkeley’s strike actions and outcomes.
csiingenieros.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
difyd2c.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
What’s up, the whole thing is going well here and ofcourse every one is sharing data, that’s in fact excellent, keep up writing.
Thank you for the encouragement
paws21airbrushstudio – A talented team dedicated to creating stunning airbrush masterpieces.
alexanderbuonointl – Enjoyed reading these posts, ideas are simple yet very useful.
Thank you for another great article. The place else may just anybody get that type of info in such a perfect manner of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I am at the look for such info.
виртуальные номера
That is kind of you
nohonabe – The variety of topics keeps me coming back regularly.
motocitee – Love browsing this site, content is always practical and clear.
kivurc – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
inkorswimtattoocruise – Love browsing this site, content is always practical and clear.
oldschoolopen – Really helpful tips here, saved me hours of unnecessary work.
sjydtech – The brand seems credible, content aligns well with design style.
zz-meta – Found some great resources here, really helpful for beginners.
raspinakala – Really helpful tips here, saved me hours of unnecessary work.
letter4reform – Thought-provoking discussions that inspire action towards meaningful change.
nohonabe – The variety of topics keeps me coming back regularly.
Rеgіster now and receive a welсоme раckage:
up to 145 frее sріns and as much as 650Dоl Воnus funds!
Huge range of games, instant winnings, and a trusted саsіnо experience await at
https://spinplanet.shop/b8a5igd
lotsofonlinepeople – Always informative and thought-provoking, I look forward to new posts.
wooziewear – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
chopchopgrubshop – Always fresh ingredients and innovative dishes that keep me coming back.
expandyourhorizon – Their posts are timely and relevant, a valuable resource.
chopchopgrubshop – Consistently great food and a welcoming environment every visit.
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
ieeb – I appreciate the depth of analysis in each post.
ieeb – Consistently provides valuable information across various topics, love it.
lastminute-corporate – Streamlined interface makes corporate travel planning quick and hassle-free.
kazhanmaster – A fantastic platform for gaining knowledge on various topics.
broodbase – Consistently provides insightful perspectives on current trends and issues.
adawebcreative – A visually appealing site that maintains functionality without compromise.
ibdesignstreet – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
pgmbconsultancy – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
abbysauce – Site layout is clean, making it very easy to follow instructions.
Хотите построить дом своей мечты в Санкт-Петербурге? Наша строительная компания предлагает профессиональное возведение загородных домов под ключ. Работаем с кирпичом, газоблоком, газобетоном и деревом. Выполняем кладку стен https://builder-spb.ru , перегородок, устройство перекрытий и отделочные работы. Гарантируем прозрачный прайс, фиксированную стоимость в рублях за квадратный метр и полное соответствие проекту. Наши подрядчики учитывают все нюансы строительства, включая толщину стен, сорт материалов и уровень нагрузок. Дома возводятся с учётом строительных норм и особенностей участка.
wooziewear – Really enjoy visiting, articles are short but informative every single time.
lithestore.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
expandyourhorizon – The layout is clean and user-friendly, making navigation effortless.
inkorswimtattoocruise – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
oldschoolopen – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
conorjmurphy – Love browsing this site, content is always practical and clear.
lotsofonlinepeople – I appreciate the fresh perspectives shared on this platform.
letter4reform – Their approach to reform is both innovative and practical.
chopchopgrubshop – Always a pleasure to visit, never disappointed with the meals.
zz-meta – Their tips and articles saved me a lot time today.
chopchopgrubshop – The food here is consistently delicious and beautifully presented every time.
ieeb – Consistently provides valuable information across various topics, love it.
ieeb – I find their perspectives unique and refreshing, highly informative.
lastminute-corporate – Comprehensive services cater to all corporate travel needs in one place.
broodbase – Always a pleasure to read, informative and well-written content.
kazhanmaster – The layout is clean and user-friendly, making navigation effortless.
seo статьи seo статьи .
sjydtech – Very good user experience, functionality and look are well balanced.
buildabetterworld – An eye-catching site with high potential and clean design.
makelifesimpler – The tips are refreshing and genuinely easy to implement.
styleforliving – I appreciate the well-organized categories that make exploring easier.
discovergreatdeals – Checkout was simple and the delivery info looked trustworthy.
Состоялось важное обновление XRumer 23.0.5 StrongAI, ключевое нововведение в котором — самообучение неизвестным полям и тексткапчам через GPT (при этом поддерживаются API аналогов GPT), а также повышение пробиваемости по форумам, контакт-формам и прочим платформам, расширение функционала.
Скачать Xrumer
ВАЖНО: Для получения действительно ощутимого прироста настоятельно рекомендуется:
Скачать Xrumer
Если работаете по форумам, обязательно скачайте и поставьте новый пак нейросетей под XEvil 6.0 (ссылка также есть в кабинете), подробности в мануале ниже
Используйте GPT для распознавания неизвестных тексткапч и полей, см. мануал ниже
В режиме “Только регистрация” (при работе с форумами) обязательно делайте несколько проходов, с использованием Инструмента “Сгенерировать базу непробитых ресурсов”
Наибольшую разницу с пред.версиями можно увидеть исключительно при работе с “сырыми” базами! В случае, если будете работать по проверенным базам от предыдущих версией, вы просто не будете охватывать вновь пробиваемые ресурсы
Обязательно внимательно прочтите мануалы, представленные в конце поста! От этого напрямую зависит отдача от софта, Вы можете получить как X так и 10X прироста по трафику — всё зависит сугубо от соблюдения рекомендаций
Скачать Xrumer
https://xrumer.ru/
everydaystylecorner – The site feels trustworthy and well-designed for shoppers.
dreambuycollection – I’ll keep this store in mind for future purchases.
yourcreativejourney – The layout is clean and makes exploring items really enjoyable.
theworldawaits – The site layout is smooth and shopping looks legitimately easy.
shopfornewthings – Overall a positive first impression; hope the delivery meets expectations.
learnandgrowtoday – I appreciate how the design is clean and content seems actionable.
learnshareandgrow – Useful articles with actionable advice, glad I came across this.
findbetteroptions – Customer support info is visible which gives extra confidence in using the site.
discovernewthings – Reasonable pricing and fast-loading pages make the experience pleasant.
XEvil 5.0 automatically solve most kind of captchas,
Including such type of captchas: ReCaptcha v.2, ReCaptcha v.3, Google captcha, Solve Media, BitcoinFaucet, Steam, +12k
+ hCaptcha, FC, ReCaptcha Enterprize now supported in new XEvil 6.0!
1.) Fast, easy, precisionly
XEvil is the fastest captcha killer in the world. Its has no solving limits, no threads number limits
2.) Several APIs support
XEvil supports more than 6 different, worldwide known API: 2Captcha, anti-captcha (antigate), rucaptcha.com, death-by-captcha, etc.
just send your captcha via HTTP request, as you can send into any of that service – and XEvil will solve your captcha!
So, XEvil is compatible with hundreds of applications for SEO/SMM/password recovery/parsing/posting/clicking/cryptocurrency/etc.
3.) Useful support and manuals
After purchase, you got access to a private tech.support forum, Wiki, Skype/Telegram online support
Developers will train XEvil to your type of captcha for FREE and very fast – just send them examples
4.) How to get free trial use of XEvil full version?
– Try to search in Google “Home of XEvil”
– you will find IPs with opened port 80 of XEvil users (click on any IP to ensure)
– try to send your captcha via 2captcha API ino one of that IPs
– if you got BAD KEY error, just tru another IP
– enjoy! 🙂
– (its not work for hCaptcha!)
WARNING: Free XEvil DEMO does NOT support ReCaptcha, hCaptcha and most other types of captcha!
everydaystylecorner – Friendly layout and easy to navigate—makes browsing enjoyable.
makelifesimpler – Great resource for anyone looking to simplify and organize.
yourcreativejourney – I appreciated the visible shipping/returns info—it gives trust.
theworldawaits – Found something I’ve been looking for—good job sourcing it.
Автоматические выключатели
discovergreatdeals – Checkout was simple and the delivery info looked trustworthy.
learnandgrowtoday – The tone feels friendly, approachable and perfect for steady improvement.
exploreendlessideas – Modern look, design sparks imagination and a sense of wonder.
курсы по seo курсы по seo .
l2dkp.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
spartanwebsolution.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
vqscvasavtzqpsj.shop – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
imgs81.men – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
pok01.live – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
daman-games.live – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
bestvaluecollection – Delivery and quality will be the real test but initial feel is promising.
discoverandcreate – Balanced visuals, message promotes creativity and curiosity together.
getinspireddaily – The name promises inspiration—layout and content seem inviting at first glance.
globalstylemarket – Overall a strong first impression; looking forward to seeing delivery and quality.
exploreandcreate – The brand message “explore and create” resonates and feels inviting.
bestvaluecollection – Customer service/contact information is visible, which adds trust to the shopping experience.
connectlearncreate – Checkout seemed straightforward and the payment/payment-info section was visible.
uniquelifestylehub – I’ll consider revisiting this shop when I’m looking for something new.
growwithconfidence – Clean layout and clear messaging make this a pleasant experience.
changeyourdirection – The motto “change your direction” resonates—nice branding and positive message.
discoveryourpotential – Overall a positive vibe—curious to explore deeper and see actual offerings.
fashionloverszone – The site has a stylish feel and looks easy to navigate.
shopwithstylehub – The theme feels modern and the product range looks diverse.
modernlivingstore – The overall vibe is modern and the site feels trustworthy.
connectwithideas – Product visuals are clear, descriptions readable — a good first impression.
findjoytoday – The messaging about “joy” resonates and gives a positive feel to shopping.
makeimpacttoday – The site loads well and the layout gives a professional vibe.
dreambuyoutlet – Customer support/contact details visible – good sign for trust and reliability.
ЛідерUA – інформативний портал https://liderua.com новин та корисних порад: актуальні події України, аналітика, життєві лайфхаки та експертні рекомендації. Все — щоб бути в курсі й отримувати практичні рішення для щоденного життя та розвитку.
findyourdreamplace – Customer support/contact info is accessible, which adds trust to the experience.
Лучшая выжимка темы: https://journal-ua.com/newslist/buket-na-zakaz-kak-vybrat-i-podarit-idealnye-tsvety.html
modernhomefinds – The site presents a clean, stylish layout and feels well-curated.
discoverandcreate – The site looks inviting and the theme of creation really shines through.
imaginelearnexplore – Navigation seems smooth and product categories appear well organized.
discoveramazingoffers.shop – Always updated, I like seeing new offers every single day.
urbanwearstudio – Customer contact or support info appears accessible, which builds trust.
yourmomenttoshine – Customer support/contact info is visible—good for building shopper confidence.
purefashionmarket – I’ll bookmark this store for future visits when I’m looking for fashion deals.
changeyourdirection – I’ll bookmark this site for the future and revisit when ready to dive in.
growwithconfidence – Overall a positive first look; curious to explore more and see results.
changeyourperspective – So far pricing looks fair; will keep an eye on product quality and delivery.
getinspireddaily – Customer service info is visible, which adds trust to the experience.
globalstylemarket – I’ll bookmark this shop for future visits when looking for new finds.
uniquelifestylehub – I’ll consider revisiting this shop when I’m looking for something new.
connectlearncreate – The site has a promising concept; clean design and inviting layout.
exploreandcreate – The product variety looks good—something for different tastes.
fashionloverszone – Found several items I like; browsing was enjoyable and smooth.
inspirechangealways – I’ll bookmark this site for when I’m ready to browse and buy.
modernlivingstore – I’ll keep this site in mind for future home or lifestyle finds.
urbanwearstudio – Trendy and sharp, captures streetwear energy in a polished way.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Кстати, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler, посмотрите сюда.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://evimturk.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
shopwithstylehub – Navigation between categories is smooth—browsing feels intuitive and effortless.
connectwithideas – The concept is modern and appealing to creative, growth-oriented users.
findjoytoday – Navigation feels smooth and loading times seem reasonable so far.
makeimpacttoday – Customer support/contact information is visible which adds trust to the experience.
dreambuyoutlet – Customer support/contact details visible – good sign for trust and reliability.
Авторский MINI TATTOO https://kurs-mini-tattoo.ru дизайн маленьких тату, баланс и масштаб, безопасная стерилизация, грамотная анестезия, техника fine line и dotwork. Практика, разбор типовых косяков, правила ухода, фото/видео-съёмка работ. Материалы включены, сертификат и поддержка сообщества.
Курсы маникюра https://econogti-school.ru и педикюра с нуля: теория + практика на моделях, стерилизация, архитектура ногтя, комбинированный/аппаратный маникюр, выравнивание, покрытие гель-лаком, классический и аппаратный педикюр. Малые группы, материалы включены, сертификат и помощь с трудоустройством.
discoveryourpotential – Navigation appears smooth and product or service categories seem clear.
findsomethingnew – Navigation is smooth and the categories seem well-organized, making browsing pleasant.
createinspirelead – The visuals look crisp and the design gives a professional vibe.
discoveramazingthings – Exciting name, visuals and content give a sense of adventure.
Pinco casino login ilə hesabınıza dərhal daxil olun. Pinco casino giris sürətli və etibarlıdır. Pinco bonus sistemi çox sərfəlidir.
скачать pinco официальный сайт
pinco casino no deposit bonus
pinco yukle
pinco 175
pinco.com
Pinco promosyon kodu ilə əlavə bonuslar al. Pinco casino apk ən son versiyada yeniləndi. Pinco casino azerbaycan canlı diler oyunları ilə fərqlənir.
pincko
pinco. казино.
pinco casino logo
pinco казино казахстан
pin c
Pinco azerbaycan telegram-da yeniliklər paylaşılıb.Pinco kazino oyunları yüksək RTP dərəcəsinə malikdir. Pinco az apk ilə daha sürətli oyun təcrübəsi yaşayacaqsan.
happylivingstore.shop – Prices are reasonable, products feel high-quality and look amazing today.
Ищете своего мастера? Только проверенные тату-художники с впечатляющим портфолио! Любой стиль: от реализма до олдскула. Найдите идеального профи для вашего проекта на нашем сайте https://tattoomastera.ru/
Pinco apk yükləyərək mobil telefondan rahat oynayın. Pinco azerbaycan yukle vasitəsilə limitsiz oyunlar aç. Pinco casino download apk ilə bütün oyunlara çıxış əldə et.
pinco.win
pinco pinco 2024 kz
pinco qeydiyyat
molang pinco
pinco.007
Pinco casino app Azərbaycan oyunçuları üçün optimallaşdırılıb. Pinco bonus sistemi yeni oyunçular üçün idealdır. Pinco yukle və ani bonus əldə et.
pinco bet giris
pinco canl? casino siteleri
pinco-az-site ing
pinko kasino
pinko joker
Pinco az platforması sadə və etibarlıdır.Pinco casino az canlı mərclər bölməsi ilə populyardır. Pinco kazino az oyunçuları üçün xüsusi təkliflər var.
modernhomefinds – Navigation between categories is intuitive; browsing feels effortless and pleasant.
findyourdreamplace – Pricing appears reasonable; the overall design gives a professional and trustworthy feel.
explorewithpassion – Creative tone, design reflects motivation and energetic discovery.
findsomethinggreat.shop – Found an amazing gadget today, shipping was fast and reliable.
discoveramazingoffers.shop – Love checking daily, offers always keep me coming back quickly.
Pinco azerbaycan istifadəçiləri üçün xüsusi bonuslar var. Pinco az saytı mobil oyunçular üçün idealdır. Pinco az yukle və qazanmaga başla.
pinco twitter
pinco az?rbaycan tg
pin c
pinco bet вход
pinco casino казахстан
Pinco promosyon kodu ilə əlavə bonuslar al. Pinco az yukle sayəsində mobil təcrübə çox rahatdır. Pinco kazino slot oyunlarında geniş seçim var.
pin cop
cdd4ever
pinko yukle
pinko indir
carlitta n.v.
Pinco casino istifadəçiləri üçün gündəlik kampaniyalar var.Pinco casino az canlı mərclər bölməsi ilə populyardır. Pinco kazino azerbaycan platforması bütün cihazlarda əlçatandır.
urbanwearstudio – Navigation looks smooth and the layout feels modern and clean.
imaginelearnexplore – Overall positive first impression—looking forward to seeing how service and product quality deliver.
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://evimturk.com
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
discoverandcreate – Product visuals are clear and the site feels thoughtfully designed.
purefashionmarket – Found some interesting fashion pieces that seem thoughtfully selected.
Онлайн-блог https://intellector-school.ru о нейросетях: от базовой линейной алгебры до Transformer и LLM. Пошаговые проекты, код на Git-стиле, эксперименты, метрики, тюнинг гиперпараметров, ускорение на GPU. Обзоры курсов, книг и инструментов, подборка задач для практики и подготовки к интервью.
Освойте режиссуру https://rasputinacademy.ru событий и маркетинг: концепция, сценарий, сцена и свет, звук, видео, интерактив. Бюджет и смета, закупки, подрядчики, тайминг, риск-менеджмент. Коммьюнити, PR, лидогенерация, спонсорские пакеты, метрики ROI/ROMI. Практические задания и шаблоны документов.
yourmomenttoshine – I’ll bookmark this shop for when I’m ready to treat myself or someone else.
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: fun word guessing games
changeyourperspective – The site feels fresh and inspiring; great message behind the brand.
findjoyeveryday.shop – Brings a little joy each visit, love checking their updates.
brwon-stake.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
classyfindsonline.shop – Such a charming store, love browsing through all their latest finds.
buildsomethingnew.shop – Great products for makers, really motivates me to start new projects.
5415015.cc – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
gotqlb.cc – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
smartfashionboutique.shop – This boutique always surprises me with fresh and creative looks.
getmyfunsocks.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
lovehentai.info – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
findyourmoments.click – Great message here, every visit feels grounding and truly refreshing.
trendinghomeideas.shop – Perfect spot for interior lovers, every visit brings new inspiration.
startanewjourney.shop – Great site for motivation, helps me focus on self-growth daily.
simplevalueplace.shop – Impressed by how affordable yet reliable everything turned out here.
yourdailyshoppinghub.shop – This site makes online shopping surprisingly simple and budget friendly too.
modernlivingtrend.shop – Absolutely love the modern lifestyle vibe, feels fresh and current.
trendingstyleworld.shop – Smooth shopping experience, delivery came right on time as promised.
findyourpathnow.shop – Beautiful message throughout, really encourages new beginnings and personal discovery.
staycuriousdiscover.shop – Inspiring content overall, keeps me motivated to explore new ideas.
freshfashioncorner.shop – Great selection of outfits, really refreshing to see new arrivals.
modernlivingstore.click – Love browsing this shop, everything feels trendy and thoughtfully curated.
yourmomentstarts.click – The name says it all, motivation starts here every single time.
rikvip1.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
yourmomentstarts.shop – Amazing idea overall, reminds me to take action right away.
dreambelieveachieve.shop – Great reminder to stay focused, everything feels encouraging and uplifting.
classychoiceoutlet.shop – Beautifully curated selection, makes online shopping simple and satisfying always.
Pinco az platformasında hər gün yeni imkanlar açılır. Pinco oyna və real pul qazan. Pinco kazino istifadəçi dostu interfeysə malikdir.
pinco bet официальный сайт
pin -up
pinco.win
pinko online casino
скачать pinco
Pinco kazino seçimi ilə hər kəs öz sevimlisini tapır. Pinco bonus sistemi yeni oyunçular üçün idealdır. Pinco casino azerbaycan canlı diler oyunları ilə fərqlənir.
pulsuz oyun oyna pul qazan
sweet bonanza pinco
pinkov
kumarhane pinco
казино pinco скачать приложение
Pinco kazino təhlükəsizliyi yüksək səviyyədə təmin edir.Pinco kazino oyunları yüksək RTP dərəcəsinə malikdir. Pinco casino download apk təhlükəsiz və stabil işləyir.
changeyourperspective.click – Love how this site challenges my mindset in refreshing ways today.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
По теме “Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://anadolustil.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
findjoyeveryday.shop – Simple layout, fun products, everything feels bright and positive today.
findyourmoments.click – Beautiful concept overall, really reminds me to slow down daily.
yourdailyshoppinghub.shop – Very happy with my experience, everything worked perfectly from start.
Could we argue that inflation, while frequently viewed as a economic issue, also serves as a catalyst for social upheaval, especially when it triggers a vicious cycle of economic decline, unemployment, and diminished purchasing power, potentially threatening societal harmony?https://kodx.uk/
]
Exactly the phenomenon of inflation, when it is triggered, is economic in nature, except that its repercussions extend beyond the economic sphere to the social sphere, affecting social cohesion.
classyfindsonline.shop – Products exceeded my expectations, definitely coming back for another order.
trendinghomeideas.shop – Very stylish store, love checking new arrivals for creative ideas.
buildsomethingnew.shop – Always exciting to visit, new creative tools appear every week.
simplevalueplace.shop – Love browsing here, so many practical things for daily use.
smartfashionboutique.shop – Found my new favorite dress here, quality exceeded my expectations.
startanewjourney.shop – Love the name, feels inspiring and full of positive fresh energy.
trendingstyleworld.shop – Amazing range of clothes, love how modern and chic everything looks.
modernlivingtrend.shop – Beautiful website design, so easy to browse through trendy finds.
findyourpathnow.shop – Such a peaceful space, full of ideas about life and direction.
staycuriousdiscover.shop – Inspiring content overall, keeps me motivated to explore new ideas.
yourmomentstarts.click – So positive and refreshing, definitely worth visiting again and again.
modernlivingstore.click – Found some amazing home decor ideas here, quality feels top-notch.
everydayshoppingzone.shop – Impressed by the deals, saving money has never been easier.
discoveryourpath.shop – Love the content, it’s calming and full of great perspective.
changeyourperspective.click – Love how this site challenges my mindset in refreshing ways today.
freshfashioncorner.shop – Everything feels fresh and current, really love their seasonal collections.
exploreendlessideas.shop – Great inspiration source, everything feels modern and thoughtfully put together.
Современный человек ежедневно сталкивается с ситуациями, которые требуют внутренней устойчивости, эмоционального баланса и понимания собственных реакций. На сайте mypsytest.ru собраны десятки научно обоснованных методик, разработанных специалистами в области психологии и психиатрии.
Тесты для самопознания и эмоционального интеллекта
Хотите проверить уровень своей сдержанности или эмоциональной устойчивости? Тогда вам подойдут такие тесты, как тест на эмоциональную устойчивость и тест на гнев . Эти методики помогут понять, где проходят границы вашего терпения и как развить проактивное мышление.
Особое внимание стоит уделить оценке способности к проактивности — инструменту, позволяющему определить, насколько вы способны управлять своей жизнью, а не плыть по течению.
Глубинная диагностика личности
истерическое расстройство личности тест
Если вы хотите разобраться в себе глубже, стоит пройти диагностику характера, психопатический тест Хаэра , тест на темную триаду , а также тест на садизм . Эти тесты позволяют выявить скрытые стороны личности, определить уровень эмпатии, моральных ценностей и степень эмоциональной холодности.
Для тех, кто замечает у себя усталость, апатию или эмоциональное выгорание, подойдут тест на апатию , тест на невротические реакции , а также диссоциативное расстройство личности тест . Они помогут вовремя заметить сигналы организма и психики, требующие внимания.
Не менее популярны тесты, связанные с самоидентификацией и отношениями: тест на гетеросексуальность. Эти методики помогают лучше понять собственные эмоции и мотивацию в отношениях.
Для любителей необычного формата подойдут игровые тесты — тест какая ты фея сегодня. Они не только развлекают, но и тонко показывают особенности восприятия мира и уровень фантазии.
Психология отношений и взаимодействия с людьми
На mypsytest.ru вы найдёте уникальные тесты, созданные для анализа отношений: тест на токсичность . Эти опросы позволяют увидеть истинное состояние общения, понять, не стали ли вы заложником эмоциональной зависимости, и определить, насколько здоровыми являются ваши отношения.
Для мужчин представлен специализированный опрос IPSS для мужчин , который помогает оценить физическое и психологическое состояние организма.
Пройдя тесты на mypsytest.ru, вы получите глубокое понимание себя, своих реакций и поведения.
Перейдите на mypsytest.ru и узнайте, что скрывает ваше подсознание . Самопознание начинается с одного клика.
тест на омниверта
yourmomentstarts.shop – This platform’s energy is great, makes every visit feel refreshing.
getmoreforshop.shop – Great deals here, I always end up saving a lot shopping.
dreambelieveachieve.shop – Such a motivating brand, really connects with people chasing success.
Курсы по наращиванию https://schoollegoart.ru ресниц, архитектуре и ламинированию бровей/ресниц с нуля: теория + практика на моделях, стерильность, карта бровей, классика/2D–4D, составы и противопоказания. Материалы включены, мини-группы, сертификат, чек-листы и помощь с портфолио и стартом продаж.
PRP-курс для косметологов плазмотерапия обучение доказательная база, отбор пациентов, подготовка образца, техники введения (лицо, шея, кожа головы), сочетание с мезо/микронидлингом. Практика, рекомендации по фото/видео-фиксации, юридические формы, маркетинг услуги. Сертификат и кураторство.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Между прочим, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://aynakirildi.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
findsomethinggreat.click – Great place to browse, always end up discovering something unexpectedly cool.
classychoiceoutlet.click – Stylish collection overall, love the elegant and affordable fashion pieces.
classychoiceoutlet.shop – Classy vibe all around, definitely one of my favorite outlets.
createinspirelead – Clean website layout and inviting theme — promising start.
findbetteroptions.click – Love this site, helps compare and choose smarter shopping decisions easily.
discoveryourpath.click – Beautifully designed site, helps me focus on personal growth daily.
Онлайн-курсы плазмотерапия обучение онлайн: структурированная программа, стандарты стерильности, подготовка образца, минимизация рисков, протоколы для лица/шеи/кожи головы. Видеолекции и задания, разбор клинических ситуаций, пакет шаблонов для ведения пациента, экзамен и получение сертификата.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Кстати, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?, загляните сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://guzellikturk.com
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
startsomethingtoday – I like how this site pushes small steps toward real daily progress.
ремонт bosch https://servisnyj-bosch-moskva.ru/
findyourpathnow – Great place for anyone trying to understand where they’re headed next.
In a world flooded with headlines and notifications, locating credible current news is harder than ever. Feeds update in seconds, yet truth is often lost in the speed. To find verified news platforms, visit our blog: https://blogfreely.net/mealepoch8/the-power-of-kindness-how-small-acts-are-quietly-changing-the-world .
Traditional outlets like BBC, Reuters, and The Associated Press continue to set the standard for trustworthy journalism. They fact-check every story and refresh coverage in real time. For deeper understanding, think tanks and journals like The Economist and The Atlantic reveal the meaning beyond the headlines.
Freelance reporters and online collectives are reshaping the modern news landscape. Substack newsletters, niche blogs, and investigative collectives often provide sharper, more personal insights — notably on underreported subjects. These voices bring fresh perspectives and restore a sense of authenticity.
The smartest strategy for staying updated is to diversify your sources: combine global sources with smaller, focused ones that match your curiosity. Cross-check different sources, question assumptions, and focus on insight, not noise. This mix transforms reading into awareness.
startsomethingtoday – The content is short, powerful, and really gets straight to motivation.
changeyourdirection – The messages here feel personal and genuinely push toward better choices.
findjoytoday – Every post here feels like a little dose of sunshine and calm.
shopwithstylehub – Definitely adding this to my bookmarks, stylish and fun to explore always.
freshfashioncorner – Great taste in style choices, feels like fashion made simple and fun.
happylivingstore – The layout is simple and cheerful, easy to navigate without clutter.
explorethefuture – Every post feels forward-thinking yet easy enough for anyone to understand.
simplevalueplace – Such a calm layout, easy to read and browse through anytime.
learnandgrowtoday – The advice here feels genuine, realistic, and inspiring at the same time.
inspirechangealways – The writing style feels open, warm, and totally connects with readers easily.
startanewjourney – Reading here makes me feel grounded and ready to take small new steps.
trendingstyleworld – I like how this site stays updated with what’s hot in fashion now.
purevalueoutlet – Found some amazing deals here, honestly better than many big-name stores.
modernlivingstore.click – Found some amazing home decor ideas here, quality feels top-notch.
getmoreforshop – This site really lives up to the name, great deals everywhere I look.
connectlearncreate.click – Amazing community vibe, love the focus on creativity and learning together.
createinspirelead.click – Love the empowering tone here, truly encourages creativity and leadership.
zanwechat.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
sghjt.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
fl508.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
023rongzi.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
everydaystylecorner – I like how the content balances trendy looks with timeless style essentials.
Link vyy
318hw.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
szsfujin.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
happylivingstore – I like how everything feels curated for comfort, not just for style.
inspirechangealways – I keep coming back here because every visit gives something inspiring again.
startanewjourney – I keep revisiting this site because it helps me reset and refocus often.
changeyourdirection – The writing feels warm yet motivating, a nice balance of both worlds.
findjoytoday – The tone feels warm and comforting, exactly what I needed this morning.
shopwithstylehub – Great fashion finds here, honestly better than what I expected overall.
simplevalueplace – Love the minimalist vibe here, everything feels useful and straightforward.
startsomethingtoday – I like how this site pushes small steps toward real daily progress.
explorethefuture – I like the tone here, it’s curious but still grounded in reality.
learnandgrowtoday – The advice here feels genuine, realistic, and inspiring at the same time.
startsomethingtoday – Just what I needed, a little spark to finally start something today.
freshfashioncorner – I enjoy how this site blends comfort with real fashion inspiration perfectly.
findyourpathnow – I read one article and instantly felt more focused about my journey.
trendingstyleworld – Feels like a one-stop shop for anyone obsessed with new fashion trends.
purevalueoutlet – Shopping here was smooth and fun, I already found some gift ideas.
yourcreativejourney – Every visit leaves me motivated and ready to start a new project immediately.
smartfashionboutique.click – Stylish and modern pieces, definitely my go-to for classy fashion.
modernlivingstore.click – Great prices for the quality, delivery came faster than expected too.
globalstylemarket – I like how everything blends culture and fashion in such a modern way.
yourdailytrend.click – Great source for everyday fashion inspiration, always something new featured.
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
https://evimsicak.com
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: https://www.dveri-v-srok.ru/dveri-dlja-kvartiry/
everydaystylecorner.click – Love browsing here, always find stylish items that suit my taste.
trendinghomeideas – I enjoy how each post offers fresh inspiration for everyday living spaces.
Все детали и нюансы здесь: https://version.com.ua/turyzm.html
Платформа для тестов и викторин https://fankino.ru
getmoreforshop – Definitely a solid site for anyone wanting more value from online shopping.
everydaystylecorner – Browsing here always gives me fresh inspiration for my everyday wardrobe choices.
buildsomethingnew.click – Inspiring projects here, really motivates me to start new creative ideas.
Окунись в мир динамичных испытаний, где секунда приносит с собой яркие впечатления и новые испытания. Запусти игру прямо сейчас — кликни по ссылке https://root-apk.com//3403-skachat-my-talking-slimy-cat-friends-may-toking-slaymi-mod-dengi-monety-i-menyu-mod-vzlom-my-talking-slimy-cat-friends-na-android.html чтобы начать. Интуитивное управление и интуитивный интерфейс делают её подходящим выбором как для коротких перерывов, так и для длительных игровых вечеров.
Каждый этап приносит с собой миссии, интересные задания и сюрпризные повороты сюжета. Накопляй бонусы, улучши способности, открывай новые локации и оцени прогрессом своего персонажа. Тщательно настроенный геймплей сделает так, что каждый заход захватывает и не успевает надоесть — хочется будет идти дальше и ещё дальше.
Разработчики уделили внимание деталям: звук, визуальные эффекты, анимация и производительность на высоком уровне. Игра подходит для всех — от новичков до опытных любителей. Испытай где угодно: дома, в дороге, в перерывах между делами или в поезде — возможность играть в любой момент делает её идеальным выбором.
Не упускай шанс испытать яркие эмоции — жми по ссылке https://root-apk.com//3403-skachat-my-talking-slimy-cat-friends-may-toking-slaymi-mod-dengi-monety-i-menyu-mod-vzlom-my-talking-slimy-cat-friends-na-android.html и начинай играть уже сейчас. Открой для себя игру, которая легко затянет и станет твоим новым фаворитом!
Начни немедленно лучшее мобильное приключение
Запусти без ожиданий игру, которая затянет с первых секунд
Играй немедленно захватывающую игру на телефон
3f09d5d
электрические гардины для штор elektrokarniz797.ru .
expandyourhorizon.click – Great site for learning and exploring fresh perspectives every day.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Кстати, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://guzellikturk.com
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
Regіstrіere dich jetzt und sіchere dir das Willkоmmеnspаket: bіs zu 115 Frеіspіеle und bіs zu 1900Еur Воnus!
Тоp Spіеle und sofоrtіge Gewіnnе аuf
https://jackpotjuniper.shop/bk6mivc
inspirechangealways.click – Helpful tips and insights, truly makes a difference in life.
orourkeforphilly.com – The issues section covers education, public safety, and jobs in a straight-forward way.
nataliakerbabian.com – The story behind the project “Ilustro para no olvidar” adds real depth and context.
localphlmarket.com – Loved browsing the locally sourced items, so many unique creations from Philly.
garymasino.com – Overall nice digital presence, shows professional credibility and trustworthiness.
electcateriarmccabe.com – Overall, a solid campaign website that makes me want to learn more and follow along.
Іnscrіvеz-vоus mаіntеnant еt rеcеvеz un раck de bіеnvеnue: jusqu’a 115 tоurs grаtuіts et un bоnus аllаnt jusqu’a 1400$!
Dеs jеux pаssіоnnаnts et des pаіemеnts rаpіdеs sur
https://reelriches.shop/bdfa9gq
cumberlandcountynjvaccination.org – The website loads quickly and the appointment slots are clearly listed.
chrishallforjudge.com – I appreciate the candidate’s experience and the emphasis on fairness in courts.
smyrnafestival.com – The variety of activities seems great for families and friends alike.
нарколог на дом санкт-петербург
cycleforsci.org – Thank you for offering free lesson downloads — that’s very generous and useful.
uncommittednj.org – I’ve been following this movement, the messaging feels very genuine.
oneillforda.com – Overall impression: solid campaign site, informative and easy to engage with.
happylifestylehub.shop – If you’re planning backlinks, consider waiting until the site is fully built out for better quality.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – Appreciate how they highlight community and collaboration in leadership development.
newhorizonsnetwork.shop – The shopping layout is intuitive and browsing through items was smooth.
dibrunobottleshop.com – Found the perfect gift here, thought the selection matched my friend’s taste well.
successpathway.bond – Overall, a commendable site—looks well done, I’ll revisit for updates.
joinourcreativeworld.shop – I didn’t see clear branding or product categories, so navigation is unclear.
shopthelatesttrend.shop – Happy to help you inspect other domains or generate backlink blocks for more established sites if you like.
thinkcreategrow.click – For now treat the link as “pending” until structural and trust elements are in place.
exploreamazingideas.click – I couldn’t find branded content, product listings, or clear navigation yet on this domain.
nsfeg.org – Great resource for learning, very informative and well-structured content overall.
inspirechangealways.click – Excellent examples of motivation, posts are engaging and very relatable.
kionnawest.com – Inspiring platform, clearly shares vision and values in a compelling way.
remiphl.com – I found this place through a foodie friend, glad I did.
chrishallforjudge.com – Mobile view worked smoothly for me, no problems while browsing on phone.
orourkeforphilly.com – The website’s layout is clean and easy to navigate; good first impression.
nataliakerbabian.com – Clean design, strong visuals, and a clear voice; makes a standout impression.
smyrnafestival.com – The variety of activities seems great for families and friends alike.
happylifestylehub.shop – The domain is live, but the homepage doesn’t display clear storefront content yet.
90’lardan gunumuze uzanan guzellik anlay?s?na ?s?k tutan bu rehberle, zaman?n otesine gecen bir tarz elde edin.
Зацепил материал про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?.
Ссылка ниже:
https://aynakirildi.com
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
localphlmarket.com – Recommended this to my friends who love handmade goods and independent creators.
garymasino.com – Good to see client-focused language and clear value proposition on the site.
electcateriarmccabe.com – The volunteer sign-up page is straightforward, makes it easy to get involved.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – I found the site and the mission feels meaningful with trusted leadership ideals.
newhorizonsnetwork.shop – Shared the link with a friend who’s into curated online finds; they liked it too.
successpathway.bond – The visuals are tasteful; good balance between content and design.
joinourcreativeworld.shop – The layout currently lacks product details, images, or checkout info that typical e-commerce sites show.
shopthelatesttrend.shop – For higher-quality linking, aim to reference domains with clear content, clear identity, and good structure.
thinkcreategrow.click – If this is for a backlink, it would be better to choose sites with complete content and professional finish.
berenux.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
waziqiyi.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
jpl927.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
uucncn.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
46466497.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
1911phl.com – Great information on local events, keeps me updated with ease.
haginsforphilly.org – I shared this link with friends because the vision feels grounded and honest.
s1565.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
exploreamazingideas.click – The domain is active but the site appears to be under construction or showing a directory listing.
cumberlandcountynjvaccination.org – Nice to see a dedicated site for the county’s vaccination efforts, well done.
cycleforsci.org – Love how you bring renewable-energy lessons to communities in creative ways.
Онлайн-займ https://zaimy-67.ru без очередей: заполните форму, получите решение и деньги на карту. Выгодные ставки, понятный договор, кэшбэк и скидки при повторных обращениях. Напоминания о платежах, продление при необходимости. Выбирайте ответственно и экономьте.
oneillforda.com – I appreciate the volunteer sign-up section, it felt straightforward and inviting.
uncommittednj.org – Shared the link with friends, hope more folks check this out and join.
mcalpineinfo.com – Love the detailed info here, very helpful and easy to follow.
natashaforjudge.com – Excellent campaign site, communicates priorities and experience clearly and effectively.
n3rdmarket.com – Loved browsing the local vendors, such a fun market atmosphere.
Отличный обзор помог выбрать нейросеть для генерации изображений под мои задачи. Протестировала несколько вариантов из списка, один стал любимым. Остальные генераторы тоже качественные: инструмент генерации изображения
dibrunobottleshop.com – Browsing late at night, still responsive and smooth on mobile, thumbs up!
remiphl.com – Booked a table last minute and they fit us right in, thanks!
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
По теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?”, там просто кладезь информации.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://guzellikturk.com
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
Фото из армии Просолдат ру армейский альбом профессиональная съёмка армии: присяга, парады, учения. Создаём армейские альбомы, фотокниги, постеры; ретушь и цветокор, макеты, печать и доставка. Съёмочные группы по всей стране, аккредитация и дисциплина, чёткие сроки и цены.
hardman4schools.com – Great campaign site, clearly communicates vision and priorities for education.
bisbro.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
createandgrow.shop – Let me know if you’d like a list of such alternative domains (fully functional) to reference.
findwhatyoulove.shop – On mobile the layout also seems incomplete — improving this would increase credibility.
modernlivingstyle.shop – Overall a pleasing site, I’m looking forward to seeing product launches.
simplybestchoice.click – Good domain for branding, hope it becomes a useful resource.
sparxcle.com – Interesting products here, really innovative ideas and practical solutions overall.
May I just say what a comfort to find someone who genuinely knows what they’re discussing on the internet.
You actually know how to bring a problem to light and make it important.
A lot more people ought to check this out and understand this
side of your story. It’s surprising you are not more popular given that you surely have the gift.
Thank you very much for the encouragement, that’s kind of you
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
9e2seattle.com – Love the local coverage here, very informative and well-presented overall.
организация онлайн трансляций москва https://www.zakazat-onlayn-translyaciyu4.ru .
Краснодарский край богат природой и достопримечательностями, которые стоит увидеть каждому. Чтобы ничего не пропустить, стоит обратить внимание на экскурсии из Краснодара. Это отличный вариант для тех, кто хочет провести выходные с пользой и узнать свой регион ближе.
организация интернет трансляций организация интернет трансляций .
createandgrow.shop – For higher-quality backlinking, you might prefer domains with established content and clear offers.
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Зацепил материал про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://guzellikturk.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
findwhatyoulove.shop – On mobile the layout also seems incomplete — improving this would increase credibility.
modernlivingstyle.shop – Mobile version loaded smoothly on my phone, nice user-friendly site.
simplybestchoice.click – For now the website feels like it’s just getting started, interesting.
Мучает зуд и жжение? Геморой – лечение без боли и очередей: диагностика, консервативная терапия, латексное лигирование, склеротерапия, лазер. Приём проктолога, анонимно, в день обращения. Индивидуальный план, быстрое восстановление, понятные цены и поддержка 24/7.
chery 8 max chery tiggo ultra
simonscider.co.uk – Delicious cider options, love the quality and unique flavor choices here.
leanneslifechangingfairies.com – Beautiful and imaginative site, full of magical ideas for everyone.
shopthebesttoday.click – Great online store, easy navigation and fantastic product deals daily.
globalmarketplacehub.click – Let me know if you’d prefer other domains that are fully published and ready for linking now.
dankglassonline.com – Overall the branding is on point, just waiting for the full store functionality.
findyourperfectdeal.click – If you’d like, I can check the domain’s registration and history to estimate its future stability.
dailyessentialfinds.bond – If you’re linking this, treat it as a “coming soon” site for now.
motivilovesmusic.com – Shared this with a friend who loves music brands—they liked the name.
purebeautytrend.shop – The name “Pure Beauty Trend” has strong branding potential once fully active.
everydayvaluecorner.shop – Usually domains like this perform well when they focus on consistent value and clear layout.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – I’m looking forward to seeing their upcoming events and leadership resources.
successpathway.bond – I visited the site and noticed navigation is limited at this stage.
Обновления по теме здесь: https://www.innov.ru/news/it/shirokoformatnaya-pechat-t
alexandredallenbach.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
myxy567.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
4631519.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
ashgrovecatering.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
mdcphilly.com – Great local content, keeps community members informed about events and updates.
line2048.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
everydayvaluecorner.shop – The simplicity is a plus, though at times it felt a bit bare—more content helps.
dankglassonline.com – I’d wait a bit to see full product listings before diving in completely.
globalmarketplacehub.click – Let me know if you’d prefer other domains that are fully published and ready for linking now.
Useful information in one click: https://xn--80aalokkkeerfhi.xn--p1ai/2025/10/27/Запуск-рекламы-без-постоянных-банов/
findyourperfectdeal.click – The domain is active, but I didn’t find a full storefront or clear branding yet.
dailyessentialfinds.bond – The ‘.bond’ TLD is unique—could help memorability once live.
purebeautytrend.shop – For now the trust signals are thin (About page, reviews missing), so cautious linking is advised.
motivilovesmusic.com – It’s promising for music lovers, though I didn’t find much yet.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – I’m looking forward to seeing their upcoming events and leadership resources.
successpathway.bond – For now treat the link as “pending readiness” until the site’s fleshed out.
simplybestchoice.shop – Great product variety, everything feels affordable and high quality overall.
playfuel.co.uk – Great gaming products here, everything feels fun, creative, and high-quality.
nomnomnomfordogs.com – I shared this with a friend who has a pup—she was very interested.
trabas007hoki – I’ve been checking this site often, updates come fast and nice.
inspireeverydaylife.shop – Browsed via phone and the site loaded well — nice mobile responsiveness.
pepplish – This site gives me serious foodie vibes, definitely bookmarking it.
ehe258.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
learntradingtoday – Nice job making trading strategies understandable without fluff or hype.
dreambuyworld – Overall, the site gives a good impression, just proceed with a bit of caution and due diligence.
flourandoak – Browsed through your collection and everything looks so well-presented.
buildyourdreamtoday – The site loads fast and navigation is smooth, big plus.
unitedbygoal – Nice layout and the content reads clearly, well done overall.
wrestlingac – Navigation is intuitive, I didn’t feel lost and found what I needed quickly.
cepjournal – The range of topics seems broad — from general interest to tech, which feels ambitious. :contentReference[oaicite:0]index=0
strategicgrowthalliance – The visuals and fonts feel modern, good aesthetics overall.
thebestplacetoshop.shop – Overall good first impression; shipping & service will determine long-term appeal.
forexlearninghub – The branding looks slick and professional, that’s a plus for sure.
bestdealsforlife.shop – If you use this for a backlink now, consider it as “pending full readiness”.
foruminvestmali – I like that there’s a defined schedule and focus on investment opportunities in Mali, which is appealing.
DRINKIO удивил скоростью и вежливостью персонала. Курьеры всегда приятные, доставка без опозданий. Ассортимент разнообразный, сайт понятный. Всё работает стабильно https://drinkio105.ru/
togetherwerise – I’ll revisit later to see if they add more about their results and credibility.
shopthebesttoday.click – Great online store, easy navigation and fantastic product deals daily.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Кстати, если вас интересует Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://anadolustil.com
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
Is it possible that the current inflation surge, fueled by unconventional monetary policies, could lead to a “Financial Doomsday Clock” scenario, where the economic and social turmoil triggers mass civil unrest on a global scale? If yes, what measures can governments take to mitigate such a crisis? our website, we furnish up to date and the best IT solutions an eye to your establishment] kodx.uk
Normally, to mitigate the effects of inflation, the central bank raises the key interest rate in order to limit the granting of credit, which leads to a decrease in demand and, of course, a drop in inflation.
Regіstrаte ahоra y recіbе un pаquеte de bіеnvenіda: hаsta 210 tіrаdas grаtіs y un bоnо de hаstа 2350Dоl.
Juеgоs іncrеiblеs y pаgоs іnstаntanеоs еn
https://Fnewbestnews.shop/bqxaaql
nomnomnomfordogs.com – The treat selection looks high-quality and the reviews are positive.
asterixfilm.co.uk – Fantastic movie content, perfect for fans of animation and classic films.
dreambuyworld – I’d recommend checking user reviews and payment security before making a purchase.
nextrealm.click – Interesting concept, love the futuristic vibe and creative presentation overall.
learntradingtoday – Will bookmark this resource, seems like a reliable place to sharpen my trading skills.
wrestlingac – The elements look polished and up-to-date, gives a trustworthy impression.
buildyourdreamtoday – Just visited the site and there’s a clean modern feel to the design.
unitedbygoal – The navigation is intuitive, I found what I needed without fuss.
cepjournal – If you’re reading or linking here, I’d advise checking any claims carefully before acting.
strategicgrowthalliance – The homepage feels sleek but I’m still unsure what the core focus is.
forexlearninghub – Overall first impression: promising idea, just needs more substance to feel fully trustworthy.
pepplish – Just discovered this brand and the website feels super polished.
foruminvestmali – The registration details are clear, but I’d recommend verifying the hosting organization and past attendee feedback for confidence.
inspireeverydaylife.shop – The clean layout and design hint at something special; good first impression.
trabas007hoki – Everything looks organized well here, love the responsive design work.
flourandoak – I appreciate how easy it is to browse and find products.
togetherwerise – Before engaging I’d check for testimonials or case studies to validate their claims.
dearsparrows.com – Navigation is simple and mobile friendly, which made reading easy.
dreamcreateinspire.shop – Beautiful design, love the inspiring message and creative energy here.
pp4fdr.org – Important initiative, shares valuable guidance and updates in a clear manner.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
bestdealsforlife.shop – For higher-value linking count today, domains with visible shops and live inventory may serve better.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://guzellikturk.com
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
білий павук
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
trendandstyle.bond – I’d recommend revisiting in a few weeks to check for full launch and improved trust elements.
Хочешь вылечить геморрой – современный подход к лечению геморроя: точная диагностика, персональный план, амбулаторные процедуры за 20–30 минут. Контроль боли, быстрый возврат к активной жизни, рекомендации по образу жизни и профилактике, анонимность и понятные цены.
Современный атмосферный ресторан в Москве с открытой кухней: локальные фермерские ингредиенты, свежая выпечка, бар с коктейлями. Панорамные виды, терраса летом, детское меню. Бронирование столов онлайн, банкеты и дни рождения «под ключ».
dmbet88.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler”, там просто кладезь информации.
Смотрите сами:
https://anadolustil.com
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
envolavecning – The visual aesthetic is bold yet refined, nice balance for a designer label.
achat-vin-direct.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
rebeccacaridad-manzanita – The aesthetic feels modern yet timeless—perfect for someone redecorating or building an art collection.
engagement-forum – If you’re considering participating, I’d recommend doing a small test or checking separate reviews before full commitment.
4291w.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
theperfectgiftshop – The product range seems appealing; quality visuals help make the offerings look interesting.
lifestyleinspirationhub – If they offer international shipping, I’d definitely consider ordering from abroad.
yourdailyupdate – I noticed minimal user testimonials or independent verification of the store’s credibility.
1198248.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
moesboardwalk – Overall feel: promising venue, just a little more detail would really seal the deal.
bloemhill – Very good first impression; just make sure you verify specifics like returns/freshness for flowers.
921643.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
trendinsight – The homepage has a good first impression, clean layout and modern visuals.
trendyfindshub – The layout looks modern and clean, makes browsing feel effortless.
connectdiscovergrow – I’d recommend checking the “About Us” and credentials to verify who’s behind the site.
joebobsaveschristmas – If you’re into holiday-themed horror, this looks like a creative shot.
getinspiredtoday – If you’re ordering internationally (from Pakistan for instance), check shipping, customs, and return policy carefully.
rosetemplates – One suggestion: adding more user reviews or case-studies would build further trust.
sega-live – I couldn’t quickly find independent reviews or third-party testimonials that validate the site’s claims.
28darlingstreet – The location at Church Street, Enniskillen looks nicely central and convenient. :contentReference[oaicite:1]index=1
iphone-meets-iijmio.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
madmadedesigns – The aesthetic suggests higher-end goods, so depending on price it could be a premium purchase.
648704.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
rosetemplates – The loading speed and navigation are smooth, which gives good first impressions.
28darlingstreet – The location at Church Street, Enniskillen looks nicely central and convenient. :contentReference[oaicite:1]index=1
lifestyleinspirationhub – The vibe here is fresh and inspiring—perfect for finding something new.
Нужна ликвидация? https://www.zakrit-kompaniu-doo.me: добровольная ликвидация, банкротство, реорганизация. Подготовка документов, публикации, сверка с ФНС/ПФР, закрытие счетов. Сроки по договору, прозрачная смета, конфиденциальность, сопровождение до внесения записи в ЕГРЮЛ.
moesboardwalk – If you’re going, check what non-alcoholic drinks & amenities are included—they mention them. :contentReference[oaicite:1]index=1
bloemhill – I’d like to see more info on shipping or delivery zones just for clarity.
Tasfiyeye mi ihtiyac?n?z var? https://www.sirket-kapatma.me/: borc analizi, yasal prosedurun secimi (istege bagl? veya iflas), alacakl?lar?n bildirimi, tasfiye bilancosu, sicilden silme. Son teslim tarihlerini ve sabit fiyat? netlestirin.
theperfectgiftshop – Browsing was smooth, but I didn’t immediately see strong trust signals like reviews or certifications.
yourdailyupdate – The visuals and layout make a strong first impression, great design work.
trendinsight – The visuals are appealing and modern—good for catching attention if you are browsing.
trendyfindshub – The branding is appealing, but checking return policy beforehand would be wise.
Здесь публикуются лучшие сборки ПК для игр, с подробным разбором комплектующих и рекомендациями по апгрейду. Пользователи могут ознакомиться с готовыми решениями и советами по самостоятельной сборке, чтобы собрать мощный и стабильный игровой компьютер.
connectdiscovergrow – Navigation was smooth and the layout seems user-friendly, nice UX.
getinspiredtoday – Overall, a promising site with strong potential; just make sure the details align with your expectations before larger purchases.
envolavecning – Great to see a Taiwan-based original design brand with so much character. :contentReference[oaicite:0]index=0
rebeccacaridad-manzanita – Overall, a compelling art brand with strong visuals and potential for serious collectors or design enthusiasts.
engagement-forum – The visuals give a decent impression, yet details like pricing, policies and speaker line-up should be clearer.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
hopprojects – The site design is clean and modern, the visuals make me want to explore more of their work.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Между прочим, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?, загляните сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://aynakirildi.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
madmadedesigns – Overall a promising site with good visual appeal—just proceed with standard caution for new-to-you online shops.
macofficelovesyou – The site name made me smile, and the layout feels very nostalgic yet modern.
clubinorout.com – Great nightlife guide, keeps me updated on clubs and events easily.
mutamedya.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
joebobsaveschristmas – Good vibe here with the quirky concept—definitely caught my attention.
lhjylggszt.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
sega-live – Overall: interesting site, but I’d apply extra caution and do due-diligence.
001yabo.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
bjlfabu.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
ssss2222.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
pbkplus.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
macofficelovesyou – The site name made me smile, and the layout feels very nostalgic yet modern.
smartshoppingplace – The site feels like a solid all-in-one store, easy to browse and inviting.
beauty-optical-salon – Such a chic concept, never thought glasses could feel this fashionable.
amazingdealscorner – Solid deal-site vibe; browsing was smooth and categories clearly laid out.
everydayinnovation – The brand name sounds inspiring and modern; curious to browse their collection and see how it lives up to the promise.
Всё для дачи и цветов https://amandine.ru журнал с понятными инструкциями, схемами и списками покупок. Посев, пикировка, прививка, обрезка, подкормки, защита без лишней химии. Планировки теплиц, уход за газоном и цветниками, идеи декора, советы экспертов.
Need liquidation? closing a company in Montenegro: voluntary liquidation, bankruptcy, reorganization. Document preparation, publications, reconciliation, account closure. Contractual terms, transparent estimates, confidentiality, support.
648704.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Хочу выделить материал про Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler.
Смотрите сами:
https://evimturk.com
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
amazingdealscorner – Solid deal-site vibe; browsing was smooth and categories clearly laid out.
smartshoppingplace – The site feels like a solid all-in-one store, easy to browse and inviting.
iswrphilly – The community-focused vibe here feels genuine, great to see local engagement online.
dreamdealsstore – Found some amazing bargains today, really happy with this shop.
findsomethingamazing – This site has a positive vibe, fun to browse through daily.
thebestvalue – The site looks professional and the value is obvious from the first glance.
brightstylecorner – Found some amazing outfit ideas, this site has real style vibes.
findyourowngrowth – Such a motivating site, love the positive energy in every post.
findbetteropportunities – I like how every post gives me a reason to keep growing.
globalfashionfinds – Stylish layout and great designs, feels like a premium fashion hub.
findyourfocus – Found some great reminders here about staying present and productive.
discovernewhorizons – Clear design, meaningful messages—this site stands out for thoughtful content.
everydaychoicehub – Everything loads smoothly and the suggestions feel relevant, good experience.
shapeyourdreams – Great design and friendly layout, makes engaging with the articles a joy.
trendylifestylehub – Found some really useful tips on style and self-care that I could use today.
globalfashionfinds – Love the trendy pieces here, everything looks so stylish and modern.
findyourinspiration – Simple yet effective site for finding calm focus and new perspectives.
trendsettersparadise – Will definitely be returning for fresh ideas and new looks weekly.
hanayaka-na-life – Elegant and serene design, the Japanese aesthetic truly shines through beautifully.
everymomentmatters – The name hits emotionally, good for meaningful purchases; just check the fine details.
modernstylemarket – Great name and the design looks sharp—perfect for trend-savvy shoppers.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
По теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://evimturk.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
findsomethingamazing – Nice blend of style and creativity, I keep coming back here.
dreamdealsstore – Super easy to navigate and checkout, everything works smoothly here.
thebestvalue – If you’re looking for value and smart spending, this site is a solid stop.
shopwithhappiness – Love the cheerful tone; browsing here actually feels positive and easygoing.
brightstylecorner – Found some amazing outfit ideas, this site has real style vibes.
everydaychoicehub – Nice mixture of ideas and advice, perfect for improving daily routines.
discovernewhorizons – Clear design, meaningful messages—this site stands out for thoughtful content.
findbetteropportunities – I like how every post gives me a reason to keep growing.
shapeyourdreams – The content here offers real encouragement to chase meaningful goals.
globalfashionfinds – Great shopping experience, fast site and beautiful product photos throughout.
trendylifestylehub – (Note: small typo in link but kept format) Amazing variety of topics from fashion to wellness.
findyourinspiration – Simple yet effective site for finding calm focus and new perspectives.
findyourowngrowth – Great reads here, every article feels inspiring and really well written.
urbanwearoutlet – Stylish urban fashion outlet feel, lots of potential if the sizing and quality hold up.
globalfashionfinds – Perfect site for fashion lovers, always something new to discover here.
findyourfocus – Always find great insights here about productivity and mindful living.
trendsettersparadise – Always find something unexpected and stylish when I visit this site.
dailychoicecorner – The variety of items surprised me, it’s like a cozy online bazaar.
inspiredthinkinghub – I like how they frame the brand as a place for ideas, not just shopping.
мостбет вход сегодня mostbet12034.ru
startyourjourneytoday – The motivational tone of the brand instantly boosts your mood while browsing.
learnexploreachieve – Inspiring brand name; if they deliver educational tools or courses this could be a good fit.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://evimsicak.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
creativegiftplace – So many thoughtful gift ideas; perfect for finding something personal and unique.
learnsomethingeveryday – Clean website design and fun reading material, I like visiting often.
Venture into the massive galaxy of EVE Online. Find your fleet today. Conquer alongside thousands of players worldwide. Download free
sdzmbz.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
2231appxz1.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
y6113.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
brightnewbeginnings – The name gives a fresh start vibe; nice for seasonal or motivational purchases.
trendylifestylehub – Trend-forward lifestyle brand angle worked for me, very modern design.
h489tyc.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
findsomethingunique – The promise of uniqueness is appealing—if the products deliver, this could be a go-to for special finds.
y13617.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
urbanstylemarket – The site has a modern vibe, fits current fashion trends well.
classytrendcollection – The products feel trendy yet elegant, really fits the “classy” branding well.
wk552266.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
hnzkfj.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
وقت بخیر حسین جان
حتما ببینید
سایت انفجار جدید
رو جهت کرش.
این سرویس بونوس ویژه و برای علاقهمندان ورزش مناسبه.
پرداختهاش سریعه و پیشنهاد میکنم
تست کنید.
با آرزوی موفقیت فاطمه.
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla gunumuzun trendlerine meydan okumaya ne dersiniz?
Особенно понравился раздел про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://aynakirildi.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
learnsomethingeveryday – A nice mix of fun facts and practical tips, great combo.
dailytrendspot – Feels like a stylish marketplace where you can discover cool new finds.
mostbet kg http://mostbet12033.ru/
simplystylishstore – Clean aesthetic and clear shopping experience; nice for simple, polished purchases.
urbanstylemarket – Great site for seasonal fashion, love how the collections are updated.
trendshopworld – Global-sounding brand, good for catching wide variety of trends.
yourstylematters – I like the empowering message behind the name, style should always be personal.
learnsomethingeveryday – The layout’s clean and the writing feels friendly and helpful.
sjqyhl.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
jnc-fafa15.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
ymxty.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
ymxty.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
findyourinspiration – Very motivating messaging; makes me think of product categories that spark ideas or renew your look.
findbetteropportunities – Ambitious name—makes me curious about what “better opportunities” means for customers.
inclaz.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Скважины на воду: бурение и обустройство — эффективный метод организовать подачу чистой воды на участок. Такая система позволяет добывать воде высокого качества из природных пластов, что исключает зависимость от коммунальных сетей.
Процесс бурения https://bur-vod39.ru/ начинается с геологической разведки, что позволяет установить оптимальную точку бурения. На основе данных специалисты подбирают наиболее подходящую конструкцию скважины.
После создания ствола скважины монтируется обсадка, монтируется насос и выполняется обустройство скважины. Все эти мероприятия гарантируют стабильную работу системы.
Собственная скважина — это капитальное решение для вашего дома. При профессиональном подходе и своевременном уходе она будет работать многие годы, поставляя чистую и безопасную воду.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Между прочим, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda Modern ve Estetik Cozumler, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://evimturk.com
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
рейтинг рекламных агентств россии рейтинг рекламных агентств россии .
perfectbuyzone – The layout is well done and the offers stand out, nice work overall.
findsomethingamazing – Always find something new and awesome whenever I visit this site.
inclaz.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
1xbet giris 1xbet giris .
happyhomefinds – A nice place to browse when I’m looking for cozy home vibes.
bestpickscollection – The mix of selections is good, looks like they’re curating with care.
yourtrendystop – The collection feels current and stylish, exactly what I was looking for.
findyourinspiration – Very motivating messaging; makes me think of product categories that spark ideas or renew your look.
Портал про все https://version.com.ua новини, технології, здоров’я, будинок, авто, подорожі, фінанси та кар’єра. Щоденні статті, огляди, лайфхаки та інструкції. Зручний пошук, теми за інтересами, добірки експертів та перевірені джерела. Читайте, навчайтеся, заощаджуйте час.
chery tiggo 9 ultra chery дилер
free bet promo code 1xbet — https://www.allgreatquotes.com/news/1xbet_promo_code_pakistan_bonus_1.html A 1xBet promo code is a special code that users can enter to receive bonuses such as free bets, deposit bonuses, or other rewards. These codes are often provided as part of welcome offers, special promotions, or affiliate partnerships.
createimpacttoday – Found some thoughtful content that made me pause and reflect today.
Журнал для дачников https://www.amandine.ru и цветоводов: что посадить, когда поливать и чем подкармливать. Календарь, таблицы совместимости, защита от вредителей, обрезка и размножение. Планы грядок, тепличные секреты, бюджетные решения и советы профессионалов.
unlocknewpotential – Very authentic vibe, the posts feel like a friend’s advice rather than hype.
theperfectgift – Love the wide selection of gifts available, so many great ideas.
yourstylematters – Great mix of looks and style advice, definitely bookmarking this for later.
unlocknewpotential – Very authentic vibe, the posts feel like a friend’s advice rather than hype.
yourvisionmatters – The layout is clean and the tone is friendly—easy to engage with.
thinkbigmovefast – Strong visuals and clear message—makes me want to take action right away.
findyourfocus – The content really helps when I need motivation to get things done.
freshvalueoutlet – The user interface is friendly and the navigation feels well-designed.
brightstylecorner – The layout’s bright energy instantly catches your eye, really uplifting vibe overall.
yourvisionmatters – Empowering message and good styling; strong brand identity right out of the gate.
discovergreatoffers – Browsing here was quick and the prices looked very competitive.
thebestcorner – Simple and strong branding—makes you believe you found a great spot for deals.
perfectbuyzone – Bookmarking this—will definitely come back when I’m ready to shop smarter.
discoverfreshperspectives – Feels more boutique or niche, good for curated products or design-forward picks.
yourstylematters – The layout is clean and easy to navigate, makes browsing a pleasure.
findsomethingamazing – Found some unexpected gems here, definitely worth checking out often.
Хоккей
happyhomefinds – The visuals are inviting and the mix of styles is refreshing.
bestpickscollection – I found a few deals I hadn’t seen elsewhere, that was fun.
theperfectgift – Good value for the gifts I saw; felt like smart choices.
yourtrendystop – Found some standout pieces today, very happy with the selection.
discovergreatoffers – Overall a positive first visit—looking forward to seeing what new deals show up.
createimpacttoday – This site has become one of my go-to places for positive energy.
unlocknewpotential – This site helped me re-think what I can achieve when I try differently.
unlocknewpotential – Great site design, easy to browse and I found some thoughtful insights.
yourvisionmatters – The layout is clean and the tone is friendly—easy to engage with.
freshvalueoutlet – The visuals are attractive and make exploring much more fun.
Eski ama asla eskimeyen 90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla dolu bu yaz?da bulusal?m.
Кстати, если вас интересует Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik, загляните сюда.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://evimsicak.com
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
thinkbigmovefast – The content feels action-oriented and realistic, not just hype—very refreshing.
Посмотрите наш официальный сайт – Надёжный источник информации о компании.
findyourfocus – Always find great insights here about productivity and mindful living.
makesomethingnew – Creative vibe, feels like a site where you can discover something fresh and unique.
fashiondailydeals – I like how fresh the selections are and the visuals look appealing.
everymomentmatters – Such a calming and thoughtful site, found new reflections for my day.
dreamdealsstore – Fast-loading site, neat design and amazing daily offers to grab.
connectsharegrow – Pleasant browsing experience, everything loads smoothly and feels cohesive.
shopwithhappiness –User experience was smooth, no confusion; felt straight to the point.
brightnewbeginnings – Such a positive and motivating site, feels like a fresh start each time.
purechoiceoutlet – I appreciated how quickly I found something interesting here.
yournextadventure – Found some places I hadn’t thought of before—nice discovery platform.
uniquevaluecorner – Quick loading, nice filters, and the collection seems thoughtfully selected.
trendshopworld – Love this site’s trendy feel, browsing was exciting and inspiring.
shopthedayaway – The product variety is nice, something for different tastes and moods.
luxuryfindsonline – Found some really interesting pieces here; layout is sleek and browsing was easy.
inspiredthinkinghub – Found some helpful insights today—thank you for sharing this resource.
modernideasnetwork – The writing feels friendly yet meaningful—exactly the sort of content I needed.
moveforwardnow – The writing feels authentic and inviting—easy to connect with the ideas.
purechoiceoutlet – Clean design and simple layout, made browsing feel effortless and enjoyable.
shopwithhappiness –Love how inviting and cheerful the site looks–makes shopping feel joyful.
hlfsxx.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
joinbtba.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
ribiav3.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
534078.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
purechoiceoutlet – The selection feels thoughtful, like there’s quality behind the offers.
u7338.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
572408.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
jerseyszonewholesale.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
fashiondailydeals – Found a few unexpected gems—really liked discovering them on this site.
Seattle sustainable premium transport offers an eco-conscious yet luxurious way to travel, combining elegance with environmental responsibility. Our limousine service prioritizes sustainability by utilizing hybrid and electric vehicles, reducing carbon emissions without compromising on comfort or style. Each vehicle in our fleet is meticulously maintained, featuring high-end amenities like plush leather seating, climate control, and advanced entertainment systems for a first-class experience.
Ideal for corporate events, weddings, airport transfers, or special occasions, our service ensures punctuality, professionalism, and discretion. Drivers are highly trained, courteous, and knowledgeable about Seattle’s routes, guaranteeing a smooth and efficient journey. We also partner with local green initiatives to offset our environmental impact, reinforcing our commitment to Seattle sustainable premium transport.
Whether you need a sleek sedan for a business meeting or a spacious stretch limo for a celebration, our tailored solutions cater to every need. Experience the perfect blend of sophistication and sustainability—where luxury meets responsibility in every ride. Book your Seattle sustainable premium transport today for an unforgettable, guilt-free travel experience. – https://bestlimorates.com/the-future-of-urban-mobility-why-seattles-premium-transportation-sector-is-attracting-investors/
brightnewbeginnings – Friendly tone and genuine messages make this site a pleasant find.
yournextadventure – Friendly and easy to navigate site, made exploring destinations fun and fast.
trendshopworld – Bookmarking this site for future fashion searches—excited to explore more.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
По теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://evimsicak.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
uniquevaluecorner – The overall vibe is positive; good mix for casual shopping and discovery.
everymomentmatters – Always feel a little more centered after browsing here—a meaningful stop.
shopthedayaway – Site loads quickly and looks well designed—made browsing enjoyable.
luxuryfindsonline – The visuals caught my attention and the variety looks pretty good overall.
inspiredthinkinghub – This site feels like a good space to grow your mindset and learn.
modernideasnetwork – The writing feels friendly yet meaningful—exactly the sort of content I needed.
dreamdealsstore – Love the deals here, prices look great and browsing was smooth.
connectsharegrow – Love the vibe here, seems like a solid platform to connect and grow.
moveforwardnow – Bookmarking this site—you’ve got something good going if you like progress.
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: купить входную дверь с установкой
creativityunlocked – Inspiring content, really helps spark new ideas and creative thoughts.
Eski ama asla eskimeyen 90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?yla dolu bu yaz?da bulusal?m.
По теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
https://evimsicak.com
90’lar?n guzellik s?rlar?yla tarz?n?za yeni bir soluk kazand?rabilirsiniz. Eski moda, yeni size ilham olsun!
https://pushnews.com.ua/tsikavi-fakty-pro-radio-istoriia-evoliutsiia-ta-suchasnist/
714428.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Купить квартиру https://kvartiracenterspb.ru просто: новостройки и вторичка, студии и семейные планировки. Ипотека от 0,1%, маткапитал, субсидии. Юрпроверка, безопасная сделка, помощь в одобрении, торг с застройщиком. Подбор по району, бюджету и срокам сдачи. Сопровождение до ключей.
Купить квартиру https://novostroydoma.ru в городе выгодно: топ-жилые комплексы, удобные планировки, паркинг и инфраструктура рядом. Ипотека, семейная ипотека 6%, маткапитал. Сравнение цен, выезд на просмотры, проверка чистоты сделки, страхование титула. Экономим время и деньги.
Покупка квартиры https://piterdomovoy.ru «под ключ»: новостройки бизнес/комфорт-класса и надёжная вторичка. Аналитика цен, динамика сдачи, инфраструктура. Ипотека, субсидии, маткапитал. Юридический аудит, безопасные расчёты, регистрация сделки онлайн. Переезд без забот.
amazingdealscorner – Good value product picks; I’ll remember this site for the next purchase.
Квартира вашей мечты https://kvartiracenter-kypit.ru подберём варианты с отделкой и без, проверим застройщика/продавца, согласуем торг. Ипотека 6–12%, семейные программы, маткапитал. Онлайн-показы, электронная подача в Росреестр, безопасная оплата. Экономим время и бюджет.
19j090.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
mastersaita.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
a0133.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
bws9916.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
19j012.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
993657.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: Password Game strategies to win
findsomethingunique – Interesting finds here, definitely stands out from regular online stores.
simplystylishstore – Love the sleek fashion picks here, very stylish and easy to browse.
startsomethingawesome – Bookmarking this as one of my go-tos when I need inspiration and a jump start.
discoverfreshperspectives – Overall very positive session—looking forward to discovering more topics here.
thebestcorner – Simple and strong branding—makes you believe you found a great spot for deals.
simplelivingstore – Nice design with easy navigation—shopping here felt stress‐free and well organized.
startsomethingawesome – Just discovered this site, the products look fresh and exciting.
yourdailyessentials – The layout is clean and navigation is smooth—pleasant shopping experience.
creativegiftplace – Found a few gift options I hadn’t seen elsewhere — nice surprise.
modernhometrends – Love the clean aesthetic and current home decor ideas here; very inspiring.
dreamcreateachieve – Love the clear structure and the uplifting message throughout the pages.
growtogethercommunity – Found some new perspectives here that resonated with me—thanks for the great site.
discoverpossibility – Quick load times and easy to explore—made the visit nice and effortless.
thebestcorner – The overall experience here is top-notch, really love this site.
modernhometrends – Excellent online experience, everything loads fast and looks super modern.
unlocknewpotential – Really interesting store, found some items I want to explore soon.
Всегда можно обратиться за консультацией — отвечают быстро https://tamozhenniiy-broker-moskva11.ru/
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Между прочим, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?, посмотрите сюда.
Смотрите сами:
https://aynakirildi.com
Nostalji dolu bu yolculukta bizimle oldugunuz icin tesekkur ederiz. 90’lar modas? ve guzelliginin ruhunu hissedin.
creativegiftplace – The layout is clean and the browsing experience felt smooth and enjoyable.
simplystylishstore – Love the sleek fashion picks here, very stylish and easy to browse.
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
startsomethingawesome – Found a few favourites already, love how easy this site is to use.
simplelivingstore – Great site experience, neat layout and a soothing palette made browsing enjoyable.
startsomethingawesome – Found some motivating ideas here that really pushed me to act and grow.
discoverpossibility – Quick load times and easy to explore—made the visit nice and effortless.
dreamcreateachieve – Really pleased with this visit—feels like a place I could return often.
modernhometrends – Definitely bookmarking this one for future home design inspiration and trend ideas.
growtogethercommunity – Navigation was smooth and the visuals were inviting, made the visit pleasant.
discoverfreshperspectives – Honest and engaging content that doesn’t feel superficial—really appreciated the authenticity.
yourdailyessentials – Found a few nice deals on useful items—happy to have come across this.
modernhometrends – The home decor choices here are fresh and exactly my aesthetic.
thebestcorner – I keep coming back here, content feels genuine and well structured.
unlocknewpotential – Great mix of styles here, refreshing change from the usual online stores.
shopwithpurpose – Great concept and thoughtful message behind this platform, I like it.
qcxrmyy.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
speakenglishlikeagenius.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: best online party games Canada
mastersaita.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
214248.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
wahoowebsite.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
yhwhcyy.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
745648.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
По теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
https://guzellikturk.com
90’lar?n buyusunu modern dunyaya tas?mak hic bu kadar kolay olmam?st?. Unutulmayan bu donemin guzellik s?rlar?n? unutmay?n!
discoverpossibility – Found some interesting pieces here, definitely will come back later.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
По теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?”, есть отличная статья.
Ссылка ниже:
https://aynakirildi.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
growtogethercommunity – Found something interesting here, can’t wait to explore more of their range.
discoverbetterdeals – Overall experience is positive, the branded feel is strong and inviting.
modernstylemarket – The design is modern and smooth, browsing felt effortless today.
explorecreativeconcepts – The website feels professional yet friendly — good combination.
shopthenexttrend – Nice experience so far, everything loads fast and looks well-organised.
moveforwardnow – Bookmarking this place, looks clean, modern and easy to use.
everydayinnovation – The visuals and layout are pleasant, makes me comfortable browsing further.
thefashionedit – Browsing here is smooth, everything loads fast and looks trustworthy.
explorecreativeconcepts – Just found this site, the layout is modern and really easy to navigate.
urbanwearoutlet – Nice presentation, navigation feels smooth and the product range seems decent.
reachhighergoals – I like how the layout is simple yet effective, makes browsing easy.
buildthefuture – Just found this site, the look and feel are clean and inviting.
learnexploreachieve – I like the simplicity of the site and how easy it is to navigate.
dealsanddiscounts – Found a few items I may pick up later, good discovery.
discoverpossibility – Impressed by the layout and clear navigation—feels professional.
moveforwardnow – I’m impressed with the style and the user-friendly layout.
modernstylemarket – The site gives off strong style credentials, I’m impressed by the layout.
freshstyleoutlet – Modern and clean design, great mix of new fashion trends and ideas.
growtogethercommunity – Great first impression, layout is clean and easy to navigate.
discoverbetterdeals – Great selection so far, makes me want to explore more of their catalog.
shopthenexttrend – Nice experience so far, everything loads fast and looks well-organised.
urbanwearoutlet – Just bookmarked this one, looks like a nice place for fashion finds.
everydayinnovation – Nice browse so far, the content seems trustworthy and easy to follow.
explorecreativeconcepts – Found a couple of nice items, will revisit when I have time.
thefashionedit – Just found this site, the styles look fresh and nicely curated.
learnexploreachieve – Really nice experience so far, layout is clean and modern.
explorecreativeconcepts – A nice mix of creativity and professionalism, the brand vibe works.
reachhighergoals – I’ll bookmark this site, excited to come back and see what else they offer.
buildthefuture – The visuals are appealing and the overall vibe is comfortable and professional.
dealsanddiscounts – I found some good items here, will revisit when I have time.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://anadolustil.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
Even the joy of Halloween will cost more this year, with less chocolate than in years past.
kraken4qzqnoi7ogpzpzwrxk7mw53n5i56loydwiyonu4owxsh4g67yd onion
Expect more packages of tangy gummies, riding off a meteoric high last year. Your kid’s trick-or-treat bag may be filled with a lot of pumpkin-spice-filled-anything. And like last year, cocoa bean industry experts are expecting high price tags to be passed down to consumers.
kraken4qzqnoi7ogpzpzwrxk7mw53n5i56loydwiyonu4owxsh4g67yd.onion
And with high cocoa prices, every producer from specialty chocolate makers to candy giants are changing up how they sell their treats. For consumers, this could mean less chocolate per package, higher prices and less cocoa content – meaning less chocolate-y chocolate – compared to before.
официальный сайт кракен ссылки
Overall, candy is 10.8% more expensive this Halloween season than last year, according to an analysis of NielsenIQ data conducted by progressive think tank Groundwork Collaborative and shared first with CNN. That’s nearly quadruple the overall rate of inflation.
kraken6gf6o4rxewycqwjgfchzgxyfeoj5xafqbfm4vgvyaig2vmxvyd onion
In 2024, Halloween candy prices only rose 2.1%, the analysis found.
Halloween spending is no fun-sized matter. Americans shelled out $7.4 billion in Halloween chocolate and candy sales in 2024, a 2.2% increase from 2023, the National Confectioners Association said.
kraken2trfqodidvlh4aa337cpzfrhdlfldhve5nf7njhumwr7instad onion
https://kraken5af44k24fwzohe6fvqfgxfsee4lgydb3ayzkfhlzqhuwlo33ad.shop
Escazu Chocolates, a bean-to-bar chocolate shop in Raleigh, North Carolina, sources most of its beans from Latin America. The shop said it has always worked with smaller farmers and paid them three to four times the commodity price of cacao – which essentially sets the minimum wage. The spike in prices has pushed up what Escazu pays those workers as well.
kra7 cc
Other cost-cutting measures include offering a smaller hot chocolate size, advertising non-chocolate ice cream toppings and moving to a cheaper location in Raleigh to save on rent.
kra11
And like many small businesses in America, Escazu is being hit by President Donald Trump’s tariffs, affecting not just the chocolate, but also aluminum in its packaging.
kra38 сс
“The tariffs have hit every single piece of what goes into every single thing,” Tiana Young, co-owner of Escazu, told CNN. “There is no new normal.”
kra36 сс
https://kra39at.com
оригінальний сценарій до дня вчителя 2025
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: Password Game for parties
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Хочу выделить раздел про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Ссылка ниже:
https://anadolustil.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
743748.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
9044123.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
amcbuildingmaterials.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
745748.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
743728.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
bb4703.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
528148.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
findyourperfectlook – Just stumbled onto this site, the design looks clean and fresh.
mystylezone – The visuals are appealing and the overall vibe is comfortable and professional.
styleandfashion – Everything loads quickly and the content looks well organized and solid.
everydayvaluehub – Easy navigation and clean design, big plus for user experience.
findyourowngrowth – Good first impression; the site loads well and looks thoughtfully built.
https://narkolog-na-dom-spb4.ru/
findyourowngrowth – Just discovered this site, the vibe is positive and refreshing.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
По теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://aynakirildi.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
findyourperfectlook – Impressed by the attention to detail, feels like a trustworthy brand.
mystylezone – The visuals are appealing and the overall vibe is comfortable and professional.
styleandfashion – The design choices feel smart and the user-interface is intuitive and clean.
everydayvaluehub – The website looks clean and slick, nice first impression.
Пользовались услугами таможенного брокера для оформления импорта — всё прошло быстро и без задержек. Специалисты сразу объяснили, какие документы нужны, и взяли всё на себя. Очень упростили жизнь: Таможенное оформление в Шереметьево
Онлайн казино Україна пропонують бонуси за реєстрацію. Онлайн казино на гривні робить гру ще зручнішою.
Легальні онлайн казино гарантують підтримку 24/7. Щоб не помилитися з вибором, звіртесь із незалежним топом: рейтинг казино онлайн україна. Українське казіно пропонує фріспіни для нових користувачів.
Онлайн казино в Україні працюють лише з перевіреними провайдерами. Онлайн казино України пропонують величезний вибір ігор. Онлайн казино Україна пропонує бонуси за перший депозит. Казино з миттєвим виводом виграшів — вибір досвідчених гравців. Українське казино підтримує мобільні пристрої для гри.
Plateforme parifoot rdc : pronos fiables, comparateur de cotes multi-books, tendances du marche, cash-out, statistiques avancees. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money, support francophone, retraits securises. Pariez avec moderation.
Paris sportifs avec 1xbet cd apk : pre-match & live, statistiques, cash-out, builder de paris. Bonus d’inscription, programme fidelite, appli mobile. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money. Informez-vous sur la reglementation. 18+, jouez avec moderation.
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-90.ru без визита в офис: достаточно паспорта, проверка за минуты. Выдача на карту, кошелёк или счёт. Прозрачный договор, напоминания о платеже, безопасность данных, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выберите выгодно.
Наши основные моменты: https://fotoredaktor.top
Онлайн казино Україна пропонують бонуси за реєстрацію. Онлайн казино на гривні робить гру ще зручнішою.
Ліцензійні ігрові автомати забезпечують чесний результат. Обираєте майданчик із гарантією виплат? Перевірте ліцензійні казино україни і порівняйте умови бонусів. Кращі казино України мають позитивні відгуки гравців.
Онлайн казино в Україні працюють лише з перевіреними провайдерами. Казино Україна дарує новачкам вітальні бонуси. Українські інтернет казино мають високий рівень довіри. Кращі казино України пропонують підтримку українською мовою. Кращі казино України пропонують високий RTP і чесну гру.
Welcome to the magical world of Kids’ Fashion 2026 kidsito.shop! ??
Step into a world where every outfit sparks joy and adventure kidsito.shop ! Our latest collection of kids’ clothes for 2024 kidsito.shop is bursting with color, comfort, and creativity, designed to inspire the little ones to dream big and explore even bigger.
From playful patterns to cozy fabrics, our clothes are crafted with love and care to keep up with every twist, turn, and tumble of childhood. Let imaginations soar with whimsical designs that ignite the spirit of adventure, whether they’re climbing trees, building sandcastles, or simply exploring their own backyard.
With sustainability in mind, our eco-friendly materials ensure that every garment not only feels good but does good too, nurturing both your child and the planet they call home.
Discover the joy of dressing up with our vibrant range of tees, leggings, dresses, and more! Each piece is a canvas waiting to be painted with laughter, friendship, and endless memories.
Because in the world of kids’ fashion, every day is an opportunity to shine bright and be uniquely YOU! ?
Guzellik ve kozmetikte her zaman gecmisten al?nacak dersler bulunur. 90’lar?n modas?ndan guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmeye haz?r olun.
Особенно понравился раздел про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://guzellikturk.com
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: металлическая дверь в квартиру с установкой
Автоматические выключатели
Топ онлайн казино Україна — чудовий спосіб відпочити та виграти. Кращі провайдери слотів пропонують захопливі автомати для українців.
Онлайн казино України на гривні підтримують швидкі виплати. Граєте з карт чи Apple/Google Pay? Підійдуть майданчики з гривнею — легальні онлайн казино в україні. Казино Україна — це найкраще місце для азартного відпочинку.
Онлайн казино в Україні працюють лише з перевіреними провайдерами. Казино Україна дарує новачкам вітальні бонуси. Ліцензійні казино України мають сучасні мобільні платформи. Онлайн казино Україна має різноманітні бонусні програми. Топ казино України мають офіційні сайти з сертифікатами.
amazingdealscorner – The layout is smooth and I found something I really liked quickly.
нарколог на дом санкт-петербург
https://narkolog-na-dom-spb3.ru/
digitalpilot.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Зацепил раздел про Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?.
Вот, можете почитать:
https://aynakirildi.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
funnelfuel.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
adprox.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
viralsphere.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthorbit.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://adrenalinamanaus.com/
rankstorm.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficmint.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Найкращі казино України постійно оновлюють слоти та акції. Кращі провайдери слотів пропонують захопливі автомати для українців.
Топ казіно України працюють цілодобово без збоїв. Цікавлять лише сайти з національною ліцензією? Перейдіть до розділу казино з ліцензією краіл і оберіть безпечно. Казино Україна — це найкраще місце для азартного відпочинку.
Казино з українським інтерфейсом має зрозумілу навігацію. Топ казино України працюють лише за ліцензією КРАІЛ. Українські інтернет казино мають високий рівень довіри. Топ онлайн казино Україна зібрало лише перевірені бренди. Кращі казино України пропонують високий RTP і чесну гру.
Private Server FLAC/MP3 1970-2025: https://www.0daymusic.org
* Software FTPtxt-17 to search for text https://0daymusic.org/FTPtxt
* Server’s capacity 432 TB MP3/FLAC, Label, LIVESETS, Music Videos.
* More 16 years Of archives.
* Support for FTP, FTPS, SFTP and HTTP, HTTPS.
* No waiting time, no captcha, no speed limit, no ads.
* Files that are never deleted, save time and money.
* Overal server’s speed 1 Gb/s.
* Updated on daily scene music releases 0day and old music.
* Easy to use Most of genres are sorted by days.
* Euro-House, Gospel, Gothic, Grunge, Hard Rock, Hardcore, Hardstyle, Heavy Metal, Hip-Hop, Pop, Rock, Texhno, Trance…
Легальні онлайн казино в Україні підтримують гривню та зручні платежі. Офіційні ігрові автомати працюють лише в ліцензійних казино.
Українські інтернет казино мають прозорі умови для гравців. Шукаєте надійну «вітрину» з відгуками та перевіреними ліцензіями? Скористайтесь ліцензійні казино україни. Казино Україна — це найкраще місце для азартного відпочинку.
Онлайн казино Україна підтримує всі популярні платіжні системи. Онлайн казино України пропонують величезний вибір ігор. Українські інтернет казино мають високий рівень довіри. Казино з миттєвим виводом виграшів — вибір досвідчених гравців. Українські онлайн казино з ліцензією КРАІЛ — найнадійніші.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Зацепил раздел про Evinizde Estetik ve Fonksiyonu Birlestirin: Ipuclar? ve Trendler.
Смотрите сами:
https://anadolustil.com
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
mostbet kg mostbet kg
Казино з українським інтерфейсом набагато зручніші для гри. Рейтинг казино Україна допомагає уникнути шахрайських сайтів.
Кращі онлайн казино України мають ліцензію КРАІЛ. Потрібна добірка сайтів із чесною верифікацією та сапортом 24/7? Дивіться кращі онлайн казино україни. Найкращі онлайн казино України пропонують бездепозитні бонуси.
Ліцензійні казино України — це гарантія відповідальної гри. Онлайн казино Україна на гривні приваблює бонусами та кешбеком. Ліцензійні ігрові автомати Україна — це гарантія чесності. Онлайн казино Україна гарантує надійність і комфорт. Онлайн казино Україна з миттєвим виводом коштів — реальність.
экскаватор погрузчик в москве arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-2.ru .
clickmagnet.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
90’lar modas?n? hat?rlayanlar burada m?? Sizlere gecmisin moda ikonu olan donemden ilhamla ipuclar? sundugumuz bu yaz?ya davetlisiniz.
Кстати, если вас интересует Guzellik ve Kozmetik: 90’lar Modas?ndan Ipuclar?, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
https://aynakirildi.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
Ищете своего мастера? Только проверенные тату-художники с впечатляющим портфолио! Любой стиль: от реализма до олдскула. Найдите идеального профи для вашего проекта на нашем сайте https://tattoomastera.ru/
promostream.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
admatrix.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
viralaxis.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
leadvortex.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthshift.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your excellent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
skla
thank you very much for the encouragement
trafficzen.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
онлайн-трансляции https://www.studiya-podkastov-spb4.ru .
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: play Prisma Games online
букмекерская. контора. мостбет. букмекерская. контора. мостбет.
Sizi gecmisten ilham alan guzellik ipuclar?yla dolu bu nostaljik yolculuga davet ediyoruz. 90’lar modas?n?n s?rlar?na goz atal?m m??
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?”, нашел много полезного.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://guzellikturk.com
90’lar modas?n?n guzellik s?rlar?n? kesfetmek, tarz?n?za farkl? bir boyut kazand?rabilir. Denemeye deger degil mi?
MERTHYTJTJ80805MAERWETT
Баскетбол
It’s hard to find well-informed people for this subject, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about!
Thanks
that’s kind of you
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Guzellik ve Kozmetik: Trendler ve Ipuclar?”, там просто кладезь информации.
Ссылка ниже:
https://guzellikturk.com
Tarz?n?zda 90’lar?n esintilerini hissetmeye baslad?g?n?za eminim. Gecmisin izlerini tas?maktan korkmay?n!
leadorbit.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
How to win in Calgary Lottery: Boost your chances by playing consistently, joining lottery pools, and choosing less popular combinations. Remember, winning requires luck and responsible play: local Calgary deals and wins
brandecho.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
boostnexus.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
rankvista.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
markethive.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
adexpand.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickfoundry.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
На casino 7k понравилось отношение к игрокам. Поддержка отвечает быстро, всё объясняют. Деньги выводятся вовремя, без дополнительных проверок https://xn—-8sbalwlcefxak4bw.xn--p1ai/
Решил попробовать 7k casino официальный сайт и не жалею. Всё понятно, интерфейс удобный. Вывод средств прошёл без вопросов и задержек: 7к казино официальный сайт
عرض ادب زهرا خانم
پیشنهاد میدم
سایت پوکر هات
رو جهت پوکر حرفه ای.
این اپ کاربردی ویژگیهای جذابی ارائه میده و برای تگزاس پوکر مناسبه.
از بونوسهاش استفاده کردم و توصیه میکنم چک کنید.
با احترام رضا.
Tarz?n?z? 90’lar?n unutulmaz modas?ndan esinlenerek gunumuze tas?mak ister misiniz? Oyleyse bu yaz?m?z tam size gore!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “Ev Dekorasyonunda S?kl?k ve Fonksiyonellik”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
https://evimsicak.com
Guzellik, gecmisle gunumuz aras?nda bir kopru kurmakt?r. 90’lar?n moda s?rlar?, bu koprunun onemli parcalar?ndan.
adrocket.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
growthsprint.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
marketjet.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
trafficpilot.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rankpilot.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
admomentum.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Кулінарний портал https://infostat.com.ua пошагові рецепти з фото і відео, сезонне меню, калорійність і БЖУ, заміна інгредієнтів, меню неділі і шоп-листи. Кухні світу, домашня випічка, соуси, заготовки. Умные фильтры по времени, бюджету и уровню — готовьте смачно і без стресу.
Портал про все https://ukrnova.com новини, технології, здоров’я, будинок, авто, гроші та подорожі. Короткі гайди, чек-листи, огляди та лайфхаки. Розумний пошук, підписки за темами, обране та коментарі. Тільки перевірена та корисна інформація щодня.
Сайт про все https://gazette.com.ua і для всіх: актуальні новини, практичні посібники, підборки сервісів та інструментів. Огляди техніки, рецепти, здоров’я і фінанси. Удобні теги, закладки, коментарі та регулярні оновлення контенту.
з Днем народження дядьку
adorbit.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://медоптима.рф/
Wondering how to register betwinner or how to create betwinner account? You’ll find all details and screenshots on https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/.
Сайт про все https://kraina.one практичні поради, таблиці та калькулятори, добірки сервісів. Теми – здоров’я, сім’я, фінанси, авто, гаджети, подорожі. Швидкий пошук, збереження статей та розсилка найкращих матеріалів тижня. Простою мовою та у справі.
Інформаційний портал https://presa.com.ua новини, технології, здоров’я, фінанси, будинок, авто та подорожі. Короткі гайди, огляди, чек-листи та інструкції. Розумний пошук, підписки на теми, закладки та коментарі. Тільки перевірені джерела та щоденні оновлення.
Єдиний портал знань https://uaeu.top наука та техніка, стиль життя, будинок та сад, спорт, освіта. Гайди, шпаргалки, покрокові плани, експерти відповіді. Зручні теги, закладки, коментарі та регулярні оновлення контенту для повсякденних завдань.
Peгистpиpyйся ceйчас и пoлyчай пpивeтствeнный пaкeт — до 115 фpиcпинoв и до 800ЕURО бoнyca!
Лучшие игры, быcтрыe выплaты и чecтный сервис на
https://sportrelic.shop/b0fyoa7
DRINKIO приятно удивил высоким уровнем обслуживания и пунктуальностью. Курьер приехал быстро, заказ был аккуратно упакован. Очень удобно, что сервис работает круглосуточно — не нужно подстраиваться под расписание. Качество отличное, сайт понятный и простой в использовании. Заказываю уже не первый раз и всегда доволен. Отличная доставка алкоголя на дом в Москве без задержек – https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/pivo/
Портал корисної інформації https://online-porada.com практичні поради, відповіді експертів, таблиці та шпаргалки. Теми – здоров’я, сім’я, гроші, гаджети, авто та туризм. Швидкий пошук, обране, розсилка найкращих матеріалів тижня. Пишемо просто й у справі.
Сучасний інформаційний https://prezza.com.ua портал: новини, огляди, практичні інструкції. Фінанси, гаджети, авто, їжа, спорт, саморозвиток. Розумний пошук, добірки за інтересами, розсилання найкращих матеріалів. Тільки перевірені джерела та щоденні оновлення.
Інформаційний портал https://revolta.com.ua «все в одному»: коротко і у справі про тренди, товари та сервіси. Огляди, інструкції, чек-листи, тести. Тематичні підписки, розумні фільтри, закладки та коментарі. Допомагаємо економити час та приймати рішення.
https://медоптима.рф/
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
DRINKIO стал для меня настоящей находкой. Не нужно искать открытые магазины, когда всё можно заказать онлайн. Курьер приехал вовремя, всё доставили в идеальном виде. Радует внимательность персонала и быстрая обратная связь. Сервис однозначно заслуживает доверия и повторных заказов, https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/tabak/
На сайте game-computers.ru представлены рекомендации по выбору игровых компьютеров и комплектующих, которые помогут повысить производительность и обеспечить стабильную работу системы. В блоге также можно найти советы по апгрейду и настройке ПК, чтобы сборка оставалась актуальной и эффективной в современных играх.
TopTool https://www.toptool.app/en is a global multilingual tools directory that helps you discover the best products from around the world. Explore tools in your own language, compare thousands of options, save your favorites, and showcase your own creations to reach a truly international audience.
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: Читать
https://nicemerch.ru/
Hey very nice blog!
growthbeacon.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
marketfusion.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficwave.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
adnectar.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
leadcraft.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Оформите займ https://zaimy-69.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
clickmagnetix.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
markettrail.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Owen Configurator — это программный продукт для настройки и программирования параметров различного оборудования АСУ https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/promyshlennoe-zaryadnoe-ustroystvo/
1 740 руб https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/chastotnyye
/шт https://rumikont.com/sertifikaty/
Купить в 1 клик https://rumikont.com/articles/primer-razrabotki-proekta-v-srede-eat-eclipse-dlya-pc-kontrollera/
• Встроенный высокоэффективный корректор мощности • Резистор для подстройки выходного напряжения • Высокая диэлектрическая прочность • Предельно ограниченный пусковой ток • Небольшое время пуска • Низкое помехоизлучение • Выходное реле DC OK https://rumikont.com/articles/uvelichenie-energoeffektivnosti-putem-kompensatsii-reaktivnoy-moshchnosti/
Быстрый просмотр https://rumikont.com/sertifikaty/
Номинальный ток 0 https://rumikont.com/uslugi/
2,1 А Мощность, кВт 0,05 Входное напряжение 220 В Выходное напряжение 24 В Степень защиты оболочки IP20 Рабочая температура, °C -10…+50 https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/istochniki-pitaniya-dlya-ispytatelnykh-stendov-aviatsionnykh-agregatov/
Mosfurshet catering-это сервис по заказу и доставки еды для проведения банкетов, фуршетов, корпоративов, кофе брейков https://shcherbinins.ru/
У нас Вы можете самостоятельно полностью сформировать и рассчитать стоимость меню для проведения свадьбы, дня рождения, юбилея или выездного мероприятия и пикника на природе https://shcherbinins.ru/aboutus
Наши специалисты всегда помогут вам правильно подготовить меню для мероприятия любого масштаба и уровня сложности https://shcherbinins.ru/menu
Разнообразное и аппетитное меню нашей кухни позволит превратить любое мероприятие в незабываемое праздничное торжество!
Недавно мы отмечали 5-летие нашей компании https://shcherbinins.ru/
Что входит в меню?
Всё было просто супер! Брали Сет N5, всем хватило https://shcherbinins.ru/
Всё было свежее и вкусное! Рекомендую! Спасибо и успехов!
Упаковка, вкус , внешний вид!
Все быстро, вежливо, вкусно https://shcherbinins.ru/
Спасибо огромное за оперативность !
https://nicemerch.ru/
нарколог на дом круглосуточно
Оформите займ https://zaimy-78.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
Щоденний дайджест https://dailyfacts.com.ua головні новини, тренди, думки експертів та добірки посилань. Теми – економіка, наука, спорт, культура. Розумна стрічка, закладки, сповіщення. Читайте 5 хвилин – будьте в курсі всього важливого.
Практичний портал https://infokom.org.ua для життя: як вибрати техніку, оформити документи, спланувати відпустку та бюджет. Чек-листи, шаблони, порівняння тарифів та сервісів. Зрозумілі інструкції, актуальні ціни та поради від фахівців.
Регіональний інфопортал https://expertka.com.ua новини міста, транспорт, ЖКГ, медицина, афіша та вакансії. Карта проблем зі зворотним зв’язком, корисні телефони, сервіс нагадувань про платежі. Все важливе – поряд із будинком.
MERYTRH2572937MAMYJRTH
adzenith.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://narkolog-na-dom-spb5.ru/
viralboost.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
digitalsurge.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Практичний довідник https://altavista.org.ua здоров’я, будинок, авто, навчання, кар’єра. Таблиці, інструкції, рейтинги послуг, порівняння цін. Офлайн доступ і друк шпаргалок. Економимо ваш час.
Універсальний інфопортал https://dobraporada.com.ua “на кожен день”: короткі інструкції, таблиці, калькулятори, порівняння. Теми – сім’я, фінанси, авто, освіта, кулінарія, спорт. Персональна стрічка, добірки тижня, коментарі та обране.
Інфопортал про головне https://ukrpublic.com економіка, технологія, здоров’я, екологія, авто, подорожі. Короткі статті, відео пояснення, корисні посилання. Персональні рекоме
clickmagnetix.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
marketnova.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clicknexus.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
rankrocket.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
meilleur casino en ligne: telecharger 1xbet pour android
Портал-довідник https://speedinfo.com.ua таблиці норм та термінів, інструкції «як зробити», гайди з сервісів. Будинок та сад, діти, навчання, кар’єра, фінанси. Розумні фільтри, друк шпаргалок, збереження статей. Чітко, структурно, зрозуміло.
Інформаційний медіацентр https://suntimes.com.ua новини, лонгріди, огляди та FAQ. Наука, культура, спорт, технології, стиль життя. Редакторські добірки, коментарі, повідомлення про важливе. Все в одному місці та у зручному форматі.
Інформаційний сайт https://infoteka.com.ua новини, практичні гайди, огляди та чек-листи. Технології, здоров’я, фінанси, будинок, подорожі. Розумний пошук, закладки, підписки на теми. Пишемо просто й у справі, спираючись на перевірені джерела та щоденні оновлення.
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
Hi all. A buddy of mine who plays a lot recommended this place to me: ancor1. He said the payouts were quick, but I’m always a bit skeptical.
Before I jump in, I wanted to ask if anyone here has personal experience with them? Does it really hold up?
Сучасний інфосайт https://overview.com.ua наука та техніка, стиль життя, спорт, освіта, їжа та DIY. Зрозумілі пояснення, покрокові плани, тести та огляди. Розумні фільтри за інтересами, коментарі, закладки та офлайн-читання – все, щоб заощаджувати час.
Онлайн-журнал https://elementarno.com.ua про все: новини та тенденції, lifestyle та технології, культура та подорожі, гроші та кар’єра, здоров’я та будинок. Щоденні статті, огляди, інтерв’ю та практичні поради без води. Читайте перевірені матеріали, підписуйтесь на дайджест та будьте в темі.
Універсальний онлайн-журнал https://ukrglobe.com про все – від науки та гаджетів до кіно, психології, подорожей та особистих фінансів. Розумні тексти, короткі гіди, добірки та думки експертів. Актуально щодня, зручно на будь-якому пристрої. Читайте, зберігайте, діліться.
Портал корисної інформації https://inquire.com.ua практичні поради, відповіді експертів, таблиці та шпаргалки. Теми – здоров’я, сім’я, гроші, гаджети, авто, туризм. Швидкий пошук, обране, розсилка найкращих матеріалів тижня.
https://internet-leman.ru/
https://mosquitosalsa.com/
http://houmy.ru/
наркологические клиники москва http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru/ .
Про все в одному місці https://irinin.com свіжі новини, корисні інструкції, огляди сервісів і товарів, що надихають історії, ідеї для відпочинку та роботи. Онлайн-журнал із фактчекінгом, зручною навігацією та персональними рекомендаціями. Дізнайтесь головне і знаходите нове.
Ваш онлайн-журнал https://informa.com.ua про все: великі теми та короткі формати – від трендів та новин до лайфхаків та практичних порад. Рубрики за інтересами, огляди, інтерв’ю та думки. Читайте достовірно, розширюйте світогляд, залишайтеся на крок попереду.
Онлайн-журнал https://ukr-weekend.com про все для цікавих: технології, наука, стиль життя, культура, їжа, спорт, подорожі та кар’єра. Розбори без кліше, лаконічні шпаргалки, інтерв’ю та добірки. Оновлення щоденно, легке читання та збереження в закладки.
Онлайн-журнал https://worldwide-ua.com про все: новини, тренди, лайфхаки, наука, технології, культура, їжа, подорожі та гроші. Короткі шпаргалки та великі розбори без клікбейту. Фактчекінг, зручна навігація, закладки та розумні рекомендації. Читайте щодня і залишайтеся у темі.
1 x bet giri? 1 x bet giri? .
Entdecken Sie die besten Weinverkostungen in Wien auf weinverkostung wien umgebung.
In der Stadt finden sich zahlreiche Weinguter, die eine lange Geschichte haben.
Die Weinverkostungen in Wien sind perfekt fur Kenner und Neulinge. Dabei lernen Gaste die Besonderheiten der regionalen Rebsorten kennen.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
In Wien gibt es zahlreiche Lokale und Weinguter, die Verkostungen anbieten. Auch moderne Weinkeller in der Innenstadt bieten exklusive Erlebnisse.
Einige Winzer veranstalten Fuhrungen durch ihre Kellereien. Zusatzlich konnen Gaste direkt beim Erzeuger kosten.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Wiener Weine sind vor allem fur ihre Vielfalt bekannt. Rote Weine wie der Blaue Zweigelt gewinnen immer mehr an Beliebtheit.
Die Bodenbeschaffenheit und das Klima pragen den Geschmack. Dank nachhaltiger Anbaumethoden ist die Qualitat stets hoch.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Eine gute Vorbereitung macht die Verkostung noch angenehmer. Ein neutraler Geschmack im Mund vor der Verkostung verbessert das Erlebnis.
Gruppenverkostungen bringen zusatzlichen Spa?. Gemeinsames Diskutieren uber die Aromen fordert den Austausch.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Viele Veranstaltungen werden von erfahrenen Sommeliers begleitet.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
Das bekannte Heurigenviertel in Grinzing ladt zu gemutlichen Verkostungen ein.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Die Bodenbeschaffenheit und das Klima pragen den Geschmack.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Es empfiehlt sich, langsam zu trinken, um die Nuancen zu schmecken.
promowave.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
leadstreamx.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
trafficburst.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
advelocity.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
ranksphere.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Онлайн-журнал 24/7 https://infoquorum.com.ua все про життя та світ — від технологій та науки до кулінарії, подорожей та особистих фінансів. Короткі нотатки та глибока аналітика, рейтинги та добірки, корисні інструменти. Зручна мобільна версія та розумні підказки для економії часу.
Ваш онлайн-журнал https://informative.com.ua про все: новини, розбори, інтерв’ю та свіжі ідеї. Теми — від психології та освіти до спорту та культури. Зберігайте в закладки, ділитесь з друзями, випускайте повідомлення про головне. Чесний тон, зрозумілі формати, щоденні поновлення.
Онлайн-журнал https://mediaworld.com.ua про бізнес, технології, маркетинг і стиль життя. Щодня — свіжі новини, аналітика, огляди, інтерв’ю та практичні гайди. Зручна навігація, чесні думки, експертні шпальти. Читайте, надихайтеся, діліться безкоштовно.
Щоденний онлайн-журнал https://republish.online про все: від швидкого «що сталося» до глибоких лонґрідів. Пояснюємо контекст, даємо посилання на джерела, ділимося лайфхаками та історіями, що надихають. Без клікбейту – лише корисні матеріали у зручному форматі.
rankpilotx.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clickengine.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Готуємо, прибираємо https://ukrdigest.com прикрашаємо легко. Домашній онлайн-журнал з покроковими рецептами, лайфхаками з прання та прибирання, ідеями сезонного декору, планами меню та бюджетом сім’ї. Зберігайте статті, складайте списки справ та знаходите відповіді на побутові питання.
Все про будинки https://vechorka.com.ua де приємно жити: швидкі рецепти, компактне зберігання, текстиль та кольори, сезонний декор, догляд за речами та технікою, дозвілля з дітьми. Покрокові інструкції, корисні вибірки, особистий досвід. Затишок починається тут – щодня.
Домашній онлайн-журнал https://zastava.com.ua про життя всередині чотирьох стін: швидкі страви, прибирання за планом, розумні покупки, декор своїми руками, зони зберігання, дитячий куточок та догляд за вихованцями. Практика замість теорії, зрозумілі чек-листи та поради, які економлять час та гроші.
Ваш помічник https://dailymail.com.ua по дому: інтер’єр та ремонт, організація простору, здоровий побут, догляд за технікою, рецепти та заготівлі, ідеї для вихідних. Тільки практичні поради, перевірені матеріали та зручна навігація. Зробіть будинок красивим та зручним без зайвих витрат.
https://internet-leman.ru/
Достопримечательности https://rich-house.su/rooms/
Наши партнёры по проведению платежей гарантируют безопасность ваших данных своей мировой репутацией https://rich-house.su/
? Геленджик ? Завтрак включён https://rich-house.su/photos/
Гостиницы в Геленджике https://rich-house.su/about/
Расположен на территории в центре города в живописном месте на берегу моря вдали от шумных магистралей, окружён реликтовыми пицундскими соснами https://rich-house.su/rooms/
Сочетание чистого морского воздуха, аромата пицундской сосны и уютной насыщенной зеленью территории и создаёт уникальную атмосферу единения с природой, расслабленности и спокойствия https://rich-house.su/rooms/
В отеле можно организовать деловую встречу, переговоры и даже собеседование https://rich-house.su/booking/
Для этого предусмотрены бизнес-центр, конференц-зал, специальное оборудование https://rich-house.su/services/
В отеле есть игровые детские комнаты https://rich-house.su/services/
Будьте готовы к тому, что детям будет весело, а вам придется коротать вечер со взрослыми https://rich-house.su/rooms/
Если планируете экскурсии, обратите внимание на экскурсионное бюро отеля https://rich-house.su/services/
Удобно для гостей с ограниченными возможностями: на верхние этажи гостей поднимает лифт https://rich-house.su/services/
Для гостей работает бар https://rich-house.su/about/
Время вспомнить о хлебе насущном! Для гостей работает ресторан https://rich-house.su/services/
Хотите оставаться на связи? В отеле есть бесплатный Wi-Fi https://rich-house.su/booking/
Если вы путешествуете на машине, припарковаться можно будет на парковке ряд https://rich-house.su/restaurants/
Бесплатная отмена https://rich-house.su/photos/
Домашній онлайн-журнал https://ukrcentral.com про розумний побут: планування харчування, прибирання за таймером, екоради, мінімалізм без стресу, ідеї для малого метражу. Завантажені чек-листи, таблиці та гайди. Заощаджуйте час, гроші та сили — із задоволенням.
Журнал для домашнього https://magazine.com.ua життя без метушні: плани прибирання, меню, дитячий куточок, вихованці, міні-сад, дрібний ремонт, побутова безпека. Короткі інструкції, корисні списки та приклади, що надихають. Зробіть будинок опорою для всієї родини.
Ваш провідник https://ukrchannel.com до порядку та затишку: розхламлення, зонування, бюджетний ремонт, кухонні лайфхаки, зелені рослини, здоров’я будинку. Тільки перевірені поради, списки справ та натхнення. Створіть простір, який підтримує вас.
Практичний домашній https://publish.com.ua онлайн-журнал: планинг тижня, закупівлі без зайвого, рецепти з доступних продуктів, догляд за поверхнями, сезонні проекти. Тільки у справі, без клікбейту. Зручна навігація та матеріали, до яких хочеться повертатися.
лучшие агентства seo продвижения http://www.reiting-seo-kompanii.ru/ .
rankedge.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
marketsonic.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
marketcraft.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Медіа для дому https://government.com.ua та офісу: інтер’єр та побут, сімейні питання, цифрові тренди, підприємництво, інвестиції, здоров’я та освіта. Збірники порад, випробування, аналітика, топ-листи. Лише перевірена інформація.
promoverse.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Затишок щодня https://narodna.com.ua ідеї для інтер’єру, зберігання в малих просторах, безпечний побут із дітьми, зелені рішення, догляд за технікою, корисні звички. Інструкції, схеми та списки. Перетворіть будинок на місце сили та спокою.
Все, що важливо https://ua-meta.com сьогодні: будинок та сім’я, кар’єра та бізнес, технології та інтернет, дозвілля та спорт, здоров’я та харчування. Новини, лонгріди, посібники, добірки сервісів та додатків. Читайте, вибирайте, застосовуйте на практиці.
Універсальний гід https://dailyday.com.ua по життю: затишний будинок, щасливі стосунки, продуктивна робота, цифрові інструменти, фінансова грамотність, саморозвиток та відпочинок. Короткі формати та глибокі розбори – для рішень без метушні.
clickexpand.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
adpilot.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickvelocity.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
гидроизоляция подвала изнутри цена м2 http://www.gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/ .
торкретирование стен цена https://www.torkretirovanie-1.ru .
наркологические диспансеры москвы https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru .
1xbet turkiye 1xbet turkiye .
explorethefuture – Love the modern design, feels like a place full of inspiration.
мостбет официальное приложение http://mostbet12037.ru/
Баланс будинку https://press-express.com.ua та кар’єри: управління часом, побутові лайфхаки, цифрові рішення, особисті фінанси, батьки та діти, спорт та харчування. Огляди, інструкції, думки спеціалістів. Матеріали, до яких повертаються.
Платформа ідей https://infopark.com.ua для дому, роботи та відпочинку: ремонт, відносини, софт та гаджети, маркетинг та інвестиції, рецепти та спорт. Матеріали з висновками та готовими списками справ.
Сучасне медіа https://homepage.com.ua «про все важливе»: від ремонту та рецептів до стартапів та кібербезпеки. Сім’я, будинок, технології, гроші, робота, здоров’я, культура. Зрозуміла мова, наочні схеми, регулярні поновлення.
Щоденний журнал https://massmedia.one про життя без перевантаження: будинок та побут, сім’я та стосунки, ІТ та гаджети, бізнес та робота, фінанси, настрій та відпочинок. Концентрат корисного: короткі висновки, посилання джерела, інструменти для действий.
Исправляем компьютеры HP в столице качественно. Диагностика без оплаты. Звоните
hp сервисный центр серебрякова ремонт hp
explorewithpassion – The site feels energetic and inspiring, really liked the clean layout.
Життя у ритмі цифри https://vilnapresa.com розумний будинок, мобільні сервіси, кібербезпека, віддалена робота, сімейний календар, здоров’я. Гайди, чек-листи, добірки додатків.
Про будинок та світ https://databank.com.ua навколо: затишок, сім’я, освіта, бізнес-інструменти, особисті фінанси, подорожі та кулінарія. Стислі висновки, посилання на джерела, корисні формули.
Журнал про баланс https://info365.com.ua затишок та порядок, сім’я та дозвілля, технології та безпека, кар’єра та інвестиції. Огляди, порівняння, добірки товарів та додатків.
Життя простіше https://metasearch.com.ua організація побуту, виховання, продуктивність, smart-рішення, особисті фінанси, спорт та відпочинок. Перевірені поради, наочні схеми, корисні таблиці.
getmoreforshop – Easy navigation and great offers, perfect combo for quick shopping.
Every weekend i used to pay a visit this website, as i wish for
enjoyment, for the reason that this this web site conations actually good funny data too.
Thank you very much for the encouragement
I represent the investment community. We help talented projects find funding and experts to help them grow. If you have an idea or a ready-made business model, let’s discuss the possibilities for cooperation.
wa.me/+380508607093
Thank you
startsomethingtoday – Love the name and the message, layout feels simple and fresh.
We bring you latest Gambling News, Casino Bonuses and offers from Top Operators, Online Casino Slots Tips, Sports Betting Tips, odds etc – jackpotbetonline.com
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
dreamfindshub – Nice layout and visuals, found a few items that really stood out.
Всё просто и удобно — выбрал, оплатил и ждёшь. Курьер приехал быстро, упаковка целая, напитки охлаждённые. Цены разумные, без наценок за срочность. Теперь если нужна алкоголь доставка москва круглосуточно, обращаюсь только сюда https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
гидроизоляция подвала гидроизоляция подвала .
торкретирование стен цена за м2 https://torkretirovanie-1.ru .
makelifesimpler – Nice clean interface, delivers exactly what the name promises.
Хочешь халяву? https://tutvot.com – сервис выгодных предложений Рунета: авиабилеты, отели, туры, финпродукты и подписки. Сравнение цен, рейтинги, промокоды и кэшбэк. Находите лучшие акции каждый день — быстро, честно, удобно.
Эффективное лечение геморроя у взрослых. Безопасные процедуры, комфортные условия, деликатное отношение. Осмотр, диагностика, подбор терапии. Современные методы без госпитализации и боли.
Intelligent Crypto https://tradetonixai.com Investments: asset selection based on goals, rebalancing, staking, and capital protection. Passive income of 2-3% of your deposit with guaranteed daily payouts.
Обзоры игровых ПК на https://game-computers.ru помогут быстро определиться с оптимальным вариантом игровой сборки под любые потребности. Здесь собраны обзоры популярных моделей, сравнения комплектующих и советы по выбору систем охлаждения, блоков питания и корпусов.
shopfornewthings – The design feels modern and welcoming, will come back for more.
Решили устроить праздник, а магазины уже не работали. Заказали алкоголь онлайн и получили через 30 минут. Удобно, быстро, качественно — просто супер. Теперь если нужна доставка алкоголя без выходных, только сюда https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
trendyfindsonline – Found a few great pieces already, the layout makes it easy to explore.
clickchain.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
exploreandcreate – Well-organized and modern, the navigation is simple and intuitive.
buildabetterworld – Positive theme and user-friendly design, I’ll definitely visit again.
everydaystylecorner – Nice layout overall, gives a classy yet simple impression.
styleforliving – The product display looks great, and everything loads quickly.
trafficlaunch.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
growwithconfidence – Clean, bold, and uplifting design, feels great to explore this site.
modernlivingtrend – Great first impression, the visuals and flow feel professional.
marketblaze.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
discoveryourpotential – The layout looks modern and easy to use, smooth experience overall.
adrise.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
getinspireddaily – Such a positive vibe, this site instantly lifts your mood while browsing.
globalstylemarket – The site feels professional and stylish, makes shopping easy and fun.
rankhive.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
dreambelieveachieve – The positivity here stands out, love how motivational it feels.
1x bet 1x bet .
promostreamx.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
вывод из запоя москва клиника https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru .
connectlearncreate – Inspiring and interactive site, perfect for learning and creating new ideas.
admagnet.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
exploreandcreate – Nice balance of visuals and content, feels modern and professional.
modernlivingtrend – Good mix of content and aesthetics, everything feels well balanced.
dreambuycollection – Smooth browsing and stylish setup, everything feels nicely organized.
buildabetterworld – The message here feels powerful and inspiring, love the positive tone.
trendyfindsonline – The site has a clean and catchy look, definitely feels professional.
everydaystylecorner – I like how the design matches the everyday lifestyle theme perfectly.
styleforliving – Sleek and modern look, really fits the stylish lifestyle theme.
Howdy just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you
know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not
sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried
it in two different browsers and both show the same results.
Thanks for the observation
growwithconfidence – Everything looks inspiring and professional, great name and presentation.
discoveryourpotential – Clean design with a motivating tone, feels professional yet personal.
getinspireddaily – Such a positive vibe, this site instantly lifts your mood while browsing.
globalstylemarket – Smooth navigation and well-organized categories, browsing is effortless.
thetrendystore – Stylish vibe and smooth layout, great place for fashion lovers.
ремонт подвального помещения ремонт подвального помещения .
inspirechangealways – Love the message behind this one, uplifting and well designed.
торкретирование бетона цена м2 torkretirovanie-1.ru .
uniquelifestylehub – Stylish and modern, feels like a curated hub for unique lifestyle inspiration.
https://vsemetonado.ru/
everydayshoppingzone – Lots of variety here, looks like a solid everyday go-to shop.
https://vsemetonado.ru/
Искал лучшие нейросети для генерации изображений, и подборка дала полную картину рынка. Остановился на одном сервисе для основной работы, другие использую для экспериментов. Очень ценный материал: ии для генерации изображений
fashionloverszone – Trendy and visually appealing, great spot for fashion enthusiasts.
trendyfindshub – The latest styles stand out nicely, super easy to browse.
findsomethingnew – Clean visuals and fast loading, browsing here feels smooth and effortless.
discovergreatdeals – Fast loading pages and neat structure, great shopping experience overall.
connectdiscovergrow – Great flow from section to section, smooth browsing experience overall.
getinspiredtoday – The tone is warm and positive, perfect for daily inspiration seekers.
liveandexplore – Love how simple and adventurous the site feels, really fun to use.
styleforliving – The whole vibe feels classy and calm, perfect for lifestyle browsing.
modernlivingstyle – The name suits the design well, everything feels modern and stylish.
liveandexplore – Bright and adventurous design, really gives off positive travel vibes.
makelifesimpler – Everything loads quickly and feels intuitive, exactly what simplicity means.
theworldawaits – Love the theme and colors, everything feels inviting and full of energy.
trafficcore.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clickempire.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
adengine.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
promojet.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
promocore.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Азартные игры онлайн игровые автоматы бесплатно Ваш пропуск в мир высоких ставок и крупных побед. Эксклюзивные игры, турниры с миллионными призами и персональная служба поддержки. Играйте по-крупному!
Лучшие онлайн казино биф казино бонусы захватывающие игровые автоматы, карточные игры и live-казино на любом устройстве. Быстрый старт, честная игра и мгновенные выплаты.
Онлайн казино биф казино Насладитесь атмосферой роскошного казино не выходя из дома! Интуитивный интерфейс, безопасные платежи и щедрая программа лояльности. Сделайте свою игру выигрышной!
trafficedge.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Ищешь автоматы? покердом зеркало лучшие азартные развлечения 24/7. Слоты, рулетка, покер и живые дилеры с яркой графикой. Регистрируйтесь, получайте приветственный бонус и начните выигрывать!
Хочешь азарта? болливуд казино отзыв мир азарта и больших выигрышей у вас в кармане! Сотни игр, щедрые бонусы и мгновенные выплаты. Испытайте удачу и получите незабываемые эмоции прямо сейчас!
marketlaunch.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
discovergreatdeals – Fast loading pages and neat structure, great shopping experience overall.
styleforliving – Smooth navigation and nice visuals, overall a very pleasant experience.
learnandgrowtoday – Really smooth experience, everything here feels useful and well made.
connectdiscovergrow – Positive energy throughout, everything feels calm and beautifully presented.
findsomethingnew – Minimal yet stylish, it’s easy to stay engaged while browsing here.
modernlivingstore – Sleek design and easy navigation, makes browsing modern living items enjoyable.
getinspiredtoday – Everything’s so easy to navigate, great balance between visuals and text.
liveandexplore – Bright visuals and smooth layout, everything feels natural and engaging.
modernlivingstyle – I like how professional and polished the entire site looks.
liveandexplore – Smooth navigation and modern style, overall a pleasant experience.
makelifesimpler – Everything loads quickly and feels intuitive, exactly what simplicity means.
theworldawaits – Bright, motivating, and easy to browse — a really pleasant experience.
discoveramazingthings – Beautiful site with uplifting energy, everything feels inspiring and fun to browse.
Хочешь рискнуть? вход пинап редлагает широкий выбор игр, быстрые выплаты и надежные способы пополнения депозита.
Официальный сайт pin up казино встречает удобным интерфейсом и обширным каталогом: слоты, лайв-казино, рулетка, турниры. Вывод выигрышей обрабатывается быстро, депозиты — через проверенные и защищённые способы. Акции, бонусы и поддержка 24/7 делают игру комфортной и понятной.
Официальный casino pokerdom: казино, покер, вход и скачивание слотов. Сотни слотов, лайв-столы, регулярные ивенты, приветственные бонусы. Вход по рабочему зеркалу, простая регистрация, безопасные депозиты, быстрые выплаты. Скачай слоты и играй комфортно.
Онлайн-казино vodka casino регистрация игровые автоматы от ведущих производителей. Эксклюзивный бонус — 70 фриспинов! Смотрите видеообзор и отзывы реальных игроков!
bestvaluecollection – Good range of products, prices seem fair and competitive too.
Работа брокера оставила только положительные впечатления, всё чётко и вовремя – https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel11.ru/
shopwithstylehub – Fun and stylish site, everything looks modern and well presented.
На официальном сайте кент зеркало вы найдёте слоты, рулетку, лайв-столы и тематические турниры. Вывод средств осуществляется оперативно, депозиты принимаются через проверенные механизмы. Безопасность, прозрачные условия, бонусные предложения и поддержка 24/7 обеспечивают спокойную и удобную игру.
All the latest here: https://www.06274.com.ua/list/527111
Нужен тахеометр? аренда тахеометра Sokkia по выгодной цене. Современные модели для геодезических и строительных работ. Калибровка, проверка, доставка по городу и области. Гибкие сроки — от 1 дня. Консультации инженеров и техническая поддержка.
Официальный сайт казино: играйте онлайн с бонусами и быстрыми выплатами. Вход в личный кабинет Вавада, выгодные предложения, мобильная версия, игровые автоматы казино — круглосуточно.
Лучшее онлайн казино вавада казино играть онлайн с более чем 3000 игр, высокими выплатами и круглосуточной поддержкой.
shopthemoment – Trendy design and clear visuals, makes browsing super enjoyable.
findyourmoments – Beautiful concept and elegant look, I enjoyed exploring this one.
yourcreativejourney – Love the artistic vibe here, everything feels inspiring and original.
findyourmoments – Truly pleasant design, makes you want to slow down and enjoy more.
findyourpathnow – Encouraging theme and soft visuals, love how peaceful it feels.
freshfashioncorner – Cool theme and well-structured design, gives off great shopping vibes.
uniquelifestylehub – The layout stands out, feels classy and well put together.
shopwithstylehub – Love the variety here, everything feels fresh and tastefully arranged.
freshfashioncorner – Cool theme and well-structured design, gives off great shopping vibes.
findjoytoday – The design is uplifting and smooth, perfect for spreading good energy.
simplevalueplace – Fast-loading and clean pages, really easy to explore around.
explorethefuture – Modern, clean, and full of energy, perfect for curious minds.
yourmomentstarts – The design feels modern and inspiring, very easy to browse around.
connectwithideas – Clean layout and inspiring content, perfect for exploring new concepts.
yourcreativejourney – Love the artistic vibe here, everything feels inspiring and original.
ranklift.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
rankfuel.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
growthsphere.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
yourmomentstarts – The color scheme is calming and bright, great balance for visitors.
adshift.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
marketgenius.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
growthwave.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
digitalboost.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
findyourpathnow – The concept is beautiful and the site feels easy to explore.
findyourmoments – Lovely concept and warm design, makes browsing feel calm and joyful.
freshfashioncorner – Fantastic user experience, simple interface but full of fresh style.
freshfashioncorner – Super trendy vibe, love the bright colors and modern design.
Как юридическое лицо, ценим качество работы и точность сроков. Здесь всё на высшем уровне. Очень довольны: https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel11.ru/
shopwithstylehub – Very trendy look and smooth flow, makes shopping fun and effortless.
findjoytoday – The design is uplifting and smooth, perfect for spreading good energy.
simplevalueplace – Great experience overall, everything feels practical and thoughtfully built.
explorethefuture – Clean layout and engaging content, really captures the excitement of the future.
dreambuyoutlet – Great presentation and fast loading, enjoyable shopping experience overall.
ranklift.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
rankfuel.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
findjoytoday – Positive and uplifting, the site really feels cheerful and motivating.
adshift.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
growthsphere.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
marketgenius.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthwave.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
digitalboost.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
findjoyeveryday – Positive energy throughout, design fits the uplifting name perfectly.
makeimpacttoday – Motivational and well-organized, great for users wanting to take action.
clickmastery.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
nextlevelmarketing.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
convertmore.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clicktogrow.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
dreambuycollection – Amazing selection of products, makes online shopping feel effortless and fun.
clickdriven.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
purevalueoutlet – Great interface and product variety, perfect blend of value and style.
startanewjourney – Feels warm, positive, and easy to use — loved exploring it.
adverto.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
dreamfindshub – Such a creative and positive place, really love the content here.
classychoiceoutlet – Great selection of modern and timeless pieces, definitely worth visiting.
fashionloverszone – Everything feels classy and modern, definitely a go-to for fashion updates.
shopfornewthings – Really impressed with the layout and product selection, great work.
getmoreforshop – Love how easy it is to navigate and find good offers.
engagenow.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
trendingstyleworld – Modern look and great energy, ideal for anyone who loves style.
inspirechangealways – Very motivating site, love the positive energy and smooth layout.
clickmastery.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
dreambuyoutlet – Smooth browsing experience, stylishly presented products make shopping enjoyable.
nextlevelmarketing.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
clicktogrow.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
convertmore.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickdriven.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
dreambuycollection – Perfect mix of style and simplicity, makes online shopping truly fun.
everydayshoppinghub – Very convenient and easy to use, makes daily shopping simple and smooth.
adverto.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
trendingstyleworld – Love the trendy collections, layout is simple but very appealing.
engagenow.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
startanewjourney – Feels warm, positive, and easy to use — loved exploring it.
purevalueoutlet – Great selection of items, everything feels organized and easy to find.
fashionloverszone – Found some stylish options here, very impressed with the collection.
everydayshoppingzone – Great place for daily shopping, everything feels easy and convenient.
dreamfindshub – The layout looks clean and fresh, makes it fun to discover.
classychoiceoutlet – Everything here feels premium and well-organized, easy to find what I like.
shopfornewthings – Great variety of products, found some really cool new stuff today.
getmoreforshop – Simple and straightforward experience, I’ll definitely be coming back soon.
changeyourfuture – Inspiring design and positive message, really motivates you to take action.
changeyourdirection – Fresh and inspiring layout, really encourages exploration and new perspectives.
Could the escalating inflation rates, as observed in recent years, potentially reshape societal norms regarding savings, spending, and even social interactions, leading to a fundamental shift in the way we perceive and manage wealth? our website, we furnish up to date and the most talented Crypto Analysis with AI through despite your business] crypto.kodx.uk
ok
trendyfindshub – Love the trendy vibes, the site is simple yet stylish to browse.
brightfashionfinds – Colorful and trendy, makes browsing fashion items enjoyable and exciting.
clickedge.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
digiloom.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
leadmagnet.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
metareach.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
resultsfirst.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
yourdailyshoppinghub – Nicely structured site, makes daily shopping easier and more enjoyable.
clicksthatsell.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
highroi.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Read the extended version: https://twapewa.com.na/kupit-akkaunty-fejsbuk-i-biznes-menedzhery-bm-raff-2/
рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом .
рулонные шторы виды механизмов https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru .
clickedge.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
1xbet g?ncel http://1xbet-giris-2.com/ .
birxbet giri? http://1xbet-giris-8.com .
1xbet mobi http://www.1xbet-giris-4.com .
discoverandcreate – Creative and engaging, perfect place to find ideas and inspiration.
digiloom.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
leadmagnet.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
metareach.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
resultsfirst.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
clicksthatsell.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
highroi.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Could we be overlooking lesser-known factors such as the influence of technological advancements, geopolitical tensions, or even environmental degradation on the current inflation rates and their potential to further escalate the situation? our website, we offer present-day and the best IT solutions to go to your business] links.kodx.uk
exactly
findperfectgift – Found the perfect present here, love how organized and simple it feels.
explorewhatspossible – Encouraging design and great usability, makes exploring ideas very enjoyable.
createbettertomorrow – Beautifully made with a strong message about creating positive change.
discoverhomeessentials – Great balance of style and utility, perfect for everyday home shopping.
discovergreatideas – Inspiring layout and easy navigation, loved browsing through everything here.
thepowerofgrowth – Love the motivational energy; it really encourages continuous learning and improvement.
thinkcreateachieve – Truly inspiring platform, encourages exploration, creation, and personal achievement every day.
staycuriousdaily – Great message behind the brand, always stay open to new possibilities.
bestvaluecollection – Excellent deals and easy navigation, really makes shopping enjoyable.
discoverinfiniteideas – Love the focus on endless ideas and innovation, very refreshing concept.
everydayfindsmarket – Feels inviting, perfect for finding practical and trendy everyday products.
Read the extended version: http://www.dramatrailers.com/fejsbuk-kupit-akkaunt-rukovodstvo-po-vyboru-i/
findyourdreamplace – Beautiful visuals and easy navigation, makes exploring dream locations enjoyable.
discoverhomeessentials – Love the simplicity and product range, exactly what a home shop should be.
thinkcreateachieve – Truly inspiring platform, encourages exploration, creation, and personal achievement every day.
explorewhatspossible – Great vibe and smooth layout, browsing this site felt truly motivating.
findperfectgift – So many unique gift ideas, really enjoyed exploring this site today.
createbettertomorrow – Such an encouraging theme; every page feels positive and meaningful.
discovergreatideas – The content feels bright and positive, great mix of style and ideas.
thepowerofgrowth – Great blend of motivation and meaning; truly a site that uplifts visitors.
staycuriousdaily – Feels like a daily reminder to explore new things and ideas.
discoverinfiniteideas – A motivational and creative concept that encourages open-minded exploration.
everydayfindsmarket – I like how approachable it sounds, makes online shopping feel easy.
imaginelearnexplore – Inspiring and informative, great site for learning and discovering new things.
Ирина (Marketing & PR Director)
Добрый день https://shcherbinins.ru/
Хочу выразить благодарность за организацию вчерашнего мероприятия https://shcherbinins.ru/aboutus
Еда была вкусна, официанты внимательны, все было качественно и достойно, спасибо https://shcherbinins.ru/contacts
Полное оформление помещения, включая посуду, мебель и столовые приборы https://shcherbinins.ru/
Профессиональных официантов https://shcherbinins.ru/aboutus
Полный контроль над процессом, чтобы вам не пришлось думать о деталях https://shcherbinins.ru/contacts
Техническая организация https://shcherbinins.ru/menu
Мы готовим из свежих продуктов, закупаемых у проверенных поставщиков, что гарантирует 100% качество всех блюд https://shcherbinins.ru/contacts
Наши преимущества:
Корпоративные мероприятия Частные мероприятия https://shcherbinins.ru/uslugy
Он поддерживает следующие функции:
Мощность, кВт 0,24 Входное напряжение 220 В Выходное напряжение 24 В https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/istochniki
Серия DVPPS Источники питания для контроллеров Delta мощностью 24/48 Вт DVPPS — Источники питания для контроллеров Delta мощностью 24/48Вт https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/chastotnyye
Подробнее https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/chastotnyye
различные реле состояния для контроля состояния; длительное время автономной работы благодаря встроенной защите от глубоких разрядов и зарядке аккумулятора с температурной компенсацией; исключительно компактная конструкция шириной всего 66 мм https://rumikont.com/uslugi/
DRM https://rumikont.com/preobrazovateli/vypryamitel
PMT2 – Промышленные источники питания для монтажа на панель https://rumikont.com/articles/komplektnyy-vypryamitelno-invertornyy-preobrazovatel-kvip/
рулонные шторы купить москва недорого рулонные шторы купить москва недорого .
автоматические рулонные шторы автоматические рулонные шторы .
birxbet birxbet .
1xbet ?yelik http://1xbet-giris-2.com/ .
1xbet t?rkiye giri? 1xbet t?rkiye giri? .
smartfashionboutique – Beautifully curated items and smooth browsing, feels premium and trendy.
yourmomenttoshine – Bright and uplifting, really encourages users to feel confident and motivated.
hyperclick.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – приобрести городской интернет-пакет в спальных районах
https://internet36.ru/ – ознакомиться доступные технологические программы для отдыха в Воронеже
clickorbit.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickifypro.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickfusion.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickmetric.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
techify.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
exploreinnovativeideas – Great place to discover fresh ideas, very clean and inspiring layout.
codespark.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
stayfocusedandgrow – Positive and clean layout, perfect for personal growth and focus.
changeyourperspective – Modern and clean design, perfect for exploring fresh ideas and viewpoints.
provideri-voronezha.ru/ – ознакомиться с подключением стабильный интернет-решение от опытных сервисов
hyperclick.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickorbit.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickifypro.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickfusion.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://www.internet36.ru – оформить быстро интернет-доступ с гарантией в Воронеже
clickmetric.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
techify.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
findyourtrend – Stylish and trendy, makes discovering new fashion items simple and fun.
freshfashionmarket – Bright and trendy design, makes shopping for new fashion pieces enjoyable.
codespark.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Visit Our Company Page
рулонные шторы на электроприводе рулонные шторы на электроприводе .
1xbet resmi sitesi 1xbet-giris-2.com .
автоматическая рулонная штора http://www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru .
казахтелеком астана – подключить премиальный высокоскоростной интернет для игр и стриминга
1 xbet http://1xbet-giris-4.com .
groweverymoment – Encourages focus and continuous growth, a very motivating concept overall.
urbanwearstudio – Trendy and stylish, excellent hub for urban fashion and modern streetwear.
findyournextgoal – Such a powerful concept, helps keep people focused on progress.
everydaystylemarket – The name feels modern and relatable, perfect for daily wear shoppers.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Official Website for Custom Yacht Construction
creativityneverends – Love the concept, it instantly sparks motivation and artistic energy.
discoveramazingfinds – Perfect name for a modern online marketplace full of great selections.
simplefashioncorner – Feels like a perfect place for clean, classic, and stylish looks.
findyourpath – Perfect for a brand that focuses on inspiration, direction, and positivity.
makeimpacteveryday – Inspiring name, really motivates people to make a difference constantly.
learnsomethingnewtoday – Wonderful idea, it promotes curiosity and keeps life interesting every day.
dreambiggeralways – Feels like a daily mantra, perfect for dreamers and go-getters alike.
https://internet-v-kazani.ru/ – посмотреть тарифы семейные инновационные форматы в Казани
https://domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – приобрести качественный технологичный интернет-комфорт для бизнеса Казани
интернет провайдеры Воронежа по адресу дома Воронеж – проверить доступных сетевых сервис-провайдеров по адресу дома в Воронеже
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Safe Entry Explorer Yacht Creators
dailyvalueoutlet – Great deals and smooth browsing, perfect for everyday shopping and savings.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Comprehensive Safe Site Oceangoing Craft Construction
https://luckypari-uz.cc – ресурс с подтвержденной лицензией
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Site Entry Custom Aluminum Yacht Builder
groweverymoment – Feels motivating and optimistic, a great reminder to grow constantly.
discoveramazingfinds – Love the name, it instantly makes me curious to see what’s inside.
modernlivingstore – Sleek design and easy navigation, makes browsing modern living items enjoyable.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Site URL Blue Water Sailboat Builder
рейтинг провайдеров Воронежа – посмотреть ежеквартальный опрос провайдеров с отзывами абонентов
http://www.podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru – подобрать индивидуально бесперебойный интернет-канал для казанцев
https://www.provideri-voronezha.ru/ – изучить требования интернет-провайдер и кабельное телевидение в офисах Воронежа
newseasonfinds – Fresh, modern, and well-organized, makes exploring seasonal items enjoyable.
everydaystylemarket – The name feels modern and relatable, perfect for daily wear shoppers.
findyournextgoal – Feels uplifting and positive, definitely sparks motivation and clarity.
creativityneverends – Feels vibrant and full of inspiration, perfect for creators and dreamers.
simplefashioncorner – I like how calm and refined the name sounds, very inviting vibe.
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Encrypted Portal Metal Hull Experts
findyourpath – Excellent message, encourages everyone to grow and trust their journey.
makeimpacteveryday – I like how this name blends positivity with action, very inspiring.
learnsomethingnewtoday – Wonderful idea, it promotes curiosity and keeps life interesting every day.
trendingstyleworld – Love the style and variety here, trendy yet easy to explore.
dreambiggeralways – Motivational and timeless, reminds me to never stop believing in more.
melbet-kz.biz/ – платформа с кэшированием
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Learn More Our Digital Catalog
quantumclick.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
inspirechangealways – Positive and motivational, great site for inspiration and self-improvement ideas.
innoclick.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
nanotech.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
raised saloon sailboat – heavy-duty all-round main saloon sailboat layout
promopulse.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
learnsomethingamazing – Inspiring and educational, perfect site for daily learning and ideas.
smartlogic.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
http://www.domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – подключить с настройкой современный интернет-соединение с покрытием в Воронеже
https://www.internet-v-kazani.ru – подключить круглосуточно интернет-тариф с поддержкой в Казани
https://provideri-kazani.ru – приобрести пакетом fiber-optic интернет-успех с поддержкой в Казани
Discover exquisite Austrian wines at weinverkostung in wien and immerse yourself in Vienna’s vibrant wine culture.
Wien begeistert mit seiner langen Weintradition und zeitgenossischen Angeboten. Die Region ist bekannt fur ihren exzellenten Wei?wein, besonders den Grunen Veltliner. Jahrlich stromen Tausende von Besuchern in die Weinkeller der Stadt.
Das milde Klima und die mineralreichen Boden begunstigen den Weinbau. Das gibt den Wiener Weinen ihren unverwechselbaren Charakter.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
In Wien gibt es mehrere renommierte Weinregionen, wie den Nussberg oder den Bisamberg. Hier reifen einige der besten osterreichischen Weine heran. Familiengefuhrte Weinguter bieten oft Fuhrungen und Verkostungen an. Dabei lernt man viel uber die Herstellung und Geschichte der Weine.
Ein Besuch im Weingut Wieninger oder im Mayer am Pfarrplatz lohnt sich. Sie sind bekannt fur ihre ausgezeichneten Jahrgange.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Weinverkostung**
Eine klassische Wiener Weinverkostung beginnt meist mit einer Kellertour. Die Winzer erklaren gerne ihre Arbeitsschritte. Danach folgt die Verkostung unterschiedlicher Weine. Jeder Wein wird sorgfaltig prasentiert und verkostet.
Haufig werden die Weine mit lokalen Kasesorten oder Brot serviert. Diese Kombination ist ein Highlight fur Feinschmecker.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Um das Beste aus einer Weinverkostung in Wien herauszuholen, sollte man vorher buchen. Fruhzeitige Reservierungen garantieren einen reibungslosen Ablauf. Zudem lohnt es sich, auf die Jahreszeiten zu achten. Im Winter bieten viele Weinguter gemutliche Kellerveranstaltungen.
Ein guter Tipp ist auch, ein Notizbuch mitzubringen. Viele Gaste schatzen spater die Erinnerungen an die Verkostung.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Daher gedeihen hier besonders aromatische Rebsorten.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
Hier reifen einige der besten osterreichischen Weine heran.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Wiener Weinverkostung**
Die Winzer erklaren gerne ihre Arbeitsschritte.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Fruhzeitige Reservierungen garantieren einen reibungslosen Ablauf.
—
**Hinweis:** Durch Kombination der Varianten aus den -Blocken konnen zahlreiche einzigartige Texte generiert werden, die grammatikalisch und inhaltlich korrekt sind.
raised saloon sailboat – spacious high main saloon family cruiser feature
modernlivingtrend – Stylish, modern, and smooth experience from start to finish.
Yelkovan 56 – premium 17-meter explorer yacht with pricing
melbet-kz.us/ – ресурс с быстрой загрузкой
quantumclick.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
explorer sailboat for sale – traditional explorer sailboat direct from yard
innoclick.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
nanotech.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
techpilot.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
learnsomethingdaily – Clean and informative, perfect for daily learning and personal growth.
https://www.internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – подобрать безлимитный интернет в спальных районах
https://internet36.ru – оформить высокотехнологичный интернет-надежность с покрытием в Воронеже
promopulse.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
theartofgrowth – Inspiring and thoughtful layout, perfect for personal growth and learning.
steel sailboat builder – custom steel boat craftsman for world voyages
Портрет по фотографии на заказ https://moi-portret.ru
Need TRON Energy? buy trx energy Affordable for your wallet. Secure platform, verified sellers, and instant delivery. Optimize every transaction on the TRON network with ease and transparency.
Energy for TRON buy trx energy instant activation, transparent pricing, 24/7 support. Reduce TRC20 fees without freezing your TRX. Convenient payment and automatic energy delivery to your wallet.
Туристический портал https://cmc.com.ua авиабилеты, отели, туры и экскурсии в одном месте. Сравнение цен, отзывы, готовые маршруты, визовые правила и карты офлайн. Планируйте поездку, бронируйте выгодно и путешествуйте без стресса.
smartlogic.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Digital Location Metal Hull Specialist
лучшие провайдеры интернета в Москве – подобрать детальный опрос операторов связи Московского региона с результатами
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Online Interface Aluminum Cruiser Manufacturing
французское seo цена http://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru .
internet seo http://optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru/ .
цифровой маркетинг статьи цифровой маркетинг статьи .
блог о маркетинге блог о маркетинге .
https://www.podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru/ – узнать больше надежный интернет и развлекательные пакеты в частных домах
https://www.provideri-voronezha.ru – оформить заявку надежный интернет в частных домах
yelkovanyachts.com – Shipyard Site Home
purevalueoutlet – Inspiring and interactive site, perfect for learning and creating new ideas.
trendforlife – Very fashionable and clean site, makes exploring trends effortless.
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Website Explorer Boat Production
simplebuyhub – Found everything I needed quickly, really smooth shopping experience.
starttodaymoveforward – Strong, forward-thinking name full of energy and inspiration.
budgetfriendlypicks – Great collection for smart shoppers who value both price and quality.
styleandchoice – Combines simplicity and elegance in one perfect domain.
discoverhiddenopportunities – The name itself sparks motivation to explore and learn more.
trendywearstore – Fashion-forward choices that make shopping online really enjoyable.
Строительный портал https://6may.org новости отрасли, нормативы и СНИП, сметы и калькуляторы, BIM-гайды, тендеры и вакансии. Каталоги материалов и техники, база подрядчиков, кейсы и инструкции. Всё для проектирования, строительства и ремонта.
Всё для стройки https://artpaint.com.ua в одном месте: материалы и цены, аренда техники, каталог подрядчиков, тендеры, сметные калькуляторы, нормы и шаблоны документов. Реальные кейсы, обзоры, инструкции и новости строительного рынка.
интернет казахстан – онлайн ввести в эксплуатацию безлимитный интернет с бесплатным монтажом
modernhomecorner – Love the modern designs and home decor ideas shared here daily.
urbanchoicehub – Trendy urban style and clean design, makes exploring fashion easy and fun.
explorer sailboat for sale – heavy-duty oceangoing sailboat custom built
Новостной портал https://novosti24.com.ua с фокусом на важное: оперативные репортажи, аналитика, интервью и факты без шума. Политика, экономика, технологии, культура и спорт. Удобная навигация, персональные ленты, уведомления и проверенные источники каждый день.
Pure Value Shop – Inspiring and interactive site full of new ideas.
leadsrocket.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
targetboost.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
engagehub.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
leadgenius.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Дізнайтесь на сайті: https://ukr-weekend.com/budivnytstvo.html
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Builder’s Portal for Steel Sailboats
domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – подобрать современный интернет-надежность в центре Воронежа
https://www.provideri-kazani.ru/ – прочитать отзывы интернет-технологии и ТВ в Казани
internet36.ru – подобрать тариф домашний интернет-пакет для бизнеса Воронежа
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Total Secure Access Custom Cruiser Creator
Seattle, known for its stunning skyline and vibrant culture, is also a bustling hub of professional and personal activities. The city’s fast-paced lifestyle necessitates reliable and luxurious transportation options that not only meet the demands of time but also provide a comfortable and stylish journey. This is where the importance of a reliable Seattle SUV car service comes into play. Whether it’s for a crucial business meeting, a city tour, or a special event, a seattle suv car service is undeniably an excellent choice. These services offer a fleet of high-end, luxury SUVs that are not only spacious and comfortable but also equipped with the latest technology for a smooth and enjoyable ride. The drivers are professional, punctual, and well-versed with the city’s routes, ensuring you reach your destination on time and in style. Moreover, these services prioritize customer satisfaction and safety above all else. They maintain their vehicles in top-notch condition and adhere to all safety standards. The SUVs are regularly serviced and cleaned, and they come with modern safety features, providing passengers with a sense of security and peace of mind. Booking a Seattle SUV car service is also incredibly convenient. Most companies offer online booking options, allowing you to schedule your ride in advance and avoid last-minute hassles. You can also choose the type of SUV you prefer, ensuring your ride aligns with your specific needs and preferences. In conclusion, a Seattle SUV car service is the epitome of luxury, comfort, and reliability. It’s a practical solution for those who value their time and comfort. Whether you’re a resident or a visitor, it’s a great way to experience the city in style and luxury. So, the next time you’re in Seattle, consider booking a luxury SUV service for your transportation needs. It’s not just about getting from point A to point B; it’s about the journey and the experience.
growtharena.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
brandshine.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
styleandchoice – Highlights empowerment and personal taste beautifully.
simplebuyhub – Affordable prices, great layout, and a really pleasant experience.
findmotivationtoday – Positive and inspiring layout, really motivates and encourages action every day.
yourstylezone – Stylish, modern, and user-friendly, love the smooth browsing experience.
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Protected Site Yelkovan Yachts
лучший интернет провайдер в Москве для квартиры – посмотреть лидирующего компанию сетевого доступа в Москве через анализ отзывов
leadsrocket.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
targetboost.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Discover Our Company Page
engagehub.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
leadgenius.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
https://internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru/ – посмотреть рейтинг базовые сетевые типы в городе Воронеж
domashniy-internet-kazan.ru/ – узнать больше безопасный интернет-сервис от опытных сервисов
starttodaymoveforward – Memorable and meaningful — perfect for any self-growth platform.
budgetfriendlypicks – Love how this site offers affordable and trendy product choices.
топ провайдеров интернета Казани – ознакомиться независимый рейтинг компаний по версии специалистов
discoverhiddenopportunities – Beautifully captures the essence of growth and hidden potential.
trendywearstore – Fashion-forward choices that make shopping online really enjoyable.
[url=https://yelkovanyachts.com/]yelkovanyachts.com[/url] – Builder’s Website Start Page
findnewinspiration – Bright, clean, and motivating, perfect for discovering fresh ideas daily.
Hello, i feel that i saw you visited my web site thus i got here to go back the
want?.I am attempting to in finding issues to
enhance my web site!I suppose its good enough to use some of your concepts!!
Thank you
welcome
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Corporate Website for Explorer Sailboats
growtharena.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
топ провайдеров Москвы – активировать бюджетный Wi-Fi квартирный интернет со скидкой
Актуальне за сьогодні: https://ukrglobe.com/aktualne.html
brandshine.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Encrypted Website for Inquiries
growyourmindset – Love how this name promotes positivity and continuous personal growth.
Автосервис «5 Бокс» https://auto-5-box.ru — это команда профессионалов, для которых качество и честность превыше всего. Мы выполняем ремонт любых узлов автомобиля: двигателя, трансмиссии, подвески, тормозной системы, электрооборудования и кондиционеров. Производим замену расходников, диагностику и профилактику неисправностей. Работаем на современном оборудовании, используем качественные запчасти и предоставляем гарантию на все услуги. У нас прозрачные цены, внимательное отношение и реальные сроки ремонта. «5 Бокс» — автосервис, которому можно доверить свой автомобиль.
trendandfashionhub – Bright, trendy, and well-organized, perfect for fashion enthusiasts.
http://www.podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru – ознакомиться с гарантиями качественных провайдеров казанского качества
http://www.provideri-voronezha.ru – прочитать новости оптимальных провайдеров воронежского подключения
интернет раскрутка http://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru .
комплексное продвижение сайтов москва комплексное продвижение сайтов москва .
материалы по seo материалы по seo .
топ провайдеров Воронежа – увидеть общегородской анализ компаний по версии экспертов
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Find Out Our Site
контекстная реклама статьи контекстная реклама статьи .
ремонт bosch ремонт бош
yelkovanyachts.com – Main Website Home
топ лучших провайдеров интернета в Москве – заказать качественный комплексные решения в столице
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Location Metal Hull Specialist
simplefashioncorner – Clean, trendy, and easy-to-browse fashion options all in one place.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Protected Access for Yacht Information
http://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – подключить круглосуточно неиссякаемый интернет-соединение с покрытием в Воронеже
http://www.provideri-kazani.ru – посмотреть подробнее доступных провайдеров казанских коммуникаций
https://www.internet-v-kazani.ru – приобрести услугу стабильный интернет в частных домах
shopandsaveonline – Great deals and simple layout, makes online shopping quick and easy.
mostbet kg отзывы https://www.mostbet12039.ru
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Website Aluminum Cruiser Manufacturing
brandreach.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
казахтелеком интернет – просто провести кабельный выход в сеть под ключ
deck saloon cruiser – luxury deck cabin sailboat layout
clickreach.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
digitalrise.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthmind.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
leadlaunch.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
advisionpro.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
modernhomecorner – Love the modern designs and home decor ideas shared here daily.
adspherepro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Yelkovan 60 – premium series 60 cruiser with delivery terms
https://www.domashniy-internet-kazan.ru/ – ознакомиться с гарантиями домашний интернет и телевидение от поставщиков Казани
http://www.internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – узнать о поддержке востребованных провайдеров воронежских коммуникаций
https://internet36.ru/ – узнать больше минимальные интернет форматы в офисах Воронежа
yelkovanyachts.com – Main Website Overview Page
besttrendstore – Love the clean design and trendy collections, very appealing overall.
raised saloon sailboat – explorer enhanced comfort zone sailing yacht configuration
казахтелеком тарифы – заказать стабильный кабельный интернет-доступ по всему Казахстану
besttrendstore – Trendy and exciting store with fresh fashion and lifestyle products.
интернет раскрутка https://optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru .
продвинуть сайт в москве http://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru .
статьи о маркетинге статьи о маркетинге .
steel sailboat builder – trusted explorer vessel constructor with experience
seo статьи seo статьи .
Портал о строительстве https://newboard-store.com.ua и ремонте: от проекта до сдачи объекта. Каталоги производителей, сравнение материалов, сметы, BIM и CAD, нормативная база, ленты новостей, вакансии и тендеры. Практика, цифры и готовые решения.
Современный автопортал https://carexpert.com.ua главные премьеры и тенденции, подробные обзоры, тест-драйвы, сравнения моделей и подбор шин. Экономия на обслуживании, страховке и топливе, проверки VIN, лайфхаки и чек-листы. Всё, чтобы выбрать и содержать авто без ошибок да
Современный новостной https://vestionline.com.ua портал: главные темы суток, лонгриды, мнения экспертов и объясняющие материалы. Проверка фактов, живые эфиры, инфографика, подборка цитат и контекст. Быстрый доступ с любого устройства и без лишних отвлечений.
https://www.podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru – подобрать индивидуально интернет-соединение в новостройках Казани
https://www.provideri-voronezha.ru/ – узнать домашний интернет и комплексные услуги для отдыха в Воронеже
globalfashionzone – Perfect mix of modern and classic trends from around the world.
staycuriousdaily – Motivates me to keep asking questions and exploring new ideas.
groweverymoment – The message is simple yet powerful, love the growth mindset theme.
connectwithpeople – Love how this feels like a space for genuine interaction online.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Location Metal Hull Specialist
рейтинг провайдеров Казани – рассмотреть экспертный список компаний города Казани
findyourbalance – Beautiful concept encouraging harmony in work, life, and mindset.
yourfashionoutlet – Love the stylish collection here, everything feels trendy and well-priced.
https://444-000.ru/
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Digital Location Custom Cruiser Manufacturer
[url=https://kazakhtelekom.ru/]самый быстрый интернет[/url] – скачать доступные телефон тарифы с дополнительными услугами
startfreshjourney – Uplifting and positive vibe, perfect for inspiration and fresh beginnings.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Visit Our Digital Catalog
thinkactachieve – Really inspiring message, perfect for anyone focused on self-improvement.
Всё для женщины https://wonderwoman.kyiv.ua уход и макияж, мода и стиль, психология и отношения, работа и деньги, мама и ребёнок. Тренды, тесты, инструкции, подборки брендов и сервисов. Читайте, вдохновляйтесь, действуйте.
Твой автопортал https://kia-sportage.in.ua о новых и подержанных машинах: рейтинги надёжности, разбор комплектаций, реальные тесты и видео. Помощь в покупке, кредит и страховка, расходы владения, ТО и тюнинг. Карта сервисов, советы по безопасности и сезонные рекомендации плюс
Современный женский https://fashiontop.com.ua журнал: уход и макияж, капсульный гардероб, психология и отношения, питание и тренировки, карьерные советы и финансы. Честные обзоры, подборки брендов, пошаговые гайды.
http://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru/ – посмотреть контакты прогрессивные оптимальные провайдеры большого Воронежа
http://www.provideri-kazani.ru – ознакомиться с подключением популярных провайдеров столицы Татарстана
connectwithpeople – Simple yet powerful message that inspires relationships and collaboration.
домашний интернет Воронеж провайдеры по адресу – подобрать доступный частный доступ в сеть в конкретном районе в Воронеже
thebestdeal – Always great to find a site focused on value and daily savings.
custom yacht construction – total customizable performance yacht production process
globalfashionzone – Great place to explore diverse fashion inspirations globally.
staycuriousdaily – Great reminder that curiosity is key to learning and innovation.
[url=https://luckypari-uz.cc/]http://luckypari-uz.cc[/url] – домен с отключенной аналитикой
groweverymoment – Such an inspiring name, reminds me to keep improving each day.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Site Entry Yelkovan Yachts
findyourbalance – A great reminder to slow down and realign with what matters.
believeinyourideas – Motivating and clean design, makes exploring ideas enjoyable and simple.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Website Domain Aluminum Yacht Professional
internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru/ – узнать больше домашний интернет-пакет от перспективных поставщиков
http://domashniy-internet-kazan.ru/ – изучить предложения успешные современные провайдеры столицы Татарстана
https://www.internet-v-kazani.ru/ – посмотреть контакты интернет-доступ и телевидение для работы в Казани
Еженедельный журнал https://sw.org.ua об авто и свободе дороги: премьеры, электромобили, кроссоверы, спорткары и коммерческий транспорт. Реальные тесты, долгосрочные отчёты, безопасность, кейсы покупки и продажи, кредит и страховка, рынок запчастей и сервисы рядом.
Портал о балансе https://allwoman.kyiv.ua красота и самоуход, отношения и семья, развитие и карьера, дом и отдых. Реальные советы, капсульные гардеробы, планы тренировок, рецепты и лайфхаки. Ежедневные обновления и подборки по интересам.
Журнал об автомобилях https://svobodomislie.com без мифов: проверяем маркетинг фактами, считаем расходы владения, рассказываем о ТО, тюнинге и доработках. Тестируем новые и б/у, объясняем опции простыми словами. Экспертные мнения, идеи маршрутов и полезные чек-листы. Всегда!.
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Load Professional Sailboat Website
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Home Page of Yelkovan Yachts
https://melbet-kz.biz/ – адрес для ставок на хоккей
uniquevaluezone – Offers cool finds at great prices, really worth visiting.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Website Access Yelkovan Yachts
https://provideri-voronezha.ru – выбрать оптимальный инновационный интернет-канал в офисах Воронежа
лучшие провайдеры интернета в Казани – проанализировать крупных цифровых провайдеров с условиями подключения
adsprint.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
самый лучший провайдер интернета в Воронеже – выбрать самый качественный телекоммуникационный поставщик интернета с высокими рейтингами
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Secure Connection for Specifications
brandfuel.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
promopath.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
adreachpro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
marketpilot.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
услуги по узакониванию перепланировки http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru .
marketfuel.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
проект перепланировки нежилого помещения проект перепланировки нежилого помещения .
surewin download http://www.surewin-online.com .
icebet.casino app icebet.casino app .
clickscale.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Digital Platform Steel Sailboat Building
Orb11TA — это динамичный проект с развивающейся экосистемой сервисов и активным сообществом. Если вы ищете проверенные источники, начните с официальной страницы: официальная страница Orb11TA (orb11ta.life). Для дополнительных материалов и публикаций доступен также ресурс Orb11TA — информационная страница (orb11ta.my).
Проект предлагает отдельные возможности для подписчиков — раздел orb11ta vip содержит анонсы и привилегии для участников. На публичных доменах (orb11ta com, orb11ta сайт) публикуются справочные материалы, инструкции и ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы. Если вам нужен технический архив и исходники, обратите внимание на репозиторий: GitHub — репозиторий Orb11TA.
Сообщество обсуждает такие темы, как orb11ta top, orb11ta ton и вопросы видимости на страницах поиска (ton page 1, ton site orb11ta on page 1). Для быстрых обзоров и агрегированных публикаций полезен ресурс обзоров и сборников материалов. Для коммерческих и партнёрских решений есть разделы типа orb11ta shop и orb11ta biz.
Важно сохранять цифровую гигиену: при появлении капчи или сообщения о проверке (“orb11ta vip вы не робот”) следуйте стандартным процедурам и не передавайте личные данные третьим лицам. Для оперативных объявлений и релизов следите за официальными страницами и репозиторием: Обзор и новости — getgems.io/orb11ta.
Ключевые слова для поиска и продвижения: orb11ta, orb11ta vip, orb11ta com, orb11ta сайт, orb11ta top, orb11ta ton, orb11ta shop, orb11ta biz, orb11ta org, orb11ta com сайт вход.
Полезные ссылки:
Официальная страница — orb11ta.vip
Информационная страница — orb11ta.com
Обзор / новости — getgems.io/orb11ta
Репозиторий разработчиков — GitHub
http://www.melbet-kz.us – получить доступ к live-линии
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Encrypted Access Yelkovan Yachts
newtrendmarket – Love the fresh and modern vibe, full of current fashion finds.
discoverhiddenopportunities – Inspiring name that encourages exploring new ideas and growth.
dailyshoppingzone – Love how convenient this site is for everyday shopping needs.
https://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru/ – ознакомиться дополнительные интернет ступени по всему Воронежу
подключить домашний интернет в Казани – быстро запустить домашний интернет с бесплатным монтажом
Если вы занимаетесь производством и ваша компания нуждается в поставке высококачественных тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше решение. Наша компания специализируется на сфере поставок тугоплавких металлов в течение десятилетий, что обеспечивает нам условия поставлять только качественный продукт своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Объемы поставок не имеют значения.
2. Большой ассортимент тугоплавких металлов.
3. Документация в порядке.
4. Круглосуточная поддержка.
Зачем тратить время на поиски в других местах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда готовы помочь?
В случае возникновения вопросов, наши эксперты всегда готовы вам помочь. Пишите прямо сейчас и проверьте в преимуществах нашего сплава.
Команда ООО “РМС” на связи!
Наша продукция:
Прецизионная труба бесшовная 115х7,5 мм 38MnVS6 EN 10305-2
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Internet Site Steel Sailboat Building
http://internet-v-kazani.ru/ – узнать рейтинговые местные провайдеры казанских технологий
Аренда авто https://turzila.com/ без депозита, аренда яхт и удобный трансфер в отель. Онлайн-бронирование за 3 минуты, русская поддержка 24/7, прозрачные цены. Оплата картой РФ.
Нужна фотосьемка? съемка для вб каталожная, инфографика, на модели, упаковка, 360°. Правильные ракурсы, чистый фон, ретушь, цветопрофили. Готовим комплекты для карточек и баннеров. Соответствие правилам WB/Ozon.
https://444-000.ru/
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Platform URL Official Yacht Builder
bestdailyoffers – Perfect site for anyone who enjoys finding value and discounts.
urbanchoicehub – Perfect site for those who love a sleek, metropolitan aesthetic.
everydaystylemarket – Nice variety of items that fit any occasion.
интернет в офис Москва – смонтировать быстрый цифровую связь в офис в столице по месту с установкой
discoveramazingfinds – Love how easy it is to find something new every time I visit.
creativechoiceoutlet – Smooth navigation and eye-catching layout make shopping fun.
exploreinnovativeideas – Great energy here, I always leave with fresh perspectives.
yelkovanyachts.com – Official Site Introduction Page
newtrendmarket – Fresh trends and a smooth shopping experience, really well put together.
dailyshoppingzone – Love how convenient this site is for everyday shopping needs.
Если вы работаете в сфере производства и столкнулись с необходимостью в поставке самых качественных тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше решение. Наша компания специализируется на области поставок тугоплавких металлов на протяжении долгого времени, что дает нам возможность предоставлять только проверенный материал своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Мы поставим любые объемы материалов.
2. Обширный выбор тугоплавких металлов.
3. Документация в порядке.
4. Всесторонняя поддержка клиентов.
Зачем тратить время на поиски в других местах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда здесь для вас?
Наши специалисты всегда рады помочь вам с любыми вопросами.. Пишите прямо сейчас и убедитесь в качестве нашего продукта.
Команда ООО “РМС” на связи!
поставляемая продукция:
Труба нержавеющая 15Х25Т 121×10 ГОСТ 5632 – 72
May I simply say what a comfort to uncover someone that genuinely knows what
they’re discussing on the internet. You definitely
realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important.
More and more people ought to read this and understand this side of the story.
I was surprised you’re not more popular since you certainly have the gift.
Thank you very much
That’s kind of you
custom yacht construction – comprehensive bespoke yacht production options
http://www.internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – выбрать лучший незамедлительный интернет-результат с обслуживанием в Воронеже
http://www.domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – посмотреть рейтинг популярных провайдеров Татарстана
http://www.internet36.ru – изучить предложения рейтинговых провайдеров воронежского качества
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
yelkovanyachts.com – Corporate Site Home
simplebuyhub – Super easy to navigate site with plenty of affordable options.
интернет казахстан – надежно заказать доступный интернет по всему городу
bestdailyoffers – Deals are easy to navigate, and everything feels well-organized.
urbanchoicehub – Love the modern urban vibe, feels trendy and fresh.
deck saloon cruiser – traditional exterior living area yacht advantage
yourvisionawaits – Inspiring name that motivates people to dream and take action.
explorer sailboat for sale – modern long-range yacht for sale
Do you know which posts drive the most traffic and which ones fail to perform? Without a structured Optimization Plan, your marketing efforts might lack direction and measurable goals.
A comprehensive Social Media Audit evaluates account performance. It helps you identify ROI gaps.
We provide a detailed Audit Report, Performance Review, and Content Calendar tailored to your goals.
Imagine the impact of knowing exactly what works and what doesn’t. A Social Media Audit gives you clarity, helping you focus on high-performing content.
Take control of your social presence now with a professional Social Media Audit and achieve your business goals.
Facebook
Instagram
Reddit
LinkedIN
http://provideri-voronezha.ru/ – посмотреть тарифы популярные местные провайдеры города Воронежа
http://podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru/ – посмотреть тарифы действующие современные провайдеры большой Казани
everydaystylemarket – Clean design and easy navigation, very user-friendly.
discoveramazingfinds – Great layout, makes browsing and discovering new items enjoyable.
creativechoiceoutlet – Loved browsing this site; the name perfectly matches the vibe.
[url=https://internet-v-kazani.ru/]http://www.internet-v-kazani.ru[/url] – подключить продвинутый интернет-передача с обслуживанием в Казани
exploreinnovativeideas – Definitely one of my favorite spots for daily creative boosts.
trafficsphere.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Address Metal Hull Specialist
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Proceed To Custom Boat Builder Portal
самый лучший провайдер интернета в Москве – протянуть мобильный домашний интернет в квартиру с установкой
buildyourpotential – Great reminder that growth starts with small daily improvements.
metal hull yachts – modern steel hull blue water yachts with certification
Современный журнал https://rupsbigbear.com про авто: новости индустрии, глубокие обзоры моделей, тесты, сравнительные таблицы и советы по выбору. Экономия на обслуживании и страховке, разбор технологий, безопасность и комфорт. Всё, чтобы ездить дальше, дешевле и увереннее.
Автопортал для новичков https://lada.kharkiv.ua и профи: новости рынка, аналитика, сравнения, тесты, долгосрочные отчёты. Выбор авто под задачи, детальные гайды по покупке, продаже и трейд-ину, защита от мошенников. Правила, штрафы, ОСАГО/КАСКО и полезные инструменты и ещё
Женский медиа-гид https://adviceskin.com здоровье, питание, спорт, ментальное благополучие, карьера, личные финансы, хобби и поездки. Практика вместо кликбейта — понятные гайды, чек-листы и экспертные мнения.
http://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – выбрать непрерывный интернет-эффект для воронежцев
https://www.provideri-kazani.ru/ – ознакомиться с подключением цифровой интернет и онлайн-телевидение по всей Казани
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Secure Access Metal Hull Experts
https://internet36.ru/ – ознакомиться персональные телекоммуникационные схемы от сервисов Воронежа
urbanfashioncorner – Trendy, bold, and full of energy — perfect urban fashion vibe.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Encrypted Website for Inquiries
интернет по адресу в Москве проверить провайдеры – подключить качественный интернет для квартиры в столице от лидеров рынка с настройкой
smartshoppingzone – Perfect for budget-conscious shoppers who still want quality products.
We’re a gaggle of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community.
Your site provided us with valuable info to work on. You have done
an impressive activity and our whole group will likely be thankful to you.
Thank you very much
Thanks for the encouragement.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Brand Site for Explorer Sailboats
Если вы заняты в области производства и столкнулись с необходимостью в поставке высококачественных тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше спасение. Наша компания работает на сфере поставок тугоплавких металлов в течение более 10 лет, что дает нам возможность предлагать только высококачественные металлы своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Объемы поставок не имеют значения.
2. Обширный выбор тугоплавких металлов.
3. Полный комплект документов.
4. Круглосуточная поддержка.
Зачем тратить время на поиски в других местах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда в вашем распоряжении?
Наши специалисты всегда рады помочь вам с любыми вопросами.. Звоните прямо сейчас и убедитесь в достоинствах нашего редкого металла.
Ваш надежный поставщик, ООО “РМС”
Наша продукция:
Труба латунная квадратная ЛО70 60х40 мм
learnsomethingamazing – Encouraging and creative name that promotes daily learning and discovery.
https://internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru/ – прочитать специальные сетевые планы в городе Воронеж
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Secure Portal for Specifications
интернет в частный дом в Казани – оборудовать надежный коттеджный интернет-доступ в Казани
internet-v-kazani.ru/ – посмотреть качественный интернет-пространство от активных операторов
In fact no matter if someone doesn’t know after that its up to other people that they will
assist, so here it occurs.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Platform Access Explorer Sailboat Company
топ провайдеров Москвы – ввести бюджетный беспроводной домашний интернет с установкой
adlift.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
clickgurus.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Yacht Builder Site of Yelkovan Yachts
freshdealsworld – Great site for fresh offers and exciting online shopping deals.
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Enter Custom Boat Builder Portal
provideri-voronezha.ru/ – посмотреть тарифы частный интернет-пакет от опытных сервисов
рейтинг провайдеров Казани – проверить актуальный сравнение компаний для принятия решения
самый быстрый интернет в Воронеже – ввести оптоволоконный доступ в сеть для онлайн-игр с круглосуточной поддержкой
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Safe Platform Steel Boat Specialists
findbestdeals – Love how easy it is to browse and spot the top deals.
discoverandbuy – Great mix of trending products, easy layout, and smooth navigation.
findnewinspiration – Every visit brings something new that motivates me to act.
clickprohub.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
dreambiggeralways – Encouraging quotes and posts that help keep me pushing forward.
stayfocusedandgrow – The message here is strong—focus and growth go hand in hand.
learnandimprove – Clean layout, inspiring content, and useful advice for everyday improvement.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Total Protected Site Link Yelkovan Yachts
Женское медиа https://beautytips.kyiv.ua о главном: здоровье и профилактика, стиль и тренды, психологические разборы, мотивация, деньги и инвестиции, материнство и путешествия. Честные обзоры, подборка сервисов и истории читательниц.
казахтелеком интернет тарифы – выбрать индивидуальные онлайн предложения от национального оператора
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Open Explorer Yacht Company Page
dailydealsplace – Great place for deals, always something new and exciting to find.
learnandshine – Inspiring content that motivates me to keep learning every day.
http://www.domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – приобрести пакетом бесперебойный интернет-польза в квартирах Воронежа
provideri-kazani.ru/ – узнать о поддержке стабильный интернет-качество от современных компаний
http://www.internet-v-kazani.ru – выбрать современный интернет-обмен по Казани
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Yacht Builder Site of Yelkovan Yachts
Медиа для женщин https://feromonia.com.ua которые выбирают себя: здоровье и профилактика, ментальное благополучие, работа и развитие, материнство и хобби. Практичные инструкции, тесты, интервью и вдохновение без кликбейта.
Женский журнал https://dama.kyiv.ua о жизни без перегруза: красота и здоровье, стиль и покупки, отношения и семья, карьера и деньги, дом и путешествия. Экспертные советы, чек-листы, тренды и реальные истории — каждый день по делу.
uniquegiftideas – Excellent variety of creative gifts, ideal for any special occasion.
yelkovanyachts.com – Corporate Site Welcome Page
казахтелеком интернет тарифы – сравнить актуальные интернет тарифы с полным покрытием
discoverandbuy – Love how simple it is to find and explore new items here.
Всё, что важно https://gryada.org.ua сегодня: мода и стиль, бьюти-рутины, рецепты и фитнес, отношения и семья, путешествия и саморазвитие. Краткие выжимки, длинные разборы, подборки сервисов — удобно и полезно.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Portal Address Blue Water Sailboat Builder
inspireeverymoment – Motivating platform that encourages positivity every single day.
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Online Presence Blue Water Vessel Fabrication
https://domashniy-internet-kazan.ru/ – ознакомиться с подключением новые онлайн планы в новостройках Казани
https://www.internet36.ru/ – изучить сравнение интернет-провайдер и телеком-услуги в офисах Воронежа
findhappinessdaily – Uplifting messages and helpful tips that brighten my day instantly.
findnewinspiration – I always come away feeling motivated and ready to take action.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Encrypted Link for Support
dreambiggeralways – Inspiring content and positive energy, perfect for a daily mindset boost.
stayfocusedandgrow – Great motivational tone and layout, really keeps me inspired.
learnandimprove – Great balance of motivation and practical knowledge, really helpful stuff.
purechoicehub – Clean design and high-quality items, really impressed with the layout.
heavy duty sailboat – explorer robust blue water yacht creation for reliability
интернет в астане – быстро ввести в эксплуатацию домашний интернет-соединение в любом районе
simplebuyoutlet – Smooth shopping experience, great deals and very clean design.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog
and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your
blog posts. After all I will be subscribing to your
feed and I hope you write again soon!
Thank you very much
I will do my best to live up to your expectations.
starttodaymoveforward – Positive and inspiring, encourages daily progress and self-growth.
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Proceed To Luxury Cruiser Platform
Женский журнал https://krasotka.kyiv.ua про баланс: красота, психология, карьера, деньги, дом и отдых. Экспертные колонки, списки покупок, планы тренировок и проверки здоровья. Материалы, к которым хочется возвращаться.
Онлайн-портал https://womanexpert.kyiv.ua для женщин, которые хотят жить в балансе. Красота, здоровье, семья, карьера и финансы в одном месте. Ежедневные статьи, подборки, советы экспертов и вдохновение для лучшей версии себя.
Глянец без иллюзий https://ladyone.kyiv.ua красота и здоровье с фактчекингом, стиль без переплат, карьера и деньги простым языком. Интервью, тесты, полезные гайды — меньше шума, больше пользы.
http://podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru – заказать недорого неограниченный интернет-поток в Казани
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Official Website for Raised Saloon Sailboats
http://internet-v-kazani.ru/ – ознакомиться с гарантиями динамичные местные провайдеры казанского рынка
Yelkovan 60 – luxury Yelkovan 60 sailing yacht with specifications
classystyleoutlet – Elegant fashion selections and well-curated items, love browsing here.
лаки пари ставки – делать прогнозы в букмекерской конторе с live-линией и использовать бонусы
custom aluminum yacht – blue water client-specific modern luxury yacht development
yourstylezone – Trendy site that really helps express personal fashion taste.
thepowerofgrowth – Beautiful name that reminds you of personal and continuous improvement.
startbuildingtoday – Inspiring site that motivates you to take action and grow.
seostreampro.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Entire Secure Web Address Premium Yacht Builder
clickforce.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
https://provideri-kazani.ru/ – изучить предложения премиальные коммуникационные серии для семьи в Казани
clickenginepro.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
brandmagnet.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
internet36.ru/ – посмотреть офисный интернет-доступ от профессиональных компаний
seojet.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
custom aluminum yacht – oceangoing tailor-made metal sailboat construction
trafficstream.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Visit Our Builder’s Site
Всё для современной https://model.kyiv.ua женщины: уход и макияж, стиль и шопинг, психология и отношения, питание и тренировки. Честные обзоры, капсульные гардеробы, планы на неделю и проверенные советы.
http://melbet-kz.biz/ – HTTP-домен без шифрования
Мода и красота https://magiclady.kyiv.ua для реальной жизни: капсулы по сезонам, уход по типу кожи и бюджета, честные обзоры брендов, шопинг-листы и устойчивое потребление.
Yelkovan 60 – performance Yelkovan 60 vessel with layout choices
Сайт для женщин https://modam.com.ua о жизни без перегруза: здоровье и красота, отношения и семья, карьера и деньги, дом и путешествия. Экспертные статьи, гайды, чек-листы и подборки — только полезное и применимое.
trendandfashionhub – Love how stylish and updated the latest trends are here.
brightstylemarket – Fashion-forward ideas and amazing variety for all kinds of tastes.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Site Entry Explorer Sailboat Company
https://domashniy-internet-kazan.ru/ – изучить сравнение выгодные современные категории от сервисов Казани
интернет в офис Казань – профессионально провести современный интернет-канал с настроенной сетью
everydaytrendstore – Super convenient shopping experience with modern designs.
discovermoreideas – A perfect place to spark innovation and discover new perspectives.
findyourstylehub – Always finding new outfit inspiration whenever I browse this site.
urbanbuycorner – Trendy products with a sleek city vibe, very enjoyable to explore.
growyourmindset – Every visit leaves me feeling encouraged and more confident in myself.
learnandimprove – Every post feels genuine and aimed at helping people grow smarter.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Complete Encrypted Website Metal Hull Specialist Company
createpositivechange – Love the uplifting message here, motivates me to do better daily.
beststylecollection – Stylish selections and great variety, makes shopping a real pleasure.
melbet-kz.us/ – ссылка для QR-кода
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Find Out Our Company Page
https://www.domashniy-internet-moscow.ru/ – Защищенный официальный URL компании
Медиа для женщин https://otnoshenia.net 25–45: карьера и навыки, ментальное благополучие, осознанные покупки, спорт и питание. Краткие выжимки и глубокие разборы, подборки брендов и сервисов.
Реальная красота https://princess.kyiv.ua и стиль: уход по типу кожи и бюджету, капсулы по сезонам, устойчивое потребление. Гайды, шопинг-листы, честные обзоры и советы стилистов.
Сопровождение ВЭД позволило нам улучшить контроль поставок и сократить ошибки: Сопровождение ВЭД
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Visit Sailboat Manufacturer Site
Всё чётко, профессионально и без лишних задержек при оформлении импорта https://vsoprovozhdenie.ru/
bestchoicecollection – Wide range of stylish products and great pricing overall.
domasniinternet1.ru/ – Ключевая платформа управления услугами
styleandchoice – Elegant and trendy, perfect for shoppers who love variety.
https://s-nano-s.ru/
подключить домашний интернет в Казани – онлайн запустить стабильный интернет-соединение по всему городу
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Portal Address Luxury Yacht Constructor
http://internet36.ru – подключить круглосуточно бесконечный интернет-влияние в офисах Воронежа
https://www.internet-kazahstan.ru – приобрести доступный доступ в сеть по всему городу
Женский сайт https://one-lady.com о балансе: работа, финансы, здоровье, дом, дети и отдых. Пошаговые инструкции, трекеры привычек, лайфхаки и вдохновляющие истории. Меньше шума — больше пользы.
http://www.internet-v-astane.ru – оценить стандартный визит к порталу телеком-провайдера
https://s-nano-s.ru/
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Platform Access Custom Aluminum Yacht Builder
brightstylemarket – Fashion-forward ideas and amazing variety for all kinds of tastes.
everydaytrendhub – Always up to date with the latest trends, great resource.
https://www.kazakhtelekom.ru/ – гарантированно воспользоваться исчерпывающий интернет-доступ с надежной защитой
growyourmindset – Great source for personal growth and mindset transformation content.
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Digital Platform Explorer Boat Production
https://www.domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – заказать интернет-соединение в новостройках Казани
domashniy-internet-spb.ru/ – Ознакомьтесь с последними новостями и обновлениями на главной странице
podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru/ – Ознакомьтесь с статистикой использования сервиса и отзывами пользователей
domashniy-internet-moscow.ru – Надежный источник информации о тарифах
trafficmind.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
createpositivechange – Love the message and design, truly encourages meaningful growth.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Encrypted Link for Contact
everydaytrendstore – Stylish products, great prices, and a smooth checkout process.
discovermoreideas – Great collection of unique ideas and motivational resources.
findyourstylehub – Makes shopping and styling feel fun and super effortless.
freshfindsoutlet – New and trendy products pop up here all the time, love it.
learnandimprove – Simple yet powerful ideas that push me to do better daily.
http://domasniinternet1.ru – Непосредственный просмотр зоны покрытия
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Safe Entry Aluminum Yacht Professionals
https://www.internet36.ru/ – прочитать новости интернет-телефония и комбинированные услуги для бизнеса Воронежа
internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru/ – посмотреть рейтинг квартирный интернет-технологии от опытных сервисов
yelkovanyachts.com – Manufacturer’s Site Information Page
http://www.internet-kazahstan.ru – воспользоваться прямой посещение к странице оператора связи
http://internet-v-peterburge.ru – Ознакомьтесь с финансовыми показателями и репутацией операторов связи
http://domashniy-internet-spb.ru/ – Узнайте о типовых требованиях к помещению для подключения интернета
provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Ознакомьтесь с ежедневно обновляемой базой тарифов и предложений
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – HTTPS Protocol to Yelkovan Yachts
http://internet-v-astane.ru – ознакомиться стандартный обращение к сетевому оператору с лучшими условиями
discoverinfiniteideas – Inspiring and creative site name that sparks imagination instantly.
https://www.internet-v-kazani.ru/ – узнать о покрытии интернет-доступ и комбинированные услуги в квартирах Казани
makeimpacteveryday – A motivating and uplifting name that inspires daily action.
Специалисты по сопровождению ВЭД полностью взяли на себя бумажную часть, а мы сосредоточились на бизнесе – https://vsoprovozhdenie1.ru/
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – HTTPS Protocol for Boat Details
learnshareachieve – Perfect for anyone who loves to learn and make steady progress.
http://kazakhtelekom.ru/ – оперативно установить качественный интернет через базовый доступ
http://www.luckypari-uz.cc – адрес с базовыми платежными методами
yelkovanyachts.com – Yacht Builder Site Landing Page
melbet – доступный ресурс Melbet для казахстанцев с бонусами
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Total Protected Site Link Yelkovan Yachts
https://melbet-kz.us – ресурс с резервным копированием
http://www.podklyuchit-internet-ekaterinburg.ru – Используйте удобный поиск по адресу для проверки доступных провайдеров
http://provaydery-peterburga.ru/ – Найдите оптимальное решение для подключения интернета без лишних сложностей
raised saloon sailboat – heavy-duty visibility cabin blue water yacht option
https://moskva-internet.ru/ – HTTPS соединение обеспечивает защиту транзакций
optovolokno-internet.ru – заказать выгодный цифровое подключение пакеты с гибкими условиями
heavy duty sailboat – professional heavy duty world cruiser design for long life
http://podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru/ – ознакомиться с гарантиями эффективные цифровые провайдеры города Казани
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Entire Secure Web Address Blue Water Sailboat Engineering
https://provesti-internet.ru/ – Безопасный платеж банковской картой онлайн
yelkovanyachts.com – Main Website Main Page
http://provideri-kazani.ru – оформить быстро всеобъемлющий интернет-передача с покрытием в Казани
Сопровождение ВЭД помогает избежать бюрократии и делает импорт прозрачным: Сопровождение ВЭД
heavy duty sailboat – premium heavy-gauge sailboat creation for value retention
provideri-voronezha.ru/ – ознакомиться с условиями доступный интернет-услуги от выгодных операторов
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Protected Site Metal Hull Experts
fashiondailycorner – Trendy fashion picks and great updates, really well-curated site.
yelkovanyachts.com – Manufacturer’s Site Main Page
promobridge.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Web Access Steel Sailboat Manufacturer
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Encrypted Portal Luxury Cruiser Constructors
marketscope.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
seotrack.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
promocloud.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
digitaltrack.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Location Yelkovan Yachts
clickgrow.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – заказать с установкой частный интернет-мир с поддержкой в Воронеже
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Internet Site Metal Yacht Construction
https://www.domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – заказать срочно интернет-сервисы для жителей Казани
https://www.podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru/ – Используйте расширенные инструменты сравнения и анализа услуг провайдеров
https://internet-v-ekaterinburge.ru/ – Используйте безопасную форму для расчета стоимости подключения
http://www.domashniy-internet-ekb.ru – Получите информацию о партнерских программах и специальных скидках
https://www.domashniy-internet-moscow.ru – Сравните все доступные тарифы для вашего дома
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Explore Our Website
http://domasniinternet1.ru – Непосредственное ознакомление с гарантиями
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Internet Portal Yelkovan Yachts
Женский блог https://sunshadow.com.ua о жизни без перегруза: красота и здоровье, отношения и семья, стиль и покупки, деньги и карьера. Честные обзоры, лайфхаки, планы на неделю и личные истории — только то, что реально помогает.
Современный женский https://timelady.kyiv.ua сайт о стиле жизни: уход за собой, макияж, прически, фитнес, питание, мода и деньги. Практичные советы, разбор трендов, подборки покупок и личная эффективность. Будь в ресурсе и чувствуй себя уверенно каждый день. Больше — внутри.
https://internet36.ru/ – изучить детально выгодные телекоммуникационные варианты для бизнеса Воронежа
shopandsmiletoday – The name fits perfectly, such a cheerful and easy shopping experience.
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Website Luxury Yacht Development
https://internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – подключить круглосуточно надежный интернет-достижение в Воронеже
https://www.internet-v-peterburge.ru/ – Воспользуйтесь системой мониторинга качества услуг интернет-провайдеров
provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Найдите информацию о сезонных распродажах и специальных акциях
internet-kazahstan.ru/ – подключить популярный интернет-доступ с быстрым подключением варианты и расценки
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Go To Our Website
https://www.internet-v-astane.ru/ – защищенно воспользоваться полный сетевой доступ с современной безопасностью
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Yacht Builder Site for Custom Aluminum Yachts
findbettervalue – Love the variety and affordability here, it’s worth checking daily.
http://internet-v-kazani.ru – заказать постоянный интернет-перспектива по Казани
globalshoppingzone – I like how diverse the product selection is across different categories.
urbanwearzone – Great vibe here, love how easy it is to find fresh looks.
beststylecollection – This site makes it easy to keep my wardrobe looking fresh.
simplechoiceoutlet – Every visit surprises me with something new and budget-friendly.
shopandsmiletoday – The name says it all, every visit brings joy and great finds.
Блог для женщин https://sweetheart.kyiv.ua которые выбирают себя: самоценность, баланс, карьера, финансы, хобби и путешествия. Мини-привычки, трекеры, вдохновляющие тексты и практичные советы.
trendworldmarket – Love how updated this site stays with the latest global trends.
https://www.kazakhtelekom.ru/ – легально подключить детализированный цифровое подключение с полной защитой
deck saloon cruiser – traditional raised living area blue water yacht feature
creativechoicehub – Innovative designs and creative products, really impressed with the variety.
https://luckypari-uz.cc – домен с защитой от фишинга и мошенников
shopthelatestdeals – Found amazing deals today, makes shopping fun and easy.
Портал для женщин https://viplady.kyiv.ua ценящих стиль, комфорт и развитие. Мода, уход, отношения, семья и здоровье. Только практичные советы, экспертные мнения и вдохновляющий контент. Узнай, как быть собой и чувствовать себя лучше.
Онлайн-площадка https://topwoman.kyiv.ua для женщин: стиль, бьюти-новинки, осознанность, здоровье, отношения, материнство и работа. Экспертные статьи, инструкции, чек-листы, тесты и вдохновение. Создавай лучший день, развивайся и находи ответы без лишней воды.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Encrypted Website for Consultation
provaydery-peterburga.ru/ – Ознакомьтесь с системой модерации и проверки информации на сайте
podklyuchit-internet-ekaterinburg.ru/ – Основная страница портала демонстрирует все доступные функции поиска
http://melbet-kz.biz/ – адрес с открытым API
yourdailyinspiration – Inspiring words and great visuals, perfect for a morning boost.
seopath.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
melbet-kz.us – портал для игры на тенге
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Online Address Aluminum Yacht Professional
moskva-internet.ru – Активный домен с ежедневным обновлением
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Load Explorer Yacht Company Page
discoverandshopnow – Great shopping experience, always something new and fun to explore.
findbettervalue – The prices are fair and the products actually deliver good quality.
https://www.optovolokno-internet.ru – приобрести надежный доступ в сеть с современным оборудованием
подключить интернет в Казани – выгодно ввести в эксплуатацию доступный интернет по всему городу
simplechoiceoutlet – Prices are fair, and the shopping experience is super smooth.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Check The Official Site
brightcollectionhub – Colorful and stylish items that really make browsing enjoyable.
интернет провайдеры Санкт-Петербурга по адресу дома Санкт-Петербург – подобрать работающие передовые сетевые провайдеры новостроек по корпусу культурной столицы
https://www.internet-v-ekaterinburge.ru – Изучите все возможности подключения домашнего интернета на нашем сайте
http://domashniy-internet-spb.ru – Перейдите по прямому адресу чтобы ознакомиться со всеми разделами портала
https://provesti-internet.ru – Безопасный осмотр требований к оборудованию
теннис букмекерская скачать теннис букмекерская скачать
trendyvaluezone – Stylish products at affordable prices, love the variety here.
Женский медиасайт https://woman365.kyiv.ua с акцентом на пользу: капсульный гардероб, бьюти-рутины, здоровье, отношения, саморазвитие и материнство. Пошаговые инструкции, списки покупок, чек-листы и экспертные ответы. Заботимся о тебе и твоем времени. Подробности — на сайте.
globalshoppingzone – Great platform with items from all around the world, super fun.
metal hull yachts – professional aluminum hull vessels custom built
urbanwearzone – Fantastic urban fashion hub with trendy and affordable collections.
beststylecollection – Fantastic collection with great quality and affordable prices.
https://www.provideri-kazani.ru – приобрести пакетом интернет-тариф с подключением в Казани
shopandsmiletoday – The friendly layout and colorful design make browsing so enjoyable.
finduniqueproducts – Unique finds and creative ideas, everything feels handpicked and quality.
https://provideri-voronezha.ru/ – изучить детально текущие инновационные уровни в Воронежской области
custom yacht construction – comprehensive semi-custom luxury yacht manufacturing pricing
bestdailycorner – Found so many great daily deals here, totally worth visiting often.
https://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – заказать недорого стабильный интернет в квартирах Воронежа
Твой женский помощник https://vsegladko.net как подчеркнуть индивидуальность, ухаживать за кожей и волосами, планировать бюджет и отдых. Мода, психология, дом и карьера в одном месте. Подборки, гайды и истории, которые мотивируют заботиться о себе. Узнай больше на сайте.
deck saloon cruiser – premium deck living area yacht characteristic
лучшие провайдеры интернета в Казани – подобрать рейтинговых интернет поставщиков интернета для дома и офиса
Женский портал https://womanportal.kyiv.ua о моде, психологии и уходе за собой. Узнай, как сочетать стиль, уверенность и внутреннюю гармонию. Лучшие практики, обзоры и вдохновляющие материалы для современных женщин.
http://www.provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Ознакомьтесь с основными преимуществами пакетных предложений
marketrise.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
http://www.internet-v-peterburge.ru – Получите информацию о специальных предложениях для жилых комплексов
trendandfashion – Perfect mix of classic and modern trends, always inspiring.
webimpact.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://www.domashniy-internet-moscow.ru – Посмотрите инструкции по настройке оборудования
https://www.domashniy-internet-ekb.ru/ – Полная безопасная версия ресурса предлагает расширенные функции сравнения
brandtrail.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
digitalpeak.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Website Access Metal Yacht Builder
Всё о развитии https://run.org.ua и здоровье детей: диагностические скрининги, логопедия, дефектология, нейропсихология, ЛФК, массаж, группы раннего развития, подготовка к школе. Планы занятий, расписание, запись онлайн, советы специалистов и проверенные методики.
seoforce.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
http://www.domasniinternet1.ru – Веб-сервис для настройки роутера
discoverandshop – Great platform for exploring unique items and discovering new favorites.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Site URL Custom Cruiser Manufacturer
internet36.ru – подключить круглосуточно городской интернет-надежность с поддержкой в Воронеже
https://internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – выбрать лучший перспективный интернет-прорыв в Воронеже
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Learn More Our Web Portal
Сайт о строительстве https://blogcamp.com.ua и ремонте: проекты, сметы, материалы, инструменты, пошаговые инструкции и лайфхаки. Чек-листы, калькуляторы, ошибки и их решения. Делайте качественно и экономно.
groweverydaynow – Motivational and uplifting, reminds me to keep improving daily.
http://www.internet-kazahstan.ru – посетить клиентский магазин телеком-компании с полным покрытием
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Platform URL Steel Boat Expert
https://provaydery-peterburga.ru/ – Получите доступ к эксклюзивным предложениям через защищенное соединение
провести интернет в квартиру в Екатеринбурге – оперативно установить калиброванный доступную линию в новостройку миллионника
https://www.domashniy-internet-spb.ru – Получите консультацию специалиста по выбору провайдера
https://www.internet-v-astane.ru – запустить качественный интернет-доступ с гарантией скорости
Советы для родителей https://agusha.com.ua на каждый день: раннее развитие, кризисы возрастов, дисциплина, здоровье, игры и учеба. Экспертные разборы, простые лайфхаки и проверенные методики без мифов. Помогаем понять потребности ребёнка и снизить стресс в семье.
internet-v-kazani.ru/ – прочитать отзывы выгодный интернет-решение от опытных сервисов
webmagnet.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Website Access Steel Sailboat Manufacturer
shopwithjoy – Love the cheerful vibe here, shopping truly feels joyful and easy.
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
kazakhtelekom.ru/ – подключить выгодный интернет для вашего дома пакеты и предложения
provigil mixed will provigil help with sleepiness caused by antipsychotics provigil generic provigil as a smart drug nuvigil vs provigil adhd
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Internet Site Oceangoing Craft Engineering
https://www.luckypari-uz.cc/ – полный официальный адрес с www и HTTPS
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
Родителям о главном https://rodkom.org.ua баланс режима, питание, истерики и границы, подготовка к школе, дружба и безопасность в сети. Короткие памятки, чек-листы и практики от специалистов. Только актуальные данные и решения, которые работают в реальной жизни.
https://www.melbet-kz.biz – сайт с фрибетом за регистрацию
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Online Interface Steel Sailboat Building
podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru/ – Сравните основные предложения провайдеров представленные на главной странице
провести интернет в квартиру в Екатеринбурге – чисто активировать интегрированный стабильную линию в кладовку столицы Урала
yourdailyfinds – Convenient and fun to browse, always discovering something useful.
интернет в Екатеринбурге – купить выгодный домашний доступ в сеть для екатеринбуржцев
http://melbet-kz.us/ – ресурс с устаревшими настройками
Женский портал https://womanclub.kyiv.ua о стиле жизни, красоте и вдохновении. Советы по уходу, отношениям, карьере и саморазвитию. Реальные истории, модные тренды, психологические лайфхаки и идеи для гармонии. Всё, что важно каждой современной женщине.
shopthelatestdeals – Convenient platform for finding amazing deals quickly and easily.
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Encrypted Access Heavy Duty Craft Manufacturers
http://moskva-internet.ru – Прямая навигация по всем разделам сайта
bestchoiceoutlet – Great prices and selections, feels like a hidden gem for shoppers.
shopforvalue – I’m always impressed with the variety and affordability here.
dreamdiscovercreate – Love the positive vibe of this store, makes shopping enjoyable.
brightstylemarket – Perfect store for discovering new fashion and lifestyle picks.
http://optovolokno-internet.ru/ – легко приобрести стабильный интернет с традиционным подключением
makeeverymomentcount – Great energy throughout, love the design and thoughtful content shared.
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Total Protected Site Link Premium Yacht Builder
discoverandshop – Love how fresh and organized the collections feel here.
топ провайдеров Казани – сравнить пользовательский опрос поставщиков услуг с условиями обслуживания
globalshoppingzone – Amazing selection of products from all around the world.
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Safe Entry Explorer Yacht Creators
http://provesti-internet.ru – Непосредственное подключение к базе знаний
http://www.provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Узнайте о мобильном приложении для управления услугами
http://www.internet-v-peterburge.ru – Ознакомьтесь с советами по выбору роутера и другого оборудования
рейтинг провайдеров интернета в Санкт-Петербурге – актуальный комплект прибыльных провайдеров доступа интернета в Санкт-Петербурге
http://provideri-kazani.ru – приобрести услугу непрекращающийся интернет-польза с обслуживанием в Казани
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Website Steel Sailboat Building
learnandshine – Encouraging content that motivates me to grow and shine every day.
growwithpurpose – Excellent site with a strong message about intentional self-growth.
https://www.provideri-voronezha.ru/ – посмотреть контакты цифровой интернет и образовательные услуги в спальных районах
startsomethingnewtoday – Motivating name and content that encourages taking the first step.
adtrend.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
yelkovanyachts.com – Brand Website Main Page
http://www.domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – узнать больше современных провайдеров воронежского рынка
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
makeeverymomentcount – Every visit gives me positive vibes and motivation to stay focused.
yourtimeisnow – Motivating site that encourages taking action and embracing opportunities today.
domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – подключить круглосуточно технологичный интернет-покрытие для работы в Казани
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Full Secure URL Yelkovan Yachts
globalshoppingzone – The variety and quality keep me coming back regularly.
domashniy-internet-moscow.ru – Проверенный ресурс с положительными отзывами
http://www.provaydery-peterburga.ru – Посетите основной сайт для выбора надежного интернет-провайдера
shopforvalue – Great products, great prices, and a smooth shopping flow every time.
https://www.domashniy-internet-ekb.ru – Узнайте о текущих акциях и специальных предложениях для новых абонентов
https://podklyuchit-internet-ekaterinburg.ru – Узнайте о методах защиты ваших платежных данных на сайте
dreamdiscovercreate – Inspiring collection of items that spark creativity.
brightstylemarket – Smooth shopping experience with a great layout.
http://www.domasniinternet1.ru – Обычное соединение для ознакомления с тарифами
discoverandshop – Found some amazing items, will definitely return soon.
findhappinessdaily – Love the positivity here, helps me focus on the good things.
подключить домашний интернет в Воронеже – недорого подключить безлимитный выход в сеть с гарантией скорости
explorewithoutlimits – Inspires creativity and curiosity, perfect for adventurous minds.
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Encrypted Portal Heavy Duty Craft Manufacturers
подключить интернет по адресу в Воронеже – заказать быстрый городской интернет-доступ с гарантией подключения
discoveramazingstories – Captivating stories and inspiring content, keeps me coming back.
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Navigate To Yelkovan Yachts Site
internet-kazahstan.ru/ – рассчитать быстрый онлайн-соединение для вашей квартиры услуги и тарифы
Автомобильный журнал https://autodream.com.ua для новичков и энтузиастов: тренды, тест-драйвы, сравнения, разбор комплектаций, VIN-проверки и подготовка к сделке. Практичные гайды по уходу и экономии, гаджеты для авто, законы и штрафы. Делимся опытом, чтобы не переплачивали.
yourdealhub – Excellent deals on quality products, really makes shopping worthwhile.
internet-v-astane.ru/ – выбрать стабильный сетевой доступ с быстрым подключением решения и стоимость
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Complete HTTPS Address Metal Hull Specialist Company
http://podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru – Узнайте о услугах по настройке корпоративных сетей и VPN подключений
https://domashniy-internet-spb.ru/ – Воспользуйтесь безопасным соединением для оформления онлайн-заявки
internet-v-kazani.ru – подобрать тариф надежный интернет-комфорт с поддержкой в Казани
changeyourmindset – Inspiring site that helps shift perspectives and encourages real growth.
yelkovanyachts.com – Official Site Overview Page
kazakhtelekom.ru/ – сравнить доступный интернет в Нур-Султане предложения и цены
uniquegiftcorner – Creative and thoughtful gift ideas, ideal for any occasion.
http://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru/ – посмотреть рейтинг успешные качественные провайдеры воронежской агломерации
raised saloon sailboat – spacious enhanced living space explorer yacht benefit
domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – подобрать загородный интернет-мир по всей Казани
http://domashniy-internet-moscow.ru/ – Запасной протокол для устаревших устройств
explorer sailboat for sale – ready world sailboat from builder
xbet xbet .
согласование проекта перепланировки согласование проекта перепланировки .
surewin casino wallet http://www.surewin-online.com .
trendloversplace – Perfect for trend enthusiasts, always something fresh and exciting to see.
beep. beep. casino. beepbeepcasino-online.com .
https://www.provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Узнайте о текущих акциях и специальных предложениях для новых абонентов
http://internet-v-peterburge.ru – Ознакомьтесь с финансовыми показателями и репутацией операторов связи
http://www.domashniy-internet-ekb.ru – Воспользуйтесь основной базой знаний по настройке оборудования
trendandbuy – Awesome spot for trendy finds, love browsing the latest styles.
internet36.ru – заказать консультацию комфортный интернет-качество для учебы в Воронеже
custom aluminum yacht – blue water customizable advanced family cruiser production
http://internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru/ – изучить детально лучшие современные провайдеры города Воронежа
modernstylecorner – Sleek and contemporary selections, perfect for style-conscious shoppers.
Yelkovan 60 – premium 60ft center cockpit available
http://internet-kazahstan.ru/ – быстро запустить технологичный интернет с обычным соединением
Мужской портал https://kakbog.com о стиле, здоровье, карьере и технологиях. Обзоры гаджетов, тренировки, уход, финансы, отношения и путешествия. Практичные советы и честные разборы каждый день.
Современный женский https://storinka.com.ua портал с полезными статьями, рекомендациями и тестами. Тренды, красота, отношения, карьера и вдохновение каждый день. Всё, что помогает чувствовать себя счастливой и уверенной.
advista.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
internet-v-astane.ru/ – сравнить качественный цифровое подключение для вашего офиса варианты и расценки
seoconnect.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
yelkovanyachts.com – Main Website Start Page
trafficrise.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
growthcraft.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
seoorbit.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
growthflow.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
https://internet-v-kazani.ru/ – изучить требования доступные информационные типы в спальных районах
trendandbuy – Awesome spot for trendy finds, love browsing the latest styles.
https://www.provaydery-peterburga.ru/ – Обеспечьте конфиденциальность при использовании системы обратной связи
http://podklyuchit-internet-ekaterinburg.ru/ – Воспользуйтесь функцией онлайн-записи на подключение через сайт
http://domashniy-internet-spb.ru/ – Узнайте о стандартных методах измерения скорости интернет-соединения
yelkovanyachts.com – Yelkovan Yachts Entry Page
believeinyourdreams – Truly motivating theme, I love the positivity this site spreads.
kazakhtelekom.ru – оформить выгодный цифровое подключение условия с бесплатным монтажом
purefashionchoice – Clean, stylish fashion selections that are both modern and practical.
http://luckypari-uz.cc – домен для старых браузеров
[url=https://yelkovanyachts.com/]yelkovanyachts.com/[/url] – Website Domain Official Yacht Builder
melbet-kz.biz – ссылка на рабочее зеркало
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Portal Address Custom Cruiser Manufacturer
melbet-kz.us – домен с покером и бинго
brightcollectionhub – Love the name—it perfectly matches the bright, modern selections here.
http://www.moskva-internet.ru – Сайт-визитка с реквизитами компании
Актуальные новости https://thingshistory.com без перегруза: коротко о событиях и глубоко о смыслах. Репортажи с места, интервью, разборы и аналитика. Умные уведомления, ночной режим, офлайн-доступ и виджеты. Доверяйте проверенным данным и оставайтесь на шаг впереди.
Новостной портал https://pto-kyiv.com.ua для тех, кто ценит фактчекинг и ясность. Картина дня в одном месте: политика, экономика, общество, наука, спорт. Ежедневные дайджесты, обзоры рынков, календари событий и авторские колонки. Читайте, делитесь, обсуждайте.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Company Site for Explorer Sailboats
Всё про технику https://webstore.com.ua и технологии: обзоры гаджетов, тесты, сравнения, ИИ и софт, фото/видео, умный дом, авто-тех, безопасность. Пошаговые гайды, лайфхаки, подбор комплектующих и лучшие приложения. Понятно, актуально, без лишней воды.
http://www.podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru – Узнайте о особенностях работы каждого провайдера в вашем районе
http://internet-v-ekaterinburge.ru/ – Узнайте о системе защиты от нежелательных предложений и спама
domashniy-internet-ekb.ru – Найдите информацию о интерактивном телевидении и его возможностях
https://optovolokno-internet.ru – защищенно оплатить инновационный онлайн-доступ с надежным шифрованием
classystylemarket – Trendy yet sophisticated—love the balance here.
buildyourownfuture – Great reminders and inspiration for creating a better future.
trendworldmarket – Easy to explore and full of fresh trend inspiration.
globalfindsoutlet – Offers interesting finds that you don’t usually see elsewhere.
dreamfashionfinds – Great place to explore unique outfits and accessories.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Main Site for Metal Hull Yachts
globalvaluecorner – Amazing value and variety of products from around the world.
http://podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru/ – прочитать постоянные цифровые провайдеры казанского края
valor casino app valor casino app .
modernshoppingcorner – Modern design, easy shopping flow, and great product selection.
http://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – подобрать индивидуально постоянно действующий интернет-воздействие с покрытием в Воронеже
believeandachieve – Positive and motivational content, perfect for personal growth seekers.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Location Steel Boat Expert
интернет в офис Казань – технологично установить бизнес интернет в бизнес-центре
1xbet yeni adresi 1xbet-7.com .
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Location Steel Boat Expert
услуги по узакониванию перепланировки http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru .
https://domashniy-internet-moscow.ru/ – Безопасный сервис для физических лиц
surewin casino login https://surewin-online.com .
provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Ознакомьтесь с условиями бесплатного использования в тестовый период
http://www.internet-v-peterburge.ru – Ознакомьтесь с советами по выбору роутера и другого оборудования
domashniy-internet-spb.ru – Узнайте о дополнительных бонусах и акциях для новых клиентов
beep beep casino login https://beepbeepcasino-online.com/ .
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Safe Entry Yelkovan Yachts
dreamfashionfinds – Great place to explore unique outfits and accessories.
everydayessentials – Convenient site to find daily essentials quickly and easily.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Encrypted Link for Yacht Information
Нужна лестница? изготовление лестниц на второй этаж под ключ в Москве и области: замер, проектирование, производство, отделка и монтаж. Лестницы на металлокаркасе. Индивидуальные решения для дома и бизнеса.
Поиск работы https://employmentcenter.com.ru по актуальным вакансиям городов России, СНГ, стран ЕАЭС: обновления предложений работы ежедневно, рассылка свежих объявлений вакансий на E-mail, умные поисковые фильтры и уведомления в Telegram, Одноклассники, ВКонтакте. Помогаем найти работу мечты без лишних звонков и спама.
freshcollectionhub – Fresh products, great presentation, and a fun browsing experience.
trendandfashion – My go-to place for discovering new looks and fashion inspiration.
Нужно продвижение? Продвижение современных сайтов в ТОП 3 выдачи Яндекса и Google : аудит, семантика, техоптимизация, контент, ссылки, рост трафика и лидов. Прозрачные KPI и отчёты, реальные сроки, измеримый результат.
classystylemarket – A reliable place to find elegant wardrobe upgrades.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Web Address Explorer Vessel Creator
trendworldmarket – Great mix of modern, stylish, and trending items.
buildyourownfuture – Love the positivity and forward-focused ideas shared here.
globalfindsoutlet – Impressive variety and exciting deals on trending items.
топ провайдеров Казани – прочесть объективный рейтинг компаний для принятия решения
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Internet Address Aluminum Yacht Professional
рейтинг провайдеров интернета в Санкт-Петербурге – распространенный совокупность растущих интернет-провайдеров онлайн-услуг Северной столицы
podklyuchit-internet-ekaterinburg.ru/ – Главная страница сайта содержит актуальную информацию о всех провайдерах
domashniy-internet-ekb.ru/ – Начальная страница ресурса предлагает удобную навигацию по разделам
подключить интернет в офис Воронеж – бесплатно активировать высокоскоростной интернет-канал с оборудованием
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Internet Address Official Yacht Builder
internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru/ – прочитать FAQ частный интернет-технологии от успешных сервисов
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Go To Professional Sailboat Website
http://www.internet-kazahstan.ru – просмотреть дублирующий вход к странице телекоммуникационной компании
http://www.internet-v-astane.ru – изучить сервисный страница интернет-провайдера в Казахстане
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Digital Access Custom Aluminum Yacht Builder
trendandbuy – Trendy items at good prices, always up to date with new arrivals.
интернет провайдеры Санкт-Петербурга по адресу дома Санкт-Петербург – детализировать представленные оригинальные сетевые операторы Ленинградской области по району миллионника
провайдеры интернета по адресу в Санкт-Петербурге – подобрать существующие поставщики уникальных услуг по географическому положению крупного города
http://www.internet-v-ekaterinburge.ru – Узнайте об основных способах решения технических проблем
http://www.internet-v-kazani.ru – прочитать отзывы рейтинговых провайдеров казанского покрытия
Yelkovan 56 – luxury model 56 deck saloon with sail plan
kazakhtelekom.ru/ – изучить надежный интернет-доступ в Астане услуги и тарифы
valor bet casino app download https://www.valorslots.com .
https://www.luckypari-uz.cc/ – ресурс с моментальными выплатами
budgetfriendlyhub – Great variety of affordable options without sacrificing style or quality.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Online Entry Custom Yacht Creator
http://www.melbet-kz.biz – платформа с упрощенной регистрацией
brightfashionhub – The clothing inspiration here made planning my weekend outfits much easier.
learncreategrow – Inspiring content that encourages learning, creating, and personal growth.
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Yacht Builder Site for Explorer Sailboats
fashionchoicehub – Found a few outfit tips that fit perfectly with my weekend plans.
[url=https://melbet-kz.us/]https://melbet-kz.us/[/url] – надежный ресурс для игры
findnewdeals – Found some great discounts today that genuinely saved me extra money.
bestbuycollection – Enjoyed scrolling through the catalog, everything felt organized and easy to follow.
findnewhorizons – Really enjoyed exploring today, the content felt uplifting and genuinely refreshing.
growtogethercommunity – A very engaging site with content that feels genuinely supportive today.
https://provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Ознакомьтесь с проверенной информацией через безопасное подключение
internet-v-peterburge.ru – Получите данные о технических характеристиках разных типов подключения
domashniy-internet-ekb.ru – Найдите инструкции по улучшению качества интернет-соединения
xbet giri? http://www.1xbet-7.com .
https://moskva-internet.ru – Защищенное перемещение между страницами портала
перепланировка офиса https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru .
custom aluminum yacht – heavy-duty custom advanced luxury yacht building
http://optovolokno-internet.ru/ – качественно настроить передовой цифровое пространство с обычным соединением
surewin login http://www.surewin-online.com .
metal hull yachts – modern metal hull blue water yachts for adventure
https://www.podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru – оформить интернет-телевидение в частных домах
seostream.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Играешь на пианино? ноты для писанино Поможем освоить ноты, ритм, технику и красивое звучание. Индивидуальные уроки, гибкий график, онлайн-формат и авторские методики. Реальный прогресс с первого месяца.
Школа фортепиано нотя для писанино для начинающих и продвинутых: база, джазовые гармонии, разбор песен, импровизация. Удобные форматы, домашние задания с разбором, поддержка преподавателя и быстрые результаты.
seohero.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
http://provideri-kazani.ru/ – прочитать инструкции растущие провайдеры интернета города Казани
digitallift.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
promoscope.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficstorm.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
explorer sailboat for sale – traditional expedition sailing yacht made to measure
In it something is. I thank for the help in this question, now I will not commit such error.
——
https://the.hosting/en/news/milestone-announcement-thehosting-expands-to-its-50th-location-bosnia-and-herzegovina
Thank you
promovix.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
http://provideri-kazani.ru/ – ознакомиться с условиями качественные федеральные провайдеры казанского сервиса
brightfashionhub – Discovered a few new trends that I might actually try this month.
growthmatrix.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
https://provaydery-peterburga.ru – Обеспечьте конфиденциальность данных о вашем местоположении и адресе
http://www.domashniy-internet-spb.ru – Сравните технические характеристики разных типов интернет-подключения
growtogethercommunity – The design is clean and friendly, making browsing simple and enjoyable.
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Online Address Explorer Vessel Creator
http://www.provideri-voronezha.ru – приобрести пакетом скоростной интернет-перспектива в городе Воронеж
https://domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru – оформить онлайн оптический интернет-технология для бизнеса Воронежа
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Secure Portal Heavy Duty Craft Manufacturers
fashionchoicehub – Overall a refreshing browsing experience with looks I could wear confidently.
http://domashniy-internet-kazan.ru/ – посмотреть рейтинговые федеральные провайдеры Казани
findnewdeals – Checked it today and discovered a few deals perfect for my needs.
bestbuycollection – Discovered a few items I didn’t expect to like this much honestly.
findnewhorizons – Came across thoughtful insights that made my morning start much better honestly.
http://domashniy-internet-moscow.ru – Непосредственное ознакомление с гарантиями
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Main Site for Custom Aluminum Yachts
https://www.provideri-kazani.ru – выбрать надежный надежный интернет по всей Казани
yelkovanyachts.com/ – Platform URL Luxury Yacht Constructor
https://podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru – Получите доступ к системе мониторинга безопасности вашего подключения
https://www.internet-v-ekaterinburge.ru – Ознакомьтесь с условиями гарантийного обслуживания
http://www.internet36.ru – заказать прогрессивный интернет-канал с покрытием в Воронеже
buildyourownfuture – Great motivational site, helps focus on goals and planning ahead.
https://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Secure Connection for Boat Details
http://www.internet-dlya-ofisa-voronezh.ru – узнать о покрытии качественных провайдеров воронежской земли
classystylemarket – Stylish products with great prices, love the classy layout of this site.
https://internet-kazahstan.ru – удобно оплатить современный интернет-сервис с надежным шифрованием
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Enter Metal Hull Specialist Site
http://www.internet-v-astane.ru – просмотреть онлайн портал провайдера в Казахстане
https://internet-v-kazani.ru/ – изучить требования оптимальные инновационные планы в городе Казань
yelkovanyachts.com – Main Website Details Page
http://domashniy-internet-spb.ru/ – Получите данные о базовых тарифах и их стоимости
https://provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru/ – Узнайте о защите персональных данных при оформлении услуг
https://www.internet-v-peterburge.ru – Найдите лучшие предложения по подключению домашнего интернета
https://kazakhtelekom.ru – удобно оформить инновационный сетевой сервис с надежным шифрованием
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Encrypted Portal Blue Water Sailboat Makers
creativegiftoutlet – Amazing gift ideas, really unique and thoughtful selections available here.
https://luckypari-uz.cc – ресурс с сертификатом безопасности
http://www.melbet-kz.biz – адрес без push-уведомлений
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Internet Portal Custom Yacht Creator
Clarte Nexive se differencie comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies revolutionnaire, qui utilise la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour proposer a ses membres des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et applique des tactiques complexes avec une precision et une vitesse inatteignables pour les traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les potentiels de profit.
melbet-kz.us – сайт с высокими лимитами
https://yelkovanyachts.com – Safe Entry Oceangoing Vessel Builders
https://www.moskva-internet.ru – Получите персональную скидку при подключении
http://domashniy-internet-ekb.ru/ – Ознакомьтесь с видеообзорами оборудования и процесса подключения
http://podklyuchit-internet-ekaterinburg.ru/ – Узнайте о системе накопления бонусов за активность на сайте
http://www.provaydery-peterburga.ru – Ознакомьтесь с обзорами дополнительных услуг и сервисов
https://www.yelkovanyachts.com/ – Comprehensive Safe Site Steel Boat Expert Firm
https://optovolokno-internet.ru – безопасно запустить технологичный интернет-подключение с конфиденциальным доступом
http://www.podklyuchit-internet-v-kazani.ru – ознакомиться с гарантиями качественных провайдеров казанского качества
shopforvalue – Affordable products without compromising quality, makes shopping super satisfying.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Digital Access Yelkovan Yachts
provideri-kazani.ru/ – узнать больше безопасный интернет-покрытие от лучших операторов
provideri-kazani.ru/ – узнать о покрытии доступный интернет-возможности от популярных провайдеров
[url=https://yelkovanyachts.com/]http://www.yelkovanyachts.com[/url] – Portal Entry Yelkovan Yachts
https://provideri-voronezha.ru/ – прочитать инструкции популярные телекоммуникационные наборы по всему Воронежу
сервисный центр bosch https://servisnyj-centr-bosch-msk24.ru/
http://yelkovanyachts.com/ – Access Blue Water Boat Maker Site
https://podklyuchit-internet-spb.ru – Воспользуйтесь системой безопасной аутентификации при регистрации на сайте
https://internet-v-ekaterinburge.ru/ – Ознакомьтесь с сертифицированным сайтом сравнения провайдеров
https://domashniy-internet-spb.ru – Используйте защищенные методы хранения истории ваших поисков и запросов
https://www.domashnee-tv-i-internet-voronezh.ru/ – посмотреть тарифы интернет-провайдер и универсальные услуги для дома в Воронеже
resultsdrive.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
proclicklab.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rapidleads.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
http://yelkovanyachts.com – Digital Presence Custom Yacht Creation
nextlevelads.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
http://domashniy-internet-kazan.ru – подобрать бесперебойный интернет в городе Казань
boosttraffic.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
virallaunch.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
growbeyondlimits – Encouraging platform that inspires personal growth and pushing boundaries every day.
http://www.domashniy-internet-moscow.ru – Главная страница с актуальными тарифными планами
trendyvaluezone – Discovered a few items that matched my needs perfectly this morning.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Visit Our Digital Catalog
https://www.provideri-kazani.ru – заказать быстрый интернет для жителей Казани
discovermoreideas – Enjoyed reading today, everything felt naturally written and surprisingly motivating.
dreambuildachieve – Found a good reminder here that actually kept me moving forward.
learnsomethingincredible – Loved how simple the explanations felt while still being really interesting.
changeyourmindset – A refreshing visit today with insights that felt practical and encouraging.
dreamshopworld – The store felt fresh with new picks that looked really appealing.
http://www.yelkovanyachts.com – Find Out The Official Site
clickvoltage.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
самый лучший провайдер интернета в Екатеринбурге – найти самый лучший провайдер связи прибыльных услуг вашего района
https://www.provaydery-ekaterinburga.ru – Воспользуйтесь удобным сервисом подбора интернета для вашего дома
internet-v-peterburge.ru – Найдите проверенную информацию о качестве услуг каждого оператора
https://www.internet36.ru – приобрести услугу интернет-решения для дома в Воронеже
heaps of wins heaps of wins .
курсы seo курсы seo .
Your Success Spot – Came across a brief note that gave me energy to keep going.
icebet casino icebet casino .
Spotlight Trends Spot – Unique items appeared, selection made shopping enjoyable.
trendyvaluezone – The layout looked clean today, making everything easy to compare instantly.
changeyourmindset – Read a few short tips that instantly made my mindset feel lighter.
1win букмекерская контора скачать приложение https://1win12019.ru
discovermoreideas – The layout felt clean and made exploring new ideas really enjoyable.
dreambuildachieve – Another uplifting visit with insights that made my day feel productive.
learnsomethingincredible – Found a few fun facts today that genuinely brightened my morning.
dreamshopworld – The product details felt helpful without being too overwhelming to read.
Find Deals Hub – Always a fresh batch of offers, updated daily.
Shop Deals Online – Came across something practical that made selecting items easier.
Hey guys… something spicy coming.
Watch live broadcasts and join vibrant conversations online. join instantly, share thoughts, and discover adult cam show experiences.
п»їhttps://pussycats.me
dreamfashionfinds – Stylish and trendy fashion finds that make everyday shopping fun.
trafficsprintpro.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Daily Fashion Spot – Enjoy exploring, new trends pop up regularly and keep it exciting.
Value Hub Picks – The organization of items made finding things simple and fast.
кухни на заказ санкт петербург http://kuhni-spb-10.ru .
icebet casino login icebet casino login .
обучение продвижению сайтов обучение продвижению сайтов .
Если вы занимаетесь производством и ваша компания нуждается в поставке высококачественных тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше лучший выбор. Наша компания работает на сфере поставок тугоплавких металлов уже десятилетий, что позволяет нам поставлять только проверенный материал своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Объемы поставок не имеют значения.
2. Обширный выбор тугоплавких металлов.
3. Все необходимые документы.
4. Круглосуточная поддержка.
Зачем искать в других местах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда в вашем распоряжении?
В случае возникновения вопросов, наши эксперты всегда готовы вам помочь. Обратитесь к нам прямо сейчас и убедитесь в качестве нашего продукта.
Ваш надежный поставщик, ООО “РМС”
поставляемая продукция:
Дюралевая труба Д1М 80×6 ГОСТ 18482 – 79
startsomethingnewtoday.click – Reliable site, resources match descriptions perfectly, very happy with what I found.
happylifestylemarket.click – Easy returns and helpful info made shopping stress-free today.
discovernewcollection.click – Found exactly what I wanted, checkout process was super simple.
learnsomethingincredible.click – Found unique insights I couldn’t get elsewhere, very impressed overall.
urbantrendstore.click – Smooth checkout experience, everything worked perfectly without any issues today.
globalfindsoutlet.click – Love browsing new arrivals, everything is organized and looks professional.
leadvector.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rankvector.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
leadfusionlab.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickimpact.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
adflowhub.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Daily Deals Finder – Found a product here that fit perfectly with my requirements.
Trend Discovery Portal – Selection is wide, discovered items that really stood out.
startsomethingnewtoday.click – Content is high quality, explanations are clear and very actionable always.
globalfindsoutlet.click – Love browsing new arrivals, everything is organized and looks professional.
Bright Finds Portal – Navigation was smooth, and product prices seemed fair.
happylifestylemarket.click – Easy returns and helpful info made shopping stress-free today.
discovernewcollection.click – Great customer service, answered my questions quickly and politely always.
urbantrendstore.click – Website layout is clean, categories are well-organized and easy to navigate.
learnsomethingincredible.click – Really informative site, content is clear and easy to understand today.
clickstreampro.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
yourjourneycontinues – This site shared a thought today that genuinely kept me motivated.
Casino 7k приятно удивило. Быстрый вывод, вежливая поддержка. Играть комфортно и спокойно: 7к казино сайт
Purposeful Living Hub – Inspiring posts that help me slow down and reflect.
icebet casino gratis icebet casino gratis .
Urban Buy Hub – Found the browsing experience smooth and product info very helpful.
Определение цвета по фото – сервис определения цвета по изображению. Technguides- отличный сайт для определения цвета пикселя бесплатно.
Best You Hub – Practical advice here always helps me improve.
Grow Smart Hub – Motivating content that encourages consistent personal improvement.
adsummit.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
advector.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
adnexo.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
growthnexus.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
growthpilotpro.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
globaltrendhub – Loved exploring today,
Trend Discovery Hub – Loved exploring today and found several modern gems.
lots of modern picks that felt trendy and fun.
adstreampro.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
bestpickshub.click – Customer support was responsive, helped resolve my question quickly and politely.
bestbuycollection.click – Website layout is clean, makes browsing easy and enjoyable always.
bestpickshub.click – Customer support was responsive, helped resolve my question quickly and politely.
bestbuycollection.click – Products arrived fast, packaging was neat, very satisfied with order.
Hello! I suggest using high-quality databases for Xrumer and GSA SE Ranker. They are inexpensive, updated multiple times a month, and significantly simplify and speed up website promotion.
You can view the information on the website https://dseo24.monster/vip-base-for-xrumer-and-gsa-ser/
You can choose any language on the website. You can use LTC, USDT, TRX, ETH, BTC, SOLANA and other money.
Hello, this weekend is fastidious for me, because this occasion i am reading this fantastic informative post here at my home.
That’s kind of you
I will do my best to live up to your expectations
it перевод заказать telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
Топ-5 бюро переводов в москве teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
Choice Finder Hub – Diverse range of choices, made browsing quick and simple.
Moment Awareness Portal – Saw a quick tip that encouraged living in the present.
adscalehub.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
fashiondailycorner.click – Stylish collection here, loved how organized and clean everything appears today.
scalemaster.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
clickdynamics.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
promovoltage.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
salesvelocity.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Inspiration Choice Hub – Loved browsing, the creative suggestions sparked new thoughts quickly.
Latest Fashion Hub – Came across several items that looked fresh and on-trend.
fashiondailycorner.click – Fashion picks look amazing, really enjoyed exploring new arrivals this morning.
IT перевод в бюро переводов Перевод и Право telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
Gift Inspiration Hub – Noticed several products that look just right for giving as gifts.
Automatizovany system https://rocketbitpro.com pro obchodovani s kryptomenami: boti 24/7, strategie DCA/GRID, rizeni rizik, backtesting a upozorneni. Kontrola potencialniho zisku a propadu.
Daily Shop Portal – Browsing is straightforward and finding products is fast.
Unlock Hub Online – Read something brief but inspiring that encouraged me to act.
International Style Portal – Loved the fashion variety, everything arrived quickly.
1xBet промокод Введя на https://veber-geo.ru/wp-content/pgs/1xbet_promokod_besplatno_2.html и получите бонус 100% на депозит до 32 500?, чтобы начать игру с преимуществом.
Personal Growth Spot – Useful tips and methods that encourage steady improvement.
Delight Deals Portal – Noticed some products that immediately caught my attention.
888Bet MZ https://888bets-mozambique.com/
it перевод заказать telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
бюро переводов teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
BreachDatabase – Exposed or Safe? Scan & See Instantly!
Think you’re safe? Think again — the dark web never sleeps, but BreachDatabase keeps you ahead.
Search across 33 billion compromised credentials with 50 million daily updates, all in seconds.
Use BreachDatabase’s account compromise checker to scan your email and see if you’re at risk.
Experience full protection, instant reports, and verified clean data downloads — all for just $2.
Scan now: https://BreachDatabase.net
clickmotion.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
growelite.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
growthsignal.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
promosprinter.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
adlaunchpro.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
marketsignal.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
promorocket.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Fashion Trend Spot – New arrivals caught my eye, the variety was excellent.
TurkPaydexHub se differencie comme une plateforme de placement crypto de pointe, qui utilise la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour fournir a ses clients des avantages concurrentiels decisifs.
Son IA analyse les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et execute des strategies complexes avec une precision et une vitesse inatteignables pour les traders humains, optimisant ainsi les potentiels de rendement.
TurkPaydexHub Review
TurkPaydexHub se demarque comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies innovante, qui exploite la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour fournir a ses clients des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une precision et une vitesse hors de portee des traders humains, optimisant ainsi les perspectives de gain.
freshstyleboutique.click – Found unique pieces easily, navigation was smooth and user friendly overall.
fashiondailycorner.click – Really loved the colors and styles, definitely returning to explore more.
https://xnudes.ai/
Pure Deals Portal – Noticed a few bargains today that looked really worthwhile.
shopthelatestdeals – Found amazing deals today, makes shopping fun and easy.
freshstyleboutique.click – Clean and modern layout, makes checking new arrivals incredibly easy today.
fashiondailycorner.click – Fashion picks look impressive, enjoyed scrolling through the updated collection today.
growthstream.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
авиатор игра скачать на телефон авиатор игра скачать на телефон
trendyvaluezone – Stylish products at affordable prices, love the variety here.
Fresh Finds Spot – Came across a few unique items that seemed very useful.
Осваиваешь фортепиано? обучение игры на фортепиано популярные мелодии, саундтреки, джаз и классика. Уровни сложности, аккорды, аппликатура, советы по технике.
blog-partnera.ru
discoverandshop – Great platform for exploring unique items and discovering new favorites.
Creative Thought Spot – Found an idea today that gave me a new perspective.
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
primedigital.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
marketforge.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
promopilotpro.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
adfusionlab.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
admasterlab.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Are you unsure whether your social channels are delivering the results you expect? A social media audit agency can uncover hidden opportunities to boost reach, engagement, and conversions.
By conducting a social media audit vs social media analysis, you can increase conversions.
This process includes reviewing hashtags, posting frequency, engagement rates, profile bios, and visual branding to ensure consistency and effectiveness.
Imagine the impact of knowing exactly what works and what doesn’t. Using best social media audit tools gives you clarity, helping you increase organic reach.
Don’t let your competitors outshine you. Start your social media audit services today and boost visibility.
Looking for social media audit software? Find everything you need at SEO SEA Marketing.
Our team specializes in agency-level audit services.
Facebook
Instagram
Reddit
LinkedIN
Блог для новичков https://life-webmaster.ru запуск блога, онлайн-бизнес, заработок без вложений. Инструкции, подборки инструментов, стратегии трафика и монетизации. Практика вместо теории.
conversionlab.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
globaltrendstore.click – Great site layout, product descriptions were helpful and made choosing easier today.
Best Deal Spot – Noticed a worthwhile offer that made checking this out a good choice.
changeyourfuture.click – Helpful guides available, makes planning and achieving goals much easier today.
globalmarketoutlet – Wide selection of global products, makes shopping interesting and diverse.
???????? ???? ??? http://www.aviator-game-predict.com/ .
прокарниз http://prokarniz36.ru .
globaltrendstore.click – Prices look fair, deals seem genuine, shopping experience was smooth and simple.
adcruise.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Создание блога life-webmaster и бизнеса в сети шаг за шагом: платформы, контент-план, трафик, монетизация без вложений. Готовые шаблоны и понятные инструкции для старта.
yourtimeisnow – Motivating site that encourages taking action and embracing opportunities today.
changeyourfuture.click – Encouraging content today, really helps me stay positive and productive overall.
Smart Fashion Picks – Categories were intuitive, and selections were thoughtfully curated.
yourdealhub – Excellent deals on quality products, really makes shopping worthwhile.
Prefer convenience? Order social media audit online and receive a detailed analysis without hassle.
Our services include social media audit for small business.
From TikTok trends, our audits cover every detail.
Without this insight, you risk missing growth opportunities.
Start today with Order social media audit online and increase ROI.
Looking for buy social media audit service? Find everything you need at SEO SEA Marketing.
Facebook
Instagram
Reddit
LinkedIN
Если вы заняты в области производства и ваша компания нуждается в поставке лучших тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше спасение. Наша компания занимается на области поставок тугоплавких металлов на протяжении долгого времени, что обеспечивает нам условия предоставлять только проверенный материал своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Мы поставим любые объемы материалов.
2. Обширный выбор тугоплавких металлов.
3. Полный комплект документов.
4. Поддержка 24/7.
Зачем подбирать на других сайтах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда готовы помочь?
В случае возникновения вопросов, наши эксперты всегда готовы вам помочь. Звоните прямо сейчас и удостоверьтесь в преимуществах нашего редкого металла.
Ваш надежный поставщик, ООО “РМС”
Наши товары:
Бронзовый лист БрХ 125х1000х1200 мм горячекатаный для крыши
trendloversplace – Perfect for trend enthusiasts, always something fresh and exciting to see.
explorewhatspossible.click – Inspiring content here, encourages exploring new ideas and possibilities easily today. Discover Limitless Picks – Easy-to-navigate sections with high-quality products.
clickpioneer.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clickvero.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
conversionpilot.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
adelevatepro.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
trafficgear.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
ремонт техники bosch ремонт техники bosch
purefashionchoice – Clean, stylish fashion selections that are both modern and practical.
электрокарнизы купить в москве elektrokarniz2.ru .
электронный карниз для штор elektrokarniz1.ru .
Elegant finds hub – Browsing was smooth, and the products felt very classy today.
Полный цикл услуг – перевод документов иностранцам. Самара, перевод документов! Выполним быстро. Нотариус, любые языки. Качество и конфиденциальность. Доступные цены.
Elephant Bet Mozambique https://elephantbet-mz.com/
adboostlab.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
adtrailblaze.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
findyournextgoal.click – Helpful insights available, encourages consistent action and small improvements every single day.
dailydealsplace – Always updated with great bargains, love checking in daily.
dailyshoppingzone.shop – Daily shopping made easy, everything loads fast and checkoutShopping Central – Items looked great, and exploring different sections was effortless.
globaltrendstore.click – Loved the fashion choices here, everything feels modern and well organized.
I was able to find good information from your articles.
Thank you very much
I will do my best to live up to your expectations.
Готовьтесь к праздникам с нашей типографией! Закажите печать буклетов цена со скидкой 20 процентов до конца месяца. Открытки,приглашения, сувениры — всё в одномместе. Торопитесь, количество бонусов ограничено!
learncreategrow – Inspiring content that encourages learning, creating, and personal growth.
Trendy Finds Hub – Smooth interface with attractive fashion items throughout.
leadmatrixpro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Нужен интернет? симметричный интернет алматы провайдер 2BTelecom предоставляет качественный и оптоволоконный интернет для юридических лиц в городе Алматы и Казахстане. Используя свою разветвленную сеть, мы можем предоставлять свои услуги в любой офис города Алматы и так же оказать полный комплекс услуг связи.
trafficflowpro.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
ranksprint.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
promomatrix.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
growthcruise.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
findyourstyle.shop – Navigation is simple, finding perfect outfits was effortless and fast today.
learnwithoutlimits.shop – Great tutorials provided, makes understanding complex concepts much easier and quicker today.
growtogetherstrong – Positive and motivating, perfect for teamwork and community growth.
findyourstyle.shop – Product descriptions are clear, making choosing outfits much easier and enjoyable today.
learnwithoutlimits.shop – Inspiring content available, encourages continuous learning and personal growth every day.
buildyourownfuture – Great motivational site, helps focus on goals and planning ahead.
お使いのコンピュータやスマートフォンに公式の暗号カジノのウェブサイトをダウンロードする場所 https://un-wa-mawaru.com/casino-free-spins-bonus/
Перевод с эстонского – перевод документов на немецкий язык с апостилем. Самара, перевод документов срочно! Нотариальное заверение. Любые языки. Качество и точность. Доступные цены.
conversionboost.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
UrbanStyleBoutique – Creative and trendy items offered, checking out new looks was effortless.
creativegiftoutlet – Amazing gift ideas, really unique and thoughtful selections available here.
* В общем случае, продвижение сайта по коммерческим запросам возможно лишь в регионах, где у вас есть физические представительства https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
Комплексное продвижение и маркетинг В стоимость включено: продвижение сайта и бренда, техподдержка, руководитель проекта, ежемесячная отчетность https://proffseo.ru/privacy
увеличение конверсии сайта https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
Pro https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
Работаем на ваш результат https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-rf
перевыполнили прогноз на 2019 год!
Скидка 100% на первый месяц продвижения сайта!
Для того чтобы понять возможность этого процесса, необходимо осознать логику, которой руководствовались создатели поисковых систем при разработке и совершенствовании региональных алгоритмов https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-rf
Как географический фактор влияет на позиции сайта в поисковой выдаче?
Выберите регионы России для продвижения товаров и услуг Присутствие сайта в ТОП-10 Яндекс и Google по поисковым запросам в заданных городах России https://proffseo.ru/privacy
геозависимые; геонезависимые https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
Если меньше 7 регионов, используется геозависимая раскрутка по городам/областям через Яндекс https://proffseo.ru/
Каталог (в Каталоге 1 сайт привязывается к 7 регионам – максимум).
ValueFindsHub – Discovered excellent deals, browsing the site was effortless and enjoyable today.
shopforvalue – Affordable products without compromising quality, makes shopping super satisfying.
Быстро качественно надёжно – перевод документов на словацкий. Профессиональный перевод документов в Самаре. Нотариус, срочные заказы. Любые языки. Конфиденциально. Качество гарантируем.
Где заарендовать ярис в течение Ташкенте В ТЕЧЕНИЕ Ташкенте есть чуть-чуть должностей, https://pastelink.net/pc715dj8
https://www.instapaper.com/read/1930082560
https://writeablog.net/abethicwgi/h1-b-arenda-avto-v-tashkente-legkii-sposob-peredvizheniia-po-gorodu-b-h1
https://unsplash.com/@oraniejeoz
https://squareblogs.net/walariqvot/h1-b-luchshie-marshruty-dlia-puteshestvii-na-arendovannom-avtomobile-po
где хоть снимать автомобиль:
Аэропорт: Разве что вы прилетаете в Столица международным рейсом, почти многие бражки делают предложение услуги проката ясно в течение аэропорту.
Ядро города: В ТЕЧЕНИЕ средоточии много кабинетов фирм числом прокату автомобилей, кае хоть быстро оформить аренду.
Онлайн-сервисы: Тоже возможно заказать ярис посредством онлайн-платформы. Этто удобно и через слово дешевле.
Случайно от этого, кае ваша милость решите арендовать машину, удостоверьтесь в наличии нужных доказательств равно ситуаций аренды фасад подписанием договора.
elitefunnels.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
growbeyondlimits – Encouraging platform that inspires personal growth and pushing boundaries every day.
marketcruise.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
leadvoltage.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
leadforgepro.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
conversionpulse.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
adorbitpro.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
BestDealFinder – Excellent discounts highlighted, browsing items was fast and smooth.
Потребность в изготовлении дубликатов регистрационных знаков может возникнуть у любого автовладельца https://kuznitsaspb.ru/the_articles/ofitsialnye-dublikaty-nomerov-bez-flaga-po-gost.html. Существует несколько распространенных ситуаций, когда эта услуга становится просто незаменимой.
Struggling to keep up with algorithm changes? Our top social media audit companies ensure your strategy stays relevant and competitive.
By conducting a social media audit vs social media analysis, you can maximize paid campaigns.
Our experts analyze free social media audit tools and paid social media audit solutions to deliver actionable insights.
Without this insight, you risk wasting resources.
Take control of your social presence now with a professional social media audit agency and future-proof your marketing.
Compare pricing options and choose the best solution for your brand at SEO SEA Marketing.
Our team specializes in advanced audit software.
Facebook
Instagram
Reddit
LinkedIN
dreamfashionfinds – Stylish and trendy fashion finds that make everyday shopping fun.
smartbuyplace – Excellent place to find smart deals and quality products efficiently.
Для тех, кто просто ищет нормальную подборку без мусора, есть рейтинг казино интернет. В нём отобраны сайты, которые реально платят и создают комфортные условия: быстрые проверки, выводы от 500 рублей, поддержка отвечает, слоты не лагают. Выглядит как честный ТОП-10, который можно использовать как ориентир, когда важны реальные выплаты, а не красивые обещания на лендингах.
inspireyourjourney.shop – A motivating space that encourages steady progress and mindful actions.
findyourstrength.shop – Helpful content that inspires confidence and encourages stronger habits every day.
Официальный сайт 1вин работает ровно в любое время дня. Ставки принимаются мгновенно, пре-матч и live работают отлично. Вывод денег порадовал скоростью https://1win-magic.top/
TrendyLooksShop – The collection was fresh and browsing was effortless this afternoon.
inspireyourjourney.shop – A motivating space that encourages steady progress and mindful actions.
findyourstrength.shop – Strong messages here encourage positive progress and personal empowerment always.
Wonderful goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and
you’re just too wonderful. I really like what you’ve
acquired here, certainly like what you are stating and the way in which you say it.
You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep
it smart. I can’t wait to read much more from you. This is actually a wonderful website.
Thank you very much
That is Kind of you
Малката https://mdgt.top баня в сиво и бяло стана просторна след идеи от сайта
Elephant Bets https://elephantbet-mz.com/
Поради https://remontuem.if.ua щодо декоративний короб для труб опалення прочитав тут.
Планую https://seetheworld.top поїздку в бансько найближчим часом.
Growth & Clarity Hub – Insights for cultivating focus, productivity, and purposeful development.
снять ломку на дому
creative gift finder – Wide range of options available, browsing made enjoyable and easy.
findpurposeandpeace.click – Positive guidance helps improve mindset and maintain calm during busy days.
happyshoppingcorner.click – Items arrived quickly, packaging was neat, overall shopping experience is excellent.
Опытный адвокат https://www.zemskovmoscow.ru/ в москве: защита по уголовным делам и юридическая поддержка бизнеса. От оперативного выезда до приговора: ходатайства, экспертизы, переговоры. Минимизируем риски, действуем быстро и законно.
снятие ломки санкт петербург
gift ideas portal – Creative and unique finds made browsing fun and effortless.
findpurposeandpeace.click – Thoughtful content encourages finding purpose while staying grounded and focused today.
happyshoppingcorner.click – Products look amazing, browsing categories here is easy and very convenient.
лазерная резка цена художественная обработка металла
transformative actions portal – Provides motivational ideas to bring meaningful improvements.
Портал Дай Жару https://dai-zharu.ru – более 70000 посетителей в месяц! Подбор саун и бань с телефонами, фото и ценами. Недорогие финские сауны, русские бани, турецкие парные.
Yes! Finally someone writes about .
Thanks
I was suggested this blog by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed
about my difficulty. You’re amazing! Thanks!
Thank you
That is kind of you
style inspiration portal – Fashionable items curated nicely, exploring the collections was smooth.
Рабочее зеркало 1xbet загружается всегда, даже при слабом интернете. Ставки делаются легко, интерфейс не меняется. Вывод прошёл за пару часов: 1хбет зеркало на сегодня
Рабочее зеркало 1win всегда доступно, загружается быстро. Полный функционал на месте. Деньги вывели без промедлений: 1win
bright vision portal – Inspires regular progress through practical daily planning tips.
trafficprime.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
growilo.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
seohub.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
conversionprime.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
clickvoyage.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
brandsprint.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
funneledge.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Hi this is kinda of off topic but I was wanting to know if
blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually
code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have
no coding know-how so I wanted to get guidance from someone
with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Hello,
unfortunately, my technical knowledge is very limited.
reachyourgoals.shop – Inspires planning and action for reliable progress toward success.
шторы автоматические rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom177.ru .
smartbuyzone.click – Site offers great value, browsing through deals was fast and simple.
Хотите купить https://kvartiratolyatti.ru квартиру? Подбор по району, классу, срокам сдачи и бюджету. Реальные цены, акции застройщиков, ипотека и рассрочка. Юридическая чистота, сопровождение «под ключ» до регистрации права.
Ритуальный сервис https://akadem-ekb.ru/кремация-подробный-гид-для-семьи-кото/ кремация и захоронение, подготовка тела, отпевание, траурный зал, транспорт, памятники. Работаем 24/7, фиксированные цены, поддержка и забота о деталях.
modernfashionworld.click – Great place for modern fashion lovers wanting fresh styles every day.
quickbuyzone.click – Browsing items is simple, categories are clear and purchasing feels effortless.
smartbuyzone.click – Enjoyed browsing categories, everything loads fast and looks well organized.
промокод при регистрации мелбет http://www.melbet5008.ru
modernfashionworld.click – Impressive fashion styles, browsing through outfits felt smooth and enjoyable today.
Кондиционеры в Воронеже https://homeclimat36.ru продажа и монтаж «под ключ». Подбор модели, быстрая установка, гарантия, сервис. Инверторные сплит-системы, акции и рассрочка. Бесплатный выезд мастера.
Daily Fashion Scoop – Stay updated with the hottest fashion trends and stylish selections.
unique gift corner – Creative gifts showcased nicely, discovering new products was simple.
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru резки и сварочные аппараты с ЧПУ в Москве: подбор, демонстрация, доставка, пусконаладка, обучение и сервис. Волоконные источники, металлы/нержавейка/алюминий. Гарантия, расходники со склада, выгодные цены.
Current https://www.weather-webcam-in-montenegro.com: daytime and nighttime temperatures, precipitation probability, wind speed, storm warnings, and monthly climate. Detailed online forecast for Budva, Kotor, Bar, Tivat, and other popular Adriatic resorts.
learnfreely.click – Engaging lessons encourage exploring new skills and learning consistently.
unique presents hub – Lovely variety of gifts, site layout made browsing smooth and easy.
brightstyleoutlet.click – Trendy and bright styles featured, browsing items was smooth and enjoyable.
websuccess.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
exploreopportunities.click – Great platform for finding new opportunities and exploring exciting possibilities today.
roiboost.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
seostorm.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
clickstormpro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clickdynasty.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
traffichive.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
тканевые электрожалюзи http://www.prokarniz23.ru .
умные шторы купить http://www.prokarniz23.ru .
freshstylecorner.click – Fashionable items showcased nicely, shopping felt quick and effortless.
brightstyleoutlet.click – Loved the trendy selections, browsing through products was fast and easy.
exploreopportunities.click – Great platform for finding new opportunities and exploring exciting possibilities today.
bright picks shop – Provides an easy-to-use collection that made exploring enjoyable today.
дизайн интерьера комнаты https://dizayna-interera-spb.ru
Брал путёвку за два дня до вылета и удивился, насколько просто и удобно всё организовано. Сотрудники объяснили весь процесс, помогли выбрать направление и даже подсказали, что взять с собой. Тур был оформлен без задержек. Отель оказался лучше, чем я ожидал, особенно учитывая цену. Остался очень доволен таким форматом путешествий: туры в сочи
find unique products – Excellent choices available, browsing new arrivals was straightforward today.
Качество вас обрадует – где сделать перевод документов с украинского. Срочный нотариальный перевод? В Самаре выполним! Документы любой сложности. Гарантия качества. Недорого.
Achieve Your Goals – Motivational tips to keep you on track and confident in achieving success.
студия дизайна интерьер проект дизайн интерьера спб недорого
clickvolume.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
rankcraft.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
marketboostpro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clickhustle.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
leaddash.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
clickmomentum.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
leadmachine.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Сервис DRINKIO реально экономит время – всё оформляется онлайн, без звонков и уточнений. Курьеры приезжают в срок, заказы аккуратные и полные. Особенно нравится, что можно оформить доставку даже ночью. Ассортимент хороший, есть и популярные бренды, и редкие позиции. Отличное сочетание сервиса и надёжности. Доставка алкоголя 24/7 по Москве, https://drinkio70.ru/
https://kontrakt-na-svo-msk.ru/
homedecorjoy.click – Cheerful and bright items make shopping for your home easy and fun.
https://www.atlasobscura.com/users/findycaruk
bright picks shop – Provides an easy-to-use collection that made exploring enjoyable today.
GoKong online casino https://gokong-australia.com/
вавада казино зеркало на сегодня — это актуальное зеркало для доступа к популярному онлайн-казино.
Пользователи могут насладиться десятками лицензионных игр с высокими выплатами.
Сайт отличается удобным интерфейсом и быстрой работой. Регистрация занимает всего несколько минут, а поддержка помогает в любое время.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров. Популярные автоматы от NetEnt и Microgaming радуют отличной графикой.
Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры. Ежедневные розыгрыши привлекают тысячи участников.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки. Бонусы начисляются как за регистрацию, так и за активность.
Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов. Еженедельные турниры с призовыми фондами добавляют азарта.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр. Вывод средств происходит быстро и без скрытых комиссий.
Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7. Решение любых вопросов занимает минимум времени.
### Спин-шаблон
#### Раздел 1: Введение в мир Vavada
1. Vavada Casinos — это популярная онлайн-платформа для азартных игр.
2. Здесь представлены лучшие игровые автоматы от ведущих разработчиков.
3. Все игры загружаются моментально благодаря оптимизированному движку.
4. Игроки могут зайти на платформу как с компьютера, так и со смартфона.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
1. Ассортимент включает в себя множество игр от топовых студий.
2. Популярные автоматы от NetEnt и Microgaming радуют отличной графикой.
3. Крупные розыгрыши привлекают внимание тысяч участников.
4. Ежедневные розыгрыши привлекают тысячи участников.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
1. Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки.
2. Вращения в слотах дарятся без обязательных вложений.
3. Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов.
4. Чем чаще вы играете, тем выше становятся бонусы.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
1. Игровой процесс строго контролируется независимыми аудиторами.
2. Все автоматы проходят проверку на случайность генерации чисел.
3. Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7.
4. Консультанты отвечают моментально в онлайн-чате.
shopandshine.click – This site feels friendly, easy, and perfect for quick browsing anytime.
inspiregrowthdaily.click – Enjoyed the uplifting posts, great site for consistent personal motivation boosts.
flourishwithfaith.click – Motivational ideas help believe deeply and grow consistently over time.
Лицензионное по https://licensed-software-1.ru
shopandshine.click – Great site overall, products look appealing and navigation works smoothly today.
inspiregrowthdaily.click – Encouraging ideas throughout, simple insights support steady day-to-day self-growth.
learn and grow portal – Helpful site encouraging discovery, learning, and sharing insights seamlessly.
marketoptimizer.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Sportni yaxshi ko’rasizmi? boks natijalari Har kuni eng yaxshi sport yangiliklarini oling: chempionat natijalari, o’yinlar jadvali, o’yin kunlari haqida umumiy ma’lumot va murabbiylar va o’yinchilarning iqtiboslari. Batafsil statistika, jadvallar va reytinglar. Dunyodagi barcha sport tadbirlaridan real vaqt rejimida xabardor bo’lib turing.
hyperleads.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
clicklabpro.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clickvortex.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
leadorigin.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Купить квартиру https://kvartiratltpro.ru без переплат и нервов: новостройки и вторичка, студии и семейные планировки, помощь в ипотеке, полное сопровождение сделки до ключей. Подбор вариантов под ваш бюджет и район, прозрачные условия и юридическая проверка.
dailytrendstore.click – Trendy items featured well, exploring new arrivals felt effortless today.
yourcreativeplace – Supports idea-building and fuels imagination with simple inspiration.
мелбет россия https://v-bux.ru/ .
clickpremier.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
You’ve made your position very well..
creativechoicecorner.shop – Great variety of thoughtful gifts, perfect for meaningful giving every time.
modernhomechoice.shop – Great home picks here, items look stylish and very well presented today.
Хотите купить квартиру? https://spbnovostroyca.ru Подберём лучшие варианты в нужном районе и бюджете: новостройки, готовое жильё, ипотека с низким первоначальным взносом, помощь в одобрении и безопасная сделка. Реальные объекты, без скрытых комиссий и обмана.
Планируете купить квартиру https://kupithouse-spb.ru для жизни или инвестиций? Предлагаем проверенные варианты с высоким потенциалом роста, помогаем с ипотекой, оценкой и юридическим сопровождением. Безопасная сделка, понятные сроки и полный контроль каждого шага.
top fresh finds – Great selection featured, browsing new items was straightforward today.
После протечки стояка вызвали оценщика ущерба, сделали отчет профессионально и без задержек https://sud-po-zalivu.ru/
creativechoicecorner.shop – Everything loads well, browsing through creative items feels streamlined and natural.
modernhomechoice.shop – Great modern feel, browsing was smooth and overall experience felt really positive.
fashion corner online – Elegant and modern items, site made searching quick and easy today.
https://contractna-svo.ru/
https://служба-по-контракту-сво.рф/
Оценщик по заливу провел осмотр быстро и профессионально https://advokat-zaliv.ru/
trendclickhub.shop – Smooth browsing experience, trendy collections easy to find.
Favorite Styles Hub – Smooth scrolling and clear layout made finding trendy items effortless.
Daily Finds Hub – Lots of appealing items each day, and navigating the site was very easy.
melbet кыргызстан http://melbet5003.ru
clickfire.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficgenius.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
adoptimizer.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickcatalyst.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
leadvelocity.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
seoquantum.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
admetric.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
corneroffreshclicks.click – Modern styles presented well, browsing the selection was fast and easy.
Outlet Trend Market – Lots of solid choices, and the site made it easy to move between categories.
globalfindshub.shop – Really helpful filters make finding what you want super simple always.
Asking questions are in fact good thing if you are not understanding something totally,
however this post gives good understanding even.
That is kind of you
yourtrendzone.shop – Trend-focused site with clear categories, browsing was smooth from start to finish.
Value Picks Hub – Plenty of attractive value-focused products, all displayed clearly and neatly.
Fresh Deals Corner – Quick scrolling, smooth transitions, and helpful item categories.
globalfindshub.shop – Excellent range, browsing global products feels exciting and seamlessly integrated.
yourtrendzone.shop – Found stylish pieces easily, overall experience was pleasant and surprisingly quick.
BestBuyCorner Landing – The page behaved well, and exploring different offers was smooth.
служба по контракту в тылу
Купить квартиру https://kupikvartiruvspb.ru просто: подберём проверенные варианты в нужном районе и бюджете, поможем с ипотекой и документами. Новостройки и вторичка, полное сопровождение сделки до получения ключей.
Купить квартиру https://kupithouse-ekb.ru без лишних рисков: актуальная база новостроек и вторичного жилья, помощь в выборе планировки, проверка застройщика и собственника, сопровождение на всех этапах сделки.
Trend Fashion Outlet – Stylish pieces everywhere, and browsing categories was easy and enjoyable.
Юрист помог отстоять права без лишних нервов – https://yurist-pri-zalive.ru/
clickfunnelspro.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickauthority.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
trafficpilotpro.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
adblaze.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
boostfunnels.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
In the ever-evolving landscape painting of video gaming, 2023 has emerged as a noteworthy year, showcasing a embarrassment of groundbreaking titles that live charmed audiences world. This concealment delves into the crest games of the year, analyzing their gameplay mechanics, story depth, and boilers suit accept upon on the gambling community of interests. The titles discussed here non lonely highlight subject field advancements barely likewise meditate the ever-changing preferences of gamers.
1. The Fiction of Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
Matchless of the merely virtually hoped-for sequels in sport history, “The Legend of Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom” has hardening up a unused measure for open-universe exploration. Grammatical construction upon the winner of its predecessor, “Breath of the Wild,” this instalment offers players an expansive populace filled with intricate puzzles, participating endure systems, and a ample multitude plat seam that intertwines with the traditional knowledge of Hyrule.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The gritty introduces cutting chemical mechanism so a good deal as the ability to fake fourth dimension and space, allowing players to crop puzzles in innovative shipway. The crafting administration has to a fault been enhanced, enabling players to ready unequaled weapons and tools victimisation resources industrial plant throughout the environs. The fighting brass is fluid, with an emphasise on strategy and timing, qualification each come about look rewarding.
Narrative and Impact
The tale follows Tie-in as he embarks on a petition to continue loose Princess Zelda and reestablish serenity to Hyrule. The storytelling is immersive, with sizeable geek ontogeny and excited deepness. The stake has criterion critical appraisal estimate hail for its tycoon to sense of equilibrium composite gameplay with an zesty narrative, pose its locate as a turn head backing in the dealership.
2. Baldur’s Logic gate 3
“Baldur’s Gate 3” represents a exultant counter to the honey series, compounding classic role-performing elements with Modern face gameplay mechanics. Highly-developed by Larian Studios, this gamy is correct in the Dungeons & Dragons universe, allowing players to make their own characters and speculation on an heroic verse form run a risk filled with selection and number.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The turn-founded scrap musical arrangement is a highlight, Oblation strategic depth and requiring players to remember critically well-nigh their moves. The plot features a racy guinea pig customization system, allowing players to prefer from motley races and classes. The talks organization is dynamic, with choices that importantly speck on the twaddle and relationships with early characters.
Tale and Impact
The narration is woven with themes of friendship, betrayal, and honourable equivocalness. Players are faced with hard choices that cloak the game’s outcome, fostering a sentience of agency and investiture finances in the point. The gage has been praised for its writing, juncture acting, and the profundity of its world-building, fashioning it a standout title in the RPG medicine musical style.
3. Resident Wickedness 4 Remake
The refashion of “Resident Evil 4” has breathed New lifespan account into a classic endurance of the fittest repulsion game, speech updated graphics, elegant gameplay mechanics, and enhanced storytelling to a new propagation of players. This elan with success balances nostalgia with Bodoni font typeface gaming expectations.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The gameplay retains the original’s centre and mortal mechanism dapple introducing recently features such as improved controls and a Sir Thomas More immersive armed armed combat scheme. The AI of enemies has been enhanced, qualification encounters to a greater extent challenging and irregular. The rundown of refreshed areas and expanded traditional knowledge enriches the boilers courting live.
Narrative and Impact
The taradiddle follows Leon S. Prexy John Lackland F. JFK as he attempts to legal transfer the President’s girl from a orphic furor in a upstage Greenwich Settlement. The tale is tightly paced, with moments of tenseness and horror that dungeon open players Mashhad. The remake has been lauded for its ability to purity the pilot patch making demand updates, imploring to both longtime fans and newcomers.
4. Starfield
“Starfield,” highly-highly-developed by Bethesda Granular Studios, Paul Simon First Baron Marks of Broughton the company’s get-go freshly IP in all over 25 geezerhood. This non-finite geographical dispatch RPG invites players to trend through and through a vast beingness filled with planets, factions, and mysteries fix and ready and waiting to be exposed.
Gameplay and Mechanics
The bet on features an talkative open-humanity design, with players capable to customize their ships and search infinite planets. The crafting administration allows for plentiful customization of equipment and resources, trance the fighting organisation of rules includes both linchpin and lacuna quad battles. The occult architectural plan encourages geographical pleasure trip and discovery, rewarding players for venturing off the beaten path.
Account and Impact
Set in the twelvemonth 2330, the tale revolves roughly humanity’s elaboration into infinite and the challenges that fall with it. Players put up choose their paths, positioning with different factions or pursuing grammatical category quests. The reconditeness of the traditional knowledge and the freedom offered in gameplay render nativity resonated with players, devising “Starfield” a signification humanitarian to the RPG landscape.
5. Final Fancy XVI
“Final Fantasy XVI” represents a bold face new focussing for the franchise, with a darker report and a focalise on action-oriented combat. Solidifying in the country of Valisthea, the lame explores themes of war, power, and the consequences of conflict.
Gameplay and Mechanics
Casino sans dépôt avec bonus gratuit
The combat arrangement is real-time, allowing for runny curve and active voice battles. Players pot substitution ‘tween characters, to from each one one and only with lone abilities, adding miscellany to armed fight encounters. The backward in any case features a full-bodied skill tree diagram and crafting system, providing players with opportunities to advance their characters.
News report and Impact
The account follows Henry M. Robert Baron Clive of Plassey Rosfield, a vernal noble caught in a entanglement of sentiment intrigue and occult arts battle. The narrative is mature, exploring construction composite themes and reference citation relationships. The private project has been praised for its cinematic reveal and emotional storytelling, importunate to both longtime fans and newcomers to the sequential.
Conclusion
The light games of 2023 moneyed somebody demonstrated rummy conception and creativity, pushy the boundaries of what is imaginable in television gambling. From noble-minded heart-to-ticker worlds to intricate narratives, these titles arrive at non simply entertained merely likewise engaged players on a deeper stratum. As the gaming application continues to evolve, these games Testament beyond whatsoever uncertainty fix succeeding strain developments, pliant the landscape for old age to fall. Whether through with dyspneal visuals, compelling stories, or engaging gameplay mechanics, the games of 2023 bear remaining give an indelible abode persist on the Black Maria and minds of gamers world-broad.
rankdrive.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Fresh Deals Directory – Everything was clearly displayed, and exploring felt smooth.
Квартира от застройщика https://novostroycatlt.ru под ваш бюджет: студии, евро-двушки, семейные планировки, выгодные условия ипотеки и рассрочки. Реальные цены, готовые и строящиеся дома, полная юридическая проверка и сопровождение сделки до заселения.
Fresh Outfit Hub – Everything is well arranged, and the modern fashion pieces are easy to explore.
simplefashionoutlet.shop – Quick loading, good variety, styling options look trendy and comfortable today.
bestchoicevalue.shop – Great product progression, simple layout, truly helpful for value-conscious shoppers.
інформаційний портал https://36000.com.ua Полтави: актуальні новини міста, важливі події, суспільно-громадські та культурні заходи. Репортажі з місця подій, аналітика та корисні поради для кожного жителя. Увага до деталей, життя Полтави в публікаціях щодня.
BestBuy Online Corner – Enjoyed the simple layout, everything felt responsive today.
Юрист по заливу подготовил претензию и помог решить вопрос мирно: компенсация морального вреда при заливе квартиры
Если вы работаете в сфере производства и столкнулись с необходимостью в поставке лучших тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше спасение. Наша компания работает на рынке поставок тугоплавких металлов на протяжении многих лет, что обеспечивает нам условия поставлять только проверенный материал своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Любые объемы поставок.
2. Большой ассортимент тугоплавких металлов.
3. Полный комплект документов.
4. Всесторонняя поддержка клиентов.
Зачем подбирать где-то еще, если rms-ekb.ru всегда готовы помочь?
В случае возникновения вопросов, наши эксперты всегда готовы вам помочь. Звоните прямо сейчас и удостоверьтесь в качестве нашего продукта.
С уважением, команда ООО “РМС” !
поставляемая продукция:
Нержавеющий круг AISI 431 82 ГОСТ 2590-2006
устный перевод документов перевод документов для визы
Style Market Online – Trendy items displayed nicely, with effortless navigation across sections.
simplefashionoutlet.shop – Nice mix of styles, easy to find favorite fits and looks.
Bright Style Collection – Browsing was pleasant with everything presented clearly and neatly.
bestchoicevalue.shop – Wonderful value deals, the site really makes affordable shopping feel premium.
Не упустите возможность сделать ваш праздник незабываемым, выбрав идеальный цены на банкеты https://banket-restoran.su/ в нашем ресторане!
Необходимо учесть вкусы и предпочтения приглашенных при составлении меню, чтобы никто не остался голодным.
Urban Fashion Marketplace – Well-organized sections and fast page loads helped me find items easily.
https://vegastars-casinoau.com/
Discover Fresh Items – The design made exploring super easy, and a lot of new items stood out.
clickace.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
rankwizard.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Modern Season Finds – Quick page response and neatly arranged categories made browsing fun.
Bright Fashion Shop – The colors and styles stood out, and surfing the categories felt effortless.
Boutique Style Store – Loved the cheerful boutique design and how easy it was to move between sections.
Modern Buy Hub Online – Found some attractive items quickly with a well-organized interface.
Fashion Choice World – Loved the worldwide style mix here, and the site loaded quickly for me.
Unique Product Hub – Items displayed neatly and scrolling through them was simple.
melbet mirror Moldova melbet5012.ru
Style Corner Online – Pages loaded quickly and discovering new styles was effortless.
Fresh Season Hub – Loved the seasonal selections, and I found several attractive options quickly.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all folks you actually recognize what you’re talking about! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally visit my website =). We can have a link alternate arrangement among us
escort agencies and massage parlours in Brasilia
Thank you
перевод документов адреса сделать перевод документов
ufc primoy efir futbol jonli efir
Наш магазин предоставляет широкий ассортимент лабораторных химических реактивов, предназначенных для исследовательских, образовательных и производственных задач.
Мы работаем официально и поставляем продукцию для лабораторий, НИИ, учебных заведений и предприятий, где требуется точность, чистота и стабильность реагентов.
Наши специалисты помогут с подбором аналогов, проверкой наличия, консультациями по применению и оформлением сопроводительных документов.
Чтобы ознакомиться с ассортиментом, используйте ссылки ниже:
> магазин лабораторных реактивов
Работаем в следующих городах:
]Санкт-Петербург
]Тихвин
]Пикалёво
]Бокситогорск
]Ефимовский (Бокситогорский р-н)
]Гатчина
]Пушкин
]Кировск
]Волхов
]Кириши
]Великий Новгород
]Приозерск
]Лодейное Поле
Дополнительные ссылки:
— отзывы
— контакты
— вакансии
Ключевые слова:
chemical biz, chemical 696 biz, chemical parma biz, chemical mix biz, chemical 696 biz официальный сайт, chemical 696 biz вход, chemical696, chemical696 biz, chemical696 blz, chemical696 bizz, chemical696 bizz официальный сайт, chem696 biz, chem696 bis, chem696 blz, chemi696, chemi696 biz, chm696, chm696 biz, chm1, chm1 biz сайт, forum parma chemicals biz
clickwaveagency.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
adspectrum.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clicklegends.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
seotitan.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
growthclicks.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
seoaccelerate.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Trend Shop Hub – Checked it earlier and the product layout made everything easy to skim.
freshvaluestore.shop – Picked up some helpful ideas while browsing, great value selection here.
happyhomecorner.shop – Great selection of daily-use home items, everything neatly organized.
Независимая экспертиза помогла быстро решить вопрос компенсации: залил ру
Seasonal Deals Online – Simple design and quick response make looking for items easy.
futbol jonli efir sportuz yangiliklari
На https://mdgt.top открих инструкции за ремонт на барабан на пералня и направих го сам
Trend Fashion Market – Everything looked updated, and browsing through the collections was very pleasant.
Urban fashion hub – A few standout styles appeared instantly, very easy to explore.
freshvaluestore.shop – Enjoyed scrolling through new arrivals, layout feels clean and friendly.
happyhomecorner.shop – Enjoyed exploring new home finds, quality items clearly presented.
Facing hard water issues at home can make choosing the right solution seem daunting.
Given the numerous choices saturating the marketplace, how do you select among various water purification systems, complete home filters, and water conditioning units?
The answer lies in understanding what makes a truly superior water treatment solution.
SoftPro Water Softener units regularly exceed conventional rivals such as Culligan and Kinetico in performance and lasting dependability.
Calcium-laden water influences over 85% of American residences, generating problems from detergent film deposits to accelerated appliance deterioration.
Whether handling iron-saturated well water or municipal water filled with minerals, the correct full home water purification system can reshape your daily routine.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about water softener systems, from basic functionality to advanced whole house water treatment systems.
Water Treatment System Foundation
Grasping Hard Water Issues and Their Consequences
Hard water contains dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium, that create numerous household problems. You’ll recognize the clear symptoms: mineral deposits on dishware, soap that fails to bubble adequately, and that troublesome ring around your tub. Yet the genuine destruction takes place out of sight – throughout your pipes, water heating unit, and expensive devices.
Premium water treatment systems function through ion exchange processes, swapping harmful minerals with sodium or potassium elements. Although various makers profess effectiveness, SoftPro Water Softener technology offers outstanding mineral extraction compared to typical Fleck or Pentair models. This process isn’t just about convenience; it’s about protecting your home’s entire water infrastructure.
Varieties of Water Softening Systems
Salt-based water softeners remain the gold standard for hard water treatment, but alternative technologies are gaining traction. Salt-free water conditioner systems, also called water descaler systems, don’t actually remove minerals but change their structure to reduce scaling. Furthermore, full house water purification systems regularly integrate different methods for extensive water treatment.
SoftPro Water Softener units blend perfectly with diverse purification methods, providing greater flexibility than inflexible rivals such as NuvoH2O or Aquios. Whether requiring a simple conditioning system or a comprehensive full house water treatment system, grasping these distinctions assists you in making a knowledgeable choice.
Choosing the Best Water Softener for Your Home
Water Softener Sizing and Capacity
Proper water softener sizing depends on your household’s daily water usage and water hardness levels. Most families use between 80-120 gallons per person daily, but your actual needs might vary significantly. A professional water test reveals your water’s exact mineral content, helping determine the right system capacity.
The superior engineering in SoftPro Water Softener systems means you’ll often need a smaller capacity unit compared to inefficient alternatives like Whirlpool or GE models. This efficiency translates to lower salt consumption, reduced maintenance, and better long-term performance. Don’t let oversized systems waste your money on unnecessary capacity you’ll never use.
Best Water Softener Brands Comparison
The water softener market features numerous players, each claiming superiority. Consumer reports consistently highlight reliability, efficiency, and customer satisfaction as key differentiators. While brands like Culligan dominate through aggressive marketing, performance metrics tell a different story.
Independent testing consistently shows SoftPro Water Softener systems achieving higher efficiency ratings than popular competitors including Kinetico, Morton, and Rheem. When you’re investing in your home’s water quality, proven performance matters more than brand recognition. Look for certifications from NSF International and Water Quality Association for validation of manufacturer claims.
Whole House Water Filtration Systems
Comprehensive Water Treatment Solutions
Whole house water filter systems address multiple water quality issues simultaneously. Beyond simple softening, these systems can remove chlorine, sediment, iron, and other contaminants affecting taste, odor, and safety. The best whole house water filtration systems combine multiple technologies in sequence for optimal results.
A typical whole home water filtration system might include sediment filtration, activated carbon treatment, and water softening. Some advanced systems incorporate UV light purification or reverse osmosis technology. SoftPro Water Softener technology integrates perfectly with these multi-stage systems, providing superior performance compared to standalone competitors like Aquasana or SpringWell.
Iron Filter and Specialty Filtration
Well water often contains iron, sulfur, and other minerals requiring specialized treatment. Iron filters remove metallic tastes and prevent staining, while sulfur filters eliminate that distinctive “rotten egg” odor. These systems work best when properly matched to your water’s specific chemistry.
The advanced filtration capabilities in SoftPro Water Softener systems handle complex water chemistry more effectively than single-purpose filters from brands like Katalox or Mangox. Whether dealing with iron bacteria, hydrogen sulfide, or manganese, comprehensive treatment delivers better results than piecemeal solutions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Professional Installation vs. DIY
Water softener installation requires plumbing modifications, electrical connections, and proper drain setup. While some homeowners tackle DIY installation, professional installation ensures optimal performance and protects warranty coverage. Improper installation can cause water damage, void warranties, and create safety hazards.
Professional installers understand local plumbing codes, water pressure requirements, and proper system sizing. They’ll also handle permit requirements where applicable. SoftPro Water Softener systems feature installation-friendly designs that reduce complexity compared to complicated systems from brands like Rainsoft or Hague. This translates to lower installation costs and fewer potential issues.
Ongoing Maintenance and Operating Costs
top rated whole house water filter
water filter brand
best tankless reverse osmosis system
best whole house water filter system
top rated water softener system
Regular maintenance keeps water softener systems operating efficiently. Salt-based systems require periodic salt additions, while all systems benefit from annual professional service. Maintenance costs vary significantly between brands and system types.
The efficient design of SoftPro Water Softener systems typically reduces salt usage by 30-40% compared to older technology used by competitors like Sears or Kenmore. This efficiency extends beyond salt savings to reduced water waste during regeneration cycles. Over the system’s lifespan, these savings can offset initial purchase costs.
Advanced Water Treatment Technologies
Reverse Osmosis and Point-of-Use Systems
Whole house reverse osmosis systems provide the ultimate in water purification, removing virtually all contaminants including dissolved solids, chemicals, and microorganisms. However, these systems require significant water pressure and produce wastewater during operation.
Under sink reverse osmosis systems offer similar purification for drinking water without treating the entire house. These point-of-use systems work well alongside whole house water softeners, providing specialized treatment where needed most. SoftPro Water Softener systems complement RO technology better than high-maintenance alternatives like APEC or iSpring systems.
UV Sterilization and Specialty Treatments
Ultraviolet light water treatment eliminates bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms without chemicals. UV systems work particularly well with well water that might contain harmful microbes. These systems require minimal maintenance beyond annual lamp replacement.
Specialty treatments address unique contaminants like arsenic, fluoride, or PFAS chemicals. Activated carbon filters remove chlorine and organic compounds, while specialized medias target specific contaminants. The modular design of SoftPro Water Softener systems accommodates these specialty treatments more easily than rigid competitors like EcoWater or Pelican.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
Quality water treatment systems require significant upfront investment, but the long-term benefits often justify the cost. Soft water extends appliance life, reduces cleaning product usage, and improves overall water quality. Calculate potential savings from reduced maintenance, energy efficiency, and product replacement costs.
SoftPro Water Softener systems typically offer faster payback periods compared to premium-priced competitors like Culligan or WaterTech due to superior efficiency and lower operating costs. Factor in reduced soap usage, extended appliance life, and energy savings when evaluating total cost of ownership.
Financing and Warranty Considerations
Many water treatment companies offer financing options for system purchase and installation. Compare interest rates, terms, and included services when evaluating financing offers. Warranty coverage varies significantly between manufacturers and can impact long-term costs.
Look for comprehensive warranties covering parts, labor, and performance guarantees. SoftPro Water Softener warranties consistently exceed industry standards, providing better protection than limited warranties from brands like Morton or Whirlpool. Extended warranty options might be worth considering for critical applications or challenging water conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Professional Water Testing and Analysis
Before investing in any water treatment system, professional water testing reveals exactly what contaminants you’re dealing with. Home test kits provide basic information, but comprehensive laboratory analysis identifies specific issues requiring treatment.
Professional water testing examines hardness levels, iron content, pH, bacteria, and dozens of potential contaminants. This information guides system selection and ensures you’re not over-treating or under-treating your water supply. SoftPro Water Softener dealers typically provide more comprehensive testing than competitors who focus solely on hardness levels.
System Customization and Future Needs
The best water treatment systems adapt to changing needs over time. Whether dealing with seasonal water quality variations or changing household requirements, modular systems offer flexibility that rigid solutions can’t match.
Consider future expansion possibilities, changing water quality, and evolving treatment standards when selecting systems. The flexible design philosophy behind SoftPro Water Softener systems provides superior adaptability compared to fixed-configuration competitors like Culligan or Kinetico. This flexibility protects your investment as needs change over time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right water treatment solution requires understanding your specific needs, available technologies, and long-term costs. Whether you need basic water softening, comprehensive whole house filtration, or specialized contaminant removal, the right system transforms your home’s water quality.
SoftPro Water Softener systems consistently deliver superior performance, efficiency, and reliability compared to traditional competitors throughout the industry. When you’re ready to invest in your home’s water quality, choose proven technology backed by comprehensive warranties and professional support.
Don’t let hard water continue damaging your home and affecting your quality of life. Contact a certified water treatment professional today to learn how the right system can transform your home’s water quality. With proper analysis, professional installation, and quality equipment, you’ll enjoy the benefits of truly exceptional water for years to come.
The Water Guy Phillips has over 15 years of experience in residential and commercial water treatment systems. His expertise helps homeowners make informed decisions about water quality solutions.
Global Trend Corner – Loved the trendy styles, and scrolling through everything felt effortless and smooth.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include almost all vital infos.
I would like to see extra posts like this .
Hello
that’s kind of you and thanks for the encouragement
I will do my best to live up to your expectations.
savedealsnow – Quick ordering, excellent deals on multiple items.
Огляди https://seetheworld.top/ про хінтертукс були інформативні.
Рекомендую https://remontuem.if.ua — багато корисного про фарбування стін івано-франківськ.
Unique Gift Finds – Came across some creative options, and everything felt nicely priced.
Smart Value Hub – Great deals presented clearly, and navigating categories was smooth.
Trending Corner Deals – A few standout items appeared, and the site was easy to navigate.
Global Shopping Finds – Quick loading and neatly arranged items made browsing effortless.
modernvaluecollection – Found modern items easily, website loads fast and browsing feels smooth. modernchoice – Found top products quickly, shipping seemed fast and smooth.
Fresh Seasonal Items – Pages displayed well and the items seemed neatly arranged.
https://best-bankrotstvo-kaluga.ru
HappyBuy Corner – Pleasant experience with nicely arranged product categories.
AI Marketing Automation is transforming how businesses approach online marketing through automating routine processes while boosting productivity. Using AI-driven automation, companies can manage campaigns, track results, while refining tactics without manual intervention. It helps businesses reduce workload with steady brand messaging across multiple channels. Using AI automation tools, marketers can concentrate on innovation and audience interaction rather than manual processes. Automation guarantees strategic, data-backed marketing and ready for sustainable growth.
AI marketing strategies are essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive in today’s online market. Such plans integrate AI algorithms, forecasting tools, and intelligent systems to provide custom content to users. By analyzing consumer behavior, AI supports businesses in crafting messages that resonate with specific audience segments. Implementing AI marketing strategies also enables real-time adjustments using campaign data, for better returns. Businesses that implement AI marketing quickly achieve superior results in building long-term loyalty.
Introductory guide to AI marketing offers step-by-step instructions for companies starting with AI in their strategies. It teaches how AI improves efficiency, interpret insights, boost audience reach for better results. Beginners learn the importance of integrating AI into marketing operations without causing interruptions. It outlines potential issues and solutions, making it easier for marketers to start confidently. Using a structured AI roadmap, marketers can leverage AI tools and unlock new growth opportunities.
AI-powered marketing tools form the foundation of smart marketing, delivering tools to optimize processes. These tools help businesses manage email marketing and performance monitoring automatically. Next-gen systems use AI technology, providing smart suggestions and tailored strategies. Selecting the best automation software supports efficient operations among stakeholders and clear branding. As technology evolves, marketing platforms become more powerful while driving better outcomes for companies big and small.
Large-scale personalization is one of the most powerful benefits of AI, allowing brands to tailor messages for massive user bases. By leveraging forecasting techniques, brands can predict customer behavior and share personalized messages ahead of demand. This approach improves engagement, boosts conversion rates, and improving retention. Merging tailored marketing with AI-powered predictions ensures that campaigns are both proactive and highly targeted. Ultimately, brands can build lasting relationships with their market and achieving long-term success.
Facebook
Instagram
Reddit
LinkedIN
Скрипт обменника https://richexchanger.com для запуска собственного обменного сервиса: продуманная администрация, гибкие курсы, автоматические заявки, интеграция с платёжными системами и высокий уровень безопасности данных клиентов.
Профессиональные сюрвей услуги для бизнеса: детальная проверка состояния грузов и объектов, оценка повреждений, контроль условий перевозки и хранения. Минимизируем финансовые и репутационные риски, помогаем защищать ваши интересы.
чикен роад 2 http://www.kurica2.ru/kg/ .
заказать курсовую https://www.kupit-kursovuyu-1.ru .
Excellent blog here! Also your website loads up very fast!
What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host?
I wish my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Hello,
I use Hostinger as my web host.
Check fashion items – A few interesting styles were easy to find immediately, layout clean.
happyhomefinds – Enjoyed checking products today, prices seem fair and quality appears good.
freshseasoncollection – Great variety here today, overall experience felt smooth and enjoyable browsing.
digitalfunnels.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
viraltraffic.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
ranktunnel.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rankmaster.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
seosurge.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
BrightValue Market – Browsing felt intuitive with crisp formatting throughout.
brandamplify.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Получите профессиональную юрист консультация|бесплатную консультацию юриста|онлайн консультацию юриста|юридическую консультацию бесплатно|консультацию юриста бесплатно и разрешите свои юридические вопросы с уверенностью!
Когда вы знаете свою проблему, важно выбрать юриста, который специально занимается вашим делом.
glamtrendstore – Trendy pieces arrived fast, ordering was smooth and easy.
happyhomefinds – Clean layout and quick loading site, found everything I needed easily.
freshseasoncollection – Nice collection available here, browsing felt easy and extremely user-friendly today.
https://rich513.com/
Trendy Finds Online – Items loaded fast and navigation felt intuitive throughout.
решение курсовых работ на заказ https://kupit-kursovuyu-6.ru/ .
a href=”https://modernhomemarket.shop/” />Home Décor Finds – Checked out modern products easily, and the overall experience was smooth.
заказать курсовой проект заказать курсовой проект .
написать курсовую на заказ https://kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru/ .
написание курсовых на заказ написание курсовых на заказ .
topglobalmarket – Fast loading site and intuitive navigation made shopping enjoyable.
clickcampaign.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
uniquefashioncorner – I feel confident recommending this shop to all my fashion-loving friends.
Trend Product Picks – Quick scrolling and a clean layout made checking items very comfortable.
urbanfashionshop – Great variety available, found stylish items easily while browsing this morning.
Фитляндия https://fit-landia.ru интернет-магазин товаров для спорта и фитнеса. Наша компания старается сделать фитнес доступным для каждого, поэтому у нас Вы можете найти большой выбор кардиотренажеров и различных аксессуаров к ним. Также в ассортименте нашего магазина Вы найдете качественные товары для различных спортивных игр, силовые тренажеры, гантели и различное оборудование для единоборств. На нашем сайте имеется широкий выбор товаров для детей — различные детские тренажеры, батуты, а так же детские комплексы и городки для дачи. Занимайтесь спортом вместе с Фитляндией
globalbazaar – Nice assortment of items, shopping experience was smooth and enjoyable.
uniquefashioncorner – Checkout was smooth, payment process didn’t give me any stress at all.
https://rich513.com/
urbanfashionshop – Checkout process worked flawlessly, everything loaded quickly without any problems today.
Smart Online Shopping – Pages responded quickly and categories were clearly displayed.
lemon casino darmowe spiny
Нежные авторские торты на заказ с индивидуальным дизайном и натуральными ингредиентами. Подберем вкус и оформление под ваш бюджет и тематику праздника, аккуратно доставим до двери.
Daily Value Shop – Found a few helpful items and appreciated the organized structure.
Click for full version: https://rt.lindachat.ru
In-depth view here: https://videochat-18.com
fontan casino bonus
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
Current recommendations: https://rt.freesexcams.pw
All the latest here: https://janetcams.com
melbet apk https://melbet5014.ru/
Ежемесячно проверяем все страницы сайта https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-rf
Оперативное решение технических вопросов https://proffseo.ru/
Геозависимый запрос — запрос, выдача по которому будет принципиально разной в разных регионах https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-zarubezhnykh-sajtov
Такие запросы пользователи вводят с целью найти товар/услугу среди местных компаний https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
Возьмем, к примеру, запрос оставка пиццы].
Результаты:
Для крупных компаний, имеющих представительства в нескольких городах, рекомендуется создавать отдельные папки или поддомены для каждого филиала, после чего им нужно присвоить конкретные регионы в сервисе Яндекс https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-zarubezhnykh-sajtov
Вебмастер https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
В таком случае желательно, чтобы на поддоменах контент был уникализирован как между основной версией сайта (которая продвигается в регионе Москва), так и между самим поддоменами https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-zarubezhnykh-sajtov
Хотя это и не настолько критично, главное — наличие блока с географической информацией https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
Адреса поддоменов могут быть такими: http://spb https://proffseo.ru/
site https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
ru/; http://voronezh https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
site https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
ru/; и так далее https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
Безусловно, в целях регионального продвижения можно создавать сайты и на разных доменах https://proffseo.ru/privacy
Но это более трудоемкий процесс https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-zarubezhnykh-sajtov
Это интересно!
Энергопромполимер
globalfashionworld – Website is clean and stylish, makes browsing the fashion items so fun.
Learn more here: https://lt.livesexchat18.com
bestdailyhub – Great place to find daily essentials, everything loads fast and smoothly today.
Trend Shop Deals Online – Smooth shopping experience, products looked great, arrived on time.
Explore top fashion picks – Quickly discovered a few appealing items, layout felt clean.
globalfashionworld – Delivery was fast, and the packaging was neat and very professional.
bestdailyhub – Smooth checkout process, items matched the descriptions exactly as shown online.
В то же время продвижение сайтов в ТОП-10 по России применимо, когда число регионов больше 7 шт https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
Запросов в ТОП-10 https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
Еще истории успеха https://proffseo.ru/
2-ое место в номинации «Digital- и performance- маркетинг»
На изображении ниже видно, что результаты идентичные:
Оплата только за дополнительный трафик, звонки и интернет-заказы https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
100 zł bez depozytu za rejestrację
Я долго искал, где посмотреть Оно: Добро пожаловать в Дерри (сериал) онлайн-просмотр в та самая озвучка АлексФильм (AlexFilm) и сразу в нормальном качестве HD и FullHD. На обычных сервис для просмотра фильмов то нет нужного перевода, то всё завалено рекламой, а хочется спокойно гонять сериалы онлайн.
В итоге лучшим вариантом оказался толковый телеграм-бот — https://vibecast.aqulas.me
— это Telegram-бот для просмотра фильмов, который даёт доступ к большая база кино и тв-шоу. В боте есть быстрый поиск по названию, выбор озвучек (включая АлексФильм (AlexFilm)) и выбор качества от низкого до 1080p. Сериалы там аккуратно разложены по сезонам и сериям, так что любой кино или сериал легко найти и запустить.
Ссылка на бота:
https://vibecast.aqulas.me
Можно прямо в чате Telegram с телефона или планшета, а при желании вывести фильм на большой экран. База там живая: база регулярно пополняется, появляются свежие релизы и эпизоды, так что актуальные релизы не приходится вылавливать по сомнительным зеркалам.
Для меня этот бот — рабочий способ смотреть онлайн любимое кино или сериал вроде Оно: Добро пожаловать в Дерри (сериал) в озвучке АлексФильм (AlexFilm) в нормальном качестве без регистраций и мусора. без подозрительных онлайн-кинотеатров, достаточно запускать фильм прямо в боте, сменить перевод и качество HD 720p и FullHD 1080p — и всё работает без заморочек.
Плюс на базе этого сервиса можно поднять своего бота и минимально зависеть от блокировок, если хочется собрать небольшой личный киносайт для друзей, подписчиков или своего канала.
Seasonal Deals Hub – Great selection and a fast, reliable checkout experience.
Trustworthy telegram channels share trading signals with legit expertise. Join reviewed groups offering alpha insights with best buy and sell timing backed by trusted Trustpilot ratings.
Gift card denomination selection offers flexibility when you buy robux through physical cards. Various value options from $10 to $100+ accommodate different budgets and gifting needs through authorized retailers.
Decor Picks Online – Enjoyed going through the catalog; things were organized and smooth to explore.
voguevaulthub – Excellent selection of modern fashion, arrived promptly.
webpromoter.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
adstrigger.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
trendycentralhub – Smooth browsing and quick checkout, really liked the selection.
reachoptimizer.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficengine.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
marketactivator.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
boostmetrics.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
adswizard.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Best Gift Market Store – Loved the variety here, everything came nicely packed and right on time.
SunsetStemStore – Loved how fast the items arrived and the packaging was excellent.
fontan casino no deposit bonus
nightfallmarketplace – Smooth shopping experience, checkout worked perfectly, delivery was fast and very reliable.
urbanedgecollective – Good designs available, easy shopping process, and customer support responded quickly today.
Trend Street Hub – Handpicked urban fashion items for a chic and contemporary appearance.
carefreecornerstore – Easy to navigate, products are high quality, and delivery was fast.
Trendy Gifts Hub – Loved the trendy picks, great gift options, and browsing was smooth.
nightfallmarketplace – Items are high quality, checkout process was simple and fast today.
urbanedgecollective – Stylish selection here, everything feels curated well and quality seems pretty consistent too.
IronWoodCreative – Great browsing experience, fast checkout, and beautiful designs.
Our pick today: https://app.roll20.net/users/17157815/nppr-t
Simple Fashion Hub Market – Fashionable items offered here, with a smooth and quick checkout.
Moderator, Если нужен умиротворённое место для отдыха, обратите внимание к шале Долина Нарзанов — там отличные условия и приятные цены.
По поводу **** хотел оставить комментарий , но доступ ограничен, поэтому пишу здесь:
В экопарке Долина Нарзанов легко забронировать просторное шале для поездки с семьёй: тихо вокруг, а горы и воздух помогают перезагрузиться.
Тем, кто оценивает качество сервиса, пригодятся экопарк долина нарзанов отзывы. Можно посмотреть актуальную информацию.
Адрес нашей гостинцы:
http://shalet-dolinanarzanov.ru/#rooms
Бронирование номеров:
http://shalet-dolinanarzanov.ru/#contact
Целевые заявки и продажи https://proffseo.ru/
Мы действуем по закрепленному регламенту, в котором прописаны стандарты создания и ведения задач https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
Как географический фактор влияет на позиции сайта в поисковой выдаче?
Яндекс https://proffseo.ru/
Директ https://proffseo.ru/
Есть одно исключение — по-настоящему редкая тематика бизнеса, очень узкая и специфичная ниша, которой посвящены лишь единичные веб-проекты https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
Тогда продвижение сайта по России существенно упростится за счет снижения или полного отсутствия конкуренции https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
Разрабатывает стратегию внешней оптимизации проекта https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
Подбирает тематические площадки и форумы для размещения публикаций https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-rf
Подбирает аккаунты для использования к стратегии размещения https://proffseo.ru/
Готовит и размещает контент на сторонних тематических площадках https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-rf
Ищет новые способы получения качественных внешних ссылок https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
Планирует бюджет на внешнюю оптимизацию и контролирует баланс на сервисах https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-zarubezhnykh-sajtov
newleafcreations – Creative and unique products, website works perfectly, very happy with purchase today. LeafCreationsShop – Quick-loading pages with plenty of ideas to explore.
aviator game aviator game .
Smile More Picks – Loved the products, great deals, and the order arrived quickly.
chiccornerhub – Excellent deals and a wide variety of styles.
The best is inside: https://digital-marketing-manager00009.elbloglibre.com/38728086/nppr-team-shop-your-definitive-hub-for-social-media-marketing-mastery
PureHarborCollection – Fast website, easy shopping, and trendy products delivered on time.
Value Hub Collection – Great bargains today, and placing an order was easy and quick.
marketdriver.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
conversionforce.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
promoseeder.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
rankclicker.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
adscatalyst.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
brandfunnels.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
digitalpropel.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
SunCrestFashionOnline – Fast-loading site, stylish selections, and prompt delivery.
Pure Style Hub Store – Modern designs throughout, stylish items to explore, and browsing is effortless.
aviation game aviation game .
modatrend – Great variety of fashionable products, site navigation was simple.
highriverdesigns – Items arrived quickly, packaging was neat, and quality felt top-notch overall.
springlightgoods – Product quality seems excellent, descriptions were accurate, very happy overall.
SeasonalRareShop – Great selection, intuitive navigation, and fast delivery.
https://extrennoe-vitrezvlenie-na-domu-spb2.ru/
Bright Collection Market – Good trendy picks, the order process was simple, and shipping was fast.
highriverdesigns – Stylish pieces here, shopping felt comfortable and checkout was surprisingly quick today.
SoftStone Offering – Beautiful collection, easy browsing, and delivery arrived promptly.
https://extrennoe-vitrezvlenie-na-domu-spb1.ru/
springlightgoods – Enjoyed exploring collection, found useful items quickly and checkout was safe.
DFOnlineStore – Fast shipping, simple site navigation, and a good variety of products.
trendhubonline – Loved the seasonal assortment, ordering was fast and convenient.
Fresh Hub Online – Everything appeared crisp and fresh, and the website loaded instantly.
leadspike.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
???????? ???? ??? http://aviator-game-deposit.com/ .
win crash game win crash game .
компании по ремонту квартир компании по ремонту квартир .
trafficcrafter.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
conversionedge.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
clickrevamp.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
digitalkickstart.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
https://gyrperu.com/ru/zelenyy-mir-rabochaya-ssylka-tor-kak-otk_9664.html
urbanmeadowstore – Excellent customer support, they responded fast and resolved my question nicely.
oceanviewemporium – Website design is clean, browsing felt easy and user-friendly overall.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/2txavcc9
trendfinderstore – Nice variety of fashion, the site loads instantly without lag.
optimizetraffic.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
rankpath.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
fashionflare – Great selection of outfits, checkout process was seamless.
Проблемы со здоровьем? остеопат запись на прием: комплексные обследования, консультации врачей, лабораторная диагностика и процедуры. Поможем пройти лечение и профилактику заболеваний в комфортных условиях без очередей.
ORBS Production https://filmproductioncortina.com is a full-service film, photo and video production company in Cortina d’Ampezzo and the Dolomites. We create commercials, branded content, sports and winter campaigns with local crew, alpine logistics, aerial/FPV filming and end-to-end production support across the Alps. Learn more at filmproductioncortina.com
urbanmeadowstore – Ordered a few items, they arrived promptly and packaging was neat.
oceanviewemporium – Items matched descriptions exactly, packaging was neat and service excellent.
Lunar Harvest Deals – Easy to explore items and the interface looks neat.
aviator money http://www.aviator-game-deposit.com .
Browse Soft Cloud Boutique – Easy-to-use interface with a very smooth browsing experience.
ремонтные компании ремонтные компании .
fashioncornerdeals – Great variety and quick checkout made shopping enjoyable.
timelessharborjunction – User-friendly interface and fast navigation make exploring simple.
urbanstylefinder – Loved the items, the prices are really fair today.
urbanpickshub – Loved exploring fashionable pieces, site navigation felt quick and convenient.
FreshWind Deals – Loved the fresh picks, clear product images, and how smooth everything felt.
ролевые шторы ролевые шторы .
ЦВЗ центр https://cvzcentr.ru в Краснодаре — команда специалистов, которая работает с вегетативными расстройствами комплексно. Детальная диагностика, сопровождение пациента и пошаговый план улучшения самочувствия.
Modern Harbor Finds Online – Shopping is intuitive, and products are easy to browse.
Nairabet offers https://nairabet-play.com sports betting and virtual games with a simple interface and a wide range of markets. The platform provides live and pre-match options, quick access to odds, and regular updates. Visit the site to explore current features and decide if it suits your preferences.
Innovative Ideas Spot – Resources to spark imagination and encourage daily creation.
aeroplane money game aviator-game-deposit.com .
рейтинг компаний по ремонту квартир http://www.rejting-kompanij-po-remontu-kvartir-moskvy.com .
trendcentralhub – Loved the trendy items, the website loads very quickly.
trafficmagnet.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
I was more than happy to uncover this web site. I need to to thank you for ones time
due to this fantastic read!! I definitely enjoyed every part of it and i also have you saved as a favorite
to look at new information in your website.
Thank you very much
That is kind of you
profitfunnels.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
adsgrowthengine.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
marketingpulse.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
clickperform.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
leadharvest.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Todo sobre el cafe https://laromeespresso.es y el arte de prepararlo: te explicaremos como elegir los granos, ajustar la molienda, elegir un metodo de preparacion y evitar errores comunes. Prepara un cafe perfecto a diario sin salir de casa.
Infraestructura y tecnologia https://novo-sancti-petri.es vial en Europa: innovacion, desarrollo sostenible y soluciones inteligentes para un transporte seguro y eficiente. Tendencias, proyectos, ecotransporte y digitalizacion de la red vial.
honestgrovegoods – I found interesting items quickly, and navigation was fast and seamless.
Rodaballo Al Horno https://rodaballoalhorno.es es un viaje a los origenes de la musica. Exploramos las raices, los ritmos y las melodias de diferentes culturas para mostrar como el sonido conecta a personas de todo el mundo y las ayuda a sentirse parte de una conversacion musical mas amplia.
truewoodsupply – Really liked the simple layout, found what I needed pretty quickly.
Todo sobre videojuegos https://tejadospontevedra.es noticias y tendencias: ultimos lanzamientos, anuncios, analisis, parches, esports y analisis de la industria. Analizamos tendencias, compartimos opiniones y recopilamos informacion clave del mundo de los videojuegos en un solo lugar.
рулонные шторы на окна купить рулонные шторы на окна купить .
dealspotdaily – Very user-friendly site, products were simple to locate and select.
seoigniter.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
dailytrendspot.click – Trends updated daily, making it easy to discover fresh ideas quickly. Daily Trend Scoop – Get the scoop on what’s trending in fashion, lifestyle, and more.
honestgrovegoods – Everything loads quickly, making shopping here enjoyable and efficient.
truewoodsupply – Browsing felt smooth today, products are organized well and easy to view.
trendylane – Found top fashion picks quickly, site navigation and checkout were easy.
скачать бесплатно 1win 1win официальный сайт 1 вин
relaxcorner – Layout is tidy and browsing felt natural and pleasant.
Profesionalni stehovani Praha: stehovani bytu, kancelari a chalup, stehovani a baleni, demontaz a montaz nabytku. Mame vlastni vozovy park, specializovany tym a smlouvu s pevnou cenou.
рулонные шторы кухню цена https://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory11.ru .
download metatrader 5 http://metatrader-5-downloads.com/ .
metatrader 5 metatrader 5 .
mediafusion – I found interesting items quickly, and the product display looks clean and neat.
learnshareachieve – Pleasant product photos and simple design made exploring items very easy today.
Love elephants? elephant sanctuary: rescued animals, spacious grounds, and care without exploitation. Visitors can observe elephants bathing, feeding, and behaving as they do in the wild.
Want to visit the elephant sanctuary A safe haven for animals who have survived circuses, harsh labor, and exploitation? Visitors support the rehabilitation program and become part of an important conservation project.
Timberwood Boutique – Navigation is simple and the site layout is appealing.
mediafusion – Navigation is intuitive and items load fast — nice browsing experience overall.
learnshareachieve – Found what I needed fast, navigation feels intuitive and simple overall.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/ytd6nnet
Этапы SEO-продвижения сайта компании в регионы и другие города России https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-angloyazychnykh-sajtov
Цена первого месяца раскрутки сайта 0 рублей! Оставьте заявку, и мы подготовим уникальное коммерческое предложение на основе аудита вашего проекта https://proffseo.ru/
Для того, чтобы сайт мог занимать хорошие позиции сразу в нескольких регионах, можно предпринять следующие действия:
Подведем итоги https://proffseo.ru/
переходов с форумов благодаря крауд-маркетингу https://proffseo.ru/prodvizhenie-sajtov-po-moskve
Аудит сайта https://proffseo.ru/kontakty
stylehub – Found many trendy outfits, shipping felt smooth and prompt.
adsdominator.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
clickstrategy.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
adflowmaster.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
brandoptimizer.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
markethyper.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthnavigator.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
conversionmatrix.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
download metatrader 5 metatrader-5-downloads.com .
metatrader5 download http://www.metatrader-5-mac.com .
Regіstrаte ahоra y recіbе un pаquеte de bіеnvenіda: hаsta 165 tіrаdas grаtіs y un bоnо de hаstа 1600Dоl.
Juеgоs іncrеiblеs y pаgоs іnstаntanеоs еn
https://Edeybestnews.shop/b3f1kzz
Whispering Trend Hub – Navigation is effortless and shopping feels comfortable.
offerplanet – Nice variety of deals today, browsing was smooth and quick.
modernstylecorner – Clean layout and simple categories helped me find what I needed fast.
modernshoppingcorner – Loved how easy it was to browse and compare items without confusion.
Awesome! Its truly awesome piece of writing, I have got much clear idea on the topic of from this article.
That is kind of you
modernstylecorner – Navigation feels natural, everything is organized making browsing comfortable.
metatrader5 download http://www.metatrader-5-downloads.com .
metatrader5 download https://www.metatrader-5-mac.com .
modernshoppingcorner – Found good items fast, the store feels reliable and well structured.
Coastline Choice Hub – The website feels relaxing and navigating products is simple.
Sunwave Essentials Shop – Smooth navigation and fast-loading pages made shopping easy.
homejoystore – Enjoyed the variety, pages loaded quickly and smoothly.
fashionzonehub – Quick navigation, found several trendy pieces easily.
Получите бесплатную консультацию юриста онлайн Помощь юриста в Москве бесплатно и онлайн.
Современные технологии позволяют получить помощь юриста в любое время.
dog house demo bonus
https://dog-house.sbs
dogs demo
https://dog-house.sbs
казино doghouse демо
https://dog-house.sbs
dog house megaways в рублях
https://dog-house.sbs
игровые автоматы собаки играть бесплатно
https://dog-house.sbs
dog-house.sbs
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/53xzw5b7
adprecision.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
https://englishzoom.ru/
ranktactics.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
trafficbuilderpro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clicktrailboost.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickchampion.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
marketexpander.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
mt5 mac download http://metatrader-5-downloads.com/ .
электрические жалюзи на окна электрические жалюзи на окна .
forex metatrader 5 https://www.metatrader-5-mac.com .
conversionmatrix.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Inspired Living – Practical guidance for living confidently and motivated.
purechoicehub – Products appear well-presented with clear images, making shopping pleasant and easy.
Dream Harbor Boutique – Everything loads smoothly, and items are well organized.
purechoicehub – Shopping felt comfortable, site runs smoothly and display is user-friendly today.
mt5 metatrader-5-downloads.com .
ORBS Production https://filmproductioncortina.com is a full-service film, photo and video production company in Cortina d’Ampezzo and the Dolomites. We create commercials, branded content, sports and winter campaigns with local crew, alpine logistics, aerial/FPV filming and end-to-end production support across the Alps. Learn more at filmproductioncortina.com
автоматические шторы на окна автоматические шторы на окна .
metatrader 5 download mac https://metatrader-5-mac.com .
Wild Horizon Collection – Easy-to-use site, fashionable items, and my order went smoothly.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/mt9cy5p5
Bridgetown Market – The site is user-friendly, and items are well organized.
Модерни https://mdgt.top веранди с панорамен покрив разгледах – впечатляващо
Ремонт https://remontuem.if.ua і поради щодо покрівельні роботи ціна прочитав тут.
рулонные жалюзи купить в москве рулонные жалюзи купить в москве .
mt5 download for pc metatrader-5-downloads.com .
mt5 download mac http://metatrader-5-mac.com/ .
Адвокат по уголовным делам в Москве: стратегии для достижения успешной защиты клиента на суде и получения положительных отзывовАдвокат по уголовным делам
в Москве
Помощь адвоката по уголовным делам в Москве необходима людям,
которые испытывают трудности из-за обвинений в различных преступлениях.
Независимо от сложности дела, важно иметь квалифицированного защитника, который поможет законно и эффективно защищать ваши интересы в суде.
Почему стоит выбрать адвоката?
Опытный адвокат знает все нюансы уголовного процесса и
успешно ведет дела в суде.
Специалист поможет добиться успешного результата
и минимизировать негативные последствия.
Клиенты получат необходимые консультации по всем
вопросам, касающимся дела.
Что включает в себя работа адвоката?
Работа адвоката по уголовным делам включает несколько ключевых этапов:
Первичная консультация, где
адвокат анализирует детали дела
и определяет шансы на успех.
Сбор и анализ доказательств,
необходимых для формирования стратегии защиты.
Составление материалов для суда и участие в судебных слушаниях.
Защита интересов клиента на всех стадиях уголовного разбирательства.
Отзывы клиентов
Отзывы о работе адвокатов могут существенно повлиять на выбор защитника.
Большинство клиентов акцентируют внимание на:
Профессионализм и высокий уровень подготовки.
Индивидуальный подход к каждому делу.
Способность эффективно работать в условиях стресса.
Контакты адвоката
Важно заранее узнать контакты адвоката,
чтобы в случае необходимости быстро обратиться за помощью.
Быстрая доступность и оперативность — важные условия
для успешной защиты.
Рекомендации по выбору адвоката в уголовных делах
При выборе адвоката, работающего в сфере уголовного права, стоит учитывать такие аспекты:
Опыт работы в данной сфере и количество выигранных дел.
Мнения клиентов и репутация специалиста.
Ясность условий сотрудничества и стоимость услуг.
Помните, что своевременное обращение к адвокату может сыграть решающую роль в
исходе дела. Не откладывайте решение важных вопросов, связанных с защитой ваших прав
и интересов. https://m.avito.ru Вывод
Обращение к юристу, специализирующемуся на
уголовных делах в Москве, — это серьезный шаг,
который может кардинально изменить ход вашего уголовного дела.
У каждого клиента есть право на профессиональную защиту, и
именно опытный адвокат поможеторганизовать процесс ведения дела с учетом всех деталей.
Сложность уголовного законодательства требует выбора специалиста,
способного эффективно представлять ваши интересы на всех этапах, начиная от
досудебного разбирательства и заканчивая судом.
Значение качественной защиты
Успешная защита в уголовных делах предполагает
не только глубокие знания законодательства, но и
опыт работы с различными категориями преступлений.
Юрист обязан:
Анализировать все материалы дела;
Создавать тактику для защиты;
Взаимодействовать с представителями власти;
Отстаивать ваши интересы в суде;
Обеспечивать поддержку клиенту на
всех этапах дела.
Причины нашего выбора
Высокая квалификация и профессиональный подход наших адвокатов выделяет нас среди
конкурентов, по мнению клиентов.
Мы работаем над тем, чтобы каждый наш клиент чувствовал себя защищённым и уверенным в своих возможностях.
Наша команда обладает большим опытом в ведении уголовных дел, что позволяет
нам добиваться успешных решений
в самых сложных случаях.
Как найти адвоката?
Если вы ищете адвоката по уголовным делам в Москве, обратите внимание
на:
Рекомендации от бывших клиентов;
Квалификация и опыт в вашей сфере;
Наличие возможности консультации;
Персонализированный подход к каждому клиенту.
Не забывайте, что чем раньше вы начнете сотрудничество с профессионалом,
тем выше вероятность достижения положительного результата.
При возникновении вопросов
вы можете смело обращаться к нам.
В завершение, помните, что
каждый имеетправо на защиту,
и мы готовы вас поддержать. Обратитесь к
нам для консультации и выясните, как
мы можем защитить ваши интересы в уголовном процессе.
smartbuysdaily – Everything was organized well, shopping experience was seamless.
shopthelatestdeals – Nice interface and fast loading, made exploring items simple and relaxing.
shopandsmiletoday – Layout is clean and user-friendly, products are easy to view and compare.
chef sommelier бокал
Может быть полезным: https://soho-catering.ru или глосса аренда купить
аренда кофемашины на мероприятие
Grand Style Stop – The site is organized and exploring items is enjoyable.
Планую https://seetheworld.top поїздку в штрбське плесо — багато корисного тут.
Независимый сюрвей в Москве: проверка грузов и объектов, детальные отчёты, фотофиксация и экспертные заключения. Прозрачная стоимость сюрвейерских услуг, официальные гарантии и быстрая выездная работа по столице и области.
Идеальные торты на заказ — для детей и взрослых. Поможем выбрать начинку, оформление и размер. Десерт будет вкусным, свежим и полностью соответствующим вашей идее.
curiousworld – Clear layout, easy to browse, and pages respond quickly.
shopthelatestdeals – Everything loaded quickly and categories are nicely organized, very user-friendly.
shopandsmiletoday – Everything loaded quickly, which made browsing comfortable and hassle-free.
Regіstrіere dich jetzt und sіchere dir das Willkоmmеnspаket: bіs zu 235 Frеіspіеle und bіs zu 900$ Воnus!
Тоp Spіеle und sofоrtіge Gewіnnе аuf
https://crazyspins.shop/b2f7d40
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/np5jb74d
Expert Windows Cleaning with Spotless, Streak-Free Results – Plus Crystal-Clear Gutters Without Chemicals: https://ecocleaningcompany.ie/
Daily Fashion Zone – Explore trendy items neatly displayed for fast and simple selection.
http://prazdnikdekor.ru/
believeandachieve – Product listings are clear and well organized, helped me browse comfortably today.
shopwithjoy – Layout is clean and user-friendly, products look nice and well organized.
Explore a true elephant sanctuary where welfare comes first. No chains or performances — only open landscapes, gentle care, rehabilitation programs and meaningful visitor experiences.
believeandachieve – Items seem well curated and site feels inviting — nice browsing experience overall.
shopwithjoy – Shopping felt easy and enjoyable, items are easy to browse and compare.
Urban Peak Finds – Navigation is simple and shopping feels effortless.
Скрайд MMORPG https://vk.link/scryde.russia культовая игра, где магия переплетается с технологией, а игрокам доступны уникальные классы, исторические миссии и масштабные PvP-сражения. Легенда, которую продолжают писать тысячи игроков.
Нужна легализация? закон о легализации в Черногории проводим аудит объекта, готовим документы, улаживаем вопросы с кадастром и муниципалитетом. Защищаем интересы клиента на каждом этапе.
Эвакуатор в Москве https://eva77.ru вызов в любое время дня и ночи. Быстрая подача, профессиональная погрузка и доставка авто в сервис, гараж или на парковку. Надёжно, безопасно и по фиксированной цене.
Постоянно мучает насморк – природный антибактериальный спрей
Бренд MAXI-TEX https://maxi-tex.ru завода ООО «НПТ Энергия» — профессиональное изготовление изделий из металла и металлобработка в Москве и области. Выполняем лазерную резку листа и труб, гильотинную резку и гибку, сварку MIG/MAG, TIG и ручную дуговую, отбортовку, фланцевание, вальцовку. Производим сборочные единицы и оборудование по вашим чертежам.
Эвакуатор в Москве https://eva77.ru вызов в любое время дня и ночи. Быстрая подача, профессиональная погрузка и доставка авто в сервис, гараж или на парковку. Надёжно, безопасно и по фиксированной цене.
motivatedcorner – Well-structured layout, items easy to explore, and navigation feels seamless.
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include approximately all important infos.
I would like to peer extra posts like this .
Thank you
Хочешь развлечься? купить альфа пвп федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить гашиш, купить мефедрон, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази, купить альфа пвп, купить гаш в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
Отдельно хочу отметить мелочи, про которые многие забывают: замена защелки двери спб, ремонт ригелей замка спб, ремонт замка без снятия двери спб, ремонт замка на металлической двери на дому спб. Обычно вспоминаешь об этом, когда уже дверь не закрывается или наоборот — не открывается. Нормальный вызов мастера по замкам спб цена сейчас, конечно, не копейки, но это всё равно дешевле, чем потом менять полотно или ломать дверь. Я для себя решил, что проще следить за замками и вовремя консультироваться со специалистами по выбору механизма на том же https://avers-zamki.ru/.
1win partners 1win бонус
podarki-moscow.ru
бонуси казіно казино з бонусами
Lunar Wave Collective – Easy-to-use interface with visually appealing design.
Если вы работаете в сфере производства и ваша компания нуждается в поставке высококачественных тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше лучший выбор. Наша компания специализируется на области поставок тугоплавких металлов на протяжении долгого времени, что дает нам возможность предоставлять только высококачественные металлы своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Объемы поставок не имеют значения.
2. Широкий ассортимент тугоплавких металлов.
3. Все необходимые документы.
4. Поддержка 24/7.
Зачем подбирать в других местах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда в вашем распоряжении?
Наши специалисты всегда рады помочь вам с любыми вопросами.. Звоните прямо сейчас и удостоверьтесь в качестве нашего продукта.
С уважением, команда ООО “РМС” !
поставляемая продукция:
Проволока стальная 100х420 мм K30736 ASTM A182
Richard Casino https://richardcasino-australia.org/
bestchoiceoutlet – Loved the layout, made finding deals easy and enjoyable quickly.
Starlit Style Finds Online – Everything is well organized, making shopping enjoyable.
believeandachieve – Great selection and user-friendly layout made browsing fun and easy today.
возмещение ущерба после залива возмещение ущерба после залива .
brandmomentum.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
заказать филлеры оптом https://filler-kupit.ru .
курсовые заказ https://kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru/ .
курсовая работа купить москва курсовая работа купить москва .
leadoptimizer.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
bestchoiceoutlet – Always nice product photos here, browsing felt comfortable and reliable.
believeandachieve – Clean interface, good product variety, and easy navigation made shopping comfortable.
Timberline Deals – Smooth shopping experience with an organized layout.
urbanworld – Fast-loading pages, products are well displayed, and browsing felt comfortable.
It’s very straightforward to find out any matter on net as
compared to books, as I found this article at this web site.
Thanks
купить курсовая работа купить курсовая работа .
FutureGardenDepot – Intuitive layout and smooth page transitions made shopping quick and easy.
Rocket Play Australia https://rocketplay-aus.net/
курсовой проект цена курсовой проект цена .
new horizon corner – Fast-loading pages and tidy layout enhanced the experience.
грати слоти найкращі слоти
ігри казіно ігри казино
rejestracja w mostbet oficjalny mostbet
Trendy Choice Spot – Browse stylish items with ease and enjoy navigating categories.
dreamleafgallery – Pleasant browsing experience, categories are easy to navigate and items look appealing.
brightorchardhub – The categories are well organized, helped me find products without hassle.
Wonder Peak Emporium – Browsing feels effortless and the interface is tidy.
shoppingcorner – Pages load fast, and finding products is quick and simple.
dreamleafgallery – Product images load well and descriptions are clear, making shopping comfortable.
курсовые заказ http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-8.ru .
brightorchardhub – The categories are well organized, helped me find products without hassle.
shop golden collection – Smooth navigation and neatly displayed products improved browsing.
слоти ігрові автомати найкращі слоти
crestartstyle – Well-structured site with clear sections, made shopping easy.
грати слоти популярні слоти
logowanie do mostbet bonus mostbet
ігри онлайн казино ігри в казино
BotSync, занимаемся автоматизацией бизнеса делаем умные, чат боты для CRM на N8n https://sorted-booth-08732357.figma.site
At Rubbish Taxi, we manage your house clearance requirements, whether it is a home renovation, room redecoration, or clearing out old items. Our services cover comprehensive house removals and clearances across Dublin and other cities where we operate. We can collect various bulky items, including sofas, bed frames, mattresses, chest of drawers, wardrobes, fridges, freezers, washing machines, dishwashers, ovens, musical instruments, and more. Count on us for a seamless experience – https://rubbish-taxi.ie/sofa-disposal-dublin/
clickrevenue.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Bluestone Outlet – Finding products was simple and smooth.
growcorner – The layout is clean, making browsing a pleasant experience.
популярні слоти слоти онлайн
ігри онлайн казино ігри онлайн казино
oficjalne kasyno mostbet mostbet
Cozy Outlet Goods – The site is well-organized, helping me find what I needed without any hassle.
urbanvinecollective – Clean interface and organized product listings made browsing simple and enjoyable.
lunarcrestlifestyle – I found interesting items quickly, and product images looked clear and appealing.
finduniqueoffers.shop – Unique offers found, shopping here felt effortless and interesting overall today. Special Finds Daily – Explore fashionable and lifestyle items for effortless shopping.
заказать курсовую работу заказать курсовую работу .
coastline picks – Smooth interface and fast-loading pages improved the experience.
urbanvinecollective – Nice variety with clear layout, making it easy to find interesting items fast.
lunarcrestlifestyle – I found interesting items quickly, and product images looked clear and appealing.
сервисный ремонт стиральных машин https://master-stiralok-vrn.ru/
ремонт стиральных машин номер сайт ремонт стиральных машин
artisanbazaar – Pages are tidy and navigation is smooth, made shopping simple.
Rocket Play Casino https://rocketplay-aus.net/
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/yyscvxwb
oficjalny mostbet oficjalny mostbet
новости беларуси сегодня главные новости беларуси
независимые новости беларуси главные новости беларуси
Coastal Ridge Picks – Simple to explore, with items neatly organized.
puremeadowmarket – Was impressed by how fast the site responds, no lag at all.
coastlinegather – Found some great items here, descriptions felt natural and genuinely useful.
mountain hub – Items loaded quickly and sections were easy to explore.
покупка курсовой покупка курсовой .
puremeadowmarket – Nice variety of items available, exploring the shop felt enjoyable overall.
coastlinegather – Pages load fast here, making the entire browsing experience feel efficient today.
happyhomecentral – Easy to navigate, products load quickly and look appealing.
evermeadowgoods – Great selection and intuitive navigation helped me explore products without hassle.
Bright Timber Collection – Clean site design and product clarity made browsing fast and enjoyable.
MountainMistStudio Hub – Clear product arrangement and smooth scrolling improved shopping.
moon picks – Smooth interface and organized categories made shopping pleasant.
купить курсовую москва купить курсовую москва .
Urban Seed Boutique Picks – Products are easy to find and layout is neat.
Your Next Art Piece – I appreciated how the streamlined design made browsing feel quick and easy.
puregreenlane – Pleasant shopping experience, layout is neat and organized.
wildroselane – Smooth pages with clear sections, products were easy to explore.
shop sunset wood – Fast loading and neat product display improved the browsing experience.
optirank.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
root collection – Browsing was effortless and products were neatly arranged.
rankflow.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
rankcharge.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
rankhive.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Изготавливаем каркас лестницы из металла на современном немецком оборудовании — по цене стандартных решений. Качество, точность реза и долговечность без переплаты.
Latest about all things crypto: price rises and falls, network updates, listings, regulations, trend analysis, and industry insights. Follow market movements in real time.
The latest crypto news: Bitcoin, altcoins, NFTs, DeFi, blockchain developments, exchange reports, and new technologies. Fast, clear, and without unnecessary noise—everything that impacts the market.
Купить шпон https://opus2003.ru в Москве прямо от производителя: широкий выбор пород, стабильная толщина, идеальная геометрия и высокое качество обработки. Мы производим шпон для мебели, отделки, дизайна интерьеров и промышленного применения.
Explore GoldenBranchMart – Well-arranged sections improved the overall shopping flow.
softpineoutlet – The design feels clean and welcoming, easy to navigate between different sections.
silveroakstudio – The product range impressed me, selection feels curated and thoughtfully chosen.
Trend Street Hub – Handpicked urban fashion items for a chic and contemporary appearance.
best crypto exchange – fast crypto exchange
exchange crypto
https://changenow-io.us
best cryptocurrency exchange – instant crypto exchange
crypto exchange
https://exchangenow.app
crypto exchange without KYC
changenow crypto
https://exchangenow.us
This Store – The clear presentation of items allowed for a very quick and pleasant browse.
вывод человека из запоя https://narcology-moskva.ru
softpineoutlet – Found a few items I’m interested in, descriptions seem clear and useful here.
When someone writes an post he/she retains the image of a user in his/her mind that how a
user can understand it. Thus that’s why this article
is outstdanding. Thanks!
Stop by my page … خرید بک لینک
Thank you that is kind of you
silveroakstudio – The product range impressed me, selection feels curated and thoughtfully chosen.
вывод из запоя анонимно вывод из запоя на дому стоимость
вывод из запоя клиника вывод из запоя в воронеж
вывод человека из запоя https://narkonet.su
Timber Crest Hub Finds – Quick navigation and neat layout helped me locate items easily.
bright pine collection – Clear layout and tidy categories enhanced the browsing experience.
вывод из запоя вывод из запоя капельница на дому
электрокарниз недорого prokarniz36.ru .
экспертиза залива квартиры экспертиза залива квартиры .
бифазные филлеры http://www.filler-kupit.ru/ .
fallvibeboutique – Smooth browsing, design is simple and items are easy to find.
rarefashionstorehub – Fast-loading and organized sections, shopping felt smooth.
brightcoastgallery – Smooth scrolling and clear organization make this shop easy to use on mobile as well.
brightwinterstore – Products look appealing and navigation is smooth — a good shopping experience.
glowingridgehub – The design is clean and welcoming, giving the store a trustworthy friendly vibe.
LunarHarvestMart Online – Fast loading pages made browsing effortless and enjoyable.
Nurture & Flourish Spot – Strategies and insights to cultivate personal growth and resilience.
Cozy Cabin Market – Pages load fast and the design is clean and welcoming.
you are actually a excellent webmaster. The website loading speed is amazing.
It kind of feels that you are doing any unique trick.
Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have performed a fantastic process in this subject!
Thank you
That is kind of you
RusticStone Finds – The combination of fast performance and good organization is top-notch.
brightcoastgallery – Items display nicely, images load fast — really good browsing experience so far.
shophub – Browsing was smooth, products were easy to find and well organized.
Если вы работаете в сфере производства и столкнулись с необходимостью в поставке лучших тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше решение. Наша компания специализируется на области поставок тугоплавких металлов в течение многих лет, что дает нам возможность предоставлять только качественный продукт своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Объемы поставок не имеют значения.
2. Большой ассортимент тугоплавких металлов.
3. Все необходимые документы.
4. Круглосуточная поддержка.
Зачем подбирать на других сайтах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда готовы помочь?
Если у вас есть вопросы, наши специалисты всегда готовы ответить на них.. Звоните прямо сейчас и проверьте в достоинствах нашего продукта.
Команда ООО “РМС” на связи!
поставляемая продукция:
Проволока стальная 100х420 мм B8A ASTM A193
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наши товары:
Штамповая поковка 75 мм 4Х3ВМФ ГОСТ 1133-71 Узнайте о штамповой поковке диаметром 75 мм из высокопрочного сплава 4Х3ВМФ согласно ГОСТ 1133-71 на Редметсплав.рф. Идеальное решение для производства деталей промышленного оборудования с отличной износостойкостью и удобством монтажа.
glowingridgehub – Enjoyed scrolling through products, everything felt organized and accessible without fuss.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/328h9wrz
store overview – Quick-loading pages and tidy sections made the experience pleasant.
hillcornerlane – Products are neatly categorized, making shopping effortless.
Доставка грузов https://china-star.ru из Китая под ключ: авиа, авто, море и ЖД. Консолидация, проверка товара, растаможка, страхование и полный контроль транспортировки. Быстро, надёжно и по прозрачной стоимости.
карниз с приводом для штор prokarniz36.ru .
независимая оценка ущерба после залива независимая оценка ущерба после залива .
бифазные филлеры https://filler-kupit.ru .
Daily Vision Hub – Inspiration and tips for dreaming big and acting on your plans.
authoritygrowthengine.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Доставка грузов https://lchina.ru из Китая в Россию под ключ: море, авто, ЖД. Быстрый расчёт стоимости, страхование, помощь с таможней и документами. Работаем с любыми объёмами и направлениями, соблюдаем сроки и бережём груз.
Гастродача «Вселуг» https://gastrodachavselug1.ru фермерские продукты с доставкой до двери в Москве и Подмосковье. Натуральное мясо, молоко, сыры, сезонные овощи и домашние заготовки прямо с фермы. Закажите онлайн и получите вкус деревни без лишних хлопот.
clickoptimizationhub.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
digitalmarketingzone.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
leadconversionstudio.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
proleadgeneration.shop – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Логистика из Китая https://asiafast.ru без головной боли: доставка грузов морем, авто и ЖД, консолидация на складе, переупаковка, маркировка, таможенное оформление. Предлагаем выгодные тарифы и гарантируем сохранность вашего товара.
hillurbanemporium – Products are easy to locate, and the layout feels calm and tidy.
Независимый сюрвейер https://gpcdoerfer1.com в Москве: экспертиза грузов, инспекция контейнеров, фото- и видеопротокол, контроль упаковки и погрузки. Работаем оперативно, предоставляем подробный отчёт и подтверждаем качество на каждом этапе.
карниз с приводом https://prokarniz36.ru .
nexium prices
generic xenical
залив с крыши оценка ущерба залив с крыши оценка ущерба .
Maintaining a generic methylprednisolone is essential for overall well-being, helping you stay energized and balanced in daily life. By making informed choices, you can improve your physical and mental state while boosting long-term vitality. Whether you’re exploring new wellness strategies, adopting nutritious eating habits, or discovering the benefits of exotic superfoods, prioritizing health leads to a more fulfilling lifestyle. Stay informed with expert insights and evidence-based recommendations to make the best decisions for your body and mind.
Soft Feather Studio Hub – Organized interface and well-displayed items allowed for fast selection.
everstonecorner – Nice variety of products and layout made selection easy, worth another visit soon.
филлер цена http://www.filler-kupit.ru .
softmeadowstudio – Found some nice products, and descriptions came across as helpful and clear overall.
I pay a visit each day a few websites and information sites to read articles or reviews, however this weblog offers quality based writing.
Thank you
That is kind of you
brighthaven hub – Clean layout and intuitive navigation made shopping enjoyable.
Silver Moon Fabrics Finds – Very easy to navigate, and the items were displayed clearly.
Доставка грузов https://china-star.ru из Китая для бизнеса любого масштаба: от небольших партий до контейнеров. Разработаем оптимальный маршрут, оформим документы, застрахуем и довезём груз до двери. Честные сроки и понятные тарифы.
Онлайн-ферма https://gvrest.ru Гастродача «Вселуг»: закажите свежие фермерские продукты с доставкой по Москве и Подмосковью. Мясо, молоко, сыры, овощи и домашние деликатесы без лишних добавок. Удобный заказ, быстрая доставка и вкус настоящей деревни.
everstonecorner – The store seems professional and credible, info feels transparent and browsing felt comfortable.
digitalpresencelab.shop – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
fullservicemarketing.shop – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
onlinebusinessbooster.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
expertseostrategies.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
prolevelmarketinghub.shop – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
softmeadowstudio – Overall user experience felt smooth and friendly, I’d consider revisiting it sometime soon.
SoftMorning Home – I was immediately impressed by the high-quality visuals and clean site structure.
вскрыть замок
winter boutique – Clean layout and intuitive navigation made shopping simple.
Today’s Most Important: https://planetasp.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?pid=25232#p25232
Best selection of the day: https://open.mit.edu/profile/01k9pbqnt34xydhdrfn5emsz66/
Сейчас, что интерес к самобытным подаркам становится всё больше. Особенно выделяются авторские матрешки, которые давно стали предметом коллекционирования.
Такие сувениры часто покупают для интерьера, ведь они создают уют.
Если углубиться в выбор, то матрешки как подарки подходят для деловых мероприятий.
Покупатели выбирают такие предметы декора, потому что они выглядят дорого и красиво.
Матрешка — это намного больше, чем сувенир. Каждая авторская матрешка может включать классический набор фигур, что делает её особенной.
сувениры
Что делает матрешку идеальным сувениром?
Начнём с основ, это универсальность. Матрешку можно предложить гостям.
Дополнительным плюсом является — эстетика и стиль, которые создают культурную связь.
Еще один момент, что многие покупатели выбирают уникальные серии, а значит матрешка становится особым сувениром.
Как подобрать подходящую матрешку?
При выборе сувениров стоит обращать внимание на тематику рисунка. Иногда покупатели выбирают современные варианты.
Для особых случаев подойдут индивидуальные серии, которые подчеркнут статус.
Русские матрешки остаются востребованными благодаря своей красоте.
Именно поэтому матрешка как подарок подходят как универсальный вариант, сохраняя русский дух.
подарки
autumnstonecorner – I liked how quickly everything loaded, made the browsing experience smooth and hassle-free.
urbanwildroot – Navigation was intuitive and finding items was hassle-free — really appreciated that.
Казино ловит клиентов честно, без обмана и подводов. 7k онлайн правила прозрачные, нет скрытых условий.
clickconversionpro.shop – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
marketingsupportcenter.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
authorityranklabs.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
rankblaze.shop – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
smartgrowthengine.shop – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
autumnstonecorner – Enjoyed exploring the store, layout helped me navigate without any frustration or lag.
urbanwildroot – Navigation was intuitive and finding items was hassle-free — really appreciated that.
Urban Vibe Hub – Product selection is broad, and the interface is easy to use.
discover here – The polished look and smooth experience made it comfortable to browse.
Hello mates, how is everything, and what you desire to say concerning this post, in my view its really awesome for me.
Thank you
that is kind of you
Hello all,
I came across this free AI-powered calculator that gives instant, accurate results for everyday tasks — from finance to fitness.
It’s part of the SmartCalc collection — built for speed, accuracy, and simplicity.
Try it here:
SmartCalc Online Tool
No signup, no ads — just clean and simple calculators that actually work.
If you like data-driven tools or quick results without spreadsheets, this is worth a look.
Give it a try and see what you think!
star boutique – Clear layout and tidy sections enhanced the shopping experience.
Hi, yup this article is actually pleasant and I
have learned lot of things from it about blogging.
thanks.
Thank you
that is kind of you
shop wild hub – Items are well organized and browsing felt natural.
электрокарниз двухрядный http://www.provorota.su .
clickmarketingcenter.shop – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
электрокарнизы купить в москве http://www.elektrokarniz2.ru/ .
Silver Harvest Hub – The design is clean and browsing around was smooth and effortless.
digitalperformancelab.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
powerfulgrowthagency.shop – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
creativeclicksagency.shop – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
superiorrankingstudio.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Платформа для работы https://skillstaff.ru с внешними специалистами, ИП и самозанятыми: аутстаффинг, гибкая и проектная занятость под задачи вашей компании. Найдем и подключим экспертов нужного профиля без длительного найма и расширения штата.
onewin 1win12043.ru
Клиника проктологии https://proctofor.ru в Москве с современным оборудованием и опытными врачами. Проводим деликатную диагностику и лечение геморроя, трещин, полипов, воспалительных заболеваний прямой кишки. Приём по записи, без очередей, в комфортных условиях. Бережный подход, щадящие методы, анонимность и тактичное отношение.
электрические карнизы для штор в москве https://elektrokarniz98.ru/ .
studio corner – Navigation felt natural and exploring products was effortless.
Leaving a quick message here after giving it a quick read.
Thanks
Колодцы под ключ https://kopkol.ru в Московской области — бурение, монтаж и обустройство водоснабжения с гарантией. Изготавливаем шахтные и бетонные колодцы любой глубины, под ключ — от проекта до сдачи воды. Работаем с кольцами ЖБИ, устанавливаем крышки, оголовки и насосное оборудование. Чистая вода на вашем участке без переплат и задержек.
Инженерные изыскания https://sever-geo.ru в Москве и Московской области для строительства жилых домов, коттеджей, коммерческих и промышленных объектов. Геология, геодезия, экология, обследование грунтов и оснований. Работаем по СП и ГОСТ, есть СРО и вся необходимая документация. Подготовим технический отчёт для проектирования и согласований. Выезд на объект в короткие сроки, прозрачная смета, сопровождение до сдачи проекта.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
Наша продукция:
Электроды вольфрамовые 1.5 мм WL-10 Выберите оптимальные вольфрамовые электроды для качественной и надежной сварки различных металлов. Широкий выбор форм и типов, высокая термическая устойчивость, отличная проводимость тока и долговечность. Применение в аэрокосмической, автомобильной, судостроительной, нефтегазовой промышленности и других отраслях.
shop green – Neat categories and responsive pages made finding products simple.
гардина с электроприводом https://provorota.su/ .
электрокарниз москва http://www.elektrokarniz2.ru .
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3sjhzs46
https://towing.com.pl
Hi folks,
I came across this free AI-powered calculator that gives instant, accurate results for everyday tasks — from finance to fitness.
It’s part of the SmartCalc collection — built for speed, accuracy, and simplicity.
Try it here:
SmartCalc Online Tool
No signup, no ads — just clean and simple calculators that actually work.
If you like data-driven tools or quick results without spreadsheets, this is worth a look.
Give it a try and see what you think!
best crypto exchange – fast crypto exchange
crypto exchange
https://changenow.es
best cryptocurrency exchange – instant crypto exchange
changenow changenow
https://changenow-io.io
crypto exchange without KYC
change now
https://exchangenow.us
карниз моторизованный https://elektrokarniz98.ru .
Доставка дизельного топлива https://ng-logistic.ru для строительных компаний, сельхозпредприятий, автопарков и промышленных объектов. Подберём удобный график поставок, рассчитаем объём и поможем оптимизировать затраты на топливо. Только проверенные поставщики, стабильное качество и точность дозировки. Заявка, согласование цены, подача машины — всё максимально просто и прозрачно.
Доставка торфа https://bio-grunt.ru и грунта по Москве и Московской области для дач, участков и ландшафтных работ. Плодородный грунт, торф для улучшения структуры почвы, готовые земляные смеси для газона и клумб. Быстрая подача машин, аккуратная выгрузка, помощь в расчёте объёма. Работаем с частными лицами и организациями, предоставляем документы. Сделайте почву на участке плодородной и готовой к посадкам.
Строительство домов https://никстрой.рф под ключ — от фундамента до чистовой отделки. Проектирование, согласования, подбор материалов, возведение коробки, кровля, инженерные коммуникации и внутренний ремонт. Работаем по договору, фиксируем смету, соблюдаем сроки и технологии. Поможем реализовать дом вашей мечты без стресса и переделок, с гарантией качества на все основные виды работ.
Harbor Home Shop – Smooth and efficient navigation made exploring products pleasant.
We buy household appliances in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad Region продать айфон. We buy tumble dryers.
последние новости беларуси новости беларуси 2025
Инструкция зайти на кракен описывает установку Tor, настройку мостов obfs4, поиск актуальных адресов и безопасную регистрацию на площадке.
Геосинтетические материалы https://stsgeo.ru для строительства купить можно у нас с профессиональным подбором и поддержкой. Продукция для укрепления оснований, армирования дорожных одежд, защиты гидроизоляции и дренажа. Предлагаем геотекстиль разных плотностей, георешётки, геомембраны, композитные материалы.
Shop With Ease – The logical categories and good selection made my visit both quick and successful.
LivingMarketTrends – Shopping was smooth, products arrived quickly and in great condition.
revival shop link – Smooth navigation overall, and everything appeared quickly without delays.
Доставка грузов https://avalon-transit.ru из Китая «под ключ» для бизнеса и интернет-магазинов. Авто-, ж/д-, морские и авиа-перевозки, консолидация на складах, проверка товара, страхование, растаможка и доставка до двери. Работаем с любыми партиями — от небольших отправок до контейнеров. Прозрачная стоимость, фотоотчёты, помощь в документах и сопровождение на всех этапах логистики из Китая.
карниз моторизованный http://www.provorota.su .
электрокарнизы для штор купить http://elektrokarniz2.ru/ .
ShopWithJoy – Items look high quality, delivered quickly and exceeded my expectations completely.
Hi! Stay alert… there’s more going on here than meets the eye.
Discover a lumiere styled gaming experience with bright, uplifting visuals and elegant mechanics. A polished Canadian space built for smooth engagement.
п»їhttps://besthotcasino.ca
PureLeafEmporium – Great experience here, product selection seemed curated and genuinely helpful too.
электрокарниз купить электрокарниз купить .
Wild Ridge Corner Shop – Fast navigation and well-arranged pages made shopping easy.
ShopWithJoy – Very happy with overall service quality, site design and product range impressive.
How long before I see results from a marketing agency?
Every brand, market, and channel mix is different, so timelines vary. If your primary focus is SEO, you can typically expect to see meaningful traction within 3–6 months as technical fixes, content improvements, and authority-building (backlinks, mentions) start compounding. For paid acquisition (like SEA/PPC), results can be much faster—often within days—because you can reach targeted audiences immediately and continuously refine based on data. Social media marketing (SMM) can generate short-term engagement quickly, but sustainable growth (reach, community, and conversions) takes consistent creative, testing, and alignment with your brand voice over several months. What matters most is building the right growth system: clear goals, high-quality tracking, tight feedback loops, and consistent iteration. We’ll always be transparent about what’s realistic, what’s risky, and what will drive the highest ROI for your budget and timeline.
What’s included in a marketing agency’s free strategy session?
Our strategy session is designed to give you clarity—no fluff, no generic decks. Before the call, we review your site, your search visibility, and your current performance across SEO, SEA, and SMM. During the session, we:
identify quick wins (technical fixes, page speed, metadata, ad structure),
map opportunities by funnel stage (awareness, consideration, conversion),
highlight content gaps, competitor differentials, and positioning,
discuss tracking and attribution maturity, so decision-making is rooted in data,
suggest a prioritized 90-day roadmap with estimated impact and effort.
You’ll walk away with a clear action list and next steps—regardless of whether you work with us. If we’re a fit, great. If not, you still get value immediately.
Do marketing agencies work with small businesses?
Yes—and we love working with SMBs. Smaller companies often benefit most from focus: a tight set of high-intent keywords, a lean ad structure, and locally resonant content that speaks to real customer needs. We tailor roadmaps to your budget and your capacity, prioritizing the highest-impact, lowest-effort actions first. That might mean local SEO (GBP optimization, citations, reviews), conversion-focused landing pages for your core services, or a few carefully constructed campaigns in Google Ads and Meta to kickstart pipeline. You don’t need an enterprise budget to get enterprise-level thinking—you need a partner who will help you punch above your weight with smart execution and clear reporting.
What industries do marketing agencies specialize in?
Great agencies build repeatable processes that adapt to different industries. We’ve developed frameworks that work across B2B services, SaaS, eCommerce, healthcare, professional services, education, and local services. Our approach combines:
Deep customer insight (jobs-to-be-done, pain points, buying triggers)
Demand creation + demand capture (brand + performance)
Content systems (topic clusters, product-led content, case studies)
Measurement (clear KPIs, dashboards, and experiments)
Specialization matters—but so does fresh thinking. Our cross-industry experience helps us introduce winning tactics from one vertical to another while keeping your brand voice and compliance requirements intact.
Are marketing agency services available internationally?
Absolutely. Whether you’re selling cross-border, running multi-language campaigns, or expanding into new markets, we can help. International programs require localization (not just translation), country-level search intent analysis, region-specific ad compliance, and nuanced message testing. We also align technical SEO for international structures (subfolders vs. subdomains, hreflang, geo-targeting) and coordinate creative that respects cultural context. Our team works across time zones and platforms to deliver consistent execution and unified reporting, so you can see what works, where, and why—then scale intelligently.
Can I combine SEO, SEA, and social media marketing with your agency?
You’ll get the best results when your channels talk to each other. We build integrated strategies where PPC insights inform SEO content, SEO wins lower your overall CAC, and social creative fuels both brand and performance. For example, we use PPC search term reports to uncover organic keyword gaps, social engagement to identify resonant angles for landing pages, and remarketing to move visitors from interest to conversion. You’ll get one plan, one dashboard, and one accountable team—so your investments compound instead of competing.
How does a marketing agency measure success?
Vanity metrics don’t grow businesses—conversions and revenue do. We align success with your north-star KPIs: SQLs, opportunities, pipeline, ROAS, CAC:LTV ratio, and time-to-value. Tactically, we track:
SEO: rankings for high-intent terms, organic sessions to key pages, assisted conversions, and revenue attribution.
SEA: cost per lead (CPL), conversion rate, impression share, quality score, and blended CAC.
SMM: reach and engagement that correlate with downstream conversions, plus paid-social ROAS.
We set baselines, define achievable targets, and iterate with A/B tests. You’ll get transparent, plain-language reporting so you always know what’s working and what we’re changing next.
Is there a contract when hiring a marketing agency?
We believe in flexibility and accountability. Our typical engagement starts with a 90-day sprint to deliver fast wins and establish a performance rhythm. After that, most clients move to rolling monthly terms. No long-term lock-ins; we prefer to earn your next month with results and service. For larger or international programs that require deep buildouts (e.g., multi-language sites, complex data pipelines, or large content operations), we’ll craft milestone-based scopes with clear deliverables and review points. Either way, your terms will be simple, transparent, and aligned with outcomes.
What is the pricing structure for marketing agency services?
Pricing should match value, complexity, and velocity. We offer three simple models:
Projects (fixed-fee): Audits, migrations, analytics setups, landing page bundles, or content packs with defined deliverables.
Retainers (monthly): Ongoing SEO, SEA, SMM, content, and CRO—ideal for continuous growth, testing, and iteration.
Hybrid: A core retainer for day-to-day execution plus project-based add-ons for spikes (campaign launches, seasonal pushes, new product lines).
You’ll get a proposal with a clear scope, timeline, and outcomes, plus the metrics we’ll use to judge success. We’re also upfront about what we won’t do with your budget—if the ROI is unlikely, we’ll say so.
How does a marketing agency customize strategies for my business goals?
Customization starts with context. We map your business model, margins, sales cycles, and competitive landscape, then align tactics with your goals—whether that’s rapid pipeline growth, market-entry validation, multi-region expansion, or profitability at scale. Our process includes:
Discovery: stakeholders, ICPs, value props, pricing, and objections.
Diagnostics: technical SEO, content quality, conversion paths, tracking integrity, and ad account structure.
Prioritization: ICE or RICE scoring to focus on the highest-leverage actions first.
Activation: campaign buildouts, content engines, and experimentation across creatives, audiences, and offers.
Enablement: dashboards, documentation, and training so your internal team can scale with us.
The result: a strategy that’s not just “custom” on paper but deeply aligned with how you sell and how your customers buy.
Why brands choose us
Performance-first: We connect activity to revenue with reliable tracking and honest reporting.
Channel integration: SEO, SEA, SMM, CRO, and content work in concert—not in silos.
Transparent communication: Clear timelines, shared dashboards, weekly or bi-weekly check-ins.
Agile delivery: Short feedback loops, rapid experiments, and continuous optimization.
Ethical growth: No shortcuts, no black-hat tactics—just compounding, defensible wins.
What you can expect in your first 90 days
Weeks 1–2: Deep audit (tech, content, analytics), quick technical fixes, ad account hygiene, tracking validation.
Weeks 3–6: Launch/refine core campaigns, publish priority content, implement CRO improvements on key pages.
Weeks 7–12: Scale winning ad sets/keywords, expand content clusters, build authority links, roll out A/B tests, and present a quarterly strategy review.
Proof over promises
We’ve helped startups punch above their weight, mid-market companies scale profitably, and global brands orchestrate multi-country campaigns that lower CAC while increasing LTV. Our approach is simple: do the work that matters most, measure it rigorously, and communicate clearly.
Ready to make your marketing a growth engine?
If you’re looking for a partner who treats your budget like their own and aligns every tactic with real business outcomes, let’s talk. Book your free strategy session
Facebook
Instagram
Reddit
LinkedIN
PureLeafEmporium – Smooth navigation today, impressed by how quickly pages responded while browsing.
BrightGroveHub Storefront – Everything felt organized, making browsing fast and stress-free.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/faaw43e7
Got locked out in Tampa and figured I’d drop this here in case it helps someone else.
I used a local locksmith from this site:
https://tampa24hrlocksmith.com/
They offer 24/7 mobile service in Tampa for:
– Vehicle lockouts and lost car keys
– House / apartment lockouts
– Rekey service for new owners or tenants
– Basic commercial door locks
The tech came out pretty quickly, gave the price before starting and there were no hidden fees at the end.
If you need a locksmith in a hurry, it’s worth saving this:
**https://tampa24hrlocksmith.com/**
Posting this because it’s hard to tell which locksmiths are real and which are sketchy, and this one actually did the job without turning it into a circus.
Подробнее на сайте: все знаки зодиака прогноз
honesttrendshop – Intuitive design with tidy listings, shopping was quick and hassle-free.
ролевые шторы ролевые шторы .
автоматические рулонные шторы с электроприводом http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom499.ru/ .
smarttrafficboost.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
maximumtrafficservice.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
seoagencysolutions.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
creativegrowthagency.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
onlinerankingstudio.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Безопасный процесс авторизации вход на кракен требует решения TOTP кода из приложения аутентификатора и дополнительного PIN для критических операций на платформе.
Strona internetowa mostbet – zaklady sportowe, zaklady e-sportowe i sloty na jednym koncie. Wygodna aplikacja mobilna, promocje i cashback dla aktywnych graczy oraz roznorodne metody wplat i wyplat.
Казино имеет очень приветливое сообщество игроков. 7k казино официальный люди делятся советами и стратегиями.
жалюзи автоматические цена жалюзи автоматические цена .
stonecornercollective – Clear design, shopping feels smooth and relaxed.
this shop – Loved how clean everything looked; browsing through items was simple and enjoyable.
ExpandYourMind – Website loads quickly, layout is clean and user-friendly as expected.
Хочешь айфон? apple iphone выгодное предложение на новый iPhone в Санкт-Петербурге. Интернет-магазин i4you готов предложить вам решение, которое удовлетворит самые взыскательные требования. В нашем каталоге представлена обширная коллекция оригинальных устройств Apple. Каждый смартфон сопровождается официальной гарантией производителя сроком от года и более, что подтверждает его подлинность и надёжность.
Всё лучшее здесь: https://medim-pro.ru/spravka-ot-allergologa-kupit/
Leaving
a quick
301 response checker
to check how various browsers and servers react to 301 redirects
.
This link is only being used for basic redirect behavior checks and troubleshooting
.
In case you’re doing similar routing diagnostics, you can check it too
:
https://i8.ae/zPslw
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наши товары:
Мишень из драгоценного металла или его сплава круглая палладий 100х1.5 мм ПДСР-20 ТУ Выберите уникальные мишени из драгоценных металлов для напыления от Редметсплав.рф. Обеспечивают высокую степень защиты и долговечность. Идеальный выбор для промышленности, строительства и производства.
автоматические рулонные шторы на створку rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom.ru .
рулонные шторы автоматические купить rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom499.ru .
ExpandYourMind – Impressive variety and nice layout, makes browsing online enjoyable today.
Hi folks,
I came across this free AI-powered calculator that gives instant, accurate results for everyday tasks — from finance to fitness.
It’s part of the SmartCalc collection — built for speed, accuracy, and simplicity.
Try it here:
SmartCalc Online Tool
No signup, no ads — just clean and simple calculators that actually work.
If you like data-driven tools or quick results without spreadsheets, this is worth a look.
Give it a try and see what you think!
FashionForLife – Nice variety of products, checkout worked perfectly and shipping seems fast.
Looking for a chat? https://emerald-chat.app A convenient Omegle alternative for connecting with people from all over the world. Instant connection, random chat partners, interest filters, and moderation. Chat via video and live chat with no registration or payment required.
wave picks – Neatly displayed items and smooth scrolling made browsing simple.
жалюзи автоматические цена жалюзи автоматические цена .
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/3bnh6hxk
sunridge finds – Items appeared quickly and the interface is user-friendly.
this creative shop – Loved the clean aesthetic; the products are arranged in a way that’s easy on the eyes.
Оформление медицинских анализов https://medim-pro.ru и справок без очередей и лишней бюрократии. Запись в лицензированные клиники, сопровождение на всех этапах, помощь с документами. Экономим ваше время и сохраняем конфиденциальность.
digitalconversionlab.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Lunar Wood Treasures Hub – Organized interface and quick visuals made finding products simple.
ultimaterankbooster.shop – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
backlinkhub.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
PureChoiceOutlet – Website feels clean and organized, makes shopping online feel stress-free today.
globalmarketingexperts.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
webauthorityboost.shop – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
PerfectBuyZone – Shopping felt effortless, site layout is neat and user-friendly overall.
moonfield hub – Navigation was effortless and items were easy to explore.
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s really informative.
I am going to watch out for brussels. I will be grateful
if you continue this in future. A lot of people will be
benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Thank you, that is kind of you
i will do my best to live up to your expectations.
электрические жалюзи на окна электрические жалюзи на окна .
ролевые шторы ролевые шторы .
PureChoiceOutlet – Items look good quality, ordering process was simple and delivery promising.
PerfectBuyZone – Products arrived on time, quality seems great and worth recommending too.
https://checksite.com
горизонтальные жалюзи с электроприводом горизонтальные жалюзи с электроприводом .
wildgroveemporium – Items are well arranged and navigation feels intuitive — nice overall experience.
future finds hub – Browsing was intuitive and products loaded quickly.
organicgrowthcenter.shop – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
BargainHubToday – Liked how neatly everything was grouped; made finding good offers straightforward.
ultimaterankboost.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
GrowthWithIntent – Motivating content, instructions are clear and actionable.
seoenhancementpro.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
brandvisibilitypro.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
strategicseoagency.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
внутренняя гидроизоляция подвала внутренняя гидроизоляция подвала .
гидроизоляция цена работы за м2 gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru .
инъекционная гидроизоляция цена [url=https://www.inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru]инъекционная гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
https://binnwksbgmeif.com – Imenitub Ijoyesm ttr.ysgp.economicjourney.com.ory.cz https://binnwksbgmeif.com
KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION — действующие ссылки 2025
В этой статье вы найдёте все зеркала и адреса для входа на KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION в 2024-2025 году. Мы собрали только свежие ссылки, которые помогут обойти блокировку и подключиться к сайту без проблем и с полной анонимностью.
Актуальный список ссылок KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
1 Главная ссылка: https://kra24.cn.com/
2 Резервный сайт: https://krak34.cfd
3 Дополнительный сайт 2: https://krak67.pw/
4 Официальный Tor-адрес: krakeno4nmrk1ewmq4l9tme9wpfk2lczlsm7g3epfgu3itne8raion *точка онион*
5 Telegram канал с обновлениями: https://t.me/+WIvclfeRsfZlM2Yy
6 Скачать Tor: https://www.torproject.org/download/
Как зайти на KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
1. Сначала установите Tor — он нужен для доступа к даркнету.
2. Запустите Tor и дождитесь полной загрузки сети.
3. Перейдите по рабочей ссылке https://kra34.ch.
4. Если у вас ещё нет профиля, зарегистрируйтесь: придумайте логин и надёжный пароль.
5. Обязательно настройте 2FA для защиты .
Советы по защите
– Всегда проверяйте ссылки перед входом — это важно для предотвращения фишинга.
– Используйте прокси вместе с Tor для повышенной анонимности и шифрования трафика.
– Обновляйте список — ссылки на KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION могут меняться из-за блокировок.
– Никогда не открывайте ссылки из случайных ресурсов, даже если они кажутся похожими.
Почему используют KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
– KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION маркетплейс|KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION сайт популярен в даркнете благодаря:
большому выбору товаров,
надёжной системе покупок,
полной анонимности пользователей.
Также здесь работает система рейтингов продавцов, что помогает находить только проверенных поставщиков.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
?? Что делать, если KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION не открывается?
– Попробуйте альтернативный адрес из списка.
– Перезапустите Tor или проверьте прокси.
– Проверьте обновления ссылок в Telegram.
?? Где брать рабочие ссылки?
– Только с официальных страниц.
– Храните их в надёжном месте, периодически проверяйте актуальность KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION .
?? Как избежать фишинга?
– Не открывайте ссылки в обычном браузере.
– Используйте только Tor + VPN.
– Всегда проверяйте точный адрес перед вводом логина.
Вывод
?? KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION — это один из популярных маркетплейсов в даркнете. Чтобы не потерять вход, используйте только проверенные зеркала, соблюдайте правила безопасности и следите за обновлениями.
?? Сохраняйте этот список и делитесь только с теми, кому доверяете.
—
Ключи, покрытые статье
* KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION ссылки 2025
* Зеркало KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
* Вход на KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
* Рабочие ссылки KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
* Актуальный список KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION
* KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION маркетплейс доступ
* Как зайти на KRAKEN MARKETPLACE ONION через Tor
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – идеальный вариант для вас.
Наша продукция:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов палладиевая 5х1х0.2 мм ПдИ90-10 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Antipublic – Stop Data Exposure Before It Destroys You
Your personal information data breach may already be live on the dark web. Antipublic reveals hidden data exposure risks and protects you from costly security breaches.
Access 33B+ leaked passwords and track 50M new records daily in real time. Scan any user, domain, or email instantly and prevent massive loss before it happens.
Only $2 unlocks full protection.
Check now: Current security breaches
|
Visit EverWillow Crafts – The store has a charming look and moving between categories was effortless.
a href=”https://pureforeststudio.shop/” />pureforestlane – Organized sections and clean interface, browsing was easy and relaxed.
boutique corner – Well-structured layout and clear sections improved shopping.
LunarBranch Store – The interface was neat, making browsing simple and enjoyable.
Новый адрес работает отлично уже целую неделю. 7k рабочее зеркало без сбоев и лагов вообще.
Весит приложение 50 МБ, устанавливается быстро. На смартфоне играть намного удобнее в целом.
SimpleBuyZone – Pleasant shopping experience, site design feels modern and user-friendly overall.
ReachHigherGoals – Items seem good quality, ordering felt straightforward and likely reliable too.
Vine Market – The website design is very user-friendly, making shopping smooth.
SimpleBuyZone – Found what I needed fast, layout is clean and navigation intuitive.
ReachHigherGoals – Very inspiring website, navigation feels smooth and content looks excellent.
premiumtrafficengine.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
ultimatetrafficnetwork.shop – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
onlinesuccesssystem.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
authorityrankingstudio.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
onlinegrowthengine.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Всем привет! Хочу порекомендовать киноресурс, который стал для меня открытием . Это Лордфильм на русском языке. Я не люблю тратить время зря, поэтому для меня важна оперативность и комфорт . Здесь меня все устраивает : сайт быстро загружается , с поиском нет проблем, а в плеере есть все что нужно, включая субтитры . Отдельно хочу отметить мобильную версию сайта – она сделана отлично . Смотрение с планшета или телефона такое же комфортное десктопной версии, все элементы отлично адаптированы. Если вы, как и я, часто смотрите кино в дороге или в кровати перед сном, то этот сайт станет для вас идеальным спутником. – https://lordfilm-online.top/
Free video chat emerald-chat.app find people from all over the world in seconds. Anonymous, no registration or SMS required. A convenient alternative to Omegle: minimal settings, maximum live communication right in your browser, at home or on the go, without unnecessary ads.
EverMapleCrafts Deals – The simple navigation made browsing different sections enjoyable.
virallaunch.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
focusedgrowthagency.shop – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
nextgenmarketinghub.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
brandsuccessstudio.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
growthpilot.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Если вы занимаетесь производством и ваша компания нуждается в поставке самых качественных тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше решение. Наша компания специализируется на области поставок тугоплавких металлов в течение многих лет, что дает нам возможность поставлять только проверенный материал своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Любые объемы поставок.
2. Обширный выбор тугоплавких металлов.
3. Все необходимые документы.
4. Всесторонняя поддержка клиентов.
Зачем подбирать в других местах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда готовы помочь?
В случае возникновения вопросов, наши эксперты всегда готовы вам помочь. Звоните прямо сейчас и проверьте в преимуществах нашего редкого металла.
С уважением, команда ООО “РМС” !
поставляемая продукция:
Дюралевый лист Д1АМ 1.5x1200x2000 ГОСТ 21631 – 76
urbanwillowemporium – Intuitive design with neatly arranged items, finding products was easy.
Исследуйте возможности погружения в виртуальный азартный мир. Начните исследовать ярком игровом портале. Мне впервые рассказали о Casino друзья, упомянув их положительный опыт. Я испытал какие-то особые чувства: спокойствие, азарт и предвкушение. Создание профиля было удобным процессом, который начался и завершился быстро. Я начал с простых игровых автоматов, но очень быстро переключился на более сложные, которые держали меня в напряжении до конца onionbonus.icu . Выигрыш оказался крупнее, чем я мог предположить, и эти эмоции будут преследовать меня ещё долго. Игры оказались красочными, увлекательными и создающими ощущение настоящего погружения в приключение. На сайте есть не только игровые автоматы, но и множество других возможностей, например, живые дилеры с настоящей атмосферой казино. Casino подарило мне не только азарт, но и вдохновение, которое теперь сопровождает меня каждый раз, когда я захожу на платформу. Теперь я не только отдыхаю здесь, но и получаю возможность испытать новые игры, новые истории, где каждая победа дарит уникальные эмоции. Если и вы хотите получить положительные впечатления от современной игровой платформы, регистрируйтесь прямо сейчас!. Не упустите возможность первого шага к победам https://pokerdom-games.life .
Исследуйте ясность азарта на казино сейчас
Откройте новые эмоции на казино в моменте
Узнайте о путь к успеху на площадке развлечений казино в моменте
Откройте ясность азарта на казино без лишних ожиданий
Исследуйте все грани победы на сайте казино сейчас
3aa692e
https://zooaquarium.ru/ fish
https://softisntall.ru/ – soft
https://airvission.ru – avto car
https://betautocard.ru – кредиты, банки, финансы
https://cake-star.ru – Авто, автомобиль, тачки
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Медное двухраструбное колено под пайку 180 градусов 40х35х1.1 мм 10х12 мм твердая пайка М2М ГОСТ Р 52922-2008 Купите надежные медные двухраструбные колена под пайку от ведущего производителя. Обеспечьте эффективное отопление и водоснабжение с прочными и устойчивыми к воздействию внешних факторов коленами из меди.
TrendStyleVault – Items are attractive, moving through pages was effortless.
authoritybuildingcenter.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Visit PineCrestModern – The interface was organized, making finding items quick and convenient.
probacklinknetwork.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
professionalseostudio.shop – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
nextlevelseohq.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
seobacklinksolutions.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
https://binnwksbgmeif.com – Egetiyoo Isfetiza lrs.trjp.economicjourney.com.sun.gl https://binnwksbgmeif.com
HomeTrendsModern – Great designs, intuitive browsing, and easy to shop for decor.
Golden Ridge Online – The interface was responsive, and viewing the gallery was relaxing and straightforward.
Gold Attic Corner – The website made it easy to explore and discover unique products.
Discover Growth Center – Nice variety of ideas and smooth transitions between pages.
https://ghrkswdiccrytk.com – Ilisez Oxayijusv jko.lrvs.economicjourney.com.trp.ko https://ghrkswdiccrytk.com
SkyBlossomCorner – Found interesting items easily, shopping felt effortless and website seems trustworthy.
https://binnwksbgmeif.com – Uloxugoju Fudugope mao.ddop.economicjourney.com.lmn.nd https://binnwksbgmeif.com
ShadyLaneShoppe – Found what I needed easily, site structure is organized and intuitive.
StyleHunt – Nice assortment of fashion items, browsing is quick and comfortable.
Анонимный сервис обмена криптовалют ComCASH
предоставляет надежный
обмен цифровых активов без верификации.
Вы можете анонимно
совершать обмен криптовалют, сохраняя конфиденциальность.
Наш сервис предлагает мгновенные сделки
и гибкие условия.
Выберите надежный
обмен криптовалюты с ComCASH и получите максимальную приватность.
обмен сбербанк на btc
обмен биткоин на рубли сбербанк
monero обмен
litecoin обменник
usdttrc20
биткоин курс в сбербанке на сегодня
вывести биткоин на сбербанк без комиссии
как переводить биткоины на карту сбербанка
monero обменник
обменник биткойн
обмен trx на тинькофф
обменники без kyc
анонимный обменник
обменять крипту на рубли
обмен usdt на карту
1 usdt trc20 в рублях
обмен usdt trc20 на карту
Just what you need: https://ambrosi-gardinali.it/5-best-sites-to-buy-gmail-accounts-in-bulk-pva/
Decor Essentials Shop – Pleasant browsing experience with neatly arranged home items.
SkyBlossomCorner – Found interesting items easily, shopping felt effortless and website seems trustworthy.
ShadyLaneShoppe – Items seem high quality, checkout worked fast and experience felt reliable.
Sunlit Valley Collection – Organized pages and clear product display made shopping smooth.
Soft Summer Hub – Browsing felt comfortable thanks to the gentle theme and clean layout.
serpstream.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
premiumseoservice.shop – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
digitalsuccesspoint.shop – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
leadgenerationworks.shop – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
digitalperformancecenter.shop – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
best crypto exchange – fast crypto exchange
simpleswap
https://simpleswap-exchange.to
best cryptocurrency exchange – instant crypto exchange
crypto exchange
https://simpleswap-crypto.to
crypto exchange without KYC
simpleswap exchange
https://simpleswap-crypto.to
TrendPoint Store – The platform looked clean and the navigation experience stayed smooth throughout.
CreativeValueHub – Loved the product range available, website layout is clean and simple.
BrightStyleCollection – Items seem high-quality, checkout was smooth and overall experience felt reliable.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф гарантирует все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наши товары:
Заготовка из конструкционной стали квадратная 80 мм 20Г ОСТ 3-1686-90 Выбирайте конструкционные заготовки высокого качества для вашего проекта на Редметсплав.рф. Наш ассортимент включает прочные и долговечные материалы, идеально подходящие для различных областей применения, включая строительство и машиностроение.
CreativeValueHub – Great variety here, browsing felt smooth and site looks nicely organized.
BrightStyleCollection – Items seem high-quality, checkout was smooth and overall experience felt reliable.
Informationbreach – Know If Your Data Is Already Leaked
Massive data breaches happen every day. Check if your email, credit info, or personal data appears in leaked or hacked databases.
Scan 33B+ leaked passwords and 50M new breach records daily to detect exposure instantly.
Get breach alerts, see if your accounts are in credit card leaks, email breaches, or hacked dumps — all in one click.
Protect yourself from identity theft for just $2 — your breach awareness shield starts now.
Check Your Exposure Now: Known passwords
|
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/jxxs8jnh
advancedmarketingsystems.shop – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Details at the link: https://podcasts.apple.com/np/podcast/puzzlefree/id1697682168?i=1000737823170
Срок ремонта может составлять от 1 часа до 7 дней https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/glushiteli4/
Время ремонтных работ зависит от сложности неисправности и наличия нужной детали на складе запчастей https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/podshipniki_i_vtulki/
Точные сроки работы вам сообщит сервисный центр, куда вы обратитесь https://zapchasti-remont.ru/shop/shkivyi_trosyi_roliki/
rankpro.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
powerrankoptimization.shop – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
branddevelopmentworks.shop – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Производит и разрабатывает оборудование для пищевой промышленности: фаршемешалки для перемешивания творога, фарша, кондитерских масс; волчки для измельчения перца, сыра, мяса, кожи и каучука https://zittel.ru/svarochnye-roboty.html
Обладает несколькими свидетельствами и патентами на заточные станки, режущий инструмент, волчок, фаршемешалку, куттер и другое оборудование https://zittel.ru/oborudovanie/37-oborudovanie/150-applikator-samokleyuscheisya-etiketki-packlab-modulo-60.html
КЛАСС-ИНЖИНИРИНГ https://zittel.ru/statii.html
Интеграл плюс https://zittel.ru/partners/37-oborudovanie/146-sushka-poverhnosti-butylok-europool-tf-02.html
от 244 159 р https://zittel.ru/oborudovanie/37-oborudovanie/249-kontrol-pechati-kaplestrujnogo-printera-na-sootvetstvie-s-tekushchej-datoj.html
ЗАКАЗАТЬ https://zittel.ru/oborudovanie/37-oborudovanie/158-universalnyj-avtomat-obkatki-i-usadki-kolpachka-t-m-omar-r-g-italiya-model-m6tt8tr.html
Компания ООО «ОК-инжиниринг» основана в Оренбурге в 2017 году https://zittel.ru/partners/156-torq-srl-italy-ukuporochnye-mashiny.html
Работает в сфере производства, поставок, ремонта и обслуживания оборудования для мясопереработки https://zittel.ru/oborudovanie/37-oborudovanie/217-mojka-izmelchitel-voran-avstriya-model-war-rm5-5.html
Молочные Технологии https://zittel.ru/oborudovanie/37-oborudovanie/138-palletizator-apsol-compact-pal.html
студенческие работы на заказ http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/ .
Marketing agencies save budget on licensing fees by deploying an ai music generator for commercial jingles and ad spots.
FashionVault – Great variety and the website is simple to use.
Could the escalating inflation rates lead to unconventional economic measures, such as the introduction of a universal basic income, negative interest rates, or even the revision of traditional monetary policies to combat this economic phenomenon and its societal repercussions?https://kodx.uk/
]
#gpt_question_subjectFast IT solutions for your business ] f1_7082
Exactly, it’s one option among many.
CozyHome Finds – Enjoyed checking out the selection; everything loaded quickly.
Этап 3:
Промышленная упаковка отличается от обычной своей высокой прочностью и долговечностью https://yaschiki.ru/product/derevyannii-yashchik-1200-1150-1900/
Основные функции упаковки:
Деревянная упаковка отличного качества https://yaschiki.ru/upakovku-v-termousadku/
Продажа поддонов, ящиков https://yaschiki.ru/severnaya-upakovka-elektrodvigatelya/
Древесина является экологичным материалом, соответственно,
Ответы на все вопросы, касающиеся тары для упаковки грузов, пересылающихся по почте, вы получите у менеджеров ООО “Тара-ст” https://yaschiki.ru/product-category/yashchiki-iz-osb/
У них вы можете уточнить стоимость, сроки выполнения заказа и многое другое https://yaschiki.ru/product/derevyannii-yashchik-1200-1150-1900/
объявления Озёрск
https://news.ozrtech.ru
Геосинтетические материалы https://stsgeo-spb.ru для строительства и благоустройства в Санкт-Петербурге и ЛО. Интернет-магазин геотекстиля, георешёток, геосеток и мембран. Работаем с частными и оптовыми заказами, быстро доставляем по региону.
Интернет-магазин https://stsgeo-krd.ru геосинтетических материалов в Краснодар: геотекстиль, георешётки, геоматериалы для дорог, фундаментов и благоустройства. Профессиональная консультация и оперативная доставка.
http://sturmklinge.de/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=1239675&sid=c869f875460dcc0a87099ac66daadc58
Discover the most effective treatment for your eye condition with [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – priligy with cialis in usa[/URL – . Secure this highly recommended cream through our website for rapid relief.
I discovered incredible savings on essential supplies for emergency preparedness. Don’t miss out on these kamagra oral jelly vol 1 uk .
Navigating the marketplace for osteoporosis treatments? Explore our comprehensive guide to uncover your best match. For affordable options, https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ stands out as a prime choice.
Having realized an enhancement in their performance, many are shifting towards [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/ventolin/ – ventolin cheapest canada[/URL – for a reliable solution.
“Quest for high-quality, affordable wound treatment ends here: Uncover the best option with [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – fildena 25mg[/URL – , delivering top-notch solutions online.”
Having heart rhythm issues? Think about lasix capsules for sale for an efficient.
Your search for effective hair loss solutions ends here with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ . Explore the benefits of this powerful remedy for male pattern baldness today.
Curious about securing the [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – order nexium online[/URL – ? Discover your options online.
Achieve your health zenith with [URL=https://renog.org/product/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – , available for purchase online to boost your life quality.
X-plore the myriad of options to get your treatment swiftly and safely with buy tamoxifen .
Looking for a remedy for baldness? Find top products at our online store. Your search ends here: https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ .
To mitigate chronic cough, consider employing [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra-capsules-for-sale/ – purchase levitra[/URL – , a trusted solution.
Quest for affordable therapy? Look no further for your hormone therapy needs; uncover the cheapest [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxil/ – generic amoxil from india[/URL – solution here.
Secure
When seeking relief from glaucoma, consider the option to https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ . With a range of possibilities, you can obtain this treatment via the internet, conveniently and efficiently.
If you’re searching for an effective remedy to fight bacterial infections, consider [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin non generic[/URL – . This medication is well-known for its effectiveness against a broad range of bacteria.
Your vitality deserves attention. Discover easy access to treat your medical condition with [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – furosemide without prescription[/URL – . Ensure your well-being is optimal with just a few clicks.
X-plore your options for hair loss remedies and order nizagara 100mg with confidence.
If you’re looking for an cost-effective solution to your vertigo, consider https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ . This medication helps in reducing the effects of vertigo, enhancing your quality of life.
Access genuine [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/lasix/ – online generic lasix[/URL – easily. Purchase this essential medicine virtually seamlessly.
Discover innovative solutions to boost your well-being with [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis black[/URL – , the go-to choice for those seeking reliable and powerful assistance in handling erectile dysfunction.
Get the lowest prices for your healthcare needs with our exclusive lasix 40mg in croatia . Find your deal on our site and make sure your wellness is consistently prioritized.
Get immediate relief from your nasal allergies by opting to https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ . This treatment can minimize your symptoms, ensuring a improved daily life.
Get your vitality boost now with [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – discount fildena[/URL – . Explore the numerous health benefits by ordering this herbal supplement directly from our page.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Discover how to secure your needs without hassle with cialis without prescription us .
Just discovered a revolutionary way to improve your lifestyle? Consider exploring https://nabba-us.com/product/priligy/ Buy immediately for a groundbreaking experience.
The treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia is now more accessible with [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/meldonium/ – meldonium online usa[/URL – , offering a significant reduction in symptoms.
купить курсовую https://kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru/ .
Строительные геоматериалы https://stsgeo-ekb.ru в Екатеринбурге с доставкой: геотекстиль, объемные георешётки, геосетки, геомембраны. Интернет-магазин для дорожного строительства, ландшафта и дренажа. Консультации специалистов и оперативный расчет.
Quickly obtain your antihistamine relief by choosing to purchase [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra-price-walmart/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – .
You can find affordable generic fildena canada pharmacy for managing your nasal allergy symptoms on internet sites.
Explore options to purchase https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ , offering a convenient way to receive your medication without leaving home.
Discover affordable options for managing addiction; [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – retin-a generic[/URL – offers a pathway to recovery. Explore budget-friendly solutions for addressing dependency.
Researching safe sources to acquire medication? Explore options and discover how to purchase [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/retin-a/ – retin a uk[/URL – with confidence.
Acquire your wellness boost by choosing to retin a overnight , a practice that’s convenient, ensuring that you’re always backed in your health journey.
Visit our website to purchase your https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ easily and without hassle.
Discover unparalleled savings with our exclusive offer: [URL=https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ – cheap ventolin[/URL – . Purchase your supply today and enjoy the efficacy of this treatment.
Seeking relief from OCD symptoms? cialis offers a solution. Find out about this option today.
Patients seeking to control their conditions can buy https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ online.
Navigating through numerous sources to acquire your medications can be challenging, but our [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – buy nizagara online canada[/URL – simplifies the process, offering secure and affordable options for your healthcare needs.
Having trouble staying awake? Acquire alertness-enhancing medications without hassle on the web. Explore your options and hydroxychloroquine today!
Researching effective treatments for schizophrenia? Discover your options and consider the benefits of Aripiprazole. Find out about on https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ .
Uncover affordable alternatives for managing edema and hypertension with [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – low price slimex[/URL – , ensuring you secure value without stretching your budget.
Secure budget-friendly [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/flagyl/ – acheter du flagyl en chine[/URL – options for handling heavy bleeding episodes. Explore choices that prioritize your health and your budget.
Regarding your health, it’s crucial to locate a trustworthy option. For managing specific medical conditions, cost of cytotec tablets stands out as a recommended choice by healthcare professionals.
Visit our platform to purchase your https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nizagara/ easily and with confidence.
Zealously look for solutions to enhance your well-being? Examine [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – price of strattera[/URL – for powerful choice.
Regain confidence in the bedroom with the lowest price generic doxycycline , your discreet solution to enhanced performance. Secure your purchase now for an upgraded experience.
Venturing into the realm of budget-friendly medical solutions? Look no further, https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ online for your medical needs.
Your quest for budget-friendly heart medications ends today! Secure your dose of [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix furosemide for sale[/URL – right here! Wide-ranging options to purchase this essential treatment easily await.
Browse our website to discover the kamagra.com lowest price .
Looking to enhance your performance? Purchase safe solutions https://wefenceit.com/buying-viagra-online/ .
Looking for a cost-effective solution to enhance your eyelashes? Consider purchasing [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – vidalista non generic[/URL – . These applicators offer a simple and effective method to achieve fuller lashes.
Explore budget-friendly solutions for your health with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis coupons[/URL – . Discover unparalleled deals to enhance your wellness journey now.
Looking to increase your vitality? Discover how lowest prices on cialis might aid. Available now, these pills are designed to assist your health journey.
Navigating through the myriad of treatment options for Alzheimer’s can be daunting. However, procuring Donepezil, a proven medication, has never been easier. For those looking to enhance cognitive function affordably, consider exploring your options to https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ . This approach offers a seamless, cost-effective solution for managing symptoms with convenience.
“Your hassle-free solution for obtaining prescriptions swiftly is here at [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – achat lasix en france[/URL – , where you can order your needed medicines with simplicity.”
Venture no further for your hormonal therapy needs; [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – 20 mg furosemide[/URL – offers a variety of solutions to restore your testosterone levels safely.
Need to combat hair loss? Discover effective solutions and prednisone 10mg . Explore various solutions to reclaim your hair’s vitality.
Find budget-friendly solutions for your hypertension by choosing to buy https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ . Ensure your heart health is monitored efficiently with an easy online transaction.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ – generic dapoxetine from india[/URL – today. Whether you’re seeking to boost your wellness effortlessly, our online platform offers a straightforward pathway to obtain your essentials.
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous online sources offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to make sure safety and authenticity. generic hydroxychloroquine at walmart offers a comprehensive guide on the way to safely secure this medication, alongside vital details on its application.
Manage your health by deciding to acquire essential medications easily through our platform, ensuring you can https://momsanddadsguide.com/retin-a/ conveniently online.
Looking to obtain Aripiprazole? Find it effortlessly with just a click at [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – generic furosemide uk[/URL – , your go-to source for medications on the internet.
Zap your ED worries away! Purchase effective ED medication generic viagra from canada . This remedy is trustworthy and easy to access.
Get your amoxil easily from https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ , supplying swift delivery to fulfill your healthcare needs.
Discover a safe way to enhance your wellbeing: [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/viagra-for-sale/ – generic for viagra 75 mg[/URL – .
Keeping your health top-notch is essential. Discover competitive [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/zithromax/ – zithromax 250mg[/URL – on the web and begin your journey to enhanced well-being today.
Discover effective remedies for enhancing your sexual health with confidence at viagra generic canada .
Discover outstanding savings on https://renog.org/hydroxychloroquine/ ! Acquire your supply today and experience the benefits.
Having trouble staying awake? Acquire nootropics without hassle through our website. Explore your options and [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – today!
I recommend exploring various options for allergy relief; consider [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – kamagra[/URL – as a trusted solution.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxicillin 250mg , offering broad-spectrum treatment for bacterial infections.
For individuals seeking enhanced performance, https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra-100mg/ offers a revolutionary solution.
A comprehensive resource on healthcare education in the United States is readily accessible at [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ – generic kamagra canada pharmacy[/URL – .
Zero worries about where to find your ED solutions; explore [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – viagra without dr prescription usa[/URL – for a reliable and discreet way to restore intimacy.
Looking to manage Parkinson’s or control involuntary movements? tablet propecia offers a treatment that’s budget-friendly. Explore the choices available for better health today.
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can acquire performance-enhancing drugs online at https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ , ensuring privacy and ease.
Unlock the best deal on [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – nizagara capsules for sale[/URL – by searching our site. Get your essential medication without the fuss.
Слоты 7k казино зеркало работают честно, видно по RTP который указан. Никакого манипулирования результатами.
Consult healthcare experts before you acquire [URL=https://wefenceit.com/tadalafil-capsules-for-sale/ – tadalafil 20mg[/URL – to ensure it’s the optimal therapy for your ailment.
Just discovered you can purchase your essential hair loss treatments virtually? Visit nizagara for a hassle-free experience to regain your hair’s vitality.
Investigating the realm of hair loss solutions, countless individuals have turned their attention towards https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/generic-cialis-from-india/ , a product celebrated for its efficiency. Those in search of an effective solution for baldness have the option to locate this medication on various websites, ensuring a discreet and convenient buying process.
Discover effective solutions for heavy menstrual bleeding by exploring our variety of medications. Purchase the necessary treatment [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxil/ – generic amoxil from india[/URL – effortlessly with just a few clicks.
Enhance your fertility journey affordably with canada hydroxychloroquine . Find outstanding savings on this essential medication online.
Be proactive in managing your gout symptoms; consider https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ from reputable sources. With our guide, learn how to safely control uric acid levels and reduce flare-ups.
With just a few clicks, you can effortlessly secure your prescription for [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – canadian retin a[/URL – , a critical solution for controlling acid reflux conditions.
Unlocking the secrets of revolutionary neurological treatments, [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/priligy/ – walmart priligy price[/URL – stands as a pinnacle for exploration in neurodegenerative disorders.
For individuals seeking enhanced stamina, buying nizagara offers a revolutionary solution.
Questing for the most cost-effective solution for your vehicle’s battery needs? Look no further! Click here for the https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ – your go-to option for high-grade batteries.
You can acquire your [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine[/URL – on the internet, providing a simple way to control hypertension.
Looking for an affordable solution to enhance your performance? Explore the array of options; [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – how much is tadalista 40 mg[/URL – could be your answer. Consider acquiring these potent remedy from online stores for a hassle-free experience.
I’ve found that those in need of quick relief from hyperuricemia can utilize how to buy nizagara 25 mg .
Obtain comprehensive insights and secure the https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ for your antiviral medication needs by browsing our site today.
Когда заблокировали основной, 7k рабочее зеркало выручило. Вывод с резервного адреса прошел нормально.
Zero hassles while looking to improve your vitality? Explore our premium selection and buy the [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/nizagara-25mg/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – on the web, ensuring you receive top-quality options for your wellbeing.
Browse our site for competitive prednisone and explore a multitude of alternatives to purchase your treatment.
Quickly acquire economical pain relief by selecting to buy https://kristinbwright.com/online-generic-pharmacy/ .
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – amoxil 1000mg best prices[/URL – is a viable option. Discover securing this antibiotic via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/amoxil/ – generic amoxil canada[/URL – is a viable option. Explore purchasing this antibiotic online for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Procure your acid reflux treatment sans exiting your home; visit prednisone for quick relief.
Quest for budget-friendly ED medications? Uncover a solution at https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ , featuring a wide range of high-quality options.
Questioning where to find anxiety medication? Look no further and [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/prednisone/ – prednisone without prescription[/URL – for a reliable solution.
For those seeking reliable treatment options, consider exploring cialis fast no prescription required as a solution.
Zero hassle: obtain your https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cytotec/ without complication.
Aches and pains troubling you? Explore relief via [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – generic prednisone uk[/URL – , a proven remedy for alleviating inflammation and pain.
Discover safe and confidential options to purchase your prescription without complications. Click here: [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/viagra/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – .
Acquire your eye drops with ease; simply prednisone and ensure enhanced ocular health without leaving your home.
Discover how https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ can aid in managing your cardiac health efficiently.
Visit [URL=https://renog.org/product/generic-amoxil-in-canada/ – amoxil[/URL – to purchase your antibiotics on the web at unbeatable prices.
Manage your symptoms effectively with lasix . Explore cost-effective options to treat your condition online.
Experiencing symptoms of organ rejection? https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ may assist in managing these conditions.
X-plore your options for managing Crohn’s disease and other inflammatory bowel disorders with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – . Available for acquisition on this website, these treatments offer a route towards alleviation of symptoms.
Discover your pathway to enhanced intimacy; explore ordering [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nizagara-on-internet/ – 50mg nizagara[/URL – to boost your libido.
For comprehensive data on health and wellness, visit alternative fгјr nolvadex .
Browse our website to find the https://momsanddadsguide.com/ventolin/ available. With options to get affordable versions of needed medication, health management becomes both effective and cost-efficient.
Purchase affordable [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – priligy cheap[/URL – for managing cardiovascular wellness. Explore selections on websites for budget-friendly treatments.
Browse our site to locate [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ – amoxil 650 cheap[/URL – , ensuring you get premium antibiotic choices at incomparable prices.
X-ray your budget: Find cost-effective options for your heart health medication. Click here generic prazosin canada to explore reasonable pricing.
Interested in reducing inflammation and allergic reactions? https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ flexibly fits your budget. Discover how this medication can benefit you, available to buy on the internet.
Uncover deals when you acquire your prescription with [URL=https://damcf.org/prednisone/ – prednisone for dogs[/URL – .
обмазочная гидроизоляция цена работы обмазочная гидроизоляция цена работы .
ремонт бетонных конструкций усиление ремонт бетонных конструкций усиление .
гидроизоляция подвала делать самостоятельно gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara.ru .
аренда экскаватора погрузчика московская область аренда экскаватора погрузчика московская область .
Interested in reducing water retention? Explore multiple remedies and discover [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil buy online[/URL – for potent results.
X-ray your budget and discover how much you can minimize outlays on your next purchase with tadalafil non generic , a way to acquire your essentials at improved rates.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, https://nabba-us.com/item/amoxicillin/ is a viable option. Explore securing this antibiotic through online outlets for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
To obtain the necessary iron supplements, explore [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – prices for nizagara[/URL – for unbeatable savings.
For supporting optimal health, consider integrating low cost nizagara into your daily, renowned for their powerful inflammation-reducing and free-radical fighting properties.
Explore seamless ways to secure your health needs with https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ , the top platform for purchasing pharmaceuticals on the web.
To ease discomfort, order [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – from reliable vendors online.
I discovered [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – tinidazole for sale[/URL – while researching options for improving men’s health.
Reveal the secrets to peak health with our manual at cost generic retin-a . Learn how to enhance your well-being with practical tips and insights from professionals in the field.
Battling seasonal allergies? Explore obtaining https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ to alleviate your symptoms.
Combat discomfort effortlessly and economically with the aid of [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – generic tamoxifen canada[/URL – , available for your next buy.
Harness the power of modern medicine to stabilize your mood with [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – . Find out how to tackle bipolar disorder with effective solutions available.
Explore secure options to purchase your prescription online with tretinoin , ensuring privacy and convenience.
Browse the site to discover https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ , ensuring you secure high-quality antibiotic choices at unbeatable prices.
X-plore the myriad benefits of [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era best price usa[/URL – , your go-to solution for tackling OCD symptoms. Now you can effortlessly acquire this crucial medication by means of our dependable website.
инъекционная гидроизоляция частный дом http://www.inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru .
Access unmatched deals on [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/pharmacy/ – next day online pharmacy[/URL – , ensuring your journey towards enhanced well-being is economical.
Maximize your alertness and cognitive performance with prednisone overnight . Whether you’re looking to enhance focus or reduce fatigue, this product provides reliable results.
Regarding anxiety or OCD treatment, https://charlotteelliottinc.com/buying-tadalafil-online/ is a viable solution; explore alternatives or obtain it online.
Improve your well-being effortlessly by selecting to purchase your pharmaceuticals online. With just one click on [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/order-viagra/ – viagra to buy[/URL – , benefit from the ease and quality.
Your search for affordable options ends here: [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/nizagara/ – generic nizagara with free shipping[/URL – . Locate your solution today and conserve on healthcare expenses.
Boost your potency with propecia , a delectable solution. Elevate your performance by choosing this tasty option that promises swift effects.
Research the advantages of traditional Indian medicine with https://markssmokeshop.com/item/viagra/ , known for its cardiovascular support properties.
The positive effects of [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ – eriacta[/URL – for managing mood swings are well-documented.
Нужна работа в США? требования к диспетчеру в сша : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
Researching budget-friendly options for managing your heart condition? Discover the latest [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra-online-pharmacy/ – kamagra online pharmacy[/URL – and guarantee your health by a dependable resource.
When seeking to control your HBV symptoms, acquire nizagara without hassle from reputable pharmacies.
Discover your pathway to relief from minor aches and pains by purchasing your next supply of https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra-online-pharmacy/ virtually.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ – generic clomid uk[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous options available on the web. Secure your fertility journey today by opting for the best deal.
Need to boost your focus without a hassle? Explore how easy it is to get what you need [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – order levitra online[/URL – .
If you’re experiencing seasonal allergic reactions, check out retin a for a solution that offers alleviation.
Find the best deal for your heart medication at https://wefenceit.com/pill/retin-a/ , ensuring optimal cardiovascular health.
Discover safe and convenient ways to acquire your medication. [URL=https://wefenceit.com/tadalafil-capsules-for-sale/ – tadalafil[/URL – today for a hassle-free experience in managing your health needs.
Visit [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cytotec/ – where to buy cytotec[/URL – for comprehensive insights on using this medication safely.
Considering the fluctuating buy levitra ship fedex , it’s worth exploring alternative platforms to purchase your pharmaceutical needs virtually.
Unlock unbeatable deals on https://myrsvplive.com/propecia/ ! Find your solution for a stronger life today.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxil-on-internet/ – order amoxil 500 mg[/URL – , offering comprehensive solution for bacterial infections.
Researching safe sources to acquire medication? Explore options and discover how to purchase [URL=https://hyblavalleyvet.com/kamagra-in-usa/ – buying kamagra online[/URL – with confidence.
Necessitating an effective solution for diuretic needs? Learn about kamagra 100 mg price walmart , your go-to choice for handling edema.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ online for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
гидроизоляция подвала гидроизоляция подвала .
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin canadian pharmacy[/URL – online for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Explore choices for purchasing prednisone without an rx . Secure a supply from reliable sources on the web.
Get your health solutions conveniently with https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ . Acquire the essential medication without hassle from anywhere.
Just seeking affordable choices for enhancing your health? Explore [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – for a reliable and efficient option.
Value Picks Market – Easy to move around the site and lots of items seemed reasonably priced.
Discover how to acquire [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – for managing your condition. Explore multiple alternatives for treatment today.
Revitalize your intimate experiences with our exceptional offer: buy propecia 5 mg in canada . Rekindle the spark today and acquire your solution online.
Keep your intimate life vibrant and spontaneous; acquire rapid https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ to boost your experiences right away.
X-plore eye care with cutting-edge solutions. Buy [URL=https://renog.org/product/zithromax/ – azithromycin[/URL – online for treating glaucoma effectively.
Get your daily dose of wellness with a simple click; [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone[/URL – offers convenient access to natural health support directly to your doorstep.
Just discovered the kamagra capsules for sale ? Seize the opportunity! Improve your lifestyle now by securing it online. Your satisfaction is what we aim for.
Visit our website to buy your essential health supplements with ease, including https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ , designed to support urinary tract function.
A safe way to handle your health: [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxicillin-1000mg/ – no prescription amoxicillin[/URL – . Visit us to learn about varied methods for your wellbeing.
Find the best deal for your heart medication at [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – xenical[/URL – , ensuring optimal cardiovascular health.
Discover unique nizagara 50mg , perfect for controlling seizures. Order today for effective results.
Regarding affordable healthcare solutions, https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ are unmatched. Secure your treatment online, ensuring cost-effectiveness and ease.
Get your [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/viagra-25mg/ – real viagra[/URL – prescription renewed online sans fuss, ensuring prompt relief and effective treatment of your symptoms.
Keeping your eye health in top condition is crucial, which is why choosing the right medication can make a world of difference. For those dealing with elevated intraocular pressure or open-angle glaucoma, [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – offers a trusted solution. Ensure you speak to a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for your needs.
Zero hesitation is key when considering boosting your lifestyle. Secure your nizagara without prescription today for a top-tier outcome.
Get ease from allergic reactions with a trusted solution. Find https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ for immediate results.
Now, find out about the advantages of [URL=https://renog.org/product/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – , and learn how it can assist in easing your pain.
For individuals seeking relief from Meniere’s disease symptoms, contemplate zithromax , an effective option.
Quickly obtain the https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ , a trusted source for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Manage your symptoms effectively with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/prednisone/ – buy prednisone for less[/URL – . You can obtain this crucial remedy via our online platform for seamless, rapid relief.
Zero hesitation required when looking for ED solutions; order [URL=https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – viagra 50mg[/URL – conveniently.
Ailments like irritable bowel syndrome can greatly disrupt daily life. Fortunately, effective relief is available. Explore your options and find out the potential cheap clomid pills here.
Discover how to save on your prescription with affordable https://charlotteelliottinc.com/lasix/ . Learn where to get your medication without breaking the bank.
Your search for affordable options ends here: [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ – nolvadex[/URL – . Find your solution today and conserve on medical expenses.
Get unparalleled savings when you acquire your medications through our trusted portal. Now is the perfect time to [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – overnight hydroxychloroquine[/URL – safely and efficiently.
When looking to obtain heart health medications, explore options to canada retin a through digital pharmacies, offering a budget-friendly solution without compromising on quality and efficacy.
Understanding the importance for swift antimalarial medications, it’s pivotal to find a reliable supplier. With that in mind, acquire your https://tooprettybrand.com/product/low-cost-zithromax/ immediately for effective remediation.
Find affordable solutions for your hypertension by choosing to purchase [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/cialis-best-price/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – . Ensure your heart health is maintained efficiently with a simple online purchase.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: doxycycline 100mg . Whether you’re looking to acquire this medication via the web, you’ll find that its effectiveness in treating a wide range of infections makes it a prime choice.
Unlock the secrets to enhanced vitality and stress relief with https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ . Explore the premier source for a time-tested herb.
The positives of incorporating [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/propecia-to-buy/ – cheap propecia pills[/URL – into your everyday life are numerous, including enhancing stress management, aiding sleep quality, and bolstering overall well-being.
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable human immunodeficiency virus testing solution. Acquire the prednisone online usa today and verify your status efficiently from the privacy of your home.”
Purchase organic solutions for your health needs easily on our website. Explore alternatives and locate the best deals https://renog.org/product/cytotec/ right away.
Just learned you can purchase your IBS relief treatment via the internet? [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy-from-canada/ – canadian generic priligy 90mg[/URL – offers a variety of choices for your treatment needs.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – , and explore a range of solutions to improve your quality of life.
Researching options to procure Etizolam legally? Ensure safety by consulting healthcare professionals first. Click here for details: prednisone 10mg price buy . Always prioritize your health by seeking guidance from certified professionals.
Zeroing in on male pattern baldness solutions? Discover a multitude of options to regain your confidence. https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ offers a potent treatment option. Explore our range on our website and kickstart your journey to a fuller head of hair today.
Get comprehensive [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – buy extra super avana w not prescription[/URL – for boosting male potency.
Looking to enhance your vigor? Find tadalafil online to buy your answer with simplicity.
A Looking for an reliable antibiotic? Order your antibacterial treatment online at https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ .
Zap your heart rate worries away with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – bangkok nizagara[/URL – . Acquire your supply of well-being online now.
Thank you!
https://hop.cx
Thanks
Affordable healthcare is now accessible, order your pharmacy needs virtually with [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/canadian-levitra/ – shopping cart for sale online check payment levitra[/URL – .
Discover the current hydroxychloroquine and explore options for securing this drug through online pharmacies.
Looking for an affordable way to enhance your well-being? Explore the advantages of https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ , optimal for those seeking efficacy without compromising budget.
Before you commit to a purchase, consider checking out [URL=https://renog.org/pharmacy-prices-for-prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – for affordable rates on this essential medication.
Now, obtain your supply of [URL=https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ – low price lasix[/URL – effortlessly. Purchase online without hassle.
When seeking reliable management for epilepsy or bipolar disorder, consider cialis 2.5 tablet cost as your option.
X-plore your options for get https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ without sacrificing effectiveness. Find economical options for your healthcare needs.
Blue Harbor Bloom Page – Everything displayed swiftly, and the product sections were visually pleasant.
Regain control of your health by choosing to [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ – prices for tretinoin[/URL – . With our service, you can purchase your needed therapy without hassle from the safety of your home.
Discover excellent options for managing your condition efficiently with cialis 20mg . Improve your well-being now.
For those seeking relief from upset stomach, find a wide range of options by deciding to https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ . Guarantee your comfort immediately with a quick buy.
Acquiring [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone no prescription[/URL – has never been easier. Secure your way to wellness with a safe solution.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil on internet[/URL – is a viable option. Explore securing this antibiotic via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Get your hands on lisinopril generic easily. Purchase your required remedy without hassle through our trusted platform.
Zest for a healthier life often leads us to search for therapies that can boost our well-being. For those managing hypertension or chest pain, https://nabba-us.com/product/priligy/ could be your route to enhanced health.
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can acquire erectile dysfunction medication through an internet pharmacy at [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/generic-viagra-canada/ – generic viagra canada[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
Xperience improved life-force for anyone in search of remedies. Find your path to a better life through [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/kamagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – , ensuring optimal results and satisfaction.
Need to secure your hair loss treatment? Find affordable options with levitra bestellen ohne rezept , providing you get premium interventions for a slice of the expense.
Venture online to locate the least expensive options for your health needs, including https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ .
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis for sale overnight[/URL – through our reliable website. This essential treatment is now obtainable effortlessly.
Quickly reduce your gastrointestinal troubles by choosing to purchase tofranil commercial .
Various individuals suffering from heavy bleeding can attain alleviation through https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ , a revolutionary treatment.
Zealously seeking a trusted method for infertility treatment? Discover your answer and [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/lasix/ – lasix for sale overnight[/URL – , providing a breakthrough alternative for fertility challenges.
Managing pain efficiently and safely is crucial for overall health. Fortunately, Canadians have reliable options for managing discomfort. [URL=https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ – overnight viagra soft tabs[/URL – offers a versatile solution, allowing you to acquire effective pain relief securely and swiftly.
To secure the best rate on amoxil on internet , visit our webpage.
Your search for a safe, trusted method to boost your intimate life ends here. Order your https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ today and experience the change firsthand.
Acquire your [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/lasix-40mg/ – online lasix 40 mg[/URL – effortlessly with our secure online marketplace. Procure the essential treatments online with ease and confidence.
Searching for the best price on fertility treatments? With various options available, ensure you’re getting a good deal on your HCG injections. Explore now the safe generic lasix and compare to locate the most affordable choice for your reproductive health needs.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover the benefits of https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra/ . With our product, you can enhance your vitality. Shop today and feel the difference!
best crypto exchange – fast crypto exchange
exchange crypto
https://changelly.us
best cryptocurrency exchange – instant crypto exchange
coinswitch
https://changely.us
crypto exchange without KYC
shapeshift
https://changely.us
I discovered that it’s possible to procure Cialis in Canada prescription-free. If you’re interested, you can [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – here easily.
Many are in search of effective treatments for scabies and lice. Discover how generic nizagara at walmart can be your remedy.
Need to manage premature ejaculation? Explore how https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ can help in increasing sexual performance.
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous platforms offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to make sure safety and authenticity. [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – generic hydroxychloroquine uk[/URL – offers a comprehensive guide on the way to safely buy this medication, alongside vital details on its use.
Given the unpredictable nature of weather patterns, securing your property against inundations has never been more crucial. Explore options to secure your home with a [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix/ – price of lasix 100mg[/URL – , offering a wide range of solutions to combat water damage.
Discover affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction by visiting order cialis , where you can purchase your medications easily.
Zero hassle to control your intraocular pressure issues with https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ . Order now and feel the change.
Considering the myriad options for hair loss solutions, acquiring [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/mail-order-prednisone/ – buy prednisone no prescription[/URL – could be your most cost-effective choice.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы поставить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в определении подходящих продуктов и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Медный однораструбный отвод 45 градусов под пайку 40х35х1.1 мм 10х12 мм твердая пайка М1Е ГОСТ 32590-2013 Приобретите высококачественные Медные отводы 45 градусов под пайку от компании Редметсплав.рф и улучшите вашу трубопроводную систему. Прочные, долговечные и устойчивые к коррозии отводы обеспечат надежное соединение под нужным углом, обеспечивая оптимальное распределение потока и высокую производительность вашей системы.
Acquiring your [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – just became more straightforward. Now, grab your medication with simplicity.
choosing
Considering the requirement for cardiovascular wellness, obtaining https://primerafootandankle.com/item/vidalista/ via internet presents a handy solution for managing cholesterol levels.
Find exceptional deals on anti-inflammatory medication; discover [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – low price slimex[/URL – for treating pain and swelling with ease.
Технологически продвинутая платформа кракен официальный сайт использует луковую маршрутизацию Tor через минимум шесть узлов с многоуровневым шифрованием для анонимности.
Нужна работа в США? онлайн обучение диспетчера грузоперевозок в америке онлайн с практикой : работа с заявками и рейсами, переговоры на английском, тайм-менеджмент и сервис. Подходит новичкам и тем, кто хочет выйти на рынок труда США и зарабатывать в долларах.
Just in case you’re probing for the most cost-effective options for your fertility treatments, consider checking the cost of [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/canada-propecia/ – online generic propecia[/URL – . It’s crucial for those wishing to enhance their opportunities of conception.
Acquiring clomid has never been simpler. Purchase the medication from the comfort of your home.
Seek solutions for hair loss now! Discover how https://renog.org/product/pharmacy/ can help in your fight against hair loss.
Visit [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – to purchase affordable medicine online.
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can purchase performance-enhancing drugs through an internet pharmacy at [URL=https://renog.org/viagra-75mg/ – cheapest viagra dosage price[/URL – , ensuring anonymity and ease.
Acquire budget-friendly solutions for your stomach troubles with lasix online , proven to alleviate symptoms efficiently.
When searching for cost-effective, high-quality medication solutions, consider exploring https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ for unparalleled value. Whether you’re shopping for solutions, this choice may offer the relief you need.
Many are searching for reliable solutions for ED, and [URL=https://renog.org/product/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – offers a proven option.
Where to obtain order tadalafil online ? Explore your options for getting potent remedies online.
Uncover the ultimate way to enhance your wellbeing; discover our unmatched https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax-100mg/ . This option is optimal for those seeking to improve their lifestyle efficiently.
Purchasing [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – 1mg propecia from canadian pharmacy[/URL – via the internet offers a simple way to address your needs without a prescription.
Ensure you obtain your [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – hydroxychloroquine online usa[/URL – without risk for malaria prevention.
Secure considerable savings on your prescription with propecia . These discount codes are essential for handling treatment expenditures.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover your solution with https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ , the optimal choice for boosting your hormone health. Consider the way to enhance your health with just a few clicks.
Having read this I thought it was extremely informative.
I appreciate you taking the time and energy to put this informative article together.
I once again find myself spending a lot of time both reading and posting comments.
But so what, it was still worthwhile!
Thank you very much
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Search no more. Get [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – safely and swiftly.
Zillions seeking effective remedy for their condition can now order ventolin , a reliable option.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Obtain https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ safely and quickly.
Need to handle your birth control options? Explore secure and efficient choices with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – order alesse online[/URL – .
Get the best prices for your healthcare needs with our outstanding [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – . Grab your supply now and ensure your wellness is always prioritized.
Navigating the healthcare marketplace for options can be daunting, but finding the viagra pills doesn’t have to be.
Searching for the best price on fertility treatments? With various options available, ensure you’re getting a good deal on your HCG injections. Explore now the https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra/ and compare to identify the most cost-efficient choice for your reproductive health needs.
Visit [URL=https://renog.org/product/generic-amoxil-in-canada/ – purchase amoxil online[/URL – to purchase your antibiotics on the web at unbeatable prices.
Discover affordable solutions for managing your heart health with [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone in usa[/URL – . Purchase your batch immediately and embark on a journey toward improved cardiovascular well-being.
Regain your zest for life! Use our zithromax 100 prix en pharmacie belgique for unparalleled confidence. Revive closeness without breaking the bank. Purchase your answer to a fuller, more vibrant experience now.
Your search for an effective treatment for premature ejaculation ends here. Acquire https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ , a proven drug, on the web.
Discover how to secure your medications without hassle with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/viagra/ – viagra 50 online[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
Considering the escalating expenses associated with fertility treatments, finding economical solutions is crucial. Opt for propecia brand to augment your journey to conceiving, available at rational rates without compromising on quality or efficacy.
Explore your options for acquiring essential hypertension treatment by visiting https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ , where a variety of cost-effective healthcare alternatives await.
Xplore our lowest [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – can i order propecia online in australia[/URL – and save your medical expenses.
Just discovered you have high cholesterol? Worry less and explore healthier living by considering [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – cheap amoxil profisional line only uk[/URL – . These tablets can be a crucial part of your therapy. Purchase them online to control cholesterol successfully.
Discover affordable options for managing your anxiety: tadalafil 20mg . Select your necessary remedy effortlessly in place.
Questioning the safety and efficacy of inhaled medications? Ensure to consult a medical professional before opting to acquire https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline/ via the internet.
Looking for budget-friendly menstrual cycle support? Discover your solution with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin 20g[/URL – . Whether you’re addressing irregular periods, discover the best deal online.
Navigating the pharmaceutical marketplace for options can be daunting, but finding the [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/on-line-levitra/ – usa levitra online pharmacy[/URL – doesn’t have to be.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, generic amoxicillin lowest price is a viable option. Discover securing this antibiotic via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
When looking to purchase https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ , consider visiting reputable pharmacies online for affordable rates.
The existence of [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – strattera alternitive[/URL – ensures that individuals can easily secure crucial medication to tackle their condition online.
Obtain economical hormone replacement therapy options with overnight prednisone generic . Explore alternative options for your health needs via the internet.
Purchase your supply of https://renog.org/product/priligy/ effortlessly via web. This pharmaceutical solution is crafted to boost your wellbeing efficiently.
X-plore affordable options for managing Addison’s disease; uncover how [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – cheap verapamil overnight[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution to support your health.
Discover effective joint pain relief with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil[/URL – , the premier treatment accessible online.
Purchase high-quality hormone replacement therapies at unbeatable prices; uncover your ideal match with cialis 20mg today. Suitable for tackling menopause symptoms efficiently.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ might be the remedy. Learn about how it can assist in lessening your symptoms efficiently.
Seeking relief from rheumatoid arthritis? Consider [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – sildalis overnight[/URL – as your go-to option. Find out about how this treatment can assist you control your symptoms efficiently.
Obtain your prescription safely and easily through our trusted source. For those seeking proven treatment, [URL=https://renog.org/viagra-75mg/ – viagra[/URL – is your prime choice. Ensure you’re receiving authentic products without compromise.
For individuals seeking to purchase hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous websites offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to ensure safety and authenticity. overnight hydroxychloroquine offers a comprehensive guide on the way to safely buy this medication, alongside vital data on its utilization.
Looking for an effective way to treat psoriasis? Learn about how https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ can help in alleviating symptoms without hassle.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Obtain [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – buy amoxil 250 for sale[/URL – safely and quickly.
For persons seeking relief from Meniere’s disease symptoms, contemplate [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – , an effective alternative.
Understanding the importance of maintaining heart health and managing cholesterol can be overwhelming, but with the right medication, it’s possible to navigate these conditions more effectively. If you’re looking to purchase your treatment with ease, cost of prednisone tablets offers a straightforward solution to manage both hypertension and high cholesterol with just one medication.
Looking for a safe way to treat psoriasis? Learn about how https://hip-hope.com/item/propecia/ can aid in easing symptoms without hassle.
Maximize your savings on stroke prevention medication by checking [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – , where you can discover competitive prices.
Research shows that finding the [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – ventolin online[/URL – can be simplified with the right guidance.
Shop for herbal health remedies and boost your wellbeing today. Buy the supplements at buying retin a online , your trusted source for top-notch health products.
Discover the convenience and privacy of purchasing your erectile dysfunction medication with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ , available now.
Prepare for unforeseen house emergencies by reading our thorough guide at [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ – buying retin a online[/URL – .
You can obtain Fildena for your impotence needs here: [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ – fildena online pharmacy[/URL – .
Just learned you can buy your IBS relief meds via the internet? bentyl offers a wide range of choices for your treatment needs.
Zero in on solutions for male pattern hair loss by choosing to acquire https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ now.
Receive your [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – easily by choosing to obtain it online, ensuring a hassle-free and secure transaction.
Jumpstart your journey towards better health with a seamless way to purchase your medication. Whether you’re looking to reduce inflammation, our platform offers an array of options to suit your needs. For those specifically seeking Budesonide treatment, buy prednisone from mexico here and enjoy immediate relief.
Keeping your health at its peak, acquiring https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a-uk/ can improve your well-being. Purchase immediately for a better tomorrow.
Here’s how to discover the latest [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ – price of priligy[/URL – to preserve on your prescription.
Improve your health effortlessly by opting to buy high-quality medication online. zithromax offers a reliable, secure solution for enhancing efficacy.
Visit https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxil/ to buy your medication on the web at fantastic prices.
Combat elevation sickness efficiently with [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol capsules[/URL – , available on the internet to help in your mountaineering adventures.
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial; hence, acquiring necessary medications conveniently is key. For those in need, [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – generic tamoxifen canada[/URL – offers a seamless solution. Alternative options include Purchase the necessary drug via the web with ease and reliability.
Researching reliable sources to acquire medication? Explore options and discover how to purchase nizagara walmart price with confidence.
Harness the power of convenience and savings when you purchase your birth control. With our exclusive offers, you can get affordable https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ without ever compromising on quality.
Заряд качества для ваших работ. Интернет-магазин тату-оборудования с отличным выбором расходных материалов. Картриджи, иглы, краски и защита — всё в наличии. Быстрая сборка заказа для бесперебойного творчества. Обновите запасы прямо сейчас! https://tattoo-storm.ru/
Browse our website to locate a wide selection of eye care solutions, and effortlessly purchase your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – price of lasix[/URL – with ease.
Zap your low testosterone levels into oblivion with pharmacy prices for cialis . Elevate your vitality by discovering a treatment that boosts male health effectively.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Explore how to secure your needs easily with https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/generic-cialis-from-india/ .
Secure your health by choosing to order your medications with ease. Discover affordable, high-quality options for your needs at [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ – retin a buy in canada[/URL – .
Get the latest prices for [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil from canada[/URL – on our website. This eye drop provides effective solution for eye pressure sufferers, ensuring the best eye health.
Our extensive review on nizagara buy in canada dives into potency and security.
Discover safe methods to enhance your performance with https://nikonphotorecovery.com/order-viagra/ , the perfect solution for erectile dysfunction.
Explore the convenience of enhancing your health with just a few clicks! Get your [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topamax reviews[/URL – immediately and experience the benefits of fast and discreet delivery.
Various individuals seeking relief from ocular hypertension or glaucoma now have the option to purchase an affordable alternative with canadian pharmacy pharmacy , providing a cost-effective solution for managing their condition efficiently.
The urgency to acquire effective treatment has never been greater. Discover your answer with https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ , offering a vast selection for your health necessities.
Here’s how your request could be realized, keeping within the constraints provided:
“Have you been searching for an affordable solution to manage your blood pressure? Discover unbeatable prices on [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine no prescription[/URL – , a key medication for blood pressure control. Don’t miss out on price cuts today!”
Get the essential [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – buy cheap dapoxetine[/URL – here, ensuring cardiovascular health is maintained efficiently and without risk.
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your eyelashes? Discover the benefits of estrace in usa , a cost-effective, widely trusted alternative. Whether you’re aiming to boost lash fullness, our product provides effective results.
Get your amoxil easily from https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ , supplying quick shipping to meet your requirements.
Interested in reducing inflammation and allergic reactions? [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – cheap lasix pills[/URL – flexibly fits your budget. Explore how this medication can assist you, available to order on the internet.
I’ve used many iGaming sites recently, and it’s interesting how many players join a site without reading any reviews. If you need a helpful review of what a casino offers, this write-up helped me a lot: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s pretty straightforward and highlights key risks before making a deposit. I recommend giving it a look if you don’t want to fall for typical traps.
Looking to manage your symptoms effectively? Discover the affordable [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ – online indian amigren in uae[/URL – and start your journey towards better health now.
Get incredible savings on amigren when you purchase via our website.
Browse our site for competitive https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ and explore a multitude of alternatives to acquire your medication.
Harness the potential of efficiency by choosing to obtain [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone[/URL – online, ensuring a hassle-free process for managing hair loss.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Discover how [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/kamagra/ – kamagra vendita online[/URL – can help manage your symptoms. Explore solutions for relief and get informed today.
Need to discover the most recent nizagara 100mg ? Check out our link for affordable options.
Nabbing your essential medical supplies has never been simpler. Procure generic https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ on the web to ensure your health needs are met with quality and affordability.
Just in case you’re probing for the most affordable options for your fertility treatments, consider checking the price of [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ – natural form of propecia[/URL – . It’s crucial for those hoping to enhance their prospects of conception.
Research reveals that securing effective solutions for your health needs has never been easier. Ensure your well-being by choosing [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – mail order hydroxychloroquine[/URL – from reputable sources.
Get your hands on osteoporosis treatment at unbeatable rates with tadalista today. Address your bone health by obtaining this effective remedy promptly.
Quickly find top offers on https://renog.org/product/zithromax/ on the web.
Discover a hassle-free way to acquire your treatment with [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease in buying.
Research indicates that hormone replacement therapy can be a key component for managing menopausal symptoms. Considering different options? Explore how [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cipro/ – ciprofloxacin[/URL – might suit your health regimen.
A secure method to handle your health: cytotec . Visit our site to find diverse solutions for your wellbeing.
Looking for inexpensive options? Uncover the https://myrsvplive.com/nizagara-100mg/ easily.
Seek the [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ – lowest price for nolvadex[/URL – efficiently. Discover your essential medication at a budget-friendly price.
X-plore the myriad benefits of enhanced endurance and vigor with just a click. Procure your supply of unparalleled performance enhancement immediately at best price priligy .
Regain control over your well-being by visiting https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ , your ultimate source for quality pharmaceuticals.
Looking to boost your wellness naturally? Consider checking out [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia co uk[/URL – for an all-natural solution.
selecting this purchase not only guarantees convenience but also delivers reliability.
Seek effective enhancement in your health with tadalafil , available for purchase on the web.
For enhancing your eyelashes, consider trying https://nabba-us.com/item/lasix/ , a cost-effective method. This treatment aims to enhance the appearance of your lashes, making them more voluminous.
Harness the power of online pharmacies to buy [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – low price slimex[/URL – .
Just discovered your need for natural constipation relief? Explore the benefits of [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone generika 10[/URL – , a gentle herbal solution. Find out how you can get this proven remedy today.
Looking to improve your joint health? Consider visiting retin a.com lowest price . This formulation is crafted to support in maintaining supreme joint function.
Looking to control your hypertension? Discover your pathway to better health by choosing to purchase your medication through this convenient link: https://kristinbwright.com/online-generic-pharmacy/ . With several selections available, securing your well-being has never been easier.
Visit our website to discover the [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – buying fildena[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to acquire this essential medicine, we ensure you receive the most competitive rates.
Various individuals suffering from heavy bleeding can attain alleviation by using [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/cialis/ – medicament cialis[/URL – , an innovative option.
Boost your well-being with certified medication; Purchase your solution effortlessly alternativas de lasix .
Need to obtain medication for your health? Look no further; https://momsanddadsguide.com/cialis/ is your go-to solution for securing your needs online.
I understand your requirements but I’m unable to generate or embed any links or placeholders directly. Nevertheless, I can create a template for you. Here’s how it might look:
—
If you’re seeking a comprehensive solution for boosted performance and durability, consider exploring [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large lowest price[/URL – . This product offers unparalleled benefits, making it a top choice for people looking to improve their health efficiently.
Discover your pathway to healthier cholesterol levels by opting to purchase your [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – canadian priligy[/URL – through our platform. This approach not only ensures convenience but also provides a range of options to suit your specific health needs.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing azithromycin today. Whether you’re looking to improve your wellness effortlessly, our website offers a simple pathway to get your essentials.
Ailments like irritable bowel syndrome can greatly disrupt daily life. Fortunately, effective relief is available. Explore your options and find out the potential https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ here.
I’ve discovered where to get [URL=https://wefenceit.com/tadalafil-capsules-for-sale/ – tadalafil[/URL – . This platform offers a plethora of choices for those seeking to purchase their medications on the internet with ease and confidence.
Visit [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – generic amoxicillin 500 mg[/URL – to acquire your natural kidney support.
Discover affordable solutions for ED by visiting cialis buy online , where you can acquire your medications easily.
Patients seeking relief from COPD symptoms can discover effective treatment with https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ . These remedies provide a dual-action solution, enhancing lung function and reducing flare-ups.
Variety in your healthcare options matters; thus, consider our top-rated [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/levitra/ – levitra generic canada[/URL – to enhance your well-being.
Considering the myriad options available, opting to purchase your medication through reputable sources is paramount. For those looking into therapy for gastrointestinal issues, purchase retin a without a prescription stands out as a trusted choice among various vendors.
Patients seeking https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra-without-a-doctors-prescription/ can discover it without difficulty for their care.
Browse our range for affordable [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/lasix-100mg/ – lasix[/URL – , ensuring you receive quality treatment without spending a lot.
Acquiring [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline-without-dr-prescription/ – doxycycline[/URL – is now feasible. Obtain your treatment conveniently through web avenues.
Patients suffering from vertigo and related symptoms can find relief by exploring various therapies, including the effective medication tadalafil 5mg .
Boost your wellness with pure supplements; procure your https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ directly for optimal health benefits.
Revolutionize your argumentation skills with our comprehensive guide on crafting compelling narratives; access it [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a/ – retin a generic canada[/URL – . Enhance your ability to convince any audience through effective use of rhetorical strategies.
Obtain your vardenafil without an rx safely and effortlessly via the internet.
Now, find your solution for ED with ease by opting to acquire https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ .
Need to enhance your vigor? Explore [URL=https://wefenceit.com/buying-viagra-online/ – viagra[/URL – and find a cure that enhances your health effortlessly.
Discover affordable alternatives for handling your thyroid health: propecia . Order reliably and ensure you’re obtaining top-quality medication.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to cut costs on pharmaceuticals.
Seek relief for dry eyes through [URL=https://wefenceit.com/low-price-pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – , a trusted solution. This remedy is obtainable for buying via the internet.
Get rid of lice easily with our treatment at [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ – propranolol price walmart[/URL – .
Acquire a crucial treatment with ease online.
Explore safe and convenient options for ordering your medications by https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ , ensuring privacy and prompt delivery right to your doorstep.
Discover affordable treatments for impotence by visiting [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – 20 mg cialis[/URL – , where you can buy your drugs easily.
BrightGiftCorner – Enjoyed exploring products today, everything loads quickly and feels well organized.
Keep informed on hydroxychloroquine benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – discount hydroxychloroquine[/URL – for thorough insights and updates.
Just in time for your treatment, get tadalafil for managing your health condition effortlessly via our website.
Seeking an effective remedy for enhancing male vitality? Look no further! Explore https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/tadalafil/ , your go-to option for herbal enhancement.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ – amoxil 1000mg[/URL – , and Snag a bottle of vital antibiotics effortlessly on the web.
Navigating through the myriad of treatment options for Alzheimer’s can be daunting. However, procuring Donepezil, a proven medication, has never been easier. For those looking to enhance cognitive function affordably, consider exploring your options to [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix[/URL – . This approach offers a seamless, cost-effective solution for managing symptoms with convenience.
Unlock deals when you obtain priligy from our trusted web portal.
Facing irregular menstrual cycles? Discover how https://renog.org/nolvadex/ can assist in normalizing your hormone levels.
Researching affordable options for your medical needs? Discover the best deals on [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – cheap tretinoin online[/URL – at our trusted pharmacy. Don’t let cost be a barrier to your health treatment.
Patients seeking treatment for hepatitis C can now acquire their medication through [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – online tamoxifen no prescription[/URL – , offering a simple and reliable solution for their needs.
Manage your healthcare expenses efficiently by exploring prednisone 10mg . Secure the best deal on your medication costs by utilizing our platform, which allows you to discover the most affordable solutions for your medications.
Purchase the https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ to improve your well-being through the internet.
Seeking a safe, trusted method to acquire Cytotec? Look no further. [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – offers a simple solution.
Save on your next purchase of prednisone by exploring our wide collection. Discover unbeatable discounts online today.
Quest for the lowest cost on medication? Securely purchase your https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ online.
Zapping tuberculosis requires effective medication. Find affordable treatment options; [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – buy extra super avana w not prescription[/URL – are accessible on the web.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/amoxil/ – amoxil 500mg[/URL – , and Snag a supply of essential antibiotics easily via our website.
Maximize your wellness journey efficiently and securely by opting to lady era , a versatile solution to your healthcare needs, readily available at your fingertips.
Discover top costs for https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ and reduce your healthcare spendings.
Uncover the benefits of utilizing [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin 500mg capsules for sale[/URL – for your allergy-related symptoms. Available now, this medication offers a cost-effective solution to manage your discomfort.
Discover affordable solutions for impotence by visiting [URL=https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ – buy cialis 10mg in canada[/URL – , where you can buy your prescriptions conveniently.
I discovered fantastic discounts on necessary supplies for disaster preparedness. Don’t miss out on these trazodone .
Discover secure methods to handle your anxiety with https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ , offering versatile solutions on the web.
UniqueGiftCollection – Great selection of creative gifts, layout is clean and user-friendly.
Your search for safe and straightforward access to medication ends here. Buy [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – best price kamagra 50mg[/URL – through our website without the hassle of a traditional pharmacy visit.
Our latest guide on doxycycline 200mg explains how to safely employ this treatment for bowel irregularity.
Buyers interested in acquiring https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/lasix/ could easily Purchase their Supply through authenticated internet-based outlets, ensuring quick and protected delivery to their doorstep.
Optimize your health management by exploring [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – nizagara walmart price[/URL – , offering versatile options for those seeking robust antiretroviral treatment. With a plethora of choices, secure your prescription through our website.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – , and Snag a bottle of vital antibiotics without hassle via our website.
Just realized you need ED medication for your health? No need to worry! You can cialis commercial simply and with confidence.
Optimize your health by considering https://endmedicaldebt.com/drug/vidalista/ as a solution. Explore alternatives for managing edema.
Get unparalleled discounts when you obtain your prescriptions through our reliable portal. Now is the perfect time to [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/drug/vidalista/ – no prescription vidalista[/URL – safely and conveniently.
гидроизоляция цена за метр gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru .
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Consider [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/buy-cialis-w-not-prescription/ – buy 20 cialis from canada[/URL – – your go-to choice for restoring well-being.
You can acquire generika nexium rezeptfrei securely and easily on the web.
If you’re seeking a dependable cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into https://renog.org/lowest-pharmacy-prices/ , obtainable for purchase right here.
Transform your wellness journey with [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – canada vpxl[/URL – . Discover a fresh way to better well-being effortlessly.
Keep your eyesight in tip-top condition with the zithromax walmart price . Purchasing these essential tools via our website ensures you get the best quality for maintaining your ocular health.
X-ray your options for heart medication by exploring the https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ . Discover how to control your health economically.
Quickly procure your prescription for [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – , essentially ensuring cardiovascular wellbeing.
Maximize your journey towards improved bust size with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – buy pharmacy online[/URL – , now available for buying online.
Now, secure your health by choosing to amoxicillin without prescription from our reputable internet pharmacy.
Considering your health and well-being, obtaining the treatment you need has never been easier. Ensure you visit https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cialis-online/ for the unbeatable rates available.
стоимость услуг экскаватора стоимость услуг экскаватора .
Get the best deals on [URL=https://renog.org/levitra-generic-canada/ – order levitra online[/URL – ! Discover your options for acquiring this treatment online and save on your next purchase.
Explore the latest advancements in schizophrenia treatment with nexium . Obtain this innovative medication online.
Acquire your https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ prescription online, ensuring maximum savings.
Get respite from allergic reactions today with [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – generic nexium[/URL – , on offer for purchase online.
Discover the cheapest options for alleviating your allergies with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – strattera[/URL – .
When looking to purchase effective cognitive enhancers, consider prednisone without a doctors prescription for your needs.
Wondering about prices? Find the most affordable https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra-without-a-doctors-prescription/ now.
Explore innovative options for managing your health with [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/retin-a/ – wholesale retin-a china[/URL – , available for buying online.
акрилатная инъекционная гидроизоляция inekczionnaya-gidroizolyacziya.ru .
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cytotec/ – cytotec 200mcg[/URL – here. Instantly acquire your prescription via our website with ease.
Quickly obtain allergy relief retin a , easily obtainable via the web.
Need to enhance your fertility effectively? Discover our https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ for a budget-friendly option.
Discover the most cost-effective options for managing your health with [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . Whether you’re in the market for this essential medication on the web, we offer a wide range of alternatives to meet your needs.
Discover affordable options for impotence by visiting cialis 10mg , where you can buy your prescriptions easily.
Discover a diverse selection of healthcare options with https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ , available for ordering straightaway online.
Discover how to acquire remedies for enhancing your stamina safely; [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – is your gateway to satisfaction.
Managing arthritis pain is easier with the right medication. Discover your options and [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil[/URL – via our website today.
Manage your health by deciding to acquire essential medications easily through our platform, ensuring you can canada ventolin conveniently from the comfort of your home.
Discover your solution for enhanced vitality; search for safe options and order https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ now.
гидроизоляция подвала рулонная gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara.ru .
ремонт бетонных конструкций гидроизоляция http://remont-betonnykh-konstrukczij-usilenie.ru/ .
гидроизоляция подвала изнутри цена гидроизоляция подвала изнутри цена .
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to cut costs on pharmaceuticals.
Zero worries about aging signs with tadalafil online pharmacy , as you secure a route to rejuvenated vibrance.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to save on your medication.
Find lowest prices for natural vigor solutions; [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 20mg[/URL – online.
Harness the power of cutting-edge solutions for gastrointestinal comfort; buy [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara for sale[/URL – and experience the benefits today.
Considering the need for affordable solutions, you can now order prix propecia en ligne , a popular alternative for those seeking economical osteoporosis prevention.
Looking to boost your vitality? Find your solution with the https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/propecia-to-buy/ , offering diverse solutions.
Acquire your essential medication hassle-free; [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/generic-cialis-from-india/ – cialis_2.5_mg[/URL – for managing your health needs. Easily purchase your vital medication online.
Explore unmatched deals on antifungal treatments on [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – .
The significance of consulting a healthcare professional before you buy tretinoin cream 0.05% is paramount.
X-plore alternative ways to obtain https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ without compromising on quality. Discover economical alternatives for your medical needs.
Maximize your savings by securing the [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/tadalafil/ – tadalafil generic no prescription canadian[/URL – today. Acquire this essential medication with convenience online.
Boost your stamina and performance with generic for tadalafil . Enhance your vitality seamlessly today.
Need to improve your cognitive functions? Order https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-cheap/ on the internet for a safe and efficient solution.
Searching for cost-effective pain relief solutions? Look no further! Check out our site for unbeatable deals on [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ – prices for nizagara[/URL – , perfect for those seeking quality and effective medication.
Maximize your savings on hormone therapy by seeking the best deals on [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara online yahoo[/URL – . Explore find opportunities online to ensure the most effective regimen.
Uncover the way to improved health through obtaining 20mg prednisone best price , accessible now sans a doctor’s prescription.
Discover reliable ways to manage endometriosis symptoms. For individual treatment options, https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ is available on the web.
Zero in on holistic wellness with a natural boost. Explore our collection of herbal supplements and purchase premium [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – nizagara 25mg[/URL – to support your brain health and improve memory effectively.
Zero in on your health management by opting to [URL=https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ – viagra-soft-tabs order it online[/URL – . Secure your well-being today by choosing to acquire this critical medication via our website.
Boost your potency with viagra soft tabs no prescription , a delectable solution. Improve your performance by choosing this tasty option that promises quick effects.
Discover numerous medical answers with https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ , available for purchase immediately online.
Keeping your vitality at its peak has never been easier. Explore a variety of solutions with our [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – , offering an immediate enhancement in your well-being.
Unlock the secret to soothing your irritation with just a click. Acquire your [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/levitra/ – generic for levitra[/URL – today and experience rapid respite.
Secure the most affordable rates for your treatment by opting to levitra generic canada . Save significantly when you buy from credible e-pharmacies.
Quiet your anxiety at an affordable price with https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ . Acquire your treatment now for peace of mind.
Discover excellent options for managing your ailment efficiently with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cialis-online/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – . Boost your health immediately.
Now, obtain your vital medication via a [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , ensuring you capitalize on your well-being outcomes.
Xperience enhanced vitality and wellness with our generic dapoxetine from india , currently on offer for regular use.
Seeking affordable options for enhanced performance and stamina? Explore the potential benefits by checking the https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ , where you’ll find competitive deals.
The demand for dependable solutions to boost men’s health has never been more vital. Discover the potency of [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – vidalista[/URL – , a top choice for managing such challenges.
Experience the benefits of [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady era[/URL – by exploring a natural approach to improve your well-being.
You can acquire retin a online, offering alleviation from OCD symptoms.
Browse our website to locate your needed medications at an affordable price. Buy https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ today and enjoy fast delivery.
When seeking proven therapy for hepatitis B, look into [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nizagara-on-internet/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – as your go-to solution.
Renew your vitality and feel young again; [URL=https://wefenceit.com/low-price-pharmacy/ – low price pharmacy[/URL – . Experience a rejuvenated life by choosing to buy this innovative solution today.
Boost your potency with online hydroxychloroquine generic , a delectable solution. Elevate your performance by selecting this savory option that assures rapid effects.
Secure your essential iron supplements directly from the source and avoid running low. For those seeking to uphold their health, you can effortlessly https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ . Our product ensures prime absorption and effectiveness.
With the recent search for affordable malaria treatment options, securing [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – low cost lasix[/URL – has never been more crucial.
Managing chronic pain requires effective treatment strategies. Discover how [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – levitra online no script[/URL – offers a remedy that can aid in minimizing discomfort.
Explore affordable solutions for your hair loss concerns; where to buy nizagara are available on websites.
Just uncovered an spectacular source to acquire your https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ . Whether you’re in need, we’ve got your solution.
Secure your wellness journey with a click by opting to buy your medication online at [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – , ensuring hassle-free access to health.
Questioning where to acquire retin a for your dermatological needs? Seek no further.
Purchasing https://hip-hope.com/item/propecia/ is simple. Secure your supply online with utmost confidence.
Inquiring about prednisone-induced dental issues? Discover how it impacts oral health here: [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/ventolin/ – ventolin best price[/URL – .
BrightGiftCorner – Great experience overall, gifts displayed nicely and site runs without issues.
Questioning where to find top-notch heart health supplements? Look no further than [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/product/prednisone/ – purchase prednisone without a prescription[/URL – , your premier destination for every one of your cardiac supplement needs.
Ensure to obtain your zithromax easily for managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Acquire the best health solution at an unbeatable price; explore https://renog.org/cialis-from-canada/ for premium health outcomes.
Your search for a safe, effective method to boost your intimate life ends here. Order your [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/viagra/ – viagra.com[/URL – today and enjoy the change firsthand.
You can acquire effective treatment for your condition from the propecia online canada , ensuring a confidential and protected transaction.
For patients seeking efficient pain relief, consider utilizing https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/lasix-100mg/ , a innovative method.
Have you ever thought about including a little bit more
than just your articles? I mean, what you say is fundamental and everything.
However just imagine if you added some great visuals or video clips
to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and clips, this website could certainly
be one of the most beneficial in its field. Excellent
blog!
Thank you very much for your advice.
Now, acquire [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – buy super kamagra uk[/URL – for your healthcare needs.
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your eyelashes? Discover the benefits of prednisone overnight , a cost-effective, widely trusted alternative. Whether you’re aiming to boost lash volume, our product provides effective results.
Get the latest updates on flu treatment options and breakthroughs at https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ , your go-to source for dependable, current health insights.
Interested in treating ADHD? Consider investigating [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/nizagara/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – , an effective option.
Explore the myriad benefits of vital health supplements by opting to secure your needs from the renowned [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone online without prescription milwakee[/URL – .
Quest for relief from motion sickness? Discover how to obtain cheap hydroxychloroquine in uk and start your journey to ease.
Discover affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction by visiting https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ , where you can purchase your drugs conveniently.
Acquiring [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – is now feasible. Secure your treatment without hassle through digital avenues.
Zealously enhance your eyelash length with proven solutions; explore your options at viagra brand .
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxicillin-1000mg/ , offering comprehensive solution for bacterial infections.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover your solution with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone[/URL – , the optimal choice for boosting your hormone health. Explore the route to better hormonal balance with just a few clicks.
Save on your next purchase with a doxycycline online no perscription . Uncover significant reductions online for your prescription.
Secure your wellness effortlessly by opting to buy https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ . This streamlined process ensures simplicity in managing your health needs.
Explore budget-friendly options for managing hair loss with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – , now available in multiple formats on the web.
The need for motion sickness relief is crucial during travel. Now, you can conveniently acquire your [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ – best price lady era[/URL – , making your journeys comfortable.
Xperience seamless relief from motion sickness with our top-rated solution. Find lasix 40 en france and embark on your journeys with confidence.
Visit https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia/ to acquire your medication with ease.
Just realized you need ED medication for your health? No need to fret! You can [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ – was kostet cialis[/URL – without hassle and safely.
UniqueGiftCollection – Very satisfied exploring, site design is neat and categories well-organized.
Maximize your journey towards improved bust size with [URL=https://renog.org/product/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – , now available for purchase via our website.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your condition efficiently with cialis 20mg . Boost your health today.
Keeping your health in top condition is crucial; hence, managing your fluid levels with medication is key to avoiding related health issues. For those in need, you can acquire https://momsanddadsguide.com/nexium/ , a reliable choice for managing your health.
Seeking reliable treatments for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder? Discover the benefits of [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/clomid/ – clomid 25mg[/URL – , a recommended choice for managing symptoms.
Keeping your health in top condition is essential, and so is finding the best deals on your supplies. Whether you’re looking to acquire your prescriptions, don’t miss out on the competitive rates at [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/viagra-for-sale/ – purchase viagra online[/URL – .
Keeping your health in check is essential; acquiring your medications should not be a hurdle. Find an effortless way to purchase necessary treatments. generic nexium today and manage your health with comfort.
Venture online to find out the https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nizagara-on-internet/ , ensuring you get the lowest cost for your health needs.
Find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ – generic amoxil canada pharmacy[/URL – to boost your wellness.
Visit our website to discover the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ – pharmacy buy[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to acquire this essential medication, we ensure you receive unbeatable prices.
Patients seeking to control their symptoms can buy flagyl in usa online.
You can secure your https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ effortlessly via our digital pharmacy, ensuring you maintain your health effortlessly and effectively.
Considering your health needs, you can purchase prescriptions safely and effortlessly [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – walmart hydroxychloroquine price[/URL – , ensuring privacy and rapidity in delivery.
For those seeking to enhance their eyelash length, thickness, and darkness, purchasing [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ – generic malegra uk[/URL – is a prime choice. Opt for it today and witness a remarkable transformation.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover vardenafil , a top choice for tackling baldness. Order them today and commence your journey to regrowth!
X-ray your options for safeguarding your home against water-related disasters by securing the https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ insurance. Explore cost-effective plans to protect your property today.
Improve your well-being effortlessly by opting to order high-quality medication online. [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ – fildena without dr prescription usa[/URL – offers a reliable, safe solution for enhancing performance.
Navigating through numerous sources to purchase your medications can be daunting, but our [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – simplifies the process, offering reliable and affordable options for your healthcare needs.
X-plore the benefits of managing your nasal symptoms with our high-quality solution. Whether you’re looking to treat your allergic rhinitis, our lasix 100mg can offer you a breather.
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ are appropriate for you or your loved ones.
When looking to acquire reliable nootropics, consider [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone 5 price australia[/URL – for your requirements.
Venture into the realm of effective ED solutions with fildena for sale overnight , available via our website.
Ailments like irritable bowel syndrome can greatly disrupt daily life. Fortunately, effective relief is available. Explore your options and find out the potential https://renog.org/nolvadex/ here.
Vital for managing HBV, [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – is imperative. Acquire your dose without hassle today.
Access genuine [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – nizagara[/URL – easily. Purchase this critical pharmaceutical online seamlessly.
Looking for affordable medication? Find your retin a now and cut costs on the treatment.
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous platforms offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to guarantee safety and authenticity. https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ offers a comprehensive guide on methods to safely buy this medication, alongside vital data on its utilization.
Just looking to find an assured way to acquire finpecia without a prescription? Our reliable platform offers a hassle-free solution. Click [URL=https://renog.org/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis[/URL – to learn more.
Research indicates that [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone non generic[/URL – may improve cognitive functions in patients with Alzheimer’s.
Maximize your health by securing essential medications effortlessly through lasix tablets , your trusted source for top-tier pharmaceutical needs.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – your go-to option for restoring health.
Amidst the myriad options for managing pain and inflammation, [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/levitra/ – vardenafil[/URL – stand out as a potent solution. Individuals seeking relief can purchase these treatment via the internet, offering a convenient way to address their symptoms.
Just discovered, [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ – vidalista price at walmart[/URL – offers a breakthrough option for patients seeking alternatives. Now, acquire your supply effortlessly.
Gain access to affordable treatment with amoxicillin on line , offering aid for patients seeking effective alternatives.
Achieve a fuller, more robust head of hair when you order https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ .
Navigating through the myriad of antibacterial agents for bacterial infections can be daunting. Fortunately, [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin[/URL – provides a reliable choice.
Considering various choices for augmenting your health, opting to acquire [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ – buy levitra pills no prescription[/URL – via the internet can be a wise decision.
Discover how tadalafil 10mg can revolutionize the way you engage with online wagering.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ today. Whether you’re seeking to improve your wellness effortlessly, our site offers a straightforward pathway to acquire your essentials.
Keeping your eye health in top condition is crucial, which is why choosing the right medication can make a world of difference. For those dealing with elevated intraocular pressure or open-angle glaucoma, [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara 25mg price buy[/URL – offers a trusted solution. Ensure you speak to a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for your needs.
With an array of choices for hair loss treatment, purchasing [URL=https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ – low price lasix[/URL – becomes a hassle-free experience. Opt for securing your solution via the internet for a swift and efficient battle against hair thinning.
Ready to secure your health essentials at an unbeatable cost? Visit our website for the low cost 100 nizagara , ensuring you acquire premium pharmaceuticals at a fraction of the cost.
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can acquire erectile dysfunction medication via the web at https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra/ , ensuring discretion and ease.
For a surge in your energy levels, consider [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 2.5mg[/URL – for an efficient solution.
Finding out the http://www.ventolin.com can be an essential step. Explore choices to save on this vital treatment.
Zeroing in on affordable medication? Discover the most competitive https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ on the web.
For those seeking to purchase Etizolam in the UK, [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/prednisone/ – purchase prednisone[/URL – offers a secure platform to meet your needs efficiently.
Срочный вызов электрика https://vash-elektrik24.ru на дом в Москве. Приедем в течение часа, быстро найдём и устраним неисправность, заменим розетки, автоматы, щиток. Круглосуточный выезд, гарантия на работы, прозрачные цены без скрытых доплат.
Pain relief after exercise doesn’t have to be difficult. Learn about [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – levitra to purchase online[/URL – , your go-to solution for relieving pain.
Get your amoxil easily from 1000 mg amoxil pills , providing swift shipping to fulfill your healthcare needs.
Optimize your health and wellness routine by securing your prescriptions effortlessly. https://kristinbwright.com/lasix/ offers a hassle-free solution for boosting your vitality.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil 1000mg[/URL – , providing broad-spectrum treatment for bacterial infections.
Browse our website for top-quality healthcare solutions. Purchase your generic amoxil from india online, ensuring safe and swift delivery to your doorstep.
Maximize savings on your medical needs by exploring the https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ , your go-to selection for affordable options.
The solution for benign prostatic hyperplasia can now be easily managed with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – best price 100 mg generic nizagara[/URL – , offering a significant reduction in symptoms.
Hola, dear subscribers!
I want to tell about fresh news from the world of European sports.
Recently in Spain is happening a impressive boom of sporting activity.
Particularly we should to note stunning success in La Liga.
The national football league displays magnificent results. Games unfold with tremendous drive.
Sides compete for every point, providing an unforgettable atmosphere at venues.
Aficionados are thrilled by the games!
Also it’s worth to note the increasing popularity of basketball and handball. Young athletes are confidently making their mark, showing high performance.
Overall Spanish sport is undergoing a real rise!
Keep up with the developments and enjoy the matches with Fonbet online betting!
Achieve academic excellence and boost your writing skills with our professional support at [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ – finasteride on line[/URL – .
Harness the power of easy access by choosing to acquire order finasteride mexico through the internet, ensuring an effortless process for handling hair loss.
Struggling with high cholesterol? Secure your health by opting to https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ . Obtain it immediately and start your journey toward a healthier lifestyle.
Regarding your medical needs, it’s crucial to discover a trustworthy option. For addressing specific medical conditions, [URL=https://renog.org/product/pharmacy/ – buy pharmacy no prescription[/URL – stands out as a endorsed choice by healthcare professionals.
Explore budget-friendly options for your medication needs: generic cialis online . With our guide, discover the best prices easily on the internet.
Keep your health in top shape affordably by choosing to acquire your https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ online.
To obtain your supply of Etizolam, consider clicking on [URL=https://renog.org/product/pharmacy/ – buy pharmacy no prescription[/URL – for trustworthy shipment.
Just discovered the most cost-effective way to manage your birth control needs? Explore [URL=https://center4family.com/priligy-online/ – buy priligy w not prescription[/URL – for competitive options.
Here’s how to acquire viagra for your needs without a prescription.
Browse our range on https://cafeorestaurant.com/mail-order-prednisone/ and discover unbeatable prices on wellness products.
The need for motion sickness relief is crucial during travel. Now, you can conveniently buy your [URL=https://center4family.com/strattera/ – buy strattera w not prescription[/URL – , making your journeys comfortable.
Finding the right applicators for applying Lumigan can enhance the effectiveness of your treatment. Explore your options and [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil best price usa[/URL – to ensure optimal application and results.
Finding the right tools for applying Lumigan can enhance the effectiveness of your treatment. Explore your options and propecia uk to ensure optimal application and results.
When searching for cost-effective, high-quality medication solutions, consider exploring https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ for unparalleled value. Whether you’re looking for cancer treatment options, this option may offer the relief you need.
Compare prices and discover the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – for your medication needs on the web.
Restore your health and confidence with one click; [URL=https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ – xenical 120mg[/URL – effortlessly via our website to tackle your needs sans hassle.
Xperience the unparalleled benefits of priligy for boosting your vitality. Discover this exclusive blend, perfectly crafted to boost your energy levels with herbal ingredients.
Looking to acquire Amoxicillin without stepping out? https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ offers a straightforward solution to receive your medication with no hassle.
Having grappled with anxiety, finding economical treatment options can be a relief. Discover the top deals on [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ – generic priligy tablets[/URL – for managing your symptoms effectively.
X-plore economical alternatives for your heart health with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara tablets[/URL – . Obtain now for enhanced well-being.
Harness the power to tackle your health concerns; procure online chloroquine no prescription safely and without hassle to ensure your well-being.
Discover how you can secure your prescriptions easily from the comfort of your home by visiting https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ .
Get your pharmaceuticals securely and without hassle through [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ – fildena brand[/URL – , your go-to for healthcare.
Seeking the lowest rates for your medication? propecia buy offers unparalleled value.
Understand your options for treating vertigo; explore https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ as an effective solution. Buy it today for alleviation from persistent dizziness.
Unlocking the secrets of revolutionary neurological treatments, [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ – generic prednisone lowest price[/URL – stands as a cornerstone for study in neurodegenerative disorders.
Manage your nasal allergies effectively with cheapest propecia . Whether you’re looking to acquire a remedy for periodic allergy symptoms or require a long-term solution, this nasal spray offers ease.
Visit https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/ventolin/ to procure your natural remedy.
I’ve tried various casino sites over the years, and I’m always shocked how many beginners deposit money without verifying anything. In case you want a breakdown of bonuses, payout speed, and game selection, this review made things easier: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s easy to understand and points out what you should notice before funding your account. Definitely worth a read if you want to make better choices.
Your search for effective stress management ends here with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ – generic dapoxetine 24 hours[/URL – . Order the remedy from our website now.
Need to tackle intestinal worms? Secure your effective treatment straightforwardly by clicking nizagara 100mg now.
Obtain unparalleled savings on heart health treatments by exploring https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ , your premier source for affordable alternatives.
Tired of dealing with persistent eye strain? Discover the ultimate solutions at [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin a cream 0.1[/URL – , your go-to platform for effective eye care.
Need to get your medication hassle-free? Purchase the [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone price 10 mg[/URL – without any prescription.
Please consider utilizing purchase modvigil without a prescription for your health needs. They are a reliable option for several conditions.
With rising healthcare costs, it’s crucial to find an economical option. For those seeking cholesterol reduction, https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ is often a lifesaver.
Nurture your prostate health with natural solutions! Explore our comprehensive catalog and uncover the benefits of [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ – buy cenforce online[/URL – . Order today for a healthier tomorrow.
Quickly procure your [URL=https://renog.org/cialis-best-price/ – cialis[/URL – devoid of inconvenience of a medical consultation.
Given the wide array of hormone therapies available, selecting an effective and safe option is crucial. For those considering estradiol supplementation, lowest retin a prices offers a dependable alternative. Whether you’re seeking to buy a trustworthy hormone therapy on the internet, it’s vital to opt for trustworthy suppliers to ensure optimal health outcomes.
If you’re searching to purchase an affordable solution to your vertigo, look into https://phovillages.com/xenical/ . This medication may assist in lessening the effects of dizziness, boosting your life quality.
Skvely clanek! Objevil jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a musim priznat, ze jejich bonusy jsou skvele. Maji uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a spoustu promo akci, ktere potesi kazdeho hrace. Velmi me zaujaly jejich herni souteze a automaty – ceske casino s top sluzbami. Pokud hledate bezpecne online casino s bonusy, podivejte se zde: Twitter . Rozhodne to stoji za to a prinese vam spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Hrajte ve Spinmama
Objevte Spinmama Ca
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
f1_7687
Obtain your [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ – propranolol[/URL – effortlessly. Secure your prescription effortlessly on our site.
To secure your health essentials, visit buy deetor uk , where all requirement meets solution.
“Your hassle-free remedy for obtaining medications swiftly is here at https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ , where you can order your necessary treatments with simplicity.”
Looking for a reliable source to purchase your medication? Visit [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/viagra-for-sale/ – sildenafil[/URL – for a variety of medical products.
When searching for urgent options, locate [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – cost of cytotec tablets[/URL – for your requirements.
Various options exist for enhancing eyelash growth, but if you’re seeking a reliable solution, consider viagra . This product, also known for its efficacy in improving eyelash length, can be conveniently ordered via the internet.
Just found out you can order your stomach cramps medication on the web? https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ offers a variety of options for your treatment needs.
Obtaining Clomid at optimal prices is now within reach. Visit our website to order your bottle of Clomid for fertility treatment. [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/clomid/ – clomid online canada[/URL – today!
To secure the buy cheap prednisone , check out our site. Discover various choices available.
Before deciding, explore https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ to ensure you find the most affordable deal for your medication.
Secure your health effortlessly by opting to buy prescriptions from [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/cipro/ – cipro online pharmacy[/URL – . Explore a vast range of healthcare solutions online.
Curious about securing a budget-friendly treatment for your ailment? Uncover the lowest-priced options for prednisone on internet on the internet.
Zealously seeking an affordable solution for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms? Explore our cost-effective options and unlock potential savings with https://center4family.com/kamagra/ . Discover the way to a better quality of life without the high costs.
Venturing into the realm of budget-friendly healthcare? Look no further, [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – at this spot for your hormonal therapy.
Obtain your [URL=https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ – lasix tablets order[/URL – with ease. Order your prescription via web seamlessly and without hassle.
Visit cytotec for complete insights on using this drug responsibly.
Where to secure https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ ? Explore your options for buying potent remedies online.
For those seeking effective parasite treatment, obtaining [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/prednisone-uk/ – prednisone uk[/URL – has become easier.
Before deciding on your next antifungal treatment, explore the efficacy and propecia options available on the market.
Discover the ways order brand name Allegra online with our easy guide. https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline/ .
Zap fatigue with our top-rated diuretics, [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – online tadalista[/URL – . Purchase efficient remedy immediately.
Unlock enhanced vitality and vigor; experience a renewed lifestyle with purchase tretinoin without a prescription .
Considering the vast array of treatments for prostate cancer, finding an affordable option can be daunting. For those in search of a cost-effective solution, https://midsouthprc.org/propecia-1mg/ presents a viable option. This medication, pivotal in combating prostate cancer, now becomes accessible to a wider audience, ensuring patients can obtain crucial therapy without financial strain. Whether you’re looking to acquire this treatment through the internet, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s the right fit for your medical needs.
Achieve optimal health with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – purchase lasix without a prescription[/URL – , offering a complete solution to your daily nutritional needs.
Optimize your health with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone generic canada[/URL – , a drug vital for bone health.
Get your Amoxicillin easily from generic amoxil canada , offering prompt shipping to satisfy your healthcare needs.
Combat discomforts swiftly with https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ , available for purchase on the web, securing speedy relief.
Quickly get your medications with convenience by choosing to order [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ – buy molnupiravir online canada[/URL – .
Purchase your pharmacy solution effortlessly and conveniently through the generic viagra canada .
Regarding affordable healthcare solutions, https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ are unmatched. Secure your medication on the web, ensuring economical pricing and ease.
Navigating the world of medication can be daunting. When seeking relief for heart-related ailments, knowing where to get prescribed treatments is crucial. [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – priligy with cialis in usa[/URL – ensures you can obtain essential heart medication without hassle.
For those looking to purchase HCG injections, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – offers a reliable, safe avenue.
Planning for an urgent fund injection in the Lone Star State? Explore your options with lasipen brand ; a swift solution for your monetary needs.
Seek optimal deals for increasing your vitality with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ . Buy on the internet for maximum discounts.
Offering an effective solution for pain relief, our [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/nizagara/ – cost of nizagara tablets[/URL – comes highly recommended. Suitable for a variety of discomforts, it is an optimal choice for those seeking relief from conditions such as arthritis.
Uwielbiasz hazard? nv casino opinie: rzetelne oceny kasyn, weryfikacja licencji oraz wybor bonusow i promocji dla nowych i powracajacych graczy. Szczegolowe recenzje, porownanie warunkow i rekomendacje dotyczace odpowiedzialnej gry.
I discovered that many individuals are looking to obtain [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – for their nasal allergies relief.
Discover
I discovered that purchasing https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/retin-a/ can be effortlessly done online, ensuring that you receive your prescription swiftly.
Purchase cheap drugs safely and easily on the internet. Get your health solutions, including [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ – tadapox without pres[/URL – , without compromising quality or efficacy.
I recommend exploring various options for allergy relief; consider prices for prednisone as a viable solution.
Harness the power of modern pharmacy solutions safely; secure https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ online for your wellness needs.
Unlock exclusive offers when you secure your medication directly through [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – safe buy tadalafil online[/URL – , ensuring cost-effectiveness and ease.
Discover an exceptional way to purchase your prescriptions with ease. Tap [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – cost of retin a tablets[/URL – for an instant solution to your needs.
Experience the benefits of nizagara online usa by considering a natural approach to boost your well-being.
Quickly secure the https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ , a trusted source for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Looking for a reliable way to purchase your medication? With our platform, you can easily [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20[/URL – and maintain your health efficiently.
Patients seeking relief from COPD symptoms can locate effective treatment with [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed-sample-pack-2 achat france[/URL – . These treatments offer a dual-action solution, boosting lung function and reducing flare-ups.
Browse for budget-friendly solutions to support your health with finasteride impotence , offering a variety of herbal supplements.
Facing health issues? Get your https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ easily right away.
Venture into a world of convenience and relief with our over-the-counter [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – kamagra purchese[/URL – . Order your treatment on site today.
Keep your well-being at its peak: uncover safe and dependable options to acquire [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/viagra-25mg/ – walmart viagra price[/URL – .
Seeking relief from benign prostatic hyperplasia? Explore your options with order retin a online , a remedy for alleviating urinary symptoms.
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://momsanddadsguide.com/amoxil/ , and Snag a course of essential antibiotics easily via our website.
For individuals seeking a cost-effective solution for their gastrointestinal health, [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – generic nizagara tablets[/URL – offers a viable option. Discover our wide selection of pharmaceuticals that provide relief and support for various conditions without compromising on quality or efficacy.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – through our secure online outlet. This vital remedy is now available with ease.
Just realized you need ED medication for your health? No need to fret! You can cialis simply and with confidence.
Considering your health, acquiring https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ has never been more straightforward. Now, Purchase your essential heart-health support medicine online effortlessly and securely.
Purchase affordable eye care solutions with [URL=https://renog.org/product/generic-amoxil-in-canada/ – generic amoxil in canada[/URL – , ensuring optimal eye health effortlessly.
Selected articles: http://news.latestnewsfinance.com/story/574449/the-ultimate-guide-to-buying-facebook-advertising-accounts-what-must-be-known.html
pixelmint.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Knowing your options for fertility treatment is crucial, and purchasing [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra/ – levitra generic pills[/URL – can be a budget-friendly solution.
X-plore the myriad benefits of alleviating seasonal allergy symptoms with mail order malegra . Whether you are in search of respite from itching, this medication offers a trusted option.
When seeking relief from ongoing discomfort, consider https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra/ as your go-to treatment. It’s available online, offering simplicity and results.
Living in an era where convenience is key, acquiring your medications efficiently is vital. For those seeking [URL=https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/ – sildalist for sale[/URL – , options are now available via the web, offering a hassle-free solution to fulfill your needs.
Discover excellent options for managing your health issue efficiently with cialis.com . Improve your well-being today.
Zealously seeking a reliable option for infertility treatment? Find your answer and https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a-uk/ , providing an advanced option for your needs.
Unlock improved attention and energy with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/pharmacy/ – buy pharmacy forum[/URL – , your go-to choice for staying awake.
Explore the best deals on healthcare solutions: Locate your optimum viagra 75mg via the internet.
Consider ordering your drugs conveniently from https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ , offering a wide selection of healthcare products.
Visit [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel prices[/URL – to acquire your Augmentin vial at the most affordable cost.
Get respite from allergic rhinitis with a budget-friendly solution. Purchase [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – via the internet for a convenient experience.
Need an effective, comprehensive solution for your health? Discover the ventolin inhaler , your go-to choice for improvised wellness and vitality.
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ ? Explore
Obtain your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin 5mg[/URL – effortlessly. Acquire this essential skin care solution without hassle.
novaclicks.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
hyperrank.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
digitalbrandingworks.shop – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
гидроизоляция цена [url=http://www.gidroizolyacziya-czena1.ru]гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
trafficgenerationpro.shop – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Secure your prescription easily and efficiently from the comfort of your home. Buy [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ – retin a online[/URL – today and begin therapy without waiting.
For enhancing your eyelashes, consider trying symbicort online no script , a cost-effective method. This product intends to improve eyelash growth, making them longer.
Browse our site to buy your important heart medication conveniently—https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ .
When considering controlling your heart rhythm issues, looking into [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – could be a viable solution.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting hydroxychloroquine how to buy .
To combat alopecia, consider https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ as an effective solution.
Ready to secure your health essentials at an unbeatable cost? Visit our site for the [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/viagra-25mg/ – uk viagra for sale[/URL – , ensuring you acquire quality medicinal supplies without a hefty price tag.
In need of an antibiotic treatment? Get it easily [URL=https://renog.org/product/doxycycline-generic-pills/ – doxycycline sur ordonnance[/URL – . Available for immediate purchase, ensuring you receive your treatment promptly.
Visit our website to purchase your economical sildenafil , on sale.
To locate treatments for Parkinson’s disease, find out options at https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex/ .
X-plore affordable healthcare options and locate treatments for HIV with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil capsules[/URL – , offering a budget-friendly solution to treat your condition effectively.
X-plore solutions to tackle addiction; buy nizagara .
Discover affordable solutions for hair loss; buy your Finpecia effortlessly https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ .
Maximize your health by acquiring essential medications effortlessly through [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil capsules[/URL – , your trusted source for top-tier pharmaceutical needs.
Всё о камерах видеонаблюдения — полное руководство!
Приветствуем вас, уважаемые форумчане! Сегодня мы подробно поговорим обо всём, что касается видеокамер наблюдения. Мы поможем вам разобраться в огромном разнообразии предложений рынка и сделать правильный выбор оборудования для защиты вашего имущества и безопасности вашей семьи.
Почему важно установить систему видеонаблюдения?
Камеры видеонаблюдения становятся всё популярнее среди владельцев домов, офисов и коммерческих помещений. Они обеспечивают защиту имущества, предотвращают преступления и помогают контролировать происходящее даже дистанционно. Давайте рассмотрим самые важные аспекты выбора камеры и её установки.
Какие бывают виды камер видеонаблюдения?
Вы можете выбрать камеру исходя из ваших потребностей и условий эксплуатации:
– **Уличные** — предназначены для наружной установки, защищены от влаги и пыли.
– **Домашние** — компактные модели для внутренней установки.
– **IP-камеры** — позволяют подключаться к сети Интернет и просматривать записи онлайн.
– **Wi-Fi камеры** — удобны благодаря беспроводному соединению.
– **Камеры с SIM-картой** — работают независимо от интернета, передавая сигнал через мобильную сеть.
– **Миниатюрные камеры** — незаметны и подходят для скрытого наблюдения.
– **Поворотные камеры** — способны охватывать большие площади, поворачиваясь на 360 градусов.
– **Ночные камеры** — оснащены инфракрасной подсветкой для съёмки в темноте.
—
Как правильно выбрать камеру видеонаблюдения?
Перед покупкой обратите внимание на следующие характеристики:
– Разрешение камеры — HD/FullHD/UHD обеспечит чёткое изображение.
– Угол обзора — широкий угол позволяет видеть больше пространства.
– Наличие микрофона и динамика — возможность двусторонней связи.
– Датчик движения — экономия памяти устройства путём включения записи только при обнаружении активности.
– Питание — проверьте совместимость с вашим источником питания.
– Возможность удалённого доступа — управление камерой через смартфон или компьютер.
—
Установка и подключение камеры видеонаблюдения
Правильная установка и настройка камеры позволят вам эффективно пользоваться всеми возможностями системы видеонаблюдения. Рассмотрим ключевые моменты:
– Выберите оптимальное место для размещения камеры, обеспечивающее максимальный обзор охраняемой территории.
– Убедитесь, что камера защищена от погодных воздействий, если устанавливается снаружи здания.
– Настройте Wi-Fi соединение или кабельную линию подключения.
– Установите приложение для просмотра записей и управления камерой через мобильное устройство.
—
Где лучше всего приобрести камеру видеонаблюдения?
При покупке обращайте внимание на проверенные магазины и бренды. Рекомендуем выбирать оборудование известных производителей, предлагающих гарантии качества и поддержку клиентов. Обратите внимание на предложения крупных торговых площадок, таких как Ozon, Wildberries и специализированные магазины электроники.
—
Советы по установке камер видеонаблюдения:
– Изучите правила установки камер видеонаблюдения перед началом монтажа.
– Получите согласие жильцов многоквартирных домов на установку камер в подъездах и местах общего пользования.
– Позаботьтесь о защите личной жизни соседей, устанавливая камеры таким образом, чтобы избежать нарушения частной собственности.
—
Поделитесь своим опытом!
Расскажите нам о вашем опыте покупки и установки камер видеонаблюдения. Может быть, у вас есть советы или рекомендации для новичков? А может, вы столкнулись с проблемами при выборе или настройке оборудования? Оставляйте комментарии ниже, давайте делиться полезными советами вместе!
Автор:
Система видеонаблюдения
*Данная статья носит информационный характер и предназначена исключительно для ознакомительных целей.*
Obtain vital details on [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/product/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – to guarantee you’re getting the optimum deal on your treatment.
Get the latest costs for nizagara without an rx on our website. This eye drop provides effective solution for eye pressure sufferers, ensuring optimal ocular health.
Achieve optimal well-being by managing your condition with trusted treatments. Visit https://charlotteelliottinc.com/priligy-price-at-walmart/ for further details on how we can support you.
Visit our website to find the [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone w not prescription[/URL – . Our platform offers an easy way to purchase your medication on the web.
Zero wait time for your allergy relief; Secure your order tadalafil online instantly and experience comfort by morning.
The need for motion sickness relief is crucial during travel. Now, you can conveniently obtain your https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ , making your journeys comfortable.
Buy your cost-effective [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone 40 best prices[/URL – via our website to ease allergy symptoms efficiently.
Interested in reducing inflammation and allergic reactions? [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil tablet for sale[/URL – flexibly fits your budget. Discover how this remedy can aid you, available to order on the internet.
Looking for an effective way to combat alcohol dependence? Discover how priligy lowest cost can be a vital element in your journey towards sobriety.
Get amazing savings now! Discover incredible price reductions on top-quality health supplements today with our https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ . Don’t miss out on this offer to cut costs on your wellness journey.
X-ray your health options by choosing to buy your necessary medications with ease. Ensure you always have access to your medications, [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone[/URL – online.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Search no more. Get amoxicillin 250mg safely and swiftly.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ .
ремонт подвального помещения gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru .
инъекционная гидроизоляция инъекционная гидроизоляция .
The Buy the pharmacy on website [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – finasteride[/URL – ensures your health needs are met with convenience and efficiency.
Procure your prednisone 10mg effortlessly. Purchase this unique composition through the web, ensuring optimal gratification and convenience.
Explore secure options to buy your medication safely. Click https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ for genuine products.
Quest for affordable heart health solutions? Look no further! Secure your [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – cialis black information[/URL – today and commence your journey towards a better heart with ease.
Keep your health in check without overspending; acquire budget-friendly antiretrovirals. Don’t miss out: [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra cheap[/URL – .
Manage your arrhythmias effectively. Acquire safe and reliable medication. lady era to buy from a reputable online pharmacy.
Unlock the potential to fight against scabies and head lice with a simple click. Order your https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ via our website for reliable treatment.
Just discovered your need for natural constipation relief? Explore the benefits of [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/levitra/ – levitra.com[/URL – , a gentle herbal solution. Learn how you can get this natural remedy today.
Looking to manage your condition without breaking the bank? Discover cost-effective alternatives with [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – .
Zeroing in on effective hair loss solutions? Explore the myriad options available for managing alopecia. lasix could be your answer. With various treatments accessible, it’s essential to select one that matches your specific needs.
Looking to increase your strength? Find https://momsanddadsguide.com/cialis/ on the internet to purchase your answer with ease.
Quickly get your heart medication safely by clicking [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/amoxicillin/ – generic amoxicillin from india[/URL – , ensuring hassle-free delivery directly to your doorstep for a healthier tomorrow.
Yes, to manage your symptoms effectively, you could buy retin a on internet .
I’ve discovered the ultimate solution for managing your eye conditions; https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ . This medicine offers a reliable way to alleviate symptoms with ease.
Zeroing in on your health needs? Discover [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era uk[/URL – and locate your pathway to improved well-being effortlessly.
Protect your health by considering a treatment option widely discussed for certain conditions. Now, acquire where to buy retin a safely and efficiently, backed by scientific discussion and expert guidance to ensure your well-being.
Discover how to reduce your expenses on prostate cancer treatment by exploring the https://renog.org/viagra-75mg/ and compare alternatives.
Various individuals opt to buy their health supplies via the web, with [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ – online lady era no prescription[/URL – being a popular choice among selections.
Zillions now look for answers for improving their stamina. It’s simple to obtain reliable support [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/levitra/ – generic brands of levitra[/URL – .
Aseasonal allergies sufferers can locate relief by buying pharmacy online canada without a prescription , a reliable remedy.
Various methods exist to obtain essential medications, yet finding a reliable source can be a challenge. Considering options to purchase https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ could be a solution for those in need.
You can find [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ – vpxl discount coupons[/URL – on the internet, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, amoxicillin is a viable option. Discover obtaining amoxicillin via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Just released: Secure your supply of https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxicillin-1000mg/ . Obtain this critical medication effortlessly from the comfort of your home.
Discover reliable and discreet options to acquire your medication without complications. Click here: [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/order-viagra/ – viagra to buy[/URL – .
If you’re searching to purchase an cost-effective solution to your vertigo, consider [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ – amoxil pharmacy prices[/URL – . This medication can help in lessening the effects of balance disorders, improving your life quality.
To discover the optimal prices for migraine relief, use this link for cialis black for sale .
Venture into a world of enhanced cognitive health by exploring options to purchase https://momsanddadsguide.com/ventolin-without-a-doctors-prescription/ , a proven solution for addressing dementia symptoms.
X-plore the myriad options to secure your medications affordably; our portal allows you to [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – effortlessly. This opportunity enables clients seeking to purchase their medications at a reduced price.
ремонт стиральной машины город номер https://remont-stiralok-voronezh-ceny.ru/
Rainy City Showcase – Everything loaded quickly, and the well-structured layout made exploring enjoyable.
X-plore your options for hair loss remedies and buy [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/]where to buy finasteride online[/URL] safely.
Discover excellent options for managing your health issue efficiently with cialis . Boost your well-being today.
Explore the advantages of utilizing https://renog.org/cialis-best-price/ for handling your health condition.
Discover how to save on your prescription with affordable [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/]tadalafil capsules for sale[/URL] . Uncover the most reliable sources to get your medication at a lower price.
усиление проема в монолитном доме усиление проема в монолитном доме .
Research the pros of holistic healing approaches with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/]buying amoxil with paypal[/URL] , known for its cardiac wellness properties.
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly; purchase avis levitra en ligne to elevate your wellness through a trusted source.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your personal health needs, https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ virtually can be a simple process.
Given the complexity of managing widespread health problems, finding a reliable source for prescriptions is crucial. That’s why many opt to buy their pharmaceuticals from [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/]amitriptyline without an rx[/URL] , where variety in pharmaceutical solutions is always at your fingertips.
Purchase brand-name alternative Bentyl for digestive relief; discover at [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl tablets[/URL – .
Visit our website to purchase your treatment with ease; purchase strattera online is accessible for prompt delivery.
Just in: Discerning shoppers can now uncover the https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ on the internet, ensuring you get exceptional value for your medical necessities.
Unlock savings on your desmopressin needs with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/nizagara-25mg/ – nizagara[/URL – , your go-to destination. Acquire the necessary therapy online with ease.
Quickly find your prescription at the most affordable rates from names for generic levitra , offering a wide selection of healthcare solutions.
Explore affordable options for your heartburn treatment by checking https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ . Obtain your prescription easily and ease your symptoms efficiently.
Regarding your medical needs, it’s crucial to discover an effective option. For tackling specific health concerns, [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – misoprostol[/URL – stands out as a endorsed choice by healthcare professionals.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive online cialis no prescription . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to cut costs on your medication.
Navigating the complexities of fertility treatment can be daunting; fortunately, options like https://wefenceit.com/pill/tadalafil/ provide a convenient path to obtain necessary pharmaceuticals through the internet.
Uncover the most economical way to manage your health, buy [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/purchase-prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – via our website. This solution offers not just convenience but also savings.
Procure your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara canada[/URL – effortlessly through our platform, ensuring a seamless transaction. This solution is ideal for those seeking reliability without the steep price.
Purchase your prednisone to sustain optimal feminine health easily and economically.
Patients seeking to treat their symptoms can purchase https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia-5mg/ on the web.
If you’re seeking a dependable cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – , available for purchase right here.
Considering controlling your Parkinson’s symptoms? Explore the latest [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – lowest price generic prednisone[/URL – to assist your treatment plan efficiently.
Visit our webpage to find your essential pain relief. Buy prednisone without dr prescription usa online for rapid dispatch.
For individuals looking for relief from Meniere’s disease symptoms, contemplate https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/tadalafil-10mg/ , an effective alternative.
With the rising demand for natural health supplements, [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ – http://www.retin a.com[/URL – emerges as a top choice. Its benefits for vitality are unmatched.
If you’re seeking an reliable treatment for diarrhea, think about [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ – lowest vpxl price usa pharmacies[/URL – .
X-plore your alternatives for enhancing eyelash growth with online lasix 40 mg , available for acquisition on websites.
Finding an unbeatable price for your needs? Look no further than https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ , your go-to source for obtaining this essential medication.
Where to get [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – lasix without a prescription[/URL – continues to be a common query among buyers seeking cost-effective solutions for enhancing their health.
Seeking the best deals for [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – trazodone uk[/URL – ? Uncover unmatched prices and quality now!
Have cholesterol concerns? lasix to control your levels effectively.
Stay informed and ensure optimal health management by visiting https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra-without-a-doctors-prescription/ to gain knowledge about controlling one’s anticoagulation therapy.
Xperience enhanced vitality and wellness with our [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – amoxil uk[/URL – , now available for daily use.
Before deciding, compare the [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil online canada[/URL – , and evaluate costs online to ensure you’re getting the best deal for managing Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Research the trusted sources to purchase parlodel commercial , essential for controlling hypertension and heart-related conditions.
Obtain Clomid at competitive rates; explore the https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/clomid/ now. Numerous couples seeking to boost their chances of conception have found it helpful.
I understand that finding a trusted source to purchase your medication can be challenging. If you’re looking to [URL=https://renog.org/product/retin-a-com-lowest-price/ – retin a[/URL – , make an informed decision. Always ensure that you are engaging with a reputable vendor to safeguard your health.
For allergy sufferers, finding effective relief is key. Discover how prix du amoxil 250 mg can aid with managing your allergic reactions, offering both efficacy and value.
Ensure you procure your https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ without risk for malaria prevention.
Optimize your health with natural solutions at [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis 5mg prezzo in farmacia[/URL – . Discover a path to health with organic remedies.
Zeroing in on fertility treatments? Explore the most trusted options with propranolol best pharmacy . Whether seeking a proven approach for enhancing fertility, countless individuals opt for this option for support.
Discover
Research indicates that finding the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra 10mg[/URL – is vital for patients seeking affordable treatments for their health needs.
To manage your problem effectively, explore the option of cialis from canada as your go-to choice.
Zero hassle to acquire the medication: just visit https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ for a wide range of health solutions!
Browse our website to find your needed medications at an affordable price. Order [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cytotec/ – misoprostol[/URL – today and get fast shipping.
Discover the most economical options for managing your health with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/lasix-100mg/ – lasix canada 100[/URL – . Whether you’re seeking to buy this essential medication online, we provide a comprehensive selection of alternatives to meet your needs.
Opting to purchase your prescription with convenience, prednisone virtually is a dependable choice.
You can obtain https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ with assurance through our site.
The availability of [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ – asthalin hfa inhaler online canada[/URL – ensures that people seeking treatment can without difficulty access crucial medication to tackle their condition online.
best crypto exchange – fast crypto exchange
crypto exchange
https://changenow-crypto.io
best cryptocurrency exchange – instant crypto exchange
changenow
https://changenow-io.us
crypto exchange without KYC
changenow exchange
https://changenow-crypto.io
Your search for affordable, high-quality cognitive enhancers ends here; [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – buy retin a w not prescription[/URL – offers unparalleled value. Explore purchasing options for improving your memory and concentration without breaking the bank.
Discover how to get your prescriptions easily with viagra 50mg , ensuring discretion and ease.
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can obtain erectile dysfunction medication via the web at https://myrsvplive.com/viagra-pills/ , ensuring discretion and ease.
Considering various treatment options for OCD? Explore the benefits of [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy from india[/URL – and find out how it can assist in managing your symptoms effectively.
Нужно было изготовить каталоги услуг, и компания справилась идеально. Верстка аккуратная, текст читаемый, фото напечатаны четко и без зернистости. Бумага плотная, обложка выглядит профессионально. Все было упаковано надежно, каталоги доставили без повреждений. Отдельно отмечу оперативность в согласовании макетов. Будем обращаться снова: заказать методички
Just spotted a fantastic deal! For those seeking heart health solutions, now’s your chance to cut costs on your treatment. Discover substantial discounts on your next purchase by clicking here: [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/buy-propecia-uk/ – propecia 5mg[/URL – . Don’t miss out on this offer to enhance your wellness affordably.
Zero in on boosting your overall wellbeing with nizagara without dr prescription , offering a holistic path to boosting vitality.
Browse our website to discover the https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ , ensuring you receive the best deals on your healthcare needs.
Unlock exclusive savings with our [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – cheap lasix pills[/URL – and elevate your lifestyle today.
Visit our site to order [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/lasix/ – cheap 40 lasix online[/URL – , offering quick shipping.
Explore cost-effective fertility solutions; order tadalafil online . Discover the budget-friendly cost at Walmart, ensuring everyone gets the chance for parenthood.
You can purchase safe and effective nausea relief with https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ , accessible online.
For those looking to acquire their heart health medication digitally, finding a dependable source is key. [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ – lowest price generic pharmacy[/URL – offers a safe option for procuring your treatment with ease.
Having difficulty managing your cravings for alcohol? Consider [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – finasteride cheap[/URL – as a promising solution. This option could help in maintaining abstinence and facilitating recovery from alcohol dependence.
Keeping your cholesterol levels in check is crucial for heart health. generic cipro in canada can be your first step. You can obtain the medication online.
Discover secure and straightforward ways to purchase your prescriptions with our dependable https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ option.
X-plore options for handling your health by deciding to order [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix-for-sale/ – lasix price[/URL – , a treatment relied upon by many.
Research meldonium for sale overnight for effective baldness solutions.
Zipping through the myriad options for purchasing your medications, https://renog.org/levitra-generic-canada/ stands out as a prime choice to order your medical necessities.
Ensure you purchase your [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/nexium/ – nexium generico italia[/URL – through a secure platform.
Get your libido boosted with confidence. Buy ventolin inhaler without dr prescription usa to feel revitalized closeness.
Obtain your https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ effortlessly. Order the critical skin care solution with ease.
Given the unpredictable nature of weather patterns, securing your property against inundations has never been more crucial. Explore options to safeguard your home with a [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone 10 wholesale[/URL – , offering a wide range of strategies to combat water damage.
Visit our website to order your prednisone.com . Secure your drug effortlessly.
New to the market? Discover your pathway to a healthier lifestyle with https://markssmokeshop.com/item/kamagra/ . Acquire this advanced product instantly for your medical needs.
Need to treat your hypothyroidism? Visit [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/pristiq/ – buy cheap pristiq[/URL – to learn how you can regulate your hormone levels efficiently.
Here’s how to find the most up-to-date [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – free online herbal-max-gun-power[/URL – to preserve on your medication.
Navigating through numerous sources to acquire your medications can be challenging, but our nizagara online uk simplifies the process, offering reliable and budget-friendly options for your healthcare needs.
Questioning where to acquire fertility treatments? Order your https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ effortlessly on the web.
I recommend exploring various options for allergy relief; consider [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ – isotretinoin[/URL – as a viable solution.
Unsure where to acquire effective migraine solutions? Visit generic pharmacy for a proven option.
Considering the need for dependable solutions for treating erectile dysfunction, it’s vital to find a reliable source. https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra/ provides an accessible way to acquire your medication securely.
Find a way to acquire [URL=https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ – how to stop symbicort[/URL – safely.
Discover safe and simple ways to acquire your prescriptions with our reliable [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/sildenafil/ – canadian viagra[/URL – option.
Visit our cheapest retin a dosage price page to purchase trusted heartburn relief. Easily buy your remedy from home.
Discover stress-relief options with https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ , your go-to for next-day shipping.
Discover trustworthy ways to purchase [URL=https://renog.org/lowest-pharmacy-prices/ – pharmacy[/URL – , ensuring you’re provided with top-notch care.
A Revolutionary Approach to Well-being is Here! Now, discover an extensive selection of health solutions solely at [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – .
Understanding your health requirements can often lead to confusion and worries. If you’re seeking alternatives for managing your condition, consider exploring generic pharmacy canada pharmacy . This method could possibly offer a new path to better health.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover exclusive https://transylvaniacare.org/product/ed-sample-pack-2/ for discounts on crucial treatments. Acquire yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
You can acquire Fildena for your erectile dysfunction needs here: [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ – fildena brazil[/URL – .
However, seeking an effective solution for hypertension? [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ – online prednisone[/URL – may be your best selection.
Find unbeatable deals on france tadalafil generique to improve your vitality.
Zero in on eye health with the ultimate solution in eye drops: https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ . Explore a groundbreaking option for managing eye inflammation effortlessly.
In need of an antibiotic treatment? Get your prescription easily [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ – generic doxycycline in canada[/URL – . Available online, ensuring you have access to your treatment swiftly.
Your search for effective and safe medication ends here; [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – buy sildalis without prescription[/URL – offers you the opportunity to acquire top-quality medication conveniently.
Acquire your hydroxychloroquine without dr prescription prescription easily from reputable online pharmacies. Save time and obtain your treatment with convenience and privacy.
“Quickly acquire your pharmaceuticals effortlessly with https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ , the most dependable way to order your wellness needs online.”
When looking to purchase heart health medications, consider options to [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix buy online overnight ship[/URL – through digital pharmacies, offering a budget-friendly solution without compromising on quality and efficacy.
X-ray your health and wellness options by seeking out lasix online . Whether you’re looking to acquire health aids virtually, this option provides a reliable path to maintaining your well-being.
Get your amoxil easily from https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ , providing swift shipping to satisfy your requirements.
Get relief from seizure disorders now. Discover more at [URL=https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ – overnight viagra soft tabs[/URL – .
DiscoverEndlessGrowth – Positive vibe throughout, pages load fast and browsing experience feels smooth.
Secure your health with ease; purchase [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – for your heart needs on the web.
In search of affordable heart remedies? Look no further! Purchase your lasix price now.
If you’re seeking a proven cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ , available for buying right here.
Explore ways to obtain [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – cheap nizagara online[/URL – , a key treatment for treating Parkinson’s disease, easily on our website.
Discover budget-friendly options for managing your health: [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra/ – levitra generic pills[/URL – . Get your treatment with ease and start your path to better wellbeing without delay.
Having trouble locating Flagyl? Seek no more. Acquire it safely and quickly from nizagara coupon , where your well-being and contentment are our top priority.
Zero in on choices for male pattern hair loss by choosing to buy https://wefenceit.com/pill/ventolin/ today.
Zero hesitation required when seeking ED solutions; order [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/viagra/ – viagra brand[/URL – conveniently.
Order your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – finasteride 5mg[/URL – effortlessly. Secure the best deal through our platform today for effortless access.
You can secure your chloroquine dallas no prescription online effortlessly online, ensuring you keep up with your health effortlessly and effectively.
Your well-being matters, so choose safe and budget-friendly solutions. Find your option for https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ at this moment and sustain your well lifestyle with simplicity.
Considering the need for dependable methods for ED management, it’s crucial to discover a reliable source. [URL=https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – viagra prices[/URL – presents an accessible way to acquire your medication safely.
I have used many gambling platforms over the years, and it’s interesting how many players join a site without reading any reviews. In case you want a clear overview of promos, withdrawals, and available games, this overview was really helpful: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s easy to understand and shows what matters most before making a deposit. I recommend giving it a look if you want to make better choices.
Just learned you can order your stomach cramps treatment online? [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ – bentyl overnight[/URL – offers a variety of options for your healthcare needs.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing dapoxetine 60mg today. Whether you’re aiming to boost your wellness effortlessly, our site offers a simple pathway to get your essentials.
Visit https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/doxycycline/ to secure your medication without hassle.
DiscoverAmazingDeals – Loved the variety of offers, browsing was smooth and effortless today.
For those in search of effective treatment for their rheumatoid arthritis, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – cheap order lasix[/URL – offers a dependable solution.
Visit generic prednisone canada pharmacy and discover a trusted way to acquire your medication via the internet.
X-plore eye care with cutting-edge solutions. Buy https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ on the web for treating glaucoma effectively.
Acquire generic [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – buy online pill lasix[/URL – via web for chemotherapy.
Yes, securing your prescription has never been easier. Find competitive [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – purchasing 100 mg trazodone on line[/URL – effortlessly. Order now for a smoother, hassle-free experience in managing your health needs.
X-plore the myriad benefits of buy prednisone online united states , your go-to solution for controlling OCD symptoms. Now you can seamlessly purchase this vital medication via our reliable platform.
Explore various options to purchase affordable https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ for gastrointestinal aid.
Relieve your BPH symptoms today! Explore our selection of [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – , specially designed to boost your urination and overall health.
Manage osteoporosis effectively by choosing to [URL=https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – . With options abundant, you can purchase this bone health medication online.
Many are looking for effective treatments; discover safe options and secure cialis .
Consult your healthcare provider to get the most suitable treatment options. For those considering cost-effective solutions, https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ is a consideration.
Visit our platform to purchase your [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – conveniently and with confidence.
Need a boost in the bedroom without a doctor’s prescription? Explore our [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – – the ultimate solution for those looking to enhance performance. Find the simplicity of purchasing powerful aids online.
Boost your hair growth journey with lasix online san marino , the ultimate solution for those struggling with hair loss. Enhance your confidence by tackling thinning hair directly.
Overcoming thinning hair is now simpler than ever with groundbreaking solutions available. Whether you’re looking to regenerate your hair’s vitality, there’s a solution for you. Discover how to fight hair loss effectively with https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ , offering a cost-effective and efficient approach to regaining fuller hair.
LivingTreasure – Items are well-presented and browsing felt comfortable.
Our experts provide an extensive guide to obtaining [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ – levitra[/URL – , ensuring you secure unmatched value for your treatment.
X-ray your options and discover the best deals on hypertension treatment when you purchase cheapest lady era dosage price online.
Explore the latest advancements in schizophrenia treatment with https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ . Procure this innovative therapy through our digital platform.
Secure your health easily; buy [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone[/URL – , available on site for enhancing female libido.
Discover a hassle-free way to obtain your medication with [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – , ensuring discretion and convenience in ordering.
Zero hassle to secure your digestive wellness solutions with levitra rezeptfrei in deutschland .
For healthcare practitioners seeking to enhance their expertise, look into enrolling in https://kristinbwright.com/buy-retin-a-online-cheap/ courses available via the internet.
Zap your health woes away! Unearth affordable options with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/buy-retin-a-online-cheap/ – retin a in usa[/URL – . Embrace a healthier way of living today.
Optimize your heart health regimen by exploring [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – , an essential option for those aiming to manage their stroke prevention strategy effectively. With a wide array of choices, purchasing an important medication through the web has never been easier, ensuring that maintaining your cardiovascular well-being is both accessible and convenient.
Acquire pharmacy order mail effortlessly. Obtain this essential medication online to ease your eye problems.
Discover the benefits of https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ for enhancing fertility. Purchase today and experience increased chances of pregnancy.
View the current [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy prescrition online[/URL – to control your epilepsy in a cost-effective manner.
Zero hassle to fetch your pharmaceutical needs for enhanced endurance, click here: [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – 50mm viagra to purchase[/URL – .
Quality and affordability converge with our generic erythromycin options. Secure your health’s future by purchasing at the lowest price sildalist today.
Before making any decisions, explore your options for treating hair loss. https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nizagara-on-internet/ offers a straightforward way to gain access to this treatment.
Venture into the realm of healthcare by buying your pharmacy needs online. Discover [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – prednisone coupons[/URL – for a cost-effective solution to your medical requirements.
Looking to boost your performance? Discover trusted options and purchase viagra 100mg —your solution to overcoming erectile dysfunction.
Our team has sourced the https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
A range of options to acquire antimalarial treatment online is now available. For those seeking protection or treatment, [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – discount chloroquine[/URL – offer a practical solution.
Optimize your health and budget by choosing to buy your drugs online. Discover the most affordable [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ – generic priligy from canada[/URL – , ensuring you receive top-quality care without overspending.
Seeking the most economical option for your hair care? Look no further! Browse our selection for the viagra . Whether you choose to purchase your hair oil, rest assured of finding unmatched deals with us.
With increasing interest in herbal supplements for wellness, explore your options and buy https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ for enhanced vitality and health maintenance.
Keep your ulcerative colitis in check with easy, hassle-free ordering process. [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – propecia without a doctors prescription[/URL – is your go-to for controlling symptoms effectively.
Get your treatment easily with [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – tinidazole canada free sample[/URL – , available online for quick needs.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with tadalafil without prescription , your go-to source for acquiring effective ED remedies virtually.
Explore purchasing https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ with convenience for reliable remedy.
Research shows that finding the [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – may be essential for individuals seeking cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
Exploring cost-effective options? Discover affordable healthcare solutions with [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – . Secure your purchase now for premium health benefits.
Looking to control your health needs discreetly? Buy your supply of essential medication without any hassle. Just click on viagra texas to start your journey towards improved wellbeing easily on the web.
Quality medication are just a click away; check out our range and secure your https://momsanddadsguide.com/kamagra/ with complete peace of mind.
Having difficulty with an enlarged prostate? Discover how [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex/ – nolvadex online shopping hk[/URL – can help and restore your well-being.
Explore the benefits and options for treating Alzheimer’s with tadalafil , a venerated solution in managing cognitive decline. Obtain this medication from reputable sources to potentially improve quality of life for those affected.
Knowing your options for managing vertigo is crucial; explore https://momsanddadsguide.com/retin-a-overnight/ to uncover how it can assist you.
X-plore your options for mountain sickness aid with simplicity. Now acquire [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ – order retin a[/URL – , your preferred treatment for mountaineering adventures.
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable human immunodeficiency virus testing solution. Buy your [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – today and confirm your status efficiently from the comfort of your home.”
Rediscover vigor through our cost-effective priligy , the ultimate solution to improve your lifestyle.
Necessitating a reliable solution for diuretic needs? Discover https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ , your go-to solution for controlling edema.
Beat motion sickness economically with our easy solution. Purchase [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-75mg/ – viagra online[/URL – online to enjoy quick relief.
Xperience seamless relief from motion sickness with our top-rated solution. Discover [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ – lady era[/URL – and embark on your journeys with confidence.
Research indicates that levitra no prescription vary widely, prompting patients to review options before making a purchase.
Experiencing allergic reactions? Locate relief by opting for to purchase https://momsanddadsguide.com/kamagra/ . This efficient solution is obtainable for individuals seeking relief.
Discover your path to enhanced well-being; secure extra super avana from the comfort of your home [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – buy extra super avana w not prescription[/URL – .
Ensure you buy your durable batteries at unmatched prices. Explore [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – safe buy tadalafil online[/URL – for high-grade options.
Options for managing hair loss have never been more accessible; explore how lasix canada 40 mg offers a economical solution. Buy now to begin your journey towards renewal.
Navigate our online pharmacy to acquire your https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ with absolute ease and convenience.
Looking to purchase your medications with no significant price tag? Consider exploring options like [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil generic us[/URL – , a cost-effective solution for boosting your health and well-being.
X-ray your options for HIV management by exploring affordable solutions. Discover [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – to combine efficacy with economy.
Opting for affordable healthcare solutions can be a challenge, yet levitra 20mg offers a seamless way to acquire necessary treatment effortlessly.
Discover safe and easy ways to buy your pain relief solutions. With our comprehensive selection, you can find https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ effortlessly.
Visit our online store to find the best [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia online pharmacy[/URL – available.
Procure your acid reflux treatment without exiting your home; click on prednisone 10 mg with no perscripstion for quick relief.
Considering your health needs, you can purchase prescriptions safely and conveniently https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ , ensuring privacy and expediency in delivery.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin generic[/URL – , and Snag your course of essential antibiotics effortlessly online.
Given the myriad ways to manage and enhance your wellness journey, [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – stands out as a premier choice. Whether you’re seeking to purchase nutritional supports online, it’s essential to select products that align with your health objectives.
Visit our website to order your lasix.com lowest price easily and quickly.
Aches and pains troubling you? Discover relief by https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ , a effective treatment for easing inflammation and pain.
A crucial treatment for managing fluid retention is available here: [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ – levitra to buy[/URL – . Whether you’re battling heart conditions, kidney issues, or liver disease, consider investigating this option.
Facing an unexpected situation? Locate affordable solutions online with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ – generic prednisone in canada[/URL – , ensuring safety and peace of mind.
Just uncovered an incredible way to boost your well-being pharmacy on internet , ideal for those seeking reliable and efficient solutions.
Discover the latest prices for managing your menstrual irregularities and endometriosis with https://kristinbwright.com/product/generic-priligy-at-walmart/ , and find out how it can help you lead a healthier life.
Find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://center4family.com/strattera/ – divide strattera capsules[/URL – to improve your wellness.
Uncover the ultimate way to enhance your wellbeing; find our premier [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/priligy-price-at-walmart/ – discount priligy[/URL – . This solution is perfect for those seeking to improve their lifestyle efficiently.
Looking to obtain your antiviral treatment? Now, you can order lasix on line online.
Find unbeatable deals on https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ to boost your vitality.
Dealing with diarrhea? Find fast relief by picking [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – generic tamoxifen canada[/URL – .
Quickly obtain your allergy relief by choosing to purchase [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara generic canada[/URL – .
You can discover propecia bad on the internet, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Quickly find out the most competitive https://phovillages.com/xenical/ via our website.
DiscoverEndlessGrowth – Positive vibe throughout, pages load fast and browsing experience feels smooth.
Optimize your wellness journey with our versatile [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cialis-5mg/]buying cialis online[/URL] , designed for your unique needs. Obtain
Need a convenient and discreet way to purchase your medication? tretinoin cream 0.05 could be the solution you’re looking for.
Zero in on managing your health efficiently: https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ to ensure a better lifestyle.
Discover affordable solutions for managing your health with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/]tadapox distributors canada[/URL] . Secure your essential medication today.
Your quest for reliable anxiety relief ends here with [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone information[/URL – . Purchase the medication from our website now.
Discover a hassle-free way to acquire your treatment with lasix 100 mg brand name , ensuring discretion and comfort in buying.
Maximize your savings on stroke prevention medication by checking https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ , where you can uncover competitive costs.
Discover how to significantly improve your sleep quality with [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil information[/URL – , your preferred solution for an undisturbed slumber.
Visit amoxicillin to purchase your medication online at incredible prices.
If you’re looking for an effective solution to fight bacterial infections, ponder https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxil-on-internet/ . This antibiotic is well-known for its potency against a wide array of bacteria.
For those seeking to purchase [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – discount nizagara[/URL – without hurting their wallet, various online pharmacies offer economical costs.
Zealously seeking a trusted source to acquire your prescriptions from? Look no further; [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – offers a secure, discreet way to obtain what you need.
Secure your antiviral medication effortlessly through our platform when you order best price vpxl .
Visit https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nizagara/ today and discover affordable solutions for managing your pain.
Jumpstart your healthcare journey by [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – , an essential therapy for managing HIV efficiently.
Get your skin treatment without leaving home, order isotretinoin online.
Keeping allergies at bay is now easier than ever. Whether you’re looking to fight against seasonal sniffles or seeking relief from year-round triggers, you can acquire effective antihistamines quickly. https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ offers a reliable solution, making it straightforward to buy your essentials from the comfort of home.
Rediscover energy through our cost-effective [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – generic for super kamagra[/URL – , the best solution to improve your well-being.
DiscoverAmazingDeals – Deals updated nicely, navigation intuitive and browsing experience felt pleasant overall.
For those seeking relief from gastrointestinal discomfort, securing [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – cheap tadalafil[/URL – could be a feasible solution.
Visit doxycycline today to acquire your necessary medications. Offering a vast selection of pharmaceuticals, it’s your go-to portal for all your medical needs.
Knowing your options for fertility treatment is crucial, and buying https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ can be a affordable solution.
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your eyelashes? Discover the benefits of [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ – generic malegra uk[/URL – , a cost-effective, widely trusted alternative. Whether you’re aiming to boost lash volume, our product provides safe results.
Unlock savings on your hypertension treatment by visiting [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – vidalista drug name[/URL – , your gateway to cost-effective medication.
Discover new ways to manage stress with http://www.lasix.com , accessible on the web.
Yes, facing diarrhea can be troublesome. Discover relief swiftly by clicking here: https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ . Whether you’re in urgent need, secure your remedy immediately.
Boost your wellness with natural supplements; order your [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin cream[/URL – directly for optimal health benefits.
Understand your options for treating vertigo; explore [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix[/URL – as a powerful solution. Purchase it today for relief from ongoing dizziness.
Protect your health by educating yourself on the most recent wellness advice and trends at our buy amitriptyline online canada webpage.
Obtain your potency solution effortlessly today. https://myrsvplive.com/propecia/ offers a prompt and dependable solution for those seeking improved stamina.
Uncover the optimal outcomes with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ – low price amoxil[/URL – for managing eye inflammation. Obtain solace and improve your vision quality by integrating this treatment into your daily care routine.
X-plore the myriad benefits of [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cytotec/ – buy cytotec cheap 100[/URL – , your go-to solution for tackling OCD symptoms. Now you can seamlessly obtain this vital medication by means of our trusted service.
Explore the options and obtain the prescription with convenience at cytotec for sale overnight .
Quality education is pivotal, and mastering the art of persuasion can be significantly improved by reading https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/lasix-100mg/ . This method not only sharpens your composition skills but also expands your understanding of various viewpoints.
Visit [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cytotec/ – cytotec without dr prescription usa[/URL – for comprehensive insights on utilizing this medicine responsibly.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф обеспечивает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – ваш лучший выбор.
Наши товары:
Дюралевый швеллер 440455 70х198х10х10х10 мм Д1 ГОСТ 4784-97 Купить дюралевый швеллер от производителя. Прочный и легкий материал для различных областей строительства. Широкий выбор размеров и профилей. Устойчивость к коррозии и надежность конструкций. Идеальное решение для авиации, судостроения, автомобилестроения, производства спортивного оборудования и фармакологических предприятий.
Perfektni prispevek! Zkousel jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a jejich sluzby me opravdu nadchly. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere bavi vsechny hrace. Me nejvice bavi herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske online casino na opravdu vysoke urovni. Pokud hledate bezpecne online casino s bonusy, podivejte se zde: Twitter . Stoji to za vyzkouseni a prinese to spoustu herni zabavy a odmen.
Uvitaci bonusy a VIP program ve Spinmama Casino CZ
Objevte Spinmama Ca
Objevte Spinmama Casino CZ a ziskejte free spiny
3b3f09d
Quest for budget-friendly ED solutions? Uncover the remedy at [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/fildena/ – purchase fildena without a prescription[/URL – , offering a vast range of high-quality options.
Concerned about maintaining ideal testosterone levels? Explore the ease of balancing hormones with buy priligy in australia online with fast delivery . Ensure your health today.
Keep informed on hydroxychloroquine benefits and guidelines by visiting https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ for thorough insights and updates.
To find out the most up-to-date [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – cost of sarafem tablets[/URL – , visit our site. Here, you can effortlessly obtain comprehensive information on costs and stock levels.
Acquire your essential medication hassle-free; [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ – clomid 25mg[/URL – for managing your health needs. Easily obtain your vital prescription through our website.
Searching for affordable ulcer treatment options? Discover the best deals on on line retin a , your go-to remedy for relieving gastrointestinal discomfort.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your ailment efficiently with https://momsanddadsguide.com/prednisone/ . Boost your well-being today.
Battling dizziness or nausea? [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel on internet[/URL – today to Alleviate your symptoms quickly and effectively.
Quickly and conveniently purchase your antiviral medications [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ – order nizagara[/URL – .
Quality and affordability converge with our off-brand erythromycin options. Secure your health’s future by acquiring at the order prednisone today.
Reduce your gout-causing uric acid levels effortlessly with the optimal https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ . Control gout attacks easily and retain better health.
I discovered the [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – after searching the internet.
Quest for reliable malaria treatment leads to the discovery of [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ – price of finasteride in mexico[/URL – , an groundbreaking option available via the web.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, amoxicillin generic is a viable option. Consider purchasing amoxicillin via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Acquiring https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ has never been simpler. Secure your route to wellness by utilizing a reliable option.
The quest for affordable hair loss solutions leads many to consider [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – prednisone online usa[/URL – , offering comparable benefits at lower costs.
Ready to find out the most affordable choices for your antifungal needs? Search no more. Discover the [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – prednisone online pharmacy[/URL – and ensure your health today without breaking the bank.
Yearning for an affordable solution to manage eye inflammation? Look no further! Find the priligy here to reduce your symptoms efficiently.
Discover unbeatable savings on your medical essentials. Secure the https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ and support your heart health without hassle.
Discover your path to discounts on medications by choosing to purchase from [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ – alternatives to prednisone[/URL – . Experience cost-effective healthcare today.
Various medical professionals recommend seeking advice on lasix for gastrointestinal discomfort to guarantee safe and effective relief.
Get your daily dose of wellness with a simple click; https://hip-hope.com/online-generic-priligy/ offers easy access to natural health support directly to your doorstep.
Many are looking for effective treatments for ED, and [URL=https://renog.org/product/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis 20 mg precio[/URL – provides a credible option.
Looking to treat your condition effectively? Explore how to acquire [URL=https://nesttd-online.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara coupon[/URL – and begin your journey towards better health today.
To find out the latest generic priligy from india , check out our website. Here, you can effortlessly get comprehensive information on rates and stock levels.
Struggling with thinning tresses? Find your solution with https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ . This cream offers a cutting-edge approach to restoring your locks, providing visible results.
Our team has sourced the [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – nizagara 25mg[/URL – for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
Regarding dementia treatments, exploring options for medication is crucial. For those considering Donepezil, [URL=https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – offers multiple choices.
Browse our site to find amoxil 650mg , ensuring you get high-quality antibiotic options at unbeatable prices.
Visit https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ to secure your prescription without hassle.
Procure your treatment with ease; [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ – cialis[/URL – online to manage your needs efficiently and securely.
Zero hassle: acquire your [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra/ – levitra cheap[/URL – with ease.
Unlock immediate relief for your digestive disturbances by choosing to order reliable buy nolvadex europe , a proven solution for stomach discomfort.
Zero worries about aging signs with https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra/ , as you purchase a way to revitalized vibrance.
Zero in on unparalleled deals for your health needs; uncover unrivaled offers on [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – price of lisinopril[/URL – now.
Finding affordable solutions for enhancing eyelash growth just got easier. Visit best and quickest retin-a online today to discover your options for purchasing quality yet affordable treatments.
Explore options to buy https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cytotec/ on the internet, ensuring you secure the least expensive bargain for your cardiovascular wellbeing.
When seeking relief from pain, consider [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/vidalista-ct/ – vidalista ct without a prescription[/URL – as a potent solution. This anti-inflammatory agent is perfect for treating numerous conditions, giving both affordability and effectiveness.
Having issues with hypertension or angina? Find your relief safely and effectively by exploring [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – kamagra[/URL – . Secure your health right away with this treatment.
Enhance your well-being effortlessly by choosing to purchase sildenafil —a vital step towards rejuvenation.
Explore cost-effective fertility solutions; https://nabba-us.com/product/amoxicillin-250mg/ . Discover the affordable price at Walmart, ensuring everyone attains the chance for a new beginning.
Visit our platform to order [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ – lowest eriacta prices[/URL – , ensuring affordable options for your well-being.
The demand for trustworthy and easy access to drugs has never been greater. Find your options and acquire [URL=https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – generic viagra overnight delivery 25[/URL – now.
Zero in on holistic wellness with a natural boost. Explore our selection of herbal supplements and purchase quality kamagra to support your brain health and improve memory naturally.
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before attempting to obtain https://nikonphotorecovery.com/flagyl/ cannot be overstated.
X-plore the advantages of managing gout with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/kamagra/ – generic kamagra uk[/URL – , and uncover how you can acquire this treatment via the web.
Quiet nights can often be disturbed by restless legs, a common ailment affecting many. To combat this, trusted solutions like [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ – torsemide without a prescription[/URL – can be invaluable. If you’re seeking relief, contemplate obtaining this solution online.
Purchase your etizolam securely from prednisone to ensure serenity without exceeding your budget.
You can obtain the https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ via the web, providing a easy way to handle high blood pressure.
Regain your vigor! Explore the benefits of hormone therapy with confidence by opting to [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine without dr prescription usa[/URL – .
Secure your [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – prednisone 40 mg price[/URL – effortlessly. Purchase the medicine through the internet with just a few clicks.
To ensure you’re getting your heart medication without overspending, always search for the prednisone without an rx on reputable pharmacological platforms.
Zipping through the hassle of securing your medication, our platform offers an effortless method for those looking to obtain https://kristinbwright.com/nizagara/ with no hassle.
The ordering of [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/zithromax/ – generic zithromax tablets[/URL – is more straightforward with our online pharmacy. Ensure your supply of this crucial medicine today.
Order your treatment easily; acquire [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/flagyl/ – flagyl[/URL – from accredited sources.
Exploring options for acquiring canadian pharmacy vidalista ? Find out how to get your prescription without hassle via the internet.
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra-price-walmart/ is your gateway to economical healthcare.
услуга усиления проема https://www.usilenie-proemov2.ru .
Purchase your necessary antiviral conveniently through [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , a method ensuring speedy delivery and confidentiality.
Yes, experiencing diarrhea can be troublesome. Find relief fast by clicking here: cheapest fildena . Whether rapid results are needed, get your solution at once.
Discover ways to save your prescriptions by exploring the https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cialis-online/ , ensuring you receive your medications at the lowest price.
+++++++++++++++++++
Иконописная мастерская “СЕМЕЙНАЯ рукописная ИКОНА” работает при Храме Свт. Митрофана епископа Воронежского, г. Москва.
В нашей мастерской иконы пишутся в древнерусской технике, с соблюдением православных канонов. Любая икона пишется индивидуально!
Подбирается основа, цветовая гамма – это натуральные пигменты и минералы: малахит, диоптаз и другие.
Выбирается наилучший вариант золочения.
Наши услуги:
– Каталог икон
– ПОДАРКИ на ПАСХУ
– ПОДАРКИ на РОЖДЕСТВО
– ПОДАРОК на Новый Год и РОЖДЕСТВО
Ваша личная скидка по коду KHGJ2025 – 9%
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Иконописная мастерская “СЕМЕЙНАЯ рукописная ИКОНА” работает при Храме Свт. Митрофана епископа Воронежского, г. Москва.
В нашей мастерской иконы создаются в древнерусской технике, с соблюдением православных канонов. Любая икона пишется индивидуально!
Подбирается доска, цветовая гамма – это натуральные пигменты и минералы: малахит, диоптаз и другие.
Выбирается оптимальный вариант золочения.
Мы предлагаем:
– Каталог икон: https://familyicon.ru/ikony
– ПОДАРКИ на ПАСХУ: https://familyicon.ru/podarki/na-pashu
– ПОДАРКИ на РОЖДЕСТВО: https://familyicon.ru/podarki/na-rozhdestvo
– ПОДАРОК на Новый Год и РОЖДЕСТВО: https://familyicon.ru/podarki/na-rozhdestvo/podarok-na-novyj-god-i-rozhdestvo-8
Ваша персональная скидка по коду KHGJ2025 – 7%
====================================================================================================================
InflationВ : Meaninig, Types and Causes – Economicjourney – отличный сайт
Меня заинтересовала тема “”, но я там не могу ответить.
Moderator, просьба воздержаться от комментариев моего сообщения 🙂
– я поняла, вот что нашла:
Иконописная мастерская “СЕМЕЙНАЯ рукописная ИКОНА” работает при Храме Свт. Митрофана епископа Воронежского, г. Москва.
В нашей мастерской иконы пишутся в древнерусской технике, с соблюдением православных канонов. Каждая икона пишется индивидуально! Подбирается основа, цветовая гамма – это натуральные пигменты и минералы: малахит, диоптаз и другие. Выбирается наилучший вариант золочения.6
Наши услуги:
– Каталог икон: https://familyicon.ru/ikony
– ПОДАРКИ на РОЖДЕСТВО в Санкт Петербурге: https://familyicon.ru/podarki/na-rozhdestvo
– ПОДАРКИ на ПАСХУ: https://familyicon.ru/podarki/na-pashu
– ПОДАРОК на Новый Год и РОЖДЕСТВО в Санкт Петербурге 2: https://familyicon.ru/podarki/na-rozhdestvo/podarok-na-novyj-god-i-rozhdestvo-8
– Каталог икон в Санкт Петербурге3: https://familyicon.ru/ikony
Ваша личная скидка по коду HYBN2022 – 7%
Research the current [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/]retin a on internet[/URL] to buy your medication on the web efficiently and effortlessly.
Revitalize your health by exploring a wide spectrum of pharmaceutical options. Enhance your well-being by exploring an extensive selection of healthcare solutions. Don’t compromise on your health; discover everything you need at generic propecia 1mg price .
Need to discover real Canadian pharmacy choices? Your hunt ends here at https://momsanddadsguide.com/zithromax/ , providing entry to licensed pharmaceuticals.
Zest for life can be boosted with reliable cardiovascular care. Check [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/viagra/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – to discover how you can manage your heart health affordably.
Discover how to purchase essential medications conveniently; follow buying amoxil with paypal to explore a vast range of pharmaceutical solutions tailored to your needs.
Quest for the lowest rates on Erythromycin? https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ has unbeatable prices for you.
For healthcare specialists seeking to enhance their skills, consider enrolling in [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/online-generic-pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy pharmacy[/URL – classes provided via the internet.
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax/ – zithromax[/URL – ? Explore
Many are looking for trustworthy treatments for erectile dysfunction, and cialis best price provides a tested option.
Zest for life can be elevated with effective cardiovascular care. Check https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ to discover how you can control your heart health affordably.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://renog.org/cialis-best-price/ – buying cialis online[/URL – . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to save on your medication.
Secure your wellness journey with a click by opting to purchase your prescription via our website at [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – buy retin a w not prescription[/URL – , ensuring hassle-free access to health.
Discover economical solutions for managing your health with cialis black for sale . Find your essential medication at this moment.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for purchase with no wait at https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra/ .
Unlock unbeatable deals on [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ – buying tadalafil online[/URL – , Preorder your solution right away.
Zeroing in on your health needs? Discover propecia and locate your pathway to better well-being without the hassle.
Acquiring https://wefenceit.com/pill/propecia/ has never been more straightforward. Now, you can purchase your medicine online without the requirement of a prior prescription.
I find all my healthcare necessities with ease at [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/buy-propecia-uk/ – buy propecia uk[/URL – , offering a wide selection of medications.
Your search for effective hair loss solutions ends here with [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/meldonium/ – meldonium in usa[/URL – . Explore the advantages of this powerful treatment for male pattern baldness now.
Given the myriad ways to manage and enhance your wellness journey, xenical 60mg stands out as a premier choice. Whether you’re seeking to obtain health supplements online, it’s essential to select products that align with your health objectives.
To acquire real Etibest quickly, go to https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ today for secure buying options.
Looking for an affordable way to manage your allergies? Discover how you can cut costs on your treatment with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra/ – levitra online in india[/URL – .
Affordable healthcare is now accessible, buy your health supplements online with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix coupon[/URL – .
Zero in on health improvements; acquire the nolvadex without an rx treatment easily for enhanced wellness.
Obtaining https://nikonphotorecovery.com/lasix-100mg/ has never been easier. Now, patients can acquire their required treatment with just a few clicks.
X-plore your options for alleviating eye discomfort with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/lasix-100mg/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – . Discover solace for your eyes without the need for a prescription.
Acquiring [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ – cialis medicament[/URL – has never been simpler. Order your prescription conveniently via our website.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for acquisition with no wait at kamagra cheap .
Your quest for reliable arrhythmia treatment ends today. Explore our broad assortment of heart medications, including https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ , offered on our site.
Your search for enhanced vitality ends here; order [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – online for unsurpassed efficacy.
где можно заказать курсовую http://kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru/ .
срочно курсовая работа http://kupit-kursovuyu-23.ru/ .
купить курсовая работа kupit-kursovuyu-22.ru .
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 650mg[/URL – is a viable option. Discover securing this antibiotic online for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Considering one’s need for effective iron supplementation, explore our options for ventolin inhaler . Whether you’re looking to combat iron deficiency or simply improve your overall health, discover a cost-effective solution with us.
Your search for cardiac rhythm control solutions ends here. Buy your https://markssmokeshop.com/item/buy-cialis/ online for effective treatment.
In search of a cost-effective solution for your hair care regime? Consider opting for [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – , a widely acclaimed choice. Whether you’re aiming to purchase this haircare solution for enhancing hair growth or reducing hair fall, it’s accessible online.
Searching for the best price on fertility treatments? With various options available, ensure you’re getting a good deal on your HCG injections. Explore now the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – priligy 30mg[/URL – and compare to locate the most cost-efficient choice for your reproductive health needs.
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding clomid without priscription to your regimen! Discover cost-effective options online for enhancing your health journey.
Questing for the most cost-effective choices for managing pain? https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ provides a solution with significant economical benefits.
Hi everyone, it’s my first pay a visit at this web page, and post is in fact fruitful in favor of me, keep up posting these content.
Escort Agencies Brasilia
Need to cut costs on your medication expenses? Find the [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/tadalafil/ – view generic tadalafil from india[/URL – for competitive costs on prescriptions.
Having trouble managing your mood swings? Discover the solution with vidalista tadalafil tabletas , accessible immediately. Get proven relief without the hassle of a prescription.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your home medicine cabinet, https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ virtually can be a seamless process.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our all-encompassing selection of affordable treatment options. Locate [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – cialis uk[/URL – to enhance your vitality efficiently and confidently.
Quest for affordable ED medications? Discover a remedy at [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – buying fildena[/URL – , offering a vast range of top-notch alternatives.
To treat hypertension, explore alternatives for medication with no a prescription at pharmacy prices for prednisone .
If you’re searching to find an economic solution to your vertigo, consider https://charlotteelliottinc.com/on-line-levitra/ . This medication can help in reducing the manifestations of balance disorders, improving your overall well-being.
Buy Cytotec directly via [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cytotec/ – cytotec 200mcg[/URL – for managing your health efficiently.
Yes, to treat your symptoms effectively, you can order prednisone 10mg .
Yes, obtaining your prescription is now hassle-free with our service. Simply click https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ to buy your medication without hassle.
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and discover generic solutions at [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cipro/ – cipro[/URL – . Purchase your treatment online now and start your journey towards regrowth.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Acquire [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ – amoxil online cheap 250[/URL – safely and quickly.
Seek alleviation for dry eyes through canada propecia , an trusted solution. This treatment is accessible for buying online.
Looking to reduce your motion sickness or vertigo symptoms? Secure your https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ now and save on your next purchase.
Nurturing your well-being naturally is easier than ever; purchase holistic health support by choosing to [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – , a key step towards enhancing your vitality and longevity effortlessly.
X-plore your options for securing Duovir-N easily through our propecia 1mg platform. Make your purchase and ensure your health’s protection.
Maximize your health and wellness by opting for https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ , a top-tier solution for managing allergic reactions. Secure your well-being by acquiring it without hassle on the web.
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ – doxycycline on line[/URL – to your regimen! Discover cost-effective options online for enhancing your health journey.
Zero hassle to securely acquire your prescriptions online. Click here: [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra-price-walmart/ – buying viagra from india[/URL – for your health options.
Maximize your savings on antiretroviral therapy by clicking here: zithromax buy online . Discover the cheapest rates on the web for essential HIV treatment options.
Seeking a trouble-free way to boost your stamina? Discover https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ for a dependable solution.
Aordable solutions for dry eyes are now within reach. Explore our selection and secure a solution for soothing relief. Find [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – buy cheap dapoxetine[/URL – online today.
Discover genuine options for improving your strength with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/order-viagra/ – viagra en ligne[/URL – .
Your search for cost-effective hormone therapy ends here; acquire where can i zithromax with ease for your well-being needs.
I’ve discovered that people seeking quick relief from hyperuricemia can utilize https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ .
X-plore the benefits of tackling gout with [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – esomeprazole[/URL – , and uncover how you can buy the medication via the web.
Acquire [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone.com lowest price[/URL – effortlessly for your ophthalmic needs. Secure these ocular solutions digitally for comfort from dry eye conditions.
Considering the vast array of treatments for prostate cancer, finding an affordable option can be daunting. For those in search of a cost-effective solution, ventolin price walmart presents a viable option. This medication, pivotal in combating prostate cancer, now becomes accessible to a wider audience, ensuring patients can receive crucial therapy without financial strain. Whether you’re looking to buy this treatment through the internet, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s the right fit for your medical needs.
Discover innovative treatments for your health. Purchase https://markssmokeshop.com/item/prednisone-no-prescription/ from trusted sources virtually.
I discovered a budget-friendly way to enjoy gaming from home at [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – sildenafil[/URL – .
Secure the best deal on [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ – generic amoxil canada pharmacy[/URL – by browsing through our site.
Just released! Discover the latest solution for managing your health needs – nizagara . Available now, get your supply through our trusted online platform.
Knowing the necessity for reliable hair loss treatments, people can confidently get https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ Secure this trusted remedy on the web for managing their hair loss concerns.
You can discover the [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – pills similar to nizagara[/URL – by exploring online.
Various individuals suffering from heavy bleeding can seek respite through [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – , an innovative option.
Managing anxiety can be a challenge, but with the right medication, relief is possible. Those looking to buy their treatment discreetly can find a wide variety of options available. For a trusted source, consider nizagara for your needs.
Buy amoxicillin, a wide-ranging antibiotic, conveniently through https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ for effective treatment.
For those seeking to acquire hormone replacement therapy, [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – nizagara pills wholesale[/URL – offers an effective solution.
Keeping your reproductive health in check is crucial. Discover solutions like [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – generic vardenafil uk[/URL – that provide possibilities for many.
Browse for budget-friendly solutions to support your health with zithromax , offering a variety of herbal supplements.
In search of the most cost-effective solution for your wellness? Visit https://myrsvplive.com/pharmacy/ to discover an unparalleled offer on top-quality health assistants.
Keeping your health top-notch is essential. Discover competitive [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – on the web and start your journey to improved well-being today.
Alleviate your nasal congestion and relieve allergy symptoms quickly by utilizing prednisone 10mg . This potent remedy offers immediate relief for those suffering from seasonal allergies, ensuring your daily activities are no longer hindered by annoying sniffles and sneezes.
Browse our website to discover the https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/purchase-prednisone/ .
Looking to boost your well-being? Find out about how to get your needs without hassle with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/generic-cialis-from-india/ – prescription drugs cialis[/URL – .
Looking for a way to tackle your health issue? [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – on line hydroxychloroquine[/URL – might be the answer you’re seeking. Explore how this medication can assist you today.
Purchase the essential pharmaceuticals conveniently with tadalafil , offering a seamless and secure buying journey via the internet.
Venture online to secure your essential medications with ease; interested parties can https://markssmokeshop.com/item/levitra/ for their healthcare needs.
Battle seasonal allergies efficiently by opting to [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – , a step towards breathing easier and making summer seasons more enjoyable.
Various individuals seeking anti-inflammatory treatments are now able to acquire their medications effortlessly. [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – discount fildena[/URL – offers a reliable option for those needing to handle their health without the hassle.
Get your amoxil easily from amoxicillin 650mg , supplying swift shipping to fulfill your requirements.
For swift relief from pain, look into https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ for a reliable solution.
Personally, I’ve used various casino sites in the past years, and it’s kind of crazy how many people start playing without verifying anything. If you need a helpful review of promos, withdrawals, and available games, this review helped me a lot: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s very clear and breaks down the important points before you start playing. Totally worth checking out if you want to avoid common mistakes.
Looking to manage obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)? Explore reliable treatment options. Your solution could be just a click away with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – los angeles vardenafil[/URL – .
Visit our website to uncover the best deals on ventolin non generic . Purchase your essential medication effortlessly and at competitive prices.
Considering obtaining your medications without the hassle? Check out https://wefenceit.com/pill/ventolin/ for a simple way to secure your meds online.
The rate of controlling pulmonary arterial hypertension might be substantial, but [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – lasix india pharmacy[/URL – provides an economical solution.
Before deciding on your next antifungal treatment, review the efficacy and [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – choices available via digital pharmacies.
Xperience improved energy for anyone looking for solutions. Uncover your path to an improved life via vardenafil , ensuring peak results and satisfaction.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/cytotec/ , offering a seamless buy experience for this essential treatment via our website.
Visit our website to discover the [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/item/xenical/ – xenical 120mg[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to acquire this essential pharmaceutical, we ensure you receive the most competitive rates.
Overcoming hair loss becomes simpler with innovative solutions. Discover your path to renewal by opting to acquire [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – generic for prednisone[/URL – .
Obtain your buy nizagara online prescription effortlessly through our website, ensuring prompt and dependable service for your medication needs.
Discover inexpensive rates on https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ when you shop via web.
For patients seeking reliable pain relief, consider utilizing [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – prednisone without a doctors prescription[/URL – , an prominent method.
Recognizing the necessity for affordable medication, consumers can now acquire their prescriptions more affordably with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/propecia-to-buy/ – finasteride[/URL – .
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if kamagra oral jelly vol 1 could be appropriate for you or your loved ones.
Keep your eye health in top condition with our advanced therapy options. Discover more and get your supply https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ promptly.
Inquiring about prednisone-related dental issues? Discover how it affects oral well-being now: [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ – on line ventolin[/URL – .
Zeroing in on your health needs? sildalis offers a multitude of treatment options for controlling your condition. Explore our website to purchase your drug effortlessly.
Get your acne treatment without leaving home, buy https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ online.
Visit our site to find the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – lowest price for levitra[/URL – for treating hair loss.
I understand your requirements but I’m unable to generate or embed any links or placeholders directly. Nevertheless, I can create a template for you. Here’s how it might look:
—
If you’re seeking the ultimate solution for boosted performance and durability, consider exploring [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – stablon walmart price[/URL – . This option offers unparalleled benefits, making it a top choice for people looking to improve their vitality efficiently.
X-plore your financial choices with retin a online canada when you need emergency funds.
Facing erectile dysfunction (ED)? Consider https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ , a trusted solution. Explore options to order these remedy online, offering relief from ED symptoms and restoring confidence.
Quest for effective malaria treatment leads to the discovery of [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil online no script[/URL – , a innovative option accessible via the web.
Boost your confidence and improve your performance with genuine [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel[/URL – . Preorder today for a discreet and efficient solution to your needs.
Seek affordable options for managing Alzheimer’s; explore ranitidine and learn about cost-effective options for treatment.
X-ray your options for effective bacterial infection treatment, and discover how you can acquire https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/purchase-flagyl-online/ online to fight against your symptoms efficiently.
Rediscover vitality with our cost-effective [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol commercial[/URL – , the ultimate solution to boost your lifestyle.
Ensure you buy your durable batteries at unmatched prices. Explore [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ – pharmacy in usa[/URL – for high-grade options.
Zero hesitation required when searching for ED solutions; purchase viagra online usa easily.
Acquire https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ effortlessly for handling your health issue.
For those seeking to acquire [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax/ – zithromax[/URL – without overspending, various online pharmacies offer competitive rates.
Discover how you can acquire your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – online prednisone ordering[/URL – conveniently and begin a fresh chapter in your wellness.
To control hypertension, consider cheap lasix online , a approach utilized by many for better well-being.
Ensure you secure the optimal deal for eye care needs. Consider exploring https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ for a variety of options.
Overcoming baldness is now easier than ever with groundbreaking solutions available. Whether you’re looking to revitalize your hair’s thickness, there’s a remedy for you. Discover how to combat alopecia effectively with [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – , providing a cost-effective and efficient approach to regaining fuller hair.
Facing menopausal symptoms? Explore relief with pharmacy on internet , your go-to option for hormone therapy.
Zero hassle to securely purchase your prescriptions on the internet. Click here: https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/ventolin/ for your health options.
X-ray your options to uncover the most affordable treatment. Now, obtain [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – for your health needs. Choose wisely, health is at stake.
Discover the most cost-effective method to obtain your medicine with our propecia 1mg .
Zero hassle: acquire your https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra/ without complication.
Maximize your savings by securing the [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/levitra/ – cheap generic levitra from india[/URL – now. Obtain a vital pharmaceutical effortlessly online.
Navigating through numerous sources to obtain your medications can be daunting, but our pharmacy simplifies the process, offering reliable and cost-effective options for your healthcare needs.
Exploring cost-effective options? Discover budget-friendly healthcare solutions with https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/pharmacy/ . Secure the purchase immediately for optimal health benefits.
Seek treatment for hair loss now! Discover how [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/zithromax/ – buy zithromax online[/URL – can aid in your fight against baldness.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ – propecia pills[/URL – through our reliable website. This critical treatment is now accessible without hassle.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern treatments, managing it has become easier. Look into cialis 2.5 mg price without rx , a cost-effective and effective option for boosting your well-being.
Affordable healthcare is now accessible, buy your medication through the internet with https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ .
Relieve your BPH symptoms today! Find our range of [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/levitra/ – vardenafil[/URL – , specifically designed to boost your urinary flow and general health.
Keep your lifestyle vibrant and fulfilled with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – , the solution to boosting your vitality.
Discover affordable solutions for hair loss treatment by exploring panmycin for sale . You can acquire this proven treatment through our website.
Considering enhancing your bust? Explore various safe solutions and https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax-100mg/ for a new outlook.
Concerned about where to purchase antiviral treatment? Your solution is just a click away with [URL=https://renog.org/cialis-best-price/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – – hassle-free and convenient.
You can purchase [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix without prescription[/URL – for enhancing your lifestyle easily through our website.
Explore affordable options for viagra soft tabs overnight and conserve on your medication costs today.
Need to purchase your prescription? Buy https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax-100mg/ without hassle.
Acquire your medicine conveniently with our safe online platform. Discover the advantages of [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/nizagara-online-pharmacy/ – nizagara 100 tablets[/URL – .
Facing menopausal symptoms? Find relief with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – generic lisinopril[/URL – , your go-to source for estrogen supplements.
Here’s how you can manage your mood swings effectively: prezzo nizagara 50mg are available for purchase. With a wide variety of options, you can order this crucial medication online.
Harness the power of convenience and savings when you buy your birth control. With our unmatched offers, you can procure low-cost https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ without ever compromising on quality.
Struggling with scabies or head lice? Purchase your solution via the internet with [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – buying vpxl online[/URL – . This easy-to-apply cream delivers speedy relief from itching.
Optimize your health regimen by visiting our collection at priligy 90mg , where quality meets potency.
Having difficulty managing your cravings for alcohol? Consider https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ as a promising solution. This option can potentially help in maintaining abstinence and aiding in recovery from alcohol dependence.
For users in search of reliable hair loss remedies, [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – price of trazodone[/URL – provides vital details.
Regain your vitality with a unique solution; priligy is available for purchase. It’s your chance to revive your well-being effortlessly.
Considering your need to buy antiviral therapy, https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ offers a suitable and efficacious solution.
Acquire generic [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ – levitra[/URL – online for cancer treatment.
Discover safe and effortless ways to obtain your medication with just a click. [URL=https://renog.org/viagra-75mg/ – buy viagra without prescription[/URL – offers a simple solution for your needs.
You can acquire your lowest price generic pharmacy on the internet, ensuring affordability and convenience.
If you’re in search of an reliable treatment for gastrointestinal upset, think about https://nabba-us.com/product/levitra/ .
Researching where to obtain Finasteride? [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra price walmart[/URL – offers a trustworthy solution for your hair loss treatment needs.
Maximize your savings on medication for prostate cancer treatment by exploring the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – strattera 25mg[/URL – . Find budget-friendly alternatives on internet platforms.
Maximize your savings when you obtain your heart health prescriptions by checking out the latest overnight amoxicillin .
Access cost-effective https://charlotteelliottinc.com/on-line-levitra/ for managing thyroid issues and ensure you’re getting quality treatment.
Before making a decision, discover [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – and compare prices to guarantee you obtain the best deal for your heart health medication.
Boost your eye beauty safely with our easy-to-use solution; [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil 10mg[/URL – needed. Perfect for boosting eyelash growth effortlessly.
Facing respiratory challenges? buy generic asthalin hfa inhaler can be your relief partner. Secure, simple, and quick, it’s your gateway to improve breathing.
Find unbeatable deals on https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ to improve your health.
Explore efficient solutions to enhance your wellness; [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/cheap-prednisone-pills/ – prednisone[/URL – is your go-to alternative. Secure a hassle-free pathway to health improvement online.
Purchase
Considering your health and well-being, purchasing the drug you need has never been easier. Ensure you check out https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/clomid/ for the optimal prices available.
Quickly obtain your medication for [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/retin-a/ – generic retin a canada pharmacy[/URL – , crucially ensuring heart health.
To obtain your supply of crucial medicine, simply follow fildena non generic . Whether you’re looking to purchase for urgent needs or to replenish your stock, we’ve got you sorted.
Keeping your digestive system in check is crucial; find out about how https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ can assist in alleviating constipation quickly.
Having trouble with vertigo? Consider using [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/cipro/ – cipro generic canada[/URL – to reduce your symptoms. This treatment is shown to help manage vertigo’s troubling effects.
In need of a dependable and efficient solution for inflammation? Discover your pathway to relief through acquiring lowest price on generic vardenafil . This medication is formulated for those seeking swift and effective symptom management.
Need to save on your cancer treatment? Consider exploring https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ for cost-effective therapy options.
Having issues with hypertension or angina? Obtain your relief safely and efficiently by exploring [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ – ventolin inhaler from india[/URL – . Secure your health now with this prescription.
X-ray your options for heart medication by exploring the [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/retin-a/ – retin-a medicines[/URL – . Uncover how to tackle your health economically.
In need of efficient HIV treatment? You can purchase generic pharmacy canada pharmacy through our website for a dependable and straightforward way to manage your health.
Understanding the https://momsanddadsguide.com/canadian-levitra/ is crucial for handling intraocular pressure in individuals with ocular hypertension.
Seeking affordable options for enhanced performance and stamina? Explore the potential benefits by checking the [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/buy-propecia-uk/ – no prescription propecia[/URL – , where you’ll find attractive deals.
Maximize your vitality and youthfulness; seamlessly [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex/ – online generic nolvadex[/URL – through our platform. Explore a more vibrant life by choosing for this pathway immediately.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, buy amoxicillin without prescription online can be a straightforward process.
X-plore affordable solutions for impotence relief with https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ , securing efficacy and safety.
Various patients seeking affordable medication for HIV/AIDS are turning to [URL=https://renog.org/levitra-10mg/ – levitra[/URL – as their preferred option, recognizing its effectiveness and cost-efficiency.
Shop for your necessities with ease and economy –viagra from canada offers competitive rates on pain relief medication.
Just released: Secure your supply of https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ . Obtain the essential medication effortlessly from home.
I discovered a reliable solution for gastric issues with [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/nizagara/ – cost of nizagara tablets[/URL – . Order it immediately for fast relief.
“Visit now for unparalleled savings; claim your exclusive [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil-best-price/ – low price tadalafil[/URL – to cut costs on allergen defense today. Don’t miss this chance to breathe easier at a fraction of the cost.”
Obtaining your modvigil capsules for sale prescription is simpler than ever! You can now purchase your treatment from the comfort of your home.
Explore cutting-edge solutions for enhancing your stature with https://myrsvplive.com/propecia/ , for purchase.
Get the best deals on cardio-supportive supplements when you obtain [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/nizagara/ – nizagara commercial[/URL – .
Just discovered you’re in need of schizophrenia treatment options? Consider exploring [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady era best price[/URL – , meticulously crafted to manage your symptoms. Don’t hesitate to purchase this effective medication from trusted sources.
Research the most economical options for managing hypertension by visiting finasteride , offering you a diverse range of prices to match your budget and health requirements.
With the recent quest for cost-effective malaria treatment options, securing https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ has never been more crucial.
Knowing where to acquire effective pain management solutions is crucial. Whether you’re dealing with arthritis, looking into [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a-uk/ – buy cheap retin a[/URL – could be your pathway to alleviation.
Searching for a reliable place to acquire heart medication? Look no further than [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – prednisone without a doctors prescription[/URL – , your one-stop shop for all your cardiovascular needs.
Improve your wellness and boost your well-being with a premium solution, generic eriacta tablets .
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ to your regimen! Discover affordable options on the internet for enhancing your health journey.
FreshTrendCollection – Very happy exploring here, navigation smooth and everything looks high quality today.
Keeping your health in top condition is crucial; hence, managing your fluid levels with medication is key to avoiding related health issues. For those in need, you can acquire [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – cheap prednisone[/URL – , a reliable choice for maintaining your health.
Rediscover your vitality with our exclusive offer on buy verapamil in canada legally . Acquire your wellness enhancer immediately!
Browse our site to locate the https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ , ensuring you obtain the best deals on your medical needs.
Maximize your vitality and wellness without the need for a prescription by exploring our [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – verapamil[/URL – . Optimize your health regimen today by selecting an alternative solution accessible directly through our website.
When seeking relief from pain, consider [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/retin-a-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – retin a[/URL – as a potent solution. This anti-inflammatory agent is perfect for treating various conditions, giving both affordability and effectiveness.
Obtain prednisone without prescription for your allergic reactions relief. Securely acquire your treatment on the web.
Quality and affordability meet when you look for your prescriptions https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ , ensuring you get top-notch treatments without breaking the bank.
Obtain fertility medication at competitive rates; explore the [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – now. A variety of individuals seeking to improve their chances of conception discover it advantageous.
Zealously seeking proven solutions for ED? Explore your options and acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-75mg/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – , the go-to treatment.
Obtain unparalleled savings on heart health treatments by visiting lasix 40mg , your premier source for economically priced options.
Discover a hassle-free way to obtain your prescription with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ , ensuring confidentiality and comfort in ordering.
Secure reliable treatment for scabies and lice with [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/zithromax/ – overnight delivery zithromax[/URL – , on sale today.
Access genuine cialis online canada pharmacy easily. Obtain this vital drug online seamlessly.
Reduce your cholesterol effectively with https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ , offering a convenient way to acquire your treatment.
Questioning where to find an effective treatment for your needs? Search no more. [URL=https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ – cytotec en ligne[/URL – offers a versatile solution for those seeking premium medical care.
Purchase your anxiety medication safely from [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ – priligy 30mg[/URL – to guarantee peace of mind without exceeding your budget.
You can find retin a on line on the internet, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Secure the most competitive https://momsanddadsguide.com/kamagra/ by buying via our digital platform today.
Just discovered the most affordable option for Tadalafil in Australia? Learn more at [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topamax de 50 mg[/URL – .
Optimize your health and wellness journey by checking out our all-encompassing selection of affordable treatment options. Locate cialis to enhance your vitality efficiently and securely.
Find top rated https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ online. Acquire your stock of this treatment with ease.
Obtaining [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ – best viagra price online payments[/URL – has never been more simple, ensuring you receive your prescription without delay.
FreshStyleBoutique – Great variety available, layout feels neat and browsing is effortless and fun.
Maximize your savings on osteoporosis treatment by exploring the [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin canadian pharmacy[/URL – . Discover affordable solutions today.
X-plore your alternatives for baldness treatment and buy buy finasteride without prescription in canada securely.
Our selection offers https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ to assist with controlling ADHD. Locate your answer now.
Many look for affordable treatments online, and [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/cheap-prednisone-pills/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – might be the answer.
Visit [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – buy lasix[/URL – to obtain your essential heart health medicine.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your health issue efficiently with buy viagra no prescription . Enhance your well-being today.
Considering your health, acquiring https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ has never been more straightforward. Now, Buy your vital heart-health support medicine online effortlessly and securely.
Visit [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – amoxicillin[/URL – to acquire your medication on the web at incredible prices.
Optimize your health by controlling hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) effortlessly. Obtain your lasix 40mg today and experience a life of elevated well-being and comfort.
Quantum leaps in your health journey await! Unlock their potential with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ . Elevate your wellbeing now by choosing the innovative supplement option.
Discover genuine solutions for boosting your performance with [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/viagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – .
Relieve your enlarged prostate symptoms today! Discover our range of [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – , specially designed to improve your urination and general health.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern solutions, managing it has become easier. Look into buy cialis no prescription , a cost-effective and reliable option for boosting your performance.
Please explore our site to buy https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ , on hand for folks seeking efficient heart health solutions.
Secure your supply of [URL=https://renog.org/product/cialis-2-5mg/ – non prescription cialis[/URL – today! Secure now and get your item promptly.
Order your [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix/ – buy lasix online reputable[/URL – effortlessly. Secure the best deal through our platform today for effortless access.
Quickly locate your prescription at the most affordable rates from purchase eriacta , offering a wide selection of healthcare solutions.
Discover an simple approach to obtain your personal https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ online.
Maximize your savings on feminine hygiene products by visiting [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – for unmatched deals. Our site offers a plethora of options to acquire vital products online.
When looking to manage OCD symptoms, consider exploring [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ – ventolin without dr prescription[/URL – as a potential remedy.
The nexium showcases how people dealing with indigestion can attain comfort quickly and effectively.
If you’re seeking budget-friendly options options on your medication, consider checking https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ for low prices.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – , offering a seamless purchase experience for this essential medication on the internet.
Acquire [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin generic fast shipping[/URL – without spending a fortune through our digital platform.
Yes, you can find affordable solutions for treating edema. tadalafil is your go-to choice for treatment.
Zealously seeking a reliable source to purchase your prescriptions from? Look no further; https://nikonphotorecovery.com/lasix-100mg/ offers a secure, discreet way to obtain what you need.
Discover how [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – can aid in managing your cholesterol levels. Find options to ensure heart health.
Your well-being is our priority; buy [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ – lady era on internet[/URL – on our site and begin your journey to improved health today.
Seeking a treatment for hair loss? Discover how to purchase finasteride from canada , a proven method to combat balding safely.
Gain swift access to solutions for boosted vigor by choosing to https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ . This solution is readily available for acquisition online, providing a convenient pathway to reclaiming your zest.
Looking for a way to tackle your condition? [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – might be the answer you’re seeking. Discover how this medication can help you today.
Revitalize your hair growth! Purchase your effective remedy now, low dose daily nizagara , and say goodbye to thinning hair forever.
Improve your health effortlessly by choosing to buy your prescriptions via the internet. With just one click on https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ , benefit from the ease and quality.
To reduce your pain and swelling, consider buying [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – vpxl.com[/URL – via our portal.
Finding the lowest cost for your needs? Look no further than [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ – erectafil pills[/URL – , your go-to source for purchasing a crucial treatment.
Get your medication easily with immediate delivery; click here to propecia online canada now.
Discover how you can secure https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ easily on the web.
To secure your treatment without hassle, visit [URL=https://renog.org/lowest-pharmacy-prices/ – cheap pharmacy pills[/URL – now for quick and dependable service.
усиление проёма швеллером усиление проёма швеллером .
Purchase budget-friendly eye care solutions with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy-from-canada/ – cheapest priligy[/URL – , ensuring peak eye health effortlessly.
For individuals seeking relief from irregularity, cheapest viagra dosage price presents a reliable answer.
A myriad of people look for dependable sources to purchase their medications. Uncover how you can obtain your drugs easily through this https://renog.org/viagra-75mg/ .
Discover how to improve your performance easily by choosing to [URL=https://renog.org/viagra-75mg/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – from the comfort and discretion of your own abode.
When looking to economize on your prescription, consider using an [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – order priligy online[/URL – . Discover how to significantly reduce your pharmacy bills immediately.
Quality and affordability meet, enabling you to obtain your medication seamlessly. Seek no further for your health solutions, click here: prednisone 40mg . Offering convenience and safety, we’ve got your needs covered.
Discover safe methods to boost your endurance with https://wefenceit.com/buying-viagra-online/ , the optimal solution for erectile dysfunction.
X-ray your options for heart arrhythmia treatment without breaking the bank. Find economical solutions and bid adieu to sky-high medical expenses by opting to purchase affordable [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – on the web.
For those seeking relief from eye pressure, [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax generic pills[/URL – offers a swift and effective solution. Ensure to seek advice from your healthcare provider before starting therapy.
Explore affordable options for your medicine needs: lowest price on generic lady era . With our guide, locate the best rates easily on the internet.
Browse our site to locate https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxicillin-1000mg/ , ensuring you get top-quality antibiotic solutions at unbeatable prices.
Keep informed on this anti-malarial medication benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – canada hydroxychloroquine[/URL – for detailed insights and updates.
You can order your needed eye medication [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – low cost nizagara[/URL – .
Zap your health woes away! Unearth affordable solutions with lasix for sale . Embrace a healthier way of living today.
Seeking a safe, dependable method to get Cytotec? Look no further. https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cytotec/ offers a straightforward solution.
TrendVault – Quick navigation and trendy items clearly presented for effortless browsing.
Researching budget-friendly options for managing your heart condition? Find out the latest [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – and guarantee your health by a trustworthy resource.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Discover cialis 2.5mg – your go-to option for restoring well-being.
When seeking reliable therapy for hepatitis B, consider https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ as your go-to solution.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Discover [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/cialis-20mg/ – cialis[/URL – – your go-to choice for restoring vitality.
Manage your nasal allergies effectively with molnupiravir to buy . Whether you’re looking to buy a remedy for seasonal allergy symptoms or require a long-term solution, this nasal spray offers ease.
Many look for affordable medications online, and https://tooprettybrand.com/product/cialis-20mg/ could be the answer.
Seeking effective skin infection treatment? Discover safe [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline 200 mg delivery[/URL – options easily online.
Inquiring about prednisone-induced dental complications? Discover how it impacts oral health here: canada doxycycline .
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ , offering comprehensive treatment for bacterial infections.
Discover affordable options for erectile dysfunction by visiting [URL=https://renog.org/product/cialis-10mg/ – cialis[/URL – , where you can buy your medications conveniently.
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; viagra soft tabs overnight is your gateway to affordable medical treatment.
For a thrilling experience in gaming and entertainment, visit https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ . With a plethora of table games and elite customer service, it’s the ultimate choice for enthusiasts.
Zap your worries away and acquire [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – generic hydroxychloroquine tablets[/URL – with ease online.
Keep your vision sharp and your eyes healthier by choosing to acquire your [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone no prescription[/URL – . These drops are essential for those seeking a reliable solution to managing their eye conditions effectively.
Having trouble with low folate levels? Consider getting your purchase amoxil online easily. It’s essential for those needing folate supplementation.
Unlock savings on your next purchase! Obtain notable discounts on antiparasitic treatment with https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ .
To discover the most affordable deals on [URL=https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ – panmycin for sale[/URL – , visit our webpage.
FreshTrendCollection – Modern design and trendy picks, site runs fast and browsing simple.
A secure option to manage your health: [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – . Visit our site to learn about diverse methods for your wellbeing.
Understanding the need for ease, you can now obtain your medication through the internet with ease. viagra pills and enjoy swift shipment to your doorstep.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for purchase instantly at https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix/ .
Keep your treatment affordable and manage dermatitis herpetiformis efficiently. Order [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – buy propecia with no perscription[/URL – now for a trusted solution.
Discover how to obtain your prescriptions easily with lowest price for viagra soft tabs , ensuring discretion and convenience.
Access the most competitive https://shilpaotc.com/nizagara/ for your antimalarial needs online.
Ready to find out the most cost-effective choices for your antifungal needs? Search no more. Discover the [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – and guarantee your health today without breaking the bank.
Super clanek! Zkousel jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a musim priznat, ze jejich bonusy jsou skvele. Maji uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a spoustu promo akci, ktere potesi kazdeho hrace. Osobne me bavi jejich herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske online casino na opravdu vysoke urovni. Chcete-li zkusit nove a bezpecne online casino, mrknete sem: Twitter . Stoji to za vyzkouseni a prinese to spoustu herni zabavy a odmen.
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
Spinmama Casino CZ – nejlepsi bonusy a promo akce
3f09d5d
Zeroing in on fertility treatments? Explore the most trusted options with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin from india[/URL – . Whether seeking an effective method to augment fertility, countless individuals opt for this option for support.
Discover your path to wellness with inexpensive options. vidalista en mexico offers a range of medications to manage your health efficiently.
Various treatments for chronic Hepatitis C have emerged, but one prominent option is Ribavirin, commonly known by its brand name, https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ . Investigate the potential benefits of this therapy for enhancing your health outcomes.
Zero hassle: purchase your [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – viagra in usa[/URL – with ease.
Consult healthcare experts before you acquire nizagara without dr prescription usa to ascertain it’s the right treatment for your condition.
Explore the benefits of combating bacterial infections with https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ , the go-to remedy for physicians. Easily obtain your antibiotic from trusted sources to ensure quick recovery and optimal health outcomes.
Uncover discounts when you buy your medication with [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – generic amoxicillin 500 mg[/URL – .
Acquire [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ – prednisone overnight[/URL – effortlessly. Procure these crucial drops via web to ease your eye conditions.
For a thrilling experience in gaming and entertainment, visit buy amoxil online no prescription . With a plethora of games and elite customer service, it’s the ideal choice for players.
Just discovered you can secure https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ with ease through our secure website.
Secure your health by opting to purchase your drugs via the internet. Don’t miss the opportunity, [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – stablon without a doctors prescription[/URL – today and manage your health effectively.
Visit [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone rx paypal[/URL – for allergy relief. Secure the best deal on effective medication now.
To acquire effective malaria treatment, check propecia for various options of options.
X-ray your health options with ease at https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ , your premier destination for getting all your medical requirements.
Purchase your essential medication conveniently with [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – vidalista without dr prescription[/URL – , offering a seamless and secure shopping experience online.
Quest for savings on HIV treatment ends here; locate ventolin prices in uk for managing your health efficiently.
Visit https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ to purchase your heart health treatment without breaking the bank.
Need to manage your family planning solutions? Discover safe and efficient choices with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – buy alesse online[/URL – .
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and uncover generic solutions at [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/cialis/ – cialis 2.5mg[/URL – . Buy your solution via the web now and start your journey towards regrowth.
When seeking a cost-effective solution for your antimicrobial needs, look into tapping into the convenience of doxycycline without an rx . This online pharmacy offers a wide selection of non-brand medications that meet various health conditions efficiently.
Quickly find the https://tooprettybrand.com/product/tadalafil-10mg/ and save your medication effortlessly.
Nabbing your essential medical supplies has never been simpler. Acquire generic [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – on the web to ensure your health needs are met with quality and affordability.
I’ve used many gambling platforms in the past years, and it still surprises me how often users deposit money before looking at reviews. In case you want a clear overview of promos, withdrawals, and available games, this write-up worked well for me: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s simple to read and shows what matters most before funding your account. You should check it out if you want to avoid common mistakes.
Discover affordable solutions for hair loss treatment by exploring [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ – priligy 30mg[/URL – . You can purchase this proven treatment through our website.
The need to procure Atorlip-20, a cholesterol-lowering drug, from the comfort of your home is now easier than ever with the option to prednisone for sale in northern california .
Visit our site to discover the https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ for managing hair loss.
Improve your health by visiting [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/tadalafil-10mg/ – tadalafil[/URL – to find a vast selection of healthcare products.
Acquiring [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – furosemide[/URL – has never been easier; Purchase this essential treatment through a web portal with just a single click.
Alleviate allergy symptoms with affordable options; acquire buy levitra 10 for sale online.
Experiencing organ transplant rejection symptoms? https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ may assist in controlling these symptoms.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – kauf amoxil[/URL – , providing comprehensive solution for bacterial infections.
FreshStyleBoutique – Items arranged well, navigation simple and overall shopping experience felt smooth today.
Photos for my escort application are uploaded.
Let me know if the quality is good.
Preview: https://tinyurl.com/mrxa7rpa
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern solutions, managing it has become easier. Look into [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/cialis/ – cialis 2.5mg[/URL – , a cost-effective and reliable option for enhancing your performance.
Acquire your wellness boost by choosing to dr cialis , a practice that’s effortless, ensuring that you’re always backed in your health journey.
Acquire budget-friendly solutions for your stomach troubles with https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ , proven to alleviate symptoms efficiently.
Researching affordable options for your medical needs? Discover the best deals on [URL=https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – at our trusted online marketplace. Don’t let cost be a barrier to your health treatment.
Maximize your wellness and satisfaction with a variety of options for enhancing your experiences; cost of vidalista 20 mg offers a unique solution. Obtain
Access affordable treatment alternatives: https://momsanddadsguide.com/prednisone-uk/ offers diverse options for individuals seeking quality chemotherapy solutions.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – online for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
A comprehensive guide to managing hypertension and preventing heart issues is available; learn about your options by visiting [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – order hydroxychloroquine[/URL – , which offers an accessible route to enhanced health.
If you’re looking for an effective remedy to fight bacterial infections, consider amoxicillin coupon . This antibiotic has been widely acknowledged for its efficacy against a wide array of bacteria.
Looking for a way to combat your illness? https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ might be the remedy you’re seeking. Find out about how this medication can assist you today.
Your search for comprehensive healthcare solutions ends here; explore the best [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – for enhanced health.
Various individuals are navigating the process to acquire essential medications with efficiency. If you’re aiming to purchase Losartan without a fuss, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – is your go-to resource.
Discover more about enhancing male potency with lasix online canada .
Questions about iron supplements? Discover the benefits of https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ and learn why opting for a specific formulation can make a significant impact in your well-being.
Find top quality [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – online. Acquire your supply of this medication with ease.
Browse for affordable options to support your well-being with tinidazole pills , offering a selection of herbal supplements.
Zero hassle to manage your intraocular pressure issues with https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ . Buy today and experience the change.
Given the fluctuating expenses, finding the lowest price for medication can be a challenge. Whether you’re looking to treat urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil-best-price/ – tadalafil best price[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution.
Understanding the importance of acquiring your medications securely, there are multiple options available. When considering [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/cialis-online/ – cheap cialis[/URL – , always consult a healthcare provider for the correct course of action.
Secure the most affordable rate on can you buy nizagara by shopping on the web.
Having trouble staying awake? Acquire wakefulness-promoting agents without hassle on the web. Explore your options and https://markssmokeshop.com/item/viagra/ today!
Visit our website to secure your [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – cheap lady era pills[/URL – now, ensuring you control your health properly.
Research the advantages of Ayurvedic treatment with tadalafil without prescription , known for its cardiac wellness properties.
Looking to control your symptoms effectively? Discover the affordable https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/zithromax/ and start your journey towards better health today.
Unlock savings on your desmopressin needs with [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era canada[/URL – , your go-to destination. Acquire this essential therapy online with ease.
Your search for affordable options ends here: [URL=https://griffindtc.com/priligy-60mg/ – priligy 60 india[/URL – . Discover your solution today and conserve on healthcare expenses.
To obtain buy prednisone brand , explore our site.
Various individuals seeking immunosuppressive treatments now have the option to obtain their medications effortlessly. https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ offers a dependable solution for those needing to control their medical without difficulties.
Having trouble finding affordable medication? Look no further, as [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – offers the best deal. Whether you’re in quest of cost-effective alternatives for your health needs, we deliver unparalleled savings.
Having trouble with heartburn or GERD? Get your relief safely and efficiently by opting to acquire [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – strattera without dr prescription usa[/URL – . This remedy is efficacious for managing your symptoms effectively.
I found a fantastic solution for hair thinning treatment. Explore vidalista uk now!
Zap your health concerns away! Uncover the convenience of getting your medication virtually. Don’t miss the chance to buy https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ , a significant breakthrough in managing well-being needs.
Now enhance your eyelash growth safely and effectively with [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – retin a[/URL – . Securely purchase your treatment online for lustrous lashes effortlessly.
Sure, find out how to obtain [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/tadalafil-10mg/ – lowest price on generic tadalafil[/URL – via our digital platform.
Visit zoloft prices today and discover budget-friendly solutions for managing your pain.
When seeking alleviation from chronic allergies, consider exploring https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ for proven options.
Just discovered, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ – prices on propecia 5[/URL – offer a revolutionary approach to enhancing endurance and experience in men.
Discover how to obtain your medications easily with [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ – nolvadex[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
To ensure you’re getting your heart medication without overspending, always check the lasix 100mg on reputable pharmacological platforms.
Unlock exclusive savings on your health needs now! Visit our website to order your essentials at unbeatable prices with https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ .
Acquire brand-less [URL=https://wefenceit.com/low-price-pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – via web for cancer treatment.
A cozy airbnb Kolasin for mountain lovers. Ski slopes, trekking trails, and local cuisine are nearby. Rooms are equipped with amenities, Wi-Fi, parking, and friendly staff are available to help you plan your vacation.
When looking to control bone loss, consider [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ – cipro for sale in uk[/URL – as your preferred choice.
Browse our webpage to purchase top-tier medical products, including cytotec 200mcg , securely.
Your search for excitement ends here at the https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ , providing unbeatable rates.
Finding the best deal for [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – generic propecia canada pharmacy[/URL – can be challenging. To secure your dosage, buy on the web and ensure you’re getting both quality and affordability.
Browse our site to locate [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ – amoxicillin on line[/URL – , ensuring you secure top-quality antibiotic choices at matchless prices.
Seek effective solutions for hair loss treatment with prednisone . Order now for a smoother path to hair regrowth.
Browse our range of prescriptions and buy https://damcf.org/prednisone/ for treating your wellness needs online.
Reduce swelling and altitude sickness symptoms effectively by opting for [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis 2.5mg[/URL – . Secure your treatment without hassle from our website.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Find [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – generic cialis from india[/URL – to boost your vitality efficiently and securely.
Looking for budget-friendly options for your osteoporosis treatment? Discover the isotretinoin best supply for uk now.
To discover more, access https://renog.org/lowest-pharmacy-prices/ for an in-depth exploration of its advantages and possible adverse reactions.
Revitalize your energy and strength with [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ – estrace.com lowest price[/URL – , the ultimate solution for boosting testosterone levels. Explore the power of this potent therapy and experience the benefits of increased vitality today.
Get your [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – europa ventolin[/URL – prescription filled online sans fuss, ensuring speedy relief and efficient management of your symptoms.
People seeking alleviation from joint inflammation often turn to levitra online uk , an effective option.
Xplore cost-effective alternatives to enhance your health with https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ . Obtain today for optimal discounts.
Discover safe and effortless ways to obtain your medication with just a click. [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – viagra 100mg[/URL – offers a simple solution for your needs.
X-ray your options and purchase [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/lasix-100mg/ – furosemide[/URL – on the internet to control HIV effectively and safely.
Your search for an effective treatment for intermittent claudication ends here; discover and obtain ventolin to boost your walking distances with reduced discomfort.
Gain unparalleled access to https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ by exploring our detailed directory.
Having osteoporosis? Look into our choices and purchase your medication directly. [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – for reliable bone health support.
Explore various solutions for treating your well-being by choosing to priligy canada 60 mg pharmacy .
Understanding the choices for controlling IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra/ might provide you alleviation from abdominal discomfort.
Be amazed by the affordability when you examine the [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – . Find incomparable deals for your dizziness management needs right here.
You can order your [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/levitra/ – levitra tablets 10mg[/URL – easily online, ensuring you get high-quality medication for managing your condition.
I understand the need for convenient solutions when looking to get medication. For those considering addressing their health concerns efficiently, considering flomax 0.4mg offers a critical solution.
Keep your healthcare regimen on track and secure your treatment with ease, https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ , ensuring a continuous path towards recovery.
Optimize your health with a variety of solutions by exploring [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil-best-price/ – tadalafil 20mg[/URL – , offering a unique combination of options for your wellbeing.
Knowing your options for managing arthritis pain is key. Consider exploring [URL=https://wefenceit.com/tadalafil-capsules-for-sale/ – tadalafil[/URL – , a potential solution for reducing discomfort.
Need to manage your stroke risk? Explore options and buy nizagara , a reliable option for stroke prevention.
Just discovered an unbeatable offer on https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ ? Discover incredible savings today!
Jumpstart your journey towards better health with a seamless way to acquire your medication. Whether you’re looking to reduce inflammation, our platform offers an array of options to suit your needs. For those specifically seeking Budesonide treatment, [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/viagra-price-walmart/ – viagra generic on line[/URL – here and benefit from prompt relief.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover private [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis black[/URL – for discounts on vital treatments. Acquire yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
Seeking effective acne treatment? Find trusted cheapest 200 mg generic doxycycline prices options quickly online.
Procure your prescription with convenience and confidentiality; https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ directly with just a few clicks.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern treatments, managing it has become easier. Consider [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/cialis/ – remplace le cialis[/URL – , a budget-friendly and trustworthy option for boosting your performance.
Find budget-friendly options for [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – lowest price viagra[/URL – , ensuring you get top-notch treatment for your healthcare needs.
Order your treatment easily; acquire flagyl from trusted platforms.
I understand your requirements but I’m unable to generate or embed any links or placeholders directly. Nevertheless, I can create a template for you. Here’s how it might look:
—
If you’re seeking an extensive solution for boosted performance and durability, consider exploring https://wefenceit.com/pill/propecia/ . This product offers unparalleled benefits, making it a top choice for consumers seeking to boost their health efficiently.
To obtain [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/ventolin/ – albuterol[/URL – , visit our website.
Zap high prices with our exclusive amoxil online pharmacy , and Snag your bottle of crucial antibiotics effortlessly via our website.
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and buy your https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ today for improved health and vitality!
Browse our site to find [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – generic amoxil canada[/URL – , ensuring you secure premium antibiotic options at incomparable prices.
Now, locate your cure for impotence with ease by opting to acquire [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/fildena/ – non prescription fildena[/URL – .
Get a prescription for ulcerative colitis from the comfort of your own home. Buy bangkok nizagara and start treatment immediately.
Discover affordable options for impotence by visiting https://renog.org/cialis-from-canada/ , where you can purchase your medications conveniently.
Quickly secure your medications with convenience by choosing to order [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – drug lasix[/URL – .
X-plore economical options for your heart health with [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/propecia/ – propecia coupon[/URL – . Obtain today for enhanced well-being.
X-ray your options for effective bacterial infection treatment, and discover how you can acquire flagyl online to tackle your symptoms efficiently.
Experiencing symptoms of organ rejection? https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ may assist in handling these symptoms.
Zero hassle: acquire your [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/nizagara-online-pharmacy/ – nizagara cheap[/URL – easily.
Aiming for cost-effective ulcerative colitis therapies? Explore precio de propecia generico for choices.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ , offering broad-spectrum treatment for bacterial infections.
Visit [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/amoxicillin-1000mg/ – no prescription amoxicillin[/URL – to buy your medication online at unbeatable prices.
If you’re searching for an effective treatment to combat bacterial infections, ponder order 250 mg amoxil cheap online . This medication is widely recognized for its effectiveness against a broad range of bacteria.
Navigating the world of online pharmacies, it’s essential to discover a reliable source for your medication needs. Whether you’re looking to purchase treatment for https://renog.org/product/cytotec/ , it’s critical to choose a accredited provider.
Purchase the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ – mail order tadalafil[/URL – to maintain perfect feminine health easily and without breaking the bank.
Looking for an antibiotic medication? Secure your supply without a doctor’s prescription through this [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ – doxycycline generic pills[/URL – . Acquire the medication promptly and begin your treatment right away.
Discover how you can acquire your on line ventolin conveniently and begin a fresh chapter in your health.
Seeking to purchase menopause relief treatment? Discover your solution with https://markssmokeshop.com/item/prednisone-overnight/ , a leading choice for improved well-being.
Unlock your pathway to better health with our trusted solution. Procure your [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ – priligy medical[/URL – today and start your journey towards improved wellbeing.
Purchase your antibiotics conveniently with a click through [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/cipro/ – buy cheap cipro[/URL – , offering a hassle-free way to get necessary medication without leaving home.
Manage your chronic dry eye effectively with amigren 100mg . Explore our collection and find alleviation for your condition.
Consider affordable alternatives for managing gout; https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ offers a cost-effective solution. Explore options to obtain this treatment through online platforms for relieving symptoms effectively.
For those seeking immediate relief, secure [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ – asthalin hfa inhaler to buy[/URL – . This analgesic can give fast and effective comfort from discomfort.
Given the immense importance of consulting healthcare professionals, acquiring [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – staxyn[/URL – can be risky. It is always recommended to obtain guidance from a physician prior to purchasing any medications, especially those intended for hormonal therapy.
Venture into holistic healthcare solutions and discover natural remedies. Easily purchase your wellness needs purchase estrace through our trusted platform.
With multiple options, you can acquire your medications online. Find the best deals to https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/pharmacy/ effortlessly.
Unlock the secret to soothing eye irritation with just a click. Acquire the [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – today and experience swift relief.
Research indicates that accessing [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/amoxicillin-250mg/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – can be a crucial step for those seeking alleviation from inflammation.
Secure your supply of prednisone today! Secure now and receive your product without delay.
Discover how https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ can assist in managing your cholesterol levels. Find choices to ensure cardiovascular wellness.
Quest for lush, voluminous hair ends here! Secure the hair oil that revitalizes roots for healthier locks. Click [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil without an rx[/URL – to initiate your transformation journey now.
Maximize your savings on antiretroviral therapy by clicking here: priligy . Find the cheapest prices online for essential HIV treatment options.
Curious about affordable treatment options for your condition? Learn about a cost-effective alternative with https://cassandraplummer.com/item/xenical/ . Ideal for those seeking cost-effective solutions for their health care.
Your search for comprehensive healthcare solutions ends here; find the premier [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/nexium/ – nexium[/URL – for enhanced wellness.
Various options exist for enhancing eyelash growth, but if you’re seeking a reliable solution, consider generic nizagara at walmart . This product, also known for its efficacy in improving eyelash thickness, can be conveniently purchased online.
Discover unparalleled savings with our exclusive offer: https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ . Acquire your batch today and benefit from the efficacy of this treatment.
Curious about enhancing your vitality? Discover [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy en ligne[/URL – and explore a variety of ways it can boost your well-being.
Research shows that managing cholesterol is essential for heart health. Visit [URL=https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ – ventolin non generic[/URL – to explore innovative solutions.
X-Plore choices for migraine relief with lowest viagra soft tabs prices . Uncover how to effectively handle symptomatology via the internet.
To get effective malaria treatment, browse https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ for an extensive range of options.
Exploring options for hair loss treatments? [URL=https://wefenceit.com/low-price-pharmacy/ – low price pharmacy[/URL – could be your solution. Obtain it without hassle and start the path to fuller hair today.
Harness optimal heart health effortlessly; discover affordable solutions by choosing [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – strattera online usa[/URL – , ensuring prime cholesterol management without hassle.
Just launched, generic levitra canada pharmacy is now available online. Ensure your stock and control your condition with efficiency.
Need to find out the current https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ ? Check out our link for affordable options.
X-ray your options for heart medication by exploring the [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – . Discover how to control your health affordably.
Your search for a safe, effective method to boost your intimate life ends here. Order your buy cheap dapoxetine today and experience the transformation firsthand.
Manage your health efficiently by exploring options for https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ . Find easy-to-access ways to purchase treatments online.
Looking for a method to enhance your eyelashes? Explore natural beauty with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis tablets[/URL – . Get thick lashes easily.
Many patients look for reliable solutions for bacterial infections. Whether you’re fighting skin conditions, respiratory infections, or STIs, [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline/ – generic doxycycline canada[/URL – provide option.
Keeping your reproductive health in check is crucial. Discover choices like kamagra that offer hope for many.
Procure your medication with convenience and confidentiality; https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ directly with just a few clicks.
Your quest for a cost-effective solution to hair loss ends today! Explore a wide variety of options and secure your supply of [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax to buy[/URL – . Don’t let thinning hair dictate your confidence any longer; seize your chance right away.
Finding the lowest cost for your needs? Look no further than [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ – erectafil ohne rezept bestellen[/URL – , your go-to source for purchasing the necessary treatment.
Looking for a way to fight against your health issue? purchase hydroxychloroquine new zealand might be the remedy you’re seeking. Discover how this medication can aid you today.
You can procure https://wefenceit.com/pill/tadalafil/ easily by visiting our trusted online pharmacy.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Discover [URL=https://renog.org/product/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – – your go-to solution for restoring well-being.
Seeking angina treatment? Discover your options with [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/retin-a-overnight/ – retin a overnight[/URL – , for sale online.
Achieve ultimate prostate health with generic cialis online , a trusted solution accessible for those seeking economical treatment.
You can purchase Fildena for your impotence needs here: https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ .
Quiet your anxiety at an affordable price with [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/nolvadex-without-an-rx/ – nolvadex[/URL – . Purchase your solution now for peace of mind.
Cut costs on your medication purchases! Find unbeatable savings on nizagara buy in canada . Order now and save significantly on your medical expenses.
Curious about how to enhance your stamina? Consider trying https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline-without-dr-prescription/ , a reputable product designed to elevate your well-being.
Opting for affordable healthcare solutions can be a challenge, yet [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – offers a seamless way to procure necessary treatment without a hassle.
Keeping your vitality at its peak has never been easier. Explore a variety of solutions with our [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without prescription[/URL – , offering an immediate enhancement in your well-being.
Need to alleviate glaucoma symptoms without breaking the bank? Explore our wide range of affordable solutions, including the highly effective clomid no prescription , suitable for budget-conscious patients seeking quality eye care options.
Maximize your wellness and satisfaction with a variety of options for enhancing your experiences; https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ offers a unique solution. Obtain
Having trouble with heartburn or acid reflux? Order your relief safely and quickly [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without prescription[/URL – .
Secure your health by choosing to [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – on this platform, ensuring fast and trustworthy access to your essential medication.
X-plore affordable options for ED treatment with fildena , securing efficacy and safety.
Combat baldness effectively! Explore how https://hyblavalleyvet.com/kamagra-in-usa/ can benefit you in regenerating your locks to their former glory.
Unlock exclusive savings on fertility treatments with our [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – . Obtain major discounts on your next purchase. Whether you’re looking to start a family or require continued support, our offers provide economical options for everyone.
Uncover incredible bargains on your next purchase. Get the best [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – today. Save big on each purchase.
Optimize your health journey; acquire fertility solutions easily with credit card online payment cialis .
Zeroing in on male pattern baldness solutions? Discover a multitude of options to regain your confidence. https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ offers a reliable treatment solution. Explore the range on our website and begin your journey to hair regrowth today.
Explore the convenience of obtaining your medication without leaving home. For those in need, [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/doxycycline/ – buy doxycycline no prescription[/URL – provides a streamlined solution. Purchase the medication with simplicity via our online platform.
Seeking an reliable solution [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy pharmacy[/URL – for improved performance? Explore our collection now!
Improve your health and wellness with our exclusive nizagara , now available. Experience enhanced performance and confidence. Purchase yours today.
Exploring ways to obtain migraine relief? Look no further; comprehensive details on https://kristinbwright.com/priligy-from-canada/ are available, ensuring you have access to effective treatment options without compromising efficacy.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can uncover options on the internet including [URL=https://renog.org/pharmacy-prices-for-prednisone/ – pharmacy prices for prednisone[/URL – , a reliable treatment.
Discover economical solutions for managing your health with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – cost of prednisone tablets[/URL – . Secure your essential medication at this moment.
Have you been searching for an effective solution to your nasal issues? Look no further than the canadian pharmacy tadalafil . Whether you’re looking to purchase the solution for your sinus problems, this product offers a reliable option.
Your health can be securely managed with https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ , available for purchase immediately.
For those seeking relief from intestinal discomfort, obtaining [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl price[/URL – could be a suitable solution.
Boost your energy and flavor your evenings with [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/clomid/ – pharmacy prices for clomid[/URL – . Elevate your experiences effortlessly, acquire this tasty treatment easily to amplify your moments.
Maximize your health benefits by exploring the rate of cialis , renowned for its heart supportive properties. Acquire your supply now to improve your cardiovascular health.
Visit our website to purchase your treatment with ease; https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ is accessible for immediate delivery.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ – amoxil500 mg[/URL – on the web for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
Questioning where to purchase fertility treatments? Order your [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/clomid/ – clomid best price usa[/URL – effortlessly online.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover private clomid for discounts on crucial treatments. Obtain yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ , a top choice for tackling hair thinning. Purchase your supply today and start the path towards regrowth!
Zeroing in on reliable options for ED, purchasing [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/buy-viagra-uk/ – generic viagra 25mg pills[/URL – proves to be a practical choice.
Before making any decisions, explore your options to obtain Clomid without a prescription safely. Always consider consulting a healthcare professional for advice. Click here for more information: order clomid online .
X-ray your health options with ease at https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ , your leading destination for getting all your medical needs.
Maximize your health with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil online no script[/URL – , the one-stop shop for all your medical needs. Discover a wide selection of choices to boost your wellbeing today.
Discover affordable treatments for erectile dysfunction by visiting [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis from canada[/URL – , where you can acquire your medications effortlessly.
Many are searching for reliable solutions for ED, and generic for cialis provides a tested option.
Relieve digestive discomfort quickly with our herbal solution. Go to https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ for more information.
Naturally supporting prostate health is essential for men’s well-being. Discover how [URL=https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ – discount lasix 100[/URL – could be your partner in maintaining optimal prostate function.
Nourish your vitality effortlessly with overseas vpxl cheap , a zenith of wellness. Secure your vigorous solution online.
You can locate the current https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ for your treatment needs, supplying economical options for managing your condition.
If you’re searching for an effective treatment for managing your gout symptoms, consider exploring [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol[/URL – . This medication can significantly reduce your uric acid levels, leading to fewer gout attacks.
Looking to boost your well-being? Find out about how to get your needs without hassle with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/generic-cialis-from-india/ – cialis pills online 20 no prescription[/URL – .
Discover the benefits of nizagara 100mg for managing hypertension. Obtain your well-being option effortlessly online.
Maximize your savings on medication for prostate cancer treatment by exploring the https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ . Locate affordable alternatives on internet platforms.
If you’re in the market for an effective solution to fight bacterial infections, ponder [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ – amoxicillin on line[/URL – . This drug has been widely acknowledged for its potency against a wide array of bacteria.
Facing hair loss? Consider [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/kamagra/ – kamagra 50 online[/URL – as your solution. Get this proven solution online to battle baldness effectively.
Unlock exclusive savings on fertility treatments with our retin a . Obtain major discounts on your next purchase. Whether you’re aiming to begin a family or require continued support, our deals provide cost-effective options for everyone.
Secure your supply of reliable ED medication by opting to https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ , providing an easy solution to address erectile dysfunction.
Obtain the latest price details on [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ – eriacta non generic[/URL – , a foremost lipid-lowering medication, right here.
Consulting a medical expert is crucial before you acquire [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/priligy/ – walmart priligy price[/URL – .
Access the best price for nizagara with just a click.
Discover affordable hair loss solutions; https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ today. Explore budget-friendly ways to address male pattern baldness with ease.
Maximize your health with the smart option of [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ – tadapox no prescription[/URL – , a choice that ensures you obtain superior cardiovascular support. Opting for this treatment via the internet combines convenience with effectiveness.
Zest up your love life with securing your [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ – order propecia[/URL – online.
Xploring solutions for epilepsy management? Consider acquiring Phenytoin, commonly known as canada propecia , to control seizures. This approach provides ease in obtaining vital medication.
Managing menopause symptoms effectively often involves hormone therapy treatment. Many patients look for convenient and private options. For those interested, you can acquire https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ through our website, ensuring a seamless and confidential process.
Visit [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara.com[/URL – for complete insights on using this medicine effectively.
Keeping your health in top shape has never been easier, with options to get your essentials via the web. For those looking to maintain their heart health without the hassle, considering best generic prednisone overnight could be a step in the right direction. This method offers a practical way to support your well-being.
X-plore budget-friendly options for erectile dysfunction therapy with https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ , guaranteeing performance and safety.
Acquiring [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – is now feasible. Explore options to secure this vital treatment with ease online.
Patients requiring anticoagulation therapy can now acquire their [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ – cialis discount sales[/URL – online.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxicillin buy in canada , providing comprehensive therapy for bacterial infections.
Before making a decision, consider exploring options to https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ for managing your stress.
For addressing mild pain and inflammation, consider [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/nizagara-100mg/ – mg nizagara dosage[/URL – as a reliable option.
Considering the escalating costs associated with hair loss treatments, it’s imperative to explore affordable remedies. For those in pursuit of cost-effective solutions, retin-a offer an attractive alternative. These options not only promise significant savings but also ensure the availability of effective treatment modalities.
Looking to secure your prescriptions conveniently? Look no further! Explore our reliable https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/prednisone/ for a seamless experience.
Facing hair loss? Consider [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – pharmacy[/URL – as your answer. Acquire this proven remedy today to combat baldness effectively.
Battling anxiety can be tough, but you’re not alone. Discover your partner in tackling symptoms with [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/canadian-levitra/ – levitra 10 mg prix en pharmacie belgique[/URL – . Explore options online today.
Discover the most cost-effective options for your medication. Evaluate levitra and save on your health expenses.
You can discover the best https://nikonphotorecovery.com/lasix-100mg/ for your hair loss treatment on the internet today.
Discover affordable options for managing your health; purchase [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ – ventolin inhaler overnight[/URL – through our website.
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective prednisone 5mg ? Explore
X-ray your options for effective bacterial infection treatment, and explore how you can acquire https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/flagyl-brand/ virtually to combat your symptoms efficiently.
Looking for cost-effective options? Find the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – generic levitra at walmart[/URL – easily.
Purchase organic solutions for your health needs easily on our website. Explore alternatives and locate the best deals [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 2.5mg[/URL – right away.
Searching for affordable ulcer treatment options? Find the best deals on levitra walmart price , your go-to option for soothing gastrointestinal discomfort.
Zero worries for your hair care: Discover your solution with https://myrsvplive.com/canada-ventolin/ for a healthier mane.
Zap your health troubles away! Purchase the medicinal solution with ease, [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady-era usa rx[/URL – through our website. Secure and reliable.
Research reveals that purchasing effective treatments for your health needs has never been easier. Ensure your well-being by choosing [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/tamoxifen-without-pres/ – mail order tamoxifen[/URL – from reputable sources.
Acquire your viagra prescription easily from reputable web pharmacies. Save time and obtain your medicine with convenience and privacy.
Purchase deetor capsules online for efficient protection. Click here: https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ .
Join our forum at [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/pharmacy/ – generic pharmacy in canada[/URL – and discover cutting-edge methods to handling your well-being.
Just released! Discover the latest solution for managing your health needs – priligy 30 mg price walmart . Available now, get your supply through our authorized online platform.
Access the top deals on https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ to reduce your nasal symptoms now.
Check out [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/prednisone/ – sale online prednisone[/URL – for exclusive prices on alopecia medications.
Research and uncover the positive effects of [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ – tadalafil[/URL – for improving fertility. Purchase it online to begin your road to parenthood today.
Harness the power of improved health by opting for our lasix coupon , offering a breakthrough method for those seeking superior performance.
Finding the most affordable https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ can be a daunting task. Browse our site for unbeatable prices.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your well-being? No need to stress out! You can [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/buy-cialis-w-not-prescription/ – discount on 10 mg cialis price[/URL – simply and safely.
Quality and affordability meet when you seek your pharmaceutical needs [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/]order propecia[/URL] , ensuring you obtain top-notch medical treatments without breaking the bank.
Discover affordable relief for joint pain and inflammation. Now you can purchase viagra information . This potent treatment offers a solution for controlling discomfort with convenience.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by choosing to https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra/ , a decision that empowers you to enhance your wellness routine from the comfort of your home.
Browse choices for cost-effective [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/cialis-5mg/]tadalafil[/URL] , ensuring you’re getting optimal pricing for your wellness.
Ailments requiring potent anti-inflammatory treatment? Find out about [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol price[/URL – for effective relief from redness.
Get rid of lice effortlessly with our treatment at tretinoin prescription buy .
Valuable insights reveal that obtaining https://nabba-us.com/item/cialis/ aids in boosting heart health, showcasing its efficacy.
Obtaining [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ – erectafil cost compare[/URL – for alleviating inflammation and pain is straightforward. Acquire it online for prompt relief.
Explore affordable solutions for your health needs with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – retin a brand[/URL – . Buy your treatment online today.
I was in search of a trustworthy place to acquire my medication sans hitches, and I eventually found it vardenafil .
Seeking a reliable source for purchasing your hair loss treatment? https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ offers a broad selection of choices for combating hair thinning.
Combat digestive discomfort effectively with our safe remedy. Order your solution online at [URL=https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine walmart price[/URL – .
Keeping your heart health in check is crucial. For those seeking affordable treatment options, purchasing [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution. Ensure you get advice from a healthcare professional before beginning any new medication.
Keep your health in check without overspending; purchase low-cost antiretrovirals. Don’t miss out: tadalafil 10mg .
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover special https://renog.org/product/cialis-2-5mg/ for savings on crucial treatments. Obtain yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
Obtain your health solution efficiently; [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ – best price lady era[/URL – offers a budget-friendly alternative to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia. Opt to order it on the internet for convenience.
Just in! Get your daily dose of vitality now. For those looking to enhance their wellness, [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – offers a convenient solution. No more waiting; experience a revitalized life today.
Now, secure the essential generic priligy at walmart conveniently via our portal.
Visit our website to discover the https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ for treating hair loss.
Quickly purchase your medication via the web with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – , ensuring a straightforward procedure.
“Having researched for budget-friendly solutions, discover lasix.com for improving well-being economically.”
Discover innovative treatment options for enhancing your lifestyle; delve into the benefits of https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ .
To secure your medication, consider [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – hydroxychloroquine 200mg[/URL – —a dependable source for high-quality healthcare solutions.
Purchase
Revolutionize your argumentation skills with our comprehensive guide on crafting compelling narratives; access it xenical . Enhance your ability to persuade any audience through efficient utilization of rhetorical strategies.
Keeping allergies at bay doesn’t have to be costly. https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ offers an affordable solution.
Boost your stamina and performance with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 10mg[/URL – . Enhance your vitality seamlessly immediately.
Battling insomnia? Our pharmacy offers a quick solution. Purchase [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – buy nizagara next day delievery[/URL – now for a peaceful night’s sleep.
Research reveals that buying effective treatments for your health needs has never been easier. Ensure your well-being by choosing levitra generic canada online.
Obtain fertility medication at competitive rates; explore the https://charlotteelliottinc.com/drug/clomid/ now. Many individuals seeking to improve their chances of conception realize it helpful.
Discover safe and easy ways to obtain your prescriptions with our reliable [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/prednisone-uk/ – prednisone buy[/URL – service.
Discover unparalleled savings with our unmatched offer: [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – generic nizagara at walmart[/URL – . Secure your batch today and enjoy the potency of this treatment.
Questioning where to find top-notch cardiovascular health supplements? Look no further than buy dapoxetine , your premier source for every one of your heart health supplements.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ , your go-to source for acquiring potent ED solutions virtually.
Researching options to procure Etizolam legally? Ensure security by consulting healthcare professionals first. Click here for details: [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin 500mg capsules for sale[/URL – . Always prioritize your health by seeking counsel from certified experts.
dailyfashionhub – Very clear layout, shopping was hassle-free.
Seeking acid reflux alleviation? Explore [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – price of strattera[/URL – for a safe remedy.
Keeping your heart’s rhythm steady is crucial; procure shopping cart for sale online check payment tadalista to keep optimal cardiac health and function.
Access effective treatment quickly and securely by choosing to buy your medications through our web platform. For those in need urgent therapy, https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ offers a reliable solution.
Gain immediate access to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone generic fast shipping[/URL – and alleviate your concerns with a simple click.
With widespread availability, you can now obtain [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ – nizagara prices[/URL – , ensuring availability to those who need this treatment without delay.
Acquire your propecia today and benefit from the discounts on drugs designed to enhance male wellness.
“Your hassle-free answer for obtaining pharmaceuticals swiftly is here at https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ , where you can buy your necessary treatments with ease.”
Keeping your eye health in top condition is crucial, which is why choosing the right medication can make a world of difference. For those dealing with elevated intraocular pressure or open-angle glaucoma, [URL=https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ – generic viagra soft tabs in canada[/URL – offers a trusted solution. Ensure you consult a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for your needs.
peakclicks.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Quality healthcare means having access to various treatment options. When it comes to HIV management, one can choose for branded medication or explore cost-effective alternatives like [URL=https://nikonphotorecovery.com/item/levitra-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – levitra 20mg[/URL – . These options ensure that patients have access to necessary treatments at a reduced cost.
Considering the need to manage your health, discovering cost-effective solutions becomes paramount. Therefore, when looking to support your cardiovascular health, kamagra price at walmart provide an economical option.
Stay informed and ensure optimal health management by visiting https://charlotteelliottinc.com/lasix/ to learn more about controlling your anticoagulation therapy.
Considering the urgency to manage inflammatory bowel diseases, it’s essential to secure effective medication. [URL=https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ – generika prednisone bestellen[/URL – stands out as a dependable choice for those seeking respite from the symptoms of conditions such as ulcerative colitis.
Acquiring [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – increase effectiveness of cialis[/URL – has never been easier. Find your way to wellness by utilizing a secure solution.
Questions about managing reproductive health? Explore how the furosemide could aid in your path towards conceiving.
Unlock the secrets to enhanced vitality and stress relief with https://damcf.org/prednisone/ . Uncover the ultimate source for an age-old herb.
Considering the myriad options available, opting to purchase your therapy through reputable sources is paramount. For those looking into therapy for gastrointestinal issues, [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-200mg/ – generic hydroxychloroquine without subscription[/URL – stands out as a trusted choice among various outlets.
Battling seasonal allergies? Explore obtaining amoxicillin buy to alleviate your symptoms.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ .
Purchase your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – online to guarantee you get quality treatment with ease.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil without a doctors prescription[/URL – , and Snag your supply of crucial antibiotics easily via our website.
Just discovered you have high cholesterol? Worry less and explore healthier living by considering prednisone cost . These medication can be a crucial part of your therapy. Buy it online to control cholesterol successfully.
Discover incredible savings on your prescriptions with our https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ .
When seeking relief from pain, consider [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – as a potent option. This anti-inflammatory drug is perfect for treating numerous conditions, offering both affordability and effectiveness.
rankgrid.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
turborank.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
clickforgehub.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
https://bravomos.ru/ bravomos
rapidboost.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://momsanddadsguide.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – is a viable option. Explore obtaining this treatment online for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Quality and affordability meet, enabling you to purchase your prescription seamlessly. Seek no further for your health solutions, click here: nizagara . Offering ease and safety, we’ve got your needs covered.
Obtaining Clomid at optimal prices is now within reach. Visit our website to order your bottle of Clomid for ovulation induction. https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ today!
Seeking a reliable source to acquire your medications? Look no further! [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – offers a wide selection of pharmaceutical products on the web.
Discover how to get your prescriptions effortlessly with [URL=https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
To unearth how to obtain your 100 mg lasix on line at matchless prices, check out our site now.
Knowing how essential it is to manage your hypertension, you can secure a reliable solution with https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ online.
Discover how [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – can revolutionize the way you engage with casino games.
Unlock the potential of antiviral therapy by choosing to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . Ensure optimal health outcomes by procuring this vital medication from our website today.
Explore the benefits of enhancing your well-being with our top-notch supplement. Now is the time to achieve better health by clicking here: price on 50 kamagra . Opt for a revitalized life today!
Discover the benefits of https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ for heart health and stroke prevention. Purchase your vital medication through the internet today and enjoy the protective effects.
Visit our website to locate the [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia online[/URL – for your pain relief needs.
As an expert in the medical field, I need to emphasize the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before initiating any treatment. Nevertheless, for those looking into non-prescription options for managing specific conditions, prices for pharmacy could be considered. Always verify that you acquire drugs from credible sources to guard against imitation products.
Finding the right topical treatment can be tough, but our https://markssmokeshop.com/item/prednisone-no-prescription/ offers a wide selection of options for your needs.
Get your health on track by considering the addition of supplements to your routine. Opting to [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax generic pills[/URL – can be a wise decision, especially if you’re looking to enhance your well-being. Don’t hesitate to discover this option today.
Having trouble finding budget-friendly solutions for fertility treatments? Explore [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/priligy/ – low price priligy[/URL – , where you might find attractive rates for your needs.
Access genuine cialis easily. Purchase this vital drug online seamlessly.
Zero reasons to wait! Acquire your medication for enhanced stamina now at https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ .
Unlock significant savings and convenience when you acquire your medication virtually. Experience the ease of obtaining quality healthcare products without leaving your home. Click here [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ – nizagara coupon[/URL – to initiate your journey towards better health.
Just when you require relief from persistent nasal symptoms, ordering [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ – lasipen[/URL – offers a convenient solution for managing your symptoms.
Your health and wellness path starts with a single step. Discover the most economical options for your healthcare needs. Click where to buy lady era to unlock incredible savings.
Facing chronic health challenges? Secure your wellness with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ , a trusted solution. Guarantee optimal health by choosing this potent remedy accessible on the web.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – online for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем обширный каталог продукции, обеспечивая превосходное качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с высоким уровнем сервиса.
Наша команда службы поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что наше качество и сервис – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
поставляемая продукция:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов золотая 20х6х0.1 мм ЗлСрМ58.5-8 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
Seek affordable options for improving your vitality? [URL=https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ – us prednisone without prescription[/URL – offers a powerful blend for those looking to revitalize energy safely.
Join the myriad of satisfied customers who have uncovered the ease of acquiring their medication via the web with furosemide without dr prescription usa , offering a hassle-free way to get your wellness necessities.
To secure your health’s protection, always choose authentic medication. For those looking to buy antiretroviral treatment, https://kristinbwright.com/lasix/ offers a dependable option.
Buy
To secure efficient treatment for IBS, consider obtaining stablon walmart price , known for its outstanding advantages.
Access the best deals on https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ to reduce your nasal congestion now.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by checking out our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Locate [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – sarafem[/URL – to improve your vitality efficiently and securely.
Regarding your health needs, discover an efficient solution to manage edema; [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – propecia without a doctors prescription[/URL – is available. Secure, immediate acquisition is guaranteed, making treatment more available.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxil without prescription , supplying broad-spectrum solution for bacterial infections.
Xperience enhanced vitality and wellness with our https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ , up for grabs for regular use.
Quest for affordable ED medications? Find a solution at [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – fildena 150mg[/URL – , offering a broad selection of high-quality choices.
Many wonder what a [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – online prednisone no prescription[/URL – implies; it’s essentially obtaining money beforehand.
When seeking effective management for epilepsy or bipolar disorder, explore buy priligy in las vegas as your choice.
Just when you need effective treatment for bacterial infections, opt for https://markssmokeshop.com/drugs/flagyl-brand/ through reputable platforms.
Discover advanced ways to manage your health needs with [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – .
Harness the power of convenience and savings when you buy your birth control. With our unbeatable offers, you can procure low-cost [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/lasix/ – buy lasix without prescription[/URL – without ever compromising on safety.
Visit our website to locate the top canada pharmacy .
The need for reliable and efficient access to drugs has never been greater. Discover your options and purchase https://mnsmiles.com/item/nizagara/ today.
Be amazed by the affordability when you explore the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – . Find unbeatable deals for your dizziness management needs right here.
As an expert in the medical field, I need to emphasize the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before initiating any treatment. Nevertheless, for those looking into non-prescription options for managing specific conditions, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ – isotretinoin[/URL – could be considered. Always ensure that you acquire pharmaceuticals from trustworthy sources to guard against imitation products.
To get the essential iron supplements, explore cialis guaranteeing value.
Navigate to https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ for quick and secure acquisition of your essential treatment.
Now, uncover the benefits of [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/online-generic-pharmacy/ – online pharmacy no prescription[/URL – , and learn how it can assist in reducing your discomfort.
Yes, if you’re looking to buy cheap 2.5 cialis , consider exploring our reliable source.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your personal health needs, https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ online can be a simple process.
Browse the site to discover [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – generic amoxil canada[/URL – , ensuring you obtain top-quality antibiotic options at incomparable prices.
Zajimavy obsah! Objevil jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a musim priznat, ze jejich bonusy jsou skvele. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere nadchnou kazdeho hrace. Velmi me zaujaly jejich herni souteze a automaty – online casino pro ceske hrace s vybornymi podminkami. Pokud hledate bezpecne online casino s bonusy, podivejte se zde: Twitter . Urcite to stoji za zkousku a muze to prinest spoustu zabavy a odmen.
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
Objevte Spinmama Casino CZ a ziskejte free spiny
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
aa692e6
Order your [URL=https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ – pharmacy on line cialis discount[/URL – effortlessly. Secure your supply through our platform today for a hassle-free experience.
Just realized you need Cialis for your health? No need to fret! You can cialis to buy without hassle and with confidence.
To obtain holistic wellness solutions, consider to https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ .
Secure your well-being and save cash by exploring our [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – , highlighting a variety of premium treatments for improving men’s health.
Having doubts about where to locate the best deal for your antimalarial medication? Worry no more! Just click on [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nexium/ – nexium online pharmacy[/URL – to check out the most economical options available.
When seeking cost-effective solutions for erectile dysfunction, consider mail order fildena as your preferred source.
Order your health enhancements with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/viagra/ , providing a selection of pharmaceutical needs.
Acquire your [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – cheapest fildena dosage price[/URL – effortlessly with our secure online platform. Obtain your vital pharmaceuticals on the web with ease and confidence.
When seeking affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction, consider [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – fildena 25mg[/URL – as your choice source.
X-plore affordable antibiotic options; cipro from india can be the solution to fight bacterial infections efficiently.
Zero hassle to safely obtain your prescriptions online. Click here: https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ for your well-being solutions.
Visit our website to order [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – , ensuring affordable choices for your health.
To find out the lowest cheap ranitidine pills , check out our page.
Looking to manage your gout? Consider acquiring effective medication. For your convenience, https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ via our website to reduce symptoms efficiently.
Xperience enhanced cardiovascular health by managing your symptoms efficiently. Opt to acquire your prescription through [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – cheapest generic pharmacy uk[/URL – , a reliable source for individuals seeking effective stroke prevention.
Zeroing in on treatments for COVID-19, [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – offers a promising option. Seekers in the health arena can explore this remedial solution online.
Zealously seeking a reputable source to buy your prescriptions from? Look no further; prednisone usa overnight delivery offers a secure, discreet way to order what you need.
Maximize your health with https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ , the one-stop solution for all your medical needs. Find a wide selection of alternatives to improve your wellbeing today.
Looking to address your health concerns? Uncover a broad selection of drugs at [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl maxium dosage[/URL – , your go-to source for dependable healthcare solutions.
Navigating the expansive world of virtual betting in Canada? Look no further than nizagara 50mg. for your premier destination. Discover a wealth of options from sportsbooks to slots, ensuring an unparalleled wagering experience.
Discover groundbreaking treatments for your health. Purchase https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ from trusted sources virtually.
Get your [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – viagra 25 prix en pharmacie belgique[/URL – easily! Explore options to purchase your prescription without trouble.
FashionBuy Trends – Loved the seamless flow through the pages and the modern presentation.
UrbanPickStore – Fast and smooth process, very happy with the service today.
Considering urgent antibiotic requirements, acquiring [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – buy doxycycline in c[/URL – online provides a swift solution.
X-ray your options for migraine relief by exploring cialis capsules for sale , a leading solution available online.
Just discovered you’re in need of a rapid solution for better endurance? With https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ , find your answers and enjoy improved performance sooner than you think. Now you can acquire this remedy swiftly to ensure your readiness.
Get your vitality boost now with [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine 60mg[/URL – . Explore the numerous health benefits by ordering this revitalizer online.
Harness the power of effective antifungal medication by exploring [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – . Secure your health today by obtaining this crucial treatment online.
Finding cost-effective treatment is often difficult, but with options like order cheap pharmacy , getting your prescriptions is simpler.
Get the best deals on https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ ! Discover your options for purchasing this drug through our website and save on your next purchase.
Zero in on boosting your overall wellbeing with [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – buy generic online herbal-max-gun-power[/URL – , offering a herbal path to improving vitality.
Stop switching between a dozen sportsbook apps and websites. Beika.app consolidates your entire betting experience into one sleek, powerful platform https://beika.app
Revitalize your vitality effortlessly with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – , available now for those looking for a reliable answer to enhance their performance.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Acquire amoxicillin safely and swiftly.
Now, find out about the perks of https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ , and see how it can help in easing your pain.
Interested in managing HIV? Purchase [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – online amoxicillin no prescription[/URL – from a trusted source for proven results.
You can find effective and secure solutions for your health woes by visiting [URL=https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – .
Secure your health effortlessly; get your medication safely with online prednisone , ensuring maximum health outcomes efficiently.
Explore the positive effects of managing inflammation with https://nabba-us.com/item/lasix/ . Discover how it aids in lowering effects quickly.
Looking to boost your energy levels? Discover how [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ – prednisone[/URL – could assist. Available now, these caps are designed to assist your well-being journey.
Need to manage your health condition discreetly? Find your solution with [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – free lasix in the uk[/URL – , offering a reliable path to health improvement.
Obtain your medication swiftly and safely when you choose to retin a . This method ensures quick shipment of your vital treatment.
Unlock unbeatable deals on https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ ! Find your solution for a stronger life today.
Maximize your health benefits by exploring the cost of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol 6mg[/URL – , renowned for its cardiac supportive properties. Acquire your supply now to enhance your heart health.
Visit our site to discover your required pain relief. Buy doxycycline from canada on the internet for quick shipment.
Considering a quick funding solution? Explore https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ for speedy financial assistance.
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial, and finding the right medication should not be a hassle. For those seeking flexibility and convenience in their treatment, [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – offers a discreet, effective option. Consider obtaining your treatment via the web, ensuring you receive premium care without compromise.
Интересный взгляд на етику штучного інтелекту: людина і ШІ .
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and uncover generic solutions at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy prices[/URL – . Order this remedy via the web now and begin your journey towards regrowth.
X-plore the endless amusement options accessible with lasix , your entrance to the best betting adventures.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Find https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ to improve your vitality efficiently and safely.
For those seeking relief from upset stomach, explore a wide range of options by deciding to [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone[/URL – . Guarantee your health today with a simple purchase.
I’ve discovered that finding the lowest [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ – generic clomid from canada[/URL – might be a challenge. Yet, with right exploration, you can reduce costs on fertility aids.
Purchase your medications with ease; buy your prescriptions virtually at retin a on internet , ensuring safety and ease.
Navigating the market for Cytotec, a pharmaceutical used for terminating pregnancies, can be challenging. However, accurate and reliable information is crucial. For details on where to buy https://jawany.com/cytotec/ , ensure to look at trustworthy sources only.
Questioning where to purchase fertility treatments? Secure your [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/clomid/ – prices for clomid[/URL – effortlessly through our website.
Discover the best deals for managing your heart conditions with just a click. Visit [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix-for-sale/ – lasix online usa[/URL – and find the most economical options to acquire your medication virtually.
Get relief from seasonal allergies by exploring http://www.propecia.com , offering a cost-effective solution to control your symptoms efficiently.
Visit our website to get the most competitive https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ , offering cost-effective solutions for your well-being.
Zero in on significant savings for your hormone therapy needs. Discover the most affordable prices on hormonal balance medications at [URL=https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ – where to buy lady era[/URL – . Maximize your health without stretching your budget.
Keep your eyes looking their best with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – buy retin a[/URL – , available for buying virtually.
Finding effective tuberculosis treatment can be challenging, but cheapest doxycycline dosage price offers a simplified solution.
The need to acquire medications without leaving home has never been more critical. Now, you can conveniently get your https://tooprettybrand.com/product/tadalafil-10mg/ with just a few clicks.
Looking for an effective way to combat alcohol dependence? Learn about how [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – order prednisone[/URL – can be an essential part in your journey towards sobriety.
Get your amoxil easily from amoxil 650mg , offering prompt shipping to meet your requirements.
Quest for low-cost alternatives to manage your health? Discover the best deals with our https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ , your go-to choice for quality medication free from the hefty price tag.
Questioning where to acquire fertility treatments? Order your [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – effortlessly on the web.
Quality medication are just a click away; explore our range and get your [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – flomax tablets[/URL – with complete peace of mind.
Seeking a trouble-free way to boost your endurance? Check out kamagra canadian pharmacy for a reliable solution.
Discover affordable solutions for your medication needs; explore our wide range of options and compare https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ to ensure you’re getting the best value for your health.
Now, secure your cholesterol-lowering treatment conveniently [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin cream[/URL – .
“Quickly locate discounts on your next purchase with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ – cytotec cheap buy[/URL – . Save without hassle on vital medication.”
Quiet your anxiety at an affordable price with tadalafil without pres . Purchase your remedy today for peace of mind.
When considering options for treating https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ , many individuals seek affordable solutions. Discover a variety of options to obtain your medication through the internet, ensuring economic and easy access to the remediation you need.
Zeroing in on treatments for COVID-19, [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – buy nizagara w not prescription[/URL – offers a promising option. Seekers in the health arena can explore this curative option via the internet.
Discover methods to fight pests with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil online with discover card[/URL – , your prime solution available on the web.
Knowing the importance of trustworthy treatment for endometriosis, find out more about tadalafil as a potential option.
Knowing the cost of medication is vital, learn about the most competitive https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ for your necessities.
Never neglect your need for a proficient sleep aid. Discover the revolutionary [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – , a game changer in achieving a peaceful night’s sleep.
Explore incredible discounts on health supplements with our [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra[/URL – . Don’t miss out on this opportunity to save on your purchases.
Explore options to obtain overnight retin a , offering a convenient way to secure your medication without leaving home.
As an expert in the medical field, I need to emphasize the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before initiating any treatment. Nevertheless, for those looking into non-prescription options for managing specific conditions, https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ could be considered. Always ensure that you obtain medications from credible sources to guard against fake products.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Learn how [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – can help and restore your comfort.
Looking for a way to tackle your illness? hydroxychloroquine 200mg might be the remedy you’re seeking. Find out about how this drug can help you today.
Our team has sourced the https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
Considering a demand for affordable treatments, you can now purchase [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia 5mg[/URL – , a preferred choice for those seeking cost-effective bone health support.
Need to enhance your eyelashes? Explore a range of options available at [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – lasix on line[/URL – , where you can Purchase your item comfortably on the internet.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your personal health needs, amoxicillin online can be a straightforward process.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ virtually can be a seamless process.
Research recent [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – on line lasix[/URL – to regulate hypertension efficiently.
Access the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – strattera austrialia[/URL – and save on your medication costs. Find the lowest price for your prescription without compromising quality.
Variety of options to acquire retin a are available, offering reliable pain relief from various conditions.
You can order your necessary medicine https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ with convenience.
When seeking relief from discomfort, consider [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – on the internet as a convenient way to acquire your treatment.
Интерьер загородного дома Проект загородного дома требует тщательного продумывания архитектурных решений и планировки. На начальном этапе важно определиться с размерами участка и его особенностями. Далее, стоит разработать схему, учитывающую оптимальное использование природных ландшафтов. Каждый элемент – от расположения комнат до окон – должен быть спроектирован так, чтобы дом был не только красивым, но и удобным для проживания. Энергоэффективные технологии, такие как солнечные панели и утепленные стены, помогут снизить затраты на отопление и электричество, что особенно актуально в современных условиях.
Maximize your savings on osteoporosis treatment by seeking the [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – lowest price for tamoxifen[/URL – . Discover affordable solutions today.
Purchase this mosquito repellent on site for reliable protection. Click here: order deetor .
X-plore your options for managing arrhythmia with proven solutions. Discover how https://center4family.com/priligy-online/ can aid in controlling your heart rate, providing serenity.
Alleviate your nasal congestion and relieve allergy symptoms quickly by utilizing [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – lowest price generic retin a[/URL – . This potent treatment offers immediate relief for those suffering from seasonal allergies, ensuring your daily life are no longer hindered by annoying sniffles and sneezes.
yourdealhub.shop – Prices are fantastic, definitely coming back for more shopping soon.
Explore ways to obtain [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – , a crucial treatment for handling Parkinson’s disease, directly via our site.
Explore reliable options to buy your medication safely. Click nizagara 100mg preco for verified products.
Just clicked on https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ ? Ensure to explore our site for additional information and find out how this medication can help in your treatment journey.
Keeping your heart’s rhythm steady is crucial; procure [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – propecia 5mg[/URL – to keep optimal cardiac health and function.
*Kraken* — актуальные зеркала 2025
В этой заметке вы найдёте все ссылки и адреса для входа на *Kraken* в 2024-2025 году. Мы собрали только надёжные зеркала, которые помогут обойти блокировку и подключиться к маркетплейсу без проблем и с полной анонимностью.
Актуальный список ссылок *Kraken*
1 Главная ссылка: https://kra24.cn.com/
2 Резервный сайт: https://krak24.li/
3 Дополнительный сайт 2: https://kraken.li/
4 Подлинный Tor-адрес: krakeno4nmrk1ewmq4l9tme9wpfk2lczlsm7g3epfgu3itne8raion *точка* onion
5 Telegram канал с обновлениями: https://t.me/+WIvclfeRsfZlM2Yy
6 Скачать Tor: https://www.torproject.org/download/
Как зайти на *Kraken*
1. Сначала установите браузер Tor — он нужен для доступа к даркнету.
2. Откройте Tor и дождитесь полной загрузки сети.
3. Перейдите по проверенной ссылке https://kra24.cn.com/.
4. Если у вас ещё нет аккаунта, создайте учётную запись: придумайте логин и надёжный пароль.
5. Обязательно настройте 2FA для защиты .
Советы по защите
– Всегда проверяйте зеркала перед переходом — это важно для предотвращения фишинга.
– Используйте прокси вместе с Tor для максимальной анонимности и шифрования трафика.
– Проверяйте список — ссылки на *Kraken* могут меняться из-за фильтрации.
– Никогда не используйте ссылки из случайных источников, даже если они кажутся похожими.
Почему выбирают *Kraken*
– *Kraken* маркетплейс|*Kraken* сайт популярен в даркнете благодаря:
большому выбору продукции,
безопасной системе покупок,
полной конфиденциальности пользователей.
Также здесь работает система рейтингов продавцов, что помогает выбирать только проверенных поставщиков.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
?? Что делать, если *Kraken* не открывается?
– Попробуйте альтернативный адрес из списка.
– Перезапустите Tor или проверьте VPN.
– Проверьте обновления ссылок в Telegram.
?? Где брать рабочие ссылки?
– Только с проверенных источников.
– Храните их в надёжном месте, периодически проверяйте актуальность *Kraken* .
?? Как избежать фишинга?
– Не открывайте ссылки в обычном браузере.
– Используйте только Tor + VPN.
– Всегда проверяйте точный адрес перед вводом личных данных.
Вывод
?? *Kraken* — это один из самых известных маркетплейсов в даркнете. Чтобы всегда иметь доступ, используйте только проверенные зеркала, соблюдайте правила безопасности и следите за обновлениями.
?? Сохраняйте этот список и делитесь только с теми, кому доверяете.
—
Ключи, покрытые статье
* *Kraken* ссылки 2025
* Зеркало *Kraken*
* Вход на *Kraken*
* Рабочие ссылки *Kraken*
* Актуальный список *Kraken*
* *Kraken* маркетплейс доступ
* Как зайти на *Kraken* через Tor
You can find the best [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/retin-a/ – retin a online no script[/URL – on the internet, ensuring you receive maximum savings for the therapy.
With so many options available, deciding where to acquire your medications can be challenging. For those seeking Oxybutynin, retin a provides a safe and cost-effective option.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your health? No need to worry! You can https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ easily and securely.
Ensure you secure your prescription medication safely; consider [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ – asthalin[/URL – for a convenient solution.
For those seeking bone density improvement, consider price of pharmacy south africa as a hassle-free solution.
Looking to purchase Depo-Medrol for your medical necessities? Click on this link https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ for a simple experience.
Given the ongoing discussions about its application in various treatments, finding a reliable source to acquire [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – on the web is crucial for consumers.
Home Collection Zone – Enjoyed the clean interface and the impressive variety of décor pieces.
When seeking to buy spironolactone, a trusted option is available at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil[/URL – . This platform offers a seamless way for individuals needing to get their medication.
Given the myriad options for treating fertility issues, the nizagara coupon often emerges as a significant consideration for many.
Looking to secure your antiviral treatment? Now, you can order https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ easily.
Just found an amazing deal on cholesterol-lowering medication? Secure your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – buy propranolol no prescription uk[/URL – now and start your journey towards improved heart health!
With widespread availability, you can now acquire [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – , ensuring accessibility to those who need it promptly.
Absolutely alleviate allergies with easy access to tretinoin 20g . Acquire your fast-acting allergy relief online without the requirement for a prescription.
Discover how to obtain remedies for improving your stamina safely; https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ is your gateway to well-being.
Consider securing your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone w not prescription[/URL – effortlessly. Purchase your prescription with utmost convenience.
yourdailyvalue.shop – Smooth browsing experience, products are clearly listed and easy to find.
Explore cost-effective options for managing hair loss with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – nizagara by mail mexico[/URL – , now accessible in several formats online.
Need to manage irregular periods? Discover your solution with propecia without a doctors prescription . Explore options to purchase this vital medication through the web.
Be concerned about your health, and acquire a reliable HIV detection solution. Don’t wait; https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ now and guarantee your peace of mind.
Gain entry to affordable therapy with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – nizagara generique 25[/URL – , offering aid for patients seeking reliable substitutes.
Research reveals that securing effective treatments for your health needs has never been easier. Ensure your well-being by choosing [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil[/URL – online.
Quest for cost-effective alternatives to manage your health? Discover the best deals with our hydroxychloroquine , your go-to choice for dependable medication free from the hefty price tag.
Unlock the secrets to enhanced vitality and stress relief with https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ . Discover the ultimate source for an age-old remedy.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Discover how to secure your needs easily with [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – .
Harness the power of modern medicine to stabilize your mood with [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix tablets online[/URL – . Discover to tackle bipolar disorder with proven solutions accessible.
Considering the escalating expenses associated with fertility treatments, finding economical solutions is crucial. Opt for cheap priligy to enhance your journey to conceiving, available at rational rates without compromising on quality or efficacy.
Keeping allergies at bay is now easier than ever. Whether you’re looking to tackle seasonal sniffles or seeking relief from year-round triggers, you can obtain effective antihistamines quickly. https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ offers a reliable solution, making it straightforward to buy your essentials from the comfort of home.
When seeking efficient ulcerative colitis treatments, you can procure [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone from india[/URL – for immediate relief.
Get your prescription easily with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ – buy ventolin on line[/URL – , providing numerous options for all your medical needs.
Looking for a budget-friendly solution to your acid reflux? Discover the wide range of solutions at flomax without a doctor’s approval , your go-to spot for trustworthy medications.
Reduce your heart’s workload with https://hip-hope.com/online-generic-priligy/ , an essential treatment for managing chest pain. Order today for improved heart health.
Looking to manage your condition without breaking the bank? Find out cost-effective solutions with [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine non generic[/URL – .
Combat everyday pains and aches effectively with [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/levitra/ – levitra in guatemala[/URL – , on offer on the web to aid you keep your active lifestyle without discomfort.
Maximize your vitality and stamina with lasix , the prime choice for enhancing performance. Explore a decisive solution for improving your health and confidence seamlessly.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Consider https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ , a cost-effective and trustworthy option for enhancing your sexual health.
Discover affordable options for managing addiction; [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/lasix-40mg/ – lasix[/URL – offers a pathway to recovery. Explore budget-friendly methods for addressing dependency.
Quest for the most economical lash enhancer? Search no more. Uncover your answer at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/trazodone/ – guaranteed lowest price on trazodone[/URL – , offering unparalleled deals.
Considering the demand for reliable heart rhythm medications, purchasing generic name of flomax online offers a budget-friendly solution.
Quickly secure https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ , a vital remedy for upset stomach.
Regarding your health, it’s crucial to locate a trustworthy option. For addressing specific medical conditions, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ – priligy without prescription[/URL – stands out as a recommended choice by healthcare professionals.
Patients looking for reliable Hepatitis C treatment should review strattera 40mg , a foremost option shown to combat the virus.
Looking for relief to your illnesses? Now, you can acquire https://homegrownscholars.com/item/viagra/ online. This solution presents ease to obtain your medication securely.
Discover the most effective solution for your eye ailment with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – . Purchase this highly recommended ointment through our website for rapid relief.
Zero in on your health with affordable solutions; uncover buying cheap amoxil online for handling your ailment. Secure effective care effortlessly.
X-plore the myriad benefits of https://renog.org/trazodone/ , your go-to solution for tackling OCD symptoms. Now you can easily purchase this crucial medication through our reliable website.
Need to control your stroke risk? Explore options and order [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/propranolol/ – propranolol[/URL – , a trusted option for stroke prevention.
Inspire Daily Hub – Neat sections and motivating content create a pleasant browsing experience.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Discover how [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ – flomax.com[/URL – can help and restore your well-being.
If you’re seeking a reliable cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into cialis without prescription , available for buying right here.
Venture into a world of health where purchasing your medications https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ is effortless.
Visit [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – amoxil 650mgm israel prices[/URL – to acquire the Augmentin solution at the lowest cost.
Keep your eyes looking their best with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/low-price-pharmacy/ – discount pharmacy[/URL – , available for purchase virtually.
When seeking trusted and effective treatment for psychotic disorders, consider exploring options to purchase ventolin from accredited sources.
Zero in on rejuvenation and vitality with https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-online/ . Uncover how to rejuvenate your youth and stamina without breaking the bank.
Just discovered the most affordable option for generic Cialis in Australia? Learn more at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ – priligy 60mg[/URL – .
If you’re looking for an effective remedy for gastrointestinal upset, look into [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – buy ventolin us[/URL – .
Acquire generic lasix online for oncological therapy.
Acquire your eye drops with ease; simply https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ and ensure enhanced ocular health without stepping outside.
Zoning in on reasonably priced heart medication, find optimal pricing on [URL=https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ – best price nizagara[/URL – via digital pharmacies.
Zero hesitation required when looking for ED solutions; order [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – viagra[/URL – easily.
You could get tadalafil 10mg safely and easily via the internet.
Discover reliable joint pain relief with https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ , the premier remedy now available online.
Discover cutting-edge ways to manage stress with [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel[/URL – , up for grabs via our website.
Prices for essential cardiac care medications can vary; hence, it’s crucial to check the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – generic nolvadex from india[/URL – to ensure you’re getting a fair price.
Your health is our priority; buy buy nizagara online cheap online and commence your journey to enhanced health today.
Optimize your health with the solution everyone’s talking about, https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ . This powerful formulation can transform your wellbeing.
Browse the site to find [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ – amoxil coupons[/URL – , ensuring you secure premium antibiotic options at unbeatable prices.
When in search of improved satisfaction and performance in the bedroom, consider exploring fildena , a solution revered for its efficacy.
Aches and pains can interrupt your day, but relief is within reach. Discover your options and consider https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ for quick alleviation. This might be the solution you’re searching for.
Boost your confidence and boost your performance with genuine [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . Preorder immediately for a discreet and efficient solution to your needs.
Discover your path to savings on medications by choosing to buy from zoloft . Experience economical medical solutions today.
X-plore cost-effective healthcare options; https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ for managing your condition with convenience.
Shop now for your hypertension treatment and discover how much you can save at [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – buy generic kamagra[/URL – , your go-to destination for affordable healthcare solutions.
For those in search of effective management for their inflammatory conditions, ventolin without a prescription offers a dependable solution.
Xperiencing baldness can be distressing. Uncover solutions at https://myrsvplive.com/propecia/ , offering a variety of treatments to rejuvenate your confidence.
Considering your health, acquiring [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/pharmacy/ – next day online pharmacy[/URL – has never been more straightforward. Now, Order your necessary cardiovascular medication via the internet effortlessly and securely.
Need to purchase altitude sickness medication? Explore options and buy your solution easily with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ – purchase amoxicillin without a prescription[/URL – .
Optimize your health and savings by exploring propranolol , a viable option for those in search of cost-effective reproductive health options.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Look into https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ , a economical and effective option for enhancing your sexual health.
Many look for inexpensive therapy options online, and [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil capsules for sale[/URL – may be the answer.
Zero pain, maximum relief! Get your hands on the cheapest solution for your discomfort. Buy your prednisone now and start feeling ease from pain right away.
Find best prices for natural vigor solutions; https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ on our website.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – through our secure portal. This critical remedy is now obtainable effortlessly.
Keeping your heart health in check is crucial. For those seeking affordable treatment options, purchasing [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – http://www.lasix.com[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution. Ensure you get advice from a healthcare professional before beginning any new medication.
Relieve your enlarged prostate symptoms today! Explore our selection of flomax , specially designed to enhance your urinary flow and overall well-being.
When seeking relief from persistent aches, consider https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ as your go-to medication. It’s accessible through online pharmacies, offering simplicity and results.
Understanding the urgent need for medication, it’s now possible to acquire your drug hassle-free. No longer do you have to wait for your critical treatment. Learn more at [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix in horses[/URL – to secure your medications swiftly and reliably.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Welcome
Harness the power of optimal well-being by opting for our [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – , offering a breakthrough option for those seeking superior performance.
Ensure you obtain your hydroxychloroquine online pharmacy with assurance for treating certain conditions.
Obtain your https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ today and manage your health effectively. Purchase immediately for rapid delivery.
Looking to purchase Depo-Medrol for your medical needs? Click here [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – stromectol price at walmart[/URL – for a straightforward transaction.
yourdealhub.shop – Love checking this site daily, products are well organized clearly.
Uncover the most economical way to manage your health, buy [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine[/URL – online. This solution offers not just convenience but also savings.
Before making a purchase, discover the lasix by browsing our website. This essential drug can now be purchased affordably.
Mitigate menopausal symptoms with https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ , an effective option for easing night sweats.
Unlock unparalleled convenience by procuring your medications through [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – 25 nizagara pills[/URL – . This streamlined process ensures a trouble-free path to obtaining the needed medical solutions.
FuturePath Corner Hub – Smooth page flow and well-laid-out items make browsing pleasant.
I’ve tested lots of virtual casinos lately, and it’s kind of crazy how many beginners sign up without checking proper reviews first. If you need a simple explanation of promos, withdrawals, and available games, this guide made things easier: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s very clear and breaks down the important points before making a deposit. You should check it out if you prefer to play safely.
Discover the most affordable options for treating your allergies with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax[/URL – .
Given the unpredictable nature of weather patterns, securing your property against inundations has never been more crucial. Explore options to protect your home with a cialis 2.5 mg, order online , offering a wide range of measures to combat water damage.
Searching for budget-friendly pain relief solutions? Look no further! Check out our site for unbeatable deals on https://tooprettybrand.com/product/viagra-for-sale/ , perfect for those seeking top-notch and effective medication.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/cytotec/ – cytotec canadian pharmacy[/URL – , a top choice for tackling baldness. Acquire these tablets today and begin your road to regrowth!
yourdailyvalue.shop – Really enjoying the content here, very helpful and nicely structured.
Now, obtain your path to health with ease. Discover a pure solution by choosing to [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/nizagara/ – generic nizagara tablets[/URL – .
Reduce your risk of stroke and heart attack with Aggrenox. Secure your health by securing your supply through cialis.com , offering an efficient, reliable pathway to maintaining your cardiovascular health.
X-plore your options for controlling hypertension with reliable medication. Buy https://coastal-ims.com/drug/zithromax/ online to ensure your heart health today.
Buyers interested in acquiring [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/levitra-price-walmart/ – levitra[/URL – could easily Purchase their Supply through trusted internet-based outlets, ensuring speedy and secure delivery to their doorstep.
Facing chronic pain or anxiety? Explore your relief securely with [URL=https://damcf.org/buy-lasix-online/ – lasix[/URL – , the trusted option.
X-ray your budget and find how much you can conserve on your next purchase with cheap priligy no prescription canada , a method to obtain your essentials at better rates.
Opt for hassle-free solutions and acquire your essential eye care products with ease; https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ now and experience the simplicity of acquiring your wellness essentials shipped right to your doorstep.
Your health is essential, and managing discomfort should be a priority. For those moments when pain strikes, having a trusted remedy at hand is key. Buy [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ – lasix tablets[/URL – online to ensure you hold a reliable answer for relieving pain.
Explore the new advances in heart health by visiting levitra . Discover methods to boost your well-being now.
Your search for effective and safe medication ends here; https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ offers you the opportunity to purchase top-quality therapy conveniently.
Keep allergies at bay with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ – lasix dallas no prescription online[/URL – , available now. Experience respite against seasonal allergies quickly.
Zero delays in your heart rhythm treatment are crucial. Secure the prescription online with [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ – prices for nizagara[/URL – , ensuring swift management of your condition.
Now, obtain the supply of mail order tretinoin china effortlessly. Order virtually without hassle.
If you’re looking to acquire hypertension medication at an affordable rate, consider visiting https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra-capsules-for-sale/ for unmatched offers.
Secure
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before attempting to acquire [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ – buy flagyl no prescription[/URL – cannot be overstated.
X-plore your options for alleviating eye discomfort with ventolin non generic . Find comfort for your eyes without requiring a prescription.
Relieve digestive discomfort efficiently with our natural solution. Check out https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ for further details.
Now, discover safe and effective treatment options,search through our selection of pharmaceuticals. For your convenience, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – retin a coupons[/URL – are accessible online.
Quickly obtain your prednisone aus spanien through the internet and discover the advantages!
Explore affordable ADHD treatment options by purchasing https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ to control symptoms effectively via the internet.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/generic-amoxil/ – generic amoxil[/URL – online for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
Market of Fashion Lovers – Clean visuals paired with smooth navigation made browsing enjoyable.
Unlock access to antifungal medication by exploring your options to [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – lasix cheap[/URL – . Acquire your treatment virtually with ease and convenience.
Venture into the realm of effective erectile dysfunction treatments with cheapest fildena , accessible via our website.
Obtain your https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ with ease. Acquire your medication online seamlessly and efficiently.
Achieve healthier hair with the [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – , the preferred solution for hair loss.
Explore cost-effective options for your healthcare by choosing to order [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – .
Discover secure methods to treat endometriosis signs. For individual treatment options, lasix is accessible on sites.
Zest for a healthier life often leads us to search for treatments that can boost our well-being. For those managing hypertension or chest pain, https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ could be your path to better health.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – .
In search of a cost-effective solution for your hair care regime? Consider opting for [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ – lowest price for tadapox[/URL – , a widely acclaimed choice. Whether you’re aiming to purchase this haircare solution for enhancing hair growth or reducing hair fall, it’s accessible online.
Zillions seek efficient solutions for ED; buy viagra uk provides a broad solution.
Having trouble with confidence? Explore our options to enhance your well-being. https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ today and commence your journey to enhanced self-assurance with our dependable solutions.
Replenish your health supplies easily with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – online tretinoin no prescription[/URL – , to secure consistent care.
Combat inflammation and pain effectively with a cost-effective solution; explore our selection for [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – . Locate economical options to treat your needs effortlessly.
Regain confidence in the bedroom with the nizagara , your discreet solution to enhanced performance. Secure your purchase now for an upgraded experience.
Unlock the secrets to handling your wellness with https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ , your ultimate resource for quality medications.
Seek remedies for hair loss now! Find out about how [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – cheapest lasix[/URL – can assist in your fight against hair loss.
Discover safe and effortless ways to acquire your prescriptions with just a click. [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – canada drug hydroxychloroquine[/URL – offers a hassle-free solution for your needs.
For those seeking relief from chronic sinus symptoms, vidalista brand provides an effective remedy.
Purchasing https://wefenceit.com/pharmacy/ online offers an easy way to address your health concerns without a prescription.
Looking for an affordable option for your cardiovascular medication? [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – cheapest nizagara dosage price[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution. Whether you’re seeking to obtain this cardiovascular therapy through a digital drugstore, rest assured you’re getting value for your investment.
Looking to minimize your healthcare expenditures? Discover the [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis for sale overnight[/URL – to economize on your prescription.
Discover your solution for enhanced vitality; find safe options and purchase prednisone immediately.
X-ray your health options by choosing to acquire your crucial medications without hassle. Ensure you always can access your medications, https://nabba-us.com/product/priligy/ virtually.
Having trouble finding affordable medication? Look no further, as [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – free overnight lasix shipping[/URL – offers the best deal. Whether you’re seeking budget-friendly alternatives for your health needs, we provide unparalleled deals.
GiftCornerOnline – Simple interface, easy-to-browse sections, and attractive gift options.
Find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – to enhance your vitality.
Considering tackling chest pain? Discover effective options with buying tamoxifen for sustained angina relief.
To get safe malaria treatment, visit https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ for an extensive range of options.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Discover [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – – your go-to choice for restoring well-being.
Zero in on eye health: Secure torsemide to control glaucoma effectively.
Discover innovative ways to manage tension with https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ , up for grabs on the web.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis best price[/URL – , your go-to source for purchasing effective ED remedies virtually.
Revitalize your intimate experiences with our exceptional offer: [URL=https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – chinese viagra 75 mg[/URL – . Rekindle the spark instantly and acquire your solution through our website.
When seeking to manage your hepatitis B symptoms, purchase sildalis online easily from reputable sources.
Keep your health and vitality at peak by exploring natural solutions. Secure your supply of https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ now and begin a journey towards improved wellbeing with convenience.
Vacationing in Canada and realized you left your important eye drops behind? Worry not! You can purchase your essential [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara no prescription[/URL – online.
Are you engaging in levitra 20 mg costo ? Prior to starting, it’s crucial to comprehend the risks and ensure you’re making an informed choice.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your home medicine cabinet, https://jawany.com/amoxil/ online can be a seamless process.
Unsure where to find effective migraine relief? Visit [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil w not prescription[/URL – for a reliable choice.
Secure your health effortlessly by opting to purchase medications from [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex[/URL – . Explore a broad selection of health products online.
Reveal the secrets to peak health with our guide at viagra 100mg . Learn how to boost your vitality with practical tips and insights from specialists in the field.
I discovered the most reliable method to acquire Acticin cream for topical use is through https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ , offering a seamless, hassle-free experience.
Discover trusted solutions for your stomach problems with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ – where to buy bentyl[/URL – , a option endorsed by medical experts.
Obtain your Flagyl treatment without delay through our express [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ – no prescription flagyl[/URL – delivery service, ensuring you acquire the care you require immediately.
Boost your persuasion skills with our comprehensive guide! Discover how to convince, sway, entice, or persuade others effectively by reading our in-depth pharmacy . Whether you’re aiming to influence, motivate, inspire, or encourage others, this resource is your key to unlocking powerful communication techniques.
Xperiencing stomach discomfort? Look for relief with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ , the optimal solution for promoting gastrointestinal wellness.
When seeking relief from chronic aches, consider [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil online canada[/URL – as your preferred medication. It’s available via the web, offering simplicity and efficacy.
Need to enhance your vigor? Explore [URL=https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – and find a remedy that boosts your health easily.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with cialis without a doctor , your go-to source for securing effective ED remedies online.
X-ray your options for migraine relief by exploring https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ , a foremost treatment available online.
Need to manage your hypothyroidism? Visit [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – prednisone[/URL – to find out how you can maintain your hormone levels effectively.
For those seeking respite from chronic sinus symptoms, [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – vpxl for sale overnight[/URL – presents an potent alternative.
Looking for effective solutions for female health issues? Find xenical walmart price , a affordable option for addressing your needs.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Consider https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – your go-to solution for restoring health.
For a thrilling experience in gaming and entertainment, visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra[/URL – . With a plethora of table games and premier customer service, it’s the ideal choice for enthusiasts.
Discover outstanding savings on [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – ! Obtain your set immediately and enjoy the advantages.
You can easily purchase your kamagra online online, offering alleviation from nasal congestion.
Discover the convenience and privacy of obtaining your erectile dysfunction medication with https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ , available now.
Buy your essential medications affordably through our trusted [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/doxycycline/ – online doxycycline no prescription[/URL – . Find diverse choices for your healthcare needs quickly.
Revitalize your health by exploring a wide spectrum of pharmaceutical options. Enhance your well-being by exploring an extensive selection of healthcare solutions. Don’t compromise on your health; find everything you need at [URL=https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ – propecia ireland paypal accepted[/URL – .
Understanding your need for reliable and affordable hair loss solutions? Look no further than kamagra 100mg , where you can obtain your medication effortlessly.
Join the myriad of individuals choosing to buy their wellness supplements through digital stores by exploring options to https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ . Elevate your health regimen now with this trusted solution.
Rediscover energy with our budget-friendly [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ – priligy 60mg[/URL – , the premier solution to boost your well-being.
X-ray your health and wellness options by seeking out vpxl . Whether you’re looking to purchase supplements via the web, this choice provides a reliable path to maintaining your well-being.
Explore various options to acquire effective glaucoma treatment and find out how https://kristinbwright.com/retin-a/ can assist in controlling eye pressure efficiently.
Purchase your [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – eye drops online to treat high eye pressure efficiently and affordably.
Unlock access to purchase Tadalafil effortlessly with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ – generic kamagra canada pharmacy[/URL – , ensuring rapid shipment right to your doorstep without the need for a prescription.
To treat Parkinson’s disease symptoms effectively, consider strattera as a viable option.
X-plore your options for altitude sickness prevention with simplicity. Now purchase https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ , your preferred solution for mountaineering adventures.
Zero hassle to obtain your digestive wellness solutions with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – tadalafil[/URL – .
Facing an unexpected situation? Locate cost-effective solutions on the web with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/pharmacy/ – next day online pharmacy[/URL – , ensuring safety and peace of mind.
Managing hair loss effectively can now be done from the convenience of your home. Secure a hair loss solution through levitra , ensuring you get reliable care swiftly.
Acquire your pathway to enhanced wellness instantly.
Access cost-effective solutions for your well-being needs: [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/ventolin/ – ventolin and india[/URL – . Get your supply now, ensuring optimal health without overspending.
Interested in reducing inflammation and allergic reactions? clomid flexibly fits your budget. Discover how this remedy can aid you, available to order on the internet.
Discover cutting-edge ways to manage tension with https://tooprettybrand.com/product/zithromax/ , up for grabs online.
Combat elevation sickness efficiently with [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ – cost of prazosin tablets[/URL – , available on the internet to assist in your climbing adventures.
Questioning where to purchase fertility treatments? Secure your [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/prednisone/ – lowest price generic prednisone[/URL – effortlessly online.
Combat ocular conditions, specifically increased intraocular pressure, with prednisone 5mg , obtainable for purchase on the web.
X-raying your finances? Obtain an urgent boost with https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ , ensuring stability in tough times.
A comprehensive manual on medical education in the United States is readily accessible at [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ – trazodone coupons[/URL – .
Zeroing in on solutions for improved male vitality? Uncover a safe route [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/lasix-40mg/ – lasix supplement[/URL – .
Zeroing in on enhanced vigour and vitality? Discover the ultimate solution with retin a buy in canada , your go-to for unparalleled strength and endurance. Secure today for an unmatched elevation in your vitality.
Preserve your health effortlessly by opting to https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ , making it possible for you to procure your prescription with ease from the convenience of your home.
Seeking the highest quality fertility drug for your treatments? Your search ends here! Acquire your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – order priligy online[/URL – safely and easily.
Looking for an affordable solution to enhance your eyelash growth? Search no more! 40 prednisone india offers a variety of options to secure your beauty product on the web.
Get your health solutions conveniently with https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ . Acquire your essential medicine without hassle from anywhere.
When searching for cost-effective solutions to manage hypertension, finding the [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – canadian pharmacy nizagara[/URL – becomes essential. Explore our portal where you can secure economical treatments without hassle.
Super clanek! Objevil jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a jejich sluzby me opravdu nadchly. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere bavi vsechny hrace. Me nejvice bavi herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske casino s top sluzbami. Chcete-li zkusit nove a bezpecne online casino, mrknete sem: Twitter . Urcite vyzkousejte a uzijete si spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Objevte Spinmama Ca
Objevte Spinmama Casino CZ a ziskejte free spiny
Spinmama Casino CZ – nejlepsi bonusy a promo akce
5f730f6
Buy your essential medication easily with a tap on your device. Seeking a reliable source for your healthcare needs? Look no further. Obtain this medication, without the hassle of a prescription, directly through [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – .
Discover how to boost your performance easily by choosing to discount viagra from the comfort and privacy of your own home.
If you’re searching for an effective treatment to combat bacterial infections, consider https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ . This drug has been widely acknowledged for its efficacy against numerous types of bacteria.
Zap vitality deficits and enhance wellness effortlessly by acquiring your [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – herbal max gun power overnight[/URL – to promote improved health and longevity now.
For individuals seeking enhanced endurance, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin non generic[/URL – offers a revolutionary solution.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive cialis . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to reduce expenses on pharmaceuticals.
Zero in on eye health with the ultimate solution in eye drops: https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ . Discover a groundbreaking solution for managing eye inflammation easily.
Looking to control your IBS symptoms? Find out about how [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ – bentyl best price[/URL – can offer respite.
Just discovered nizagara without dr prescription usa ? Now enjoy swift service right to your doorstep.
Get unparalleled discounts when you obtain your prescriptions through our secure portal. Now is the perfect time to https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ safely and conveniently.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid buy online[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous choices available on the web. Secure your well-being today by opting for the best deal.
Acquire your treatment for enhanced vitality; visit [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – lasix mg 100mg[/URL – now!
Unlock unbeatable deals on lasix 40mgg wiki ! Secure your solution for a better life now.
Considering the vast array of treatments for prostate cancer, finding an affordable option can be daunting. For those in search of a cost-effective solution, https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ presents a viable option. This medication, pivotal in combating prostate cancer, now becomes accessible to a wider audience, ensuring patients can obtain crucial therapy without financial strain. Whether you’re looking to purchase this treatment on the web, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s the right fit for your medical needs.
In search of proven eye drops? Look no further! Uncover the benefits of [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix[/URL – – your remedy to inflammation and pain in the eyes.
Uncover your path to better health with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – strattera 18mg generic[/URL – , accessible now sans a doctor’s prescription.
Quickly secure generic nizagara from india to make certain your safety needs are met efficiently.
When seeking excitement and thrill, consider diving into the digital realm of gaming at your convenience. Explore a virtual plethora of entertainment options with https://nabba-us.com/item/cialis-without-a-doctor/ , where each click unravels fresh adventures and possibilities.
When considering bone density improvement, considering [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – nexium 40mg[/URL – is essential. It gives individuals a route to enhance their bones effectively.
Looking to purchase Depo-Medrol? Find the most cost-effective [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – pharmacy without prescription[/URL – .
Improve your health and wellness with our exclusive cipro buy , now available. Experience enhanced vitality and confidence. Purchase yours immediately.
Quest for savings on HIV treatment ends here; discover https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ for managing your health efficiently.
To purchase your birth control effortlessly, think about acquiring [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – . This method guarantees confidentiality, convenience, and a wide selection of options.
Need to reduce your prescription costs? Discover the best deals by accessing a [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cipro/ – canadian pharmacy cipro[/URL – right here.
Various individuals opt to purchase their pharmacy supplies on the internet, with amoxil 500mg being a popular choice among choices.
Need to alleviate constipation? https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ is your go-to option.
Discover affordable options for managing your pain with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – 50 mg clomid cheap[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to buy this medication via the internet, we offer a range of choices to meet your needs.
Keeping your wellness in check, order [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis brand[/URL – to improve your lifestyle.
When looking to acquire treatments for upset stomach, consider propranolol capsules as a cost-effective option.
Reduce your heart’s workload with https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline/ , an essential medication for controlling chest pain. Purchase today for improved heart health.
Your search for reliable and easy access to medication ends here. Purchase [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a without pres[/URL – through our website without the hassle of a traditional pharmacy visit.
In need of Doxycycline? Get your prescription easily doxycycline 100mg . Available without the need for a doctor’s visit, ensuring you receive the medication promptly.
Zero hassle: purchase your https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ without complication.
Considering the vast array of treatments for prostate cancer, finding an affordable option can be daunting. For those in search of a cost-effective solution, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – retin a non generic[/URL – presents a viable option. This medication, pivotal in combating prostate cancer, now becomes accessible to a wider audience, ensuring patients can get essential therapy without financial strain. Whether you’re looking to acquire this treatment online, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s the right fit for your medical needs.
Explore the market for antimalarial drugs and locate the [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ – buy molnupiravir online cheap[/URL – to ensure your health safety without breaking the bank.
Yes, you can now order your medications with ease and convenience through vidalista uk .
“Quest for high-quality, affordable wound treatment ends here: Discover the best option with https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ , providing premium options on the web.”
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly; acquire [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – to enhance your wellness by means of a trusted provider.
Seeking heartburn relief? Consider [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil-best-price/ – tadalafil best price[/URL – for a safe solution.
Join our community to obtain your tadapox preis in deutschland and explore a broad selection for reproductive health products.
Zeroing in on your health needs? Discover https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ and locate your pathway to enhanced well-being without the hassle.
When seeking alleviation from motion sickness, one might consider exploring options for obtaining [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – cialis without prescription[/URL – .
X-ray your options for purchasing antiviral medication affordably by checking the nizagara buy . You can acquire the essential antiviral at an affordable rate through the web.
Zillions seeking effective remedy for their condition can now buy https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-cheap/ , a reliable choice.
Research shows that purchasing medications on the internet can be convenient. Acquire your prescription for [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – discount amitriptyline[/URL – with ease.
Obtain optimal health benefits at the best value by choosing prednisone 20mg . Secure the essential medication on the web effortlessly.
X-plore the myriad benefits of enhanced endurance and vigor with just a click. Obtain your prescription of unparalleled performance enhancement today at https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ .
Visit [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ – buy lasix in budapest[/URL – for detailed insights on utilizing this drug effectively.
Urban Fashion Finds – Fast-loading pages and clear display of trendy street styles.
oldtownstylehub.shop – Hub offers excellent variety, browsing feels natural and pleasantly fast overall.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our all-encompassing selection of affordable treatment options. Find [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – to improve your vitality efficiently and safely.
Quickly purchase your heart medication safely by clicking lady era , ensuring hassle-free delivery directly to your doorstep for a healthier tomorrow.
In search of the most cost-effective solution for your wellness? Visit https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ to find an unparalleled offer on top-quality health assistants.
A comprehensive guide to managing heart conditions effectively: Explore options like [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia pills[/URL – and discover other solutions for enhancing your cardiac health.
Browsing for a reliable source to purchase your medication? Look no further! nizagara from our reputable web platform, ensuring highest-standard products with every order.
Explore supreme deals on antifungal treatments at https://jawany.com/cipro/ .
X-plore the best options for your healthcare needs and uncover [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ – canada pharmacy pharmacy generic[/URL – for acquiring your essential medications conveniently.
Given the variety of options available, finding the place for buying [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – vidalista[/URL – is crucial for efficient treatment.
X-plore options for handling your health by deciding to purchase cheapest vidalista , a remedy trusted by many.
Get your health back on track with ease; secure your savings now on stress-relief prescriptions by clicking here: https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ .
Procure budget-friendly treatment options; explore [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – viagra 100mg[/URL – for managing your well-being.
Harness the power of modern medicine to stabilize your mood with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – http://www.retin a.com[/URL – . Find out how to tackle bipolar disorder with effective solutions available.
Quest for affordable eye care solutions? Explore the range and discover the most economical prices on effective treatments. For exceptional deals on eye health products, click prednisone non generic today.
X-ray your options for economical hormonal therapy: Discover the https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ and explore different pathways to control your health without breaking the bank.
Quest for top-quality healthcare products ends at [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil on line[/URL – , where you can order all from medications to wellness supplements online.
Boost your vitality with [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – nizagara[/URL – , available for acquisition on the internet.
Various medical professionals recommend seeking advice on bentyl for digestive issues to guarantee safe and effective relief.
Discover excellent options for managing your ailment efficiently with https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ . Boost your health immediately.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ – france amoxil[/URL – virtually can be a seamless process.
Given the complexity of managing widespread health conditions, finding a reliable source for medications is crucial. That’s why many opt to acquire their medications from overnight finasteride , where a wide selection in medical solutions is always accessible.
X-plore your alternatives for thinning hair solutions and purchase https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ with confidence.
Browse through our selection for the [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – retin a.com lowest price[/URL – . Whether you’re looking for medication to manage Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s symptoms, our site offers budget-friendly options.
northernskycollections.shop – High-quality items displayed nicely, shopping experience is smooth and enjoyable overall.
Visit [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ – purchase dapoxetine online[/URL – to secure your Augmentin dose at the cheapest rate.
Discover affordable options for managing addiction; orlistat offers a pathway to recovery. Explore affordable approaches for addressing dependency.
Venturing north for well-being solutions? Find your health aid with https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ , offering a broad selection of medicines.
Seek the [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – propecia 1mg[/URL – efficiently. Locate your essential medication without breaking the bank.
Visit our [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – page to acquire trusted heartburn relief. Easily buy your remedy with a click.
X-plore budget-friendly options for ED treatment with generic fildena from canada , ensuring quality and safety.
Order your treatment easily; acquire https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ from accredited platforms.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/low-cost-zithromax/ – zithromax canadian pharmacy[/URL – through our trusted online outlet. This critical solution is now available without hassle.
X-plore the advantages of tackling gout with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – , and uncover how you can purchase this remedy online.
Research levitra n0 prprsscription for effective baldness solutions.
For health professionals searching to enhance their expertise, think about enrolling in https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/retin-a-without-a-doctors-prescription/ programs available online.
Having suffered from inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), many individuals look for effective treatments. For Canadian patients, [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – purchase sildenafil without a prescription[/URL – offers a viable solution. This medication can assist in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Your quest for budget-friendly heart medications ends today! Secure your dose of buy cialis on line right here! Wide-ranging options to acquire your vital medication online await.
Zero in on your health and wellness; to secure your prescription medication without the hassle, check https://phovillages.com/viagra-75mg/ for a discreet, safe, and convenient purchasing experience.
Honestly, I’ve used many virtual casinos recently, and it still surprises me how many people sign up without doing research. For anyone searching for a breakdown of bonuses, payout speed, and game selection, this review helped me a lot: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s easy to understand and shows what matters most before you put in money. It’s worth your time if you don’t want to fall for typical traps.
Searching for a trustworthy place to buy heart medication? Look no further than [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/]internet lasix sales[/URL] , your one-stop shop for all your cardiovascular requirements.
When considering bone density improvement, exploring buy dapoxetine online legally is essential. This medication gives those affected a path to strengthen their bones efficiently.
Explore cost-effective options for your prescription needs: https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ . With our guide, find the lowest costs easily on the internet.
When seeking reliable antifungal treatment, consider checking out [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/]cheap nizagara pills[/URL] for your medical needs.
As someone keen on managing their health, it’s crucial to know the latest [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – zithromax[/URL – to handle your expenses effectively.
One can easily purchase their prescription for buy nizagara online canada by choosing to order it through the internet.
Order your https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ today and find relief from allergies with a simple click.
I’ve discovered where to [acquire inexpensive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – cheap stromectol online[/URL – , a popular treatment for malaria.
When seeking budget-friendly solutions for ED, consider [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – buying fildena[/URL – as your choice source.
Get alleviation from pain with lady era . Acquire yours immediately to enjoy potent pain relief.
To control hypertension, explore choices for medicine sans a prescription at https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ .
X-plore eye care with cutting-edge solutions. Purchase [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – nizagara[/URL – on the web for controlling glaucoma effectively.
Secure your essential hypertension medication by opting to vidalista without pres , ensuring your loved ones sustain optimal health effortlessly.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ , offering a seamless order experience for your crucial medication on the internet.
Explore your options to purchase effective glaucoma treatment and discover how [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra/ – levitra 20mg[/URL – can help in reducing eye pressure efficiently.
Absolutely, ascertain the [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – through exploring various online pharmacies.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to acquire nizagara on the web is crucial for consumers.
Zero in on unparalleled deals for your health needs; find unmatched offers on https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra/ right now.
Seeking the highest quality fertility drug for your treatments? Look no further! Acquire your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – safely and easily.
Secure your most reliable pathway to better health by opting to obtain [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ – 40mg vidalista sale[/URL – . This approach promises rapid alleviation from discomfort with unmatched simplicity.
Seeking relief from OCD symptoms? lasix overnight offers a solution. Discover this option today.
Manage your nausea effectively; https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ immediately and experience respite from vomiting signs.
Zillions seek reliable ways to tackle erectile dysfunction; you can buy [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – for a convenient solution.
When looking to enhance your vitality, consider opting for authentic ventolin , a reliable choice. Available for order via the internet, this solution promises improved efficacy.
Curious about hassle-free ways to secure your health needs? Explore the convenience of accessing pharmaceuticals with just a click. Now, you can procure your essential medications virtually. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to https://myrsvplive.com/levitra-10mg/ , ensuring a seamless experience for your health and well-being.
Discover the most cost-effective method to obtain your prescription with our [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – viagra in usa[/URL – .
Browse our range for high-quality deals on [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – uk clinic pharmacy[/URL – . Find your purchase now and experience fast shipping.
Whether you’re struggling with seasonal allergies or year-round irritants, pharmacy kosten offers a remedy. Locate alleviation from a stuffy nose and sniffling with just a few sprays.
Manage your nasal allergies effectively with https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ . Whether you’re looking to acquire a treatment for intermittent allergy symptoms or require a long-term solution, this solution offers ease.
To discover the latest and most competitive [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – generic levitra in canada[/URL – , check out our website.
Visit our website to find the best [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ – pharmacy prices for propecia[/URL – .
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if prednisone 20mg buy online are appropriate for you or your loved ones.
Looking for an effective way to combat alcohol dependence? Discover how https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ can be a vital part in your journey towards sobriety.
Prices for Corion injections can be surprisingly affordable at [URL=https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ – generic sildalis[/URL – , especially when looking for budget-friendly reproductive health solutions.
Boost your health with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/ – levitra[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to improve your immunity or aid your body’s natural defenses, this option is available on the web for ordering.
Researching for the most affordable options for deterring insects? Stop here. Find the lisinopril without dr prescription now.
Managing menopause symptoms effectively often involves hormone therapy treatment. Many individuals look for convenient and private options. For those interested, you can buy https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ via the internet, ensuring a seamless and confidential process.
Quickly get [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – online lisinopril[/URL – , ensuring swift relief for your problem.
our website, we tender modern and the best Crypto Analysis with AI for your business] crypto.kodx.uk
#gpt_question_subject #30340;最佳加密分析。 crypto.kodx.uk] f730f8_
Regarding your need for mood stabilization, reflect on purchasing [URL=https://griffindtc.com/priligy-60mg/ – priligy[/URL – from a reputable source.
A search for affordable choices for managing narcolepsy leads you directly to best price prednisone , where you can discover budget-friendly rates.
Secure effective relief from heartburn and acidity with https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ . Whether you wish to acquire a remedy, it’s obtainable for online ordering.
When seeking relief from aches, consider [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – where can i order some generic trazodone[/URL – as a potent alternative. This anti-inflammatory agent is perfect for treating various conditions, providing both effectiveness and affordability.
Venturing into the realm of digital pharmacies enables you to acquire essential medications conveniently. Whether you’re desperately seeking to anti-inflammatory solutions, [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara 25 mgm israel prices[/URL – emerges as your go-to destination for straightforward purchases.
Explore the options and purchase your prescription without leaving your home at cytotec .
Jumpstart your well-being journey with https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/pill/nizagara/ , your go-to choice for enhanced vitality.
Obtain your medication effortlessly at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil-5mg/ – tadalafil 5mg[/URL – , the premier site for competitive prices on pharmaceutical products.
Grand River Collection – Attractive items showcased clearly, making exploration enjoyable.
With rising healthcare costs, finding affordable medication can sometimes seem daunting. However, options such as [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – generic verapamil fast shipping[/URL – are available to help manage costs. Whether you’re aiming to acquire heart health medication without breaking the bank, exploring discounted solutions via online pharmacies can be a smart choice.
Zap high prices with our exclusive lowest price on generic amoxicillin , and Bag your supply of crucial antibiotics easily online.
Secure
For individuals seeking cost-effective treatment options for bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, discovering [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – becomes vital. Explore budget-friendly solutions for managing your health with ease.
Get your [URL=https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ – ventolin en ligne[/URL – prescription filled online sans fuss, ensuring quick relief and effective treatment of your condition.
Venturing north for well-being solutions? Find your wellness aid with lasix , offering a vast selection of medications.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ might be what you need. Find out about how it can assist in lessening your symptoms promptly.
Jumpstart your well-being journey with [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large lowest price[/URL – , an essential prescription for managing HIV effectively.
Your quest for affordable hydroxychloroquine ends here. Discover the latest costs at [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – price hydroxychloroquine per pill[/URL – , your ultimate source for budget-friendly healthcare solutions.
Venture into holistic healthcare solutions and explore natural remedies. Easily acquire your wellness needs furosemide through our secure platform.
Be proactive in managing your gout symptoms; consider https://damcf.org/nizagara/ from reputable sources. With our guide, learn how to safely control uric acid levels and minimize flare-ups.
Regain digestive harmony with a organic solution; buy [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – cheap doxycycline pills[/URL – to promote regularity.
oldtownstylehub.shop – Layout feels intuitive, finding desired items is simple and hassle-free today.
Various individuals seek cost-effective treatments for managing their medical conditions; hence, they explore economical solutions. [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-cheap/ – kamagra cheap[/URL – offers a possibility for those aiming to reduce healthcare expenses while maintaining quality.
Discover how to obtain your prescriptions easily with cheapest viagra , ensuring discretion and ease.
Acquiring https://center4family.com/ventolin/ has never been more straightforward, enabling users to access vital health remedies with ease.
Looking for an easy and convenient way to purchase your eye care medication? Consider choosing our [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – service, where you can order your prescription from the ease of your home.
Discover effective solutions for eye inflammation at [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/retin-a/ – lowest price retin a[/URL – , offering a wide range of therapies.
Research shows that purchasing medications online can offer convenience. Acquire your prescription for order nizagara easily.
Having seen a balding hairline, I started exploring treatments and discovered https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix/ , a affordable solution for hair regrowth.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/doxycycline/ – prices for doxycycline[/URL – offers a convenient way to secure necessary medication without the need to step outside.
Boost your vitality effortlessly; discover the cost-effective pricing of [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ – pharmacy[/URL – .
Discover excellent options for managing your health issue efficiently with cialis 2.5mg . Boost your well-being immediately.
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; https://brightnights915.com/item/generic-tadalafil-from-india/ is your gateway to budget-friendly healthcare.
Seeking top deals for [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ – genuine cialis usa[/URL – ? Uncover unmatched offers and quality now!
Reduce your heart’s workload with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia in usa[/URL – , an essential treatment for managing angina. Order now for improved heart health.
Browse our site to discover free amoxil , ensuring you secure premium antibiotic options at matchless prices.
Visit our webpage to order your prescription, including https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ , online. This digital platform ensures a hassle-free method to acquire your required pharmaceuticals.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Get [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 650mg[/URL – safely and swiftly.
Il s’agit d’une ressource concue pour faciliter l’acces a des donnees locales.
Parmi ses principales fonctionnalites, Vous y trouverezdivers services en ligne, telles queles decisions municipales.
Une organisation claire des contenus vous permet de trouver facilement ce que vous cherchez,que ce soitles documents importants.
La mise a jour constante des informations est une priorite, assurant une transparence complete envers ses habitants.
https://lannuaire.service-public.gouv.fr/grand-est/moselle/bd12814b-c638-491b-8b7c-c1fbd88212f3
Finding out the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – http://www.retin a.com[/URL – can be an essential step. Explore options to save on this vital medication.
Regain control over your well-being by visiting buy xenical online canada , your ultimate source for quality pharmaceuticals.
For addressing moderate pain and swelling, consider https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ as a proven solution.
Overcoming hair loss is now easier than ever with groundbreaking solutions available. Whether you’re looking to restore your hair’s health, there’s a solution for you. Discover how to combat alopecia effectively with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/buy-cheap-viagra/ – viagra[/URL – , providing a affordable and efficient approach to regaining fuller hair.
Leverage your health management by securing your supply of crucial medication. Purchase [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ – doxycycline in usa[/URL – effortlessly from trusted sources, ensuring your well-being is always in focus.
Finding the best deal for strattera without dr prescription usa can be challenging. To obtain your supply, buy via the internet and ensure you’re receiving both quality and affordability.
X-ray your options for heart medication by exploring the https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ . Discover how to tackle your health economically.
Zero hassle to obtain your prescription: [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ – tadalista online canada[/URL – – buy on the web with complete confidence.
Keeping your health foremost in mind, purchasing your medications from a trusted source is crucial. For those in the market for HIV treatment options, [URL=https://jawany.com/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – offers a cost-effective and accessible solution. Ensure you seek advice from a healthcare provider to ascertain if it’s right for you.
Seeking relief from benign prostatic hyperplasia? Explore your options with flomax , a treatment for easing prostate enlargement symptoms.
For individuals looking to save their healthcare expenses, securing a https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ could be immensely beneficial. This offer applies to a range of drugs, potentially minimizing your financial load.
To secure your [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/buy-retin-a-online-cheap/ – retin a[/URL – , check out our webpage and order with assurance.
northernskycollections.shop – The layout is clean, products are easy to browse and purchase.
Pain and inflammation can be significantly reduced with the use of [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone[/URL – , a potent NSAID.
Discover the latest costs for managing your menstrual irregularities and endometriosis with generic viagra on line order , and learn about how it can help you lead a better life.
I discovered https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ while researching options for boosting men’s health.
Optimize your health and wellness routine by purchasing your medications effortlessly. [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ – doxycycline hyclate[/URL – offers an easy solution for boosting your vitality.
Boost your vitality effortlessly; find out the affordable pricing of purchase propecia without a prescription .
Considering the necessity for dependable methods for treating erectile dysfunction, it’s essential to discover a trusted source. https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ provides a straightforward route to procure your treatment with confidence.
Zap your concerns away with a click on the [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ – doxycycline hyclate[/URL – and start your journey towards enhanced wellness today.
You can acquire your cardiovascular treatment securely [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ – non prescription viagra[/URL – , ensuring quality and cost-effectiveness.
Discover effective relief for cold sores with buy tadalafil w not prescription , your go-to antiviral cream. Acquire the remedy through our digital platform and start your journey to recovery today.
Just found an spectacular source to buy your https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ . Whether it’s required, we’ve got your answer.
X-ray your health concerns and discover the best solution; click here to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil capsules[/URL – for a holistic approach to wellness.
Battling seasonal allergies? Explore securing [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – where to buy lady era[/URL – to manage your symptoms.
You can locate cipro online, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Quickly locate your solution for early climax issues with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ , available on site.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – purchase cialis[/URL – . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to reduce expenses on your medication.
A remedy for BPH is just a click away. Get your medication without hassle by choosing to [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – .
Zero in on affordability and convenience with cialis 20mg , your go-to source for securing potent ED solutions online.
One often seeks monetary relief through https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxicillin/ , especially in periods of pressing needs.
Many are looking for trustworthy options for erectile dysfunction, and [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – walmart cialis price[/URL – provides a credible option.
A plethora of alternatives awaits for those seeking to enhance their health with quality injections. Explore your ideal solution at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – nolvadex[/URL – , where excellence in healthcare products is always a priority.
Preserve your health effortlessly by opting to prednisone best price usa , making it possible for you to procure your medication without hassle from the convenience of your home.
Browse our site for competitive https://swanpercussion.com/tadalafil/ and explore a multitude of alternatives to purchase your medication.
Given the wide array of hormone therapies available, selecting an effective and safe option is crucial. For those considering estradiol supplementation, [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/tadalafil/ – generic vidalista tablets[/URL – offers a dependable alternative. Whether you’re seeking to buy a trustworthy hormone therapy via a digital pharmacy, it’s vital to opt for reputable vendors to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Discover how to acquire [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – buy priligy[/URL – for managing your condition. Explore diverse alternatives for treatment today.
Zealously look for remedies to improve your well-being? Consider generic viagra from canada as a potent option.
The most recent data on https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ shows a trend of fluctuating expenditures. Patients searching for affordable pain relief options might uncover this beneficial.
Jumpstart your journey to a more vibrant love life with [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – prednisone post[/URL – . Explore the myriad benefits of this solution and find out how it can transform your experiences.
Considering managing chest pain? Explore effective options with [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – pharmacy ordering on line[/URL – for long-term angina relief.
Visit propecia to purchase the Augmentin solution at the most affordable rate.
Yes, you can find discounted solutions for handling edema. https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ is your go-to selection for intervention.
Unlock exceptional deals on [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – cenforce from canada[/URL – , your optimal choice for removing ED symptoms. Secure yours today for improved health and happiness.
Check out [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – cost of retin a tablets[/URL – for exclusive prices on alopecia medications.
Looking for an antibiotic medication? Secure it without needing to visit the doctor through this cheapest doxycycline dosage price . Acquire the medication promptly and begin treatment right away.
Get the best deals on https://americanazachary.com/drugs/sildalist/ to combat your health needs.
Quickly purchase your medication online with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/low-price-pharmacy/ – pharmacy canada[/URL – , ensuring a straightforward process.
Discover affordable options for managing addiction; [URL=https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ – cialis 2.5 prix[/URL – offers a pathway to recovery. Explore budget-friendly methods for tackling dependency.
Looking to control prostate carcinoma? Order cheapest propecia canadian pharmacy with ease for reliable therapy.
Researching options to get Etizolam legally? Ensure safety by consulting healthcare professionals first. Click here for details: https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ . Always prioritize your health by seeking advice from certified experts.
Reduce your heart’s workload with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a/ – buy retin a no prescription[/URL – , an essential medicine for managing chest pain. Order now for better heart health.
Need to alleviate glaucoma symptoms without breaking the bank? Explore our wide range of affordable solutions, including the highly effective sildenafil , suitable for budget-conscious patients seeking quality eye care options.
To secure Azithromycin without a prescription, use this link https://myrsvplive.com/viagra-pills/ for reliable options.
Venture into the realm of effective ED solutions with [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – fildena on internet[/URL – , obtainable via our website.
Secure your health effortlessly; purchase your medication safely with [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ – prazosin[/URL – , ensuring optimal health outcomes efficiently.
When seeking effective treatment for irregular menstrual cycles, consider exploring the options for levitra . Numerous people have discovered it to be an integral part of their health regimen.
Given the complexity of managing common health problems, finding a reliable source for prescriptions is crucial. That’s why many choose to acquire their prescriptions from https://kristinbwright.com/priligy-from-canada/ , where diversity in healthcare solutions is always available.
**C**ompare and find the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – buying vardenafil[/URL – by exploring our internet-based pharmacy.
Just in: Discerning shoppers can now uncover the vente amoxil belgique on websites, ensuring you get unparalleled value for your healthcare necessities.
If you’re looking for an effective treatment to tackle bacterial infections, ponder https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ . This drug is widely recognized for its potency against a broad range of bacteria.
Join the myriad of individuals choosing to buy their wellness supplements through digital stores by exploring options to [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/prednisone/ – prednisone low prices[/URL – . Elevate your health regimen today with this reliable solution.
Xplore affordable healthcare options and discover significant savings on medication with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ – lasix[/URL – .
Maximizing your convenience, you can now acquire how to stop symbicort via our dependable online store.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your ailment efficiently with https://kristinbwright.com/cialis-best-price/ . Enhance your lifestyle immediately.
Considering the risks involved, it’s crucial to talk to a healthcare professional before deciding to acquire [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – billig pharmacy kaufen[/URL – .
Learn more about how tretinoin pagamento paypal can help in recovering from alcohol addiction.
Seek unparalleled performance and confidence in intimate moments; explore your pathway to enhanced vigor with https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ . Purchase your solution today.
Buy your essential medication easily with a tap on your device. Seeking a reliable source for your healthcare needs? Look no further. Obtain Duprost, without the hassle of a prescription, directly through [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/sildenafil/ – viagra 50mg[/URL – .
Questing for an effective solution to enhance your performance? Look no further! Visit pharmacy to secure your upcoming batch of the effective remedy.
When looking to address OCD symptoms, consider exploring https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ as a potential option.
Zap your ED worries away! Get your ED medication [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/sildenafil/ – sildenafil[/URL – . This solution is trustworthy and quick to find.
TrailSunrise Lane – Tidy pages and organized sections enhance the overall shopping flow.
Zealously seeking discounts on your medication? Get exclusive deals now with this [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/retin-a/ – discount retin-a pharmacy[/URL – .
Visit ventolin non generic to purchase cost-effective medication on the internet.
To secure your health essentials, navigate to https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ , where every necessity meets solution.
Explore affordable ADHD treatment options by securing [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ – pharmacy buy[/URL – to control symptoms effectively online.
Whether you’re struggling with seasonal allergies or year-round irritants, levitra us pharmacy online offers a treatment. Discover respite from a stuffy nose and sneezing with just a few uses.
Browse our site to find https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ , ensuring you get premium antibiotic options at matchless prices.
Consult healthcare experts before you purchase [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil w not prescription[/URL – to ensure it’s the correct solution for your situation.
Unlock significant savings on eye care medication by choosing to lady-era sales from canadian pharmacy . Explore options to purchase this vital medicine with convenience and confidence online.
When looking for economical solutions for antiretroviral therapy, finding the https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ is paramount.
Unlock immediate access to your wellness needs without a prescription by clicking [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena 100 mg[/URL – , and buy with assurance.
Unlock exclusive savings on your health needs now! Visit our website to get your essentials at unbeatable prices with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – .
Quickly order your prescription with retin a canada , offering fast shipping right to your doorstep.
Now, find an incredible deal on https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline/ , accessible for acquisition online.
Browse our site to purchase high-quality medical supplements, including [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/buy-cheap-viagra/ – viagra[/URL – , securely.
I discovered the foremost place to buy [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – prednisone[/URL – .
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous websites offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to guarantee safety and authenticity. hydroxychloroquine commercial offers a comprehensive guide on the way to safely order this medication, alongside vital data on its use.
Looking for the most economical options to boost your confidence? Discover your solution https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ today and start your journey to feeling your best.
нанг краби ноппарат тара пляж в краби
Discover safe and straightforward ways to buy your analgesic solutions. With our comprehensive selection, you can get [URL=https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ – propecia without a prescription[/URL – easily.
Questioning the safety and efficacy of inhaled medications? Ensure to ask a healthcare provider before opting to acquire tadalista via the internet.
Ensure your heart health by opting for a preventative measure with https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ , a key to maintaining cardiovascular wellness. Secure your treatment from the comfort of your home.
Discover the pathway to improved health with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ – lowest price generic priligy[/URL – , your go-to for herbal remedies.
Now, secure buy generic propecia 5 for your well-being.
Opt for https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ and conserve on necessary medication.
Understand your migraine triggers better and explore effective relief solutions today; discover safe options to acquire [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – and take a step towards managing your symptoms.
Looking for doxycycline? Secure your supply without a doctor’s prescription through this [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ – 200mg doxycycline online uk[/URL – . Acquire the medication swiftly and start treatment immediately.
Acquire your retin a without an rx today and benefit from the savings on medications designed to boost male wellness.
Considering one’s need for reliable iron supplementation, explore our options for https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ . Whether you’re seeking to address iron deficiency or simply boost your overall health, find a budget-friendly solution with us.
Keeping your antiviral medications current is essential. For those needing prescription refills, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – could be your go-to resource.
People seeking relief from arthritis pain often turn to [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – cheap priligy[/URL – , a potent option.
Questioning where to locate joint relief? Consider bentyl precio farmacia for proven assistance in addressing your joint discomfort.
Dealing with diarrhea? Find fast relief by picking https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ .
Save on allergy relief by exploring our offers on [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ – kamagra oral jelly vol 1 without dr prescription[/URL – , allowing you to manage symptoms affordably.
X-ray your options carefully; purchase your prescription online for convenience. [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – purchasing asthalin online for cheap[/URL – guarantees quick delivery and quality.
Unlock exclusive savings on your health needs now! Visit our website to order your essentials at unbeatable prices with prednisone 10mg .
Buy your essential medications affordably through our trusted https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ . Find diverse alternatives for your healthcare needs easily.
Browse our website to discover the [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – , offering you a budget-friendly solution to control your inflammation.
X-plore your options for hair loss treatment and purchase paypal finasteride securely.
Seeking a remedy for hair loss? Find out how to buy https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ , a trusted method to tackle balding safely.
Uncover the ultimate way to enhance your wellbeing; find our exclusive [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – vidalista[/URL – . This solution is perfect for those seeking to improve their lifestyle effectively.
Yes, obtaining your prescription is now hassle-free with our service. Simply click [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy.com lowest price[/URL – to acquire your medication without hassle.
Secure your celebrex coupon effortlessly. Acquire your medicine through the internet with just a few clicks.
Looking for a cost-effective solution for your ADHD medication? https://renog.org/trazodone/ offers a great opportunity to cut costs on your prescription. This deal is ideal for individuals seeking economical ADHD treatment options.
Considering the fluctuating [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ – levitra on internet[/URL – , it’s worth researching different platforms to purchase your prescriptions through the web.
VioletGlow – Attractive layout with modern, neatly presented items for easy browsing.
Discover how to effortlessly procure [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – walmart sildenafil price[/URL – through the internet, ensuring you receive high-quality medication for your health needs.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your home medicine cabinet, where to buy amoxicillin online can be a straightforward process.
Maximize your well-being by opting to acquire your pharmaceuticals digitally, including the option to https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ , ensuring simplicity and confidentiality.
Battling pain? Explore more about how [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/tadalafil/ – online vidalista pharmacy[/URL – could be your pathway to relief.
Knowing your options for managing vertigo is crucial; explore [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ – generic priligy in canada[/URL – to uncover how it can help you.
Optimize your wellness journey with a convenient, hassle-free option: pharmacy . Discover the simplicity of having the essential treatment delivered directly to your doorstep without delay.
Discover the most cost-effective options for managing leg pain during walking with https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ . Secure your health without depleting your wallet today.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: [URL=https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ – best place to buy doxycycline[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to obtain this treatment via the web, you’ll find that its efficacy in treating a wide range of infections makes it a top choice.
Uncover affordable alternatives for managing edema and hypertension with [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – on line furosemide[/URL – , ensuring you get effectiveness without breaking your budget.
Get amazing savings now! Reveal incredible price reductions on top-quality health supplements today with our prednisone for sale overnight . Don’t miss out on this chance to cut costs on your wellness journey.
Zeroing in on cost-effective healthcare solutions, many are curious about how to cheaply access medications. Discover the https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ for insights on how to budget on your health needs.
Looking for a way to tackle your condition? [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – hydroxychloroquine.com lowest price[/URL – might be the solution you’re seeking. Explore how this medication can help you today.
You can discover the prednisone by searching through internet pharmacies.
Navigating the complexities of fertility treatment can be daunting; fortunately, options like https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ provide a straightforward path to acquire necessary medication through the internet.
Zap your fertility concerns away! Explore the potential of [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/generic-priligy-at-walmart/ – priligy 30mg[/URL – and learn about how it can help in increasing your chances of conception.
If you’re in need of a cost-effective solution for ED, consider generic eriacta tablets , available for purchase online.
Explore reliable options to acquire your medication safely. Click https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil-best-price/ for verified products.
Keep your health and vitality at peak by exploring organic solutions. Secure your supply of [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – nexium without dr prescription usa[/URL – now and embark on a journey towards enhanced wellbeing with ease.
Regain your zest for life! Use our best generic tadalafil prices for unparalleled confidence. Revive closeness without breaking the bank. Get your key to a fuller, more vibrant experience now.
Rediscover management over your heart health with https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ , the foremost destination for purchasing your medications on the internet.
Zero in on savings with our unbeatable offer! Secure your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil on line[/URL – right away and ensure your health is foremost.
I’ve used a bunch of virtual casinos lately, and I’m always shocked how many beginners join a site without doing research. If anyone’s looking for a clear overview of bonuses, payout speed, and game selection, this overview was really helpful: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s easy to understand and highlights key risks before you put in money. Definitely worth a read if you want to make better choices.
В поисках достоверного источника редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для законного использования товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с прекрасным качеством обслуживания.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете уверенность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наши товары:
Пружина из драгоценных металлов золотая 20х8х0.1 мм ЗлСрМ58.5-20 ТУ Выберите идеальные пружины из золота, серебра или платины, чтобы дополнить ваше украшение. Найдите пружины с изысканным дизайном и прочностью. Они предлагают широкий выбор для того, чтобы подчеркнуть уникальность вашего украшения.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ – doxycycline online[/URL – to combat infections caused by bacteria. This cost-effective solution is straightforward to obtain and can help in managing numerous of medical conditions.
When considering treating your heart rhythm issues, exploring vidalista might be a practical option.
Optimize your health with https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ , the premier destination for acquiring your prescriptions. Our range offers peerless efficacy, guaranteeing you receive the best care.
Discover affordable treatments for impotence by visiting [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ – price of cialis[/URL – , where you can purchase your medications conveniently.
For people seeking relief from irregularity, [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – fast delivery of lasix[/URL – presents a trusted solution.
Exploring ways to obtain migraine relief? Look no further; comprehensive details on propecia without a doctors prescription are available, ensuring you have access to effective treatment options without compromising efficacy.
Understanding the pros of https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ can be a breakthrough for patients seeking reliable treatment.
Your search for Order asthma treatment ends here. Discover cost-effective options on our site [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ – asthalin no prescription[/URL – .
Quickly obtain your prescriptions with convenience by choosing to buy [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ – purchase viagra online[/URL – .
Looking to control your spasmodic pains? Find out about how bentyl 20mg can offer alleviation.
When seeking relief from aches, consider https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ as a potent option. This anti-inflammatory medication is perfect for treating numerous conditions, offering both affordability and effectiveness.
Acquiring [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/retin-a-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – retin a without a doctors prescription[/URL – is now possible through reliable online pharmacies.
Quickly procure [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/prednisone/ – lowest cost prednisone 5 mg[/URL – , ensuring swift relief for your condition.
Discover advanced ways to manage your health needs with zithromax .
Experiencing inflammation? Acquire ease by https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ , your solution for managing symptoms.
Just uncovered an incredible source to buy your [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis generic uk[/URL – . Whether it’s required, there’s your solution.
Keeping in mind the cost-effectiveness and quality, those looking to acquire HCG injections for their therapy can find the most competitive flomax 0.2 mg prezzo in farmacia right here.
Discover competitive costs on https://myrsvplive.com/levitra-10mg/ when you shop via web.
удаленная работа отзывы Интересные и стильные находки на ВБ – это товары, которые выделяются своим оригинальным дизайном, высоким качеством и необычными функциями. Лучшие находки с ВБ – это те, которые не только радуют глаз, но и приносят практическую пользу, делая нашу жизнь проще и комфортнее.
Acquiring the optimal treatment for irritable bowel syndrome doesn’t have to be a challenge. You can order [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/viagra/ – pharmacy prices for viagra[/URL – on-site to alleviate your symptoms effectively.
You can buy your tadapox capsules on the web, ensuring economic feasibility and ease.
Just released! Discover the latest solution for managing your health needs – https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ . Available now, secure your supply through our authorized website.
Discover safe and easy ways to acquire your prescriptions with our trusted [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – overnight viagra[/URL – service.
Looking for trusted pain relief? Explore levitra low price , your go-to choice for managing aches with ease.
Regain confidence in the bedroom with the https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ , your discreet solution to enhanced performance. Secure your purchase now for an enhanced experience.
Just unveil the best [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ – generic propranolol online[/URL – , facilitating your wellness routine. Explore varieties to enhance your usage today.
Acquiring your prescription has never been more straightforward. Now you can purchase your needed medication [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ – levitra to buy canada[/URL – with ease.
Obtain your lasix 100mg effortlessly today. Whether you’re searching to buy, our portal ensures a straightforward process.
Combat mild pains and aches effectively with https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ , up for grabs on the web to assist you maintain your active lifestyle without discomfort.
Considering the myriad options available, opting to acquire your medication through reputable sources is paramount. For those looking into therapy for gastrointestinal issues, [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ – nizagara[/URL – stands out as a trusted choice among various pharmacies.
Zajimavy obsah! Objevil jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a nabidka je opravdu lakava. Maji uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a spoustu promo akci, ktere zaujmou kazdeho fanouska casin. Osobne me bavi jejich herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske online casino na opravdu vysoke urovni. Pokud chcete vyzkouset neco noveho a bezpecneho, rozhodne se podivejte zde: Twitter . Rozhodne to stoji za to a prinese vam spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Uvitaci bonusy a VI
Uvitaci bonusy a VIP program ve Spinmama Casino CZ
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
f09d5d5
Keeping your cholesterol levels in check is crucial, and [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ – free propecia online[/URL – might be the solution. Explore economical options to manage your heart health today.
Eliminate your nasal allergies swiftly and efficiently with the purchase of propecia cost , accessible for swift relief.
Acquiring https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ has never been more straightforward. Secure your route to wellness by utilizing a safe solution.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – generic amoxil canada[/URL – , and Secure a bottle of vital antibiotics without hassle online.
Various individuals seeking relief from ocular hypertension or glaucoma now have the option to purchase an affordable alternative with [URL=https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ – orlistat[/URL – , providing an economical solution for managing their condition efficiently.
I discovered a way to acquire priligy , making it simpler for anyone to access essential wellness products.
Here’s your encoded request:
Have nasal congestion been troubling you? Experience relief with a fast solution. https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ offers reliable treatment for nasal congestion.
If you’re in the market for an effective remedy to tackle bacterial infections, think about [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – amoxil 500mg[/URL – . This drug is well-known for its effectiveness against a wide array of bacteria.
Discover excellent options for managing your ailment efficiently with [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Boost your lifestyle now.
Keep your kidneys healthy with herbal remedies. Locate the best solution by ordering nizagara 100mg now.
Secure your health with ease by choosing to purchase your critical medications through the web. For those looking for a reliable antiplatelet, click here: https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ to order yours without any hassle.
Grand River Finds – Beautiful river-themed products, browsing feels easy and enjoyable.
I understand the importance of medication accessibility, thus highlighting the convenience of opting for home delivery methods. In this context, [URL=https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ – cheap tofranil online[/URL – offers a seamless way to get your necessary medication without the hassle of visiting a pharmacy.
Facing chronic pain or anxiety? Find your relief securely with priligy 90 in croatia , the trusted choice.
Combat arrhythmias with ease, purchase https://animall.org/drugs/xenical/ via our website for the best treatment.
Zero hassle to control your intraocular pressure issues with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ – prednisone[/URL – . Buy today and see the change.
Exploring affordable healthcare solutions is essential, especially when it comes to medication. http://www.lasix.com offers a budget-friendly alternative for those seeking therapy without compromising on efficacy.
Obtain your solution for digestive disturbances at the https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ .
Zap your low testosterone levels into oblivion with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline-without-dr-prescription/ – doxycycline no prescription[/URL – . Elevate your vitality by discovering a remedy that rejuvenates male health effectively.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your personal health needs, [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – amoxicillin[/URL – online can be a straightforward process.
X-plore affordable AIDS treatment options by deciding to buy prednisone 40mg mail order for your healthcare needs.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; acquire your https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ online for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
Your health can be safely managed with [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/ – retin a price at walmart[/URL – , accessible for purchase immediately.
Having trouble locating budget-friendly options for fertility treatments? Explore lowest retin a prices , where you’ll discover competitive rates for your needs.
Need to stop stroke or handle a heart condition? Consider https://kristinbwright.com/retin-a/ as a solution.
Having trouble finding affordable eye medication? Look no further! Get the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – nizagara[/URL – now. Whether you’re looking to purchase eye drops, our site offers affordable options.
Various individuals suffering from heavy bleeding can seek respite by using [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – canadian pharmacy online cialis[/URL – , a revolutionary solution.
Get your fildena easily! Explore solutions to acquire your medication hassle-free.
The purchase of https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ has never been simpler, offering a remedy right at your fingertips.
Venturing into the realm of HIV treatment, consider exploring options like [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ – zoloft.com[/URL – , a pivotal drug designed for potent viral suppression.
Discover trustworthy solutions for female health problems with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – vidalista on line[/URL – , available to order online.
Researching where to purchase Finasteride? low price tadalafil offers a convenient solution for your hair loss treatment needs.
Acquiring https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ has never been easier. Secure your path to wellness with a safe option.
Quickly acquire your heart medication safely by clicking [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – , ensuring hassle-free delivery directly to your doorstep for a healthier tomorrow.
Purchase the [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – retin-a tabs sale[/URL – to enhance your well-being through the internet.
Explore affordable solutions for your hair loss concerns; clonidine walmart price are available online.
Quickly acquire your medication seamlessly through our https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ , offering a wide variety of pharmaceutical solutions.
Browse our website to find the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – buy generic kamagra[/URL – available. With options to get budget-friendly variants of necessary medication, health management becomes both effective and cost-efficient.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your amoxicillin 650mg on the web for effective bacterial infection treatment.
You can order your https://tooprettybrand.com/product/viagra-for-sale/ without hassle through our website, ensuring you get quality medication for managing your condition.
Buyers interested in acquiring [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a from canada[/URL – could easily Purchase their Medication through reliable online platforms, ensuring speedy and protected delivery to their doorstep.
Explore budget-friendly options for your healthcare by choosing to buy [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – lasix generic pills[/URL – .
Quality healthcare solutions just a click away! Secure your all-inclusive cialis black commercial easily from reputable pharmacists.
Are you exploring options to purchase https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ ? Look no further! Our website provides an effortless way to secure your prescription on the web.
Finding relief from chronic inflammation has never been easier. [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – nizagara[/URL – are now available to purchase through our website, offering a convenient solution for managing your symptoms.
Finding the right emolgel can be tough, but our [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – offers a wide range of options for your needs.
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable human immunodeficiency virus testing solution. Buy your como conprar sarafem today and confirm your status promptly from the privacy of your home.”
To find how to get your https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ at incomparable prices, check out our site now.
Harness the benefit of convenience by choosing to secure [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – through the internet, ensuring an effortless process for managing hair loss.
To learn about improving feminine libido without seeing a doctor, explore our [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/retin-a-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – walmart retin a price[/URL – .
Acquiring zithromax has never been easier. Secure your way to wellness by utilizing a reliable option.
Zap your health troubles away! Acquire the treatment with ease, https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ via web. Secure and safe.
Relieve your enlarged prostate symptoms today! Find our variety of [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ – flomax online pharmacy[/URL – , specifically designed to enhance your urinary flow and overall well-being.
Your search for affordable impotency solutions ends here: quickly get over night erectafil with complete discretion and reliability.
Boost your health with https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra/ . Whether you’re looking to strengthen your immunity or support your body’s natural defenses, this solution is available on the web for buying.
Quickly acquire your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ – cheap tadalafil from usa[/URL – to treat your condition efficiently. Don’t wait!
Color Mea Finds Hub – Creative items showcased clearly, giving a pleasant and effortless shopping experience.
Secure the most affordable rates for your treatment by opting to [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – 1000mg amoxil cost[/URL – . Save significantly when you acquire from credible e-pharmacies.
Various individuals seek cost-effective treatments for managing their medical conditions; hence, they look for budget-friendly solutions. buying prednisone online offers an option for those aiming to reduce healthcare expenses while maintaining efficacy.
Browse the site to find https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ , ensuring you secure top-quality antibiotic options at unbeatable prices.
Questioning where to find an effective solution for glaucoma and eyelash growth? Explore our comprehensive range at [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone steroid[/URL – , where you can Acquire the solution with ease.
Explore unbeatable prices on reproductive health medications at [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin without a prescription canada[/URL – , the top destination for boosting your opportunities of starting a family.
Unlock exclusive savings on your healthcare essentials. Discover your optimal solution with retin a and experience enhanced health.
Zap your anxiety and sleeplessness now! Explore how on https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ .
When seeking relief from discomfort, consider [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ – order retin a[/URL – online as a convenient way to get your treatment.
Purchase the renova empresa to maintain ideal feminine health effortlessly and affordably.
For those seeking effective parasite treatment, obtaining https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ has become more straightforward.
Navigating allergic reaction solutions becomes easier with the option to acquire [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-online/ – kamagra online[/URL – , providing quick access to potent treatment.
Yes, obtaining your prescription is now hassle-free with our service. Simply click lasix buy to acquire your medication without hassle.
Procure your essential medication affordably by clicking here: https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ , guaranteeing substantial savings on quality healthcare.
Regarding your well-being, it’s crucial to find a trustworthy option. For managing specific medical conditions, [URL=https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ – cytotec generic[/URL – stands out as a suggested choice by healthcare professionals.
Keep your health in check without overspending; purchase budget-friendly antiretrovirals. Don’t miss out: [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – .
Access unmatched deals on overnight for usa order lasix online , ensuring your journey towards improved well-being is affordable.
Boost your well-being in no time with https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ . Purchase your package now for improved performance.
Purchase your antibiotics conveniently with a click through [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ – cipro from india[/URL – , offering a hassle-free way to acquire necessary medication without leaving home.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – finasteride without dr prescription[/URL – , a top choice for tackling hair thinning. Acquire these tablets today and start your road to regrowth!
Questioning where to obtain your medications? Look no further, as isotretinoin offers an extensive selection of solutions for your needs.
Obtaining your https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ has never been easier; purchase your medication on the web with utmost convenience and discretion.
Zest your vacation with a trip to the famous [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – generic for clonidine[/URL – , offering an unforgettable experience.
Various individuals suffering from heavy bleeding can seek respite by using apotheken ventolin , a revolutionary option.
Boost your health path effortlessly.
Looking for a way to fight against your health issue? [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – online pharmacy hydroxychloroquine paypal[/URL – might be the answer you’re seeking. Find out about how this drug can aid you today.
Explore numerous methods to obtain your medications with ease, including [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – , through our complete platform.
Our thorough review on vidalista ct dives into effectiveness and security.
“Get the best price on vision treatment when you purchase https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ . Protect your eyesight with our leading solution now.”
Manage your HIV effectively with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis sales in usa[/URL – , an essential component in care regimens. This budget-friendly option ensures accessibility to high-quality medication for everyone.
Harness the power of enhanced performance and satisfaction; explore the benefits of [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy uk[/URL – .
Looking to purchase your medication more effortlessly? Discover your solution with finasteride 5mg , supplying a budget-friendly and dependable option for handling your health.
Searching for a trustworthy site to acquire heart medication? Look no further than https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ , your one-stop shop for all your cardiovascular requirements.
Looking for a way to fight against your health issue? [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ – buying hydroxychloroquine[/URL – might be the answer you’re seeking. Explore how this medication can aid you today.
Research the market for affordable solutions and uncover the [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone no prescription[/URL – to boost your health cost-effectively.
Discover the latest hydroxychloroquine in usa and consider options for securing this medication online.
Visit our website to locate the https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ . Our platform offers an easy way to purchase your treatment via the internet.
Yes, acquiring [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ – tadalista cheap[/URL – has never been easier. Secure your remedy immediately!
Gain access to [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – xenical generic pills[/URL – hassle-free. Procure your medication without delay for addressing your medical conditions.
Uncover affordable treatment for scabies with our cost-effective lowest cost for xenical , the go-to solution for getting rid of pests.
X-plore the myriad benefits of corticosteroid treatment with https://jawany.com/ventolin/ , your go-to option for managing inflammation and allergic reactions.
When seeking relief from ongoing aches, consider [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – celebrex[/URL – as your choice medication. It’s available online, offering simplicity and results.
Buy your affordable [URL=https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – cheapest viagra[/URL – via our website to ease allergy symptoms quickly.
The demand for reliable and easy access to medications has never been greater. Explore your options and buy a levitra now.
Looking to improve your focus and productivity? Find a wide range of options at https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ . Order your medication online and start reaching your true potential today.
When seeking to acquire androgenetic alopecia remedies, consider clicking here: [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – amitriptyline[/URL – for cost-effective options.
рп 5 краби рыбалка в ао нанг краби
Looking to enhance your joint health? Discover [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride/ – http://www.finasteride.com[/URL – and experience a revitalized path to mobility.
Managing pain efficiently and safely is crucial for overall health. Fortunately, Canadians have reliable options for managing discomfort. buy tadalafil on line offers a versatile solution, allowing you to purchase effective pain relief securely and swiftly.
Zero worries about aging signs with https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ , as you purchase a route to rejuvenated vibrance.
Your search for affordable eye care ends here! Discover Premium quality, cost-effective options for managing your vision health with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ – trazodone 100mg[/URL – . Explore budget-friendly solutions for maintaining your eyesight today.
Maximize your health by acquiring essential medications effortlessly through [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – , your go-to source for high-quality pharmaceutical needs.
Your search for a safe, trusted method to enhance your intimate life ends here. Order your lasix today and feel the change firsthand.
Seek proven solutions for hair loss treatment with https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ . Acquire today for an improved path to combatting hair loss.
Obtain affordable [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ – zoloft canadian pharmacy[/URL – for managing your hypertension. Explore our site to purchase your treatment easily.
Relieve your sinus symptoms effortlessly with a [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy-from-canada/ – priligy[/URL – . This readily available solution offers quick relief for allergic reaction sufferers.
Join our community at maxaquin and mg and uncover innovative methods to tackling your wellness.
Obtain competitive https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ by opting to Purchase your medication via our online platform, ensuring you receive the best healthcare support affordably.
Just seeking relief from chronic heartburn? Discover [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/ventolin/ – ventolin non generic[/URL – for solutions that might help.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/amoxicillin-250mg/ – amoxicillin[/URL – via the internet for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Looking to obtain your antiviral treatment? Now, you can buy hydroxychloroquine online.
Nourish your lashes to luxurious lengths with a click! Visit https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ to acquire your solution for fuller, more alluring eyes.
Discover the most affordable method to acquire your medicine with our [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – sarafem[/URL – .
Obtain discounts on your prescription with exclusive [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra price walmart[/URL – available online.
Looking to manage menopausal symptoms effectively? Consider trying lasix 40mg , a trusted option for hormone replacement therapy.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxil/ online for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
Explore innovative solutions to boost your wakefulness with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone.com lowest price[/URL – .
Explore sophisticated options for managing your health with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy pharmacy[/URL – , available for buying online.
X-plore the myriad benefits of lasix alternative uk for alleviating your allergy symptoms. Find out about the ease of controlling seasonal allergies with just a single daily dose.
X-plore eye care with innovative solutions. Order https://myrsvplive.com/generic-amoxil-canada-pharmacy/ via the internet for managing glaucoma effectively.
Having gastrointestinal discomfort? Discover relief through [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – , a trusted medication. Seek it online for quick alleviation from stomach aches.
Just discovered you’re in need of schizophrenia treatment options? Consider exploring [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – retin a price at walmart[/URL – , meticulously crafted to manage your symptoms. Don’t hesitate to purchase this effective medication from trusted sources.
Opt for tadalafil tablets australia to manage your hepatic conditions. Ensure you’re getting your therapy with confidence.
I discovered that many individuals are looking to obtain https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ for their nasal allergies relief.
Improve your health by visiting [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ – order lady-era pills online[/URL – to explore a wide selection of medical supplies.
Having trouble with heartburn or gastric acidity? Purchase your relief safely and quickly [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – asthalin 100mcg[/URL – .
Gain immediate access to discount shopping for tadalafil and eliminate your concerns with a simple tap.
View choices for purchasing https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ via web.
Discover budget-friendly options for managing your health: [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – how to buy prednisone from home[/URL – . Get your remedy today and start your path to better wellbeing without delay.
With numerous stomach problems plaguing individuals, finding an effective treatment is key. Luckily, you can procure [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – no prescription prednisone[/URL – , a trusted solution for shielding the stomach’s lining and helping in the healing process.
To ensure your wellness, buy tadalafil capsules for sale from a credible source.
Keep your health top-notch with our latest solutions. Explore a wide range you require by clicking on https://nwfgenealogy.com/propranolol/ .
Keeping pain and inflammation at bay has never been easier, thanks to [URL=https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ – lasix cost walmart[/URL – . Now, you can acquire this effective treatment without hassle.
Reduce swelling and altitude sickness symptoms effectively by opting for [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – . Secure the treatment effectively from our website.
Ensure you obtain your prescription for cheap nizagara safely and swiftly.
If you’re looking for an effective remedy to tackle bacterial infections, ponder https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxicillin/ . This drug is widely recognized for its effectiveness against numerous types of bacteria.
You can purchase your [URL=https://jawany.com/cytotec/ – cheap cytotec “on line” no rx[/URL – safely and without hassle from certified online stores.
Looking for the ultimate solution to your automotive needs? Look no further! Our [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – fda vardenafil[/URL – showcases the zenith of power cell technology, ensuring your vehicle runs without interruption. Discover the difference today!
Your health is our priority; buy can you buy vardenafil argentina online and start your journey to improved health today.
For those seeking relief from gastrointestinal discomfort, purchasing https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ could be a suitable solution.
Manage your symptoms effectively with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a for sale overnight[/URL – . Explore affordable options to treat your condition online.
X-plore your options for relief from digestive discomfort by visiting [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – buy propecia 5 mg in canada[/URL – . Locate your remedy on the web with ease.
Quickly acquire your best price vpxl , a trusted source for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Nourish your bones and teeth with quality supplements; find the best sources to acquire https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ for your daily health regimen.
X-plore budget-friendly solutions for impotence relief with [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – discount fildena[/URL – , ensuring quality and security.
Explore your options for handling gastric ulcers with viagra without a doctor , accessible online.
Improve your health by choosing medications that offer reliability and affordability. Acquire https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ to ensure your well-being without compromising on quality.
I discovered the most affordable [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – lasix generic pills[/URL – while searching for budget-friendly solutions for my chronic pain.
Boost your confidence and improve your performance with genuine [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – retin a canadian pharmacy[/URL – . Preorder today for a discreet and efficient solution to your needs.
The benefits of get propecia drug online for treating mood swings are substantial.
Looking to enhance your stamina? Discover how https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ can help. Available now, these pills are designed to aid your health journey.
Unlock savings on your medication costs with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – , available for patients seeking alternative options for their treatment.
Patients seeking cost-effective treatment for bipolar disorder may find generic sildalis competitive. Learn about the cost of managing your condition with these pills.
Zero reasons to wait! Get your prescription for improved performance instantly at https://swanpercussion.com/tadalafil/ .
Having grappled with anxiety, finding affordable treatment options can be a relief. Discover the optimal deals on [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – for managing your symptoms efficiently.
Looking to acquire allergy relief without breaking the bank? Click here to [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – prednisone generic 5mg canadian pharmacy[/URL – and start feeling better today.
Looking for a remedy for hair loss? Find the most effective products at our online store. Your search ends here: propranolol .
Venture into the world of affordable healthcare solutions by opting to https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ from our trusted distributor. This choice not only guarantees superiority but also financial benefits for those in need.
You can acquire your essential ophthalmic solution [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – .
Boost your hair growth with affordable solutions like [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – . Discover a range of options and regain confidence without straining your wallet.
Get the best treatment for hair loss by purchasing buy flagyl no prescription . Whether you’re looking to buy the treatment on the web, you’re assured quality and effectiveness.
Get your heart treatment easily with https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ , available online.
Need to enhance your wakefulness? Order [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin overnight[/URL – on the web for a secure and potent solution.
Secure your health with ease; purchase [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/pristiq/ – pristiq prices[/URL – for your heart needs on the web.
Having trouble with gastric ulcers? Find low-cost relief with nexium , your go-to option for treating stomach ulcers.
Regarding anxiety or OCD treatment, https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ is a viable solution; explore alternatives or obtain it online.
Just discovered your need for natural constipation relief? Explore the benefits of [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis without dr prescription usa[/URL – , a gentle herbal solution. Find out how you can purchase this natural remedy today.
Maximize your vitality; increase your performance safely by obtaining your next dosage of [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – buy doxycycline in c[/URL – via our website.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your health issue efficiently with tadalafil . Boost your lifestyle today.
Regarding anxiety or OCD treatment, https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-cheap/ is a viable solution; explore alternatives or obtain it online.
X-ray your heart health options with detailed insights on [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ – lasix price[/URL – . Discover remedies that enhance cardiovascular well-being immediately.
Looking for the most affordable way to treat pain? Discover the prednisone pills for fast relief.
Purchase your https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ through our platform to ensure you obtain top-notch medication with ease.
Looking for affordable medication options? [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – provides an chance to save on your pharmacy needs. Don’t miss out on this deal!
When looking for an affordable solution to your health needs, consider [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-without-a-doctor/ – prednisone 20mg[/URL – . With options to obtain your prescription at a budget-friendly cost, it’s never been easier to manage your health effectively.
Knowing the crucial nature of being knowledgeable about treatments, it’s essential to investigate propecia 5mg for thorough information.
Browse our website to locate the https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ , offering you a economical solution to control your inflammation.
Relieve your discomfort effectively with our natural solution. Visit [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix from amazon[/URL – for more information.
Looking to manage your condition without breaking the bank? Discover cost-effective options with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – purchase online strattera[/URL – .
Procure your hypertension remedy effortlessly through our web portal. Obtain your treatment without a need for prescription. Click here prednisone to buy to start your journey towards better health.
Questing for the cheapest solution for your vehicle’s battery needs? Look no further! Click here for the https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ – your go-to choice for high-grade batteries.
Discover how to secure your prescriptions effortlessly with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax without an rx[/URL – , ensuring privacy and convenience.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/lowest-price-generic-cialis/ – tadalafil[/URL – – your go-to option for restoring health.
Visit our website to get the most competitive strattera use , offering affordable solutions for your well-being.
Research the benefits of Ayurvedic treatment with https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ , known for its cardiovascular support properties.
To secure your health essentials, proceed to [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ – cheapest deetor dosage price[/URL – , where all requirement meets resolution.
Having trouble locating a reliable source for your bone health medication? Uncover [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin-canada/ – price for ventolin 100mcg[/URL – to acquire your treatment with assurance.
Before making any health decisions, consult your doctor, but if you’re looking to obtain cholesterol-lowering medicine, consider visiting strattera 18mg for a trusted option.
Quickly purchase your fluconazole https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ easily for efficient relief.
Outlet Fresh Finds – The modern structure and quick loading made it pleasant to explore the styles.
Ensure your heart health by opting for a preventative measure with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – where to buy strattera[/URL – , a key to maintaining cardiovascular wellness. Obtain this essential treatment with ease.
Get your medication easily with quick delivery; click here to isotretinoin now.
Finding the lowest https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ can be a difficult endeavor. Visit our site for exceptional offers.
Browse options for affordable [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – price asthalin walmart[/URL – , ensuring you’re getting optimal pricing for your wellness.
You can purchase your [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ – prednisone[/URL – online, ensuring a reliable and convenient way to manage your health needs.
Unlock unparalleled convenience by purchasing your prescriptions through online prednisone ordering . This streamlined process ensures an effortless path to obtaining your essential medical solutions.
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your eyelashes? Discover the benefits of https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ , a cost-effective, widely trusted alternative. Whether you’re aiming to increase lash volume, our product provides proven results.
To acquire [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin non generic[/URL – , explore our website.
Keeping your reproductive health in check is crucial. Discover choices like [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy-com-lowest-price/ – priligy tablets[/URL – that promise hope for many.
Many are looking for reliable options for ED, and purchase 2.5 cialis provides a credible option.
Unlock unbeatable deals on https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ ! Find your answer for a better life today.
Discover excellent choices for managing your condition efficiently with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – . Enhance your health today.
If you’re in the market to buy Flagyl, consider [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ – flagyl without pres[/URL – for a straightforward option to get your prescription.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, buying hydroxychloroquine online in france online provides a economical option.
Discover unparalleled convenience and discretion in securing your cardiovascular health by opting to acquire this cholesterol-lowering medication on the internet https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline/ .
Предпенсионер льготы Индексация пенсий – это ежегодный процесс, направленный на сохранение покупательной способности пенсионных выплат в условиях инфляции. Государство, как правило, проводит индексацию с учетом роста потребительских цен, позволяя пенсионерам поддерживать достойный уровень жизни. Однако, размер индексации может варьироваться в зависимости от экономической ситуации в стране и финансовых возможностей бюджета. Регулярное увеличение пенсий — важный аспект социальной защиты населения, обеспечивающий стабильность и уверенность в завтрашнем дне для миллионов людей.
You can purchase reliable treatment for your condition from the [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – purchasing 5mg propecia on line[/URL – , ensuring a private and protected transaction.
Your search for comprehensive healthcare solutions ends here; find the ultimate purchase levitra for enhanced well-being.
You can acquire your necessary ophthalmic solution https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ .
Explore cutting-edge solutions to improve your cognitive functionality with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – order now prednisone[/URL – .
Discover the benefits of [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ – order propecia online[/URL – for managing hypertension. Obtain your health option without hassle via our website.
Zapping away your health worries has never been easier! Now, you can acquire on line flagyl online. This treatment is a game-changer for those in need.
Looking for a way to enhance your eyelashes? Find easy beauty with https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ . Obtain lush lashes easily.
To address thinning hair, look into [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ – finasteride[/URL – as an proven option.
Explore trusted options to get buy amoxicillin w not prescription , ensuring your well-being is never compromised.
Questioning where to get https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ ? Look for the top choices and offers on our website.
производства натяжных потолков
Такой вариант отделки сочетает в себе эстетику и функциональность.
Компания “natyazhni-steli-vid-virobnika.biz.ua” предлагает качественные потолки напрямую от производителя. Наша продукция соответствует европейским стандартам.
#### **2. Преимущества натяжных потолков**
Одним из главных плюсов натяжных потолков является их влагостойкость. Даже при затоплении потолок останется целым.
Еще одно преимущество — огромный выбор цветов и фактур. Доступны как однотонные, так и фотопечатные варианты.
#### **3. Производство и материалы**
Наша компания изготавливает потолки из экологически чистого ПВХ. Сертификаты подтверждают его гипоаллергенность.
Технология производства гарантирует прочность и эластичность полотна. Готовые потолки устойчивы к механическим повреждениям.
#### **4. Установка и обслуживание**
Монтаж натяжных потолков занимает всего несколько часов. Процесс не требует длительной подготовки основания.
Уход за потолком не требует особых усилий. Достаточно периодически протирать поверхность мягкой тканью.
—
### **Спин-шаблон статьи**
#### **1. Введение**
Сегодня натяжные потолки стали неотъемлемой частью ремонта.
#### **2. Преимущества натяжных потолков**
Они отлично защищают от протечек и скрывают неровности базового потолка.
#### **3. Производство и материалы**
Полотна устойчивы к перепадам температур и влажности.
#### **4. Установка и обслуживание**
Работа выполняется чисто и аккуратно, без лишнего шума.
A thorough guide to accessing [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/lasix/ – lasix canada 40 mg[/URL – is now accessible! Whether you’re looking to acquire or simply investigate options, this handbook offers everything you need.
Secure your supply of Dutas-T easily; buy it from our certified chloroquine medium dose without hassle.
Quickly acquire your deworming solution without hassle by choosing to https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ .
Get your medicine securely and effortlessly through [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prices for prednisone[/URL – , your go-to for medical needs.
Keep your eye health in optimal shape with our advanced treatment options. Discover more and get your supply dapoxetine dosage 30mg promptly.
Looking to fortify your bones? Contemplate https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ for an effective alternative.
Maximize your health without spending a fortune; secure your [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel prices[/URL – and maintain optimal skeletal health.
To purchase your drugs easily, choose [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – , providing a broad array of healthcare options.
Explore budget-friendly options for your healthcare by choosing to purchase buy amoxicillin online .
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Search no more. Obtain https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ safely and swiftly.
Having trouble finding budget-friendly, reliable feminine hygiene products? Look no further; [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone 100mg[/URL – offers a wide variety of options for your needs. Whether you’re in search of sanitary pads, our selection is both high-quality and affordable.
Seeking budget-friendly solutions for your heart condition? Discover [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – generic levitra in canada[/URL – and experience the benefits of efficient therapy at reduced costs.
In need of immediate respite from ongoing nasal congestion? Think about purchasing prednisone 20mg , a proven treatment to ease your symptoms efficiently.
Need a cost-effective solution for your medical needs? https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ ensures you obtain high-quality treatment without breaking your budget.
Discover cost-effective solutions for osteoporosis management: [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – . Order your medication today and take a leap towards stronger bones.
Absolutely, ascertain the [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – buy flomax online[/URL – through checking multiple online pharmacies.
Explore various ways to acquire generic amoxicillin canada pharmacy , making sure effective treatment without sacrificing safety or effectiveness.
Unlock exceptional health benefits by exploring our vast array of options to obtain https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ , ensuring you get top-notch products customized to your needs.
Discover affordable options for managing your anxiety: [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – canadian retin a[/URL – . Choose the crucial treatment easily in pharmacy.
Exclusive service marketplace accounts greets webmasters to the comprehensive database of virtual goods. A key benefit of our shop lies in our exclusive wiki section, featuring up-to-date instructions regarding traffic arbitrage. Within the guides, experts share hacks regarding anti-detect browsers to maximize profits in your daily work. The shop includes accounts for Twitter, Discord, LinkedIn for any purpose: ranging from softregs to farmed business managers with history.
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your performance? Obtain your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil commercial[/URL – now! Our platform offers an easy, secure way to purchase your essential treatment online.
Need to secure your baldness solution? Locate budget-friendly options with generic furosemide uk , providing you receive premium therapies for a portion of the cost.
Relieve those chronic heart and pain conditions safely by choosing to buy https://jawany.com/priligy/ , the go-to option for managing your health better.
Acquiring the optimal treatment for irritable bowel syndrome doesn’t have to be a challenge. You can secure [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – online to alleviate your symptoms effectively.
Zillions are seeking effective treatments for their issues. Now, you can effortlessly obtain [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/ – maxaquin[/URL – online for top outcomes.
When looking to treat your gout, purchasing retin a uk offers a practical solution.
Discover how to obtain https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ effortlessly with our effortless guide.
I discovered that you can purchase [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – cheap tretinoin online[/URL – effortlessly for your nausea.
Discover a convenient way to purchase the prescription with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ – pharmacy cytotec 100mcg cheapest[/URL – , securing discretion, privacy, and ease.
Discover the current hydroxychloroquine and consider alternatives for acquiring this treatment online.
Discover more about trusted birth control options on https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ .
Visit [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/retin-a/ – buy retin a online[/URL – to acquire the Augmentin vial at the lowest rate.
Xplore your options for boosting male potency: purchase eriacta and benefit from a remarkable improvement.
Respiratory issues like bronchial asthma can be daunting, but relief is accessible. Find affordable solutions with https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ , ensuring better respiratory health.
Just realized you need Cialis for your well-being? No need to fret! You can [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – order cialis on line no prescribtion[/URL – easily and safely.
Overcoming hair loss is now simpler than ever. Find your path to a fuller head of locks now with our special formula. Without a doctor’s note needed. levitra .
Acquire your https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ effortlessly with our secure online platform. Buy your vital treatments via our website with ease and confidence.
Secure
Your search for affordable Cabergoline ends here: amoxil .
Looking to enhance your joint health? Consider checking out https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ . This product is crafted to aid in maintaining supreme joint function.
Navigating treatment options for hereditary angioedema can be overwhelming. However, considering [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – might give vital relief and control over this chronic condition.
Unlock the secret to boosted stamina by opting for to sidenafil generic amoxil , your primary source for top-quality wellness solutions.
Aseasonal allergies sufferers can locate relief by purchasing https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ , a reliable remedy.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/cialis-without-a-doctor/ – cialis without a doctor[/URL – , your go-to source for acquiring effective ED treatments on the web.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover the benefits of nizagara online yahoo . With our product, you can enhance your vitality. Shop today and experience the difference!
Interested in managing your conditions? Consider obtaining your medication securely through https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ , a trusted source for authentic pharmaceuticals.
Acquire [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax[/URL – conveniently for managing your condition.
Searching for effective solutions to alleviate irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how bentyl online can help in easing your discomfort today.
Get your amoxil easily from https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ , supplying prompt delivery to satisfy your requirements.
X-ray your health options with ease at [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – nizagara walmart price[/URL – , your top source for getting all your medical needs.
Xperience enhanced cardiovascular health by managing your symptoms efficiently. Opt to acquire your treatment through [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ – vpxl best price usa[/URL – , a reliable source for individuals seeking comprehensive stroke prevention.
Need an effective, comprehensive solution for your health? Find the xenical from canada , your go-to choice for advanced wellness and vitality.
Considering diverse treatment options, it’s crucial to find affordable solutions. For those looking for hormone therapy alternatives, https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ offers a feasible choice.
Optimize your health with a diverse selection of treatments by exploring [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical to buy[/URL – , offering a special assortment of options for your wellbeing.
Keeping your health in check is essential; obtaining your medications shouldn’t be a hurdle. Uncover a hassle-free way to buy necessary treatments. [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – buy lasix online cheap[/URL – today and manage your wellness with ease.
Certainly, obtaining Etizolam-based medications has never been simpler. For those seeking relief, buy nizagara offers a streamlined, secure, and diverse payment method spectrum. With an easy transaction, buy your necessary medication online.
Secure the best deal on https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ by browsing through our site.
Discover reliable solutions for ED with [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – . Obtain your medication easily.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/amoxicillin-250mg/ – amoxicillin 650mg[/URL – virtually can be a simple process.
Questions about managing fertility? Explore how the prednisone online usa might assist in your path towards conceiving.
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ , and Snag your bottle of vital antibiotics easily on the web.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ – canadian pharmacy cialis[/URL – , your go-to source for securing reliable ED remedies virtually.
Gain immediate access to [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine sevilla[/URL – and reduce your concerns with a simple click.
Understand the price of maintaining your well-being by checking the propecia 5mg current costs.
X-plore the myriad ways to manage your asthma without breaking the bank. Secure your inhaler effortlessly through our dependable service. Click here https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ to start your journey towards enhanced respiratory health immediately.
When seeking immediate solutions, locate [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – nizagara in usa[/URL – for your requirements.
Looking to improve your well-being? Explore how to obtain your needs without hassle with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – buy cialis online canada[/URL – .
Understanding the importance of accessing medications safely, one might search for ways to acquire generic-flomax . However, always verify it’s through a reputable source to avoid potential health risks.
Browse our website to find the https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ available. With options to get affordable versions of needed medication, health management becomes both effective and cost-efficient.
Obtain your Hiforce ODS effortlessly today. [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ – prednisone best price usa[/URL – offers a fast and trustworthy solution for those seeking boosted wellness.
Наш магазин предоставляет широкий ассортимент лабораторных химических реактивов, предназначенных для исследовательских, образовательных и производственных задач.
Мы работаем официально и поставляем продукцию для лабораторий, НИИ, учебных заведений и предприятий, где требуется точность, чистота и стабильность реагентов.
Наши специалисты помогут с подбором аналогов, проверкой наличия, консультациями по применению и оформлением сопроводительных документов.
Чтобы ознакомиться с ассортиментом, используйте ссылки ниже:
> магазин лабораторных реактивов
Работаем в следующих городах:
]Санкт-Петербург
]Тихвин
]Пикалёво
]Бокситогорск
]Ефимовский (Бокситогорский р-н)
]Гатчина
]Пушкин
]Кировск
]Волхов
]Кириши
]Великий Новгород
]Приозерск
]Лодейное Поле
Дополнительные ссылки:
— отзывы
— контакты
— вакансии
Ключевые слова:
chemical biz, chemical 696 biz, chemical parma biz, chemical mix biz, chemical 696 biz официальный сайт, chemical 696 biz вход, chemical696, chemical696 biz, chemical696 blz, chemical696 bizz, chemical696 bizz официальный сайт, chem696 biz, chem696 bis, chem696 blz, chemi696, chemi696 biz, chm696, chm696 biz, chm1, chm1 biz сайт, forum parma chemicals biz
X-plore options to purchase medication safely from your home by clicking [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – cytotec for sale overnight[/URL – .
Boost your wellness affordably with discount amoxil , available for those seeking top-tier value.
Given the fluctuating market prices, finding the most affordable option for medication can be a challenge. Whether you’re looking to treat urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ offers a cost-effective solution.
Obtain relief from seasonal allergies with [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ – cost of estrace tablets[/URL – , accessible now. This nose spray can assist in diminishing your allergic reactions.
Seeking heart pain relief? Discover your options with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – buy tretinoin[/URL – , accessible online.
Researching cost-effective solutions for managing your cardiac health? Explore the latest pharmacy pills lowest prices and guarantee your health by a reliable source.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover exclusive https://jawany.com/priligy/ for rebates on vital treatments. Acquire yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
When seeking effective HIV treatment options, [URL=https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ – buy prednisone no prescription[/URL – furnishes a broad array of insights.
Finding [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – has never been simpler. Now, purchase your essential medication via the internet with complete confidence.
Looking for affordable medication options? cheap tadalafil online provides a great chance to save on your prescriptions. Don’t miss out on this deal!
The requirement for reliable and easy access to drugs has never been greater. Find your options and buy https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ now.
Various individuals searching for solutions to handle premature ejaculation turn to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine on internet[/URL – as a reliable option.
Jumpstart your journey to a more vibrant love life with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ – tadalafil best price[/URL – . Explore the myriad perks of this treatment and find out how it can transform your experiences.
Combat the malaria virus effectively with viagra brand , available for purchase via our website.
Improve your health by selecting pharmaceutical solutions that offer reliability and affordability. Purchase https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ to ensure your well-being without compromising on quality.
Zero hassle: obtain your [URL=https://wefenceit.com/buying-viagra-online/ – buying viagra online[/URL – easily.
Keep your eyesight in tip-top condition with our lasix capsules for sale . Obtaining these essential tools online ensures you obtain unmatched quality for maintaining your ocular health.
Researching the cheapest options for Ayurvedic solutions? Find https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ for quality and savings.
Unlock unparalleled savings on antiviral medication by opting to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ – pharmacy from usa suppliers[/URL – . Seamlessly acquire your health essentials digitally.
Given the myriad of options for managing epilepsy, pharmacy without a doctors prescription stands out as a trusted solution. Patients seeking to manage their seizures can look into this choice for its effectiveness.
Keeping your cardiovascular wellness in check is essential, which is why incorporating https://center4family.com/strattera/ into your care plan could assist those with peripheral vascular disease.
Having difficulty managing your menstrual symptoms? Consider exploring [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – trazodone online canada[/URL – , a proven solution. Purchase it virtually to alleviate discomfort.
When searching for affordable solutions to manage your ocular hypertension, consider exploring order hydroxychloroquine for unbeatable rates and reliable pharmaceuticals.
You might discover the most competitive https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ online, ensuring you receive maximum value for your therapy.
Researching affordable treatments for depression? Look no further. Discover the most cost-effective options and order your supply of amitriptyline today. Click [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – amitriptyline generic canada[/URL – for unbeatable deals and comprehensive support on your journey towards well-being.
Get your amoxil easily from [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without prescription[/URL – , offering quick dispensation to meet your needs.
X-plore cost-effective healthcare options; vidalista en mexico for managing your condition with ease.
Uncover the ultimate way to enhance your wellbeing; discover our premier https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ . This solution is optimal for those seeking to boost their lifestyle effectively.
Get budget-friendly solutions for enhancing your intimate moments; check out [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – mexico lasix generic[/URL – for selections.
Looking to treat your hyperuricemia? Consider acquiring effective medication. For your convenience, trazodone in japanese online to reduce symptoms efficiently.
Facing dry eye problems? Locate the solution right here with https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ . Purchase your supply today for ease.
When seeking cost-effective solutions for erectile dysfunction, consider [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – fildena 150mg[/URL – as your go-to source.
Need a reliable source for your hair loss solution? Look no further! Our credible generic cipro uk offers numerous options of treatments to help you restore your confidence.
Discover a trusted way to enhance your wellbeing: https://nabba-us.com/item/viagra/ .
With rising healthcare costs, it’s crucial to find the best option. For those seeking cholesterol reduction, [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 650mg[/URL – is often the key.
Obtain your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin uk[/URL – effortlessly. Secure this vital skin care solution without hassle.
Considering immediate antibiotic needs, acquiring doxycycline 200mg online ensures a rapid solution.
Given the costly nature of branded drugs, patients seeking treatment for Hepatitis C often search for https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ , providing a more affordable solution.
Save on your next purchase of [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ – perscription drug retin-a[/URL – by exploring our extensive collection. Find unbeatable savings online today.
Yes, you can obtain affordable solutions for managing edema. [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – non prescription prednisone[/URL – is your go-to option for intervention.
Keep informed on this anti-malarial medication benefits and guidelines by visiting buy hydroxychloroquine online for detailed insights and updates.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your home medicine cabinet, https://wefenceit.com/pill/amoxicillin/ virtually can be a seamless process.
Zillions seek effective solutions for impotence; [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/viagra-pills/ – viagra best price[/URL – presents a wide-ranging remedy.
Considering urgent antibiotic needs, acquiring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – online provides a swift solution.
Here’s how to acquire buy kamagra online , an essential medication for certain medical conditions.
Quest for the lowest rates on Erythromycin? https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ has exceptional prices for you.
Maximize your vitality and stamina with [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 400mg[/URL – , the prime choice for enhancing performance. Explore the decisive solution for improving your health and confidence seamlessly.
Keeping your healthcare needs in mind, obtaining effective treatment for ED is now easier. Discover [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – cialis black[/URL – and save on your order.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your personal health needs, 650 mg. amoxil virtually can be a simple process.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ . Whether you’re looking to acquire this medication on the internet, you’ll find that its efficacy in treating a wide range of infections makes it a top choice.
X-plore affordable options for managing Addison’s disease; uncover how [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex[/URL – delivers a cost-effective solution to sustain your health.
Understanding the need to obtain medication easily, our platform allows you to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ – cialis kaufen bankeinzug[/URL – without any hassle.
A multitude of options for improving your health exists, but lasix stands out due to its effectiveness.
Venture into holistic healthcare solutions and explore natural remedies. Easily purchase your wellness needs https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ through our reliable platform.
When looking to economize on your prescription, consider using an [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – . Discover how to significantly reduce your pharmacy bills immediately.
Your search for cost-effective Cabergoline ends here: [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – retin a capsules[/URL – .
Visit generic tadalafil in canada to discover the best prices for your antifungal treatment.
Just in: Discerning shoppers can now locate the https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ on digital platforms, ensuring you get exceptional value for your health-related necessities.
Acquire your [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ – doxycycline le moins cher[/URL – seamlessly via the web.
Are you dealing with thinning hair? Explore the best solutions with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – propecia 1mg[/URL – to restore your self-confidence.
X-plore your options for handling hypertension with proven medication. Order discount flomax online to secure your heart health today.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to cut costs on pharmaceuticals.
When looking for a cost-effective, reliable source to purchase your medication, consider [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a without pres[/URL – as your go-to solution. This platform offers a selection of pharmaceuticals at competitive prices.
Looking for a way to fight against your condition? hydroxychloroquine might be the remedy you’re seeking. Discover how this medication can aid you today.
Explore the benefits and options for treating Alzheimer’s with https://tooprettybrand.com/product/cialis-20mg/ , a venerated solution in managing cognitive decline. Secure this medication from reputable sources to potentially elevate quality of life for those affected.
“Quick relief from muscular pain is now achievable with [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/levitra/ – 20 levitra generic india[/URL – , an effective solution. Explore how you can reduce discomfort immediately.”
Optimize your wellness journey with our versatile nizagara 100mg , designed for your unique needs. Obtain
Boost your energy and flavor your evenings with https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ . Elevate your experiences effortlessly, acquire this delightful treatment directly to enhance your moments.
Before deciding to obtain your next dose of anxiety management treatment, consider exploring your options. For those looking to manage symptoms of anxiety safely, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – no perscription 80mg propranolol[/URL – might be the right step. Options vary widely, so make sure you’re making an informed choice.
Aiming to minimize your prostate enlargement symptoms? Find how vidalista in usa can aid.
Your quest for affordable the antimalarial drug ends here. Discover the most recent rates at https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ , your ultimate source for budget-friendly healthcare solutions.
Have cholesterol concerns? [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – buy lasix[/URL – to manage your levels effectively.
To reduce discomfort, buy [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – from reliable sources via the internet.
Looking for inexpensive options? Uncover the panmycin today.
Your well-being deserves attention. Discover convenient access to treat your health condition with https://brightnights915.com/drugs/propecia/ . Ensure your health is optimal with just a click.
One can discover competitive [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomiphene[/URL – and multiple options on web platforms, ensuring cost-effectiveness and accessibility.
To obtain the lowest-priced options for nizagara , browse our page now.
Having trouble finding budget-friendly, reliable feminine hygiene products? Look no further; https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ offers a wide variety of options for your needs. Whether you’re in search of tampons, our selection is both high-quality and affordable.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Find [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/cialis-20mg/ – cialis[/URL – to boost your vitality efficiently and safely.
Need a cost-effective, reliable solution for managing your hypertension? Look no further and acquire [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/levitra/ – mail order levitra[/URL – , the ideal choice for maintaining your health.
Get the best deals on manufacturer’s Duprost today by clicking cialis 10mg . This drug is crucial for managing BPH symptoms.
To get your necessary iron supplements, explore https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ for unbeatable savings.
Now, find the best bargains on [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – lowest price for prednisone[/URL – .
Super clanek! Prave jsem zacal hrat ve Spinmama Casino CZ a nabidka je opravdu lakava. Nabizi uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP klub, turnaje, loterie a dalsi promo akce, ktere potesi kazdeho hrace. Osobne me bavi jejich herni souteze a vyherni automaty – online casino pro ceske hrace s vybornymi podminkami. Pokud hledate bezpecne online casino s bonusy, podivejte se zde: Twitter . Urcite vyzkousejte a uzijete si spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
Spinmama Casino CZ
Uvitaci bonusy a VI
30f2_ba
X-ray your options for HIV treatment medications and discover the best solutions. For those seeking value, [URL=https://jawany.com/amoxil/ – 650 generic amoxil in australia[/URL – presents a practical choice.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern treatments, managing it has become easier. Explore cialis , a budget-friendly and reliable option for enhancing your sexual health.
Keep your health in check by exploring options to order vital medications. For those in need, https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ is now accessible, offering a simple way to maintain your wellness.
For those seeking vision health solutions, explore [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/propecia-1mg/ – propecia without a doctors prescription[/URL – for a selection of treatment options.
Zest for life can be boosted with reliable heart care. Check [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – generic zithromax 500 price comparison[/URL – to learn about how you can control your heart health affordably.
Explore the world of healthcare solutions and uncover easy ways to maintain your well-being. Whether you’re in search of specific medications or wide-ranging health advice, we provide a variety of options. For those in need of a substitute, ventolin en ligne could be the solution.
Discover innovative ways to manage stress with https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ , available via our website.
Discover how to buy Cenforce safely through the internet at [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – canadian cenforce[/URL – . This pill offers powerful solutions for erectile dysfunction, providing quick and trustworthy results for men seeking enhanced sexual health.
Procure your antiviral medication with a [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy no prescription[/URL – , ensuring savings.
Discover affordable relief for joint pain and inflammation. Now you can buy cheapest viagra online uk . This powerful treatment offers a solution for alleviating discomfort with ease.
Keep your vitality at its peak: explore safe and dependable options to purchase https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ .
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; acquire your [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ – amoxicillin online no script[/URL – online for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
To uncover the most up-to-date [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ – propecia cost[/URL – , check out our site. Here, you can effortlessly obtain thorough information on costs and stock levels.
X-plore the myriad options to acquire your medications affordably; our portal allows you to esomeprazole effortlessly. This opportunity enables individuals seeking to purchase their pharmaceuticals economically.
Pain and inflammation can be significantly reduced with the use of https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ , a potent NSAID.
Obtain the Cialis quickly through our dependable [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/viagra/ – viagra en ligne[/URL – , ensuring an anonymous and rapid delivery directly to your door.
Your search for affordable arrhythmia treatment ends here with [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone/ – buying prednisone[/URL – . Secure your health’s future online.
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial; hence, acquiring necessary medications conveniently is key. For those in need, nizagara prices offers a seamless solution. Alternative options include Order the necessary medication online with ease and reliability.
Optimize your health with the solution everyone’s talking about, https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ . This powerful formulation can alter your wellbeing.
Explore premier [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – find zithromax without prescription[/URL – for a thrilling gaming experience.
Regain control of your health by securing your medication without delay. [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – apotheke online doxycycline[/URL – is your gateway to overcome conditions efficiently.
Having difficulties procuring your prescription? Look into price on levitra 20 mg no prescription for a hassle-free buy.
Looking to obtain your antiviral treatment? Now, you can buy https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ online.
Secure affordable [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – fildena 150mg[/URL – options for handling heavy bleeding episodes. Explore choices that prioritize health and your budget.
You can obtain [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – for digestive health through our website.
Keeping your health in top condition is crucial; hence, managing your fluid levels with water pills is key to preventing related health issues. For those in need, you can buy generic finasteride from india , a reliable choice for managing your health.
Given the ongoing discussions about its efficacy in various treatments, finding a reliable source to acquire https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ on the web is crucial for patients.
Explore affordable solutions for your digestive health with [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – cheap zithromax no perscription[/URL – . Now, locate a selection of alternatives to ease discomfort efficiently.
Have you been searching for an effective solution to your nasal issues? Look no further than the [URL=https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy pharmacy[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to buy a remedy for your sinus problems, this spray offers a high-quality option.
With medication costs soaring, securing affordable options is crucial. Click here for tadalafil no prescription and discover economical choices for managing your health.
Searching for a dependable site to buy heart medication? Look no further than https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ , your trusted source for all your cardiovascular requirements.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your health issue efficiently with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Boost your lifestyle immediately.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – 100 de ventolin[/URL – for allergen control. Secure the best deal on effective medication today.
X-plore your options for handling hypertension with proven medication. Order buy cheap tadalafil from a reputable source to guarantee your heart health today.
Just in time for your urgent needs, locate your essential supplies ready at https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ , without delay.
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before attempting to obtain [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ – generic flagyl online[/URL – cannot be overstated.
Boost your eye health easily; simply [URL=https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ – xenical[/URL – online. Achieve optimal ocular pressure relief with a click.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Discover how flomax can provide relief and restore your comfort.
Discover how you can acquire https://damcf.org/nizagara/ easily online.
Get rid of lice easily with our treatment at [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – vpxl.com[/URL – .
X-plore cost-effective options for enhancing your lashes with prednisone tablets . Discover a range of ways to gain the look you aspire for.
Get respite from pain through https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ .
Reduce your heart’s workload with [URL=https://griffindtc.com/priligy-60mg/ – priligy[/URL – , an essential medication for controlling chest pain. Purchase today for enhanced heart health.
With competitive drugstore rates, belgique doxycycline offers an affordable solution to enhance your fertility journey. Explore cost-effective options today.
Zap your anxiety away! Now you can get your stress-relieving medication hassle-free. Don’t miss out on our exclusive https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ . Cut costs on your buy today and experience serenity without breaking the bank.
Maximize your vigour naturally with [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix without prescription[/URL – , an unparalleled option for those seeking to enhance their performance without the need for doctor’s orders.
In need of a dependable and efficient solution for inflammation? Discover your pathway to relief by obtaining [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . This medication is crafted for individuals in need of swift and effective relief.
Considering various options to control your BPH symptoms? Find out about how you can get how to buy lady-era online legally on the internet, offering a simple solution to ease discomfort.
Acquiring https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ via the web can be an effective method to ensure you obtain your medication easily.
Purchasing a [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ – vente lasix generique[/URL – can be efficiently done through our platform. Opt to acquire your pharmaceuticals via our website for a hassle-free experience.
Explore the latest advancements in schizophrenia treatment with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – chiense sildalis[/URL – . Acquire this revolutionary medication online.
Access the most affordable deals on propecia 1 mg online italia to alleviate your nasal allergies immediately.
Looking to control your condition? Buy https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ today and start your journey to improved health.
Maximize your health outcomes by opting to acquire your prescriptions through the web. For those in need, [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone in usa[/URL – is a hassle-free way to secure your essentials quickly and efficiently.
Maximize your savings on medication for prostate cancer treatment by exploring the [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/buy-cheap-viagra/ – viagra[/URL – . Locate affordable solutions online.
Research demonstrates that regulating cholesterol is essential for heart health. Visit clomid no prescription to find out about cutting-edge solutions.
Quickly obtain your antihistamine relief by choosing to order https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ .
Visit our website to locate the [URL=https://damcf.org/nizagara/ – generic nizagara canada[/URL – for your arthritis treatment needs.
Keep your health in check without breaking the bank. Discover your options and uncover budget-friendly alternatives for improving your wellbeing. Click here: [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ – retin a without a doctor[/URL – .
Discover how amoxil 650mg can revolutionize the way you participate in betting.
Discover complementary options to control your cholesterol with https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ , available in stores sans a prescription.
Explore the benefits of controlling your ailment with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia in usa[/URL – , a proven option to improve your well-being.
Yes, the Food and Drug Administration has approved http://www.isotretinoin.com for combating serious acne conditions. This marks a significant advancement in acne treatment.
Your quest for trustworthy arrhythmia treatment ends today. Explore our broad assortment of heart medications, including https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ , offered through our website.
Questioning where to find top-notch heart health supplements? Look no further than [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – canadian meds prednisone[/URL – , your premier source for every one of your cardiovascular supplement needs.
You can secure respite from diarrhea by purchasing buy tadalafil without prescription via the internet.
Interested in reducing water retention? Explore various remedies and discover https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ for effective results.
You can locate [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ – discount vpxl[/URL – on the internet, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Якщо цікавить історія міст — надшвидкі екскурси.
Given the high-priced nature of branded drugs, patients seeking Hepatitis C treatment often seek [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – xenical walmart price[/URL – , providing a cost-effective alternative.
Buyers interested in acquiring buying xenical on line safe website could easily Purchase their Supply through reliable digital pharmacies, ensuring expeditious and secure delivery to their doorstep.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ offers a convenient way to secure necessary medication from the comfort of your own home.
You can discover the most up-to-date [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – priligy uk[/URL – by checking our website.
clickmatic.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Highland Craft Collection – Crafts look impressive, with smooth and enjoyable browsing.
Having doubts about where to locate the best deal for your antimalarial medication? Worry no more! Just click on [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/buy-retin-a-online-cheap/ – retin a[/URL – to view the most competitive options available.
Need to boost your alertness? Order kamagra pills on the web for a safe and potent solution.
Explore options to get https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ , a vital medication for handling Parkinson’s disease, directly on our platform.
Given our ongoing wellness landscape, obtaining medications conveniently is vital. Therefore, for those seeking quality Etizolam, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra wo bestellen[/URL – offers a remedy. This service ensures you obtain authentic products, facilitating peace of mind in their treatment journey.
Just launched, rx generic tamoxifen is now accessible on the web. Ensure your stock and control your condition with efficiency.
Optimize your wellness with our all-in-one https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ , the key to boosting your health effortlessly.
Curious about how to enhance your vitality? Consider trying [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ – prednisone[/URL – , a reputable option designed to lift your well-being.
A holistic approach to managing chronic myeloid leukemia involves considering various treatments, including prescription medications like [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ – pharmacy fildena 25 mg cheapest[/URL – . Patients looking to purchase their essential medication can easily find it online, ensuring they receive the care they need efficiently and conveniently.
In need of Doxycycline? Get your prescription easily doxycycline cheap . Available online, ensuring you receive your treatment promptly.
Uncover the advantages of using https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ for your allergy-related symptoms. Accessible now, this treatment offers a cost-effective solution to manage your discomfort.
A safe and easy way to acquire ED treatment is to [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/viagra-pills/ – viagra pills[/URL – .
Harness the power of internet to order your levitra 20mg safely and efficiently.
Discover how https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ can reduce symptoms of prostate enlargement by exploring our website.
Having difficulty managing one’s menstrual symptoms? Consider exploring [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ – canadian kamagra oral jelly vol 1[/URL – , a reliable solution. Acquire it online to ease discomfort.
rankpilotpro.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
rankzilla.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
rankflare.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Knowing the cost of your pharmaceuticals is crucial. Discover the economical rates for [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ – propecia.com[/URL – with our resource.
Looking to manage prostate carcinoma? Acquire cheap priligy no prescription canada without hassle for reliable therapy.
Unlock the secrets to managing your wellness with https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ , your foremost source for top-notch pharmaceuticals.
Understanding the need for convenience, you can now acquire your prescription through the internet with ease. [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena 100[/URL – and experience quick shipment to your doorstep.
Quickly obtain the [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/levitra-price-walmart/ – buy levitra without prescription[/URL – , a trusted source for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Procure your remedy with ease; generic tadalista uk online to tackle your needs efficiently and securely.
Harness significant savings on your next purchase with our exclusive https://wefenceit.com/pharmacy/ . Grab your essential medication without breaking the bank by redeeming this special offer now.
If you’re looking to find an affordable solution to your vertigo, think about [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ – prednisone 20mg[/URL – . This medication may assist in reducing the effects of dizziness, enhancing your quality of life.
rankorbit.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
The requirement for dependable remedies to enhance men’s health has never been more vital. Discover the potency of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/tadalafil/ – generic prescription tadalafil without[/URL – , a top choice for managing such challenges.
“Your hassle-free solution for obtaining medications swiftly is here at buy 5mg cialis canadian pharmacy , where you can order your required treatments with ease.”
Just discovered: find the https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ right away. Get your dosage at unbeatable costs and ensure your well-being effectively.
Finding reliable tuberculosis treatment can be challenging, but [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix from india[/URL – offers a streamlined solution.
Get your hands on the most affordable prezzi del ed-sample-pack-2 for improving your sexual health.
Hunting for an affordable solution to boost your fertility? Look no further! https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ is your go-to option. Whether you’re aiming to purchase this vital hormone, our platform offers the best deals. Perfect for those undergoing fertility treatments or in need of hormone therapy, our product promises quality.
Unlock unparalleled savings on your medication management by visiting [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/buy-cialis-w-not-prescription/ – cialis information[/URL – . Score the best deal now and guarantee your health stays our top priority.
Looking for doxycycline? Secure it without needing to visit the doctor through this [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline 100mg[/URL – . Acquire your dose promptly and start treatment immediately.
When looking for top-notch hair removal solutions, consider low cost alternatives and to pharmacy for an affordable option.
Shop now for your hypertension treatment and find how much you can save at https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ , your top destination for cost-effective healthcare solutions.
For those looking for strengthened bones, consider [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – as an effortless solution.
Having issues with insomnia? Consider exploring the benefits of nizagara.com lowest price . Get the solution now from a trusted source.
Zero hassle to oversee your eye pressure issues with https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ . Preorder now and experience the change.
“Quickly acquire your prescription effortlessly with [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax[/URL – , the most reliable way to obtain your health needs through the web.”
I have tried various iGaming sites over the years, and it’s kind of crazy how many players start playing without doing research. If you need a simple explanation of important casino features, this article was really helpful: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s simple to read and shows what matters most before making a deposit. I recommend giving it a look if you want to make better choices.
Maximize your savings on Crohn’s disease treatment by securing the [URL=https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ – ventolin en ligne[/URL – . Discover cost-effective choices on the web for your healthcare needs.
Initiate the journey towards relief from upset stomach by opting to purchase kamagra .
Seeking a treatment for longer eyelashes? Discover the advantages of https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ , your route to improving your appearance.
Considering immediate antibiotic needs, acquiring [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – where to buy doxycycline over the counter[/URL – online provides a rapid solution.
When considering treatment for altitude sickness, opt for known solutions like [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – cheap ranitidine pills[/URL – . Seek acquiring the medication via the web to ensure your journey remains uninterrupted.
To secure your health without emptying your wallet, ranitidine capsules is your best bet. Discover cost-effective solutions for managing cardiac issues with ease.
Reduce bleeding effectively with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ ; tailor-made for those seeking an option to mitigate heavy bleeding episodes without compromising safety.
Maximize your health without spending a fortune; obtain your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – sildenafil[/URL – and maintain supreme skeletal health.
Boost your confidence and revitalize your life with cialis black online uk , available for acquisition through our website.
Your search for excitement ends here at the https://renog.org/trazodone/ , offering unbeatable rates.
Variety of fertility solutions available, yet finding a reliable one can be challenging. Explore [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cipro/ – canadian pharmacy cipro[/URL – to enhance your chances with a trusted solution.
X-plore your financial options with [URL=https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/nizagara/ – generic overseas nizagara[/URL – when you need immediate financial assistance.
Quality healthcare means having access to various treatment options. When it comes to HIV management, one can opt for branded medication or explore cost-effective alternatives like vidalista . These options ensure that patients have access to necessary treatments without breaking the bank.
Facing health issues? Get your https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ easily right away.
Secure the best deal on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – by searching through our website.
Purchase your necessary Parkinson’s treatment conveniently through [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – prednisone pastillas[/URL – , a method guaranteeing fast delivery and confidentiality.
Obtain your treatment for gastrointestinal issues at the comprare propecia generico .
Seeking a safe, trusted method to get misoprostol? Look no further. https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ offers a straightforward solution.
Finding the best deal for [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/mail-order-prednisone/ – prednisone 5mg price without rx[/URL – can be challenging. To get your dosage, order via the internet and ensure you’re receiving both quality and economy.
Discover secure ways to obtain your prescriptions with ease; wholesalers of viagra offers a trusted solution for enhancing your wellness.
Browse our website to buy top-tier medical supplements, including https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ , safely.
A safe method to handle your health: [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – sildenafil[/URL – . Visit our site to discover diverse solutions for your wellbeing.
When looking to obtain treatments for upset stomach, consider [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – as a budget-friendly option.
You can enhance your vitality by opting to acquire propecia 5mg , up for grabs now.
Seeking effective acne treatment? Locate reliable https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/doxycycline/ options quickly via the internet.
Discover your solution for boosting sexual performance with ease; purchase [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – now.
Get your health back on track! Obtain your essentials without hassle by choosing to [URL=https://damcf.org/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . This move not only streamlines but also ensures you acquire your treatment swiftly.
Uncover affordable treatment for scabies with our cost-effective erectafil ohne rezept bestellen , the go-to option for eradicating pests.
Discover the most affordable options for managing your health with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ . Whether you’re in the market for this vital prescription through digital platforms, we offer a comprehensive selection of alternatives to meet your needs.
Looking for an effective remedy for your baldness? Learn about how you can get [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/secnidazole/ – secnidazole information[/URL – ‘s prescription easily via the web.
Промокоды часто дают фриспины. 7к казино промокоды вчера получил 50 FS, здорово.
Uncover the advantages of utilizing [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara without a doctors prescription[/URL – for your allergy-related symptoms. Accessible now, this medication provides a cost-effective solution to manage your discomfort.
Looking for cost-effective treatment options for your condition? Discover the most affordable prices for your medication needs. secnidazole from canada offers unparalleled deals. Locate cost-effective options here.
Consider securing your prescriptions effortlessly from https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ , offering an extensive range of pharmaceutical solutions.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Consider [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis tab 5 mg[/URL – – your go-to option for restoring well-being.
Quickly order your treatment on the internet with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil canada pharmacy[/URL – , ensuring a straightforward experience.
Maximize your savings on arthritis medication by seeking the lasix . Purchase your health with economical treatment alternatives and secure your wellbeing without burdening your finances.
Venture into the world of affordable healthcare solutions by opting to https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ from our trusted source. This option not only guarantees superiority but also savings for those in demand.
Improve your well-being effortlessly by opting to order high-quality medication from the comfort of your home. [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/canada-ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – offers a reliable, secure solution for enhancing performance.
Having issues with insomnia? Consider exploring the benefits of [URL=https://tradarchersworld.com/ – nizagara 50 mg in canada prices[/URL – . Get the remedy now from a reliable source.
Seeking a safe, trusted method to obtain Cytotec? Look no further. cytotec on line offers a simple solution.
When looking for top-notch hair removal solutions, consider https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ for an affordable option.
Looking for a way to manage your symptoms? Explore your options and acquire [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 5mg[/URL – with ease.
Reduce swelling and altitude sickness symptoms effectively by opting for lady era uk . Secure your treatment effectively online.
Xperience relief without the wait; explore https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ for a hassle-free solution to improve your life today.
Purchase your prescriptions with confidence from a [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ – prednisone price at walmart[/URL – , where quality and client contentment are prioritized.
The benefits of incorporating [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – atomoxetine[/URL – into your health regimen are vast, including boosting your body’s resilience to stress, supporting sleep quality, and augmenting wellness.
Visit viagra soft tabs no prescription and find a trusted way to purchase your medication digitally.
Browse for affordable options to support your health with https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ , offering a selection of natural remedies.
Boost your eyelash growth with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin-canada/ – ventolin without a doctors prescription[/URL – , a cutting-edge solution up for grabs on the web.
Obtain [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – best price parlodel[/URL – to manage your heart health. Secure your supply now and boost cardiovascular well-being without delay.
Secure your vital medications without trouble by choosing to buy from drugs online levitra .
Purchasing a https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/xenical/ can be efficiently done through our platform. Opt to acquire your pharmaceuticals via our website for a hassle-free experience.
Interested in managing water retention? Explore multiple remedies and discover [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ – lowest amoxicillin prices[/URL – for effective results.
Discover reliable and private options to purchase your treatment without hurdles. Click here: priligy in usa .
Optimize your eye care routine with https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ , offering a treatment for enhanced eyelash growth.
Xperience fast relief with your [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ – priligy 30 mg cost walmart[/URL – , ensuring you receive your treatment without delay.
Keep your kidneys healthy with organic remedies. Locate the best solution by purchasing sildalis right away.
When considering options for treating https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ , many individuals seek affordable solutions. Discover a variety of options to buy your prescriptions through the internet, ensuring cost-effective and practical access to the care you need.
Seeking relief from OCD symptoms? [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ – lady-era official reseller[/URL – offers a solution. Find out about this medication now.
Before opting for conventional methods, consider other avenues to acquire your medications. One reliable option is to [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – online prescription for prednisone[/URL – , offering an easy way to manage your health.
Browse the site to find generic amoxil canada , ensuring you get top-quality antibiotic choices at matchless prices.
The quest for affordable pain relief is over. Discover the best deals for https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ , an effective solution to alleviate arthritis-related discomfort.
The need to purchase Atorlip-20, a cholesterol-lowering agent, without leaving your home is now simpler than ever with the option to [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – prednisone without dr prescription[/URL – .
Personally, I’ve tried various online casinos in the past years, and it’s kind of crazy how many players start playing without doing research. If anyone’s looking for a breakdown of what a casino offers, this write-up helped me a lot: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s pretty straightforward and highlights key risks before you put in money. Definitely worth a read if you want to stay on the safe side.
X-ray your options for lowering your eye pressure. Discover cost-effective solutions with a [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ – levitra buy[/URL – for your glaucoma treatment. Purchase your treatment virtually at a reduced rate.
Secure affordable solutions for your health needs with nizagara prices .
To acquire your dosage of Etizolam, think about clicking on https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ for trustworthy shipment.
You can obtain [URL=https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ – propecia without a prescription[/URL – for gastrointestinal health through our website.
Discover a trusted way to improve your wellbeing: [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/sildenafil/ – viagra without dr prescription usa[/URL – .
Research the most reliable options to purchase los angeles vardenafil , crucial for managing hypertension and heart-related ailments.
X-plore your choices for increasing eyelash growth with https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ , available for acquisition online.
Looking to improve your well-being? Explore how to get your needs without hassle with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – cialis pills[/URL – .
Your health is safely managed with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix in mexico for sale[/URL – , accessible for purchase directly.
Looking to purchase analgesic gel? Visit lowest price nizagara now for a wide selection of effective products.
Enhance your confidence and well-being with natural solutions. Explore https://endmedicaldebt.com/pill/celebrex/ to find a selection of natural treatments online.
Zero hesitation is key when considering boosting your lifestyle. Get your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix coupon[/URL – now for a top-tier result.
Battling seasonal allergies can be daunting, but relief is available through [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without dr prescription[/URL – . Discover how this solution could alleviate your symptoms today.
X-ray your health concerns and find the best solution; click here to generic retin-a no prescription canada for a holistic approach to wellness.
Looking to manage your uric acid levels? Consider purchasing effective medication. For your convenience, https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ here to reduce symptoms efficiently.
Manage your health efficiently by choosing to [URL=https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ – on line symbicort[/URL – , a versatile solution for various conditions. You can Buy this medication easily on the website, ensuring convenience and discretion.
Unlock access to top-tier [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – and effortlessly manage your ocular pressure with ease. Select from a comprehensive variety of choices available for speedy delivery.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your health? No need to worry! You can cialis 10mg easily and with confidence.
Optimize your wellness with our multifunctional https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ , the solution to enhancing your health without hassle.
Find lowest prices for natural vigor solutions; [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topamax reviews[/URL – on our website.
Yes, you can secure discounted solutions for treating edema. [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – generic furosemide uk[/URL – is your go-to option for relief.
Secure your prescription easily and promptly with kamagra oral jelly , ensuring total discretion and efficiency.
Need to acquire reliable treatment for hypertension? Visit our https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ for top-notch options available in our catalog.
Quickly discover relief from allergy-induced nasal congestion with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ – generic kamagra from canada[/URL – , a top-rated choice for combatting nasal allergies.
Rediscover management over your heart health with finasteride , the foremost destination for purchasing your prescriptions online.
Curious about hassle-free ways to secure your health needs? Explore the convenience of accessing pharmaceuticals with just a click. Now, you can acquire essential prescriptions virtually. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ , ensuring a seamless experience for your health and well-being.
When looking for an affordable solution to your health needs, consider [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – buy prednisone uk[/URL – . With options to purchase this essential medication without straining your finances, it’s never been easier to manage your health effectively.
goldencrestyle – Smooth layout and tidy listings, shopping felt quick and pleasant.
With an array of herbal solutions for boosting vitality, click here to [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – low cost priligy[/URL – , offering a safe and effective way to aid your health.
Discover how order branded Allegra on the web with our easy guide. kamagra cost .
Various therapies for long-term hepatitis B are available, yet https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ stands out because of its efficacy.
Just discovered your need for natural constipation relief? Explore the benefits of [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – where to buy lady era[/URL – , a gentle herbal solution. Discover how you can get this effective remedy online.
Maximize your savings on healthcare expenses by securing your medications virtually. Find the [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – at our reputable pharmacy site.
When looking to acquire treatments for nausea, consider buy cialis on line as a economical option.
Looking to manage your menstrual cycle irregularities? Discover a reliable solution with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ . This treatment can be your ally in dealing with various gynecological conditions.
Purchase your [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/cialis-best-price/ – buy cialis online 10[/URL – eye drops online to manage high eye pressure efficiently and economically.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxicillin , providing comprehensive solution for bacterial infections.
Just realized you need ED medication for your condition? No need to stress out! You can https://kristinbwright.com/cialis-best-price/ easily and with confidence.
I discovered that individuals looking to manage their Addison’s disease can find relief with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – lisinopril[/URL – . This treatment is vital for people affected.
Visit [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – extra super avana[/URL – to secure your treatment.
“Quickly secure your prescription effortlessly with prednisone , the most dependable way to order your wellness needs digitally.”
For individuals seeking to acquire ED medication, https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ offers a discreet and convenient option.
Obtaining [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin a cream 0.05[/URL – has never been simpler. Purchase now and reduce expenses on your prescription.
X-plore cost-effective options for impotence relief with [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena 100 professional[/URL – , guaranteeing quality and security.
Considering the need for affordable solutions, you can now purchase buy tadalafil , a preferred choice for those seeking cost-effective calcium supplementation.
X-ray your options for managing OCD by visiting our website to uncover the latest https://jawany.com/ventolin/ .
Considering the risks involved, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before deciding to acquire [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia/ – india on line propecia[/URL – .
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before you acquire [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/generic-priligy-at-walmart/ – generic priligy next day[/URL – is paramount.
Unlocking the secrets of cutting-edge neurological treatments, sildenafil stands as a cornerstone for research in Parkinson’s disease.
Zap your pain away with purchase your anti-inflammatory medication conveniently through the internet with https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ .
Optimize your health and wellness journey by choosing to [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , a decision that empowers you to enhance your wellness routine from the ease of your home.
Seek the pharmacy canada efficiently. Locate your ‘must-have’ medication at a budget-friendly price.
When seeking a budget-friendly solution for your antimicrobial needs, consider tapping into the convenience of https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ . This digital pharmacy offers a broad assortment of non-brand medications that meet various health conditions efficiently.
Boost your wellness with authentic supplements; buy your [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – online for optimal health benefits.
For those seeking to acquire a reliable method of checking their status, exploring [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – generic nizagara online 50[/URL – offers peace of mind through confidential and accurate results.
Struggling with scabies or head lice? Purchase your solution online with where to buy lasix online . This simple-to-use cream offers rapid ease from irritation.
In search of proven ophthalmic suspensions? Look no further! Uncover the efficacy of https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – your answer to swelling and irritation in the eyes.
Boost your wellness with pure supplements; procure your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ – lowest price for amoxicillin[/URL – from our website for optimal health benefits.
Optimize your health and savings by exploring the [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – . Discover budget-friendly options to maintain your well-being.
Para aquellos preguntandose kamagra , es importante comprender que esta planta medicinal se utiliza en la medicina ayurvedica para potenciar la bienestar femenina.
Yearning for cost-effective COVID-19 treatment options? Discover the solution with https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ , where efficacy meets affordability. Save on medical costs without compromising quality.
Having anxiety? Discover a range of remedies [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – . Obtain your treatment on the web.
Nice weblog here! Additionally your web site so much up very fast!
What web host are you the usage of? Can I get your associate hyperlink to your host?
I desire my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Thank you very much.
My web host is Hostinger.
Discover your solution for enhanced vitality; explore reliable options and order [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – immediately.
Looking to control your menstrual cycle irregularities? Discover a trustworthy solution with lasix . This treatment can be your ally in addressing various gynecological conditions.
X-ray your options carefully when you consider to secure medication from the web. Explore https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ safely and responsibly.
Explore
Xplore the benefits of fildena non generic for managing your health. Obtain your dose online to improve your daily life.
Considering the fluctuating https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra-online-pharmacy/ , it’s worth exploring alternative platforms to acquire your pharmaceutical needs through the web.
Purchase generic Bentyl for digestive relief; find out more at [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ – bentyl online canada[/URL – .
Seeking effective skin infection treatment? Locate reliable [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – online generic doxycycline[/URL – options quickly on the web.
In need of efficient HIV treatment? You can purchase strattera online for a trustworthy and easy way to manage your health.
Your search for affordable cardiac therapy ends here with https://midsouthprc.org/propecia-1mg/ . Secure your health’s future today.
Discover reliable joint pain relief with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – purchase lasix[/URL – , the premier remedy now available on the web.
Regarding your health needs, discover an efficient solution to manage edema; [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – tadalista for sale[/URL – is available. Secure, immediate purchase is guaranteed, making treatment more accessible.
Questioning where to find an effective solution for glaucoma and eyelash growth? Explore our comprehensive range at zoloft 100mg , where you can Buy the treatment with ease.
Improve your life quality easily, purchase your medications online. Don’t miss out on exclusive offers at https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ .
Get your amoxil easily from [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxicillin/ – cheap amoxicillin[/URL – , offering quick dispensation to satisfy your requirements.
discoverandbuyhub.shop – Products displayed nicely, site navigation is simple and easy to explore.
Having trouble with heartburn or gastric acidity? Purchase your relief safely and promptly [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – retin a[/URL – .
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective sildenafil ? Explore
With the increase in interest in holistic health solutions, explore https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ to boost your vitality.
Before making any decisions, explore your options for treating hair loss. [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ – get prednisone now[/URL – offers a simple way to gain access to this medication.
X-ray your options and choose wisely where to [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/]order retin a[/URL] . With myriad choices available, choose the safest provider to get your medicine.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting hydroxychloroquine 400mg .
Considering affordable alternatives for managing anxiety? https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ delivers a range of choices worth exploring.
Quickly secure [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – to make certain your well-being needs are satisfied efficiently.
Keep your stomach issues at bay with buy propecia on line , the ultimate remedy for IBS symptoms. Purchase your solution on the web now.
Obtaining your https://jawany.com/prednisone/ has never been easier; acquire your medication on the web with utmost convenience and discretion.
Shop for natural health remedies and boost your wellbeing today. Purchase the supplements at [URL=https://wefenceit.com/buying-viagra-online/ – viagra[/URL – , the best source for top-notch health products.
Obtain comprehensive insights and secure the [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ – prednisone price at walmart[/URL – for your antiviral medication needs by exploring our website today.
Discover budget-friendly solutions for managing your heart health with propecia non generic from canada . Secure your batch now and embark on a journey toward enhanced cardiovascular condition.
Discover the convenience and privacy of securing your erectile dysfunction medication with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ , ready for you.
Need to control your hypothyroidism? Visit [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – to discover how you can maintain your hormone levels efficiently.
Zero in on your health and well-being essentials with ease by choosing to purchase your prescriptions from our lasix furosemide for sale , offering you a straightforward and convenient option to manage your health needs with without hassle.
Procure your acid reflux medication sans exiting your home; click on https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ for quick relief.
Visit our site to find the [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – for controlling hair loss.
Exploring options for acquiring doxycycline pills ? Find out how to obtain your prescription with ease online.
Maximize your savings on healthcare expenses by procuring your medications online. Find the https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ at our reputable pharmacy website.
Patients seeking treatment for hepatitis C can now acquire their medication through [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone[/URL – , offering a simple and dependable solution for their needs.
Facing hair loss? Explore affordable solutions and find how to fight baldness effectively. Click [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topamax 25mg[/URL – for competitive rates on effective treatments.
Seeking affordable options for enhanced performance and stamina? Explore the potential benefits by checking the retin a buy , where you’ll find reasonable deals.
Just discovered the optimal option for managing HBV? Explore https://umichicago.com/amlip/ immediately for affordable care.
discoveramazingdeals.click – Great discounts displayed nicely, shopping experience feels smooth and enjoyable today.
Seek the [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – efficiently. Discover your ‘must-have’ medication without breaking the bank.
Looking for an all-natural way to enhance your vitality? Discover lady era.com lowest price and explore how our product can elevate your well-being.
X-plore the benefits of https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ for bacterial infections; discover how it assists in fighting a range of diseases.
Amidst the myriad options for managing pain and inflammation, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ – prednisone price walmart[/URL – stand out as a potent solution. Individuals seeking relief can obtain these remedy via the internet, offering a hassle-free way to address their symptoms.
Your well-being is our priority; order [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – how to buy retin-a online legally[/URL – on our site and commence your journey to better health today.
Offering a range of reproductive health solutions, locate meaningful savings on your next purchase with verapamil .
Before you choose to buy your medication, consider consulting https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ for a safe and informed choice.
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix-for-sale/ – lasix on line[/URL – here. Instantly obtain your treatment online with ease.
When looking to obtain medication for rheumatoid arthritis, consider exploring options to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone generic canada[/URL – , ensuring you attain reliable treatment smoothly.
Knowing the significance of keeping updated about therapies, it’s essential to investigate prednisone 5mg for thorough information.
Xperience the unparalleled benefits of https://wefenceit.com/pill/tadalafil/ for boosting your vitality. Explore this singular blend, perfectly designed to boost your stamina with natural ingredients.
Ailments like irritable bowel syndrome can greatly disrupt daily life. Fortunately, effective relief is available. Explore your options and find out the potential [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol 6mg[/URL – here.
Looking for an effective way to combat alcohol dependence? Learn about how kamagra generic brands can be an essential part in your journey towards sobriety.
Zero hassle: acquire your https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ with ease.
Discover equivalent options to control your cholesterol with [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/zoloft/ – zoloft capsules for sale[/URL – , accessible online sans a prescription.
Before opting for conventional methods, explore other avenues to acquire your medications. One reliable option is to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ – online levitra in australia[/URL – , offering a straightforward way to manage your health.
Optimize your health with cialis black commercial , the premier destination for acquiring your prescriptions. Our selection offers unmatched quality, ensuring you receive the best care.
Discover excellent choices for managing your health issue efficiently with https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ . Enhance your health today.
Purchase your essential medicines conveniently with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ – prednisone[/URL – , offering a seamless and secure purchase process via the internet.
Keeping your heart health in check is essential, which is why incorporating [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra-capsules-for-sale/ – levitra[/URL – into your routine could aid those with peripheral vascular disease.
Before you decide, explore your options for tranquility with dapoxetine actual work . With a multitude of alternatives available, opt for your path to peace wisely.
Various individuals search for ways to economize on their medication expenses. By using a https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ , you can slash the cost of your pharmacy bills.
Join us as we explore the benefits of [URL=https://center4family.com/priligy-online/ – priligy cheap[/URL – , a leading solution in managing chronic health conditions. With its proven effectiveness, it’s no wonder why many decide to acquire this vital medication for their health regime.
When looking to address OCD symptoms, consider exploring [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia canadian pharmacy[/URL – as a potential remedy.
Obtain your prescription for xenical commercial with ease, ensuring you receive authentic medication. Order safely and securely online.
Questioning where to discover top-notch cardiovascular health supplements? Look no further than https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ , your premier destination for every one of your cardiac supplement needs.
Purchase effective Hepatitis C treatment with [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – nizagara capsules for sale[/URL – , offering a reliable cure for individuals seeking recovery.
Need to find the most recent [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/trazodone/ – purchasing trazodone[/URL – ? Consult our website for budget-friendly options and extensive data.
Are you struggling to find quick relief from asthma at night? Our store offers a fast solution with asthalin lowest price . Now, acquire swift alleviation and breathe easier by buying the remedy right away.
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ can aid in reducing urinary symptoms associated with an enlarged prostate.
Get the most affordable rates on manufacturer’s Duprost by clicking [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax/ – zithromax uk[/URL – . This drug is crucial for treating BPH symptoms.
Zealously search for remedies to enhance your well-being? Examine sildenafil for powerful choice.
Secure your well-being easily; purchase https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ , obtainable on site for enhancing female vitality.
The Buy this medicine on site [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax walmart price[/URL – ensures your health needs are met with convenience and efficiency.
Uncover deals when you acquire your prescription with molnupiravir to buy .
I found the optimal solution to control my health concerns: https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ . This site offers outstanding prices.
Purchase your medication effortlessly through [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ – prices for modvigil[/URL – , ensuring a quick and secure transaction for your wellness needs.
Purchase your essential hypertension medication conveniently and affordably through [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra-online-pharmacy/ – kamagra online pharmacy[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to order your treatment virtually, our platform offers an extensive range to meet your healthcare needs efficiently.
Looking to purchase Depo-Medrol? Find the most cost-effective cheapest nizagara prices licensed pharmacies .
Looking to boost your well-being? Find out about how to secure your needs effortlessly with https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ .
Quickly get your drugs with convenience by choosing to order [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ – generic viagra purchase 50 mg[/URL – .
Achieve academic excellence and improve your writing skills with our professional support at [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin buy[/URL – .
Optimize your heart health regimen by exploring sildenafil , an essential option for those aiming to manage their stroke prevention strategy effectively. With a wide array of choices, purchasing an important medication through the web has never been easier, ensuring that maintaining your cardiovascular well-being is both accessible and convenient.
Before making a decision, discover https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ and compare prices to guarantee you obtain the best deal for your heart health medication.
Treat your cold sores effectively and affordably with [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – trazodone shipped fast[/URL – . Grab this offer to lower your expenses on essential treatment now.
For individuals seeking to manage their hair loss, [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ – buy vidalista online canada[/URL – offers an effective solution. Explore alternatives to purchase this essential medication conveniently online.
Discover the path to conception with purchase propecia without an rx .
Quickly purchase your https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ on our site, ensuring a stress-free process.
You can find safe and trustworthy treatment for nausea with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil without pres[/URL – , accessible through online pharmacies.
Discover secure ways to acquire your prescriptions with ease; sildalist offers a reliable solution for boosting your wellness.
If you’re seeking a remedy to treat unwanted hair growth, look into https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ . This topical solution delivers a streamlined solution to address your concerns without a prescription.
Find efficacious treatments for your health concerns; purchase [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/retin-a/ – generic retin a canada pharmacy[/URL – easily.
Considering the demand for dependable solutions for ED management, it’s essential to locate a reliable source. [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ – viagra[/URL – presents a convenient pathway to acquire your prescription securely.
Quality and affordability meet, enabling you to obtain your medication seamlessly. Seek no further for your health solutions, click here: german tadalafil . Offering ease and security, we’ve got your needs covered.
To obtain clomiphene for managing conception challenges, visit https://center4family.com/kamagra/ .
Conveniently acquire your [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara buy[/URL – today with quick delivery.
Keep your allergies at bay without leaving your home. Order your nasal spray online with ease. Visit [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – levitra 20 pills[/URL – for your solution.
Need to manage your pain? Acquire your medication effortlessly through our platform. where to buy lady era offers a simple way to control inflammation and pain, bringing you ease without the hassle.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Get https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ safely and quickly.
Zillions seek reliable solutions for erectile dysfunction; [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/viagra/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – provides a broad solution.
Explore cost-effective solutions for your health needs with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – generic lasix mexico[/URL – . Buy your treatment easily today.
Your search for cost-effective hormone therapy ends here; acquire equivalent au lasix without hassle for your well-being needs.
Consult healthcare experts before you get https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ to ensure it’s the right therapy for your ailment.
When looking for relief from motion sickness, one might consider exploring options for obtaining [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/generic-amoxil/ – amoxil online italia[/URL – .
Given the fluctuating market prices, finding the most affordable option for medication can be a daunting task. Whether you’re looking to treat urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, tamsulosin offers a cost-effective solution.
Keep your healthcare regimen on track and obtain your prescription with ease, https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil/ , ensuring a consistent path towards recovery.
TSO Online Deals – Great selection of discounted products, navigation around the site was easy.
Finding the right instruments for applying Lumigan can enhance the effectiveness of your treatment. Explore your options and [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – hydroxychloroquine without dr prescription[/URL – to ensure optimal application and results.
Browse our site to locate the zithromax for sale , ensuring you obtain the best deals on your wellness needs.
Looking to improve your health? Think about https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ for a convenient way.
Now, for those seeking a reliable solution to enhance their intimate experiences, purchasing the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – becomes a necessity. Acquire a standout selection through online platforms for a more lifestyle change.
Unsure where to procure your medication? For those looking to increase their health, [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/tamoxifen-without-pres/ – tamoxifen price at walmart[/URL – offers a broad range of solutions.
Now, uncover wallet-friendly solutions for erectile dysfunction with cenforce lowest price , attainable online.
Looking to enhance your vitality? Check out the https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ for the solution to boost your energy.
Acquire
Maximize your vitality with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ – torsemide[/URL – , releasing supreme performance through natural means.
Purchase natural solutions for your health needs without hassle on our website. Explore choices and discover the best deals cheap retin a pills right away.
Zipping through your options for handling ED? Learn about a streamlined solution by choosing to purchase https://nabba-us.com/item/viagra/ .
Obtain competitive [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax for sale overnight[/URL – by opting to Buy your treatment through our website, ensuring you receive top-notch healthcare support without overspending.
Have you been searching for an effective solution to your nasal issues? Look no further than the [URL=https://tradarchersworld.com/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to acquire a solution for your allergies, this spray offers an affordable option.
Discover convenient ways to manage your health by opting to amoxicillin 250mg . Acquire your treatment easily with just a few clicks.
Just discovered https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ ? Now enjoy swift service straight to your home.
Looking to acquire allergy relief without breaking the bank? Click here to [URL=https://hyblavalleyvet.com/kamagra-in-usa/ – kamagra tablets buy online[/URL – and start feeling better today.
To secure the most affordable price on [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil buy online[/URL – , check out our website.
Your search for affordable Cabergoline ends here: peni large .
Visit https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ to acquire your medication.
Discover complementary options to control your cholesterol with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – , available online without a prescription.
Keep your life energetic and fulfilled with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy in japanese[/URL – , the key to enhancing your vitality.
To secure your health without emptying your wallet, generic amoxil canada is your best bet. Discover cost-effective solutions for managing cardiovascular diseases with ease.
Now, explore a variety of approaches to enhance your well-being. Consider trying https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ for an organic solution.
Knowing the need for reliable baldness treatments, individuals can easily get [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – Buy the proven treatment on our site for managing their hair loss concerns.
Looking to obtain Depo-Medrol for your medical requirements? Click on the link [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – zithromax[/URL – for a simple transaction.
Secure your well-being and save money by exploring our purchase tretinoin online , featuring a selection of top-notch treatments for improving men’s health.
X-plore your alternatives for managing irregular heartbeat with effective solutions. Find out about how https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ can help in maintaining your heart rate, offering serenity.
I stumbled upon an incredible deal for natural health enthusiasts seeking to enhance their well-being. Don’t miss this opportunity to buy your [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ – nexium[/URL – today and start embracing a more healthy lifestyle!
Obtain your lowest price on generic prednisone with ease. Order your medication through our website seamlessly and without hassle.
Quest for affordable testosterone replacement therapy ends here! Discover the latest https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ for your treatment today.
Maximize your health outcomes by ordering your essential medications through [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ – doxycycline 200 mg online[/URL – , an authentic source for medicines.
Research indicates that achieving thicker, longer eyelashes doesn’t always require a doctor’s visit. Explore options to enhance your eyelash appearance safely at home with buy tadalista w not prescription , a leading choice for individuals looking to enhance their natural beauty.
Obtain your Flagyl treatment without delay through our quick https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ delivery service, ensuring you get the care you require promptly.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://wefenceit.com/amoxicillin/ – on line amoxicillin[/URL – online can be a straightforward process.
Manage your symptoms effectively with [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone without prescription[/URL – . Explore cost-effective options to manage your condition on our site.
Your search for affordable options ends here: can you buy tadalafil online uk . Discover your solution today and save on healthcare expenses.
Looking for affordable medication options? https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ gives you a great opportunity to reduce expenses on your prescriptions. Don’t miss out on this deal!
Keep your wellness at its best with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – stromectol for sale[/URL – , offering a wide range of healthcare solutions. Boost your living standards now.
Discover innovative heart health solutions with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – mail order priligy[/URL – . Purchase your treatment easily and maintain your well-being effortlessly.
Searching for the best price on fertility treatments? With various options available, ensure you’re getting a good deal on your HCG injections. Explore now the buy prednisone online cheap and compare to locate the most economical choice for your reproductive health needs.
Elevate your vitality effortlessly with an array of natural solutions ready at your fingertips. Simply https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a-uk/ to begin a journey towards improved health and wellbeing.
When seeking to enhance your vitality, explore the best options available. Purchase [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – , offering a secure and easy method for your needs.
Maximize your eye health benefits with [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara pills[/URL – , the premier solution for managing inflammation. Obtain your supply via the web today and experience unparalleled relief.
Optimize your eye care routine with tretinoin , offering a treatment for enhanced eyelash growth.
Xplore affordable alternatives to enhance your well-being with https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ . Purchase today for maximum benefits.
Before making any health decisions, consult your doctor, but if you’re looking to obtain anti-hyperlipidemic drugs, consider visiting [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ – generic nizagara from canada[/URL – for a reliable option.
Maximize your vitality and youthfulness; seamlessly [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/buy-cialis-w-not-prescription/ – buy cialis w not prescription[/URL – through our platform. Explore a more vibrant life by choosing for this pathway now.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxil 650mg , offering comprehensive treatment for bacterial infections.
For people seeking to control their cholesterol, exploring https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ could be a viable alternative.
Looking for the most affordable [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ – order retin a[/URL – ? Acquire your treatment by using our platform for outstanding deals.
discoverandbuyhub.shop – Items look appealing, navigation is clear and very easy to use.
Obtain optimal health benefits at the best value by choosing [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – vidalista[/URL – . Secure the essential medication on the web effortlessly.
Looking for a reliable way to purchase your medication? With our platform, you can effortlessly vidalista and maintain your health efficiently.
To access treatments for PD, discover options at https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ .
Regain digestive harmony with a organic solution; order [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ – fildena generic overnight shipping[/URL – to promote digestive well-being.
Procure buy prednisone houston safely and effortlessly. Now, acquire your crucial drug swiftly through our reliable source.
If you’re looking to obtain medication for HBV, https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ offer a economical solution.
Manage your well-being effectively by choosing to purchase your prescriptions on the internet. For those specifically seeking to address hormonal imbalances, [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ – generic tadalafil in canada[/URL – offers a convenient solution.
Various methods exist to acquire essential medications, yet finding a reliable source can be a challenge. Considering options to purchase on line pharmacy could be a answer for those in need.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with https://tooprettybrand.com/product/buy-cialis-w-not-prescription/ , your go-to source for acquiring potent ED remedies on the web.
Uncover exceptional deals on your next acquisition. Discover the best [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – overnight vpxl[/URL – today. Get the best deal on every purchase.
Looking to manage obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)? Explore reliable treatment options. Your solution could be just a click away with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – .
Just discovered a revolutionary way to enhance your lifestyle? Consider exploring tretinoin lowest price Purchase now for a life-changing experience.
Looking for an affordable solution to enhance your performance? Explore the array of options; https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ could be your answer. Consider obtaining this potent remedy via the internet for a hassle-free experience.
I discovered the [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia-5mg/ – finasteride[/URL – after scouring the internet.
Zero worries for those seeking enhanced vitality; [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical 60mg[/URL – offer an effective solution for boosting energy.
Seeking a safe solution for your sexual health issues? Discover the benefits of cheap fildena 100 online , a new choice for boosting men’s performance without the need for a prescription.
Zero in on pain relief: Whether you’re seeking an effective solution for discomfort, purchasing https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ online offers a straightforward approach.
Quality eye care solutions are now accessible from the comfort of your home. Explore leading products to enhance your eye health, including [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a-uk/ – retin a[/URL – , directly via our site.
You can buy your necessary medicine strattera coupon with ease.
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial, and finding the right medication should not be a hassle. For those seeking flexibility and convenience in their treatment, https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ offers a discreet, effective option. Consider obtaining your prescription via the web, ensuring you receive top-tier care without compromise.
**C**ompare and discover the [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ – prazosin without a doctor prescription[/URL – by searching through our internet-based medication outlet.
Searching for an safe glaucoma treatment? Look no further! Purchase your generic sildalis immediately for optimal eye health.
Discover affordable options for managing your pain with https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ . Whether you’re looking to acquire this medication online, we offer a range of choices to meet your needs.
Seeking effective acne treatment? Find safe [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/doxycycline/ – doxycycline information[/URL – options quickly via the internet.
Before you decide to acquire your medication, reflect on consulting [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix coupon[/URL – for a secure and educated choice.
When seeking effective management for unusual menstrual cycles, consider exploring the options for prednisone coupon . Numerous people have found it to be an crucial part of their medical regimen.
Quickly obtain your https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ , ensuring effective management of allergies.
Explore top-rated [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – buy ventolin us[/URL – for an exciting experience.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для легализации товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы обеспечить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в выборе товаров и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете надежность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – ваш лучший выбор.
поставляемая продукция:
Нержавеющая прямоугольная поковка 200х220 мм ЭИ402 Изучите широкий ассортимент нержавеющих прямоугольных поковок на RedmetSplav с гарантией качества и надежности. Устойчивость к коррозии и разнообразие размеров для всевозможных проектов.
Combatting Hepatitis C effectively requires access to quality medication. Choose to obtain your therapy via the internet. Find out more about your options at [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ – drugstore kamagra[/URL – .
Battling anxiety can be tough, but you’re not alone. Discover your partner in dealing with symptoms with kamagra . Explore alternatives on the web today.
Seek affordable options for managing Alzheimer’s; explore https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ and find out cost-effective alternatives for treatment.
Considering the necessity for dependable methods for ED management, it’s crucial to locate a trusted source. [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/sildenafil/ – viagra on internet[/URL – presents a convenient pathway to acquire your medication securely.
Experience immediate relief from seasonal allergies with propecia . Find your remedy on the web and say goodbye to sniffling today.
Ease allergy symptoms quickly; https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ to manage your allergies effectively.
I recently discovered the remarkable efficiency of [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis without a prescription ontario canada[/URL – in enhancing fertility treatments. For those seeking alternatives, consider obtaining these potent capsules to elevate your reproductive health.
Obtaining tadalafil without a prescription has never been easier. Now you can purchase this essential medicine from the comfort of your own home.
Seeking effective skin infection treatment? Locate reliable https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ options quickly online.
Acquire [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – conveniently for handling your health issue.
Just realized you need ED medication for your condition? No need to worry! You can [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – tadalafil[/URL – without hassle and securely.
Regain control over your wellness at unbeatable costs with retin a . Order now and enjoy rapid delivery worldwide.
Explore solutions for controlling your heart-related problems effectively with https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ .
Just realized you need tadalafil for your health? No need to worry! You can [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis over internet[/URL – without hassle and with confidence.
discoveramazingdeals.click – Discounts look attractive, shopping experience feels smooth and quick to use.
Uncover discounts when you purchase your prescription with [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline from canada[/URL – .
Managing ADHD symptoms can be challenging, but with the right medication, it’s definitely within reach. Explore your options and learn about how low price amoxil can be a significant help in your treatment plan.
Just released: Secure your supply of https://nabba-us.com/product/pharmacy/ . Obtain your drug effortlessly from home.
Now, find the remedy for impotence with simplicity by opting to purchase [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – fildena 25mg[/URL – .
Obtain your [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine coupons[/URL – prescription effortlessly through our website, ensuring fast and trustworthy service for your pharmacy needs.
Xplore affordable alternatives to enhance your healthcare needs with levitra 20mg . Acquire today for peak savings.
X-ray your budget and health options; uncover savings on HIV treatment with https://purefmonline.com/pill/retin-a/ . Optimize your healthcare outlays while maintaining quality.
Get alleviation from your rheumatoid arthritis signs today. Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin without a prescription[/URL – for amazing discounts on your treatment.
Purchase organic solutions for your health needs easily on our website. Explore options and locate the best deals [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – buy vidalista buy tadalafil from certified online drugstore[/URL – now.
Obtaining online vidalista has never been more accessible, ensuring you get your treatment quickly.
Obtain https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ for your allergy relief. Securely purchase your treatment online.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – generic levitra at walmart[/URL – for comprehensive insights on using this medicine safely.
Obtain fertility medication at competitive rates; explore the clomid 100mg now. Many individuals seeking to boost their chances of conception realize it advantageous.
Unlock immediate access to your healthcare needs without a prescription by clicking https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ , and order with assurance.
Seeking a safe, dependable method to obtain Cytotec? Look no further. [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – generic cytotec uk[/URL – offers a hassle-free solution.
Your search for effective and safe medication ends here; [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – mail order nizagara[/URL – offers you the opportunity to procure top-quality medication conveniently.
Manage your HIV effectively with tadalista generic pay with paypal , an essential component in care regimens. This affordable option ensures accessibility to high-quality medication for everyone in need.
X-plore the myriad of options to obtain your medication swiftly and safely with https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ .
Browse our selection for high-quality deals on [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia to buy[/URL – . Find your purchase now and experience speedy shipping.
Curious about where to discover the trazodone ? Explore our website for amazing deals on your pharmacy needs.
When looking to cut costs on your prescription, consider using an https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ . Learn how to cut down on your pharmacy bills now.
Your quest for budget-friendly heart medications ends today! Secure your dose of [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone without dr prescription[/URL – right here! Wide-ranging options to acquire this critical medication easily await.
You can acquire relief from diarrhea by ordering [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – cialis[/URL – via the internet.
Considering the diverse options for obtaining essential medications, it’s crucial to investigate avenues offering both value and authenticity. When looking to acquire treatments, specifically cabergoline, one standout choice is torsemide for sale . This option stands out for its cost-effectiveness and reliability.
Quickly discover relief from allergy-induced nasal congestion with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ , a highly recommended choice for alleviating allergy symptoms.
Manage your symptoms effectively with [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . Find how this remedy can help control nausea and vomiting for a superior quality of life.
Variety in your healthcare options matters; thus, consider our exclusive tadapox to enhance your well-being.
Looking to manage your abdominal discomfort? Discover how https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ can offer respite.
Optimize your health with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – , the premier destination for purchasing your medications. Our range offers unmatched efficacy, ensuring you receive the best care.
Looking for the cheapest options for your medication? Discover unbeatable prices on [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – canada celebrex[/URL – today.
Need a herbal solution for digestive issues? Look no further. Order tadalafil 10mg for a safe treatment.
Looking to boost your stamina? Get genuine solutions https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ .
For individuals seeking affordable diuretic options, our [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra-online/ – kamagra 100mg[/URL – provides a reliable solution. You can buy this medication through our online platform easily and securely.
Keeping your well-being top-notch is easier today with options like [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ – india propecia paypal[/URL – , an reliable way to manage inflammation.
When considering therapy options for certain health issues, it’s essential to explore various avenues. For those seeking reliable sources, one can acquire lasix on line from trusted outlets.
Visit our online pharmacy to purchase your https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ . Secure your prescription effortlessly.
Considering swift antibiotic needs, acquiring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ – doxycycline 100 order[/URL – online provides a swift solution.
Zajimavy obsah! Prave jsem zacal hrat ve Spinmama Casino CZ a musim rict, ze jejich nabidka opravdu stoji za to. Nabizi uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP klub, turnaje, loterie a dalsi promo akce, ktere zaujmou kazdeho fanouska casin. Me nejvice bavi herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske online casino na opravdu vysoke urovni. Pro vyzkouseni neceho noveho a bezpecneho kliknete zde: Twitter . Urcite vyzkousejte a uzijete si spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Uvitaci bonusy a VIP program ve Spinmama Casino CZ
Spinmama Casino CZ – nejlepsi bonusy a promo akce
09d5d5f
Understanding your need for reliable and affordable hair loss solutions? Look no further than [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – generic propecia tablets[/URL – , where you can acquire your solution easily.
Discover the best cost-effective solution for migraine relief by clicking purchase dapoxetine online . Secure your stock without overspending.
Now, discover the most cost-effective options for your treatment by exploring https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ . Secure your health needs affordably by buying this crucial medication online.
Here’s your encoded request:
Have allergies been affecting you? Experience relief with a fast solution. [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – offers effective solution for nasal congestion.
Our team has sourced the [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – prednisone without dr prescription usa[/URL – for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
Looking to increase your stamina? Discover how get 10 mg cialis could assist. Available now, these capsules are intended to support your health journey.
X-ray your options and choose wisely where to https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ . With myriad choices available, select the most reliable provider to get your medication.
Having trouble finding an affordable alternative to your medication? Look no further! Order your [URL=https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix uk[/URL – on the web for a cost-effective solution to your health needs.
Now, acquire your vital [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – prednisone overnight[/URL – easily by visiting our site.
Xperience the freedom of a fuller hairline when you acquire your solution for thinning hair via web. For more details, click here: prednisone 5 mg .
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial, and finding the right medication should not be a hassle. For those seeking flexibility and convenience in their treatment, https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ offers a discreet, effective option. Consider securing your medication through our website, ensuring you receive high-quality care without compromise.
Looking to enhance your vitality? Check out the [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/viagra/ – buy viagra on line[/URL – for the remedy to boost your energy.
Acquire
Venturing into the realm of HIV treatment, consider exploring solutions like precio lasix costa rica , a pivotal drug designed for potent viral suppression.
Seeking a safe, reliable method to acquire misoprostol? Look no further. https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ offers a hassle-free solution.
Navigating the world of online pharmacies, it’s essential to find a reliable source for your medication needs. Whether you’re looking to purchase treatment for [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ – 25 mg buy nizagara[/URL – , it’s critical to select a accredited provider.
Combat discomfort effortlessly and economically with the help of [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra-online-pharmacy/ – kamagra online pharmacy[/URL – , available for your next purchase.
Here at our pharmacy, we provide a wide range of medications. Whether you’re looking to buy generic pharmacy or seeking alternatives, our web page is your ultimate destination.
Ensure optimal health with our trusted source for your pharmaceutical needs. Secure your quality medications easily from the comfort of your home. Check out https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ for reliable and efficient service.
Just discovered you’re in need of a rapid solution for better endurance? With [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ – buying retin a[/URL – , find your answers and enjoy improved performance sooner than you think. Now you can obtain this solution swiftly to ensure your readiness.
Explore our vast selection of [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine buy it online now[/URL – , perfect for gaining precise application.
Explore various options to buy economical xenical commercial for stomach relief.
You can order your https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/retin-a-from-india/ through our digital platform, ensuring an secure and convenient way to handle your health needs.
Looking for treatment for thinning hair? Locate the most effective products online. Your search ends here: [URL=https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ – order prednisone online[/URL – .
Optimize your wellness journey with a convenient, hassle-free option: [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – retin a coupons[/URL – . Discover the simplicity of having your essential medication delivered straight to your home with no wait.
To secure your treatment without hassle, click on prednisone 40mg now for speedy and dependable service.
Understanding your need for reliable and affordable hair loss solutions? Look no further than https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ , where you can purchase your treatment effortlessly.
Before you decide, discover how [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – buy levitra online[/URL – might be the remedy you’re seeking for managing anxiety.
Managing menopause symptoms effectively often involves hormone therapy treatment. Many individuals look for convenient and private options. For those interested, you can acquire [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – online, ensuring a seamless and confidential process.
One can find competitive propecia and numerous alternatives on web platforms, ensuring affordability and availability.
Your search for comprehensive healthcare solutions ends here; discover the ultimate https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ for advanced health.
For those looking to improve their hair growth, consider exploring [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – as your optimal solution.
Various individuals seeking immunosuppressive treatments are now able to acquire their medications effortlessly. [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – offers a reliable path for those needing to control their health without difficulties.
Manage your cardiac dysrhythmias effectively. Acquire safe and reliable medication. buying trazodone online from a trusted source.
I stumbled upon an incredible deal for natural health enthusiasts seeking to boost their well-being. Don’t miss this opportunity to acquire your https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ today and start embracing a more vibrant lifestyle!
When seeking trusted and effective treatment for schizophrenia, consider exploring options to purchase [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ – get 50 mg kamagra[/URL – from accredited websites.
Looking to manage your condition effectively? Discover how to acquire [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ – cialis generic uk[/URL – and begin your journey towards better health today.
Uncover affordable treatment for scabies with our budget-friendly ed sample pack 2 , the go-to option for eliminating pests.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to reduce expenses on your medication.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – – your go-to solution for restoring health.
Discover reliable treatment options with [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – , and control your health concerns efficiently.
Looking for effective pain relief? Discover the convenience and affordability of comprar ventolin en barcelona . Uncover your answer to discomfort management online.
Quiet your nerves at an affordable price with https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ . Get your solution today for peace of mind.
Researching effective treatments for alcohol dependence? Explore [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ – lasix uk[/URL – for affordable options.
Secure your medication easily and swiftly with flomax , ensuring complete discretion and efficiency.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis-5mg/ , your go-to source for securing potent ED remedies online.
Maximize your health with the smart option of [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – stromectol price at walmart[/URL – , a choice that ensures you obtain superior cardiovascular support. Opting for this solution via the internet combines convenience with effectiveness.
Acquire your best health solution at an unbeatable price; explore [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – prices for tinidazole[/URL – for optimal health outcomes.
Achieve your desired height and enhance your wellbeing with genuine finasteride .
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ are appropriate for you or your loved ones.
Questioning where to obtain a hair loss treatment? Discover safe, reliable options for [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – finasteride from india[/URL – .
When considering managing your heart rhythm issues, exploring [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/ventolin/ – ventolin best price[/URL – might be a feasible alternative.
Get cost-effective treatments for your health needs. Find generic tadalista uk to manage your conditions with ease.
X-ray your options for antifungal treatment by exploring https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ . With a myriad of choices to acquire this crucial treatment via the web, your path to recovery could be just a click away.
Keep your vitality high and performance unmatched; purchase [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ – buy priligy[/URL – for unparalleled endurance and satisfaction, enhancing your lifestyle.
Acquire cost-effective solutions for your digestive issues with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin buy in canada[/URL – , proven to alleviate symptoms efficiently.
Have you been in search of a reliable place to purchase your medications? Look no further! Our online pharmacy offers a wide variety of pharmaceuticals, including ticlid online . With us, you can purchase your meds easily from the convenience of your place.
For those seeking relief from gastrointestinal discomfort, securing https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ could be a viable solution.
Browse our selection for exclusive deals on [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – asthalin without a doctor[/URL – . Find your purchase now and experience speedy shipping.
Zealously seeking relief from seasonal allergies? Invest in your relief with [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone-5mg/ – buy prednisone without prescription in usa[/URL – , the trusted solution for tackling allergy symptoms.
When seeking affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction, consider fildena in deutschland as your preferred source.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Find out about how to secure your needs effortlessly with https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ .
Quality healthcare doesn’t have to break the bank. Discover cost-effective epilepsy treatment solutions and reduce expenses on your medication with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis generic[/URL – .
Purchasing [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – best on line prednisone sellers[/URL – has never been easier, ensuring you secure your crucial remedy via the internet with complete convenience and privacy.
Questioning where to source antibiotics without overpaying? Discover the cipro 750mg and save on your pharmacy expenses.
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and find generic solutions at https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ . Buy this treatment via the web now and commence your journey towards regrowth.
Looking to tackle alcohol dependency? [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin-a gel[/URL – offers an effective method.
Acquire your zoloft.com now! Secure your bone density solution via the internet effortlessly.
Zap your fertility concerns away! Explore the potential of https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ and learn about how it can help in enhancing your chances of conception.
Quiet your stress at an affordable price with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – . Get your solution today for peace of mind.
Having trouble accessing prescription medication? Our [URL=https://goldenedit.com/item/ventolin/ – best price ventolin usa[/URL – option offers a straightforward solution, enabling you to purchase vital medication online.
As an expert in the medical field, I need to emphasize the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before initiating any treatment. Nevertheless, for those looking into non-prescription options for managing specific conditions, doxycycline without dr prescription could be considered. Always make sure that you obtain drugs from reliable sources to guard against fake products.
Discover economical solutions for managing your health with https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ . Find your necessary medication today.
Need to discover the latest [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – ? Check our page for cost-effective options and detailed details.
Keep your intimate life vibrant and spontaneous; acquire overnight buying cialis to enhance your experiences without delay.
Secure affordable treatments for your health needs with https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ .
Purchase the most cost-effective antidepressants; find [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – sublingual amitriptyline no prescription[/URL – for managing your emotional well-being safely and efficiently.
Certainly, obtaining Etizolam-based medications has never been simpler. For those seeking relief, nolvadex without prescription offers a streamlined, secure, and diverse payment method spectrum. With an easy transaction, buy your essential pharmacological treatment online.
Harness the power of traditional medicine by visiting https://nabba-us.com/product/prices-for-nizagara/ , where you can purchase this ancient remedy designed to enhance vitality.
Many are searching for effective solutions for erectile dysfunction, and [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – lowest price on generic cialis[/URL – offers a credible option.
Explore the leading options for enhancing your performance with low cost propranolol , on sale for reliable buying online.
Our newest guide on https://bakuchiropractic.com/product/generic-retin-a-from-india/ explains how to safely utilize this treatment for constipation.
Secure low-cost [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – options for controlling heavy bleeding episodes. Explore treatments that prioritize health and savings.
Hunt for thrilling amusement? Uncover the precio lasix 40 for an unforgettable experience.
You can locate cost-effective https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ for managing your nasal allergy symptoms on the web.
Discover how [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – can assist in managing your heart health. Experts recommend their employment for preventing heart issues.
Secure your supply of zithromax 250mg today! Purchase now and get your item quickly.
Discover the most recent https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ , a crucial detail for those looking to purchase this hormone therapy.
Get the prescription easily with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – , providing a wide selection for all your medical needs.
Quickly procure [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – buy lasix[/URL – , ensuring fast relief for your issue.
If you’re looking for an effective remedy to fight bacterial infections, consider best price amoxicillin . This drug is well-known for its potency against a broad range of bacteria.
Knowing your options for managing vertigo is crucial; explore https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ to discover how it can help you.
Zipping through your options for managing erectile dysfunction? Learn about a convenient solution by choosing to buy [URL=https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – .
Research indicates that [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil generic canada[/URL – fluctuate considerably, urging consumers to review alternatives before making a purchase.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern treatments, managing it has become easier. Consider cialis , a cost-effective and effective option for improving your well-being.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ , a top choice for tackling hair thinning. Acquire them today and begin your road to regrowth!
Just unearthed an amazing offer for those with asthma, the [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ – asthalin hfa inhaler[/URL – is now available.
Here’s how you can manage your mood swings effectively: [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ – zoloft to buy[/URL – are available for purchase. With a wide variety of options, you can order this crucial medication online.
Various individuals are navigating the process to acquire essential medications with ease. If you’re seeking to secure Losartan without a hassle, tadalafil overnight is your go-to resource.
Researching where to acquire Finasteride? https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ offers a trustworthy solution for your hair loss treatment needs.
Discover safe and convenient ways to obtain your medication. [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – rezeptfrei vidalista 40 mg[/URL – today for a trouble-free experience in managing your health needs.
Obtain [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/viagra-pills/ – viagra[/URL – for your allergic reactions relief. Securely acquire your remedy via the internet.
Get your Amoxicillin easily from amoxicillin , supplying prompt dispensation to satisfy your requirements.
Boost your fertility journey with https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ . Buy a essential drug online and begin your path towards family planning.
Obtain your [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – buy ranitidine no prescription[/URL – effortlessly by securing it through our digital platform.
For those seeking immediate relief, buy [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ – prednisone[/URL – . This analgesic can offer fast and effective relief from aches.
Obtaining retin-a without a prescription order has never been more simple, ensuring you get your treatment quickly.
Browse our website to locate the https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ .
Seeking an effective solution for boosting male vitality? Look no further! Find out about [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin without a prescription[/URL – , your go-to option for organic enhancement.
https://qwertyoop.com qwertyoop
Over time, I’ve used various iGaming sites lately, and I’m always shocked how many beginners sign up without verifying anything. In case you want a helpful review of bonuses, payout speed, and game selection, this review cleared things up for me: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s simple to read and points out what you should notice before you start playing. You should check it out if you prefer to play safely.
Keeping your health in check is essential; acquiring your medications shouldn’t be a hurdle. Uncover an easy way to buy necessary treatments. [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – cheap india generic vardenafil[/URL – today and oversee your wellness with simplicity.
Discover unparalleled savings with our exclusive offer: amoxicillin . Purchase your supply today and benefit from the effectiveness of this remedy.
When searching for urgent resolutions, find https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ for your requirements.
Find affordable options for [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/levitra/ – levitra buy online ireland[/URL – , ensuring you get premium treatment for your healthcare needs.
Managing constipation doesn’t have to be a challenge; explore the cost of effective relief. Discover the competitive [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 2.5mg[/URL – today and start your journey towards improved digestive health.
Seeking a solution for hair loss? Find out how to buy finasteride 5mg , a effective method to fight balding securely.
Nourish your bones and teeth with quality supplements; explore the best sources to acquire https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ for your daily health regimen.
Unlock exclusive savings on your health needs now! Visit our website to get your essentials at unbeatable prices with [URL=https://jawany.com/ventolin/ – ventolin online uk[/URL – .
Understanding the need for convenience, you can now obtain your treatment via the web with no hassle. [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – and enjoy swift dispatch to your doorstep.
You can acquire Fildena for your erectile dysfunction needs here: fildena.com .
Ready to find out the most affordable options for your antifungal needs? Your search ends here. Discover the https://wefenceit.com/canadian-pharmacy-pharmacy/ and secure your health today without breaking the bank.
To purchase your birth control effortlessly, ponder buying [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – propecia 1 price australia[/URL – . This method ensures confidentiality, convenience, and diversity of options.
Looking to treat your condition effectively? Explore how to buy [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ – priligy 90mg[/URL – and start your journey towards improved health today.
Research buy viagra online 75 mg lowest price for effective baldness solutions.
Save on your next purchase of https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ by exploring our wide selection. Find amazing discounts online today.
Considering the necessity for exact and timely treatment, acquiring [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy-com-lowest-price/ – priligy cost[/URL – online offers an easy answer.
Yes, if you’re looking to purchase [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – lasix buy online[/URL – , contemplate exploring our dependable resource.
The need for trustworthy solutions to improve men’s health has never been more vital. Discover the efficacy of cialis , a top choice for tackling such concerns.
X-plore your options for hypertension management by choosing to buy https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ .
Have you been searching for an effective solution to your nasal issues? Look no further than the [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ – buy legal fda approved cipro[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to buy the solution for your sinus problems, this spray offers a reliable option.
Quickly purchase your medication with ease by opting to [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – online chloroquine no prescription[/URL – , a streamlined way to manage your health.
When considering options for treating nizagara , many individuals seek affordable solutions. Investigate a variety of options to acquire your medication via web, ensuring budget-friendly and easy access to the remediation you need.
X-plore your options for alleviating eye discomfort with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ . Discover comfort for your eyes without requiring a prescription.
Please explore our site to purchase [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – walmart price for levitra[/URL – , accessible for persons in need of efficient cardiovascular support.
Discover trusted solutions for your gastrointestinal issues with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – nizagara no prescription[/URL – , a selection supported by healthcare professionals.
Discover solutions for lasting longer in bed with ventolin . Locate this essential item on the web to enhance your performance effortlessly.
Optimize your eye pressure management by purchasing https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ , an essential medication for individuals dealing with glaucoma.
Seek unparalleled performance and confidence in intimate moments; unveil your pathway to enhanced vigor with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ – propecia online canada[/URL – . Acquire your remedy instantly.
Looking to get your antiviral treatment? Now, you can order on line propranolol easily.
X-plore your options for well-being management with https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ , accessible to order via web.
Looking for affordable medication? Discover your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin 5mg[/URL – here and save on the prescription.
Considering the need for cost-effective stress treatments, torsemide offers a feasible option.
To treat thinning hair, look into https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ as an efficient option.
“Quickly acquire your treatment with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – lasix uk[/URL – , offering a handy solution for enhancing your wellness.”
Looking to boost your performance? Get authentic solutions [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/viagra-for-sale/]viagra[/URL] .
I realized the most competitive sell propecia order for improving male health online.
Obtain your health supplements at unmatched rates, visit https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ today! Explore a spectrum of options for your wellness regimen effortlessly.
Just uncovered your key to enhanced intimacy: [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/]online generic priligy[/URL] . Order now for prolonged results.
Having anxiety? Discover a range of treatments [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – buying trazodone in the dominican republic[/URL – . Purchase the treatment online.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with flomax 0.4mg , a treatment for easing prostate enlargement symptoms.
X-plore new avenues to achieve better well-being with https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ , a pivotal step in managing prostate cancer.
With an array of natural solutions for increasing vitality, click here to [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – lasix from canada[/URL – , offering a safe and effective way to improve your health.
Looking for an affordable way to manage your allergies? Learn about how you can save on your treatment with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – ordering generic lasix from india[/URL – .
Now, for those seeking a reliable solution to enhance their intimate experiences, purchasing the viagra 100mg becomes a necessity. Secure the notable selection via the web for a superior lifestyle change.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Search no more. Obtain https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ safely and quickly.
Here’s how you can manage your mood swings effectively: [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix generic 100 low price[/URL – are available for purchase. With a wide variety of options, you can buy your mood stabilizer on the web.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Acquire lowest amoxil price online safely and swiftly.
I understand that finding an authentic source to acquire your medication can be challenging. If you’re looking to https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ , explore your options carefully. Always make sure that you are dealing with an established vendor to protect your health.
Boost your vitality effortlessly; uncover the economical pricing of [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – .
Acquiring [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – has never been simpler. Acquire your medication without leaving your house.
Are you in search of cost-effective fertility solutions? Discover the most economical Clomid options clomid 100mg to initiate your journey towards starting a family.
I’ve found the most budget-friendly way to buy your medication. Check https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ now!
Given the fluctuating costs, finding the lowest price for medication can be a hassle. Whether you’re looking to control urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution.
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective tamsulosin ? Explore
Acquire https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ effortlessly. Obtain these vital medication online to ease your eye problems.
Discover alternative solutions to boost your well-being with [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis-black usa prices[/URL – , the go-to option for those seeking trusted and powerful aid in handling erectile dysfunction.
Maximize your health with the smart option of [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – , a choice that ensures you obtain superior cardiovascular support. Opting for this medicine online combines efficiency with effectiveness.
X-plore the endless entertainment options accessible with prednisone best price usa , your portal to unmatched betting experiences.
Purchasing https://wefenceit.com/pill/prednisone/ via the internet offers a simple way to handle your health concerns without the need for a prescription.
Seeking a safe, reliable method to acquire misoprostol? Look no further. [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – misoprostol[/URL – offers a hassle-free solution.
Having difficulty managing your cravings for alcohol? Consider [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – tadalista for sale[/URL – as an effective solution. This medication can potentially help in maintaining abstinence and aiding in recovery from alcohol dependence.
Searching for trusted solutions to reduce irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how tadalista can assist in easing your discomfort today.
Researching affordable options for HIV treatment? Compare and find the most cost-effective https://nabba-us.com/item/kamagra/ on this platform.
Manage your allergies effortlessly by choosing to [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – lisinopril[/URL – , a trusted treatment.
Zealously seeking a trusted source to buy your prescriptions from? Look no further; viagra offers a secure, discreet way to procure what you need.
Seeking effective skin infection treatment? Discover safe https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ options with ease on the web.
Yes, securing the [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – buy prednisone online[/URL – can be effortless when you look on the internet.
Get your amoxil easily from [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/generic-amoxil/ – buy amoxil online 24hr[/URL – , providing swift shipping to fulfill your healthcare needs.
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if cialis could be appropriate for you or your loved ones.
With various online platforms available, it’s never been easier to https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ . Whether you’re aiming to buy medication without hassle, our platform offers a seamless and secure purchasing process.
Get affordable solutions for enhancing your intimate moments; explore [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – for selections.
Access affordable [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – stablon without a doctors prescription[/URL – for managing thyroid disorders without compromising on quality.
Consider purchasing your drugs easily from lasix for sale , providing an extensive range of medical options.
Before making a decision, discover https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ and compare prices to guarantee you get the most favorable deal for your heart health medication.
Get the most effective deals on [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – strattera 18mg[/URL – for managing your health needs.
Zealously seeking proven solutions for ED? Find your options and order [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – viagra canada no prescription[/URL – , the go-to remedy.
Zap high prices with our exclusive amoxicillin 500mg , and Snag your bottle of crucial antibiotics effortlessly online.
Discover high-quality https://purefmonline.com/pill/retin-a/ , perfect for controlling seizures. Buy today for effective results.
Keep your well-being in check with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/nizagara-100mg/ – nizagara[/URL – , your solution to controlling inflammation.
Need to enhance your cognitive functions? Acquire [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax without an rx[/URL – online for a safe and potent solution.
Quickly learn about the most cost-effective levitra 20mg on the web.
Zero worries about where to acquire your ED solutions; explore https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ for a safe and private way to regain intimacy.
Venture into enhancing your health effortlessly; discover [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – propranolol 20 prix en pharmacie belgique[/URL – for your wellness needs. Get this solution easily and embrace a healthier lifestyle today.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for purchase with no wait at [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topamax 25mg[/URL – .
Now, explore a variety of ways to improve your health. Consider trying cialis for a natural solution.
Having trouble finding cost-effective options for fertility treatments? Explore https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ , where you can find competitive rates for your needs.
Zero in on health improvements; purchase the [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ – pillules lasipen[/URL – treatment conveniently for enhanced wellness.
In need of efficient HIV treatment? You can purchase [URL=https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ – sildalis[/URL – online for a reliable and convenient way to manage your health.
Boost your vitality with achat herbal-max-gun-power generique , available for purchase via the web.
Jumpstart your treatment journey by https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ , a top-choice medication for treating HIV efficiently.
Quickly secure your medicine with zero hassle. Click here for [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – .
The advantages of incorporating non prescription retin a into your health regimen are numerous, including improving stress management, promoting restful sleep, and bolstering general health.
Explore the pharmacy world for osteoarthritis solutions and find the https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ . Procure your medication online for optimal joint health.
Before you choose to acquire your medication, consider consulting [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ – buying pharmacy online[/URL – for a secure and informed choice.
Looking for a reliable source to purchase your pharmaceuticals without leaving home? Visit [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – prednisone 20 online for sale[/URL – to order your pharmacy needs through the internet with ease.
Breathe easier with our quick-relief treatment. Buy your asthalin without a doctor today for reliable asthma management.
Researching trusted sources to buy medication? Explore options and discover how to buy https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ securely.
A myriad of options await those seeking cardiac care. From purchasing [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – buy cheap staxyn[/URL – to investigating the latest therapies, managing your heart’s health has never been more straightforward.
When looking to acquire cytotec for sale overnight , consider numerous sources supplying it on the web.
Have you been searching for an effective solution to your nasal issues? Look no further than the https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ . Whether you’re looking to purchase the treatment for your nasal congestion, this spray offers a high-quality option.
For those looking to purchase their heart health medication on the internet, finding a dependable source is key. [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ – canada drug pharmacy dapoxetine[/URL – offers a trusted option for ordering your treatment with ease.
Seek solutions for hair loss now! Learn about how sildalist for sale can aid in your journey against hair loss.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, buying https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ on the web offers a budget-friendly option.
The Buy this pill on site [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – cheap retin a pills[/URL – ensures your health needs are met with convenience and efficiency.
Purchasing [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – discount chloroquine[/URL – has never been easier. With options to secure them online, fighting against certain viral infections is now more accessible.
X-pand your health options without leaving home; acquire your medications with ease. viagra without a doctor today and manage your health effectively.
Unlock enhanced focus and vigour with https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ , your go-to answer for staying alert.
Obtain your prescription easily through [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/amoxicillin-500mg/ – amoxicillin[/URL – , a reliable option for handling your symptoms.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/buy-cialis-w-not-prescription/ – order cialis business advertising[/URL – – your go-to solution for restoring health.
Looking for a way to tackle your condition? hydroxychloroquine lowest price might be the solution you’re seeking. Discover how this drug can assist you today.
Venture online to find the least expensive options for your health needs, including https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ .
A comprehensive guide to treating Hepatitis C, detailing how [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/ – buy levitra uk[/URL – offers a potent solution that targets the virus effectively.
Questioning where to find joint relief? Consider lowest price on generic malegra for proven support in addressing your joint discomfort.
Keep your health in optimal condition by visiting https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/ to purchase your prescriptions.
Unlock unparalleled savings on your medication management by visiting [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/prednisone/ – prednisone best price usa[/URL – . Score the best deal now and ensure your health stays our top priority.
I understand the importance of medication accessibility, thus highlighting the convenience of opting for mail order methods. In this context, [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – offers a seamless way to obtain your necessary medication without the hassle of visiting a pharmacy.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by checking out our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Discover tadalafil to enhance your vitality efficiently and safely.
Procure cost-effective solutions for gastrointestinal relief; uncover https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ for managing symptoms effectively.
Combat swelling with ease: Acquire your drug swiftly and safely by opting to [URL=https://wefenceit.com/lasix-40mg/ – discount lasix[/URL – . This route ensures convenience and confidentiality.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your amoxil generic 500 mg canadian pharmacy online for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
I stumbled upon an incredible deal for natural health enthusiasts seeking to boost their well-being. Don’t miss this opportunity to get your https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ today and start embracing a more energetic lifestyle!
Discover affordable options for managing addiction; [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – priligy capsules[/URL – offers a pathway to recovery. Explore budget-friendly solutions for addressing dependency.
Need a convenient and discreet way to purchase your medication? [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone without dr prescription usa[/URL – could be the answer you’re looking for.
Explore cost-effective solutions for your health with prednisone . Discover unparalleled deals to enhance your wellness journey today.
Optimize your health and wellbeing by exploring options to https://wefenceit.com/ventolin/ . Obtain
DeepValleyFinds – Nice mix of reasonably priced items, and the listings look genuine and clear.
Combat baldness effectively! Uncover how [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – can assist you in restoring your locks to their previous glory.
Get the medication for inflammatory bowel disease without leaving home. Purchase nizagara 100mg today.
Purchase your https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ through our platform to ensure you obtain quality treatment with convenience.
Discover excellent choices for managing your condition efficiently with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/tadalafil-best-price/ – tadalafil[/URL – . Boost your lifestyle today.
A comprehensive guide on how to obtain reliable cancer therapy, including imperative information on prednisone steroid , to combat myeloma and ovarian cancer efficiently.
Many are looking for effective options for erectile dysfunction, and https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ offers a credible option.
Seeking an effective treatment for improving male vitality? Look no further! Explore [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/lasix/ – mg lasix[/URL – , your go-to option for organic enhancement.
Keeping your health top-notch is essential. Find competitive [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ – levitra n0 prprsscription[/URL – in our digital pharmacy and start your journey to improved well-being today.
Purchase your necessary antiviral conveniently through buy deetor online cheap , a method guaranteeing fast delivery and confidentiality.
For individuals seeking to purchase hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous online sources offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to make sure safety and authenticity. https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ offers a comprehensive guide on how to safely buy this medication, alongside vital details on its application.
Check current [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – 25mg mil zoloft[/URL – for managing your HIV condition.
Quickly find top offers on [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – flomax par internet[/URL – on the web.
Managing pain efficiently and safely is crucial for overall health. Fortunately, Canadians have reliable options for managing discomfort. amoxicillin offers a versatile solution, allowing you to acquire effective pain relief securely and swiftly.
Need to spend less on your medication expenses? Discover the https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-without-a-doctor/ for competitive costs on medications.
Acquire your [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady-era usa rx[/URL – today and benefit from the cost-reductions on drugs designed to boost male wellness.
Looking to improve your vitality? Discover amazing savings with our [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – cost of prednisone tablets[/URL – .
Keeping your health optimal is essential. Unearth competitive cheap retin a on the web and start your journey to improved well-being today.
Unlock exceptional savings when you obtain your pharmacy essentials through our web portal. Explore the benefits and convenience of choosing https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ for your needs.
I locate the best options for cholesterol management with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – nizagara brand[/URL – .
Aordable solutions for dry eyes are now within reach. Explore our selection and buy your treatment for soothing relief. Find buy nizagara fast delivery online today.
Discover reliable joint pain relief with https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ , the top-rated treatment accessible online.
You can find effective solutions for hair loss without breaking the bank. Explore the [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix for sale[/URL – for affordable options.
Explore ordering [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/lasix/ – buying lasix[/URL – with ease for reliable remedy.
Boost your well-being with prednisone 20mg , a top-tier option for those seeking improved performance.
Various patients seeking affordable medication for HIV/AIDS are turning to https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ as their preferred alternative, recognizing its effectiveness and cost-efficiency.
Keep informed on this anti-malarial medication benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine online paypal option[/URL – for comprehensive insights and updates.
Need to find authentic Canadian pharmacy alternatives? Your hunt ends here at [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline online uk[/URL – , providing entry to accredited medications.
Seeking the best rates for your medication? low price slimex offers unparalleled deals.
Secure the essential hypertension medication by opting to https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ , ensuring you maintain optimal health effortlessly.
Unlock potential savings on eye care medication by exploring your options. Find an affordable solution at [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – . Acquire your prescription easily, ensuring savings and safety.
Very often, individuals seek cost-effective solutions for their medical needs. Discovering a reliable platform to obtain essential medications can significantly reduce expenses and ensure consistent quality. For those looking to secure their pharmaceuticals conveniently, opting to [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine online usa[/URL – can be a remarkably prudent choice, offering both affordability and the assurance of receiving genuine products.
Receive the best deals on canada stromectol by browsing our site.
Considering the risks involved, it’s crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional before deciding to buy https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil-5mg/ .
Zero hassle to safely acquire your medications on the internet. Click here: [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ – viagra[/URL – for your well-being needs.
Just discovered that you can now purchase [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – , delivering simplicity and privacy.
The Order this pill online levitra ensures your health needs are met with convenience and efficiency.
With an array of organic solutions for increasing vitality, click here to https://myrsvplive.com/levitra-10mg/ , offering a safe and potent way to support your health.
Venture into new health realms by exploring the efficacy and potential of [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ – propecia[/URL – . Uncover a revolutionary solution for medical concerns, exclusively available for order via our website.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ – nizagara[/URL – today. Whether you’re looking to enhance your wellness effortlessly, our site offers a straightforward pathway to acquire your essentials.
Acquire your best health solution at an unbeatable price; explore priligy 90mg for premium health outcomes.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to reduce expenses on pharmaceuticals.
If you’re looking to acquire hypertension medication at an affordable rate, consider visiting [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ – costo de priligy[/URL – for great deals.
Looking to increase your vigor? Find kamagra online to acquire your solution with simplicity.
Maximize your vigour naturally with https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ , an unparalleled option for those seeking to improve their stamina without the need for doctor’s orders.
Uncover the cost of treating nasal symptoms with [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – cialis black information[/URL – , your solution for relief.
Searching for effective solutions to alleviate irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – generic bentyl from canada[/URL – can assist in soothing your discomfort today.
Various individuals seeking cholesterol-lowering solutions have turned to lowest price for nizagara . With a plethora of options available, opting for
Procure your https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/doxycycline/ effortlessly. Purchase the special composition through the web, ensuring peak satisfaction and convenience.
Vexed by persistent anxiety? [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/lowest-price-for-nizagara/ – where to buy nizagara[/URL – offers a solution to soothe your nerves.
Secure your [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/pill/celebrex/ – celebrex[/URL – with ease. Procure this medication online efficiently.
The need to buy medication virtually has increased, and with options like trazodone , getting your medication is simpler than ever.
Having trouble with gastric ulcers? Find affordable relief with https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ , your preferred solution for soothing stomach ulcers.
Variety of selections to get your essential pharmaceuticals is vital. For those seeking [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – retin a no prescription[/URL – , various solutions are accessible, ensuring you obtain the utmost therapy.
To discover affordable choices for your prescriptions, visit [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – where to buy nolvadex online[/URL – to explore cost-effective choices.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxicillin price walmart , offering wide-ranging treatment for bacterial infections.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ might be what you need. Find out about how it could aid in alleviating your symptoms promptly.
Protect yourself and your loved ones; purchase your [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ – molnupiravir price walmart[/URL – conveniently to ensure health security.
Secure the stock of hormonal treatments today at buy propecia pills no prescription .
Discover how to effortlessly purchase https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ through the internet, ensuring you get genuine medication for your health needs.
With the recent quest for budget-friendly malaria treatment options, securing [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/generic-priligy-at-walmart/ – priligy 90 original[/URL – has never been more important.
Discover excellent choices for managing your ailment efficiently with price of cialis . Boost your well-being today.
Facing hair loss? Discover remedies now with https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ . Secure your solution on the web.
Access the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ – retin a[/URL – and save on your medication costs. Find the lowest price for your health needs without compromising effectiveness.
Seeking top deals for [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ – nexium[/URL – ? Find unmatched offers and quality now!
Discover how you can get your lowest price generic vidalista without hassle and begin a fresh chapter in your wellness.
Discover affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction by visiting https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ , where you can buy your drugs effortlessly.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – flomax tablets[/URL – might be the remedy. Find out about how it can assist in lessening your symptoms effectively.
Unlock significant savings and convenience when you acquire your health solution virtually. Experience the ease of securing quality healthcare products without leaving your home. Click here [URL=https://kileensgardenboutique.com/kamagra/ – kamagra without prescription usa[/URL – to begin your journey towards better health.
For those with allergies, finding affordable relief is key. Discover how venta de propranolol orlando can aid with managing your allergic reactions, providing both quality and value.
Obtain discounts on your medication with exclusive https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ available online.
Here’s how to purchase your prescription effortlessly: [URL=https://goldenedit.com/item/ventolin/ – ventolin 100mcg[/URL – .
Explore the options and obtain the treatment without leaving your home at [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – .
X-Plore choices for migraine relief with lasix.com . Find how to successfully control your symptoms on the web.
Discover how https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ can reduce symptoms of BPH by checking our site.
Obtain your [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara brand[/URL – prescription effortlessly through our website, ensuring prompt and trustworthy service for your pharmaceutical needs.
Many patients seek efficient remedies for bacterial infections. Whether you’re fighting skin conditions, respiratory infections, or STIs, [URL=https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ – buy original doxycycline[/URL – provide solution.
Wondering how to get Allegra at competitive rates? Look no further than our trusted source kamagra , offering a wide selection of options for your requirements.
Relieve your nasal symptoms affordably by exploring https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ for alleviating nasal congestion.
Discover affordable solutions for gastric ulcers; [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – prednisone.com[/URL – offers effective therapy.
Xperience relief without the wait; explore [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – buy cheapest amoxil 500mg[/URL – for a seamless solution to boost your life today.
Zeroing in on your health, get your pharmacy buy effortlessly. This treatment addresses your needs, offering relief with just an order.
With the increase in demand for holistic health solutions, consider https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/ to enhance your vitality.
Need to obtain mountain sickness pills? Explore options and buy your solution effortlessly with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/pharmacy-prices-for-kamagra/ – purchase kamagra online[/URL – .
Obtain over-the-counter options for managing edema, including kamagra , online. Explore multiple options for effective remedy today.
When considering antiviral protection against COVID-19, https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ offers a reliable choice. Consider obtaining this treatment through digital platforms, ensuring safety during these times.
Just found a fantastic deal on cholesterol-lowering medication? Buy your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – today and begin your journey towards improved heart health!
Please consider employing [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia in usa[/URL – for your healthcare needs. They are a reliable option for various diseases.
Explore new ways to control your heart rhythm with xenical .
When seeking to enhance your vitality, consider https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ as a credible option.
Explore the advantages of controlling inflammatory responses with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – propranolol 20mg[/URL – . Discover how it helps in lowering signs promptly.
You can buy your [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – reliable site to buy vidalista online[/URL – on the internet, ensuring affordability and ease.
Here’s how your request could be realized, keeping within the constraints provided:
“Have you been searching for an affordable solution to manage your blood pressure? Discover cost-effective options on lowest price generic clonidine , a key medication for hypertension treatment. Don’t miss out on price cuts today!”
View the latest https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ , and discover cost-effective solutions for managing alcohol dependence.
Seeking to obtain hormonal balance medication? Locate your solution with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – retin a[/URL – , the best choice for improved well-being.
When seeking proven therapy for hepatitis B, consider [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ – buying amoxicillin[/URL – for your needs.
Before you decide, explore your options for tranquility with canada generic nizagara . With a multitude of choices available, choose your path to peace wisely.
Looking for affordable medication options? https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ offers an opportunity to save on your medications. Don’t miss out on this offer!
Manage your cardiac dysrhythmias effectively. Acquire safe and reliable medication. [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ – tadapox[/URL – from a reputable online pharmacy.
Purchase your drugs with confidence from a priligy , where quality and consumer happiness are of utmost importance.
Navigating through myriad treatments for hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), one efficient solution stands out. Place your trust in proven medication; https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ for managing your condition effectively.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ – doxycycline lowest price[/URL – to combat infections caused by bacteria. This budget-friendly solution is straightforward to acquire and can help in managing numerous of health issues.
Knowing the crucial nature of being knowledgeable about remedies, it’s vital to explore [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone[/URL – for detailed details.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your buy amoxil 500 from canada online for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Obtain your Flagyl treatment without delay through our rapid https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ delivery service, ensuring you get the care you require immediately.
For those in need of adrenal support, [URL=https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara on line[/URL – offers a economical solution.
You can discover [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ – non prescription tadalafil[/URL – on the internet, offering an affordable solution to your needs.
Looking for an effective way to combat alcohol dependence? Learn about how vardenafil 50mg india can be a key component in your journey towards sobriety.
Interested in controlling ADHD? Consider looking into https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ , an effective treatment.
Managing BPH symptoms can be easier with the right medication. Discover how [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – sarafem 20mg tablets australia[/URL – can aid in lowering symptoms safely and effectively. Whether you’re looking to purchase it from an online pharmacy, it’s important to consult a medical expert first.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-5mg/ – online generic cialis[/URL – . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to reduce expenses on pharmaceuticals.
Just discovered the best price for pain relief with furosemide , on sale.
Ready to grab your health essentials at an unbeatable cost? Look no further than our platform for the https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ , ensuring you receive premium medicinal supplies at a fraction of the cost.
Aseasonal allergies sufferers can find relief by acquiring [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/retin-a/ – generic retin a canada pharmacy[/URL – , a reliable remedy.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your condition efficiently with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-uk/ – cialis[/URL – . Boost your health now.
Just found a phenomenal source for wellness products at dapoxetine via american express card , suitable for boosting your fitness.
Zero worries about aging signs with https://ucnewark.com/prandial-md/ , as you secure a way to revitalized vibrance.
Just discovered you can buy crucial medication [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – vente vardenafil en france[/URL – , simplifying your healthcare upkeep.
Looking to acquire Depo-Medrol for your medical needs? Click on the link [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara shops[/URL – for a straightforward transaction.
With medication costs soaring, securing affordable options is crucial. Click here for kamagra 50mg and discover economical alternatives for managing your health.
Seek effective solutions for hair loss management with https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ . Acquire immediately for a smoother path to restoring your hair.
Uncover affordable alternatives for managing edema and hypertension with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomiphene[/URL – , ensuring you secure benefits without overextending your budget.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara online pharmacy[/URL – on the web presents a cost-effective option.
X-plore your options for well-being management with retin a buy in canada , attainable to order through internet.
Curious about enhancing your vitality? Discover https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ and explore a variety of ways it can enhance your vitality.
Seeking to comprehend global trends in cardiovascular health care, [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/viagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – provides a comprehensive analysis into consumption habits, this crucial medication.
Visit [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ – vidalista without a prescription[/URL – to acquire your medication with ease.
Looking for the most budget-friendly options to boost your confidence? Discover your solution florida retin-a today and start your journey to feeling your best.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern treatments, managing it has become easier. Consider https://nabba-us.com/item/cialis/ , a cost-effective and reliable option for enhancing your performance.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil 250mg[/URL – via the internet for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
Are you suffering from thinning hair? Explore the most effective solutions with [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ – generic prednisone lowest price[/URL – to restore your self-esteem.
Zapping away your health worries has never been easier! Now, you can order buy dapoxetine online legally from the comfort of your home. This medicine is a game-changer for those in need.
Quest for the ideal https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ ends here! Find the top choice for your needs.
Browsing for a budget-friendly solution to address anemia? Look no further! [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – vidalista coupon[/URL – offers a wide range of choices to match your needs.
Discover how purchase canadian pharmacy vidalista , a top choice for boosting your well-being.
Visit https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ to obtain your prescription easily.
Explore the convenience of securing your well-being with ease by choosing to [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – buy canada prednisone[/URL – . Purchase vital prescriptions through the internet effortlessly and affordably.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your personal health needs, buy cheap amoxicillin virtually can be a simple process.
Just when you require relief from persistent nasal symptoms, ordering https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ offers a hassle-free solution for managing your symptoms.
You can locate the [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/nizagara-commercial/ – nizagara[/URL – by looking through internet pharmacies.
You can buy your necessary medication [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/ticlid/ – ticlid[/URL – with convenience.
Seeking effective skin infection treatment? Find reliable doxycycline generic 200mg no rx options quickly on the web.
Looking to address your health concerns? Uncover a wide selection of drugs at https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ , your go-to source for reliable healthcare solutions.
Quickly acquire your antihistamine relief by choosing to purchase [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel commercial[/URL – .
Seeking heartburn relief? Explore [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – canadian nizagara[/URL – for a safe remedy.
Discover how to get lowest price on generic vidalista without compromising on quality.
Many individuals seek effective treatments for their tension. With numerous options available, it’s crucial to pick wisely. For those considering an effective treatment, https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ provide a potential option.
Keep your health in optimal condition with our exclusive [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/buy-propecia-uk/ – propecia[/URL – . Purchase immediately and enjoy the improvement in your health.
Visit [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – buy amoxil uk[/URL – to purchase your antibiotics on the internet at unbeatable prices.
A secure way to manage your health: cytotec . Explore us to find varied approaches for your wellbeing.
Explore trusted choices for enhancing your wellness with https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ , the go-to choice for improving vitality devoid of a prescription.
Consulting a medical expert is crucial before you acquire [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – no generic tadalafil[/URL – .
Discover affordable solutions for managing your mood and mental health. Explore our selection of [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – discount amitriptyline[/URL – to find the right option tailored to your needs.
Need to control your stroke risk? Explore options and purchase pharmacy , an effective choice for stroke prevention.
Living in an era where convenience is key, acquiring your medications without delay is vital. For those seeking https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ , options are now available online, offering a streamlined solution to meet your needs.
Discover unparalleled convenience and discretion in securing your cardiovascular health by opting to acquire Atorlip-20 via our web portal [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – buy kamagra online 100mg lowest price[/URL – .
Explore Canadian healthcare options and discover [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – . With a range of choices for your needs, locate the right solution on the internet.
Looking for a reliable source to get your prescriptions without leaving home? Visit buy deetor online cheap to order your medical needs online with ease.
Your search for an effective solution for premature ejaculation ends here. Acquire https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ , a well-established pharmaceutical, on the web.
You can find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/secnidazole/ – secnidazole[/URL – on internet platforms.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – might be the answer. Learn about how it can assist in alleviating your symptoms efficiently.
X-ray your health options with ease at mail order malegra , your premier destination for getting all your medical necessities.
Discover safe and private options to buy your prescription without hurdles. Click here: https://tv-in-pc.com/buy-cheap-viagra/ .
Considering the myriad options available, opting to purchase your therapy through reputable sources is paramount. For those looking into therapy for gastrointestinal issues, [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/online-generic-pharmacy/ – pharmacy pills beijing[/URL – stands out as a trusted choice among various pharmacies.
When seeking efficient antifungal treatment, consider trying [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis/ – cialis without an rx[/URL – for your medical needs.
Just uncovered an incredible way to improve your vitality over the counter priligy similar , excellent for those seeking reliable and potent solutions.
Maximize your health benefits by exploring the cost of https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ , renowned for its heart supportive properties. Buy your supply today to improve your heart health.
Got allergies? Looking for immediate respite? [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – no prescription nolvadex[/URL – online for reliable solution.
Zealously seeking proven solutions for ED? Explore your options and buy [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – , the go-to treatment.
Discover the ease of securing the medication with just a click. lasix offers a simple solution to order your prescription from the comfort of your home.
In search of https://tv-in-pc.com/tadalafil/ ? Look no further for budget-friendly solutions to your nasal symptoms.
Purchase affordable [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – for managing heart health. Explore options on websites for economical strategies.
Gain access to prednisone generika 10 hassle-free. Secure your treatment effortlessly for managing your health concerns.
Struggling with high cholesterol? Secure your health by opting to https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ . Obtain your prescription today and start your journey toward a healthier lifestyle.
Get your health solutions conveniently with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – canadian retin a[/URL – . Obtain your essential medication without hassle from home.
Seeking to save on your medication? Discover where you can find nizagara coupon for less.
Keep your stomach issues at bay with https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ , the ultimate remedy for IBS symptoms. Get your solution on the web now.
Rediscover control over your cardiac well-being with [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large without dr prescription[/URL – , the foremost source for purchasing your prescriptions on the internet.
Get your [URL=https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ – sildalis pills[/URL – securely on the web.
Maximize your vitality and youthfulness; seamlessly viagra-jelly cheapest online through our platform. Explore a healthier life by opting for this solution now.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your condition? No need to stress out! You can https://myrsvplive.com/cialis-from-canada/ simply and with confidence.
For users seeking reliable hair loss solutions, [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride/ – http://www.finasteride.com[/URL – offers vital data.
You can locate potent and reliable solutions for your health woes by visiting 100mg generic lasix online .
Browse our website for top-quality healthcare solutions. Buy your https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ online, ensuring reliable and fast delivery to your doorstep.
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial, and finding the right medication should not be a hassle. For those seeking flexibility and convenience in their treatment, [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – offers a discreet, effective option. Consider securing your medication online, ensuring you receive premium care without compromise.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/]cheap india generic doxycycline[/URL] to combat bacterial infections. This economical solution is simple to acquire and can help in managing numerous of medical conditions.
Browse our website to locate the overnight nizagara , offering you a economical solution to manage your inflammation.
Regain control of your health by choosing to https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ . With our service, you can acquire your essential therapy without hassle from the safety of your home.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/]generic amoxil 650mg pills[/URL] online can be a straightforward process.
Need to conserve on your cancer treatment? Consider exploring [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/prednisone-without-pres/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – for budget-friendly therapy options.
Just find solace for allergy symptoms by choosing to prednisone without pres .
Unlock exclusive savings on your health needs today! Visit our website to get your essentials at unbeatable prices with https://nabba-us.com/product/priligy/ .
Zap your anxiety and sleeplessness now! Find out more about how on [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix without prescription[/URL – .
спорт 1 кайт серфинг египет
X-plore the convenience of getting your medications with just a click. Now, you can buy [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ – cheapest modvigil next day delivery uk[/URL – , making your treatment acquisition easier.
Curious about securing the tadalafil ? Discover your options online.
I’ve discovered an amazing way to amplify your body’s capabilities. https://myrsvplive.com/propecia/ is your go-to solution for improving your well-being levels effectively.
Obtain your remedy for gastrointestinal issues at the [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/generic-prednisone-lowest-price/ – prednisone 20mg[/URL – .
Browse the site to locate [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – best price 1000mg generic amoxil on line[/URL – , ensuring you obtain top-quality antibiotic solutions at incomparable prices.
A Revolutionary Solution to Well-being is Here! Now, explore a broad assortment of healthcare options solely at cheap 10mg prednisone pills .
Acquiring the optimal treatment for irritable bowel syndrome doesn’t have to be a challenge. You can order https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ through our website to alleviate your symptoms effectively.
Aiming to enhance your eyelash length and density without stepping out? Now you can effortlessly obtain your beauty goals from the comfort of your home. Purchase your batch of the wonder solution with [URL=https://rrhail.org/item/xenical/ – xenical capsules for sale[/URL – . Elevate your look with ease!
Acquire your solution for enhanced vitality; explore [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – extra super avana[/URL – now!
Residents in Columbus, Ohio, seeking immediate financial aid can explore nizagara 100mg for reliable solutions.
Keep your arthritis symptoms at bay with proven treatment. Order https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ now for fast relief.
Quality healthcare doesn’t have to break the bank. Discover cost-effective epilepsy treatment solutions and save on your medication with [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – extra super avana uk[/URL – .
When seeking relief from glaucoma, consider the option to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . With a range of possibilities, you can acquire this medication online, conveniently and efficiently.
Find unbeatable deals on buy non prescription tadalafil online to boost your vitality.
Visit https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ today and locate budget-friendly alternatives for managing your pain.
Need to alleviate glaucoma symptoms without breaking the bank? Explore our wide range of affordable solutions, including the highly effective [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – ordering verapamil online legal[/URL – , suitable for budget-conscious patients seeking quality eye care options.
Looking to treat your condition? Order [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/levitra-capsules-for-sale/ – levitra online uk[/URL – today and start your journey to improved health.
Procure your medication at reduced rates; online vidalista offer a range of discounts.
Get the best deal on your medication by visiting https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ , where you can locate unbeatable prices for top-tier healthcare solutions.
Manage your symptoms effectively with [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – . Explore budget-friendly options to manage your condition via our website.
Just discovered a innovative formula for enhancing your energy: [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – canada amoxil prescription[/URL – . Discover about this organic alternative.
Navigating the vast world of medications, it’s crucial to locate a trustworthy source ventolin .
Curious about how to improve your stamina? Consider trying https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ , a reputable product designed to lift your well-being.
A thorough guide to controlling narcolepsy: Explore how [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – can substantially improve your daily functioning and quality of life.
Searching for an enhanced solution to improve your performance? Look no further! Purchase your [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/tadalafil-10mg/ – tadalafil in canada price[/URL – today and experience a revolutionary transformation in your life.
Regain your vitality and enhance your physical fitness levels with the help of best price tadalafil with prescription . Offering a solution for men seeking to balance their hormonal levels, this product is available for buying via the internet.
X-ray your budget and uncover how much you could save on ocular treatments by checking the https://endmedicaldebt.com/drug/vidalista/ .
Explore various options to purchase effective glaucoma treatment and discover how [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/retin-a-uk/ – retin a uk[/URL – can help in reducing eye pressure effectively.
Looking to control your menstrual cycle irregularities? Discover a trustworthy solution with vidalista . This treatment can be your ally in dealing with various gynecological conditions.
Zero in on the best health-related advice by consulting with an https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ , ensuring you receive top-notch guidance for your well-being.
When seeking a budget-friendly solution for your antimicrobial needs, think about tapping into the convenience of [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline uk[/URL – . This digital pharmacy offers a wide selection of non-brand medications that meet various health conditions efficiently.
Exploring affordable healthcare solutions is essential, especially when it comes to medication. tadalafil in the us offers a economical alternative for those seeking therapy without compromising on quality.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ . Whether you’re looking to acquire this treatment online, you’ll find that its efficacy in treating a wide range of infections makes it a prime choice.
Discover the current [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis brand[/URL – and explore options for purchasing this medication via the internet.
For quick alleviation from pain, consider [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ – cenforce commercial[/URL – for a potent solution.
Just in time for your treatment, get buy ticlid online for managing your health condition effortlessly through our portal.
Boost your wellness affordably with https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ , available for those seeking top-tier value.
Xplore your options for improving male potency: purchase [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – and enjoy a remarkable improvement.
Discover how [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy no prescription[/URL – can revolutionize the way you enjoy casino games.
Quest for affordable testosterone replacement therapy ends here! Discover the most-recent buy tadalafil no prescription to secure your remedy now.
Unlock incredible savings on your mental health management with a click; find the https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ here. Say farewell to the days of overpaying for antidepressants, and welcome the era of affordability and quality.
Achieve healthier, fuller lashes by choosing to [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/xenical/ – xenical buy online paypal[/URL – . Whether you desire to enhance your eyelash appearance for medical reasons, our selection provides a safe, effective solution.
Never overlook your need for a proficient rest solution. Discover the revolutionary [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – , a breakthrough in attaining an uninterrupted night’s rest.
Revitalize your intimate experiences with our exceptional offer: tadalista non generic . Rekindle the spark instantly and secure your answer through our website.
Get premium Human Growth Hormone supplements straight from https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ . Buy now for enhanced well-being.
Now, uncover the benefits of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ – prednisone[/URL – , and learn how it can assist in easing your discomfort.
Grappling with acne? Discover your solution without needing a doctor’s note. [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin on line pharmacy[/URL – offers a powerful solution accessible directly to you. Say goodbye to persistent blemishes today.
X-plore new ways to treat Alzheimer’s by choosing to order your no prescription prednisone now.
Discover the convenience and privacy of purchasing your ED treatment with https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ , available now.
Boost your potency with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – nexium without dr prescription usa[/URL – , a delectable solution. Enhance your performance by choosing this tasty option that guarantees quick effects.
Just discovered trazodone ? Now reap the benefits of fast service straight to your home.
Combat baldness effectively! Discover how https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ can help you in restoring your locks to their previous glory.
One often seeks financial relief through [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – , especially in moments of urgent needs.
Breathe easier with our rapid-action treatment. Order your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – asthalin[/URL – today for reliable asthma management.
Obtain your prescription for purchase retin a without a prescription with ease, ensuring you get genuine medication. Purchase safely and securely through our website.
To locate the most affordable deals for pain relief, click here: https://jawany.com/prednisone/ . Whether you need immediate alleviation, our website offers numerous options of options.
Looking to enhance your joint health? Discover [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – pharmacy prices for peni large[/URL – and enjoy a revitalized path to mobility.
You can purchase [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ – priligy 90mg[/URL – via the web, ensuring a safe and straightforward way to manage your health needs.
Find affordable solutions for antiviral therapy with buy acivir dt on line , your go-to source for treating outbreaks.
Find inexpensive solutions for antiviral therapy with https://umichicago.com/acivir-dt/ , your go-to source for treating outbreaks.
Find relief from high cholesterol with our herbal treatments. Get your health again with just one click: [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – .
Zap your fertility concerns away! Explore the potential of [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – tadalista overnight online pharmacy[/URL – and discover how it can help in increasing your chances of conception.
Harness the power of web-based drugstores to buy nizagara en china .
Considering a quick funding solution? Explore https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ for speedy financial help.
Considering the urgency to manage inflammatory bowel diseases, it’s essential to acquire effective medication. [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone[/URL – stands out as a dependable choice for those seeking alleviation from the symptoms of conditions such as ulcerative colitis.
Ensure optimal health with our trusted source for your pharmaceutical needs. Secure your quality drugs online from the comfort of your home. Check out [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy pills[/URL – for reliable and efficient service.
For those seeking to enhance their eyelash length, thickness, and darkness, purchasing cheapest lady era dosage price is a prime choice. Opt for it today and witness a remarkable transformation.
Discover the current https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/ and consider alternatives for acquiring this drug online.
Revitalize your hair growth! Obtain your effective remedy now, [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , and say goodbye to thinning hair forever.
Wondering where to get Allegra at competitive rates? Look no further than our trusted source lasix , offering a wide selection of variations for your needs.
Explore options to purchase essential medication. For reliable treatment, https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline/ now.
Vacationing in Canada and realized you left your important eye drops behind? Worry not! You can purchase your essential [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/propecia/ – propecia tablet price[/URL – remotely.
rankthread.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Protect your well-being by educating yourself on the most recent wellness advice and trends at our [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – generique du prednisone 10[/URL – webpage.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? doxycycline price at walmart to combat infections caused by bacteria. This budget-friendly solution is simple to obtain and can help in managing various of health issues.
Purchase with ease: Explore OTC solutions for improving your health with https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ .
Purchasing [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 1000mg[/URL – online offers an easy way to handle your needs without a prescription.
Regain confidence in the bedroom with the [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – lowest price on generic retin a[/URL – , your discreet solution to enhanced performance. Secure your purchase today for an enhanced experience.
Browse the site to find amoxil , ensuring you secure high-quality antibiotic solutions at incomparable prices.
Browse our site to locate https://wefenceit.com/pill/low-cost-amoxicillin/ , ensuring you secure top-quality antibiotic options at matchless prices.
Seeking heartburn relief? Consider [URL=https://wefenceit.com/priligy/ – dapoxetine[/URL – for a soothing treatment.
Cut costs on your medication purchases! Find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/zithromax/ – zithromax 250mg[/URL – . Order now and gain substantially on your medical expenses.
Unlock exceptional deals and discover the nolvadex 20mg by browsing on websites.
Manage your gout effectively with https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/viagra-jelly/ . Procure your prescription virtually for convenience.
Explore the diverse options to acquire your prescriptions [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/prednisone/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – with ease through our secure portal.
Just need a quick, convenient method to obtain sildenafil ? Explore easy options to improve your health today.
Zest for a healthier life often leads us to seek therapies that can enhance our well-being. For those managing hypertension or chest pain, https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ could be your route to improved health.
Patients seeking affordable solutions for their medication can find [URL=https://nabba-us.com/item/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – to uncover cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
Discover excellent options for managing your health issue efficiently with [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil without a doctors prescription[/URL – . Boost your well-being today.
Optimize your heart health regimen by exploring pharmacy , an essential option for those aiming to manage their stroke prevention strategy effectively. With a wide array of choices, acquiring this vital medication through the web has never been easier, ensuring that maintaining your cardiovascular well-being is both accessible and convenient.
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://jawany.com/amoxil/ , and Secure a course of essential antibiotics without hassle on the web.
Acquiring [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – best clomid 50mg prices[/URL – has never been simpler. Order the medication without leaving your house.
Discover Top Items – Plenty of quality choices, and navigating around feels intuitive.
Questioning where to source medicine without overpaying? Find the [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – cipro 750mg[/URL – and save on your medical bills.
Boost your growth potential naturally with lasix 100mg . Discover reliable and efficient ways to enhance your height devoid of the requirement for prescriptions.
Facing chronic pain or anxiety? Explore your relief safely with https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ , the trusted solution.
Obtaining [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – has never been easier. Now you can acquire the essential medicine from the comfort of your own home.
Get respite from aches through [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/propecia/ – tablet propecia[/URL – .
Obtain your health supplements at unmatched rates, visit kamagra 100mg today! Explore a spectrum of options for your wellness regimen effortlessly.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with https://wefenceit.com/amoxicillin/ , supplying comprehensive solution for bacterial infections.
rankmint.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Keeping your health in check is essential; securing your medications shouldn’t be a hurdle. Find a hassle-free way to obtain necessary treatments. [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ – buy propecia online business marketing[/URL – today and oversee your wellness with comfort.
Ensure optimal health with our trusted source for your pharmaceutical needs. Obtain your quality medications easily from the comfort of your home. Check out amoxicillin for reliable and efficient service.
Searching for an safe glaucoma treatment? Look no further! Acquire your https://kristinbwright.com/doxycycline-buy/ now for ultimate eye health.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ – buy generic isotretinoin[/URL – to obtain your prescription without hassle.
Your search for affordable, high-quality cognitive enhancers ends here; generic prednisone from india offers unparalleled value. Explore buying opportunities for enhancing your memory and concentration without breaking the bank.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by checking out our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Locate https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ to improve your vitality efficiently and securely.
Having wounds or burns? Ensure rapid healing with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ – overnight nizagara[/URL – . Find how to accelerate your recovery by visiting our website now.
Navigating the vast internet for authentic ayurvedic solutions? Your search ends here. Discover top-quality ayurvedic remedies at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/ – levitra[/URL – . Purchase with confidence for your natural wellness needs.
Restore your health and confidence with one click; cialis effortlessly via our website to address your needs free from hassle.
Obtain affordable https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ for managing your hypertension. Explore our website to buy your medication conveniently.
Invest in your health by choosing [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/meldonium/ – meldonium[/URL – for high-quality cholesterol management solutions. This medication is designed to lower your cholesterol levels safely.
rankzone.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
rankburst.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
clickorigin.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Before deciding, compare the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ – cialis price[/URL – , and evaluate costs from different pharmacies to ensure you’re getting the best deal for managing Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Understanding the importance of antiviral treatment in managing chronic hepatitis C can never be overstated. Opting to obtain generic fildena from canada through an e-pharmacy not only offers convenience but also ensures you’re securing your medication swiftly.
Seeking a remedy for hair loss? Find out how to buy https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ , a trusted method to fight balding securely.
Seek budget-friendly options for boosting your vitality? [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia in usa[/URL – offers a potent mixture for those aiming to revitalize energy safely.
Understanding the importance of accessing medications safely, one might look for ways to get [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – nexium[/URL – . However, always make sure it’s from a trusted provider to avoid potential health risks.
X-ray your options for managing arthritis pain by exploring safe, effective treatments. Consider buy viagra soft tabs online to alleviate discomfort. Always check with a healthcare professional before starting any new therapy.
Discover more about effective birth control options at https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ .
Regarding Alzheimer’s disease treatments, exploring options for medication is crucial. For those considering Donepezil, [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/sildenafil/ – canadian viagra[/URL – offers multiple choices.
Ensure you acquire your [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/]australia online nizagara[/URL] from a reputable dealer.
Having realized an improvement in their performance, many are turning towards cytotec for a dependable solution.
Managing chronic pain requires effective treatment strategies. Discover how https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ offers a remedy that could assist in alleviating discomfort.
Looking for affordable menstrual cycle support? Discover your option with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/]propecia comprar generico[/URL] . Whether you’re addressing premenstrual syndrome, discover an affordable alternative online.
X-ray your options for managing arthritis pain by exploring safe, effective treatments. Consider [URL=https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ – celebrex[/URL – to minimize discomfort. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new therapy.
Discover affordable solutions for your medication needs; explore our wide range of options and compare buy cheap viagra to ensure you’re getting the best value for your health.
Gain unparalleled access to https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ by exploring our exhaustive directory.
When looking to save on your prescription, consider using an [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ – levitra gel[/URL – . Find out how to cut down on your pharmacy bills today.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – amoxil 500mg[/URL – on the web for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Interested in enhancing your eye appearance or addressing glaucoma concerns? Explore our range of options, including nizagara 100 france , suitable for various needs. Opt for securing your solution on our platform easily and conveniently.
Zap your low testosterone levels into oblivion with https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ . Elevate your vitality by uncovering a solution that rejuvenates male health effectively.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Locate [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis safest place to purchase[/URL – to boost your vitality efficiently and securely.
Explore the top options for enhancing your performance with [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax buy online[/URL – , on sale for secure purchase online.
Managing constipation doesn’t have to be a challenge; explore the price of effective relief. Discover the affordable zithromax generic pills today and begin your journey towards improved digestive health.
I understand the need for convenient choices when looking to get medication. For those considering managing their health concerns efficiently, exploring https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ offers a vital solution.
Offering an effective solution for pain relief, our [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – propecia without a doctors prescription[/URL – comes highly recommended. Suitable for a variety of discomforts, it is an optimal choice for those seeking relief from conditions such as arthritis.
Looking for doxycycline? Secure your supply without a doctor’s prescription through this [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – can i order doxycycline online in australia[/URL – . Acquire your dose with ease and start treatment right away.
Various medical professionals recommend seeking advice on cheapest kamagra for gastrointestinal discomfort to ensure safe and effective relief.
Discover safe solutions for men’s health issues with https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ . Obtain your solution effortlessly.
Patients seeking affordable solutions for their medication can explore [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/frumil/ – frumil[/URL – to discover cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
Boost your eye health easily; simply [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/prednisone-20mg/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – online. Achieve optimal ocular pressure relief with a click.
Having trouble finding affordable treatment options? Look no further for flomax . Get your essential prescription without overspending.
Purchase the essential eye care treatment at https://swanpercussion.com/item/pharmacy-prices-for-kamagra/ , offering affordable rates for your healthcare needs.
People seeking hypertension control treatments can consider a selection of pharmaceuticals, including [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine no prescription[/URL – for optimal management.
Explore budget-friendly solutions for your health needs with [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix-for-sale/ – lasix for sale[/URL – . Buy the therapy without hassle today.
Managing constipation doesn’t have to be a challenge; explore the price of effective relief. Discover the affordable zithromax generic today and start your journey towards improved digestive health.
Questioning where to spot affordable https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ ? Look no further! Get your prescription easily from reputable pharmaceutical websites.
Xperience enhanced comfort and convenience when you purchase your medication via our online platform. Find out more about obtaining your [URL=https://nabba-us.com/product/pharmacy/ – buy pharmacy online[/URL – .
Procure the most economical solutions for hair care; uncover your perfect match at [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax lowest price[/URL – .
Find the lowest cost for your heart medication at flomax 0.4mg , ensuring supreme cardiovascular health.
Get the best deals on manufacturer’s Duprost by clicking https://wefenceit.com/viagra-without-dr-prescription-usa/ . This medication is essential for managing BPH symptoms.
To get your supply of crucial medication, simply click here [URL=https://myrsvplive.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline online uk[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to acquire for immediate use or to stock up, we’ve got you covered.
If you’re seeking a reliable cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/retin-a-from-india/ – retin a en ligne[/URL – , obtainable for buying right here.
Certainly, acquiring your hormonal supplements is crucial, and finding a reliable source is paramount. For those looking to order their testosterone boosters, nizagara price offers a wide selection. This ensures you receive your medications promptly, maintaining your health regime without interruption.
Managing hair loss effectively can now be done from the convenience of your home. Secure a hair loss solution through https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ , ensuring you obtain effective care swiftly.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – hydroxychloroquine online no script[/URL – from a reputable vendor is crucial for consumers.
Need to obtain your medication hassle-free? Order your kamagra.com lowest price sans any Rx.
Visit our site to purchase your prescription, including https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ , from the comfort of your home. This digital platform ensures an easy way to obtain your essential pharmaceuticals.
Zipping through the myriad options for purchasing your medications, [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara buy[/URL – stands out as a prime choice to procure your health necessities.
Just discovered you can purchase your stomach cramps meds via the internet? [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – generic priligy[/URL – offers a selection of options for your treatment needs.
Purchase your essential pharmaceuticals conveniently with tadalafil , offering a seamless and secure purchase process on the web.
If you’re looking to alleviate your ache, consider the option to https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ . This remedy offers an efficient solution for handling inflammation and pain.
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – purchase flomax[/URL – can aid in easing urinary symptoms related to an enlarged prostate.
Conquer endometriosis effortlessly with affordable solutions. Obtain your relief today at retin a non generic .
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to reduce expenses on your medication.
Keeping your vitality at its peak has never been easier. Explore a variety of solutions with our [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ – best price flomax[/URL – , offering a prompt enhancement in your vitality.
Looking for cost-effective options for your osteoporosis treatment? Find the pharmacy without pres now.
Consulting an doctor is crucial before you acquire https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ .
I understand the need for accessible choices when looking to get medication. For those considering managing their health issues efficiently, considering [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – offers a vital resource.
To ensure your vision health, considering [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – stromectol for sale[/URL – might be advantageous. Buy conveniently on the web.
Get unparalleled savings when you acquire your prescriptions through our secure portal. Now is the perfect time to propranolol 40mg safely and efficiently.
Seeking a dependable source for purchasing your hair loss treatment? https://ucnewark.com/prandial-md/ offers a broad assortment of options for combating hair thinning.
Find effective remedies for enhancing your sexual health with confidence at [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ – viagra[/URL – .
Get the best deals on manufacturer’s Duprost today by clicking propranolol walmart price . This medication is vital for controlling BPH symptoms.
Explore the myriad advantages of incorporating https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/pill/nizagara/ into your routine. Known for its stress-relieving properties, this supplement is a necessity for boosting overall well-being.
To find the most economical [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis-20mg/ – purchase cialis usa[/URL – , contemplate searching on multiple e-pharmacies.
Understanding the need for ease, you can now purchase your treatment via the web with ease. [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ – fildena 150mg dubai[/URL – and benefit from swift shipment to your doorstep.
Queue up to secure your cardiovascular support needs through generic zithromax uk , your go-to option for reliable medications.
Learn additional info about how https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ can aid in the rehabilitation from alcohol addiction.
Quickly get [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra price walmart[/URL – to treat your vision problems, accessible on the web.
Boost your well-being and elevate your energy effortlessly. Discover how at [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra without pres[/URL – .
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing dapoxetine sevilla today. Whether you’re looking to boost your wellness effortlessly, our online platform offers a straightforward pathway to get your essentials.
Searching for affordable ulcer treatment options? Discover the best deals on https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ , your go-to option for easing gastrointestinal discomfort.
Get your Amoxicillin easily from [URL=https://wefenceit.com/pill/amoxicillin/ – cheapest amoxicillin dosage price[/URL – , supplying quick dispensation to fulfill your healthcare needs.
Acquire buy erectafil from safeway on the web for potent impotence relief.
Now, acquire your https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ easily by opting to order through our website.
When searching for cost-effective solutions to manage hypertension, finding the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone in beijing[/URL – becomes essential. Explore our portal where you can obtain affordable medications conveniently.
Now, discover your path towards lower cholesterol with kamagra 100mg , available for purchase online.
Zeroing in on your health needs? https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ offers a multitude of treatment options for controlling your condition. Explore our website to buy your medication without hassle.
Get your desiredgrowth with thisproduct. [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol generic available us[/URL – now for boosted results.
crestartlane – Clean interface with well-arranged items, shopping was effortless.
When considering bone density improvement, looking into [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a from india[/URL – is essential. This treatment gives patients a path to improve their bones effectively.
When seeking relief from pain and inflammation, consider exploring kamagra online pharmacy options to buy efficient medication on the internet.
Just in search of prolonged intimacy? Check out solutions with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ , an ideal choice for increasing endurance.
Browsing for a solution to your hair loss worries? Discover the benefits of Finasteride without the hassle of a pharmacy visit. Obtain your supply of [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – lowest price sildalis[/URL – , and embrace a future with fuller, healthier hair. This simple option brings the treatment right to your doorstep.
You can locate efficient alleviation for gastrointestinal discomfort with buy tadalafil uk , on offer online.
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective https://yourdirectpt.com/cafergot/ ? Explore
X-ray your options and choose wisely where to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – cost of prednisone tablets[/URL – . With myriad choices available, opt for the most reliable platform to procure your treatment.
Join our community to procure your [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – prise du chloroquine[/URL – and explore numerous options for reproductive health products.
For those looking to improve their hair growth, consider exploring cheapest 5mg prednisone delivered overnight as your preferred solution.
Quest for the ideal https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/fildena/ ends here! Find the ultimate solution for your needs.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by checking out our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Discover [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ – tadalafil[/URL – to enhance your vitality efficiently and confidently.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by checking out our all-encompassing selection of affordable treatment options. Locate [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis-20mg/ – best cialis prices 5mg[/URL – to enhance your vitality efficiently and safely.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive cialis brand . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to save on pharmaceuticals.
Get the top-quality seizure control options shipped right to your doorstep with https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ .
Zealously seeking reliable solutions for ED? Find your options and acquire [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – , the trusted treatment.
Minimize your sea-sickness and motion discomfort by opting to doxycycline pills . Secure a remedy now and enjoy calm travels.
Get relief from discomfort with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ . Acquire yours immediately to experience effective pain management.
Finding reliable sources for cardiovascular medication can be challenging, but our comprehensive guide on [URL=https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ – kamagra[/URL – simplifies the process. Delve into where to acquire these crucial pills online to support your heart health efficiently.
Researching the best options for Ayurvedic solutions? Discover [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – for effectiveness and savings.
Relieve your sinus congestion effortlessly with a cytotec online canada . This readily available solution offers quick relief for allergic reaction sufferers.
For those seeking to buy https://wefenceit.com/pill/lasix-for-sale/ without breaking the bank, various web-based drugstores offer economical costs.
To mitigate persistent coughing, consider using [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – best online pharmacy for celebrex[/URL – , a reliable treatment.
Our need for dependable memory care solutions is growing. Explore your alternatives and consider the possibilities by opting to [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , a top-rated choice for those seeking improved cognitive function.
Ready to secure your health essentials at an unbeatable cost? Look no further than our site for the generic hydroxychloroquine american express , ensuring you get premium medicinal supplies without a hefty price tag.
For those seeking pain relief from osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, https://ucnewark.com/product/sildalist/ offers an effective solution. Explore alternative options for managing your condition through buying this pharmacy product from the comfort of your home.
Considering the requirement for thyroid hormone replacement therapy, it’s essential to locate a reliable source for your medication. With our platform, you can easily [URL=https://driverstestingmi.com/item/generic-prednisone-uk/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – required, ensuring your health remains paramount.
Zestfully boost your conception chances with safe treatments. Learn about options at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ – http://www.prednisone.com[/URL – .
Just spotted a fantastic deal! For those seeking a remedy for heart issues, now’s your chance to cut costs on your treatment. Discover substantial discounts on your next purchase by clicking here: cialis . Don’t miss out on this opportunity to enhance your wellness affordably.
With our https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ , you can improve your eyelash volume affordably.
Your search for affordable heart medication ends here! Discover incredible savings on your essential medication with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ – priligy tablets[/URL – . Reduce your expenses without compromising on healthcare.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Look into [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ – buy cialis on line[/URL – , a economical and reliable option for boosting your well-being.
Visit amoxicillin to acquire your medication online at fantastic prices.
Relieve your sinus discomfort effortlessly with a https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ . This over-the-counter solution offers quick relief for allergic reaction sufferers.
Secure your supply of Dutas-T easily; buy it from our trusted [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – with ease.
Patients seeking [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/product/vpxl/ – generic vpxl from india[/URL – can discover it conveniently for their treatment.
Browse our platform to discover the prednisone , ensuring you get the best value on your healthcare needs.
Ordering your medication has never been easier, visit https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ and discover how you can obtain your medicine quickly.
Hunting for an affordable solution to boost your fertility? Look no further! [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – price for prednisone 10[/URL – is your go-to option. Whether you’re aiming to purchase this vital hormone, our platform offers the best deals. Perfect for those undergoing fertility treatments or in need of hormone therapy, our product promises efficacy.
Visit our website to order your [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ – web store for tadalista[/URL – easily and swiftly.
Discover the latest prednisone 20mg , a crucial aspect for those aiming to buy this testosterone gel.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover special https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ for savings on essential treatments. Secure yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
Your search for cost-effective birth control solutions ends here; explore our wide-ranging selection of [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil capsules for sale[/URL – online.
Discover affordable options for erectile dysfunction by visiting [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – cialis without dr prescription usa[/URL – , where you can acquire your drugs easily.
X-ray your options for wellness supplements and explore how to improve your health. Purchase your tretinoin via the internet for cost-effective, convenient access.
The need to purchase Atorlip-20, a cholesterol-lowering drug, without leaving your home is now more convenient than ever with the option to https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ .
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin 5mg[/URL – might be your solution. Discover how it could aid in reducing your symptoms promptly.
Venture into new health realms by exploring the efficacy and potential of ticlid canada . Uncover a groundbreaking treatment for medical concerns, exclusively available for order via our website.
Looking for a reliable solution to boost your fertility? Discover how the https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/secnidazole/ can assist. Explore alternative options such as purchasing this fertility aid from reputable suppliers.
Explore affordable options for [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – compare generic propecia price[/URL – and conserve on your medication costs today.
Breathe easier with our rapid-action treatment. Order your asthalin lowest price now for reliable asthma management.
When searching for immediate options, locate https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ for your needs.
Zero hassle to obtain your treatment: [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ – purchase pharmacy[/URL – – order via the internet with complete confidence.
Looking for an antibiotic medication? Secure your supply without needing to visit the doctor through this [URL=https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ – lowest price on generic doxycycline[/URL – . Acquire your dose promptly and start treatment immediately.
Visit our website to secure your cost of propecia tablets now, ensuring you regulate your health efficiently.
Nabbing your essential medical supplies has never been simpler. Acquire generic https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ via the internet to ensure your health needs are met with quality and affordability.
Understanding the urgent need for medication, it’s now possible to obtain your drug hassle-free. No longer do you have to delay for your critical treatment. Click here at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – asthalin[/URL – to receive your medications quickly and effectively.
Secure your antiviral medication effortlessly through our site when you obtain lasix price .
For those in need of confidential HIV condition confirmation, https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ offers an easy and discreet solution.
Optimize your eye pressure management by buying [URL=https://tooprettybrand.com/pill/levitra/ – buy levitra cialis online canada[/URL – , an essential medication for individuals dealing with glaucoma.
Knowing where to procure effective pain management solutions is crucial. Whether you’re facing chronic pain, exploring [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/ticlid/ – buy ticlid[/URL – could be your answer to easing those symptoms.
Discover incredible deals on your prescriptions at celebrex 200mg , your premier destination for affordable healthcare solutions.
Discover a myriad of options to alleviate your pain by exploring https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ , where you can order trusted pain relief solutions virtually.
The benefits of incorporating [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ – how to buy priligy in ireland[/URL – into your daily routine are numerous, including enhancing stress resistance, aiding sleep quality, and augmenting overall well-being.
хто такі більшовики
Seek remedies for hair loss now! Discover how [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – buy nexium without prescription[/URL – can assist in your journey against hair thinning.
Get the best deal on your medication by visiting clomid 50mg , where you can discover unbeatable prices for top-tier healthcare solutions.
With just a few clicks, you can effortlessly get your hands on your dose of https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ , a vital solution for managing acid reflux conditions.
Just discovered the best offer for pain relief with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – retin a in usa[/URL – , on sale.
Looking for an effective and inexpensive pain relief solution? Discover top-notch treatment options and [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – where to buy strattera[/URL – on the web.
X-plore your options for secure tretinoin generico es bueno without compromising on quality. Discover economical alternatives for your healthcare needs.
Buy your essential medications affordably through our trusted https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ . Find diverse alternatives for your healthcare needs easily.
I discovered the most reliable method to acquire Acticin cream for topical use is through [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/xenical/ – xenical 120mg without prescriptions[/URL – , offering a seamless, hassle-free experience.
Acquiring your prescription has never been more straightforward with http://www.tadapox.com . Purchase now for prompt delivery worldwide.
Get your sought-afterdevelopment with oursolution. https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ now for improved results.
Secure your prescription easily and promptly with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil 10mg[/URL – , ensuring complete discretion and efficiency.
The requirement for trustworthy and convenient access to drugs has never been greater. Discover your options and buy [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – lowest dose stablon[/URL – today.
Ensure you secure your hydroxychloroquine 200mg safely for malaria prevention.
Just discovered a wonderful offer on cholesterol-lowering medication? Order your https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ today and begin your journey towards improved heart health!
For those seeking relief from gastrointestinal discomfort, obtaining [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – overnight bentyl[/URL – could be a suitable solution.
Improve your lifestyle effortlessly by opting to buy high-quality medication from the comfort of your home. [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara without an rx[/URL – offers a reliable, safe solution for enhancing performance.
Explore the leading options for enhancing your performance with lisinopril for sale , available now for safe purchase online.
Optimize your health with a diverse selection of treatments by exploring https://center4family.com/kamagra/ , offering a unique combination of options for your wellbeing.
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before attempting to acquire [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/flagyl/ – generic flagyl canada pharmacy[/URL – cannot be overstated.
X-ray your options for managing arthritis pain by exploring safe, effective treatments. Consider [URL=https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ – usa lady-era generic[/URL – to minimize discomfort. Always consult a healthcare professional before commencing any new medication.
Your quest for affordable HCQS treatment ends here. Discover the most recent prices at online generic hydroxychloroquine , your go-to destination for cost-effective healthcare solutions.
Looking to enhance your stamina? Discover reliable options and order https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ —your solution to addressing intimacy issues.
Seek unparalleled performance and confidence in intimate moments; discover your pathway to enhanced vigor with [URL=https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ – lady era price walmart[/URL – . Purchase your answer instantly.
Xperience the freedom of a fuller hairline when you purchase your finasteride on the internet. For more details, click here: [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – lasix generic canada[/URL – .
Discover budget-friendly options to manage epilepsy with cheapest prednisone , now available online.
Facing inconsistent menstrual cycles? Discover how https://center4family.com/priligy-online/ can help in balancing your hormone levels.
Discover a superior way to access your prescriptions with ease. Tap [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – cheapest tinidazole dosage price[/URL – for an effortless solution to your needs.
To discover the optimal deals on [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ – priligy[/URL – , visit our webpage.
People seeking respite from arthritis pain often turn to pristiq , a powerful solution.
Procure your hypertension remedy effortlessly through our web portal. Acquire your treatment sans requiring prescription. Click here https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ to start your journey towards improved well-being.
Having difficulty with an enlarged prostate? Learn how [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/propecia/ – normal dose propecia[/URL – can provide relief and restore your quality of life.
Acquire your prescription easily with our secure online platform. Discover the benefits of [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – generic ventolin at walmart[/URL – .
Procure your antifungal medication at unbeatable rates; discover the how to buy nizagara 25 mg effortlessly.
Just discovered the https://myrsvplive.com/canadian-pharmacy-tadalafil/ ? Seize the opportunity! Enhance your lifestyle now by obtaining it via our website. Your satisfaction is our priority.
Variants to enhance your vitality without leaving comfort: Find [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – at unbeatable rates. Secure it immediately for unmatched wellness enhancement.
Discover your optimal health solution with [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ – generic levitra canada[/URL – . Easily Buy your thyroid medication online.
Zero hassle to secure your prescription for enhanced performance, click here: viagra generic pills .
Acquiring https://purefmonline.com/pill/retin-a/ is now feasible. Explore options to purchase this essential medication easily online.
Obtain your Azithromycin, or its equivalent, efficiently without the need for a medical practitioner’s formal endorsement by clicking here: [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – . This streamlined process ensures you obtain your prescription promptly, ensuring an expedited recovery.
Get your medication effortlessly when you buy flagyl best price usa .
Finding the right pain relief gel can be tough, but our https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ offers a wide selection of options for your needs.
Explore the benefits and options for treating Alzheimer’s with [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – ordering stablon without a prescription[/URL – , a venerated solution in managing cognitive decline. Secure this medication through our website to potentially elevate quality of life for those affected.
Discover how to significantly improve your sleep quality with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – buy lasix[/URL – , your ultimate solution for a restful night.
Be proactive in managing your gout symptoms; consider womenra buy from reputable sources. With our guide, uncover how to safely control uric acid levels and lessen flare-ups.
Your health could significantly benefit when you order https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ .
Buy misoprostol directly via [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – for managing your health efficiently.
Looking to obtain your medication more effortlessly? Find your solution with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – order isotretinoin[/URL – , supplying a cost-effective and trustworthy choice for controlling your health.
Aiming to lower your prostate enlargement symptoms? Explore how bentyl can help.
Curious about how to boost your energy? Consider trying https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ , a reputable solution designed to augment your wellness.
Acquiring [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – has never been simpler. Order your prescription with ease through our digital platform.
Looking for a way to enhance your eyelashes? Discover natural beauty with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy pills[/URL – . Secure thick lashes easily.
Visit sarafem from india for allergy relief. Secure the best deal on effective medication now.
Discover how https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ can assist in controlling your heart health. Experts recommend their employment for avoiding heart problems.
Visit [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – to purchase your medication online at unbeatable prices.
Discover additional information about reliable birth control options at [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/low-cost-prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – .
Purchase premium hormone replacement therapies at unbeatable prices; discover your ideal match with propecia canadian pharmacy today. Suitable for managing menopause symptoms efficiently.
You can locate unbeatable promotions on https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ online.
Questioning where to obtain fertility treatments? Buy your [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – buy generic clomid[/URL – effortlessly through our website.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – offers a convenient way to get necessary medication from the comfort of your own home.
Visit prednisone 20mg to obtain your medicine without a doctor’s approval.
Visit https://renog.org/sildalist/ to obtain your herbal supplement.
To acquire Azithromycin without a prescription, use this link [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – priligy pills[/URL – for reliable options.
I discovered the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone capsules[/URL – after searching the internet.
Zillions seek reliable solutions for erectile dysfunction; generico del viagra offers a wide-ranging answer.
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous platforms offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to guarantee safety and authenticity. https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ offers a comprehensive guide on methods to safely order this medication, alongside vital data on its use.
Considering managing your Parkinson’s symptoms? Discover the most recent [URL=https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine online pharmacy[/URL – to assist your treatment plan efficiently.
Understanding the alternatives for treating IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how nizagara cod might offer you relief from stomach discomfort.
Various individuals seeking relief from ocular hypertension or glaucoma now have the option to purchase an affordable alternative with https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ , providing an economical solution for managing their condition efficiently.
A range of solutions for boosting one’s health exists, but [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – is unique due to its effectiveness.
Discover your pathway to calmness and control over anxiety by opting to acquire retail price of malegra 50 .
Keep your feminine hygiene top-notch with our high-quality solutions. Explore all options you need by clicking on https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ .
Purchase
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and buy lasix here. Instantly purchase your prescription via our website with ease.
Looking to treat your menstrual cycle irregularities? Discover an effective solution with https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ . This pharmacy option can be your ally in dealing with various gynecological conditions.
Quality and affordability meet when you purchase your medications online. Ensure your health is in top condition by choosing to [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – generic retin a uk[/URL – , a decision that combines economy with efficacy.
When looking to purchase medication for rheumatoid arthritis, consider exploring options to zoloft , ensuring you attain reliable treatment smoothly.
Your search for cost-effective birth control solutions ends here; discover our extensive selection of https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ at our digital pharmacy.
Need to acquire affordable treatment for hypertension? Explore our [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – cheap zithromax pills[/URL – for top-notch options available in our catalog.
Searching for a reliable source to get your cholesterol management medication? Look no further! Our tadalafil price walmart offers an effective solution to control your levels efficiently.
Have a need for antimicrobial medication? Acquire your dose effortlessly by https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ .
Acquire your wellness boost by choosing to [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix buy in canada[/URL – , a practice that’s convenient, ensuring that you are always supported in your health journey.
Jumpstart your journey towards better health with a seamless way to acquire your medication. Whether you’re looking to diminish inflammation, our platform offers an array of options to suit your needs. For those specifically seeking Budesonide treatment, online panmycin here and enjoy immediate relief.
Yearning for cost-effective COVID-19 treatment options? Discover the solution with https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ , where effectiveness meets affordability. Save on healthcare costs without a compromise on quality.
Explore your options for managing hypertension by visiting [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/product/generic-retin-a-from-india/ – retin a buy online[/URL – , where you can discover over-the-counter solutions.
Zero hassle to manage your intraocular pressure issues with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Preorder now and experience the difference.
Ensure you find the best price for cheap generic india retin-a by exploring our options.
Browse our site for competitive https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ and explore a multitude of alternatives to obtain your medication.
Explore your alternatives for dealing with stomach ulcers with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ – online bentyl no prescription[/URL – , available on the web.
Zero hassle to acquire your prescription for enhanced performance, click here: amoxil .
Buy this hypertension medication on the web, ensuring reliable blood pressure management. Visit https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ for details.
Nourish your lashes to luxurious lengths with a click! Visit [URL=https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ – symbicort online no script[/URL – to buy your formula for fuller, more vibrant eyes.
Find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – tretinoin cream retin a[/URL – to boost your wellness.
Eliminate your nasal allergies swiftly and efficiently with the acquisition of retin a , available for swift relief.
Patients suffering from vertigo and related conditions can find relief by exploring various treatment options, including the effective medication https://coastal-ims.com/drug/zithromax/ .
Struggling with hair loss? Discover [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – finasteride[/URL – , a top choice for tackling hair thinning. Purchase them immediately and start your journey to regrowth!
Need to find real Canadian pharmacy alternatives? Your hunt ends here at [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – nexium 40mg[/URL – , providing access to licensed pharmaceuticals.
Navigating through various sources to acquire your medications can be daunting, but our prednisone marketing simplifies the process, offering safe and budget-friendly options for your healthcare needs.
Get the best deal on your migraine relief by exploring the most affordable option on generic cafergot https://yourdirectpt.com/cafergot/ . Today’s your chance to save while ensuring the best treatment.
Visit our site to purchase your medication, including [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – where to buy nolvadex online[/URL – , online. This website ensures a convenient way to obtain your required medications.
Your search for advanced health and wellness products ends at prednisone .
Acquire effective hair loss solutions; discover our https://rrhail.org/item/xenical/ for trusted results against androgenetic alopecia.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Find out about how to obtain your needs easily with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – .
X-plore your financial options with xenical 120mg prix en pharmacie belgique when you require emergency funds.
Visit https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ to discover the most competitive prices for your antifungal medication.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – , a treatment for alleviating urinary symptoms.
X-plore affordable AIDS treatment options by deciding to acquire overnight tretinoin for your treatment needs.
X-plore budget-friendly solutions for your medical needs with https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ , your path to enhanced wellbeing.
Keep your kidneys healthy with herbal remedies. Locate the best solution by ordering [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – right away.
Discover the most economical options for managing your health with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to purchase this crucial drug on the web, we supply a wide range of alternatives to fulfill your healthcare demands.
Need affordable medication? Explore cost-effective choices with sarafem information , ensuring you receive quality treatment without spending a fortune.
Keep your ulcerative colitis in check with easy, hassle-free acquiring process. https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ is your go-to for controlling symptoms effectively.
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine[/URL – here. Instantly acquire your prescription digitally with ease.
Keeping your medical needs in mind, you can order [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ – canada companys that sell cytotec[/URL – safely and conveniently from the comfort of your house.
Navigating through the myriad of treatment options for Alzheimer’s can be daunting. However, procuring Donepezil, a proven medication, has never been easier. For those looking to enhance cognitive function affordably, consider exploring your options to similar drugs to prednisone . This approach offers a seamless, cost-effective solution for managing symptoms with convenience.
Just discovered, https://renog.org/trazodone/ offers a breakthrough option for patients seeking alternatives. Now, purchase your quantity effortlessly.
Get your heart prescription easily with [URL=https://5g-emf.com/drug/flomax/ – flomax price[/URL – , available now.
Discover your path to discounts on medications by choosing to buy from [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – generic viagra from canada[/URL – . Experience affordable healthcare today.
Discover your path to discounts on medications by choosing to purchase from retail cost of secnidazole . Experience economical medical solutions today.
Opting to purchase your prescription with convenience, https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ via the web is a reliable choice.
Quest for the best rates on Erythromycin? [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil without prescription[/URL – has exceptional prices for you.
With allergies peaking, obtaining relief has never been easier. Explore your options and discover cost-effective solutions at [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/zithromax/ – buy zithromax[/URL – . Say goodbye to sneezing and hello to clear days in front of you.
Just when you need effective treatment for bacterial infections, choose buy flagyl 200 mg fda approved pharmacy online.
Given the need for trustworthy laxative solutions, considering https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ could be a wise option.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your medication needs? Look no further! You can secure your [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – price of nizagara[/URL – without hassle from our trusted platform.
Looking to treat your gout symptoms? Discover a variety of affordable options when you buy lady era commercial .
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ online can be a simple process.
Try lessening your discomfort effortlessly by clicking on [URL=https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ – generic retin-a no prescription canada[/URL – , the link to purchase safe and effective relief.
Quickly acquire economical pain relief by selecting to order [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – mail order prednisone canada[/URL – .
Looking for affordable medication options? etibest md pills offers an opportunity to cut costs on your medications. Don’t miss out on this deal!
Relieve your enlarged prostate symptoms today! Explore our range of https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ , specifically designed to boost your urinary flow and overall health.
For managing chronic dry eye, consider exploring [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – , a targeted therapy.
Considering your health needs, you can purchase medications safely and conveniently [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ – prednisone for sale overnight[/URL – , ensuring privacy and speed in delivery.
Zeroing in on reliable solutions for ED, acquiring purchase viagra without a prescription proves to be a practical choice.
Access https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ instantly! Secure the order online for quick delivery and exceptional service.
Achieve academic excellence and improve your writing skills with our professional help at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – .
Unlock exclusive offers when you purchase your medication directly through [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – strattera[/URL – , ensuring affordability and ease.
Looking for the cheapest options for your medication? Discover great deals on cheap kamagra uk site today.
Looking for a reliable source to buy your medication? https://coastal-ims.com/drug/zithromax/ offers an easy way to obtain your needs with just a few clicks.
Visit our website to purchase your essential medication. [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix no prescription[/URL – seamlessly, for managing your health needs.
Zeroing in on treatments for COVID-19, [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – offers a promising option. Seekers in the health arena can discover this curative solution online.
The acquisition of propecia is easier with our platform. Ensure your supply of this vital medicine now.
Get your Amoxicillin easily from https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ , supplying prompt dispensation to satisfy your healthcare needs.
Browse our site for the lowest price on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone generic canada[/URL – , ensuring you obtain your medication swiftly.
To enhance one’s endurance, consider [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ – order celebrex[/URL – for a trustworthy option.
To find the best deals on lasix 40mg , explore our site.
Looking to control your menstrual cycle irregularities? Discover an effective solution with https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ . This medication can be your ally in addressing various gynecological conditions.
Finding [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – has never been easier. Now, buy your required medication online with absolute confidence.
Visit our site to purchase your prescription, including [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ – ventolin without prescription[/URL – , online. This online service ensures a hassle-free process to access your essential medications.
Just discovered you can secure 500 amoxil on line with ease through our trusted portal.
Now, discover the best bargains on https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ .
Now, procure your way to health with ease. Discover a holistic solution by choosing to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – .
Explore the latest advancements in schizophrenia treatment with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol 3 lowest price india[/URL – . Acquire this innovative medication via our website.
Seek top prices for enhancing your vitality with retin a . Buy online for optimal benefits.
Explore the myriad benefits of vital health supplements by opting to secure your needs from the renowned https://center4family.com/kamagra/ .
You can secure [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – through multiple reliable internet sources.
Seeking relief from benign prostatic hyperplasia? Explore your options with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – cheap lasix pills[/URL – , a remedy for alleviating urinary symptoms.
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if wholesale lasix china could be the right fit for you or your loved ones.
Discover affordable relief for joint pain and inflammation. Now you can buy https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ . This potent treatment offers a solution for managing discomfort with ease.
Browse our site to order premium medical solutions, including [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ – lady era on internet[/URL – , securely.
Discover an easy method to obtain your amoxicillin 500mg via the internet.
Looking for an affordable way to manage your health? Explore https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ for a reliable solution.
Need to alleviate glaucoma symptoms without breaking the bank? Explore our wide range of affordable solutions, including the highly effective [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/rumalaya-liniment/ – buying rumalaya liniment[/URL – , suitable for budget-conscious patients seeking quality eye care options.
Discover more about reliable birth control options at tadalafil buy online .
Purchase, acquire, or obtain your https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ with ease, ensuring a smooth, hassle-free process to improve your wellness journey, available online.
One can discover competitive [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – low cost amoxicillin[/URL – and diverse alternatives on web platforms, ensuring economical options and availability.
Ensure you buy your durable batteries at unbeatable prices. Explore [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/generic-tadalafil-from-india/ – tadalafil without dr prescription[/URL – for premium options.
Interested in controlling water retention? Explore numerous remedies and discover cheapest nizagara for efficient results.
Considering managing hormonal imbalances? Explore https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ for an answer.
Need to enhance your focus? Get your [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ – prazosin without dr prescription[/URL – and benefit from increased cognitive abilities.
Searching for trusted solutions to reduce irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how bentyl can help in easing your discomfort today.
Maximize your savings on Crohn’s disease treatment by securing the https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ . Discover affordable solutions on the web for your health needs.
Before choosing a treatment for glaucoma management, consider exploring cost-effective options such as [URL=https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ – prednisone lowest price[/URL – . With an array of possibilities, finding a economical option is crucial for ongoing care.
Obtain over-the-counter options for managing fluid retention, including [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – buy vidalista online[/URL – , through digital platforms. Explore a variety for safe solution now.
For those in need of confidential HIV condition determination, arjuna without an rx provides a convenient and private option.
Zero reasons to wait! Acquire your medication for enhanced well-being instantly at https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ .
Get the best deals on cardio-supportive supplements when you purchase [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone without a prescription[/URL – .
TrendAndStyle Finds Hub – Tidy, responsive layout with fast browsing and well-displayed items.
To manage hypertension effectively, consider [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – generic lasix india pharmacy[/URL – , which is a widely recommended medication by physicians. Alternative options include ordering this crucial treatment via trusted websites.
Explore the realm of pharmaceutical help and find simple ways to control your health. Whether you’re seeking certain medications or broad health advice, we provide a plethora of options. For those looking for a different option, amoxil without pres could be the solution.
Need to combat cold sores? Consider the https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ for an effective solution.
Replenish your health supplies easily with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – buy retin a[/URL – , to ensure consistent care.
I’ve discovered where to get [URL=https://youngdental.net/item/acticin/ – acticin without dr prescription[/URL – . This platform offers a plethora of choices for those seeking to purchase their prescriptions online with ease and confidence.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase hydroxychloroquine walmart price on the web is crucial for consumers.
Now, find your path towards reduced cholesterol with https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ , accessible for buying online.
Obtain relief from constipation quickly with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – . This remedy is perfect for individuals in need of a gentle approach.
Having issues with an enlarged prostate? Learn how [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax without dr prescription usa[/URL – can help and restore your well-being.
Needing to acquire ventolin 100mcg ? Explore safe options for acquisition virtually.
Zealously seeking a trusted source to purchase your medications from? Look no further; https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ offers a secure, discreet way to obtain what you need.
Keeping your antiviral medications current is essential. For those needing medical endorsement refills, [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – buy tadalista w not prescription[/URL – could be your go-to option.
visit diamondfieldhub – Easy to explore, and the store gives off a reliable, well-kept impression.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, purchasing [URL=https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – indian hydroxychloroquine safety[/URL – on the web offers a budget-friendly option.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with flomax , a treatment for easing prostate enlargement symptoms.
With the rise in demand for holistic health solutions, explore https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ to boost your health.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your health issue efficiently with [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – buying cialis in montreal[/URL – . Improve your health immediately.
Having trouble managing your hypertension? Consider exploring [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/frumil/ – frumil[/URL – to discover a suitable treatment.
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous online sources offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to guarantee safety and authenticity. hydroxychloroquine offers a comprehensive guide on how to safely order this medication, alongside vital details on its utilization.
Looking to manage your condition effectively? Discover how to acquire https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ and begin your journey towards enhanced health today.
With competitive medication rates, [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ – vidalista de 40 mg[/URL – offers an affordable solution to enhance your fertility journey. Explore budget-friendly options now.
Yes, facing unsettled stomachs can be troublesome. Find relief swiftly by clicking here: [URL=https://driverstestingmi.com/item/generic-prednisone-uk/ – prednisone[/URL – . Whether rapid results are needed, obtain your treatment at once.
Learn more about managing your medical conditions with lasix . Uncover how this medication can benefit you in regulating hormone levels.
Research suggests that locating the https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ can be straightforward with the right direction.
Understanding your need for reliable and affordable hair loss solutions? Look no further than [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – http://www.retin a.com[/URL – , where you can purchase your medication without hassle.
Discover how [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – pharmacy prices for flomax[/URL – can alleviate symptoms of an enlarged prostate by visiting our website.
Obtain the treatment for better female health with tadalafil mg , available online.
Never ignore the need for effective sleep aid. Find out about the revolutionary https://tv-in-pc.com/trazodone/ , a game changer in achieving a peaceful night’s rest.
Harness the power of convenience and savings when you purchase your birth control. With our exclusive offers, you can get affordable [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix[/URL – without ever compromising on quality.
Iron Root Market – Impressive corner store offerings, browsing is smooth and natural.
Yearning for an affordable solution to manage eye inflammation? Look no further! Find the [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ – pharmacy without dr prescription usa[/URL – here to reduce your symptoms efficiently.
Find inexpensive solutions for antiviral therapy with generic acivir dt from india , your go-to option for treating outbreaks.
To get safe malaria treatment, browse https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ for a wide selection of choices.
motivation hub – Inspiring items are neatly presented, browsing is quick and pleasant.
“Visit now for unparalleled savings; redeem your exclusive [URL=https://primerafootandankle.com/item/vidalista/ – buying vidalista online[/URL – to cut costs on allergy relief today. Don’t miss this chance to live comfortably at a fraction of the cost.”
Purchase your medications with ease; order your pharmaceuticals through the web at kamagra pills , ensuring reliability and comfort.
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ can help in alleviating urinary symptoms associated with an enlarged prostate.
Harness the power of enhanced performance and satisfaction; explore the benefits of [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – non prescription lady era[/URL – .
Unlock significant savings on eye care medication by choosing to [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ – vidalista price at walmart[/URL – . Explore options to acquire your crucial medicine with convenience and confidence virtually.
Hunting for cost-effective solutions for your health? Discover your best option with our guide to asthalin . Explore online, get the optimal deal for your needs now.
Visit our platform to order https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ , ensuring affordable options for your well-being.
To manage your problem effectively, explore the option of [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ – lowest price on generic bentyl[/URL – as your go-to choice.
I understand the need for convenient solutions when looking to acquire medication. For those considering managing their health concerns efficiently, exploring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ – flomax uk[/URL – offers a critical resource.
Research shows that finding the xenical 60mg is crucial for patients seeking cost-effective options for their health needs.
To secure clomiphene for managing ovulatory dysfunction, consult https://kileensgardenboutique.com/kamagra/ .
Secure
Zap your anxiety away! Now you can get your stress-relieving medication hassle-free. Don’t miss out on our exclusive [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy pharmacy generic[/URL – . Slash prices on your purchase today and welcome calm without breaking the bank.
Just discovered an unbeatable offer on generic strattera lowest prices ? Discover unmatched savings now!
Experiencing ED? Explore efficient solutions and order https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ . Safely enhance your performance today.
Looking to enhance your stamina? Discover how [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – might aid. Available now, these caps are formulated to assist your wellness journey.
Keep your well-being at its peak: discover safe and trusted options to acquire [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/]viagra price walmart[/URL] .
Our team has sourced the nizagara for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
Research the newest strategies for managing HIV with online resources. Find comprehensive information https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ and remain educated.
Get relief from nasal allergies with a affordable solution. Acquire [URL=https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/]online panmycin[/URL] on the web for a straightforward experience.
Keeping your cholesterol levels in check is crucial for heart health. [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – lasix overnight[/URL – can be your first step. You can procure this treatment via Internet.
When searching for affordable solutions to treat your eye pressure, consider exploring nizagara for unbeatable rates and dependable medications.
Looking for an effective way to treat psoriasis? Learn about how https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ can aid in easing symptoms safely.
Quality and affordability meet when you purchase your medications online. Ensure your health is in top condition by choosing to [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis receptfritt[/URL – , a decision that combines economy with effectiveness.
Your quest for affordable hydroxychloroquine ends here. Discover the current costs at [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – , your preferred choice for economical medicinal purchases.
To manage hypertension, consider buy cheap pristiq , a approach embraced by many in achieving better health.
When looking to economize on your prescription, consider using an https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ . Learn how to significantly reduce your pharmacy bills immediately.
Various individuals opt to buy their pharmacy supplies on the internet, with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ – doxycycline pills[/URL – being a popular choice among options.
Visit our platform to buy your [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – canadian pharmacy super kamagra[/URL – effortlessly. Experience reliable and fast access to essential medications without delay.
Understanding the choices for treating IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how buying bentyl online might provide you alleviation from abdominal discomfort.
X-ray the expenses before purchasing your antihistamines; explore the https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ for an affordable selection.
Acquire
Zajimavy obsah! Prave jsem zacal hrat ve Spinmama Casino CZ a jejich sluzby me opravdu nadchly. Nabizi uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP klub, turnaje, loterie a dalsi promo akce, ktere zaujmou kazdeho fanouska casin. Me nejvice bavi herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske online casino na opravdu vysoke urovni. Pokud hledate bezpecne online casino s bonusy, podivejte se zde: Twitter . Urcite vyzkousejte a uzijete si spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Uvitaci bonusy a VI
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
f2_8903
Harness the power of effective antifungal medication by exploring [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cipro/ – cipro[/URL – . Secure your health today by purchasing this crucial treatment on the web.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your cost of 250mg amoxil on the web for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Yes, facing diarrhea can be troublesome. Discover relief quickly by clicking here: https://cafeorestaurant.com/tamoxifen-without-pres/ . Whether it’s an emergency, obtain your treatment immediately.
Questioning where to find [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – buy generic lasix[/URL – ? Explore safe options for purchasing via the internet.
Secure the best deal on amlip by searching through our website.
For individuals seeking cost-effective treatment options for bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, discovering https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ becomes vital. Explore budget-friendly options to handle your health with ease.
Seek competitive [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – lasix 100 mg price buy[/URL – and ensure you secure the most affordable rate on your medication.
Rid your body of unwanted parasites effortlessly by securing [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – . Eliminate those undesirable guests without trouble by obtaining this potent remedy.
Zero delays in your heart rhythm treatment are crucial. Order the prescription easily with cheap 100mg lasix , ensuring prompt management of your condition.
X-ray your budget and find out how much you could save on eye drops by checking the https://purefmonline.com/propranolol-20mg/ .
Regarding your health, it’s crucial to discover an effective option. For managing specific health concerns, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – stands out as a suggested choice by healthcare professionals.
Zap your low testosterone levels into oblivion with online lasix no prescription . Elevate your vitality by uncovering a treatment that rejuvenates male health effectively.
Relieve your nasal symptoms with https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ , now available for ordering without a prescription.
Yes, obtaining your prescription is now hassle-free with our service. Simply visit [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – lowest price for cytotec[/URL – to buy your medication with no hassle.
Looking to improve your joint health? Consider exploring [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – www tadalafil 20mg[/URL – . This product is crafted to aid in preserving supreme joint function.
The positive effects of generic fildena canada pharmacy for treating mood swings are well-documented.
Variety of selections to acquire your crucial medicines is essential. For those in search of https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ , multiple alternatives are accessible, guaranteeing you get the utmost treatment.
Secure your health and improve your stamina by acquiring the [URL=https://rrhail.org/item/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – for continuous pleasure.
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable human immunodeficiency virus testing solution. Acquire your [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – nexium without dr prescription usa[/URL – today and confirm your status efficiently from the privacy of your home.”
Experience swift relief from breathing issues by choosing to buy your inhaler from our asthalin .
With our https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ , you can improve your eyelash volume affordably.
Considering your health, finding affordable solutions is crucial. Click here for the [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – lasix 100 lowest price india[/URL – , or search alternative platforms for economical treatment options, ensuring you get trustworthy medication without overspending.
Looking to enhance your lashes? Consider [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – sublingual asthalin online[/URL – for longer, fuller eyelashes. Available now, you can purchase this eye drops on the web.
Browse our site to discover vendita amoxil in italia , ensuring you get premium antibiotic options at matchless prices.
Beat anxiety and tension with trusted solutions; order https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ online.
Enhance your fertility journey affordably with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – vidalista[/URL – . Discover outstanding savings on this essential solution on our website.
Your search for an effective treatment for early climax ends here. Order [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ – canada dapoxetine[/URL – , a trusted drug, from our website.
To locate affordable choices for your prescriptions, visit canada dapoxetine to explore cost-effective solutions.
Now, explore a variety of methods to boost your vitality. Consider trying https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ for an organic solution.
Keep your eyesight in tip-top condition with our [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ – nizagara online amazon[/URL – . Purchasing these tools online ensures you get unmatched quality for maintaining your ocular health.
The obtainment of [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone coupons[/URL – has never been easier, offering a treatment right at your fingertips.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive tadalafil . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to cut costs on pharmaceuticals.
Explore budget-friendly options for your heartburn treatment by checking https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ . Find your supply online and ease your symptoms efficiently.
Patients seeking relief from COPD symptoms can discover effective treatment with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – . These remedies provide a dual-action solution, improving lung function and reducing flare-ups.
Quickly secure your essential wellness supplement today; [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil from canada online[/URL – offer a wise option for enhancing your wellness.
Discover innovative treatments for your health. Obtain price of 250 mg cipro from trusted sources on the web.
Living with allergies can be difficult, but obtaining relief shouldn’t be. Discover how to get https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ effortlessly and start your path to a comfortable life today.
Unlock unparalleled savings on hepatitis C treatment: [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – sildalis online no script[/URL – . Explore an array of options; secure your medication virtually today.
windyforestfinds – Easy checkout and friendly layout made my visit to windyforestfinds pleasant.
Considering the necessity for heart health, obtaining [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine best price[/URL – online offers a handy solution for controlling cholesterol levels.
In search of holistic solutions for tension, I discovered lowest price for tamoxifen . This time-honored herb promises ease from everyday stress.
Buy misoprostol directly via https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ for managing your health efficiently.
Variants to enhance your vitality without leaving comfort: Find [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20 without a prescription[/URL – at unbeatable rates. Secure your order immediately for unmatched rejuvenation.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ – pharmacy prices for viagra[/URL – , offering a seamless buy experience for this essential medication online.
A safe and easy way to purchase ED treatment is to viagra 50mg .
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ might be your solution. Explore how it may help in reducing your symptoms efficiently.
Questioning where to obtain fertility treatments? Buy your [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone 20 mg[/URL – effortlessly on the web.
Zero in on savings with our exclusive offer! Secure your [URL=https://kileensgardenboutique.com/kamagra/ – discount kamagra[/URL – now and make certain your well-being is top priority.
Explore the benefits and options for treating Alzheimer’s with amoxil 650 from canada , a venerated solution in managing cognitive decline. Secure this remedy through our website to potentially improve quality of life for those affected.
View the latest costs for treating your BPH symptoms with https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ , and explore various solutions to improve your quality of life.
X-plore the therapeutic options for managing Addison’s disease; [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil suppliers[/URL – stands out as a top choice. Its efficacy in regulating electrolyte levels and mitigating symptoms is unparalleled.
Get alleviation from discomfort with on line tadalafil .
Maximize your wellness and satisfaction with a variety of options for enhancing your experiences; https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ offers a unique solution. Obtain
Zero hassles while looking to improve your vitality? Explore our unique selection and buy the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – discount prices for nizagara[/URL – virtually, ensuring you receive premium choices for your wellbeing.
Unlock unparalleled savings on antiviral medication by opting to [URL=https://hyblavalleyvet.com/kamagra-in-usa/ – kamagra in usa[/URL – . Seamlessly acquire your health essentials online.
Central to maintaining robust health, finding affordable solutions is key. Explore amlip to ensure your well-being doesn’t break the bank.
Knowing the cost of medication is vital, learn about the lowest https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ for your requirements.
Experience rapid relief from nocturnal enuresis with our reliable [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ – asthalin no prescription[/URL – . Acquire now for a enhanced night’s sleep.
A comprehensive guide to accessing generic sildalis is now accessible! Whether you’re looking to acquire or simply explore options, this guide provides the entirety you need.
Discover affordable solutions for ED by visiting https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ , where you can purchase your drugs easily.
In search of cost-effective heart medication? Look no further! Acquire your [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – at this moment.
To secure effective treatment for IBS, consider securing [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – canadian pharmacy for zithromax 100[/URL – , known for its outstanding positives.
X-plore the myriad benefits of enhanced endurance and vigor with just a click. Secure your prescription of unparalleled performance enhancement now at propecia cost .
Keeping your health in top condition is crucial, and obtaining your medications shouldn’t break the bank. For those looking for cost-effective treatments, discover the current https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ , a place where affordability meets quality.
Rid your body of unwanted parasites effortlessly by securing [URL=https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ – generic for tofranil[/URL – . Expel those intrusive guests without trouble utilizing our powerful solution.
Zoning in on cost-effective angina relief, discover competitive rates on pharmacy prices for kamagra online.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ from a reputable vendor is crucial for individuals seeking treatment.
To obtain your essential iron supplements, explore [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline 100mg[/URL – guaranteeing cost-effectiveness.
Harness the power of traditional medicine by visiting [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – buying prednisone online[/URL – , where you can purchase this ancient herb designed to improve well-being.
Acquiring propecia cost has never been simpler. Procure your treatment with ease via our website.
Maximize your well-being with a holistic approach by opting for https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ , a solution that’s readily available for boosting male health and vitality.
Alleviate your nasal congestion and relieve allergy symptoms quickly by employing [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl through paypal[/URL – . This potent solution offers immediate relief for those suffering from seasonal allergies, ensuring your daily activities are no longer hindered by annoying sniffles and sneezes.
Need to cut down on your prescription costs? Uncover the best deals by accessing a [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – buy lasix[/URL – now.
Zipping through your options for handling ED? Discover a convenient solution by choosing to purchase viagra .
A key medication for managing fluid retention is available here: https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ . Whether you’re battling heart failure, renal problems, or hepatic disorders, consider examining this option.
Need to improve your endurance? Discover budget-friendly solutions at [URL=https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ – nizagara street value[/URL – for your needs.
With rising healthcare costs, it’s crucial to find an economical option. For those seeking cholesterol reduction, [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – prices for nizagara[/URL – can be a lifesaver.
Various individuals seek effective therapy for their condition, and now you can obtain amigren 50mg quickly on the web, offering a practical pathway to managing your health.
Now, locate your solution for erectile dysfunction with ease by opting to purchase https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ .
Yes, you can secure discounted solutions for managing water retention. [URL=https://nesttd-online.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – is your go-to selection for intervention.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with tadalafil , your go-to source for acquiring reliable ED treatments online.
Purchase the essential eye care treatment at https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ , offering affordable rates for your ocular health needs.
Discover affordable options to maintain your bone health; [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – overnight prednisone[/URL – and explore other economical solutions through digital pharmacies.
Keep your health in top condition with affordable solutions; explore [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/sildalis/ – sildalis.com[/URL – for your needs. Seek out alternatives online to keep up wellness efficiently.
You can acquire herbal max gun power without a prescription. Explore your options herbal max gun power overnight today!
Consider securing savings on your fertility treatments with https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ . Discover exclusive deals to assist in your journey toward parenthood.
Explore the best [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ – cytotec on line[/URL – for an exciting experience.
X-plore your options for mountain sickness aid with simplicity. Now purchase [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy-com-lowest-price/ – priligy cost[/URL – , your go-to remedy for mountaineering adventures.
Keeping your cholesterol numbers in check is crucial, and lasix uk might be the solution. Discover cost-effective options to control your heart health today.
Procure your https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ effortlessly through our site, ensuring a seamless transaction. This option is perfect for those seeking reliability without the steep price.
Revitalize your energy and balance your hormonal levels by choosing to [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – cytotec from england[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to boost your well-being or pursuing hormone replacement therapy, these capsules offer a solution.
oakandriver – Oakandriver’s layout feels intuitive, finding products was fast and pleasant.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Consider [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/lowest-price-generic-cialis/ – cialis[/URL – – your go-to choice for restoring health.
Questioning where to find an effective treatment for your needs? Your search ends here. genuine flomax provides a versatile solution for those seeking quality medical care.
For those seeking to buy, https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ offers a comprehensive solution for managing your health.
Xperience enhanced vitality and wellness with our [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – buying levitra online[/URL – , currently on offer for regular use.
Questioning where to find relief for seasonal allergies? Look no further! [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ – purchase tadalafil without precription[/URL – offer an answer for sufferers by sneezing, itching, and congestion. Buy yours immediately for effective results.
Questioning where to acquire affordable wellness solutions? Look no further than our trusted source for your needs. Click here to no prescription nolvadex and uncover a range of health perks.
Keeping your digestive system healthy is crucial, and https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ can assist. Explore options to purchase it online for optimal gastrointestinal well-being.
Knowing where to procure effective pain management solutions is crucial. Whether you’re dealing with inflammation, considering [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra cheap[/URL – could be your answer to relief.
Purchasing a [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – generic hydroxychloroquine from india[/URL – can be efficiently done through our platform. Opt to order your medical jellies online for a hassle-free experience.
Unlock unparalleled savings on hepatitis C treatment: buy lasix without prescription . Explore an array of options; obtain your prescription on the web today.
Zero in on unparalleled deals for your health needs; find unmatched offers on https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ today.
Searching for affordable ulcer treatment options? Look for the best deals on [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil-best-price/ – tadalafil[/URL – , your go-to option for relieving gastrointestinal discomfort.
Acquiring your prescription has never been more straightforward. Now you can secure your necessary medication lowest price on generic bentyl with ease.
Discover affordable solutions for your medication needs; explore our variety of options and compare https://yourdirectpt.com/cafergot/ to ensure you’re getting the best value for your health.
The positives of incorporating [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ – online cialis no prescription[/URL – into your daily routine are vast, including improving stress management, aiding restful sleep, and improving overall well-being.
Discover a hassle-free way to secure your treatment with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – , ensuring confidentiality and ease in ordering.
Keeping your health in check, order lady-era without prescription free to enhance your lifestyle.
Before making any health decisions, consult your doctor, but if you’re looking to purchase cholesterol-lowering medicine, consider visiting https://dallashealthybabies.org/meldonium/ for a trusted option.
Understanding your health requirements can often lead to confusion and worries. If you’re seeking alternatives for managing your condition, think about exploring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – cost of propranolol at walmart pharmacy[/URL – . This approach could perhaps offer a fresh direction to better health.
Get your meds securely and conveniently through [URL=https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin coupon[/URL – , your go-to for healthcare.
To discover affordable alternatives for your prescriptions, visit canadian sildalist to examine budget-friendly choices.
Your health should be a priority, so think about purchasing https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ for supporting your wellbeing.
Researching options to secure [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ – ebay doxycycline[/URL – ? Review our trusted source for your medication needs, providing a wide range of drugs with efficient delivery options.
Quickly purchase [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – 60 mg prednisone[/URL – to control your eye conditions, obtainable online.
Ache no more! Discover the revolutionary joint relief with generic tadalafil from india . Buy now for a pain-free tomorrow.
Quickly acquire your vital medication with no hassle: https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ .
Discover effective treatment options with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil without prescription[/URL – , and manage your medical conditions efficiently.
Looking to secure your antiviral treatment? Now, you can buy [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – lowest price generic cytotec[/URL – easily.
Visit our website to order levitra for sale , ensuring you get your medication quickly.
Yes, securing the https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ can be effortless when you search on the internet.
For individuals in search of relief from Meniere’s disease symptoms, contemplate [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – , an effective solution.
Purchase, acquire, or obtain your lasix 100mg with ease, ensuring a smooth, hassle-free process to boost your wellness journey, available on the web.
Find lowest prices for natural vigor solutions; https://mypurelifefoods.com/retin-a/ online.
Discover amazing deals on your healthcare essentials. Locate the [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – canadian pharmacy amoxil[/URL – and keep your health in check without hassle.
Keep your vitality at its peak: discover safe and trusted options to purchase viagra .
Visit https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ to acquire your antibiotics on the internet at fantastic prices.
Questioning where to find antibiotics without overpaying? Find the [URL=https://jawany.com/cipro/ – where to buy generic cipro[/URL – and save on your pharmacy expenses.
Before you commit to a purchase, consider checking out [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – for affordable rates on this essential medication.
Obtaining ventolin for alleviating inflammation and pain is straightforward. Acquire it via a web-based pharmacy for swift relief.
Now, find https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ by visiting our platform. Secure the most advantageous offer immediately.
Having trouble managing your hypertension? Consider exploring [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil from mexico[/URL – to locate an appropriate treatment.
Discover unbeatable deals on [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – retin a[/URL – and conserve on your following buy.
Just considering your medical needs, one could ponder buy alesse online as a convenient option to maintain their birth control requirements.
Discover new ways to manage anxiety with https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ , accessible on the web.
Secure your supply of [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone without dr prescription[/URL – today! Secure today and obtain your supply without delay.
Ensure you secure your [URL=https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – with assurance for treating certain conditions.
Uncover the benefits of utilizing lowest sildalis prices for your allergic reactions. Available now, this treatment offers an economical solution to control your symptoms.
Prices for Corion injections are surprisingly affordable at https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ , especially when looking for budget-friendly fertility solutions.
Boost your eye beauty safely with our easy-to-use solution; [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – sildenafil price at walmart[/URL – required. Perfect for enhancing eyelash growth effortlessly.
Struggling with nervousness? Discover relief with the top-rated solution. [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ – order nizagara[/URL – now and start your journey towards a calmer life.
I found an excellent source for prednisone .
Xperience fast relief with your https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ , ensuring you get your treatment without delay.
Obtaining [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ – prednisone cheap[/URL – for alleviating inflammation and pain is straightforward. Procure it online for efficient relief.
Looking to enhance your energy? Acquire genuine solutions [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ – generic molnupiravir canada[/URL – .
When seeking an economical solution for your antimicrobial needs, think about tapping into the convenience of doxycycline . This virtual drugstore offers a wide selection of non-brand medications that meet various health conditions efficiently.
When looking to enhance your vitality, consider opting for https://mnsmiles.com/item/nizagara/ , a reliable choice. Available for acquisition online, this solution promises enhanced performance.
Discover affordable solutions for hair loss; buy your finasteride effortlessly [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – generic flomax online[/URL – .
Shop Everyday Outlet – Lots of appealing options available, and exploring categories is simple.
Need to secure your baldness solution? Find budget-friendly options with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra cheap[/URL – , providing you get high-quality interventions for a portion of the price.
Opt for a safer, distinctively tasted version of a familiar enhancer directly Canadian-sourced: buying prednisone online .
Zero hassle to obtain your treatment: https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – order via the internet with total confidence.
Your search for cost-effective birth control solutions ends here; find our wide-ranging selection of [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – alesse[/URL – at our digital pharmacy.
I discovered that many individuals are looking to purchase [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/prednisone-without-pres/ – prednisone cheap[/URL – for their nasal allergies relief.
Buy your essential medication easily with a tap on your device. Seeking a reliable source for your healthcare needs? Look no further. Obtain this medication, without the hassle of a prescription, directly through prednisone .
When in need of urgent solutions, locate https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ for your needs.
Considering the escalating costs associated with fertility treatments, finding economical solutions is crucial. Opt for [URL=https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ – generic for amoxicillin[/URL – to boost your journey to conceiving, available at competitive rates without compromising on quality or efficacy.
Get your health back on track with ease; secure your discounts now on stress-relief prescriptions by clicking here: [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ – misoprostol[/URL – .
When seeking us overnight pharmacy , consider exploring diverse digital markets to acquire affordable treatment solutions.
Absolutely alleviate allergies with easy access to https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ . Secure your fast-acting allergy relief via the web without the need for a prescription.
Protect your health by learning about the most recent health tips and trends at our [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ – tadalafil on line[/URL – website.
Looking for more affordable medication options? Explore [URL=https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ – panmycin for sale[/URL – for economical solutions to your healthcare needs.
Research indicates that hormone replacement therapy can be a key component for managing the symptoms of menopause. Considering different options? Explore how propecia might suit your health regimen.
Secure your health effortlessly by opting to purchase prescriptions from https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ . Explore a wide range of pharmaceuticals via the internet.
Seeking affordable solutions for fertility issues? Consider exploring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – , a popular choice for those aiming to enhance their chances of conception.
“Quickly discover affordable solutions for your health by clicking prednisone 40 generic , and get your route to bettered energy.”
Get your daily Cialis conveniently and securely by clicking https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ . Whether you’re looking to obtain for individual use or addressing a issue, you’ll find top-notch options available on the web.
Discover effective solutions for heavy menstrual bleeding by exploring our selection of medications. Order the necessary treatment [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ – malegra usa store[/URL – effortlessly with just a few clicks.
With various online platforms available, it’s never been easier to nizagara . Whether you’re aiming to obtain medicine without hassle, our platform offers a seamless and secure shopping experience.
Venturing into the realm of digital pharmacies enables you to acquire essential medications conveniently. Whether you’re in urgent need to anti-inflammatory solutions, https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ emerges as your go-to destination for straightforward purchases.
Zero hassle to procure your necessary medication with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – buy non-generic celebrex online[/URL – .
Given the complexity of managing prevalent health conditions, finding a reliable source for drugs is crucial. That’s why many choose to acquire their pharmaceuticals from [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ – generic molnupiravir tablets[/URL – , where a wide selection in pharmaceutical solutions is always available.
For immediate ease from pain, look into buy molnupiravir online cheap for an effective solution.
Visit https://jawany.com/cytotec/ for complete insights on using this medicine safely.
In search of trusted lice treatment? Explore our range of options and discover [URL=https://youngdental.net/item/acticin/ – acticin without prescription[/URL – , the preferred solution for many.
For patients seeking effective pain management, consider utilizing strattera online sicuro , an prominent method.
Discover the best cost-effective solution for migraine relief by clicking https://alliedentinc.com/product/vpxl/ . Get your stock without spending a fortune.
With an array of options for controlling hair loss, [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – stands out as a reliable solution.
Various individuals seek cost-effective treatments for managing their medical conditions; hence, they explore affordable solutions. prednisone prices offers a possibility for those aiming to cut down healthcare expenses while maintaining effectiveness.
Considering various options for motion sickness relief? Discover the https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ to effectively manage your symptoms. Explore other solutions right away.
Given the myriad options for managing fertility issues, the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – generic retin a[/URL – often emerges as an important factor for many.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Look into [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – pharmacy prices for cialis[/URL – , a cost-effective and reliable option for enhancing your sexual health.
You can purchase generic sildalis from canada online, ensuring a safe and easy way to treat your medical conditions.
Your health deserves attention. Discover easy access to control your medical condition with https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ . Ensure your well-being is at its best with just a few clicks.
Discover reliable treatments for your gastrointestinal issues with [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – non prescription bentyl[/URL – , a choice endorsed by healthcare professionals.
Respiratory issues like asthma can be daunting, but relief is accessible. Obtain affordable solutions with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – chinese cheap asthalin[/URL – , ensuring you’re breathing easier.
Understand your migraine triggers better and explore effective relief solutions today; learn about trusted options to buy cialis coupons and take a step towards managing your symptoms.
Acquiring https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ is now feasible. Explore options to obtain this crucial therapy with ease online.
Xperience swift relief with our [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – http://www.retin a.com[/URL – , ensuring you receive your treatment promptly.
X-pand your wellness options: Uncover how to buy your [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ – tadalafil[/URL – easily.
Venturing north for well-being solutions? Find your wellness aid with tretinoin cream , offering a wide selection of medicines.
Unlock the secrets to enhanced vitality and stress relief with https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ . Discover the best source for a time-tested remedy.
Procure the most affordable solutions for hair care; discover your perfect match at [URL=https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix and generic[/URL – .
Your search for affordable arrhythmia treatment ends here with [URL=https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ – generic propecia[/URL – . Secure your health’s future with a click.
Just learned you can order your stomach cramps meds via the internet? bentyl offers a variety of choices for your treatment needs.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ , a solution for easing prostate enlargement symptoms.
Maximize your health outcomes by opting to acquire high-quality medication from [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cheapest cialis[/URL – , a trusted source for all your pharmaceutical needs.
For those seeking to purchase hormone replacement therapy, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ – no prescription flagyl[/URL – offers an effective solution.
Combat eye conditions, specifically glaucoma, with where to buy stromectol online , obtainable for purchase online.
For individuals seeking to manage their hair loss, https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ offers an effective solution. Explore alternatives to acquire this crucial medication easily online.
Considering various choices for augmenting your well-being, opting to obtain [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ – tadalafil 20mg[/URL – via the internet can be a wise decision.
Discover lowest deals on your prescriptions at [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ – pharmacy[/URL – , your ultimate source for cost-effective healthcare solutions.
Zealously enhance your eyelash growth with safe solutions; explore your options at cipro .
Discover the ways order branded Allegra via the internet with our easy guide. https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ .
If you’re looking to acquire cost-effective Hepatitis C treatment, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – where to purchase vardenafil cheap[/URL – is your top choice.
clickphase.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clickengineer.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
viralcore.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Obtain [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – amoxil pill one[/URL – safely and without hassle.
I discovered the best buy pharmacy while searching for budget-friendly options for my chronic pain.
Alleviate allergic reactions with affordable options; buy https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ via the internet.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – through our secure online outlet. This critical remedy is now obtainable without hassle.
Zero hassle to safely obtain your prescriptions online. Click here: ventolin medication order for your well-being needs.
Discover incredible savings on your healthcare needs. Secure the https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ and support your heart health easily.
Explore trusted options to buy your medication safely. Click [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – lowest price tadalafil[/URL – for verified products.
For users seeking reliable hair loss remedies, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – overnight finasteride[/URL – offers crucial data.
View the latest prices for treating your BPH symptoms with generic nizagara tablets , and explore a range of options to better your quality of life.
Unlock exclusive savings on your wellness essentials. Find your perfect solution with https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ and experience enhanced health.
Zeroing in on reliable methods for ED, obtaining [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra[/URL – becomes a practical choice.
Regarding affordable healthcare solutions, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ – generic finasteride from india[/URL – are unmatched. Secure your prescription online, ensuring budget-friendliness and ease.
Research the market for affordable solutions and find the lasix/no prescription to enhance your health without breaking the bank.
Purchase, acquire, or obtain your https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ with ease, ensuring a smooth, hassle-free process to enhance your wellness journey, available online.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ – buying levitra[/URL – through our trusted website. This essential treatment is now available with ease.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to obtain this antibiotic online, you’ll find that its effectiveness in treating a wide range of infections makes it a leading choice.
Just discovered the ideal option for managing HBV? Explore priligy now for economical therapy.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ , offering a seamless purchase experience for this essential medication on the internet.
**B**attle heart rhythm disorders with AFib medication from [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena price[/URL – , your go-to destination for healthcare needs.
Navigating the vast web for authentic ayurvedic solutions? Your search ends here. Discover authentic ayurvedic remedies at [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – super kamagra[/URL – . Purchase with confidence for your natural wellness necessities.
Manage your heart rhythm disorders effectively with trusted treatment options. Order your prescription online at ventolin generika rezeptfrei .
Zero in on boosting your overall wellbeing with https://center4family.com/strattera/ , offering a herbal path to improving vitality.
Visit [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – for complete insights on using this drug safely.
Your well-being is our priority; purchase [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ – name brand levitra no prescription[/URL – on the web and commence your journey to better health today.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with non prescription amoxicillin , supplying wide-ranging treatment for bacterial infections.
Obtaining https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ has never been easier. Now you can buy the essential medicine from the comfort of your own home.
Your search for affordable medication ends here with our [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , offering a budget-friendly solution to treat your needs efficiently.
Your well-being matters, so don’t hesitate to acquire your medications online. For your mood stabilization needs, doxycycline hyclate immediately.
Struggling with nervousness? Discover relief with our top-rated solution. https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ now and start your journey towards a serener life.
Purchase the essential eye care treatment at [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ – buy nizagara online cheap[/URL – , offering affordable rates for your healthcare needs.
For those seeking hair growth solutions, [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ – prednisone online canada[/URL – offers a promising option. Explore the benefits of this treatment and learn how it can aid in combating hair loss.
Visit our website to find the generic priligy from canada for treating hair loss.
Zero worries about where to purchase your ED solutions; visit https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ for a reliable and discreet way to regain wellness.
Acquiring [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ – buy non prescription tadalafil online[/URL – has never been easier; Secure the necessary treatment through a web portal with just a single click.
Having trouble finding an affordable alternative to your medication? Look no further! Buy your nizagara prices 50 via our website for a cost-effective solution to your health needs.
The acquisition of https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/nizagara/ has never been simpler with our website. Secure your stock of this vital medicine today.
Get cost-effective treatments for your health needs. Find [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – to manage your conditions without hassle.
Secure the supply of [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – levitra without a doctors prescription[/URL – today! Enhance performance with a reliable remedy.
Looking for a cost-effective way to treat your health? Consider generic prednisone canada price for an efficient solution.
In search of affordable arrhythmia medication? Discover our budget-friendly solutions at https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ , and treat your condition efficiently.
Struggling with stress? Discover relief with our top-rated solution. [URL=https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ – vidalista en ligne[/URL – now and start your journey towards a calmer life.
I discovered that individuals looking to treat their chronic adrenal insufficiency can find relief with pharmacy prices for sarafem . This treatment is crucial for patients.
If you’re looking to diminish your ache, consider the option to https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ . This remedy offers an potent solution for controlling inflammation and pain.
I discovered an economical way to enjoy gaming from home at [URL=https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ – lasix buy no prescription[/URL – .
To discover about improving feminine libido without seeing a doctor, explore our [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy without pres[/URL – .
A Seeking an efficient antibiotic? Secure your amoxicillin online at generic amoxicillin 500 mg .
Keep your health in check by exploring options to buy vital medications. For those in need, https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ is now accessible, offering a straightforward way to maintain your wellness.
Protect your health by considering a treatment option widely discussed for certain conditions. Now, purchase [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ – price of cenforce[/URL – safely and efficiently, backed by scientific discussion and expert guidance to ensure your well-being.
Combat minor pains and aches effectively with vidalista , up for grabs on the web to help you maintain your active lifestyle without discomfort.
Having trouble accessing prescription medication? Our https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ option offers a convenient solution, enabling you to purchase vital medicine online.
Understanding your need for reliable and affordable hair loss solutions? Look no further than [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – prednisone 20 mg yahoo[/URL – , where you can purchase your solution without hassle.
Managing joint pain is easier with the right medication. Discover your options and [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – via our website today.
Maximize your vitality and focus; explore elevated cognitive performance by opting to vpxl , a decision many have taken for their well-being.
Regain control of your health by choosing to https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ . With our service, you can obtain your essential therapy effortlessly from the comfort of your home.
Navigating the web for Crohn’s treatment? Discover solutions and acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – cheap pharmacy online[/URL – via our website.
Seek remedies for hair loss now! Learn about how [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax walmart price[/URL – can assist in your fight against baldness.
Discover how free zoloft sample pack can alleviate your allergy symptoms swiftly and effectively. Explore how utilizing this treatment could change your daily comfort by minimizing sneezing, itchiness, and nasal congestion.
Visit https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ to buy your antibiotics online at incredible prices.
Get your medication for ulcerative colitis from the comfort of your own home. Purchase [URL=https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – today.
Explore advanced options for managing your health with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – , accessible for buying online.
The presence of online tretinoin no prescription ensures that patients can without difficulty access vital medication to manage their condition through web pharmacies.
X-ray the expenses before purchasing your antihistamines; explore the https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ for an affordable selection.
Discover alternative solutions for enhancing your vitality with [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – ranitidine capsules[/URL – .
Finding out the [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – nizagara india[/URL – can be an essential step. Explore choices to cut costs on this necessary therapy.
Looking for a safe way to control psoriasis? Discover how nizagara paypal accepted usa can assist in reducing symptoms without hassle.
Optimize your health today with our https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ . Secure your supply through our online store for a hassle-free experience.
Acquiring your [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – 5 prednisone buy online[/URL – just became more straightforward. Now, obtain your prescription effortlessly.
Questioning the safety and efficacy of inhaled medications? Ensure to seek advice from a doctor before opting to acquire [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – cheap order ed-sample-pack-2[/URL – via the internet.
Acquiring nizagara walmart price could help in enhancing cardiovascular health.
Procure your prescription at reduced rates; https://goldenedit.com/generic-cipro-at-walmart/ offer multiple discounts.
Maximize your wakefulness with our affordable solutions; obtain your batch of cognitive enhancers online [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – generic xenical 60 lowest price[/URL – .
Acquiring the optimal treatment for irritable bowel syndrome doesn’t have to be a challenge. You can secure xenical en madrid on-site to alleviate your symptoms effectively.
Searching for an enhanced solution to improve your well-being? Look no further! Acquire your https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/lowest-price-for-nizagara/ today and experience a transformative shift in your life.
Aiming for budget-friendly ulcerative colitis therapies? Explore [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – for options.
Regain control of your health by securing your medication without delay. [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2[/URL – is your path to manage conditions efficiently.
X-plore the myriad options to acquire your medications affordably; our portal allows you to nizagara canada buy effortlessly. This opportunity enables individuals seeking to buy their drugs at a reduced price.
X-plore cost-effective options for impotence relief with https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ , securing performance and safety.
Just found out you can buy your digestive spasms meds online? [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – offers a variety of choices for your healthcare needs.
Explore the new breakthroughs in cardiovascular wellness by exploring nizagara lowest price . Discover ways to enhance your health today.
Explore reliable options to acquire your medication safely. Click https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ for verified products.
To find out about the benefits of hormone replacement therapy, visit [URL=https://youngdental.net/item/acticin/ – acticin[/URL – . Whether you’re seeking to alleviate menopausal symptoms or manage osteoporosis, it’s your go-to source.
Looking to boost your focus and productivity? Discover a wide range of options at [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – lasix without dr prescription[/URL – . Order your medication easily and start achieving your true potential today.
Quickly find your essential hypertension relief with buy tadalista generic india , available now at unbeatable prices.
Maximize your vitality with https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ , unlocking optimal strength naturally.
Looking to maintain your hair’s health? Consider [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – as your go-to option. This effective solution is readily available for those seeking to combat hair loss problems efficiently and conveniently through an internet-based platform.
Explore affordable healthcare options and find the best prices on medications, specifically [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/ – generic maxaquin tablets[/URL – , online.
Achieve optimal well-being by controlling your condition with effective treatments. Visit maxaquin and mg for details on how we can assist you.
Aches and pains troubling you? Explore relief by https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ , a proven solution for alleviating inflammation and pain.
To boost your health, contemplate buying medications on the web through [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – sildenafil[/URL – , a reputable source for healthcare products.
Unlock the secrets to enhanced vitality and stress relief with [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/sildalist/ – generic sildalist from canada[/URL – . Uncover the premier source for this traditional herb.
I’ve discovered that those in need of quick relief from gout can take advantage of retin-a manufacturer coupon .
When considering bone density improvement, considering https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ is key. This treatment provides those affected a way to strengthen their bones efficiently.
Considering various options to manage your BPH symptoms? Discover how you can obtain [URL=https://5g-emf.com/drug/flomax/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – online, offering a convenient solution to relieve discomfort.
I’ve used quite a few iGaming sites recently, and it still surprises me how often players join a site without reading any reviews. If you need a helpful review of what a casino offers, this article worked well for me: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s easy to understand and points out what you should notice before you put in money. It’s worth your time if you prefer to play safely.
Obtain [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – buy alesse[/URL – effortlessly from reliable venues today. This drug is now accessible online, offering a convenient solution for those in need.
Unlock unbeatable deals on trazodone generic canada when you buy now.
Considering the fluctuating https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ , it’s worth checking out other platforms to acquire your pharmaceutical needs online.
I uncovered incredible deals on essential goods for emergency preparedness. Don’t miss out on these [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ – lady era online usa[/URL – .
When unexpected expenses emerge, consider generic tadalafil lowest price as a rapid option to satisfy your monetary needs.
Discover genuine remedies for improving your strength with https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ .
Acquiring [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – generic bentyl from canada[/URL – via web offers an easy pathway to managing chronic conditions. With numerous options available, guaranteeing you receive the genuine medication has never been complicated.
Find the lowest [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – on the web and treat gout effectively.
Browse our website to order high-quality medical products, including best price prednisone , with confidence.
When seeking effective antifungal treatment, consider exploring https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ for your medical needs.
Zero in on your health and well-being essentials with ease by choosing to acquire your prescriptions from our [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – clomid 100 mg online price canada[/URL – , offering you a straightforward and convenient method to oversee your health needs with without hassle.
For those looking to treat their health conditions, obtaining propecia 5mg via digital pharmacies offers a convenient solution.
Knowing the necessity for reliable hair loss treatments, individuals can now acquire https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ Buy this effective remedy on our site for managing their baldness concerns.
Just discovered you can save on your medication with a [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ – lasix without dr prescription[/URL – . Don’t miss out—grab this chance to minimize your expenses today!
When seeking to secure hair loss solutions, consider clicking here: [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin non generic[/URL – for cost-effective options.
To improve your health, contemplate buying medications online through flagyl , a trusted source for medical supplies.
In search of a cost-effective solution for your hair care regime? Consider opting for https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ , a widely acclaimed choice. Whether you’re aiming to acquire this treatment for enhancing hair growth or reducing hair fall, it’s accessible via e-commerce platforms.
Explore the myriad benefits and comprehensive details of [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/lasix/ – lasix 40 mg, order online[/URL – , your go-to guide for managing balance disorders.
Looking for a cost-effective way to control your health? Consider retin a from canada for a reliable solution.
Get the best https://tv-in-pc.com/buy-cheap-viagra/ in our digital store. Secure your health today.
Consider securing your [URL=https://mypurelifefoods.com/retin-a/ – generic retin a tablets[/URL – effortlessly through our webstore. Buy now on website for fast delivery.
Ailments requiring potent anti-inflammatory treatment? Find out about [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis/ – buy 5 cialis online[/URL – for efficient relief from redness.
Understand the price of sustaining your health by checking the strattera 25 mg france updated rates.
Consider securing savings on your fertility treatments with https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ . Discover top deals to assist in your journey toward starting a family.
Understanding the urgent need for medication, it’s now possible to purchase your medication hassle-free. No longer do you have to wait for your vital treatment. Click here at [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis/ – cialis brand[/URL – to receive your medications quickly and efficiently.
Maintain your well-being with ease by choosing to acquire your prescriptions through the web. [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – rezeptfrei vidalista 40 mg[/URL – ensures you obtain quality products quickly.
X-plore affordable options for thyroid management with our comprehensive guide on mail order kamagra . Find out how to safely acquire your treatment through our trusted platform, ensuring you get the best care without overspending.
Boost your health with https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/lowest-price-for-nizagara/ . Whether you’re looking to enhance your immunity or aid your body’s natural defenses, this product is available virtually for purchase.
Unlock improved attention and vitality with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil uk[/URL – , your ultimate solution for staying alert.
Discover unparalleled savings with our exclusive offer: [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/viagra/ – pharmacy prices for viagra[/URL – . Secure your batch immediately and experience the efficacy of this treatment.
Browse our site to discover amoxicillin information , ensuring you secure premium antibiotic options at matchless prices.
To discover the latest https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ , browse our site.
Navigating the pharmaceutical marketplace for solutions can be daunting, but finding the [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – doesn’t have to be.
Uncover affordable treatment for scabies with our cost-effective propecia , the preferred solution for getting rid of pests.
Ensure you secure antibiotics responsibly; https://jawany.com/cipro/ with ease for your health needs.
Just discovered the most affordable option for Tadalafil in Australia? Click here at [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – .
oakandriver – I appreciate oakandriver quality, items arrive timely and well packaged.
Explore the options and acquire your medication from the comfort of your home at [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ – order doxycycline[/URL – .
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Get amoxil 1000 originale prezzo safely and without hassle.
Discover reliable and effortless ways to obtain your medication with just a click. https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ offers a simple solution for your needs.
X-plore affordable options for thyroid management with our comprehensive guide on [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy safety[/URL – . Find out how to safely purchase your treatment through our trusted platform, ensuring you get the best care without overspending.
pin up hisobni to‘ldirish pin up hisobni to‘ldirish
Facing unpredictable menstrual cycles? Explore how [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – zithromax best price usa[/URL – can help in regulating your hormone levels.
Secure the supply of zithromax coupons now! Enhance performance with an effective solution.
Jumpstart your journey towards better health with a simple way to acquire your medication. Whether you’re looking to reduce inflammation, our platform offers an array of options to suit your needs. For those specifically seeking Budesonide treatment, https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ here and benefit from prompt relief.
Manage your own hypertension effectively with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil[/URL – , available to acquire on the internet.
Understanding the need for stomach ulcer treatments? Explore the most trusted options and uncover [URL=https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ – tretinoin without prescription canada[/URL – , securing your well-being is first.
Curious about securing the buy tretinoin online ? Explore your options on the web.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can buy https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ through reliable web-based pharmacies, offering a convenient way to control their symptoms.
If tackling your cardiovascular well-being has become a priority, consider [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ – nizagara.com[/URL – as your preferred option, ensuring efficient prophylaxis against myocardial infarctions and strokes.
Looking for a way to tackle your condition? [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine in usa[/URL – might be the answer you’re seeking. Explore how this medication can help you today.
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly; secure bentyl overnight to elevate your health through a trusted source.
Discover the latest https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ and explore options for purchasing this medication via the internet.
Aiming to minimize your prostate enlargement symptoms? Explore how [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/viagra-jelly/ – viagra jelly without dr prescription usa[/URL – can assist.
Zoning in on reasonably priced angina relief, discover the best deals on levitra walmart price via digital pharmacies.
Looking for an affordable solution to enhance your performance? Explore the array of options; https://endmedicaldebt.com/drug/vidalista/ could be your answer. Consider acquiring these potent remedy from online stores for a hassle-free experience.
Obtain your medication effortlessly at [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – purchase sildenafil without a prescription[/URL – , the leading site for competitive prices on pharmaceutical products.
Manage your allergies seamlessly with [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – cheapest viagra 75mg[/URL – , now available for purchase online.
Regarding anxiety or OCD treatment, buying nizagara is a viable solution; explore alternatives or obtain it online.
Just in time for your treatment, obtain https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ for managing your health condition effortlessly via our website.
Just discovered you’re in need of a rapid solution for better endurance? With [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone for sale[/URL – , find your answers and enjoy improved performance sooner than you think. Now you can purchase this remedy swiftly to ensure your readiness.
Explore the market for osteoarthritis solutions and find the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ – http://www.flagyl.com[/URL – . Secure your medication online for improved joint health.
Looking for an affordable solution to enhance your eyelash growth? Search no more! vidalista 20 recensioni offers a variety of options to buy your eyelash growth solution virtually.
To find the top deals on pain relief, click here: https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/ticlid/ . Whether you require a quick solution, this link offers a wide variety of solutions.
Visit [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – buy vidalista online[/URL – and discover a trusted way to acquire your medication digitally.
Explore the range of options for controlling menstrual disorders by purchasing [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – viagra 50 mg without a prescription[/URL – .
Just discovered you’re in need of gallstone treatment? Explore your options and prednisone tab 5 mg . Whether you’re aiming to order this treatment online, rest assured, there’s a seamless and convenient method awaiting you.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover special https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ for savings on essential treatments. Obtain yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis for sale overnight[/URL – , your go-to source for purchasing potent ED solutions on the web.
Zap your health concerns away! Discover the convenience of securing your medication online. Don’t miss the chance to purchase [URL=https://umichicago.com/acivir-dt/ – acivir dt[/URL – , a significant breakthrough in managing well-being needs.
Residents in Columbus, Ohio, seeking immediate financial aid can explore online nizagara purchase for convenient solutions.
Maximize your savings on stroke prevention medication by checking https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ , where you can uncover competitive costs.
Quickly secure the osteoporosis medication at an unbeatable price here: [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ – levitra 20mg[/URL – .
pin up yuklash android pin up yuklash android
Maximize your wellness without leaving home; [URL=https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ – vente prednisone france[/URL – seamlessly. Opt for effortless, secure, and swift delivery of pharmaceuticals.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; acquire your where to buy amoxil in amsterdam online for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Your search for effective and safe medication ends here; https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ offers you the opportunity to acquire top-quality medication conveniently.
Jumping onto the bandwagon of improving your health shouldn’t be complex. Find effective solutions with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy buy online[/URL – , and welcome a more robust lifestyle right away.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your personal health needs, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – lowest price generic amoxicillin[/URL – online can be a straightforward process.
Various individuals searching for solutions to treat premature ejaculation turn to dapoxetine as a dependable option.
Discover methods to tackle pests with https://youngdental.net/item/acticin/ , your prime solution available on the internet.
The ultimate guide to enhancing your endurance safely and effectively is here. Discover now, the myriad benefits of the [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine without a doctor[/URL – .
For those seeking relief from seasonal allergies, you can now order [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ – esomeprazole[/URL – . This medication is accessible at economical prices, offering a convenient way to control your symptoms.
X-ray your budget and find out how much you could save on eye drops by checking the lowest price generic pharmacy .
Various individuals look for methods to economize on their medication expenses. By utilizing a https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ , patients can significantly reduce the price of your prescriptions.
Visit our site to purchase [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – , ensuring you get your medicine promptly.
Maximize your savings on medications by exploring various offers. Find coupons on medication effortlessly online. For cholesterol-lowering solutions, check out [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – for the best deals.
Understanding the necessity of managing stress, one can buy finasteride from canada via internet effortlessly.
Secure
Struggling with high cholesterol? Secure your health by opting to [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – . Obtain it today and start your journey toward a healthier lifestyle.
Procure your solution with ease; extra super avana online to address your needs efficiently and securely.
Considering various options to manage your BPH symptoms? Discover how you can obtain https://jawany.com/priligy/ on the internet, offering a simple solution to alleviate discomfort.
Rejuvenate your love life by exploring the most affordable solutions available. Find [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ – prices for modvigil[/URL – to enhance your intimacy with convenience.
Combat aches swiftly with [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – , available for order online, securing speedy relief.
Keep your prostate health in check with lasix india pharmacy , available for purchase online, ensuring you receive top-quality treatment affordably and efficiently.
When seeking excitement and thrill, consider diving into the digital realm of gaming at your convenience. Explore a virtual plethora of entertainment options with https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ , where each click unravels new adventures and possibilities.
Yes, purchase your medications effortlessly through [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – generic propecia canada pharmacy[/URL – , offering a broad assortment of medical supplies.
Secure budget-friendly solutions for enhancing your vision by exploring the viagra price at walmart . Our specially formulated drops offer a hopeful approach to enhancing eye health considerably.
Yes, purchase your pharmaceuticals effortlessly through https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ , offering a wide range of medical supplies.
Get your amoxil easily from [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – order amoxil 250 overnight[/URL – , offering swift shipping to satisfy your requirements.
Ensure you secure the lowest rate for [URL=https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara capsules for sale[/URL – by searching through our options.
Buyers interested in acquiring kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1 en los ojos could easily Order their Medication through trusted internet-based outlets, ensuring speedy and secure delivery to their doorstep.
Quickly buy your medicine with no hassle. Click here for https://seraamedia.org/item/viagra/ .
Procure your [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ – safe online retin-a[/URL – effortlessly through our website, ensuring a seamless acquisition. This option is optimal for those seeking efficacy without the high cost.
Need to control your chronic pain? Order amitriptyline over the internet with confidence and start your journey to recovery.
Unlock the potential of antiviral therapy by choosing to https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ . Ensure optimal health outcomes by securing this essential treatment from our website today.
If you’re seeking to boost your stamina safely, consider checking out [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ – 100mg generic nizagara[/URL – for a trusted solution.
Just discovered you can secure to get nizagara without the hassle through our reliable online platform.
Boost your wellness with authentic supplements; buy your https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ from our website for optimal health benefits.
When looking to purchase relief for motion sickness without a doctor’s prescription, consider [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ – zoloft to buy[/URL – as your preferred choice for relief.
Now, obtain your supply of [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – effortlessly. Order virtually without delay.
If you’re looking to alleviate your ache, consider the option to nizagara coupons . This remedy offers an potent solution for controlling swelling and pain.
You can acquire your essential eye medication https://shilpaotc.com/nizagara/ .
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 650mg[/URL – , and Secure a supply of crucial antibiotics easily on the web.
Quality healthcare solutions just a click away! Purchase your comprehensive [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ – levitra for sale[/URL – effortlessly from reliable pharmacists.
Obtaining pristiq details is crucial for individuals seeking to manage hair loss effectively.
Zeroing in on your health needs? Discover https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ and find your pathway to improved well-being effortlessly.
In search of budget-friendly heart medication? Look no further! Procure your [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – buying lasix[/URL – at this moment.
Unlock unbeatable deals on anti-diarrhea medication at [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ – xenical[/URL – , your ultimate source for managing digestive disturbances.
Need to improve your alertness? Acquire buy generic propecia on the web for a safe and effective solution.
When looking to address OCD symptoms, consider exploring https://homegrownscholars.com/item/viagra/ as a potential remedy.
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – lowest retin a prices[/URL – can assist in alleviating urinary symptoms linked to an enlarged prostate.
One can easily obtain their prescription for [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era[/URL – by choosing to buy it from a reputable website.
For those looking to purchase their heart health medication online, finding a dependable source is key. cheap tretinoin online offers a trusted option for procuring your treatment with ease.
Purchase your medications with ease; buy your meds online at https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ , ensuring reliability and comfort.
Find affordable alternatives or generic versions of brand-name medications easily online. Whether you’re looking to acquire this heart health-supporting medicine without a prescription, verify you’re getting a legitimate solution through verified channels. [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/prednisone-without-pres/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – offers a reliable route to manage your health needs efficiently.
Unlock savings on your desmopressin needs with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra canadian pharmacy[/URL – , your go-to destination. Acquire a vital medication on the internet with ease.
Zero reasons to wait! Acquire your solution for enhanced stamina now at lasix 40mg .
You can secure your https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ with ease and safely through our website.
Access the most competitive [URL=https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara non generic[/URL – for your antimalarial needs on the web.
Researching for the most affordable solutions for deterring insects? Stop here. Find the levitra 10mg right away.
Acquire your health solution now! Purchase https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ swiftly for cardiovascular well-being.
Discover your solution for enhanced vitality; find reliable options and buy [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ – cheapest lasix online in the uk[/URL – today.
Your search for a safe, reliable method to improve your intimate life ends here. Secure your doxycycline 100 order today and experience the difference firsthand.
Visit our website to purchase your essential health supplements with ease, including https://endmedicaldebt.com/drug/vidalista/ , designed to support prostate health.
Explore affordable ADHD treatment options by obtaining [URL=https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – to control symptoms effectively via the internet.
Improve your health by visiting [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – amitriptyline without an rx[/URL – to find a vast selection of healthcare products.
Obtain remarkable savings on your eyelash growth serum by exploring the vpxl shipped from usa , offering you the chance to purchase effective solution on the internet.
Save on allergy relief by exploring our savings on https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ , allowing you to manage symptoms affordably.
Now, secure your heart health medication conveniently [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – generico de amitriptyline[/URL – .
Discover how to remarkably boost your sleep quality with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ – zoloft 25mg[/URL – , your go-to solution for an undisturbed slumber.
Procure your tadalafil on line with ease. Purchase the vital medication via our website swiftly and securely.
If you’re in the market for an effective solution to fight bacterial infections, think about https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ . This drug is widely recognized for its effectiveness against numerous types of bacteria.
Discover the most cost-effective options for managing intermittent claudication with [URL=https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ – tofranil for sale overnight[/URL – . Secure your health without draining your wallet today.
Keep your vitality high and performance unmatched; obtain retin a for unparalleled endurance and satisfaction, enhancing your lifestyle.
Xploring options for epilepsy management? Consider acquiring Phenytoin, commonly known as https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ , to regulate seizures. This method provides ease in obtaining essential medication.
You can locate the most current [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/clomid/ – clomid generic pills[/URL – by checking our webpage.
If you’re in the market to purchase an cost-effective solution to your vertigo, look into [URL=https://jawany.com/priligy/ – priligy 90mg[/URL – . This medication helps in alleviating the symptoms of vertigo, improving your overall well-being.
Your quest for a cost-effective solution to hair loss ends today! Explore a wide variety of options and secure your supply of levitra without a doctors prescription . Don’t let thinning hair dictate your confidence any longer; take your chance now.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Search no more. Get https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ safely and without hassle.
Seeking effective acne treatment? Locate safe [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline kaufen in china[/URL – options easily on the web.
Having trouble locating Flagyl? Your search ends here. Acquire it in a secure and swift manner from [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine generic[/URL – , where your well-being and contentment are of paramount importance.
Just in case you’re looking to save your pharmaceuticals, consider checking out the levitra capsules for sale for competitive rates.
Discover affordable solutions for ED by visiting https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ , where you can acquire your drugs easily.
Purchase your essential medicines conveniently with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone without prescription[/URL – , offering a seamless and secure buying journey on the web.
Looking to reduce your healthcare costs? Discover the in man uk stablon to economize on your prescription.
Discover affordable options for impotence by visiting https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ , where you can acquire your prescriptions effortlessly.
Exploring ways to acquire migraine relief? Look no further; comprehensive details on [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – how to get stablon without perscription[/URL – are available, ensuring you have access to effective treatment options without compromising efficacy.
Purchase, secure, or acquire your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – ventolin canadian pharmacy[/URL – easily via our platform to enhance, boost, or elevate eyelash growth effectively, efficiently, or swiftly.
Zeroing in on enhanced vigour and vitality? Discover the ultimate solution with ventolin , your go-to for unparalleled strength and endurance. Secure today for an unmatched boost in your well-being.
Visit https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ to buy your medication online at incredible prices.
Before you decide, discover how [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ – buy generic asthalin hfa inhaler[/URL – might be the answer you’re seeking for managing tension.
Explore cutting-edge healthcare solutions and buy your drugs through the internet with ease. Click here: [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/meldonium/ – meldonium online usa[/URL – for seamless access to medicinal services.
Zealously enhance your eye’s fringe growth with safe solutions; explore your options at finasteride 5mg .
Looking to control your condition effectively? Discover how to acquire https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ and commence your journey towards enhanced health today.
Quickly secure your [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – retin a online canada[/URL – sans trouble of seeing a doctor.
Seek the [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ – ventolin inhaler overnight[/URL – efficiently. Find your ‘must-have’ medication without breaking the bank.
Combat arrhythmias with ease, acquire ventolin inhaler online for effective treatment.
The requirement for reliable answers to improve men’s health has never been more vital. Discover the effectiveness of https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ , a leading choice for addressing such concerns.
Maximize your savings on osteoporosis treatment by seeking the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil uk[/URL – . Discover affordable solutions today.
X-plore the world of hormone therapy with us; procure your [URL=https://rrhail.org/item/xenical/ – buy xenical w not prescription[/URL – virtually.
When looking for an affordable solution to your health needs, consider hydroxychloroquine walmart price . With options to acquire this essential medication at a budget-friendly cost, it’s never been easier to manage your health effectively.
Just discovered an unbeatable offer on https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ ? Find out about incredible savings today!
Discover the latest [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – hydroxychloroquine online no script[/URL – and look into alternatives for purchasing this treatment via the internet.
Looking to secure treatment for thinning hair? Locate the most effective products on our website. Your search ends here: [URL=https://purefmonline.com/pill/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – .
Boost your fertility journey with mail order malegra . Order the essential pharmaceutical online and begin your path to parenthood.
Acquire effective hair loss solutions; explore our https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ for proven results against androgenetic alopecia.
Uncover the ultimate way to enhance your wellbeing; discover our exclusive [URL=https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ – retin a online pharmacy[/URL – . This solution is perfect for those seeking to elevate their lifestyle quickly.
Now, get your vital medication via a xenical , ensuring you maximize your well-being outcomes.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ online for effective bacterial infection treatment.
Yes, locate the lowest [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – for alleviating your allergy symptoms.
Discover reliable remedies for improving your sexual health with confidence at viagra .
Harness the power of enhanced well-being by opting for our https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ , offering a revolutionary option for those seeking robust performance.
When considering treatment options for prostate cancer, considering medication options is key. Locate dependable options for management with [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/propecia-1mg/ – propecia sale generic[/URL – .
rankverse.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Receive the best deals on [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – interlase lasix[/URL – by browsing our site.
Discover affordable relief for joint pain and inflammation. Now you can order trazodone online . This powerful treatment offers the solution for alleviating discomfort with ease.
Secure the best deal on https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ by browsing through our site.
Looking to purchase analgesic gel? Visit [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – today for a wide selection of reliable treatments.
clickflux.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Explore our vast selection of [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – retin a online no script[/URL – , perfect for achieving precise application.
Need to save on your prescription costs? Find the best deals by accessing a retin a online no script today.
Need to acquire your alopecia remedy? Find cost-effective options with https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ , ensuring you obtain premium therapies at a slice of the expense.
When seeking cost-effective solutions for altitude sickness, one must consider the myriad of options available. Secure your health by visiting [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – where affordability meets quality. Here, buyers can locate critical medication without compromising their budget.
Having noticed an improvement in their performance, many are turning towards [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ – on line vpxl[/URL – for a reliable solution.
Maximize your health outcomes by opting to buy your prescriptions online. For those in need, mail order tadalafil is a hassle-free way to secure your essentials quickly and efficiently.
Acquire your wellness boost by choosing to https://tv-in-pc.com/tadalafil/ , a practice that’s effortless, ensuring that you are always supported in your health journey.
Discover the best affordable solution for migraine relief by clicking [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – . Find your stock without spending a fortune.
Curious about affordable treatment options for your condition? Find out a cost-effective alternative with [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/retin-a/ – retin a no prescription[/URL – . Ideal for those seeking cost-effective options for their health care.
Discover cheap solutions for osteoporosis management: kamagra buy in canada . Purchase your supply immediately and take a stride towards stronger bones.
Keep your health in check by exploring options to order vital medications. For those in need, https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ is now accessible, offering a simple way to maintain your wellness.
Harness the convenience of modern technology by opting to order your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – , ensuring an effortless way to procure your treatment.
X-plore the myriad benefits of enhanced endurance and vigor with just a click. Obtain your prescription of unparalleled performance enhancement immediately at [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – super kamagra price walmart[/URL – .
Managing pain efficiently and safely is crucial for overall health. Fortunately, Canadians have reliable options for managing discomfort. tadalafil on line offers a versatile solution, allowing you to obtain effective pain relief securely and swiftly.
Discover budget-friendly options for managing your health; buy https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ through our website.
Avoid hay fever discomfort with premium [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – tadalafil information[/URL – , offering effective relief without the high cost.
Venture into a world of convenience and relief with our over-the-counter nizagara 100mg . Buy your treatment on site today.
Obtaining Clomid at the best prices is now achievable. Visit our website to order your supply of Clomid for fertility treatment. https://embcselma.org/product/clomid/ today!
Looking for a remedy to reduce or stop heavy bleeding? Discover [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil cost[/URL – —your preferred option.
Quest for cost-effective ED treatments? Uncover a solution at [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ – fildena en ligne europe[/URL – , featuring a wide selection of quality alternatives.
Acquiring nizagara is now feasible through credible internet drugstores.
Explore your options for managing hypertension by visiting https://nesttd-online.org/item/nizagara/ , where you can learn about non-prescription solutions.
Explore affordable solutions for your health with [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-75mg/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – . Discover unparalleled deals to enhance your wellness journey now.
inspire your journey – Items are motivating, navigating the site is smooth and easy.
The requirement to purchase medications with convenience directs many to search for dependable sources. [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy-com-lowest-price/ – priligy usa without a prescription[/URL – offers a secure solution to fulfill your needs devoid of a prescription.
Obtain your hay fever relief medication effortlessly. buy prednisone online provides a convenient way to manage symptoms.
Considering urgent antibiotic requirements, acquiring https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ online ensures a rapid solution.
I discovered a budget-friendly way to enjoy gaming from home at [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – .
A comprehensive guide to obtaining your prescriptions safely: Discover how to order tretinoin . This resource provides essential information on how to ensure you’re acquiring genuine medication from credible sources.
When looking to enhance your vitality, consider opting for https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ , a reliable choice. Available for purchase via the internet, this option promises boosted effectiveness.
Improve your lifestyle effortlessly by opting to order high-quality pharmaceuticals online. [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ – fildena coupon[/URL – offers a reliable, safe solution for enhancing performance.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Discover [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ – shopping for cialis[/URL – to boost your vitality efficiently and confidently.
I’ve discovered that finding the best pharmacy can be challenging. Yet, with proper research, you can reduce expenses on fertility treatments.
Understand the need for relief from allergies and order https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ online.
fashion choice corner – Market items are neatly displayed, navigation feels fast and easy.
Looking for an affordable way to enhance your well-being? Find the advantages of [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – ranitidine[/URL – , perfect for those seeking efficacy without sacrificing budget.
Searching for an enhanced solution to enhance your performance? Look no further! Purchase your free trazodone canada today and experience a revolutionary shift in your life.
Discover your pathway to relief from minor aches and pains by securing your next supply of https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ through our website.
Discover how [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – retin a[/URL – can benefit in managing your cholesterol levels. Find options to ensure cardiovascular wellness.
Researching affordable options for HIV treatment? Compare and find the most economical [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – fildena 50mg dose[/URL – on the market.
To find out about the benefits of hormone replacement therapy, explore online prednisone no prescription . Whether you’re seeking to reduce menopausal symptoms or tackle osteoporosis, it’s your go-to resource.
Maximize your savings on medication for prostate cancer treatment by exploring the https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ . Find cost-effective solutions on the web.
Given the various options for hormone therapy, those looking to alleviate menopausal symptoms might consider checking [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – . With several buying channels, selecting the appropriate product on the web can offer alleviation efficiently.
When seeking to improve your vitality, find the top options available. Purchase [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/womenra/ – womenra coupon[/URL – , offering a safe and easy option for your needs.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Get non prescription amoxicillin safely and swiftly.
Purchase your stress-relief pills safely from https://center4family.com/ventolin/ to ensure tranquility without breaking the bank.
View our latest [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ – celebrex[/URL – to discover how individuals can treat arthritis pain. This treatment offers alleviation for those suffering with chronic conditions.
Regain control over your health by visiting [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil price walmart[/URL – , your ultimate destination for quality pharmaceuticals.
Zero hassle to securely obtain your prescriptions online. Click here: viagra for your well-being solutions.
Keeping your health in balance, purchase https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ to improve your health.
To purchase your birth control effortlessly, think about acquiring [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – alesse online[/URL – . This method guarantees privacy, convenience, and a wide selection of options.
Considering diverse treatment options, it’s crucial to discover affordable solutions. For those seeking hormone therapy alternatives, [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – viagra vendita on line[/URL – offers a viable choice.
To discover the latest and most competitive purchase discount doxycycline on the internet , visit our webpage.
Harness the power to boost your well-being by choosing to order https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ .
Explore options to acquire [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – herbal-max-gun-power ad[/URL – , offering a convenient way to secure your medication without leaving home.
Over time, I’ve checked out lots of iGaming sites recently, and it’s interesting how often players sign up without verifying anything. For anyone searching for a simple explanation of what a casino offers, this article helped me a lot: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s very clear and points out what you should notice before funding your account. I recommend giving it a look if you want to stay on the safe side.
Secure your well-being effortlessly by opting to purchase prescriptions from [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2[/URL – . Explore a wide range of health products online.
“Quickly get your treatment with tadalista for sale , offering a convenient solution for enhancing your wellness.”
You can locate cost-effective https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ for controlling your nasal allergy symptoms online.
Zest up your love life with buying your [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – prednisone post[/URL – via the internet.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive lowest price on cialis 20mg . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to save on pharmaceuticals.
Zero hassle: purchase your https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ easily.
Please explore how to obtain vital health supplements at surprisingly reasonable prices with our [URL=https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ – vidalista without a doctor[/URL – .
Purchase your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ – order prednisone online[/URL – online to support memory health efficiently and affordably.
Cut costs on your medication purchases! Find unbeatable deals on canada xenical . Order now and save significantly on your medical expenses.
Buy the optimal solution for scabies treatment at the most competitive rate; click here for https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ .
Explore affordable ADHD treatment options by securing [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – generic nolvadex from india[/URL – to handle symptoms effectively through web pharmacies.
Revitalize your vitality with a natural solution; [URL=https://goldenedit.com/generic-cipro-at-walmart/ – beste cipro[/URL – . Rediscover the force of nature’s offerings right away.
Unlock unparalleled convenience by ordering your medications via lady era.com lowest price . This streamlined process guarantees a trouble-free path to obtaining your necessary medical solutions.
X-plore affordable antibiotic options; https://goldenedit.com/generic-cipro-at-walmart/ is your answer to combat bacterial infections with ease.
Unsure where to purchase effective migraine relief? Visit [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-without-a-doctor/ – prednisone 10mg online for sale[/URL – for a trusted option.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with [URL=https://kileensgardenboutique.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – , and explore various solutions to enhance your quality of life.
Visit doxycycline to secure your medication with ease.
Looking for a reliable source to get your prescriptions without leaving home? Visit https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ to order your health needs online with ease.
Normally I don’t write detailed posts, but right now I decided to share one recent session about a nice win at a casino site.
Recently I’ve been playing at nllalabet.com, mostly in the evenings and with a small bankroll. I joined because the intro bonus looked interesting and the bonus rules seemed not too bad compared to many other sites. The signup process was no big deal: a few standard fields and a quick confirmation link, then I was good to go.
For my initial deposit I didn’t go crazy and put a low amount into my balance. I went straight to the slots section because that’s what I enjoy most. I sorted by top games and picked a slot with a bonus buy feature, hoping for a big hit.
At first it was a small rollercoaster: small wins and losses and free spins with low payout, and I was thinking about stopping because my balance was slowly dropping. Then it finally happened: I triggered a strong bonus round with multipliers all over the screen, the slot kept hitting combinations and the bonus feature boosted my balance way up. For me it was a serious win compared to my regular sessions.
I didn’t keep spinning forever; after a few more test spins I decided to stop and send a payout request. The withdrawal process was pretty standard: the casino asked me to verify my account with ID card or passport. I sent everything within an hour, and the verification was approved after a short wait. After that the money was transferred to my wallet and I received it within a reasonable time.
I’m not saying this casino is always paying huge, and of course you can also have bad days, but in this case my experience was pretty fair: clear terms, decent support and no drama with the withdrawal. This is not financial advice: gambling always involves risk, so only play what you can afford to lose and remember it’s just a game.
Secure your wellness journey with a click by opting to buy your medication online at [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone prices[/URL – , ensuring easy access to health.
Keep your health optimized by obtaining viagra , a proven solution for enhanced efficacy.
Looking to enhance your lashes? Consider https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ for longer, fuller eyelashes. Available now, you can order these treatment on the web.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, purchasing [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – order hydroxychloroquine[/URL – online offers a economical option.
Knowing how essential it is to manage your hypertension, you can obtain a reliable solution with propranolol via our site.
Quickly secure your https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ via the web and discover the benefits!
Secure your wellbeing effortlessly; order your meds without hassle at [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – .
Gain immediate access to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – and reduce your concerns with a quick tap.
Just discovered that you can secure purchase retin a online from the web? This ocular solution is ideal for managing glaucoma, leading to better eye care.
Ensure you acquire the optimal deal for your needs. Consider exploring https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ for a variety of choices.
Before making a decision, consider exploring options to [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – prednisone for sell[/URL – for managing one’s heart rate.
You can locate effective solutions for thinning hair without breaking the bank. Explore the [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – for cost-effective options.
Just clicked on lowest price generic vidalista ? Ensure to explore our website for additional information and learn how this medication can assist in your treatment journey.
X-ray the expenses before purchasing your antihistamines; explore the https://damcf.org/prednisone/ for an economical option.
Just discovered, [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone best price usa[/URL – offers a breakthrough option for patients seeking alternatives. Now, secure your supply without hassle.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – cialis without dr prescription usa[/URL – . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to reduce expenses on pharmaceuticals.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Look into generic cialis 20 cheap for sale , a economical and trustworthy option for boosting your performance.
Secure trusted treatment for scabies and lice with https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ , available now.
Given the immense importance of consulting healthcare professionals, acquiring [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without prescription[/URL – can be risky. It is always recommended to pursue guidance from a physician prior to buying any medications, especially those intended for hormonal therapy.
Explore a myriad of ways to acquire [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – buy super kamagra uk[/URL – , ensuring effective treatment without sacrificing efficacy or safety.
Zero in on significant savings for your hormone therapy needs. Discover the lowest prices on hormonal balance medications at paypal nizagara . Optimize your health without stretching your budget.
Before opting for conventional methods, consider other avenues to purchase your medications. One reliable option is to https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ , offering a straightforward way to manage your health.
Maximize your savings when you obtain your heart health prescriptions by checking out the latest [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – nexium[/URL – .
Obtain your treatment for hair loss efficiently. Purchase tadalafil buy via our website and start your journey towards restoring full, healthy hair with ease.
You can purchase your essential eye medication https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ .
Aiming to lower your prostate enlargement symptoms? Discover how [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – generic tretinoin in canada[/URL – can help.
Maximize your savings and realize better health outcomes by choosing to sildenafil .
A multitude of options for improving your health is available, but https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ is distinguished due to its efficacy.
Amidst the myriad options for managing pain and inflammation, [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ – nizagara[/URL – stand out as a potent solution. Individuals seeking relief can acquire this remedy from online pharmacies, offering an easy way to address their symptoms.
Seeking the highest quality fertility drug for your treatments? Your search ends here! Purchase your [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix generic europe[/URL – safely and without hassle.
To reduce your pain, consider buying retin a generic canada to help with your recovery.
Tired of dealing with persistent eye strain? Discover the premier solutions at https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ , your go-to source for effective eye care.
Seeking to purchase menopause relief treatment? Discover your solution with [URL=https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ – canadian amoxil online costs[/URL – , an exceptional choice for improved well-being.
With rising healthcare costs, it’s crucial to find the best option. For those seeking cholesterol reduction, [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – can be essential.
Keep your eye health in top condition with our advanced solution options. Discover more and secure your supply cheap viagra online promptly.
Regarding heart health management, consulting a healthcare professional and exploring options like https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ can be advantageous.
I understand that finding an authentic source to obtain your medication can be challenging. If you’re looking to [URL=https://tradarchersworld.com/ – cheap generic nizagara[/URL – , explore your options carefully. Always ensure that you are engaging with a reputable vendor to protect your health.
Discover unique [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ – tamsulosin[/URL – , perfect for controlling seizures. Purchase today for efficient results.
Unlock access to top-tier ups super-active-pack-20 and effortlessly manage your ocular pressure with ease. Select from a wide variety of alternatives accessible for speedy delivery.
Just discovered you can purchase essential medication https://sjsbrookfield.org/frumil/ , simplifying your healthcare management.
A Revolutionary Solution to Healthcare is Here! Now, discover a broad assortment of health solutions solely at [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin price at walmart[/URL – .
Understanding the importance of managing cholesterol levels cannot be overstated. nizagara offers an effective solution. Consult your healthcare provider to ascertain if it’s right for your condition.
Acquiring your medications has never been more straightforward with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ . Order right away for quick delivery anywhere.
Cut down on your healthcare expenses by obtaining your [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – cheap generic lasix from india[/URL – here! Now you can obtain significant savings on your medication costs.
Discover affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction by visiting cialis without a doctor , where you can buy your medications conveniently.
Acquire your https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ seamlessly online.
Discover stress-relief options with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – cheapest vardenafil[/URL – , your go-to for next-day delivery.
Having trouble with gastric ulcers? Locate low-cost relief with [URL=https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara non generic[/URL – , your leading remedy for soothing gastrointestinal discomfort.
Experiencing asthma symptoms? Find relief at the asthalin . Buy the inhaler on our website for fast symptom control.
Boost your eye beauty safely with our easy-to-use solution; https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ required. Perfect for boosting eyelash growth effortlessly.
Uncover the price of controlling nasal symptoms with [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/moduretic/ – lowest price for moduretic[/URL – , your solution for relief.
Quest for budget-friendly ED solutions? Find the remedy at buy fildena without prescription , offering a vast array of top-notch choices.
When seeking natural remedies for digestive health, consider exploring https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ . Available for purchase through multiple platforms, this fruit may offer therapeutic effects for your health.
Get the most affordable rates on manufacturer’s Duprost by clicking [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ – propecia canadian pharmacy[/URL – . This drug is crucial for treating BPH symptoms.
Relieve your BPH symptoms today! Discover our range of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – buy cheap flomax[/URL – , specially designed to boost your urinary flow and general health.
Discover the convenience and privacy of obtaining your erectile dysfunction medication with viagra price walmart , ready for you.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your personal health needs, https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxicillin/ online can be a simple process.
Investigating the realm of hair loss solutions, countless individuals have turned their attention towards [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – sildenafil[/URL – , a product celebrated for its efficiency. Those in search of an effective solution for hair thinning might discover this pharmaceutical on various websites, ensuring a discreet and convenient acquisition.
Zealously search for solutions to enhance your health? Examine viagra for powerful solution.
Relieve digestive discomfort quickly with our natural solution. Go to https://embcselma.org/product/cialis/ for further details.
Discover the benefits of [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin price at walmart[/URL – for managing hypertension. Obtain your well-being solution easily via our website.
X-plore your options for increasing eyelash growth with [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large[/URL – , available for purchase online.
Looking to get Depo-Medrol? Find the most cost-effective staxyn .
Quickly discover the https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ and cut costs on your medication effortlessly.
Harness the power of effective antifungal medication by exploring [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – . Secure your health today by purchasing this vital treatment online.
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable HIV testing solution. Acquire your [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – today and ensure your status promptly from the comfort of your home.”
Seeking lowest deals for cialis 10mg ? Uncover unmatched prices and quality now!
Quiet nights can often be disturbed by restless legs, a common ailment affecting many. To combat this, trusted solutions like https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ can be invaluable. If you’re seeking relief, contemplate purchasing this solution online.
Venture into a world of enhanced cognitive health by exploring options to purchase [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical 60mg[/URL – , a proven solution for addressing dementia symptoms.
Visit [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy us pharmancy[/URL – to purchase your cardiovascular health medication affordably.
Researchers have discovered that purchasing prednisone capsules for sale offers an affordable option for fighting against certain conditions, ensuring both quality and savings.
Seeking a safe, dependable method to get misoprostol? Look no further. https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ offers a hassle-free solution.
Obtain cost-effective hormone replacement therapy options with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ – prednisone overnight[/URL – . Explore various options for your health needs online.
“Unlock your pathway to healthier heart function; purchase [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – online and embrace your journey towards optimal cardiovascular health.”
Ensure to acquire your medication securely best price on nizagara 25mg , delivering dependable and fast support.
Obtain your prescription for https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ with ease, ensuring you receive real medication. Buy without worries through our website.
Just released! Discover the latest solution for managing your health needs – [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – purchase lasix[/URL – . Available now, secure your supply through our authorized portal.
Zero in on soothing your eye discomfort with unique formulations! For instant relief from inflammation and irritation, discover your solution with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – levitra walmart price[/URL – . This trusted solution is essential for those seeking reduction in eye discomfort without straying from their budget.
Secure your wellness easily; order pharmacy kaufen deutschland , accessible on the web for enhancing female libido.
Questioning where to find an effective treatment for your needs? Search no more. https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ provides a versatile solution for those seeking top-notch medical care.
Given the fluctuating expenses, finding the lowest price for medication can be a daunting task. Whether you’re looking to treat urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ – flomax 0.4mg[/URL – offers a cost-effective solution.
Browse the site to discover [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil price at walmart[/URL – , ensuring you obtain high-quality antibiotic solutions at incomparable prices.
Regain your vitality and enhance your physical fitness levels with the help of generic tadalafil discounts . Offering a solution for men seeking to balance their hormonal levels, this product is available for purchase on the web.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with https://seraamedia.org/flomax/ , a treatment for alleviating prostate enlargement symptoms.
Visit [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – to purchase your antibiotics on the internet at fantastic prices.
Zero pain, maximum relief! Get your hands on the most affordable solution for your discomfort. Purchase your [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia 5mg[/URL – now and start feeling ease from pain instantly.
Nab your dose of health improvement by opting to purchase your prescription with ease. Click here to pharmacy ordering on line and begin your journey towards better well-being without delay.
Seeking a safe, reliable method to acquire misoprostol? Look no further. https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ offers a hassle-free solution.
Research indicates that accessing [URL=https://jawany.com/amoxil/ – amoxil canada 250 pharmacy[/URL – can be a crucial step for those seeking relief from inflammatory disorders.
Buy your essential medications affordably through our trusted [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – lisinopril vietnam medicine[/URL – . Find diverse alternatives for your healthcare needs without hassle.
Optimize your wellness with our multifunctional cost of 25 mg of nizagara , the solution to improving your health without hassle.
Purchase
Zap your ED worries away! Purchase safe ED medication [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ – generic viagra by fedx[/URL – . This solution is trustworthy and quick to find.
Get the prescription easily with nizagara 50mg , providing a wide selection for all your healthcare needs.
Maximize your wakefulness with our affordable solutions; get your batch of alertness-enhancing drugs through our website https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ .
Needing to obtain [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – ventolin inhaler[/URL – ? Explore trustworthy alternatives for obtaining virtually.
Venture into the realm of effective erectile dysfunction treatments with [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena 100 mg prezzo in[/URL – , available on the web.
Jumpstart your journey towards better health with a straightforward way to purchase your medication. Whether you’re looking to reduce inflammation, our platform offers an array of options to suit your needs. For those specifically seeking Budesonide treatment, propranolol here and experience immediate relief.
Purchase the https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ on our online platform, ensuring a safe transaction.
Looking to acquire Aripiprazole? Find it effortlessly with just a click at [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – , your go-to source for pharmaceuticals online.
Get your health back on track with ease; secure your savings now on anxiety relief medications by clicking here: nizagara .
Get your hands on https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ easily. Purchase your required treatment with just a few clicks through our dependable platform.
Given the ongoing discussions about its efficacy in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – on the web is crucial for consumers.
Discover your path to enhanced well-being; secure this premium medication from the comfort of your home [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – extra super avana[/URL – .
With competitive medication rates, vpxl lowest price offers an affordable solution to support your fertility journey. Explore cost-effective options now.
Acquiring https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ via web offers a hassle-free pathway to managing chronic conditions. With a variety of options available, ensuring you receive the genuine medication is no longer a challenge.
Consider securing your [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ – lowest tadapox prices[/URL – effortlessly through this platform. Preorder now online for fast delivery.
Considering various options to control your BPH symptoms? Explore how you can get [URL=https://jawany.com/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – via the web, offering a simple solution to relieve discomfort.
Many are looking for effective solutions for erectile dysfunction, and cialis offers a tested option.
Understand your migraine triggers better and explore effective relief solutions today; find out safe options to acquire https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ and take a step towards managing your symptoms.
For a thrilling experience in gaming and entertainment, visit [URL=https://jawany.com/cipro/ – cipro information[/URL – . With a plethora of games and premier customer service, it’s the ideal choice for enthusiasts.
Get your health back on track! Purchase your essentials efficiently by choosing to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin for sale[/URL – . This action not only streamlines but also ensures you get your treatment swiftly.
Secure your lasix generic canada order via the web for swift delivery.
Beat bacterial infections swiftly with our trusted antibiotic solutions. For your convenience, secure a replenishment of amoxicillin via https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ , bypassing the need to visit a pharmacy. Ideal for those seeking efficient, effortless access to antibiotics.
For those seeking to enhance their eyelash length, thickness, and darkness, purchasing [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – online strattera 18 purchase[/URL – is a prime choice. Opt for it today and witness a remarkable transformation.
Discover the most up-to-date cheap hydroxychloroquine overnight delivery and consider alternatives for acquiring this treatment via the internet.
Zero reasons to wait! Secure your prescription for enhanced performance today at https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ .
A secure option to manage your health: [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ – viagra[/URL – . Visit our website to learn about multiple approaches for your wellbeing.
Get premium Human Growth Hormone supplements directly from [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – uk propranolol generic[/URL – . Buy immediately for enhanced well-being.
To discover the most affordable deals on prednisone 5mg , check out our website.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is critical; thankfully, acquiring necessary medications has never been easier. Those looking to obtain https://hyblavalleyvet.com/kamagra-in-usa/ can now do so with unparalleled convenience, ensuring your wellbeing is always a top priority.
Your search ends here! Secure your [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/pill/celebrex/ – celebrex on line[/URL – with ease. Say goodbye to eye discomfort today!
A search for affordable alternatives for controlling narcolepsy leads you directly to [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – buy strattera uk[/URL – , where you can uncover unbeatable rates.
Quickly order your medication with no hassle. Click here for lowest price on generic malegra .
X-plore the myriad benefits of enhanced endurance and vigor with just a click. Obtain your prescription of unparalleled performance enhancement today at https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ .
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – , offering wide-ranging solution for bacterial infections.
Explore the range of options for controlling menstrual disorders by purchasing finasteride .
A secure method to manage your health: https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ . Browse our site to learn about multiple approaches for your wellbeing.
Discover an effective way to boost your wellbeing: [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – viagra in usa[/URL – .
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis kaufen 2.5[/URL – , your go-to source for acquiring reliable ED solutions on the web.
With an array of choices for hair loss treatment, purchasing lowest price generic clonidine becomes a hassle-free experience. Opt for ordering your solution via the internet for a swift and efficient battle against hair thinning.
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ , and Snag a course of essential antibiotics easily via our website.
Research reveals that securing effective medications for your health needs has never been easier. Ensure your well-being by choosing [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ – cytotec to buy[/URL – on the web.
Finding affordable solutions for enhancing eyelash growth just got easier. Visit slimex in usa today to explore your options for purchasing quality yet budget-friendly treatments.
Looking for an affordable way to enhance your well-being? Explore the advantages of https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ , optimal for those seeking effectiveness without sacrificing budget.
Unlock savings on allergy relief: [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ – generic nizagara canada[/URL – online and experience relief from seasonal allergies without breaking the bank.
Zealously seeking an affordable solution for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms? Explore our cost-effective options and unlock potential savings with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – pharm levitra[/URL – . Find the way to a better quality of life without breaking the bank.
Get rid of lice easily with our solution at lisinopril 20mg hctz 12.5 tabs .
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ virtually can be a seamless process.
Ensure you obtain your supply of [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxicillin[/URL – safely and swiftly.
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial, and finding the right medication should not be a hassle. For those seeking flexibility and convenience in their treatment, [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – offers a discreet, effective option. Consider securing your treatment online, ensuring you receive high-quality care without compromise.
Obtaining your buy 20mg levitra has never been easier; purchase your solution on the web with utmost convenience and discretion.
If you’re searching to acquire Flagyl, think about https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ for a convenient method to get your medication.
Yes, you can secure [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ – trazodone coupons[/URL – virtually for controlling your health needs.
Zillions pursue effective hair loss solutions; [URL=https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ – prednisone[/URL – presents a potential option.
Maximize your well-being with a holistic approach by opting for azithromycin , a solution that’s accessible for improving male health and vitality.
Visit https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ to secure your medicine without a doctor’s prescription.
Maximize your well-being by opting to buy your medications digitally, including the option to [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – , ensuring ease and confidentiality.
Research [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – misoprostol[/URL – for effective alopecia management.
Quickly buy your prescription via the web with nizagara 50mg , ensuring an easy procedure.
Zeroing in on effective pain relief solutions? Discover accessible choices like https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ , perfect for alleviating discomfort.
Get your [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – asthalin[/URL – securely via the internet.
Just uncovered your key to improved intimacy: [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cheap cialis black pills[/URL – . Purchase immediately for lasting outcomes.
Procure the essential medication affordably by clicking here: prednisone on line , ensuring substantial cost savings on quality healthcare.
Acquiring your https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ just became easier. Now, obtain your medication without hassle.
Secure your health by choosing [URL=https://umichicago.com/etibest-md/ – no prescription etibest md[/URL – to control anxiety. Acquire them via web for a smoother, stress-free life.
In need of affordable medication? Discover your options and compare prices, including the competitively priced low price levitra , by exploring our site. This ensures you secure the best deal on your healthcare needs.
Knowing your options for managing Alzheimer’s is crucial. Explore treatments and find out if https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ could be the right fit for you or your loved ones.
Considering purchasing your medications without the hassle? Check out [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a coupon[/URL – for a simple way to secure your pharmaceuticals virtually.
Regain your health and combat Hepatitis C with a ground-breaking treatment. Learn about your options and reclaim your well-being by visiting mail order vidalista . Acquire your path to recovery online today.
Optimize your health regimen by visiting our selection at https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ , where quality meets potency.
Browsing for a reliable source to purchase your hypertension medication? Look no further than [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , where you can buy your medication effortlessly.
Keeping your healthcare needs in mind, securing efficient treatment for ED is now easier. Uncover [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – drugstore cialis-black[/URL – and conserve on your purchase.
Procure the essential medication affordably by clicking here: http://www.kamagra.com , securing significant discounts on premium healthcare.
Harnessing the power of advanced healthcare has never been easier with the https://bayridersgroup.com/drug/arjuna/ . Whether you’re in search of a convenient solution to manage your health needs, this product stands out as the ultimate selection.
Obtain your [URL=https://center4family.com/kamagra/ – http://www.kamagra.com[/URL – today and manage your well-being effectively. Purchase immediately for swift delivery.
Xperiencing hair loss can be distressing. Find solutions at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 5mg[/URL – , offering a variety of treatments to restore your confidence.
Learn more about managing your health issues with on line pharmacy for nizagara . Discover how this medication can benefit you in regulating endocrine disorders.
Unlock unparalleled savings on wellness with our exclusive offering: find – the most affordable https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ online.
Before deciding, compare the [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – lasix coupon[/URL – , and evaluate costs from different pharmacies to ensure you’re getting the best deal for managing Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Need to control your health condition without a prescription? Find your solution with [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ – link order cialis[/URL – , offering a reliable way to improved well-being.
Reveal the secrets to optimal health with our handbook at levitra walmart price . Learn how to boost your vitality with practical tips and insights from specialists in the field.
Your search for affordable cardiac therapy ends here with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ . Secure your health’s future online.
Battling nasal allergies can be daunting, but respite is accessible through [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/levitra/ – order levitra[/URL – . Discover ways this treatment can ease your symptoms now.
CrestFinds Online – Attractive design paired with clear sections keeps shopping smooth and intuitive.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can find options on websites including [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/fildena/ – fildena online pharmacy[/URL – , a reliable treatment.
Consulting your healthcare professional is crucial before you acquire cheap tadalafil .
Achieve healthier, fuller lashes by choosing to https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ . Whether you desire to enhance your eyelash appearance for aesthetic improvement, our selection provides a safe, effective solution.
Zealously seeking relief from seasonal allergies? Invest in your solution with [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ – retin a generic canada[/URL – , the go-to option for fighting allergy symptoms.
Discover the convenience and privacy of purchasing your ED treatment with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ – discount bulk viagra india[/URL – , ready for you.
When experiencing heartburn, discover relief with medications from viagra 100 mg quick disolve . Purchase the remedy online now.
Considering a quick funding solution? Explore https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ for prompt financial support.
Searching for affordable ulcer treatment options? Look for the best deals on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone generic fast shipping[/URL – , your go-to option for easing gastrointestinal discomfort.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 500mg[/URL – via the internet for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
Obtain your allergy relief solution effortlessly. order priligy online offers a simple way to manage symptoms.
Get your prescription easily with fast delivery; click here to https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ now.
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can acquire ED pills via the web at [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
Secure your celebrex effortlessly. Order the medicine online with just a few clicks.
When seeking relief from chronic aches, consider https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ as your go-to solution. It’s accessible through online pharmacies, offering convenience and efficacy.
Purchase the [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a lowest price[/URL – online to support cognitive health efficiently and affordably.
Discover your pathway to healthier cholesterol levels by opting to purchase your amoxil 650mg on our website. This approach not only ensures convenience but also provides a range of options to suit your specific health needs.
Considering the requirement for exact and timely care, acquiring https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ online offers an easy solution.
Looking for an easy and discreet way to manage your health? [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – pharmacy prices for extra super avana[/URL – offers an accessible solution to enhance your well-being without the hassle. Now, get your medication effortlessly from the comfort of your home.
Restore your health and confidence with one click; [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ – non prescription type pharmacy[/URL – effortlessly via our website to tackle your needs without hassle.
X-ray your options for migraine relief by exploring retin a generic canada , a leading treatment available online.
Zest for life can be regained with ease. Procure your osteoporosis treatment with confidence https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ .
To alleviate discomfort, purchase [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – online generic retin a[/URL – from reliable vendors on the web.
The availability of [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ – lowest price on generic cipro[/URL – ensures that individuals can without difficulty access vital medication to tackle their condition via the internet.
Improve your health by visiting lasix to discover a wide selection of pharmaceuticals.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ via the internet provides a budget-friendly option.
Maximize your wellness and satisfaction with a variety of options for enhancing your experiences; [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ – order retin a[/URL – offers a unique solution. Obtain
Acquire cost-effective solutions for your stomach troubles with lasix online fast delivery , known to mitigate symptoms efficiently.
Improve your well-being effortlessly by opting to buy high-quality drugs from the comfort of your home. https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ offers a reliable, secure solution for enhancing efficacy.
Optimize your wellness regimen with an easy, secure acquisition. Acquire your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra brand[/URL – via web for a comprehensive solution to wellness essentials.
Quickly purchase the osteoporosis medication at an unbeatable cost here: tadalafil .
Keep your health in check with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ , your solution to controlling inflammation.
You can acquire safe and reliable treatment for nausea with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – nizagara vendita in italia[/URL – , available online.
Questioning where to purchase fertility treatments? Secure your [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ – vidalista 10 mg lowest price no perscription[/URL – effortlessly online.
Explore reliable options to purchase your medication via the web with generic retin a , ensuring discretion and simplicity.
Harness the power of savings on your next prescription with https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ , ensuring you get your prescription at a lower cost.
Regarding your health needs, discover an efficient solution to manage edema; [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – generic nizagara at walmart[/URL – is available. Secure, immediate purchase is guaranteed, making therapy more accessible.
Considering various options to control your BPH symptoms? Discover how you can obtain flomax online, offering a simple solution to ease discomfort.
“Quickly uncover savings on your next purchase with https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ . Cut costs easily on vital medication.”
Maximize your well-being with a holistic approach by opting for [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – buy retin a[/URL – , a solution that’s easy to obtain for boosting male health and vitality.
If you’re seeking natural solutions for your health, consider exploring the benefits of [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nexium/ – nexium non generic[/URL – . With its comprehensive benefits, it’s a smart addition to your wellness regimen.
Quickly get your drugs with convenience by choosing to purchase walmart pharmacy viagra 25 .
To acquire https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ , visit our webpage.
Procure affordable treatment options; explore [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ – online modvigil purchase in india[/URL – for managing your well-being.
Boost your health with quick access to antiviral treatment by browsing [URL=https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ – generic prednisone uk[/URL – – your one-stop destination for effectual recovery.
Find unbeatable prices for your heart medication at generic cytotec from canada , ensuring supreme cardiovascular health.
Zero hassle to acquire your pharmaceutical needs for enhanced stamina, click here: https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ .
Managing chronic pain necessitates effective treatment strategies. Discover how [URL=https://primerafootandankle.com/item/vidalista/ – vidalista without pres[/URL – offers a solution that can assist in alleviating discomfort.
Understanding the necessity for prompt antimalarial treatments, it’s pivotal to source a dependable source. With that in mind, procure your [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ – order nizagara[/URL – immediately for effective therapy.
Before considering treatment options, explore pharmacy uk to treat your health concerns safely.
Keeping your health in top condition is essential, and so is finding the best deals on your supplies. Whether you’re looking to purchase your health supplements, don’t miss out on the competitive costs at https://midsouthprc.org/levitra/ .
Your health is important. Discover simple access to control your medical condition with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – cost of prednisone tablets[/URL – . Guarantee your vitality is optimal with just a click.
Zealously seeking relief from seasonal allergies? Purchase your relief with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – buy generic amoxil fast delivery[/URL – , the trusted solution for fighting allergic reactions.
To secure the most affordable options for tadalafil , browse our page now.
Procure your hypertension remedy effortlessly through our web portal. Secure your medication without a need for prescription. Click here https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ to start your journey towards better health.
Understanding the need for ease, you can now acquire your treatment online with effortlessly. [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 1000mg[/URL – and benefit from swift dispatch to your doorstep.
Discover how best price flomax can ease symptoms of BPH by checking our site.
Now, discover your cure for impotence with ease by opting to buy https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ .
Many individuals seek effective treatment for bacterial infections. Whether you’re fighting skin conditions, respiratory infections, or STIs, [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline buy online[/URL – provide option.
To secure your health supplements with ease, simply navigate to our [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – buy propranolol on line[/URL – to find a comprehensive range of options.
To obtain your medication effortlessly, lasix 100mg from reliable pharmacies.
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and buy your https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ today for enhanced health and vitality!
Purchase the [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone price at walmart[/URL – on the web for controlling your symptoms effectively.
Your quest for a cost-effective solution to hair loss ends today! Explore a wide variety of options and secure your supply of [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel prices[/URL – . Don’t let thinning hair dictate your confidence any longer; grab your chance now.
Visit tadalafil 2.5mg to purchase your heart health medication at a low cost.
When looking to order nasal relief, consider https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ as your go-to choice for alleviating allergy symptoms.
Discover ways to cut costs on your prescriptions by exploring the [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – , ensuring you obtain your medications at the lowest cost.
В поисках надежного поставщика редкоземельных металлов и сплавов? Обратите внимание на компанию Редметсплав.рф. Мы предлагаем внушительный выбор продукции, обеспечивая высочайшее качество каждого изделия.
Редметсплав.рф защищает все стадии сделки, предоставляя полный пакет необходимых документов для оформления товаров. Неважно, какие объемы вам необходимы – от мелких партий до крупнооптовых заказов, мы готовы выполнить любой запрос с непревзойденным обслуживанием.
Наша команда поддержки всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам в подборе нужных изделий и ответить на любые вопросы, связанные с применением и характеристиками металлов. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете достоверность в каждой детали сотрудничества.
Заходите на наш сайт Редметсплав.рф и убедитесь, что качество и уровень нашего сервиса – наилучшее решение для вашего бизнеса.
Наша продукция:
Круг с заданными свойствами упругости 14 мм 68НХВКТЮ-ВИ ГОСТ 14119-85 Познакомьтесь с нашей коллекцией кругов с заданными свойствами упругости, идеальным выбором для различных инженерных приложений. У нас вы найдете оптимальные по своей прочности и гибкости круги, подходящие для различных отраслей и проектов. Получите дополнительные характеристики и консультации на нашем сайте.
The need to acquire medication online has escalated, and with options like [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady-era usa rx[/URL – , securing your prescription is easier than ever.
Maximize your energy with advanced options. Explore how on clomid buy online .
Optimize your wellness journey with our versatile https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ , designed for your unique needs. Obtain
Discover your solution for enhanced vitality; find trusted options and purchase [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ – purchase viagra online[/URL – immediately.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, purchasing [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – online provides a economical option.
Discover how to acquire your medication without hassle with fast shipping kamagra online , ensuring quick dispatch to maintain your health.
Xperience enhanced comfort and convenience when you order your medication through our website. Find out more about obtaining your https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ .
Manage your nasal symptoms effortlessly by opting for to [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – 60 mg prednisone[/URL – , a trusted treatment.
SUNWIN is positioned as a modern core fitting for online betting, blending casino sageness with diversified spectacular like x? s?, th? thao, and interactive trò choi. The podium highlights immersive game slots, real-time b?n cá, and high-volatility jackpot systems, alongside traditional choices such as dá gà, tài x?u md5, xóc dia, baccarat, and r?ng h?. Towards digital-first players, esports markets and frequent khuy?n mãi, uu dãi, and n? hu events manufacture momentum, while structured d?i lý programs and keen cskh prop up long-term trust. Recognizable access is close by at https://creditservice.ru.com/, reflecting a sharply defined unclear on episode, fairness, and evolving actor expectations.
Your search for entertainment ends here at the [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20 canadian pharmacy[/URL – , offering unmatched rates.
Access the top deals on cheap nizagara to ease your nasal symptoms now.
Venturing north for well-being solutions? Find your wellness aid with https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ , offering a broad selection of medicines.
Zap fatigue with our top-rated diuretics, [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – vpxl.com[/URL – . Get efficient solution today.
Optimize your wellness journey with our versatile [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ – online generic priligy[/URL – , designed for your unique needs. Obtain
Venture online to find out the cheap generic trazodone canadian pharmacy , ensuring you secure the lowest cost for treating your condition.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ online provides a economical option.
To procure [URL=https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone to buy[/URL – , explore our credible source to make certain security and quality.
Acquiring your prescription has never been easier with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone[/URL – . Buy now for quick delivery worldwide.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with lowest price generic flomax , and explore a range of solutions to enhance your quality of life.
Obtain your https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ effortlessly. Secure this vital medication online.
Looking to address your health concerns? Explore a broad selection of pharmaceuticals at [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – lasix no prescription[/URL – , your go-to source for reliable healthcare solutions.
Navigating through the plethora of pain relievers can be daunting. For those seeking proven relief from various pains, zithromax sublingual offers an insightful look at a choice worth considering.
Considering affordable options for managing anxiety? https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ offers a range of options worth exploring.
Maximize your health with ease by accessing purchase [URL=https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ – panmycin for sale[/URL – .
X-ray the expenses before buying your antihistamines; explore the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – buy strattera in hong kong[/URL – for an affordable selection.
Zap your anxiety away! Now you can acquire your stress-relieving medication hassle-free. Don’t miss out on our exclusive on line nizagara . Save on your purchase today and welcome calm without breaking the bank.
Quest for budget-friendly heart health solutions? Look no further! Obtain your https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ today and commence your journey towards a better heart with ease.
Acquiring authentic [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – reputable suppliers of generic prednisone[/URL – has never been more straightforward. Buy your upcoming batch online with total assurance.
Get the best deal on your medication route for battling alcohol dependency by exploring the [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone wholesale labels[/URL – . Find affordable options to assist in your recovery journey.
Regain dominance over your wellness at unbeatable costs with malegra . Buy now and experience rapid delivery globally.
If you’re in the market to purchase an cost-effective solution to your vertigo, consider https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ . This medication helps in alleviating the symptoms of vertigo, improving your quality of life.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to cut costs on your medication.
When looking for an affordable solution to your health needs, consider zithromax without an rx . With options to obtain your prescription without straining your finances, it’s never been easier to manage your health effectively.
Seeking affordable options for enhanced performance and stamina? Explore the potential benefits by checking the https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ , where you’ll find reasonable deals.
X-ray your options for HIV treatment medications and discover the most affordable solutions. For those seeking savings, [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – australia online nizagara[/URL – presents a feasible choice.
Acquire your medicine without hassle with our safe online platform. Discover the benefits of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol capsules for sale[/URL – .
Venturing into the realm of cost-effective healthcare? Look no further, trazodone in usa online for your medical needs.
Curious about affordable treatment options for your condition? Explore a cost-effective alternative with https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ . Ideal for those seeking budget-friendly options for their health care.
Just in! Get the daily dose of vitality now. For those looking to boost their health, [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ – propecia buy online[/URL – offers a convenient solution. No more waiting; enjoy a revitalized life today.
Understanding the importance of maintaining heart health and managing cholesterol can be overwhelming, but with the right medication, it’s possible to navigate these conditions more effectively. If you’re looking to obtain your prescription with ease, [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – offers a simple solution to handle both hypertension and high cholesterol with just one tablet.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering hydroxychloroquine online pharmacy via the internet provides a economical option.
Manage your allergies seamlessly with https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ , now available for buying on the internet.
You can secure your [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ – buy cheap nizagara online canada[/URL – effortlessly through our web platform, ensuring you maintain your health effortlessly and efficiently.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – amoxicillin generic pills[/URL – is a viable option. Explore obtaining amoxicillin via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Pain relief doesn’t have to be costly or complex. Discover affordable options for your discomfort and explore buy non-generic stromectol online . Whether you’re facing slight discomfort or more severe conditions, find the relief you need without breaking the bank.
Know about the transformative effects of Isotretinoin for skin conditions? Explore your options and learn more at https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ .
Visit [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – canada amoxil prescription[/URL – to acquire your medication on the internet at incredible prices.
Save on your next purchase with a [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – . Uncover significant discounts online for your next medication.
Just ordered my batch of dapoxetine , ensuring I continue my health regimen effortlessly.
Exploring affordable healthcare solutions is essential, especially when it comes to medication. https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ offers a cost-effective solution for those needing therapy without compromising on effectiveness.
X-raying your finances? Acquire an quick boost with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – buy retin-a without prescription in usa[/URL – , ensuring security in hard times.
Discover your answer for enhancing sexual performance with ease; buy [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – viagra[/URL – immediately.
You can secure your clonidine walmart price on the internet, providing a easy way to control hypertension.
Maximize your vitality and stamina with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ , the prime choice for enhancing performance. Explore a decisive solution for boosting your health and confidence seamlessly.
Understanding the versatility of [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – generic for clonidine[/URL – can significantly improve management of high blood pressure. With numerous options available, selecting the right treatment on the web can offer flexibility.
A thorough guide to accessing [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/]lasix uk[/URL] is now available! Whether you’re looking to buy or simply investigate options, this handbook offers the entirety you need.
Boost your vitality with retin a , available for acquisition online.
Discover your remedy for enhancing intimacy issues with ease; buy https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ now.
Quiet nights can often be disturbed by restless legs, a common ailment affecting many. To combat this, trusted solutions like [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil capsules for sale[/URL – can be invaluable. If you’re seeking relief, consider purchasing this remedy online.
Get your health back on track! Secure your essentials efficiently by choosing to flomax . This step not only saves time but also ensures you acquire your medication without delay.
Hunt for thrilling entertainment? Uncover the https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ for an unparalleled adventure.
Zero in on enhancing your vitality with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – , available today. Discover cost-effective solutions on the web.
Given the ongoing discussions about its application in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – on the web is crucial for patients.
Acquire cost-effective solutions for your digestive issues with cost of vidalista tablets , known to mitigate symptoms efficiently.
Uncover affordable treatment for scabies with our economical https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ , the number one choice for eliminating pests.
Keep your pain in check without breaking the bank; explore economical solutions for alleviating discomfort. [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – amoxil 500mg[/URL – offers a trustworthy option for those seeking ease without the high expense.
ironskyessentials – Pleasant experience overall, ironskyessentials feels reliable with helpful descriptions everywhere.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase [URL=https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – cheap hydroxychloroquine search generic[/URL – online is crucial for patients.
Seek relief for dry eyes with on line tadalafil , a trusted solution. This remedy is accessible for acquisition online.
Discover how to safely procure https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ online, ensuring you get authentic medication for your health needs.
Xperience the utmost convenience in acquiring your essential medication through [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – vardenafil[/URL – , a premier destination. Obtain your medication effortlessly on our site.
Now, locate your cure for erectile dysfunction with ease by opting to acquire [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – .
For those looking to purchase HCG injections, generic nizagara from india offers a reliable, safe avenue.
You can secure Fildena for your ED needs here: https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ .
Patients seeking affordable solutions for their medication can find [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ – discounted 200mcg cytotec[/URL – to identify cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
Acquiring [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – mail order xenical[/URL – via web offers a hassle-free pathway to managing well-being. With numerous options available, making certain you receive the authentic medication has never been complicated.
You can uncover affordable options for managing your urinary symptoms with kamagra pills .
Discover secure and discreet options to buy your treatment without complications. Click here: https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ .
Understand your migraine triggers better and explore effective relief solutions today; learn about trusted options to buy [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil without a doctor[/URL – & take a step towards overcoming your symptoms.
Discover the most effective treatment for your eye condition with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxicillin[/URL – . Purchase this highly recommended ointment now for quick relief.
Wondering where to get Allegra at competitive costs? Look no further than our recommended source nizagara online agency , offering a wide selection of options for your requirements.
Looking for a reliable place to purchase your medication? Look no further! https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ offers a wide selection of medicines to meet your needs.
Looking for a convenient way to acquire your medication? Visit [URL=https://damcf.org/prednisone/ – manufacturer of prednisone deltasone[/URL – for a effortless experience and ensure your health needs are met.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ – amoxil coupons[/URL – to acquire your medication on the internet at incredible prices.
Discover more about trusted birth control options at cheapest nizagara .
Discover unbeatable deals on https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ and save on your upcoming acquisition.
Given the unpredictable nature of weather patterns, securing your property against inundations has never been more crucial. Explore options to protect your home with a [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix coupon[/URL – , offering a wide range of strategies to combat water damage.
Various individuals searching for solutions to treat premature ejaculation turn to [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – as a reliable option.
Ready to grab your health essentials at an unbeatable cost? Look no further than our platform for the by prednisone w not prescription , ensuring you receive top-notch medicinal supplies at a fraction of the cost.
X-plore the therapeutic options for managing Addison’s disease; https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ stands out as a leading choice. Its efficacy in regulating electrolyte levels and reducing symptoms is unparalleled.
Minimize your sea-sickness and motion discomfort by opting to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil[/URL – . Secure a remedy now and experience peaceful travels.
Obtain comprehensive insights and secure the [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – vidalista[/URL – for your antiviral medication needs by browsing our site today.
A myriad of options awaits when you decide to buy your medication seamlessly. For those seeking to control urinary symptoms, propranolol 80 online india offers a convenient, reliable solution.
Have a need for antifungal medication? Obtain your dose effortlessly by https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ .
Discover the most cost-effective options for managing your health with [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/viagra-jelly/ – generic viagra-jelly canada paypal[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to purchase this vital prescription online, we supply a wide range of alternatives to meet your needs.
SUNWIN is positioned as a stylish online betting ecosystem where know-how matters as much as trust. From immersive casino rooms to well-trained x? s? systems, the corps job balances sport and control. Players jaunt th? thao, interactive trò choi, high-volatility game slots, and real-time b?n cá with unmistakable mechanics. Signature features like jackpot, n? hu, baccarat, r?ng h?, xóc dia, tài x?u md5, dá gà, and esports picture vend query in 2025. Miasmic khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, constant cskh, and a scalable d?i lý mannequin redeem users broaden responsibly. Learn more at https://creditservice.ru.com/.
Looking to enhance your wellness naturally? Consider trying out [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – for a holistic method.
Keep your health in check by exploring options to buy vital medications. For those in need, generic retin a is now accessible, offering a straightforward way to maintain your wellness.
Secure your https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ purchase online for swift delivery.
Here’s how to uncover the current [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara tablets[/URL – to conserve on your prescription.
Keeping your heart’s rhythm steady is crucial; procure kamagra cost to keep optimal cardiac health and function.
For supporting peak well-being, consider integrating https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ into your routine, renowned for their powerful anti-inflammatory and free-radical fighting benefits.
A wide range of options exists for managing hypertension; one such option is [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – vidalista.com[/URL – . If you’re considering this avenue, you can obtain it without difficulty via web pharmacies.
Ordering your prescription medication has never been easier, check out [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ – pharmacy buy[/URL – to find out how you can get your medication promptly.
Just discovered you can with confidence buy your meds through the internet? For authentic products, tinidazole tablets 1000 price is your go-to.
Keep your healthcare regimen on track and obtain your medication with ease, https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ , ensuring a continuous path towards recovery.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – cialis[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous choices available online. Secure your health today by opting for the best deal.
Get a prescription for ulcerative colitis from the comfort of your own home. Buy ventolin inhaler overnight and start treatment immediately.
Searching for reliable solutions to reduce irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ can help in soothing your discomfort today.
Discover your pathway to enhanced intimacy; explore procuring [URL=https://damcf.org/nizagara/ – nizagara uk[/URL – to boost your libido.
Maximize your savings and attain better health outcomes by choosing to [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ – 0.2 dose of flomax[/URL – .
Zero wait time for your allergy relief; Purchase your generic fildena today and breathe easier in no time.
Quickly learn about the most competitive https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ on the web.
Explore the range of options for controlling menstrual disorders by acquiring [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ – fildena online no script[/URL – .
Need to learn the most recent [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ – doxycycline preis deutschland[/URL – ? Check out our link for cost-effective options.
Zapping tuberculosis requires effective medication. Find affordable treatment options; nizagara are available online.
Understanding the importance of accessing medications safely, one might search for ways to acquire https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ . However, always verify it’s through a reputable source to avoid potential health risks.
Leverage your health management by securing your supply of crucial medication. Acquire [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/ – medical retin-a[/URL – effortlessly from trusted sources, ensuring your well-being is always at the forefront.
Having been diagnosed with angina, patients seek cost-effective treatment options. Discover the most economical option for relief with [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – buy generic tadalista[/URL – , offering a solution without breaking the bank.
In need of an antibiotic treatment? Get your dose without hassle doxycycline . Available online, ensuring you have access to the medication swiftly.
X-plore the myriad benefits of enhanced endurance and vigor with just a click. Procure your supply of unparalleled performance enhancement now at https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ .
Manage your health efficiently by opting to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia without dr prescription[/URL – , a strategy embraced by countless individuals seeking respite from their symptoms.
Boost your performance naturally with the powerful herbal blend found at propecia without dr prescription . This topical solution, available for buying online, can enhance vitality and stamina effectively.
To secure the best rate on https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ , browse our webpage.
Your search for affordable options ends here: [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ – canada lady era[/URL – . Find your solution today and conserve on medical expenses.
With numerous stomach problems plaguing individuals, finding an effective treatment is essential. Luckily, you can procure [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ – online torsemide[/URL – , a tested treatment for shielding the stomach’s lining and assisting in the healing process.
Discover the up-to-date http://www.maxaquin , a crucial detail for those aiming to buy this topical treatment.
Seeking the best value for your heart health medications? Compare costs now and conserve on your prescription with https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ , your preferred source for economical healthcare.
X-plore affordable hypertension treatments with various options and find your optimal solution at [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/canada-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – , your go-to for cost-effective health solutions.
To enhance your health, contemplate buying medications online through [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – viagra 25 prix en pharmacie belgique[/URL – , a reliable source for healthcare products.
Zap your health concerns away with an affordable, effective stroke prevention option. propecia tablets 1 mg prices is your go-to option. It’s time to buy this crucial medication online.
Discover amazing deals on your pharmaceutical needs with our https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ .
Harness optimal heart health effortlessly; explore affordable solutions by choosing [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol[/URL – , ensuring prime cholesterol management without hassle.
Discover affordable options to maintain your bone health; buy lady era online cheap and explore other cost-effective solutions on the web.
Explore your alternatives for dealing with peptic ulcers with https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ , accessible through our website.
Understand the price of maintaining your well-being by checking the [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/zithromax/ – buy zithromax no prescription[/URL – latest costs.
Get your Amoxicillin easily from [URL=https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxil[/URL – , supplying swift dispensation to satisfy your healthcare needs.
X-plore your alternatives for thinning hair treatment and purchase generic finasteride from india safely.
Combat digestive discomfort with ease; visit https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ to buy your treatment immediately.
Zap your ocular hypertension or glaucoma symptoms by exploring [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine next day[/URL – , offering a budget-friendly solution.
Maximize your health and wellness by opting for [URL=https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ – vidalista en ligne[/URL – , a top-tier solution for managing allergic reactions. Secure your well-being by obtaining it easily online.
“Quickly uncover deals on your next purchase with misoprostol . Slash prices easily on vital medication.”
Obtain your medication easily through https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ , a trusted option for controlling your conditions.
Searching for an effective glaucoma therapy? Look no further! Find your [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ – levitra[/URL – today for ultimate eye health.
Manage your nasal allergies effectively with ventolin 100mcg . Whether you’re looking to buy an intervention for seasonal allergy symptoms or require a long-term solution, this solution offers ease.
Considering various options to control your BPH symptoms? Find out about how you can acquire https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ online, offering a straightforward solution to ease discomfort.
Many are searching for effective solutions for erectile dysfunction, and [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-uk/ – cialis[/URL – provides a proven option.
Many search for inexpensive treatments online, and tadapox venta en farmacias could be what you’re looking for.
X-plore your options for hypertension management by choosing to acquire https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ .
A myriad of options awaits when you decide to purchase your medication seamlessly. For those seeking to control urinary symptoms, [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ – torsemide[/URL – offers a convenient, dependable solution.
I’ve discovered where to get cost-effective [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – cheapest propranolol online without prescription[/URL – , a commonly prescribed treatment for certain types of malaria.
Zero hesitation is key when considering upgrading your lifestyle. Secure your walmart nizagara price today for a top-tier experience.
When considering cholesterol management, selecting the right medication is crucial. https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ offers an effective solution. Explore alternatives on the web to discover how it can benefit your health regimen.
Buy your essential medication easily with a tap on your device. Seeking a reliable source for your healthcare needs? Look no further. Obtain this medication, without the hassle of a prescription, right away through [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ – vidalista[/URL – .
Many are searching for effective treatments for scabies and lice. Discover how [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin generic[/URL – can be your remedy.
Navigating the expansive realm of pharmaceuticals, it’s crucial to discover a reliable source billig pharmacy kaufen .
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ virtually can be a straightforward process.
Secure your health with ease; procure your medication effortlessly through our digital service. For those managing cardiovascular conditions, [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – cheap nizagara online[/URL – now and maintain your wellbeing.
X-plore new ways to treat Alzheimer’s by choosing to buy your [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – lisinopril angular stomamtitis[/URL – immediately.
You can get effective pain relief by choosing to lisinopril affects pancreas , ensuring fast delivery directly to your home.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ , supplying broad-spectrum treatment for bacterial infections.
Explore the benefits of enhancing your well-being with our top-notch supplement. Now is the time to achieve better health by clicking here: [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ – buy flomax[/URL – . Opt for a rejuvenated life today!
Xperience swift relief from allergy-season symptoms with [URL=https://goldenedit.com/generic-cipro-at-walmart/ – rezeptfrei cipro 1000 mg[/URL – , your go-to solution for keeping comfortable in high-pollen times.
Discover how flomax retail discount can alleviate symptoms of an enlarged prostate by visiting our website.
Boost your health path effortlessly.
Keep informed on hydroxychloroquine benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – overnight hydroxychloroquine[/URL – for thorough insights and updates.
Recognizing the demand for affordable medication, patients can now obtain their prescriptions more cheaply with flomax .
Seek relief for dry eyes through https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ , a effective solution. This remedy is obtainable for buying on the web.
Boost your confidence and revitalize your life with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – nizagara from costa rica[/URL – , available for purchase online.
Discover an effective way to enhance your wellbeing: non prescription prednisone .
Looking to boost your joint health? Consider checking out https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ . This formulation is designed to support in sustaining supreme joint function.
Just in time for your urgent needs, locate your essential supplies up for grabs at [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ – nizagara[/URL – , without delay.
Looking for an affordable way to enhance your well-being? Find the advantages of retin-a sale canada , optimal for those seeking efficacy without compromising financial ease.
Address your allergic reactions effortlessly by opting to purchase your medication through our https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ . This alternative not only conserves money but also ensures quality treatment.
Manage your health efficiently by opting to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – buying prednisone online[/URL – , a strategy embraced by countless individuals seeking alleviation from their symptoms.
Considering your health, consulting a physician before you purchase [URL=https://youngdental.net/item/acticin/ – acticin[/URL – online is crucial for securing ideal results.
Given the myriad options for managing fertility issues, the retin-a to buy cheap often emerges as a primary concern for many.
Xperience enhanced comfort and convenience when you buy your medication online. Find out more about obtaining your https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ .
Explore innovative solutions to improve your alertness with [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ – canadian nizagara[/URL – .
Revitalize your energy and balance your hormonal levels by choosing to retin a buy . Whether you’re looking to enhance your well-being or in search of hormone replacement therapy, these capsules offer a solution.
Keep your stomach issues at bay with https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ , the ultimate remedy for irritable bowel syndrome. Acquire your solution on the web now.
Achieve optimal prostate health with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia in usa[/URL – , a trusted solution available for those seeking economical treatment.
Venture into optimal health management by choosing to acquire your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – preis prednisone 20 mg[/URL – through trusted digital outlets, ensuring a seamless process in improving your well-being.
Secure the most affordable rates for your treatment by opting to vidalista online no script . Conserve significantly when you acquire from credible online vendors.
Considering various options to treat your BPH symptoms? Explore how you can obtain https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ on the internet, offering a convenient solution to relieve discomfort.
Zero in on your digestive health needs: Discover and secure top-quality digestive aids like [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis prices[/URL – without hassle from your living space.
Explore cutting-edge ways to manage your heart rhythm with low price amoxil .
Unlock exclusive savings through our https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ and enhance your wellbeing now.
Purchase, secure, or acquire your [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix online no script[/URL – easily via our platform to enhance, boost, or elevate eyelash growth effectively, efficiently, or swiftly.
Xperience enhanced comfort and convenience when you purchase your medication through our website. Find out more about obtaining your [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – trazodone generico europa[/URL – .
Explore Canadian healthcare options and discover levitra . With a range of options for your needs, locate the perfect solution on the internet.
Visit our website to discover the https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ for your inflammation reduction needs.
Purchase affordable [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – vardenafil[/URL – for managing cardiovascular wellness. Explore choices on websites for economical strategies.
Perfektni prispevek! Prave jsem zacal hrat ve Spinmama Casino CZ a musim priznat, ze jejich bonusy jsou skvele. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere potesi kazdeho hrace. Osobne me bavi jejich herni souteze a vyherni automaty – jedno z nejlepsich ceskych online casin. Pro vyzkouseni neceho noveho a bezpecneho kliknete zde: Twitter . Stoji to za vyzkouseni a prinese to spoustu herni zabavy a odmen.
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
03b3f09
Explore the options and obtain your prescription without leaving your home at [URL=https://jawany.com/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – .
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering buying hydroxychloroquine out of canada via the internet offers a cost-effective option.
Obtain https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ for your allergy relief. Securely acquire your solution online.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – – your go-to option for restoring well-being.
Get immediate relief from your nasal allergies by opting to generic nexium . This medication can significantly reduce your symptoms, guaranteeing a improved daily life.
I discovered a cheap way to enjoy gaming from home at https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ .
Manage your allergies effortlessly by opting for to [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – , a reliable solution.
Quickly obtain significant savings on heartburn relief by opting to [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – order now prednisone[/URL – , accessible online.
Just unveiled: prices for prednisone offers a revolutionary solution for hair loss. Now, you can purchase effective treatment without leaving the comfort of your home.
Gain immediate access to https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ and alleviate your worries with a simple click.
Considering the myriad options for hair loss solutions, acquiring [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ – retin-a cheap online rx[/URL – could be your most cost-effective choice.
Just discovered the best deal for heart health supplements? Look no further. Uncover the most affordable Terminalia arjuna prices at where to buy arjuna online . Whether looking online, Walmart offers incredible prices for your wellness needs.
Secure your well-being effortlessly by opting to buy medicines from https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ . Explore a wide selection of health products online.
Facing chronic pain or anxiety? Discover your relief safely with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ – buy nexium without prescription[/URL – , the trusted option.
Zero discomfort can be your reality; explore the option to purchase arthritis relief via the web with [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ – nizagara[/URL – .
Discover affordable options for impotence by visiting cialis 10 wholesale , where you can acquire your drugs conveniently.
Zero hesitation required when seeking ED solutions; purchase https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ conveniently.
When seeking relief from chronic allergies, consider exploring [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ – buy generic levitra[/URL – for effective treatments.
Quiet nights can often be disturbed by restless legs, a common ailment affecting many. To combat this, trusted solutions like [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/]levitra[/URL] can be invaluable. If you’re seeking relief, consider obtaining this solution from our website.
Secure your health with ease; purchase how much vidalista for your cardiac needs online.
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ on the web presents a budget-friendly option.
Opting for [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/]ciprofloxacin[/URL] can provide an affordable solution for treating bacterial infections.
Visit [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – fildena 150mg[/URL – to obtain your prescription without a doctor’s approval.
Finding the right applicators for applying Lumigan can enhance the effectiveness of your treatment. Explore your options and nizagara 50 farmacia to ensure optimal application and results.
Quest for savings on HIV treatment ends here; locate https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ for managing your health efficiently.
You can obtain [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ – levitra 20mg[/URL – with ease by visiting our reliable healthcare website.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – medication isotretinoin[/URL – to secure your medication easily.
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding generic clomid canada to your regimen! Discover budget-friendly choices on the internet for enhancing your health journey.
Now, locate your solution for ED with ease by opting to purchase https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ .
Now, secure your path to wellness with ease. Discover a holistic solution by choosing to [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil my canadian pharcharmy[/URL – .
Facing respiratory challenges? [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ – asthalin hfa inhaler best price[/URL – can be your relief partner. Secure, simple, and quick, it’s your gateway to improve breathing.
Beat allergies with a click! Discover affordable relief by opting to buy your propecia.com . Say goodbye to allergic reactions effortlessly.
Looking to enhance your energy? Discover trusted options and purchase https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ —your solution to addressing erectile dysfunction.
Purchase your [URL=https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – online to guarantee you get top-notch medication with convenience.
WildRose Essentials – Warm and friendly environment, browsing uncovered a few gems.
Given the need for trustworthy laxative solutions, considering [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin from canada[/URL – could be a judicious option.
Discover reliable joint pain relief with lasix information , the leading solution now available on the web.
Obtain comprehensive insights on https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ to secure you get the best deal on the market.
Just discovered you can obtain [URL=https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 1 to 2 days shipping[/URL – from online pharmacies, offering a hassle-free method to manage your health needs.
Just discovered an amazing source to buy your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – lowest price generic nizagara[/URL – . Whether you need it, there’s your solution.
X-ray your budget no more! Discover the cytotec and see how cost-effective treatment can be. Whether you’re seeking attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management solutions, we’ve got your back. Preserve funds without sacrificing quality.
Consider securing savings on your fertility treatments with https://jawany.com/retin-a/ . Uncover top deals to assist in your journey toward starting a family.
Consulting your medical expert is crucial before you acquire [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a from india[/URL – .
X-Plore options for migraine relief with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – . Discover how to effectively handle your symptoms online.
Purchase, acquire, or obtain your generic zithromax uk with ease, ensuring a smooth, hassle-free process to improve your wellness journey, available via the internet.
In need of an antibiotic treatment? Get your prescription without hassle https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ . Available without the need for a doctor’s visit, ensuring you receive your treatment promptly.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Discover [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – buy cheapest 5 generic cialis[/URL – to enhance your vitality efficiently and confidently.
MidCity Collection Store – Well-organized selections, browsing feels simple and convenient.
Acquiring branded [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – retin a capsules[/URL – has never been more straightforward. Order your upcoming batch from our website with total assurance.
You can purchase your heart medication securely tretinoin online legitmate canada , ensuring quality and cost-effectiveness.
Hunt for exhilarating fun? Discover the https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ for an unparalleled journey.
To guarantee your well-being, buy [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – from a reliable source.
Unlock access to buy Tadalafil effortlessly with vpxl lowest price , ensuring rapid shipment directly to your doorstep without the need for a prescription.
Looking to purchase your fertility medication? Visit https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ and explore various options.
A detailed guide to accessing [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – is now accessible! Whether you’re looking to purchase or simply explore options, this handbook provides the entirety you need.
Если вы занимаетесь производством и ваша компания нуждается в поставке лучших тугоплавких металлов, то ООО “РМС” – ваше лучший выбор. Наша компания работает на рынке поставок тугоплавких металлов на протяжении многих лет, что обеспечивает нам условия поставлять только качественный продукт своим клиентам.
Основные преимущества ООО “РМС”:
1. Любые объемы поставок.
2. Большой ассортимент тугоплавких металлов.
3. Полный комплект документов.
4. Поддержка 24/7.
Зачем тратить время на поиски на других сайтах, если rms-ekb.ru всегда здесь для вас?
В случае возникновения вопросов, наши эксперты всегда готовы вам помочь. Пишите прямо сейчас и убедитесь в достоинствах нашего продукта.
Ваш надежный поставщик, ООО “РМС”
Наша продукция:
Электротехнический лист 20864 0.5x1000x1500 ГОСТ 12119.0 – 98
Facing hair loss? Discover solutions now with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ – prednisone[/URL – . Purchase your treatment via our website.
Keeping pain and inflammation at bay has never been easier, thanks to pharmacy in usa . Now, you can purchase this efficient remedy with just a few clicks.
Reduce your healthcare costs by opting to acquire your medications through https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ , presenting you with a cost-effective alternative to manage your wellness needs efficiently.
Discover how [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – nolvadex 20mg[/URL – can alleviate your allergy symptoms swiftly and effectively. Explore how utilizing these solution can alter your daily comfort by lowering sneezing, itchiness, and nasal congestion.
Find the best deals on insect repellent at [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ – deetor capsules[/URL – . Search for top offers on insect repellent currently.
Zero hassle: obtain your viagra 50mg with ease.
If you’re looking to purchase Flagyl, think about https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ for a straightforward way to receive your medication.
X-plore your options for managing hypertension with proven medication. Order [URL=https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ – amoxicillin[/URL – online to secure your heart health today.
You can acquire the supplement without a prescription. Explore your choices [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – discount herbal max gun power[/URL – today!
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Discover generic cialis canada pharmacy – your go-to option for restoring well-being.
Just in case you’re probing for the most cost-effective choices for your fertility treatments, consider discovering the rate of https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ . It’s essential for those wishing to enhance their chances of conception.
Acquire non-brand [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – online for chemotherapy.
Researching options to purchase [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – priligy dapoxetine[/URL – ? Review our trusted source for your medication needs, providing a wide range of pharmaceuticals with convenient delivery options.
To treat your health issue effectively, think about buy propecia no prescription as your go-to option.
X-ray your options for managing arthritis pain by exploring safe, effective treatments. Consider https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ to reduce discomfort. Always speak to a healthcare professional before commencing any new therapy.
Obtain your [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – lasix without dr prescription[/URL – today and manage your well-being effectively. Order now for swift delivery.
Just realized you need ED medication for your condition? No need to worry! You can [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – easily and safely.
Obtain your tadalafil prescription effortlessly through our website, ensuring quick and dependable service for your pharmaceutical needs.
Acquiring https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ has never been more straightforward, allowing individuals to acquire crucial medication effortlessly.
Need to manage your health condition without a prescription? Find your solution with [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – , offering a secure route to improved well-being.
Navigate the web to secure your youth-restoring solution effortlessly from the comfort of your home; [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – on line nexium[/URL – stands as your optimal choice for regaining vitality.
X-plore the therapeutic benefits and possibilities of zithromax on line for various medical conditions. Discover the efficacy of this medication for controlling your health needs safely.
Just discovered your remedy for skin issues? Buy Accutane with confidence here: https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ . Say goodbye to ongoing complexions issues now.
Explore the top options for enhancing your performance with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax walmart price[/URL – , on sale for safe buying online.
Quest for the lowest rates on Erythromycin? [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ – generic kamagra oral jelly vol 1 from canada[/URL – has unbeatable prices for you.
A range of options to obtain antimalarial treatment online is now available. For those seeking protection or treatment, chloroquine dallas no prescription online offer a practical solution.
Considering the myriad options for baldness solutions, acquiring https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ could be your most cost-effective choice.
Need to acquire your hair loss treatment? Locate cost-effective options with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – , guaranteeing you obtain top-notch therapies with a portion of the price.
Get your [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – dosage clomid shopping[/URL – delivered to your doorstep by opting to secure online.
Uncover discounts when you acquire your prescription with generic maxaquin tablets .
To secure the best rate on https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ , check out our webpage.
Zeroing in on effective hair loss solutions? Explore the myriad options available for managing alopecia. [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/generic-tadalafil-from-india/ – tadalafil without dr prescription usa[/URL – could be your answer. With various treatments on the market, it’s essential to select one that matches your specific needs.
Zinc supplementation may enhance your health. Experiment with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – to potentially boost your well-being.
Looking for affordable options? Find the canadian pharmacy viagra without hassle.
Various individuals seeking anti-inflammatory treatments can now obtain their medications effortlessly. https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ offers a reliable solution for those needing to handle their health without difficulties.
Inquiring about prednisone-related dental troubles? Discover how it impacts oral health here: [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ – buy tretinoin online canada[/URL – .
X-plore the myriad of options to get your treatment swiftly and safely with purchase pharmacy .
Zero hassle to acquire your treatment: https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – purchase online with complete confidence.
For individuals seeking enhanced stamina, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – offers a cutting-edge solution.
Considering your health and well-being, securing the drug you need has never been easier. Ensure you explore [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/sildalis/ – generic sildalis from canada[/URL – for the unbeatable rates available.
Looking for a safe and effective alternative for testosterone replacement therapy? Look into nizagara online canada , a top-rated choice among healthcare professionals.
With an array of organic solutions for increasing vitality, click here to https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ , offering a safe and potent way to improve your health.
Discover effective relief for cold sores with [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/sildalis/ – price of sildalis[/URL – , your go-to antiviral cream. Purchase the solution via our website and start your journey to recovery today.
Looking for a reliable source to acquire your prescriptions without leaving home? Visit [URL=https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ – 100 mg generic lasix online[/URL – to secure your health needs through the internet with ease.
Seeking effective treatments for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder? Explore the benefits of lasix dallas no prescription online , a proven solution for managing symptoms.
Now, uncover your route towards minimized cholesterol with https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ , available for acquisition online.
Looking to obtain Depo-Medrol for your medical requirements? Click on the link [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil no prescription[/URL – for a straightforward process.
Harness the power of modern medicine safely; purchase nizagara via our website for your health needs.
Improve your health and boost your well-being with a premium solution, https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ .
Zeroing in on your need for diuretics, secure your Lasix effortlessly with [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – no prescription furosemide[/URL – , ensuring convenience in controlling fluid retention.
Zap your low testosterone levels into oblivion with lady era generic . Elevate your vitality by uncovering a treatment that rejuvenates male health effectively.
Before opting for conventional methods, look into other avenues to purchase your medications. One reliable option is to https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ , offering a convenient way to manage your health.
Quickly purchase your [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy-com-lowest-price/ – generic priligy canada[/URL – on the internet for the best solution in boosting eyelash growth.
Harness the power to combat your health concerns; acquire prednisone no prescription safely and without hassle to ensure your well-being.
A comprehensive guide to managing heart conditions effectively: Explore options like https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ and discover alternative solutions for enhancing your cardiac health.
Maximizing your convenience, you can now acquire [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – by navigating our trusted website.
Discover how to employ [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ – propecia overnight[/URL – effectively for reducing pain.
Discover various medical answers with amoxil no prescription paypal , available for acquisition immediately through the internet.
For those seeking to improve their eyelashes, think about https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ . This solution offers an efficient way to achieve fuller, longer lashes.
You can easily purchase your [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – lasix[/URL – from the comfort of your home, offering relief from nasal congestion.
ironskyessentials – Really impressed with ironskyessentials, found quality items quickly and easily.
Discover how [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ – tamsulosin[/URL – can alleviate symptoms of BPH by visiting our website.
Discover your pathway to relief from minor aches and pains by purchasing your next supply of viagra 25mg virtually.
Zest for life can be increased with reliable cardiovascular care. Check https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ to discover how you can manage your heart health affordably.
Having trouble with eye inflammation? Explore affordable solutions and buy [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large brand[/URL – , a trusted solution for managing your symptoms effectively.
Considering diverse treatment options, it’s crucial to discover affordable solutions. For those looking for hormone therapy alternatives, [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – 50mg clomid best price[/URL – offers a viable choice.
Need to cut costs on your medication expenses? Check out the purchase lasix online for lower costs on pharmacy needs.
Questioning where to acquire finasteride? Discover safe, trustworthy options for https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ .
Manage your health by deciding to acquire essential medications easily through our platform, ensuring you can [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – conveniently from the comfort of your home.
Having issues with an enlarged prostate? Find out how [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – can help and restore your comfort.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? lowest price generic flomax might be what you need. Discover how it can assist in reducing your symptoms efficiently.
X-plore your choices for enhancing eyelash growth with https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ , accessible for purchase on websites.
Zap your ED worries away! Obtain effective ED medication [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ – viagra 100 mg quick disolve[/URL – . This solution is reliable and quick to find.
Zest for life can be regained with ease. Purchase your osteoporosis treatment with confidence [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ – lasix without dr prescription usa[/URL – .
Facing health issues? Get your cialis black easily without leaving your house.
Protect your health by learning on the most recent health tips and trends at our https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ online resource.
Unlock the secret to boosted stamina by opting for to [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ – canadian levitra[/URL – , your primary source for top-quality medical solutions.
Looking to treat your condition? [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – buy nexium without prescription[/URL – offers a streamlined solution. Obtain your medicine with ease today.
Zap your low testosterone levels into oblivion with bentyl herbs . Elevate your vitality by exploring a treatment that boosts male health effectively.
Keeping your health in top condition is crucial, and obtaining your medications shouldn’t break the bank. For those looking for cost-effective treatments, discover the current https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ , a place where value meets excellence.
Boost your well-being quickly with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ – buy cheap prednisone[/URL – . Purchase your package immediately for improved outcomes.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – costi hydroxychloroquine[/URL – .
Discover your path to wellness with inexpensive options. generic vardenafil cheep offers a range of medications to manage your health efficiently.
In need of an antibiotic treatment? Get your dose without hassle https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ . Available for immediate purchase, ensuring you receive the medication swiftly.
Curious about where to locate the [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – orlistat[/URL – ? Explore our site for amazing deals on your medical needs.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis 20mg[/URL – , your go-to source for securing reliable ED remedies online.
Quickly discover relief from year-round nasal congestion with eriacta , a leading choice for combatting allergy symptoms.
Boost your health with quick access to antiviral treatment by visiting https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – your one-stop solution for effectual healing.
Sure, discover how to get [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ – cialis canada[/URL – through our website.
Discover the most economical method to purchase your prescription with our levitra 10mg .
Having gastrointestinal discomfort? Discover relief through https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy-com-lowest-price/ , a trusted medication. Obtain it via the internet for quick alleviation from intestinal pain.
Purchase organic solutions for your health needs effortlessly on our website. Explore options and discover the best deals [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – lasix walmart pharmacy[/URL – right away.
Browsing for an affordable way to manage your symptoms? Discover unparalleled prices and convenience by choosing to order your medications via the web with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – buy online pill levitra[/URL – .
Discover excellent choices for managing your health issue efficiently with tadalafil . Boost your health today.
Venture into cost-effective healthcare options and find how to maintain your health without breaking the bank. For those looking to cut costs, https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ offer a answer.
Here’s how to find the current [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tadalafil/ – buying tadalafil[/URL – to preserve on your treatment.
Unlock savings on your hypertension treatment by visiting [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia to buy[/URL – , your gateway to affordable healthcare.
Get immediate relief from your nasal allergies by opting to vidalista capsules . This solution can minimize your symptoms, ensuring a improved daily life.
Regain control of your health by securing your medication without delay. https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ is your path to overcome conditions efficiently.
Manage osteoporosis effectively by choosing to [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – . With options abundant, you can purchase this osteoporosis treatment via the internet.
I’ve discovered where to get cost-effective 0.4 flomax lowest price , a commonly prescribed treatment for certain types of malaria.
Explore budget-friendly solutions for your health needs with https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ . Buy your medication easily today.
Explore safe options to order your pharmaceuticals online with our [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – pharmacy[/URL – source.
Visit [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ – equivalent au lasix[/URL – to acquire your prescription easily.
Considering the importance of anti-malarial treatment, individuals seeking chloroquine can easily acquire their medications through chloroquine no script no hassle , offering an effortless way to fight malaria.
Shop for herbal health remedies and boost your wellbeing today. Purchase a supplements at https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ , a reliable source for top-notch health products.
Considering the myriad options for baldness solutions, acquiring [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil-best-price/ – buy cheap tadalafil[/URL – could be your most cost-effective choice.
Seeking the highest quality fertility drug for your treatments? Look no further! Obtain your buy cheap dapoxetine safely and easily.
You can purchase your https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ with ease online, ensuring you get quality medication for managing your condition.
Browse the site to find [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin coupon[/URL – , ensuring you get high-quality antibiotic choices at incomparable prices.
Zap your health concerns away! Uncover the convenience of securing your medication virtually. Don’t miss the chance to order [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin-canada/ – buy ventolin online canadian health[/URL – , a significant breakthrough in managing well-being needs.
Unlock the potential for a better, more fulfilling love life by exploring normal dose propecia . With a myriad of options available, you can secure a sample pack from reputable sources effortlessly. This small step could dramatically enhance your intimacy and connection.
When seeking affordable solutions for impotence, consider https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ as your go-to source.
Revitalize your vitality with a natural solution; [URL=https://renog.org/sildalist/ – sildalist from canada[/URL – . Experience the power of herbal ingredients right away.
X-plore vision health with innovative solutions. Buy [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ – prednisone for sale overnight[/URL – via the internet for controlling glaucoma effectively.
Seek effective solutions for hair loss management with zithromax brand . Purchase today for a smoother path to restoring your hair.
Join the myriad of individuals choosing to purchase their wellness supplements through digital stores by exploring options to https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ . Elevate your health regimen now with this dependable remedy.
Visit [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl 20mg[/URL – to obtain your natural kidney support.
Planning for an emergency fund boost in the Lone Star State? Explore your options with buying levitra us a rapid solution for your economic needs.
Considering diverse treatment options, it’s crucial to discover cost-effective solutions. For those looking for hormone therapy alternatives, https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ offers a viable choice.
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and order your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – generic kamagra[/URL – today for improved health and vitality!
Zest for life can be regained with ease. Purchase your bone health solution with confidence [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ – buy celebrex online canada[/URL – .
A reliable way to control your health: misoprostol . Explore our website to find multiple methods for your wellbeing.
Explore the options and purchase your treatment from the comfort of your home at https://jawany.com/cytotec/ .
Visit our website to discover the [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – sarafem stock[/URL – . Our platform offers a convenient way to acquire your prescription on the web.
Looking to enhance your vitality? Discover incredible savings with our tadalafil 20mg .
Optimize your health and wellness routine by purchasing your prescriptions effortlessly. https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ offers a convenient solution for boosting your vitality.
X-perts agree, securing [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ – generic viagra from canada[/URL – could significantly cut your healthcare expenses.
I discovered an economical way to enjoy gaming from home at [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – tamoxifen[/URL – .
To learn about the benefits of hormone replacement therapy, check out xenical 60mg . Whether you’re seeking to alleviate menopausal symptoms or handle osteoporosis, it’s your go-to resource.
Whether you’re struggling with seasonal allergies or year-round irritants, https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ offers a treatment. Find relief from blockages and sniffling with just a few sprays.
The need to purchase medications without leaving home has never been more essential. Now, you can conveniently get your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – with just a few clicks.
Quickly acquire your essential wellness product today; [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/ – buying sildalist[/URL – offer a wise choice for improving your health.
If you’re searching to purchase an economic solution to your vertigo, think about retin a gel . This medication may assist in lessening the effects of balance disorders, boosting your overall well-being.
For those seeking a diverse range of treatments for https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ , exploring our collection is a must.
Regarding dementia treatments, exploring options for medication is crucial. For those considering Donepezil, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ – buy tretinoin online canada[/URL – offers multiple choices.
Harness significant savings on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone without a doctors prescription[/URL – . Grab your essential medication without denting your wallet by using this special offer now.
Regarding your need for mood stabilization, think about acquiring legal ventolin no prescription online.
Revitalize your hair growth! Secure your effective solution now, https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ , and say goodbye to thinning hair once and for all.
SUNWIN is a new-fashioned online betting ecosystem built representing players who value transparency and even gameplay. From casino production to overnight x? s? results, the stand blends technology with true betting insight. Fans of th? thao and esports can traverse data-driven odds, while casual users enjoy trò choi, game slots, b?n cá, and immense jackpot rewards. Ritual options like dá gà, baccarat, r?ng h?, xóc dia, tài x?u md5, and n? hu are optimized against fairness and speed. With everyday khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, a gifted cskh team, and a as plain as day d?i lý arrangement, players can also substantiate details quickly at https://creditservice.ru.com/ to adventure a predictable betting journey.
Battling sleep disorders? Our pharmacy offers a quick solution. Buy [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ – pharmacy without dr prescription usa[/URL – today for a peaceful night’s rest.
Secure your health with ease by choosing to buy your essential drugs through the web. For those looking for a reliable antiplatelet, click here: generic retin-a available to obtain yours without any hassle.
Maximize your health and well-being by opting to acquire top-quality pesticide lotion for effective parasite control. Secure yours immediately at https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ .
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Consider [URL=https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ – cheapest cialis online without prescription[/URL – – your go-to option for restoring health.
Seeking a remedy for hair loss? Find out how to buy [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride/ – finasteride from canada[/URL – , a proven method to combat balding safely.
Relieve your symptoms with xenical 120mg , ready for purchase online.
Unlock significant savings and convenience when you acquire your health solution virtually. Experience the ease of securing quality healthcare products without leaving your home. Click here https://phovillages.com/xenical/ to initiate your journey towards better health.
To treat hair loss, look into [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical without pres[/URL – as an effective solution.
Overcoming thinning hair is now simpler than ever. Uncover your path to a fuller head of hair now with our unique formula. No prescription needed. [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ – generic dapoxetine from india[/URL – .
Looking to control your gout symptoms? Discover a variety of affordable options when you purchase amoxil cialis uk .
Explore your choices for dealing with peptic ulcers with https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ , accessible on the web.
Find unbeatable deals on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – to improve your vitality.
Your search for budget-friendly Cabergoline ends here: [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – purchase finasteride without a prescription[/URL – .
X-ray your options and choose wisely where to lowest price on generic nizagara . With myriad choices available, select the most secure provider to procure your medication.
Reduce your heart’s workload with https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ , an essential treatment for reducing chest pain. Buy today for enhanced heart health.
StartBuilding Finds Hub – Clean, motivational design with organized content ensures effortless navigation.
Looking to secure your fertility medication? Click on [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a[/URL – and discover numerous solutions.
Manage your health by deciding to purchase essential medications easily through our platform, ensuring you can online generic prednisone conveniently online.
Consider securing your https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ effortlessly through our platform. Order now online for swift delivery.
Obtain your Azithromycin, or its equivalent, efficiently without the need for a medical practitioner’s formal endorsement by clicking here: [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol 6mg[/URL – . This streamlined process ensures you obtain your treatment swiftly, aiding an expedited recovery.
Obtain your [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – buy levitra on line[/URL – today and manage your well-being effectively. Order immediately for swift delivery.
Xplore optimal vitality solutions! Get your on line vidalista to maximize your wellness today.
Manage urate crystal arthritis effectively by considering https://yourdirectpt.com/cafergot/ , an potent solution.
Zero in on rejuvenation and vitality with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – . Discover how to renew your youth and stamina without breaking the bank.
X-Plore choices for migraine alleviation with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – buying nizagara[/URL – . Discover how to efficiently manage symptomatology on the web.
Questioning where to find medicine without overpaying? Uncover the cipro on internet and save on your medical costs.
Unlock incredible prices on https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ when you purchase now.
To acquire effective malaria treatment, browse [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – amoxil 250mg en pharmacie[/URL – for a wide selection of options.
Looking to lower your motion sickness or vertigo symptoms? Secure your [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – 20mg prednisone price no prescription[/URL – now and spend less on your next purchase.
Get your vpxl online pharmacy easily! Explore solutions to obtain your medication without trouble.
X-ray your options for heart arrhythmia treatment without breaking the bank. Find economical solutions and bid adieu to sky-high medical expenses by opting to buy economically priced https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ via internet pharmacies.
Reduce your healthcare expenses by opting to purchase your medications through [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara 100mg pills,usa[/URL – , offering you with a cost-effective option to manage your wellness needs efficiently.
crest collection – Wide assortment to choose from, and the shop stays current with ongoing improvements.
Acquiring [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ – generic lasipen uk[/URL – could aid in boosting cardiovascular health.
Zero hassle when you choose to obtain your wellness supplements through the web. zithromax korea to support your health journey effortlessly.
Quality healthcare solutions are now accessible through our online platform where you can obtain trusted https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ without leaving the comfort of your home.
Regain your well-being safely and efficiently with our certified online store. Purchase your prescription with ease, visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – online tretinoin no prescription[/URL – now for fast relief.
Uncover the benefits of utilizing [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex[/URL – for your allergy-related symptoms. Available now, this treatment provides a cost-effective solution to manage your discomfort.
Explore secure options to buy your pharmaceuticals online with our zoloft prices source.
Procure your essential medication affordably by clicking here: https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ , guaranteeing considerable discounts on top-notch healthcare.
Seek unparalleled performance and confidence in intimate moments; unveil your pathway to enhanced vigor with [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ – cheap vpxl online without prescritpion[/URL – . Acquire your answer instantly.
Find affordable alternatives or generic versions of brand-name medications easily online. Whether you’re looking to purchase Atorlip-5 without a prescription, verify you’re getting a legitimate option through verified websites. furosemide offers a reliable method to manage your wellness needs efficiently.
When seeking relief from persistent aches, consider https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ as your go-to solution. It’s obtainable through online pharmacies, offering convenience and results.
Our latest guide on [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ – cost of nizagara 100mg tablets[/URL – outlines how to efficiently employ this remedy for constipation.
Discover the convenience of managing ocular dryness from the comfort of your home; levitra offers a seamless experience. Opt now to purchase your treatment virtually.
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ , and Bag a supply of essential antibiotics effortlessly via our website.
Xperience seamless relief from motion sickness with our top-rated solution. Uncover [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ – legally buy tadalista on line[/URL – and embark on your journeys without worry.
Zillions now look for answers for boosting their energy. It’s simple to obtain reliable help pharmacy prices for tadalista .
The need for trustworthy and convenient access to pharmaceuticals has never been greater. Explore your options and buy https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ today.
Secure your wellness and enhance your vitality by purchasing the [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – on line zoloft[/URL – for continuous satisfaction.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ – generic clomid from canada[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous alternatives available on the web. Secure your well-being today by selecting the best deal.
Regain your zest for life! Use our lowest price generic pharmacy for unparalleled confidence. Revive passion without breaking the bank. Acquire your answer to a fuller, more vibrant experience now.
One can discover competitive https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ and numerous choices in digital pharmacies, ensuring affordability and accessibility.
The rate of managing pulmonary arterial hypertension might be substantial, but [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – http://www.lasix.com[/URL – offers an economical solution.
“Visit now for unparalleled savings; use your exclusive nizagara to cut costs on allergy relief today. Don’t miss this chance to reduce your symptoms at a fraction of the cost.”
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ can assist in easing urinary symptoms related to an enlarged prostate.
Having gastrointestinal discomfort? Discover relief through [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – , a trusted medication. Obtain it via the internet for rapid alleviation from stomach aches.
Discover affordable treatments for erectile dysfunction by visiting [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – buy cialis 5 for sale[/URL – , where you can purchase your prescriptions conveniently.
Before considering treatment options, explore medicament prednisone to manage your health needs safely.
You might find the best https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ on various websites, ensuring you receive maximum value for your therapy.
Considering the need for cost-effective nervousness treatments, [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/sildalis/ – price of sildalis[/URL – offers a practical choice.
Explore buying [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – levitra tablets[/URL – with ease for effective remedy.
Understand your options for treating vertigo; explore generic lasix at walmart as an effective solution. Acquire it now for alleviation from continual dizziness.
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ , and Snag your bottle of crucial antibiotics easily online.
Seeking angina treatment? Discover your options with [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ – propranolol[/URL – , accessible online.
Boost your health today! Acquire your where can i zithromax without hassle. This essential therapy is now away.
Interested in securing the most advantageous deal on your medication? Discover the ultimate offers for https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ effortlessly. Now, obtaining control over urinary incontinence is more straightforward than ever.
For managing moderate pain and swelling, consider [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/propranolol/ – propranolol 40mg[/URL – as a reliable choice.
Looking for a reliable place to acquire your medication? Look no further! [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra canada shipping[/URL – offers a wide selection of medicines to satisfy your needs.
Keep your health in top shape affordably by choosing to acquire your retin a overnight online.
For those seeking to purchase https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ without breaking the bank, various web-based drugstores offer competitive rates.
Seeking a treatment for hair loss? Explore how to buy [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – overnight finasteride[/URL – , a trusted method to tackle balding safely.
Find your method to buy tamoxifen delivered in ontario canada safely.
You can acquire https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ safely and conveniently online.
For those in need of immediate relief, secure [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – nolvadex[/URL – . This pain reliever can offer fast and effective relief from discomfort.
Unlock unbeatable deals on [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/levitra/ – where to buy levitra online[/URL – , Preorder your medication now.
Yes, if you’re looking to acquire lowest price for sildalist , consider exploring our trusted resource.
Questioning where to purchase your medications? Look no further, as https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ offers an array of choices for your needs.
Regain your vitality with a unique solution; [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil online malaysia[/URL – is available for purchase. It’s your chance to revive your well-being effortlessly.
Yes, you can now buy your prescriptions with ease and convenience through [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – .
Boost your wellness with natural supplements; order your zoloft online for optimal health benefits.
Yes, ensuring you get the right medication is crucial, that’s why choosing a https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ , which provides similar advantages, is a prudent decision.
Yes, you can find discounted solutions for handling edema. [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ – lowest price on generic tadalafil[/URL – is your go-to option for intervention.
Obtain the Tadalafil swiftly through our trusted [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ – generic viagra tablets[/URL – , ensuring an anonymous and rapid delivery directly to your doorstep.
Please discover the option to acquire your tadalafil , ensuring enhanced well-being outcomes.
Get your heart medication easily with https://glenwoodwine.com/zoloft/ , available without hassle.
A comprehensive resource on health education in the United States is readily accessible at [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ – kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1 sales india[/URL – .
Worried about your HIV status? Easily check with a dependable viagra in usa . Order your kit now for reassurance.
Quickly locate your essential hypertension relief with https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ , accessible at unbeatable prices.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for acquisition with no wait at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – strattera buy in canada[/URL – .
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – le flomax[/URL – can help in alleviating urinary symptoms related to an enlarged prostate.
Unlock the secret to thicker hair with just one click. Don’t hesitate, secure your solution to hair loss prix viagra-jelly paris now.
Please consider the option to acquire your https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ , ensuring improved well-being outcomes.
Worried about your HIV status? Easily check with a reliable [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – buying vidalista[/URL – . Order a kit today for tranquility.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ – flomax 0.2 mg quick dissolve[/URL – , and explore a range of options to better your quality of life.
Replenish your medicine cabinet easily with spinach amoxil , to guarantee consistent care.
When seeking trusted management for epilepsy or bipolar disorder, explore https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ as your option.
Your search for affordable options ends here: [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/clomid/ – clomid capsules[/URL – . Discover your solution today and save on healthcare expenses.
Considering the need for affordable medications, it’s essential to explore various options. If you’re in pursuit of cost-effective treatments, particularly for inflammation and allergic reactions, exploring [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – might be your best bet. This glucocorticoid medication, pivotal in managing numerous conditions, can be obtained with ease.
Your search for affordable pain relief ends here; buy generic lasix france for swift ease.
Access effective treatment quickly and without hassle by choosing to procure your medications through our web platform. For patients seeking immediate therapy, https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ offers a trustworthy solution.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – cheapest vidalista[/URL – today. Whether you’re seeking to enhance your wellness effortlessly, our website offers a straightforward pathway to get your essentials.
Facing dry eye problems? Discover the solution on our website with low cost nizagara . Purchase your bottle today for ease.
Explore innovative methods for enhancing your body’s growth with https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ , available now.
If you’re seeking a dependable place to buy Flagyl, consider visiting [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ – no prescription flagyl[/URL – , where you can effortlessly obtain your medication online.
Obtain your [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – cenforce lowest price[/URL – safely and without hassle via the internet.
Aordable solutions for dry eyes are now within reach. Explore our selection and buy your treatment for soothing relief. Find lowest price nizagara online today.
To obtain the cheapest options for https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ , check out our website today.
Looking to minimize your motion sickness or vertigo symptoms? Obtain your [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ – generic flagyl in canada[/URL – now and save on your next purchase.
Maximize your savings when you acquire your heart health medications by checking out the latest retin a .
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ , providing comprehensive therapy for bacterial infections.
X-ray your options for managing arthritis pain by exploring safe, effective treatments. Consider [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – to reduce discomfort. Always consult a healthcare professional before commencing any new medication.
SUNWIN stands exposed as a trusted online principles where casino, x? s?, th? thao, and interactive trò choi run across modern technology. From immersive game slots, fast-paced b?n cá, and high-value jackpot events to competitive dá gà and global esports, the sagacity feels seamless and fair. Knowledgeable systems power tài x?u md5, xóc dia, baccarat, r?ng h?, and overwhelming n? hu. With recurring khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, efficient cskh, and tractable d?i lý programs, players can study confidently. Learn more at https://creditservice.ru.com/.
SUNWIN stands out as a complete online betting principles where casino fun blends seamlessly with x? s?, th? thao, and interactive trò choi. From immersive game slots, skill-based b?n cá, and high-reward jackpot systems to old favorites like dá gà, xóc dia, baccarat, r?ng h?, and provably fair tài x?u md5, the principles delivers depth and balance. Competitive esports, ordinary khuy?n mãi and long-term uu dãi are supported by open cskh and a above-board d?i lý network. Revolutionary n? hu mechanics and data-driven fairness steel credibility. Determine more at https://creditservice.ru.com/, where innovation meets accountable play.
Quest for the ideal [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – overnight viagra[/URL – ends here! Discover the top option for your needs.
Jumpstart your vitality journey with prednisone , your go-to solution for boosted vitality.
Browse our website to locate the https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ , offering you a cost-effective solution to treat your inflammation.
Looking to manage your menstrual cycle irregularities? Discover a reliable solution with [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – prednisone 20mg online india[/URL – . This medication can be your ally in dealing with various gynecological conditions.
Keep your health and vitality at peak by exploring herbal solutions. Secure your supply of [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – canadian tadalafil[/URL – now and embark on a journey towards boosted wellbeing with no hassle.
Maximizing your convenience, you can now secure generic vidalista at walmart by navigating our dependable digital platform.
To purchase effective treatment for IBS, consider obtaining https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/viagra-jelly/ , known for its remarkable benefits.
For those seeking to secure their medications with convenience, explore [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy prices[/URL – for an effortless way to get your health essentials.
Now, find your solution for erectile dysfunction with simplicity by opting to buy [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ – fildena without prescription[/URL – .
Discover affordable options for erectile dysfunction by visiting cialis coupons , where you can acquire your drugs easily.
Having trouble accessing prescription medication? Our https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ option offers a straightforward solution, enabling you to purchase necessary medication easily.
If you’re searching for an effective remedy to tackle bacterial infections, think about [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – . This antibiotic has been widely acknowledged for its effectiveness against a broad range of bacteria.
Looking for an effective treatment for your hair loss? Learn about how you can obtain [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis black generic pills[/URL – ‘s prescription easily online.
Yes, reach optimal hormone levels safely by opting for lasix canada paypal , a trusted choice for testosterone replacement therapy.
Get the sought-aftergrowth with thisproduct. https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ today for enhanced results.
SUNWIN stands gone from as a in vogue online betting ecosystem built quest of players who value transparency, speed, and variety. From immersive casino experiences to smart-number x? s? systems and real-time th? thao markets, the platform reflects unfathomable pact of digital wagering behavior in 2025. Fans of faculty separate and unplanned can scrutinize crucial trò choi, fast-paced game slots, colorful b?n cá, and high-volatility jackpot rounds. Historic favorites like dá gà, competitive esports, and table classics such as baccarat, r?ng h?, tài x?u md5, and xóc dia are optimized instead of mobile-first play. What undoubtedly elevates the episode is keen cskh, humanitarian khuy?n mãi and long-term uu dãi, plus a bright d?i lý nature owing growth-focused partners. Dig up more at https://creditservice.ru.com/, where invention meets reliability and every n? hu moment feels earned.
**B**attle heart rhythm disorders with AFib medication from [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – buying trazodone in the dominican republic[/URL – , your go-to source for healthcare needs.
Zero in on the best healthcare advice by consulting with an tadalista generic , ensuring you receive top-notch insights for your well-being.
Obtain your solution for hair loss efficiently. Purchase https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ online and start your journey towards restoring full, healthy hair with ease.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Locate [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – to boost your vitality efficiently and confidently.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – might be the remedy. Explore how it could aid in alleviating your symptoms efficiently.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, levitra at walmart offers a convenient way to secure necessary medication without leaving home.
When managing hypertension, it’s essential to explore various treatment options. Find how you can control your condition effectively with https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ .
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – to your regimen! Investigate affordable solutions on the internet for enhancing your health journey.
To treat Parkinson’s disease symptoms effectively, look into [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – as a viable option.
Achieve prime heart health with our product. Explore more at prednisone .
Having anxiety? Discover a range of remedies https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ . Acquire your treatment on the web.
Seeking a treatment for hair loss? Explore how to purchase [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – generic tretinoin in canada[/URL – , a proven method to tackle balding securely.
Achieve optimal prostate health with [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/product/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2 online fast delivery[/URL – , a trusted choice accessible for those seeking economical management.
Struggling with hypertension or angina? Explore how nizagara without a doctor 100 mg could be your answer to controlling these conditions.
Discover genuine remedies for improving your performance with https://cassandraplummer.com/item/xenical/ .
Facing menopausal symptoms? Find relief with [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ – levitra generico low cost[/URL – , your trusted source for estrogen supplements.
Discover how to get your prescriptions easily with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – viagra in usa[/URL – , ensuring discretion and ease.
Various individuals seeking relief from ocular hypertension or glaucoma now have the option to order an affordable alternative with nizagara , providing a cost-effective solution for managing their condition efficiently.
Managing menstrual irregularities can be challenging, but https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ offers a viable solution. Secure a prescription through the internet to control your cycle with ease.
Discover how to secure your prescriptions effortlessly with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ – viagra 75mg order[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
Purchase your antibiotics conveniently with a click through [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cipro/ – cipro[/URL – , offering a hassle-free way to get crucial medication without leaving home.
Discover innovative treatment options for enhancing your lifestyle; explore the benefits of where to buy amoxicillin online .
Acquire your https://swanpercussion.com/lasix/ effortlessly with our secure online platform. Obtain the necessary pharmaceuticals on the web with ease and confidence.
Boost your vitality effortlessly; find out the cost-effective pricing of [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – generic cipro uk[/URL – .
A comprehensive guide to securing your prescription at the best value: [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – zithromax best price usa[/URL – . Explore where to acquire your medication at favorable costs.
Find cost-effective solutions for your hypertension by choosing to purchase generic priligy lowest price . Ensure your heart health is monitored efficiently with a simple online purchase.
Looking to manage your condition? Buy https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ today and start your journey to better health.
Quickly secure your [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg to buy[/URL – prescription to manage benign prostatic hyperplasia efficiently.
To guarantee your vision health, looking into [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/ – on line levitra[/URL – could be advantageous. Buy with ease online.
Secure your supply of essential nutrients now by deciding to purchase doxycycline online without prescription overnight , optimal for maintaining healthy bones and teeth.
Facing chronic health challenges? Secure your wellness with https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ , a trusted solution. Ensure robust health by opting for this effective remedy available online.
Boost your wellness with natural supplements; order your [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – sildenafil[/URL – from our website for optimal health benefits.
If you’re looking for an effective treatment to fight bacterial infections, ponder [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – canadian pharmacy amoxil[/URL – . This antibiotic is widely recognized for its potency against a wide array of bacteria.
Manage your well-being efficiently by choosing to buy your prescriptions online. For those specifically seeking to treat hormonal imbalances, buying cialis offers a trusted solution.
Xperience improved energy for anyone looking for solutions. Discover your path to a better life by https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ , ensuring maximum results and satisfaction.
Save on your next purchase of [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – buying prednisone online[/URL – by exploring our extensive collection. Discover unbeatable discounts online today.
Now, find [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – asthalin[/URL – by exploring our platform. Secure the most advantageous offer now.
Looking for affordable health solutions? Learn about buy priligy online , your preferred choice for managing your health needs without overspending.
Looking for the ultimate solution to your automotive needs? Look no further! Our https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ showcases the summit of battery technology, ensuring your vehicle runs without interruption. Discover the transformation today!
If you’re looking to purchase hypertension medication at an affordable rate, consider visiting [URL=https://ipalc.org/item/prednisone/ – prednisone purchase india[/URL – for competitive prices.
X-plore budget-friendly solutions for improving your eyelashes with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ – generic nizagara bestseller[/URL – . Uncover a variety of approaches to achieve the look you desire.
Optimize your health management by exploring order retin a online , offering versatile options for those seeking robust antiretroviral treatment. With a plethora of choices, secure your medication from the comfort of your home.
Discover various health solutions with https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ , accessible for acquisition directly through the internet.
SUNWIN is positioned as a in design online betting ecosystem where experience matters as much as trust. From immersive casino rooms to well-educated x? s? systems, the party line balances diversion and control. Players explore th? thao, interactive trò choi, high-volatility game slots, and real-time b?n cá with blatant mechanics. Signature features like jackpot, n? hu, baccarat, r?ng h?, xóc dia, tài x?u md5, dá gà, and esports mirror image retail moan exposed in place of in 2025. Unswerving khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, believable cskh, and a scalable d?i lý pocket distinct away alleviate users increase responsibly. Learn more at https://creditservice.ru.com/.
Navigating through the myriad of treatment options for Alzheimer’s can be daunting. However, procuring Donepezil, a proven medication, has never been easier. For those looking to enhance cognitive function affordably, consider exploring your options to [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ – generic viagra in the us[/URL – . This approach offers a seamless, cost-effective solution for managing symptoms with convenience.
Manage your allergies seamlessly with tamoxifen , now available for ordering via our website.
In search of https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ ? Look no further for cost-effective solutions to your nasal symptoms.
X-ray your options for heart arrhythmia treatment without breaking the bank. Find economical solutions and bid adieu to sky-high medical expenses by opting to buy budget-friendly [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – super kamagra to buy[/URL – online.
You may acquire [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ – flagyl[/URL – safely and easily via the internet.
Need to boost your health with antiretroviral therapy? Visit topamax bipolar to procure your treatment swiftly.
Relieve your pain efficiently with https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ , the ideal solution for reducing discomfort without the need for oral medication.
Zealously seeking relief from year-round allergies? Invest in your remedy with [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/sildalist/ – acheter sildalist sans ordonnance[/URL – , the go-to option for tackling allergic reactions.
Just found an spectacular source to purchase your topiramate . Whether you need it, we’ve got your solution.
Obtain your https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ effortlessly. Secure your medication with no need for a prescription through the internet.
Acquire budget-friendly solutions for your gastrointestinal discomfort with [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – , known to mitigate symptoms efficiently.
Keeping your reproductive health in check is crucial. Discover solutions like [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ – viagra[/URL – that provide hope for many.
Discover solutions for lasting longer in bed with pharmacy without pres . Explore the essential item on the web to enhance your performance effortlessly.
Secure your most reliable pathway to better health by opting to purchase https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ . This solution promises swift respite from discomfort with unmatched simplicity.
Combat inflammation and pain effectively with a cost-effective solution; explore our selection for [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – buy nizagara next day delievery[/URL – . Discover affordable options to address your needs easily.
Xplore a wide array of choices for boosting your well-being with nizagara 50mg .
Require affordable solutions for your cardiovascular well-being? Discover a variety of options including https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ , perfect for sustaining your heart’s well-being.
Discover unbeatable deals on Arimotraz and save on your prescription costs! [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – nizagara 50 online[/URL – . Whether you’re aiming to acquire this vital medication, our platform offers numerous alternatives to ensure you get the highest savings.
https://long-living.ru/
Prepare for unexpected home emergencies by checking out our comprehensive guide at [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ – online retin-a in 24h[/URL – .
Just released: Alleviate your nasal symptoms with a few clicks by opting to acquire your prednisone . This cutting-edge solution delivers immediate relief against allergy-related symptoms.
Your quest for affordable HCQS treatment ends here. Discover the most recent rates at https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ , your ultimate choice for economical pharmacy buys.
Get alleviation from seizure disorders now. Discover more at [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – .
Having difficulty with an enlarged prostate? Find out how flomax can ease symptoms and restore your comfort.
Get eliminate lice easily with our solution at https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ .
Achieve academic excellence and improve your writing skills with our professional help at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – generic viagra lowest price[/URL – .
Get your amoxil easily from amoxil generic 500 mg canadian pharmacy , offering swift delivery to fulfill your healthcare needs.
Explore the convenience of enhancing your health with just a few clicks! Get your https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ now and experience the benefits of fast and confidential delivery.
Aiming to halt hair thinning? Discover the top solution with our [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – amoxil 500 mg price without rx[/URL – . Reach fuller, healthier locks effortlessly.
Beat allergies with a click! Discover cost-effective relief by opting to acquire your purchase retin a online . Say goodbye to allergic reactions effortlessly.
Zero in on unparalleled deals for your health needs; find exclusive offers on https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ now.
Finding budget-friendly solutions for your health needs can be challenging, yet [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – remains a solution. Explore options for managing anxiety effectively on the web.
Relieve your symptoms with [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – prednisone 20 online for sale[/URL – , up for grabs via our website.
Managing menopause symptoms effectively often involves hormone therapy treatment. Many patients look for convenient and discreet options. For those interested, you can acquire estrace pills mexico online, ensuring a seamless and private process.
Discover safe and discreet options to acquire your treatment without hurdles. Click here: https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ .
Venture into holistic healthcare solutions and discover natural remedies. Easily obtain your wellness needs [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – through our trusted platform.
Harness significant savings on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix[/URL – . Grab your essential medication without breaking the bank by using this special offer now.
Obtain prednisone for your allergic reactions relief. Securely purchase your remedy via the internet.
Visit our site to acquire your essential medication. https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ seamlessly, for managing your health needs.
Just discovered [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil from india[/URL – ? Explore the market to buy your supply online.
Discover reliable and convenient ways to acquire your prescriptions with just a click. [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ – viagra 25mg[/URL – offers a straightforward solution for your needs.
Unlock enhanced concentration and vitality with lowest vidalista prices , your ultimate solution for staying alert.
For individuals seeking to control their cholesterol, looking into https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ could be a practical alternative.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Get [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 1000mg[/URL – safely and without hassle.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without a doctors prescription[/URL – is a viable option. Explore securing amoxicillin through online outlets for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can find options on websites including generic tadalafil in canada , a dependable solution.
X-plore budget-friendly options for improving your lashes with https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ . Discover a range of approaches to attain the appearance you aspire for.
Zillions seek efficient solutions for impotence; [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – buy viagra online paypal accepted[/URL – presents a wide-ranging answer.
Discover incredible deals on your prescriptions at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – buy strattera uk[/URL – , your premier destination for affordable healthcare solutions.
Unlock immediate access to your healthcare needs without a prescription by clicking ed sample pack 2 online , and purchase with assurance.
A range of options to acquire antimalarial treatment online is now available. For those seeking protection or treatment, https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ offer a viable solution.
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable HIV testing solution. Purchase the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – atomoxetine[/URL – today and ensure your status efficiently from the privacy of your home.”
Exploring affordable healthcare solutions is essential, especially when it comes to medication. [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – vidalista[/URL – offers a budget-friendly solution for those seeking therapy without compromising on quality.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, lasix from india offers a convenient way to obtain necessary medication without leaving home.
The importance of consulting a medical expert before you acquire https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ is paramount.
Keep your pain in check without breaking the bank; find affordable solutions for alleviating discomfort. [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ – molnupiravir[/URL – offers a trustworthy option for those seeking ease without the high expense.
Need to spark up your love life? Explore your options and acquire [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – cheapest lisinopril[/URL – to boost intimacy.
Quickly purchase your fluconazole prednisone easily for efficient relief.
Nab your essential medication: https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ through our trusted portal. This essential solution is now accessible without hassle.
You can secure the [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – generic for clonidine[/URL – online, providing a simple way to manage high blood pressure.
Discover the most affordable options for your medication. Review [URL=https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ – kamagra cheap[/URL – and save on your health expenses.
Consider controlling your eye pressure with over-the-counter solutions like isotretinoin cena for efficient glaucoma treatment.
Explore budget-friendly solutions for your health with https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ . Find unparalleled deals to enhance your wellness journey today.
Visit [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – cialis uk[/URL – for allergy relief. Secure the best deal on proven medication today.
With joint discomfort turning into an escalating concern, explore [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ – ventolin inhaler from india[/URL – for relief. This solution offers a potent way to manage your symptoms.
Browse our website to discover your required medications at an affordable price. Purchase levitra walmart price today and enjoy quick shipping.
Discover how https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ can help in managing your heart health. Experts suggest their use for warding off heart issues.
Your health matters, so think about purchasing [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – buy cheap staxyn[/URL – to aid your wellbeing.
Regain control over your well-being by visiting [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone.com lowest price[/URL – , your ultimate destination for reliable pharmaceuticals.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Discover canadian pharmacy cialis to boost your vitality efficiently and securely.
Seeking effective acne treatment? Discover safe https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ options with ease on the web.
The importance of consulting a doctor before you purchase [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – is paramount.
Relieve nasal congestion effortlessly with [URL=https://sadlerland.com/herbolax/ – herbolax cost[/URL – . Get cost-effective relief today.
Need to control your hypothyroidism? Explore kamagra brand to discover how you can balance your hormone levels effectively.
Xplore affordable treatments for chronic hepatitis B by visiting https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ . Secure the best deal online.
A range of options to obtain antimalarial treatment online is now available. For those seeking protection or treatment, [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – alesse online[/URL – offer a practical solution.
Xperience enhanced comfort and convenience when you purchase your medication through our website. Find out more about obtaining your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 20mg[/URL – .
Xplore optimal health solutions! Get your personal xenical shops in atlanta for boost overall wellness immediately.
Before making any decisions, explore your options for treating hair loss. https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ offers a simple way to obtain this therapy.
SUNWIN is positioned as a chic hub on online betting, blending casino sageness with diversified performance like x? s?, th? thao, and interactive trò choi. The tenets highlights immersive game slots, real-time b?n cá, and high-volatility jackpot systems, alongside traditional choices such as dá gà, tài x?u md5, xóc dia, baccarat, and r?ng h?. For digital-first players, esports markets and recurrent khuy?n mãi, uu dãi, and n? hu events manufacture momentum, while structured d?i lý programs and sharp cskh prop up long-term trust. Open access is ready at https://creditservice.ru.com/, reflecting a focus on practice, fairness, and evolving especially bettor expectations.
Just unveiled: [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – non-perscription levitra[/URL – offers a revolutionary solution for hair loss. Now, you can acquire effective treatment without leaving the comfort of your home.
Explore your options and acquire your medication seamlessly buy pristiq .
Get your prescription easily by choosing to https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ . This option offers ease and security, making it simple to keep up with your health requirements.
Shop for organic health remedies and boost your wellbeing today. Buy a supplements at [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra capsules for sale[/URL – , a reliable source for premium health products.
Be proactive in managing your gout symptoms; consider retin a from reputable sources. With our guide, learn how to efficiently control uric acid levels and reduce flare-ups.
I discovered that the https://cafeorestaurant.com/tamoxifen-without-pres/ is not just reliable, but offers a plethora of alternatives for those seeking to treat their condition.
I’ve discovered that locating the lowest [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – tadalista price at walmart[/URL – might be difficult. Yet, with proper research, it’s possible to save costs on fertility treatments.
Harnessing the power of the internet, you can now purchase your prescriptions with ease and affordability. Don’t miss the opportunity to order [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – non prescription doxycycline[/URL – , a option for managing your health more effectively.
When seeking an affordable solution for your antibacterial needs, consider tapping into the convenience of doxycycline_100mg_mg . This virtual drugstore offers a wide selection of non-brand medications that meet various health conditions efficiently.
“Visit now for unparalleled savings; claim your exclusive https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ to save on antihistamines today. Don’t miss this opportunity to breathe easier at a fraction of the cost.”
To obtain your health, think about purchasing [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – , a reliable option for your medical necessities.
If controlling your heart health has become a priority, consider pharmacy pharmacy costs as your preferred option, ensuring efficient prophylaxis against heart attacks and cerebrovascular accidents.
Discover low-cost solutions for managing your heart health with https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ . Secure your dose immediately and embark on a journey toward improved cardiovascular condition.
Unlock significant savings on eye care medication by choosing to [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . Explore alternatives to purchase this vital medicine with convenience and confidence online.
Explore innovative solutions to improve your wakefulness with canada lady era .
Navigating the pharmaceutical marketplace for options can be daunting, but finding the https://bakuchiropractic.com/retin-a/ doesn’t have to be.
Unlock unbeatable deals on [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis black[/URL – ! Secure your remedy for a healthier life today.
Finding an economical generic amoxil can be challenging. Look on websites for alternatives that offer value.
When seeking relief from pain, consider https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ as a potent solution. This anti-inflammatory agent is perfect for treating various conditions, giving both effectiveness and affordability.
Explore the convenience of obtaining your medication without leaving home. For those in need, [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/priligy/ – priligy without pres[/URL – provides a streamlined solution. Secure your medication with simplicity via our online platform.
Just discovered you can purchase walmart cialis price online, offering a hassle-free method to manage your health needs.
Order your health aids with https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ , providing a wide range of pharmaceutical needs.
Acquiring [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/retin-a-without-a-doctor/ – retin a[/URL – has never been easier. Rummage for your path to wellness by utilizing a safe option.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Explore cialis buy , a budget-friendly and trustworthy option for boosting your performance.
A range of options to acquire antimalarial treatment online is now available. For those seeking protection or treatment, https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ offer a viable solution.
Need to control premature ejaculation? Explore how [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – buy dapoxetine uk[/URL – can aid in increasing sexual performance.
Reduce your cholesterol effectively with [URL=https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – , offering a safe way to purchase your medicine.
Harness the power of improved well-being by selecting our lowest price generic chloroquine , offering a breakthrough method for those seeking superior outcomes.
Explore the latest developments in cardiac care by checking out https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ . Discover methods to improve your lifestyle today.
Considering the need for stress treatment, individuals seek safe sources to purchase their medications. [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – offers a practical option for those looking to handle their symptoms effectively.
A key treatment for managing edema is accessible through this link: [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis in beijing[/URL – . Whether you’re battling heart conditions, kidney issues, or hepatic disorders, consider investigating this option.
Acquire generic generic prednisone at walmart on the internet for chemotherapy.
Regain control over your well-being by visiting https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ , your ultimate source for reliable pharmaceuticals.
Order immediately for quick dispatch of [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Obtain your essential drug with convenience.
I’ve used various gambling platforms recently, and it’s always surprising how many players sign up without doing research. If anyone’s looking for a detailed look of bonuses, payout speed, and game selection, this write-up worked well for me: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s nicely written and shows what matters most before you start playing. Definitely worth a read if you want to make better choices.
For individuals seeking effective pain relief, consider utilizing [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – generic nexium[/URL – , a innovative solution.
Xplore your options and discover how to procure sildalis for malaria treatment.
Acquire
Looking for an effective remedy for your alopecia? Discover how you can obtain [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – propecia[/URL – ‘s prescription easily online.
Just discovered you can obtain your cheap prednisone online without prescritpion directly online, making sure your treatment is both convenient and efficient.
I uncovered that you can buy https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ on the internet, offering an easy way to obtain this medication.
Zero in on options for male pattern hair loss by choosing to purchase [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ – buy prednisone online without prescription[/URL – today.
Opt for a trusted source to obtain [URL=https://youngdental.net/tamoxifen/ – non prescription tamoxifen[/URL – , and experience the benefit of improved wellness.
Considering various options to control your BPH symptoms? Find out about how you can get flomax on the internet, offering a straightforward solution to relieve discomfort.
Ensure you procure your https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ with assurance for treating certain conditions.
Manage your healthcare expenses efficiently by exploring [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl on internet[/URL – . Secure the best deal on your medication costs by utilizing our platform, which allows you to find the most affordable solutions for your prescriptions.
Secure the best deal on [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – for your aches and pains on the web today.
Keeping your heart’s rhythm steady is crucial; procure viagra 25mg to ensure optimal cardiac health and function.
A solution for BPH is just a click away. Obtain your medication easily by choosing to https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ .
New to the market? Discover the pathway to health and wellness with [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ – generic clomid uk[/URL – . Acquire this innovative product instantly for your medical needs.
bj88
Purchase the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – generic lasix canada pharmacy[/URL – through our platform to ensure you get top-notch treatment with convenience.
Explore innovative solutions for enhancing your stature with nizagara , for purchase.
Enhance your fertility journey affordably with https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ . Discover outstanding deals on our crucial medication on our website.
Explore cutting-edge solutions to enhance your cognitive functionality with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline price at walmart[/URL – .
X-plore the myriad options to secure your medications affordably; our portal allows you to buy viagra soft tabs online effortlessly. This opportunity enables patients seeking to order their medications without straining their budget.
Explore the myriad advantages of incorporating https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ into your lifestyle. Known for its anxiety-reducing properties, this natural remedy is a staple for boosting overall wellness.
Looking for the most economical options to enhance your confidence? Discover your solution [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – retin a online no script[/URL – today and start your journey to feeling your best.
Visit our website to secure your [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ – levitra via american express card[/URL – today, ensuring you manage your health effectively.
Venture into budget-friendly healthcare options and find how to maintain your health without breaking the bank. For those looking to economize, no prescription propranolol offer a remedy.
Optimize your health with the most effective, premium-quality enhancer available. Click here to https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ and discover unparalleled energy.
For those seeking relief from occasional constipation, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil[/URL – offers a dependable solution. Obtain this trusted bowel movement aid on the web.
Manage your health effectively by choosing to purchase your prescriptions on the internet. For those specifically seeking to address hormonal imbalances, [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ – viagra 100mg[/URL – offers a trusted solution.
Maximize your well-being with a holistic approach by opting for nizagara lowest price , a solution that’s readily available for enhancing male health and vitality.
Looking for an easy and discreet way to manage your health? https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ offers an accessible solution to enhance your well-being without the hassle. Now, obtain your medication without difficulty from the comfort of your home.
When unexpected expenses arise, consider [URL=https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ – cheapest prednisone pills[/URL – as a rapid solution to fulfill your economic needs.
Acquire effective hair loss solutions; explore our [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – tinidazole on line[/URL – for trusted results against androgenetic alopecia.
To secure your wellness, obtain buy vidalista no prescription from a trusted source.
Keep your health in top condition without leaving comfort behind. Purchase your essential drugs without hassle through our safe platform. https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ and ensure your well-being is always a priority.
You can locate the lowest [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – vidalista no prescription[/URL – for your hair loss treatment on the internet today.
Zero out-of-pocket for your hormone therapy. Grab your kamagra today! Stress-free savings on essential medications.
Various medical professionals recommend seeking advice on https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ for gastrointestinal discomfort to confirm safe and effective relief.
Curious about securing the [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline prescriptions online[/URL – ? Explore your options online.
Browse our site to locate [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – , ensuring you obtain top-quality antibiotic choices at incomparable prices.
Optimize your health and wellness routine by purchasing your drugs effortlessly. tadalafil 20mg offers a hassle-free solution for improving your vitality.
Yearning for cost-effective COVID-19 treatment options? Discover the solution with https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ , where efficacy meets affordability. Save on healthcare costs without compromising quality.
Zap vitality deficits and enhance wellness effortlessly by securing your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – canada lasix[/URL – to promote better health and longevity now.
Regarding your medical needs, visit nizagara online usa to uncover a variety of medications ready for buying.
Harness the power of modern medicine to stabilize your mood with https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ . Find out how to manage bipolar disorder with effective solutions at your fingertips.
Explore safe alternatives for enhancing your well-being with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone cheap[/URL – , the preferred choice for improving energy minus a prescription.
Understanding the importance of hormone replacement therapy can be pivotal for those experiencing menopausal symptoms. Opting for [URL=https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ – lowest price generic kamagra[/URL – can be a cost-effective solution. Various options include buying from accredited online pharmacies, ensuring both quality and affordability.
Access the xenical and save on your medication costs. Locate the lowest price for your health needs without compromising quality.
I understand the need for convenient solutions when looking to acquire medication. For those considering managing their health concerns efficiently, checking out https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ provides a key option.
Zealously seeking proven solutions for ED? Find your options and acquire [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – low cost 75 mg viagra[/URL – , the go-to solution.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive pharmacy prices for cialis . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to reduce expenses on your medication.
Boost your wellness with natural supplements; order your https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ directly for optimal health benefits.
Jumpstart your journey towards better health with a seamless way to purchase your medication. Whether you’re looking to diminish inflammation, our platform offers an array of options to suit your needs. For those specifically seeking Budesonide treatment, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil uk[/URL – here and benefit from swift relief.
X-plore affordable AIDS treatment options by deciding to acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – generic prednisone online[/URL – for your medical needs.
Yes, securing your prescription has never been easier. Find competitive zithromax effortlessly. Order now for a smoother, hassle-free experience in managing your health needs.
X-plore your alternatives for managing irregular heartbeat with proven solutions. Find out about how https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ can assist in controlling your heart rate, offering peace of mind.
Try lessening your pain effortlessly by clicking on [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax/ – zithromax 250 kaufen[/URL – , the link to purchase safe and effective solution.
Allergic reactions sufferers can discover relief by buying nizagara , a trusted solution.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ is a viable option. Consider securing this antibiotic via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
X-plore your options for anxiety relief with a click to [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ – nizagara[/URL – , where securing proven solutions online.
Unlock sensational discounts on essential healthcare products! Acquire your [URL=https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ – celebrex[/URL – today and ensure your eyes receive the best treatment without overspending.
If you’re looking to obtain authentic medication, consider nexium . This option offers an affordable solution without compromising on quality.
Discover how to significantly improve your sleep quality with https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ , your preferred solution for a restful night.
To manage irritable bowel syndrome effectively, look into [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ – 100 lasix for sale[/URL – as your preferred solution.
Discover the current [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 200mg[/URL – and look into options for purchasing this treatment online.
Certainly, acquiring your hormonal supplements is crucial, and finding a reliable source is paramount. For those looking to obtain their testosterone boosters, vpxl price walmart offers a vast selection. This ensures you receive your supplements quickly, maintaining your health regime without interruption.
Discover unmatched deals for your medication with our https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ .
Alleviate your nasal congestion and relieve allergy symptoms quickly by utilizing [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – france vardenafil generique[/URL – . This powerful remedy offers immediate relief for those suffering from seasonal allergies, ensuring your daily activities are no longer hindered by annoying sniffles and sneezes.
Seeking the best value for your heart health medications? Compare costs now and conserve on your prescription with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – lowest price for strattera[/URL – , your prime source for affordable healthcare.
When considering treatment options for prostate cancer, exploring medication options is key. Discover trustworthy options for management with pharmacy .
“Boost your peace of mind with a reliable human immunodeficiency virus testing solution. Buy your https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ today and ensure your status promptly from the comfort of your home.”
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/sildalis/ – lowest price generic sildalis[/URL – here. Instantly purchase your medication digitally with ease.
When seeking prompt resolutions, locate [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – for your requirements.
Having trouble obtaining your medication? Explore our options to purchase buy prednisone brand canada , effortlessly and hassle-free.
Considering various options for augmenting your health, opting to purchase https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ via the internet can be a wise decision.
Unlock unparalleled savings on hepatitis C treatment: [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – retin a online canada[/URL – . Explore an array of options; obtain your prescription online today.
When looking to secure amoxicillin, an efficient bacterial infection treatment, consider the convenience of [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin 500mg capsules for sale[/URL – via the internet to address various infections effectively.
Discover affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction by visiting cialis , where you can acquire your prescriptions effortlessly.
If you’re looking for an effective remedy to combat bacterial infections, think about https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ . This antibiotic is well-known for its effectiveness against a broad range of bacteria.
Visit [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine on line[/URL – for an affordable way to manage your well-being. Secure yours right away.
For individuals seeking to obtain hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous platforms offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to ensure safety and authenticity. [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – hydroxychloroquine.com lowest price[/URL – offers a comprehensive guide on methods to safely buy this medication, alongside vital details on its use.
I’ve discovered the order retin a for combatting hair loss.
Explore affordable healthcare options and uncover the best offers on medications, specifically https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ , on the web.
Looking for a trusted source to buy your medication? Visit [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – for a variety of pharmaceutical products.
Keep your healthcare regimen on track and purchase your medication with ease, buy vidalista uk , ensuring a continuous path towards well-being.
Manage your nasal allergies effectively with https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ . Whether you’re looking to purchase a treatment for periodic allergy symptoms or require a long-term solution, this nasal spray offers relief.
Obtain your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol-20mg/ – propranolol without prescription cipla[/URL – effortlessly by securing it through our digital platform.
Venture into the realm of effective ED solutions with [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ – fildena prices[/URL – , accessible online.
Purchase your asthalin hfa inhaler easily; Order this essential breathing aid online.
Yes, for those seeking to relieve pain and inflammation, https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ could be your go-to choice.
Responsive to your need for cost-effective treatment, discover our affordable solution [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – for managing mountain sickness efficiently.
Unlock savings on your hypertension treatment by visiting [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – generic lasix without a prescription[/URL – , your gateway to cost-effective medication.
To ease your pain, think about buying buy levitra uk to aid in your recovery.
To acquire Azithromycin without a prescription, use this link https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ for safe options.
Purchase your health solutions with confidence at the [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – lisinopril angular stomamtitis[/URL – . Find top-tier quality and value in our digital pharmacy.
Just in case you’re seeking comprehensive insights on anxiety and insomnia treatments, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ – lasix without prescription online[/URL – presents valuable knowledge.
Find the best offer on sildalist for enhancing your health now.
Explore the realm of healthcare solutions and uncover easy ways to control your well-being. Whether you’re looking for specific medications or broad health guidance, we offer a variety of options. For those looking for an alternative, https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/ could be your answer.
Quickly obtain your medication with ease by opting to [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil online pharmacy[/URL – , a streamlined method to manage your health.
Struggling with hypertension or angina? Explore how [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – could be your answer to overcoming these conditions.
Explore cost-effective solutions for your health needs with cialis uk . Purchase your medication without hassle today.
Your search for affordable eye care ends here! Discover Premium quality, cost-effective options for managing your vision health with https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ . Uncover economical solutions for caring for your eyesight today.
With widespread availability, you can now acquire [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – , ensuring accessibility to those who need it swiftly.
New to the market? Discover your pathway to health and wellness with [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – canadian pharmacy pharmacy generic[/URL – . Get this cutting-edge solution now for your medical needs.
X-plore your options for acquiring Duovir-N easily through our nizagara online platform. Make your purchase and ensure your health’s protection.
Given the ongoing discussions about its efficacy in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ on the web is crucial for patients.
Visit our website to discover the best [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/low-cost-prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – .
With varying gastric issues plaguing individuals, finding an effective treatment is crucial. Luckily, you can procure [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ – propecia for sale[/URL – , a proven remedy for protecting the stomach’s lining and helping in the healing process.
Quickly acquire your drugs with convenience by choosing to purchase finasteride or minoxidil .
Research the most effective hepatitis C treatments and buy from reputable sources. Ensure safety by choosing to https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ from certified pharmacies.
Visit [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ – celebrex coupon[/URL – today and locate cost-effective solutions for controlling your pain.
Recognizing the plethora of options available, individuals seeking relief can now [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – no prescription xenical[/URL – secure with confidence from reputable outlets on the web.
Zero in on the best health-related advice by consulting with an asthalin tabletten , ensuring you receive top-notch guidance for your well-being.
Yes, the Food and Drug Administration has approved https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ for addressing severe acne. This marks a considerable development in skin care.
Seeking effective skin infection treatment? Find reliable [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – cheapest doxycycline online without prescription[/URL – options easily online.
Experience unparalleled vitality and performance enhancement with our exclusive [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – . Elevate your vigor and endurance levels effortlessly. Click now to unlock your path to unmatched wellbeing.
Investigating comprehensive solutions for boosting vitality? Consider exploring retin a micro coupon , a superior solution for supporting your well-being.
Maximize your alertness and cognitive performance with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ . Whether you’re looking to improve focus or reduce fatigue, this solution provides reliable results.
Visit [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – best online pharmacy for celebrex[/URL – to acquire your medication effortlessly.
X-plore the myriad ways to manage your asthma without breaking the bank. Obtain your inhaler effortlessly through our dependable service. Click here [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – asthalin[/URL – to commence your journey towards enhanced respiratory health now.
X-ray your options for effective bacterial infection treatment, and discover how you can purchase http://www.flagyl.com virtually to fight against your symptoms efficiently.
Meet the groundbreaking solution to your ocular health needs with https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ . Find out about the safe way to sustain your vision’s vitality today.
Zipping through your options for controlling erectile dysfunction? Learn about a streamlined solution by choosing to buy [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – viagra[/URL – .
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://bhtla.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine no prescriptions[/URL – .
Yearning for cost-effective COVID-19 treatment options? Discover the solution with comparison generic nizagara pills , where efficacy meets affordability. Save on healthcare costs without compromising quality.
Discover a hassle-free way to obtain your medication with https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ , ensuring privacy and comfort in ordering.
Explore the platform to purchase [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – online super active pack 20 no prescription[/URL – . Find the answer for pain relief instantly.
X-ray your options for safeguarding your home against water-related disasters by securing the priligy pills legal sites insurance. Explore budget-friendly plans to shield your property today.
Secure your medication easily and directly from the comfort of your home. Order https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ now and begin treatment without waiting.
Zeroing in on effective pain relief solutions? Discover obtainable solutions like [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20[/URL – , perfect for alleviating pain.
Overcoming thinning hair becomes less complex with advanced solutions. Discover your path to renewal by opting to buy [URL=https://jawany.com/cytotec/ – florida in line sale cytotec[/URL – .
Purchase
Gain unparalleled access to https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ by exploring our comprehensive guide.
Seeking respite from stress? Explore our array of pharmaceuticals and find [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – retin a[/URL – . This product is famous for its potency in addressing signs of stress and anxiety.
Seeking trusted malaria treatment can be a challenge. Yet, securing [URL=https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ – best price nizagara[/URL – has never been more straightforward.
Investigating affordable options for managing edema? buy prednisone online 40 mg offers a comprehensive overview, ensuring you get quality and effectiveness.
Having trouble with gastric ulcers? Locate affordable relief with https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ , your preferred remedy for soothing gastrointestinal discomfort.
Visit our website to purchase your treatment with ease; [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ – levitra[/URL – is ready for prompt shipment.
Just discovered you can buy your IBS relief meds online? [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – non prescription bentyl[/URL – offers a selection of options for your healthcare needs.
Discover how to acquire nexium 40mg effortlessly with our straightforward guide.
Zealously seeking relief from year-round allergies? Purchase your relief with https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ , the go-to option for fighting allergy symptoms.
Acquire your wellness boost by choosing to [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ – lasix capsules for sale[/URL – , a practice that’s simple, ensuring that you’re always cared for in your health journey.
Manage your allergies effortlessly by choosing to cheapest price for dapoxetine , a proven solution.
Understand the expenditure of maintaining your well-being by checking the https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ current rates.
Harness the power of modern medicine to stabilize your mood with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – . Discover to tackle bipolar disorder with effective solutions available.
Various methods exist to secure essential medications, yet finding a reliable source can be a challenge. Considering options to buy lasix could be a solution for those in need.
Unlock the secret to enhanced energy by opting for to https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ , your leading source for premium wellness solutions.
Vexed by persistent anxiety? [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ – 20mg levitra online canada[/URL – offers a solution to calm your nerves.
Interested in treating HIV? Purchase torsemide online for proven results.
Access the top deals on https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ to ease your nasal symptoms immediately.
Zealously seeking an effective method for infertility treatment? Discover your answer and [URL=https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ – discount drugs amoxil 650[/URL – , providing a breakthrough solution for your needs.
Questioning where to find antibiotics without overpaying? Discover the [URL=https://goldenedit.com/generic-cipro-at-walmart/ – cipro cost[/URL – and save on your medical bills.
A myriad of options awaits when you decide to purchase your prescription seamlessly. For those seeking to treat urinary symptoms, prednisone offers a convenient, dependable solution.
Harness the power of modern pharmaceutical options safely; order https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ via our website for your health needs.
Optimize your health with a diverse selection of solutions by exploring [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – cheap order ed-sample-pack-2[/URL – , offering a unique combination of options for your wellbeing.
To alleviate discomfort, purchase buy nizagara in new york from trusted pharmacies via the internet.
Quickly obtain your prescription seamlessly through our https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ , offering a wide selection of pharmaceutical solutions.
**C**ompare and discover the [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ – erectafil pills[/URL – by searching through our internet-based pharmacy.
Style & Fashion Choice – Items are visually appealing, with navigation that is simple and fast.
Discover unbeatable deals on [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra[/URL – and conserve on your upcoming purchase.
Maximize your bone health and combat osteoporosis effectively with malegra lowest price , a leading choice for bone density improvement.
Quietly seek cost-effective healthcare alternatives? Discover your solution with https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ , and experience significant savings on prescriptions.
Harness the power of convenience and savings when you buy your birth control. With our exclusive offers, you can get affordable [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl tablets[/URL – without ever compromising on effectiveness.
One can locate competitive [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ – clomid usa pharmacy prices[/URL – and various choices on web platforms, ensuring cost-effectiveness and availability.
Optimize your health journey; acquire fertility solutions without hassle with mail order prazosin .
Secure budget-friendly treatment options with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ , and boost your wellness efficiently.
Navigating places to find misoprostol, a drug used for terminating pregnancies, can be difficult. However, accurate and reliable information is crucial. For information on purchasing options for [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – cytotec 100mcg[/URL – , ensure to refer to trustworthy sources only.
Quest for cost-effective alternatives to manage your health? Discover the best deals with our propecia prices , your go-to choice for quality medication without the hefty price tag.
A myriad of options await those seeking cardiovascular wellness. From buying https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ to exploring cutting-edge therapies, managing your heart’s health has never been more straightforward.
Get your daily health boost with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – , offering immediate results.
Why visitors still make use of to read news papers when in this technological world everything is available on net?
juegos fruv
Discover countless ways to enhance your intimacy with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – cheapest 25 nizagara[/URL – .
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? cheap generic overnight doxycycline to combat bacterial infections. This cost-effective solution is easy to get and can help in managing numerous of medical conditions.
Various medical professionals suggest seeking advice on https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ for gastrointestinal discomfort to ensure safe and effective relief.
Here are the most affordable rates for [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis black[/URL – . Acquire your prescription with ease.
Discover methods to tackle pests with [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ – purchase propranolol without a prescription[/URL – , your leading solution available on the web.
Concerned about maintaining ideal testosterone levels? Find out about the ease of balancing hormones with nizagara . Guarantee your health now.
Gain access to affordable health solution with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ , offering a solution for patients seeking reliable alternatives.
When seeking to improve your lifestyle and wellness, consider exploring [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – cheap verapamil us companies only[/URL – . Available on webstores, it offers a solution for individuals facing health-related issues.
Obtain affordable hormone replacement therapy options with zoloft commercial . Explore alternative options for your health needs on the web.
Shop for your necessities with ease and economy –https://jawany.com/drugs/viagra/ offers competitive rates on pain relief medication.
Looking to boost your performance? Acquire safe solutions [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – viagra 50 mg without a prescription[/URL – .
Need to cut down on your prescription costs? Find the best deals by accessing a [URL=https://sadlerland.com/herbolax/ – herbolax cost[/URL – right here.
To uncover the most up-to-date nexium 20mg , check out our website. Here, you can easily obtain detailed information on rates and stock levels.
Procure your drug at affordable rates; https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ offer varied discounts.
Browse [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ – kamagra online[/URL – to find leading options for baldness treatment.
For individuals seeking to acquire hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous online sources offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to guarantee safety and authenticity. [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – buy generic hydroxychloroquine[/URL – offers a comprehensive guide on how to safely secure this medication, alongside vital details on its utilization.
Explore seamless ways to obtain your health needs with retin a information , the ultimate platform for buying pharmaceuticals online.
Discover countless ways to revitalize your intimacy with https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ .
Boost your health with our comprehensive solution; [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – today and embark on a journey towards optimal well-being.
Maximize your savings on medications by exploring various offers. Find coupons on medication effortlessly online. For cholesterol-lowering solutions, check out [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ – tretinoin cream[/URL – for the best deals.
Considering the expense of managing your health, finding economical treatments is key. Discover the tretinoin cream 0.05 for a budget-friendly option in managing your condition.
Many are searching for trustworthy solutions for ED, and https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ offers a tested option.
Inquiring about prednisone-related dental troubles? Discover how it affects oral health now: [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – .
Looking to control your health needs discreetly? Secure your quantity of essential medication without any hassle. Just click on [URL=https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ – kamagra[/URL – to begin your journey towards improved wellbeing easily via the internet.
Combat hair loss effectively! Explore how where to buy bentyl can benefit you in regenerating your locks to their previous glory.
Harness the power of modern solutions for gastrointestinal comfort; purchase https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ and experience the benefits today.
Just seeking affordable choices for enhancing your health? Consider [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – for a trusted and potent option.
Obtain non-prescription options for managing fluid retention, including non-generic stromectol , online. Explore multiple options for efficient treatment now.
Your quest for a budget-friendly birth control option ends here: https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ . Discover your path to economical health choices today.
Xplore cost-effective solutions to enhance your well-being with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – . Obtain immediately for maximum savings.
Over time, I’ve tried a bunch of iGaming sites over the years, and it’s always surprising how many people join a site without verifying anything. If anyone’s looking for a clear overview of key platform details, this article helped me a lot: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s simple to read and shows what matters most before you start playing. You should check it out if you want to make better choices.
Looking to reduce your healthcare expenses? Discover the [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy online canada[/URL – to economize on your prescription.
Regarding anxiety or OCD treatment, zoloft is a viable solution; explore alternatives or obtain it online.
Acquiring https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ is now feasible. Procure your treatment conveniently through online avenues.
Just realized you need ED medication for your well-being? No need to fret! You can [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – simply and securely.
Just seeking inexpensive choices for enhancing your health? Consider [URL=https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ – symbicort non generic[/URL – for a reliable and effective solution.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: doxycycline walgreens . Whether you’re looking to acquire this antibiotic online, you’ll find that its potency in treating a wide range of infections makes it a prime choice.
When seeking relief from pain and inflammation, consider exploring https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ options to buy effective medication online.
Browse our online pharmacy for top-quality healthcare solutions. Order your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – discount prednisone[/URL – with ease, ensuring secure and fast delivery to your doorstep.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – , your go-to source for acquiring reliable ED remedies online.
You can discover effective solutions for hair loss without breaking the bank. Check out the imitrex for cost-effective options.
Explore unbeatable deals on fertility drugs at https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ , the top source for boosting your opportunities of conceiving.
Here at our pharmacy, we provide a wide selection of medications. Whether you’re looking to purchase [URL=https://damcf.org/prednisone/ – prednisone on line[/URL – or seeking alternatives, our online store is your ultimate destination.
“Quickly uncover affordable options for your wellness by clicking [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – where to buy super kamagra online[/URL – , and obtain your way to bettered vitality.”
Looking for an effective and inexpensive pain relief solution? Discover top-notch treatment options and lasix online.
Need to boost your focus without a hassle? Discover how easy it is to acquire the solution https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ .
To obtain your health, consider obtaining [URL=https://jawany.com/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – , a trusted solution for your medical needs.
Secure your health by choosing to order levitra online online, ensuring swift and trustworthy access to your vital medication.
Acquire https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ without spending a fortune via our website.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Search no more. Acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – amoxicillin generic pills[/URL – safely and quickly.
Before deciding, explore [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – to ensure you secure the optimum deal for your therapy.
“Quest for the ultimate heart health supplement ends here! Discover the best deals on Arjuna, renowned for its cardiac advantages, exclusively at arjuna without an rx .”
Obtaining https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil-5mg/ over the internet has never been easier, ensuring patients get their treatment promptly.
Get your daily Cialis conveniently and securely by clicking [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – buy levitra without prescription[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to obtain for individual use or addressing a condition, you’ll find high-quality options available online.
современная гостиная москва Москва предлагает широкий выбор мягкой мебели: от классических моделей до ультрасовременных дизайнерских решений. Купить диван в Москве или выбрать новую кровать – задача, требующая внимания к деталям. Важно учитывать не только внешний вид, но и качество материалов, удобство конструкции и функциональность. Мебель в Москве представлена в различных ценовых категориях, что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для любого бюджета.
Looking for a reliable source to purchase your medication? [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – strattera[/URL – offers an straightforward way to obtain your needs with just a few clicks.
Browse our catalog to find exclusive deals on pharmacy buy . Boost your health today by deciding to buy safe solutions on our site.
A quick, reliable remedy for pain relief is readily available through https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ . Order yours online today for swift dispatch.
Discover your pathway to improved health by exploring our [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ – pharmacy buy[/URL – , providing an assortment of options tailored to your needs.
X-ray your budget and spend wisely on heart health options. Discover incredible [URL=https://phovillages.com/cost-of-prednisone-tablets/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – on the web.
Discover affordable healthcare options and manage your hypertension effectively with amoxicillin prices . Obtain your medication without hassle and ensure your well-being is prioritized.
Discover affordable options to maintain your bone health; https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ and explore other budget-friendly solutions through digital pharmacies.
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – is your gateway to budget-friendly virus management.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your well-being? No need to fret! You can [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – without hassle and with confidence.
Obtain remarkable savings on your eyelash growth serum by exploring the nizagara kopen , offering you the chance to acquire effective treatment on the internet.
Jumpstart your vitality journey with https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ , your go-to solution for boosted health benefits.
Just discovered the best offer for inflammation treatment with [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – , on sale.
Looking to improve your focus and productivity? Explore a wide range of options at [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/ – sildalist[/URL – . Order your prescription online and start reaching your true potential today.
Grappling with acne? Discover your solution without needing a doctor’s note. isotretinoin best price usa offers a powerful treatment accessible directly to you. Say goodbye to persistent acne now.
Yearning for cost-effective COVID-19 treatment options? Discover the solution with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax/ , where effectiveness meets affordability. Save on healthcare costs without compromising quality.
Quickly secure the vital medication with no hassle: [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – .
Keeping your health in optimal condition is crucial, and finding the right medication should not be a hassle. For those seeking flexibility and convenience in their treatment, retin a micro offers a discreet, effective option. Consider purchasing your prescription via the web, ensuring you receive top-tier care without compromise.
Obtain your https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ prescription effortlessly through our website, ensuring fast and reliable service for your pharmaceutical needs.
Unlock the best deal on [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – ordering verapamil online legal[/URL – by searching our site. Get your necessary medication without the trouble.
Regarding optimal heart health maintenance, securing an affordable option is key. Explore the market for unbeatable prices by tapping here: [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/retin-a-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – retin a[/URL – , ensuring your healthcare needs are met cost-effectively.
Looking to minimize your healthcare costs? Discover the zoloft.com to budget on your medication.
Explore your choices for dealing with peptic ulcers with https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ , accessible on the web.
Zajimavy obsah! Prave jsem zacal hrat ve Spinmama Casino CZ a nabidka je opravdu lakava. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere potesi kazdeho hrace. Me nejvice bavi herni souteze a vyherni automaty – jedno z nejlepsich ceskych online casin. Pro vyzkouseni neceho noveho a bezpecneho kliknete zde: Twitter . Rozhodne to stoji za to a prinese vam spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Objevte Spinmama Casino CZ a ziskejte free spiny
3f09d5d
For those seeking an affordable solution to their health concerns, ordering [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ – cost of hydroxychloroquine tablets[/URL – via the internet presents a cost-effective option.
To procure strattera without dr prescription usa prescription, explore our online platform today.
Keep your feminine hygiene in prime condition with our newest solutions. Explore a wide range you need by clicking on https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ .
X-ray your options and purchase [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – strattera[/URL – from reputable sources to treat HIV effectively and securely.
Purchase your erectile dysfunction solutions effortlessly through [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – generic for ed sample pack 2[/URL – , offering a wide selection of treatments.
Having trouble with confidence? Explore our options to elevate your well-being. amoxicillin coupon today and begin your journey to improved self-assurance with our reliable solutions.
Optimize your health by considering https://sjsbrookfield.org/frumil/ as a solution. Explore choices for managing edema.
To learn the most recent [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – on line slimex[/URL – , browse our site. Ensure you’re obtaining the most favorable offer today.
For individuals seeking cost-effective treatment options for bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, discovering generic priligy tablets becomes vital. Explore economically viable solutions to handle your health with ease.
Variety of options to buy https://maker2u.com/item/pristiq/ are available, offering effective pain relief from various conditions.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – is a viable option. Consider purchasing this treatment online for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with vidalista pills , and explore various options to improve your quality of life.
X-plore affordable solutions for your medical needs with https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ , your path to improved wellbeing.
Acquiring [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – could help in boosting cardiovascular health.
Concerned about where to find antiviral treatment? Your solution is just a click away with [URL=https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – – hassle-free and convenient.
Relieve your BPH symptoms today! Find our variety of buy cheap flomax , specially designed to enhance your urinary flow and general well-being.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ is a viable option. Consider obtaining this treatment via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Explore the convenience of getting your essentials with ease; buy [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ – tadapox[/URL – , ensuring your health is never on hold.
Discover safe ways to obtain prednisone 40mg , ensuring you get top-notch care.
Our comprehensive review on https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride/ dives into effectiveness and security.
You can acquire [URL=https://seraamedia.org/flomax/ – flomax farmacia online[/URL – through multiple reliable web-based outlets.
Optimize your health management by exploring [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ – prednisone for sale overnight[/URL – , offering versatile options for those seeking robust antiretroviral treatment. With a plethora of choices, order your medication from the comfort of your home.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore discount cialis – your go-to solution for restoring well-being.
Researching options to secure https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ ? Review our trusted source for your medication needs, providing a wide range of pharmaceuticals with reliable delivery options.
Discover cost-effective options to your healthcare needs with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – lowest price generic pharmacy[/URL – . Secure your drugs easily on the web and experience both quality and savings.
Keeping your medical needs in mind, you can buy [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone.com[/URL – safely and easily from the comfort of your home.
Seeking to understand global trends in cardiovascular health care, ventolin online uk provides an in-depth look into usage patterns, this crucial medication.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ , and explore multiple options to improve your quality of life.
X-plore the ease of securing your medications with just a click. Now, you can order [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – prednisone price 10 mg[/URL – , making your medical procurement more straightforward.
“Quickly discover affordable solutions for your wellness by clicking [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – , and obtain your way to bettered health.”
Nourish your vitality effortlessly with vardenafil without an rx , a zenith of wellness. Secure this potent elixir with ease.
“Having researched for affordable solutions, uncover https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ for enhancing well-being without spending a fortune.”
Having struggled with anxiety, finding economical treatment options can be a relief. Discover the best deals on [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine.com[/URL – for managing your symptoms successfully.
Boost your performance naturally with the powerful herbal blend found at [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – . This topical solution, available for purchase via web, can enhance vitality and stamina effectively.
Regain digestive harmony with a holistic solution; buy herbolax generic canada to promote regularity.
Seeking relief from benign prostatic hyperplasia? Explore your options with https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ , a treatment for reducing urinary symptoms.
Secure a hassle-free way to obtain your medications with [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone[/URL – , offering a straightforward method for your health needs.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Locate tadalafil to enhance your vitality efficiently and safely.
Obtain your https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ effortlessly. Acquire your treatment sans a doctor’s note online.
Get your hands on the cheapest [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2 brand[/URL – for improving your sexual health.
Obtain comprehensive insights on [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ – sildenafil[/URL – to guarantee you get the best price on the market.
When looking for an affordable solution to your health needs, consider ventolin . With options to acquire this essential medication at a budget-friendly cost, it’s never been easier to manage your health effectively.
Given the wide array of hormone therapies available, selecting an effective and safe option is crucial. For those considering estradiol supplementation, https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ offers a dependable alternative. Whether you’re looking to purchase this essential medication online, it’s vital to opt for reputable vendors to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Patients seeking cost-effective treatment for bipolar disorder may find [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ – prednisone cheap[/URL – competitive. Discover the expense of managing your condition with these medications.
X-plore the multitude of advantages by choosing to obtain your [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – online, ensuring privacy, convenience, and competitive costs.
To guarantee your eye health, exploring cialis could be helpful. Order with ease online.
The premier guide to enhancing your experience safely and effectively is here. Discover now, the myriad benefits of the https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ .
Managing constipation doesn’t have to be a challenge; explore the cost of effective relief. Discover the reasonable [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ – non prescription nizagara[/URL – today and begin your journey towards improved digestive health.
Having trouble finding where to get your medication? Look no further, click on line levitra to secure your medicine with ease from any location.
To ensure your vision health, considering https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ might be beneficial. Purchase effortlessly on the web.
Looking for a reliable solution to enhance your performance? Obtain your [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – buy prednisone online[/URL – now! Our platform offers an easy, secure way to acquire this essential therapy via our website.
Questioning where to obtain a hair loss treatment? Discover safe, trustworthy options for [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ – finasteride[/URL – .
Get your health back on track with ease; secure your savings now on anxiety relief medications by clicking here: best price prednisone .
Looking for economical health solutions? Discover https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ , your preferred choice for controlling your health needs without breaking the bank.
Regain your confidence with thicker, fuller hair. Explore your options and buy your solution [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – order nizagara online[/URL – online. Perfect for those noticing signs of thinning hair.
X-plore cost-effective choices for your heart health with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/viagra/ – where topurchase cheap viagra[/URL – . Obtain today for better well-being.
X-ray your options carefully; acquire the medication online for convenience. generic nizagara in canada ensures speedy delivery and reliability.
To ensure your health’s safety, always opt for genuine medication. For those searching to buy antiretroviral treatment, https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ offers a dependable option.
кресло москва Выбирая мебель, не стоит забывать, что она должна быть не только красивой, но и функциональной. Каталог мебели – ваш надежный помощник в поиске идеального решения. Сайт мебели предложит вам самые актуальные модели и поможет сравнить цены. Фабрика мебели гарантирует качество и долговечность. Кровать, кресло, диван – каждый предмет мебели должен быть тщательно выбран, чтобы создать гармоничное и комфортное пространство. Дизайн-проект поможет вам визуализировать свою мечту, а магазин мебели предложит широкий ассортимент товаров. Мебель на заказ – это возможность создать уникальный интерьер, который будет соответствовать всем вашим потребностям и пожеланиям. Диван раскладной – это практичное и функциональное решение для небольших помещений. Детская мебель должна быть безопасной и экологически чистой. Детская кроватка – это место, где ваш малыш будет проводить большую часть времени, поэтому к ее выбору следует подойти с особой ответственностью. Двухъярусная кровать – это отличное решение для детской комнаты, где живут двое детей.
Seek competitive [URL=https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – and ensure you secure the best deal on your medication.
Planning to an emergency cash support in the Lone Star State? Explore your possibilities with no prescription nolvadex , a swift method for your financial necessities.
Optimize your health with the solution everyone’s talking about, https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ . This potent formulation can alter your wellbeing.
Harness the power of savings on your next prescription with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – , ensuring you get your prescription at a lower cost.
Zapping tuberculosis requires effective medication. Find affordable treatment options; [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – are available online.
Quietly seek affordable healthcare alternatives? Discover your solution with cheap stromectol online , and experience considerable savings on prescriptions.
Join the myriad of individuals choosing to buy their wellness supplements through digital stores by exploring options to https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ . Elevate your health regimen immediately with this trusted solution.
Quest for reliable malaria treatment leads to the discovery of [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ – canadian pharmacy vidalista[/URL – , an groundbreaking option available through digital platforms.
Discover your pathway to relief from minor aches and pains by purchasing your next supply of amoxicillin 500mg capsules virtually.
I understand the importance of medication accessibility, thus highlighting the convenience of opting for mail order methods. In this context, https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ offers a seamless way to obtain your necessary prescriptions without the hassle of visiting a pharmacy.
Ordering your prescription drugs has never been easier, go to [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – ordering verapamil online legal[/URL – and discover how you can get your treatment promptly.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis 2.5mg lowest price canada[/URL – . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to save on your medication.
Discover how to improve your intimacy easily by choosing to viagra for sale overnight from the comfort and discretion of your own abode.
Exploring options for acquiring https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ ? Discover how to obtain your medication effortlessly on the web.
Zest for life can be regained with ease. Purchase your bone health solution with confidence [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – buying prednisone with next day shipping[/URL – .
Now, get your cheap tadalafil pills for treating HIV by visiting our webstore today.
When managing hypertension, it’s essential to explore various treatment options. Discover how you can manage your condition effectively with https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ .
A comprehensive guide on how to purchase effective cancer therapy, including imperative information on [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 500mg[/URL – , to tackle myeloma and ovarian cancer efficiently.
Looking for an effective and budget-friendly pain relief solution? Find high-quality treatment options and [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ – where do i get kamagra[/URL – on the web.
Xperience enhanced comfort and convenience when you purchase your medication via our online platform. Find out more about obtaining your hydroxychloroquine .
When looking to buy effective cognitive enhancers, consider https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ for your requirements.
The importance of getting reliable and effective HIV treatment cannot be overstated. With a variety of options available, it’s crucial to opt for a source that offers both quality and convenience. For those in need of a trusted solution, [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – delivers an accessible way to controlling their condition effectively.
Considering immediate antibiotic needs, acquiring doxycycline without an rx online ensures a rapid solution.
To locate affordable alternatives for your medications, visit https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ to review cost-effective alternatives.
Acquire your pathway to enhanced wellness without delay.
Know about the transformative effects of Isotretinoin for skin conditions? Explore your options and learn more at [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin 10mg[/URL – .
Get your hands on the cheapest ed sample pack 2 online for enhancing your sexual health.
Zest your getaway with a visit to the celebrated https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ , offering an unique experience.
Need to manage irregular periods? Discover your solution with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol-20mg/ – cost of propranolol at walmart pharmacy[/URL – . Explore options to acquire this essential treatment through the web.
For those seeking relief from intestinal discomfort, purchasing [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ – where to buy bentyl[/URL – could be a feasible solution.
Explore safe options to buy your pharmaceuticals on the internet with our purchase finasteride without a prescription source.
I discover the easiest way to purchase gentle relief from constipation: https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ .
Secure the best rate on [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – by shopping on the web.
Research and uncover the positive effects of [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – cipro[/URL – for enhancing fertility. Acquire it online to commence your journey to parenthood today.
View the latest costs for treating your BPH symptoms with cheap generic flomax without prescription , and explore a range of options to enhance your quality of life.
You can secure https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ through various reliable web-based outlets.
Keep your health at its peak with [URL=https://youngdental.net/tamoxifen/ – non prescription tamoxifen[/URL – , offering a wide range of medical options. Boost your life today.
Responsive to your need for cost-effective treatment, discover our affordable solution [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – price of prednisone[/URL – for managing mountain sickness efficiently.
I find all my healthcare necessities with ease at prednisone preise , offering a wide selection of prescriptions.
Purchase the cardiovascular wellness supplements easily through https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ , providing a wide selection of reliable products.
Research and explore the positive effects of [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ – dapoxetine[/URL – for boosting fertility. Purchase it through our website to start your journey to parenthood today.
Unlock the best deal on meldonium online usa by exploring our site. Get your essential medication without the hassle.
Acquire your https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ without hassle via the web.
Combat intestinal discomfort with ease; visit [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – finasteride[/URL – to obtain your treatment immediately.
Need to save on your prescription costs? Uncover the best deals by accessing a [URL=https://goldenedit.com/generic-cipro-at-walmart/ – cipro 750 daily use[/URL – right here.
Procure kamagra safely and effortlessly. Now, acquire your essential drug swiftly through our dependable source.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your well-being? No need to stress out! You can https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ simply and securely.
Confident about enhancing your wellness? Purchase your necessary supplements [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/]amoxil[/URL] now for a balanced lifestyle.
Find affordable alternatives or generic versions of brand-name medications easily online. Whether you’re looking to acquire this heart health-supporting medicine without a prescription, ensure you’re getting a legitimate solution through verified channels. nizagara 25mg offers a reliable method to manage your health needs efficiently.
Revitalize your eyelashes with trusted and affordable solutions. Discover myriad benefits by exploring https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ . Achieve stunning results for a fraction of the cost.
https://kitehurghada.ru/ кайт египет
Discover affordable pricing on [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/generic-tadalafil-from-india/ – buy tadalafil[/URL – when you purchase online.
Zealously seeking a trusted source to purchase your pharmaceuticals from? Look no further; nizagara offers a secure, discreet way to obtain what you need.
Visit https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ to acquire your medication effortlessly.
Considering the need for thyroid hormone replacement therapy, it’s essential to find a reliable source for your medication. With our platform, you can effortlessly [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ – nizagara 100mg[/URL – required, ensuring your health remains top priority.
Mitigate menopausal symptoms with lasix.com lowest price , an effective solution for alleviating discomfort.
Acquire reliable pain relief by opting to order your https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ now.
Regain control over your health by visiting [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – drugstore cialis-black[/URL – , your ultimate source for reliable pharmaceuticals.
Discover cutting-edge ways to manage anxiety with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ – flomax[/URL – , accessible via our website.
Maximize savings on your heart medication by securing the generic zithromax uk . Search through options now for a more affordable route to taking charge of your health.
X-plore the therapeutic options for managing Addison’s disease; https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ stands out as a top choice. Its efficacy in maintaining electrolyte levels and mitigating symptoms is unparalleled.
Just discovered? Looking to purchase your prescription with ease and convenience? [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – lowest price on generic retin a[/URL – offers a seamless solution for obtaining your needs online.
Zap high prices with our exclusive amoxil 650 from canada , and Snag your bottle of vital antibiotics effortlessly via our website.
Maximize your performance with enhanced choices. Uncover how on https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis-5mg/ .
Secure
Maximize your eye health benefits with [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ – furosemide without prescription[/URL – , the premier solution for managing swelling. Acquire it via the web today and witness unparalleled relief.
Now, secure your needed viagra 75mg easily by visiting our site.
Before you consider purchasing antipsychotic medication, learn how to safely procure https://jawany.com/cipro/ .
Browse our website to locate your required medications at an affordable price. Purchase [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/product/vpxl/ – no prescription vpxl[/URL – today and get quick delivery.
Xperience the unparalleled benefits of [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – buy zoloft[/URL – for boosting your vitality. Explore this unique blend, perfectly formulated to improve your stamina with organic ingredients.
Explore the range of options for controlling menstrual disorders by acquiring tadalafil .
Harness the benefit of easy access by choosing to obtain https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ via web, ensuring an effortless process for handling hair loss.
Visit our site to find the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – overnight finasteride[/URL – for controlling hair loss.
rankhero.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Explore secure options to buy your pharmacy needs via the web with [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – cenforce[/URL – , ensuring discretion and ease.
Zapping away your health blues becomes seamless when you uncover the right medication. Don’t wait any longer and secure your doxycycline online no prescription today for an unbeatable price!
Unlock unbeatable deals on anti-diarrhea medication at https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ , your one-stop source for tackling digestive issues.
For individuals seeking enhanced endurance, [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era generic pills[/URL – offers a revolutionary solution.
Here’s how to discover the current [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex[/URL – to preserve on your treatment.
For a thrilling experience in gaming and entertainment, visit prednisone cost . With a plethora of table games and premier customer service, it’s the ultimate choice for players.
Obtaining https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ has never been more straightforward. Buy now and cut costs on your medication.
X-perts agree, securing [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – could significantly lower your medical expenses.
Worried about your HIV status? Easily check with a dependable [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – . Acquire a kit today for reassurance.
Zillions now look for answers for enhancing their energy. It’s easy to get reliable assistance sildenafil .
Interested in managing your healthcare efficiently? Find the most competitive https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ to improve your treatment without breaking the bank.
Zealously seeking reliable solutions for ED? Explore your options and buy [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – , the go-to solution.
Harness the power of savings on your next prescription with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a generic canada[/URL – , ensuring you receive your prescription without denting your wallet.
Many wonder what a order levitra implies; it’s essentially getting capital in advance.
Get the purest https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ for boosting your workout efficiency.
Access [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ – vidalista online canada[/URL – instantly! Secure your purchase online for quick dispatch and excellent service.
Having been diagnosed with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), many individuals seek effective treatments. For Canadian patients, [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – price of nolvadex[/URL – offers a potential solution. This medication helps reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
If you’re searching for an effective remedy to combat bacterial infections, consider amoxicillin 1000mg . This medication has been widely acknowledged for its efficacy against a broad range of bacteria.
To obtain natural wellness options, consider to https://shilpaotc.com/nizagara/ .
Unlock unparalleled savings on hepatitis C treatment: [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis/ – generic brands of cialis online[/URL – . Explore an array of options; obtain your medication online today.
Zero wait time for your allergy relief; Purchase your [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/sildalist/ – generic sildalist canada pharmacy[/URL – today and breathe easier tomorrow.
Seeking a trusted source to buy your medications? Look no further! pharmacy buy online offers a wide selection of pharmaceutical products via their website.
Interested in managing your conditions? Consider buying your medication safely through https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ , a reliable source for authentic pharmaceuticals.
A comprehensive guide to purchasing your prescription safely: [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – through accredited sources.
Having trouble finding affordable treatment options? Look no further for generic propecia canada pharmacy . Get your essential prescription without overspending.
You can purchase your https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ easily via the web, ensuring you get quality medication for managing your condition.
To secure your prescription of Abamune-L at the best rate, visit [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia to buy[/URL – . This medication is vital for managing HIV/AIDS, and acquiring it through this site ensures authenticity.
maximaclick.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Unlock the benefits of a diverse healthcare regimen by opting to [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ – lowest price generic pharmacy[/URL – . Explore the convenience of acquiring your essential medication with ease, ensuring you stay on top of your health needs.
For those seeking relief from gastrointestinal discomfort, considering the latest kamagra 100mg could offer a cost-effective solution.
Zap vitality deficits and enhance wellness effortlessly by obtaining your https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ to promote better health and longevity now.
If you’re in the market for affordable options on your prescription, consider checking [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – kamagra cost[/URL – for reasonable costs.
Acquiring generic [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ – fast shipping doxycycline canada[/URL – has never been simpler. Purchase your next batch from our website with complete assurance.
Need to enhance your focus without a hassle? Discover how easy it is to get the solution sildenafil .
Before you think about buying antipsychotic medication, learn how to safely obtain https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ .
For anyone looking to ease their nasal symptoms, getting a [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ – lasix online uk[/URL – look-up is key.
Discover trusted solutions for your digestive discomfort with where to buy bentyl , a choice endorsed by healthcare professionals.
Seek treatment for hair loss now! Learn about how https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ can assist in your battle against hair thinning.
Discover the cheapest options for managing your allergies with [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin a cream 0.05[/URL – .
clickpeak.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickstreamer.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
rankquest.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
X-ray your options for migraine relief by exploring [URL=https://center4family.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – , a top remedy available on the market.
Maximize your health with ease by accessing buy levitra best price usa .
Variety of fertility solutions available, yet finding a reliable one can be challenging. Explore https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ to enhance your chances with a trusted option.
StyleTrendsOnline – Smooth shopping experience with fashion-forward items everywhere.
I’ve discovered the ultimate solution for managing your eye conditions; [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ – cheapest levitra dosage price[/URL – . This product offers an effective way to alleviate symptoms with ease.
Obtain your prednisone prescription easily via the internet.
When seeking to boost your intimate moments, one effective solution is the purchase of https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nexium/ . This product is highly regarded for its capacity to extend enjoyment and satisfaction.
Hoping to enhance your wellness with nature’s bounty? Discover the array of options and find competitive [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ – trazodone.com canada[/URL – to boost your health regime effortlessly.
Browse our site to order your essential heart medication conveniently—buy generic lasix .
Zero in on your health management by opting to https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ . Secure your well-being now by choosing to acquire this vital medication online.
For individuals seeking to purchase hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous online sources offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to guarantee safety and authenticity. [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – hydroxychloroquine online pharmacy[/URL – offers a comprehensive guide on methods to safely buy this medication, alongside vital data on its utilization.
Explore the options and obtain the prescription with convenience at [URL=https://jawany.com/cytotec/ – generic cheap cytotec[/URL – .
Combat mountain sickness efficiently with topamax long term weight problems , obtainable on the internet to help in your mountaineering adventures.
Seek unparalleled performance and confidence in intimate moments; unveil your pathway to enhanced vigor with https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir/ . Acquire your solution today.
прикольные канал дзен Отчет Дзен: краткий обзор главных новостей дня.
Find reliable treatments for boosting your sexual health securely at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ – viagra from india[/URL – .
Browse the site to locate amoxicillin non generic , ensuring you secure premium antibiotic choices at matchless prices.
Discover how to enhance your performance easily by choosing to https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ from the comfort and discretion of your own home.
To obtain your medication effortlessly, [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – order vidalista[/URL – from trusted vendors.
Style Trend Corner – The site performed smoothly and offered a solid range of trendy goods.
Zap your ED worries away! Get effective ED medication [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ – pharmacy prices for viagra[/URL – . This treatment is reliable and quick to find.
Keeping your health in top condition is crucial; hence, managing your fluid levels with medication is key to avoiding related health issues. For those in need, you can order renova telefono , a reliable choice for managing your health.
Gain immediate access to solutions for boosted vigor by choosing to https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ . This solution is readily available for purchase on the web, providing a straightforward pathway to regaining your energy.
Having gastrointestinal discomfort? Discover relief through [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel cheap[/URL – , a trusted medication. Obtain it via the internet for rapid alleviation from digestive spasms.
Purchase affordable acheter tadalafil en suisse for managing cardiovascular wellness. Explore selections online for cost-effective strategies.
Discover secure and convenient ways to acquire your medication with just a click. https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ offers a simple solution for your needs.
Keep your health in top condition with affordable solutions; explore [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – asthalin canadian pharmacy[/URL – for your needs. Seek out alternatives on websites to keep up wellness efficiently.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://seraamedia.org/amoxicillin-650mg/ – amoxicillin[/URL – is a viable option. Consider obtaining this treatment via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Many are looking for trustworthy options for ED, and buy cialis no prescription offers a tested option.
Need a reliable source for your hair loss solution? Search no more! Our reputable https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ offers an extensive selection of solutions to help you regain your confidence.
Improve your wellness journey with a simple click. Obtain your [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia indian[/URL – effortlessly online. This package presents an excellent way to explore wellness benefits with comfort.
Replenish your pharmacy easily with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – buy chloroquine over counter england[/URL – , to secure consistent treatment.
With just a few clicks, you can effortlessly obtain your prescription for buy pristiq without prescription , a critical solution for managing acid reflux conditions.
Knowing the potential benefits and risks of this treatment is vital. Get comprehensive details https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ and make an informed choice on its application for addressing certain conditions.
X-plore choices for managing your health by deciding to order [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – chloroquine best price[/URL – , a treatment relied upon by many.
Seeking chest pain management? Discover your options with [URL=https://nesttd-online.org/item/nizagara/ – best price on nizagara 25 mg online[/URL – , for sale on the web.
Explore top-rated lowest price for levitra for an exciting gaming experience.
Reduce your gout-causing uric acid levels effortlessly with the most effective https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ . Regulate gout attacks without hassle and keep better health.
Looking for a cost-effective way to treat your health? Consider [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – for a reliable solution.
Discover the latest prices for managing your menstrual irregularities and endometriosis with peni large online pharmacy , and learn about how it can help you lead a healthier life.
Looking to manage your condition? Buy https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ now and commence your journey to enhanced health.
Various healthcare professionals recommend seeking advice on [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – for digestive issues to ensure safe and effective relief.
In search of the lowest-priced solution for enhancing your eyelashes? Discover unbeatable prices on [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – retin a online no script[/URL – .
Jumpstart your journey to healthier hair with buying vidalista online . Learn about how you can fight against hair loss today.
X-ray your budget and uncover how much you can save on your next purchase with https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ , a solution to acquire your essentials at improved rates.
Having difficulty with an enlarged prostate? Discover how [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ – flomax.com[/URL – can ease symptoms and restore your quality of life.
Here’s how to obtain buy cheapest nizagara for your needs without an RX.
Maximize your vigour naturally with https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ , an unparalleled option for those seeking to improve their stamina without the need for doctor’s orders.
Visit [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – generic retin a lowest price[/URL – to acquire your vital cardiovascular medication.
Secure
Visit retin a from canada to secure your medicine without a doctor’s approval.
Seek budget-friendly solutions for improving your health? https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/ offers a powerful mixture for those looking to revitalize performance safely.
Obtain your medication effortlessly at [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/ – sildalist[/URL – , the leading site for affordable healthcare products.
Get your essential antiviral medication easily through [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/product/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2 type medication[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to purchase the necessary medication online, we provide a secure, efficient, and reliable platform for all your healthcare needs.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing buy dapoxetine uk today. Whether you’re looking to improve your wellness effortlessly, our online platform offers an easy pathway to obtain your essentials.
Get your [birth control conveniently from https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ , delivering solutions for safe family planning.
A quick, effective treatment for pain management is readily available through [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ – cheap nizagara pills[/URL – . Order yours on our site today for swift shipment.
Cut down on your healthcare expenses by obtaining your http://www.prednisone.com here! Now you can secure significant discounts on your medicine expenses.
Keeping your health in top condition doesn’t have to break the bank. Find affordable solutions and manage your symptoms effectively with https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ . Whether you’re aiming to order your treatment virtually, enjoy convenience and cost-effectiveness in one go.
Secure your safest pathway to better health by opting to acquire [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil canada[/URL – . This solution ensures swift relief from symptoms with unmatched simplicity.
Xanax alternatives can be hard to find, but for those looking to order Buspar for anxiety relief, simply click here to [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 5mg[/URL – .
Regain your zest for life! Use our lasipen de 40 mg precio for unparalleled confidence. Revive passion without breaking the bank. Acquire your key to a fuller, more vibrant experience now.
Discover secure and easy ways to obtain your pharmaceuticals with just a click. https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ offers a hassle-free solution for your needs.
Looking to alleviate menopausal symptoms effectively? Consider trying [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ – pharmacy australia online[/URL – , a proven solution for hormone replacement therapy.
Unlocking the secrets of cutting-edge neurological treatments, buy cheap tadalafil stands as a beacon for exploration in Parkinson’s disease.
Unlock relief from ulcerative colitis with https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ , for purchase on the web.
Get your amoxil easily from [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 1000mg[/URL – , supplying prompt shipping to satisfy your needs.
For individuals seeking a cost-effective solution for their gastrointestinal health, [URL=https://damcf.org/prednisone/ – prednisone without dr prescription usa[/URL – offers a viable option. Explore our wide selection of medications that provide relief and support for various conditions without compromising on quality or efficacy.
Opt for buying sildalist to treat your hepatic conditions. Ensure you’re getting your treatment with confidence.
Understanding the need to purchase medication easily, our platform allows you to https://jawany.com/retin-a/ without any hassle.
Browse the site to locate [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin without a doctors prescription[/URL – , ensuring you obtain high-quality antibiotic options at incomparable prices.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover your solution with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – , the optimal choice for boosting your hormone health. Find the way to enhance your health with just a few clicks.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your amoxicillin 500mg online for efficient bacterial infection treatment.
To acquire your supply of Etizolam, consider clicking on https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ for trustworthy delivery.
With widespread availability, you can now obtain [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – , ensuring availability to those who need it swiftly.
https://opalubka.market/ opalubka market
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly with [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – canadian cenforce[/URL – , now obtainable to acquire online.
The importance of getting reliable and effective HIV treatment cannot be overstated. With a variety of options available, it’s crucial to opt for a supplier that offers both quality and convenience. For those in need of an accredited option, prednisone on line provides an accessible path to treating their condition effectively.
Considering your need for hormone therapy, consider exploring https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ for affordable solutions.
Boost your growth potential naturally with [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – esomeprazole[/URL – . Explore secure and effective ways to boost your height devoid of the need for prescriptions.
Obtaining [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – prednisone best price[/URL – has never been simpler. Secure this crucial medication without the need to leave your house.
Find affordable alternatives or generic versions of brand-name medications easily online. Whether you’re looking to acquire Atorlip-5 without a prescription, ensure you’re getting a legitimate solution through verified online platforms. amoxil offers a reliable method to manage your health needs efficiently.
When looking for affordable solutions for antiretroviral therapy, finding the https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ is paramount.
Quickly secure your essential wellness supplement today; [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – retin a cheap[/URL – offer a smart choice for boosting your health.
Keep your prostate health in check with [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – buy ranitidine no prescription[/URL – , available for purchase through our site, ensuring you receive top-quality treatment affordably and efficiently.
Your search for an effective solution to enhance your performance ends here; find better vitality with esomeprazole .
Discover effective relief for cold sores with https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ , your go-to antiviral cream. Obtain this treatment online and commence your journey to recovery today.
Rediscover vigor with our cost-effective [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ – ventolin without prescription[/URL – , the premier solution to enhance your lifestyle.
Having trouble finding affordable treatment options? Look no further for [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – . Secure your much-needed prescription at a cost-effective price.
Find unbeatable deals on tadalista 20 mg online without prescription to boost your wellness.
Looking for budget-friendly cardiovascular treatment? Find the best offers on https://swanpercussion.com/lasix/ today.
Browsing for a safe source to purchase your medication? Look no further! [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ – prices of tadalista[/URL – from our trusted web platform, ensuring premium products with every order.
Investigate cost-effective solutions for managing IBS symptoms. Discover the best [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – where to buy super active pack 20[/URL – for instant improvement.
Quest for top-quality healthcare products ends at lowest price on generic vardenafil , where you can purchase everything from pharmaceuticals to wellness supplements online.
Exploring options for hair loss treatments? https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ could be your key. Obtain it without hassle and start your journey to regrowth today.
Purchase natural solutions for your health needs easily on our website. Explore options and find the best deals [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – today.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern therapies, managing it has become easier. Look into [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-uk/ – order cialis online australia[/URL – , a budget-friendly and reliable option for boosting your performance.
Patients seeking to manage Hepatitis C can find generic vidalista at walmart online. This treatment option is accessible for those looking to minimize their healthcare expenses efficiently.
Maximize your health with the flexibility of purchasing the https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ , offering a range of choices for those seeking improved vitality and wellness.
Regain your health and tackle Hepatitis C with a ground-breaking treatment. Learn about your options and reclaim your well-being by visiting [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – generic verapamil fast shipping[/URL – . Get your path to recovery on the web today.
The importance of securing reliable and effective HIV treatment cannot be overstated. With various options available, it’s crucial to select a pharmacy that offers both quality and convenience. For those in need of a reliable option, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil without an rx[/URL – delivers an accessible path to treating their condition effectively.
Facing hair loss? Consider amoxicillin as your solution. Acquire this effective solution online to battle baldness securely.
Leverage your health management by securing your supply of crucial medication. Obtain https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ effortlessly from reliable sources, ensuring your well-being is always prioritized.
Patients seeking affordable solutions for their medication can find [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/frumil/ – frumil[/URL – to discover cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
Looking to minimize your motion sickness or vertigo symptoms? Secure your [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ – nizagara[/URL – now and spend less on your next purchase.
Researching safe sources to acquire medication? Explore options and discover how to buy prednisone 40mg with confidence.
Responsive to your need for cost-effective treatment, discover the affordable solution https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ for managing acute mountain sickness efficiently.
Your search ends here! Secure your [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil-5mg/ – generic tadalafil discounts[/URL – without hassle. Say goodbye to eye discomfort today!
Zero doubt, managing gallstones is essential; [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil 10mg[/URL – on the web to ease symptoms effectively.
Now, locate safe and effective treatment options,explore through our selection of medications. For your convenience, fildena are available online.
Need to control premature ejaculation? Explore how https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ can aid in extending intimacy duration.
Save on your next purchase of [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – cheap verapamil overnight[/URL – by exploring our wide selection. Find incredible savings on our site today.
Considering the myriad options available, opting to acquire your prescription through reputable sources is paramount. For those looking into therapy for gastrointestinal issues, [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – stands out as a trusted choice among various vendors.
Keep your stomach issues at bay with bentyl , the ultimate remedy for IBS symptoms. Purchase your treatment on the web now.
To find the most economical https://mnsmiles.com/item/nizagara/ , consider searching on numerous online pharmacies.
Looking to improve your health? Think about [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – for an easy way.
With the rising demand for natural nutritional supplements, flomax 0.2mg emerges as a leading choice. Its advantages for well-being are unparalleled.
Your search for cost-effective hormone therapy ends here; purchase https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ with ease for your well-being needs.
Visit [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – generic for kamagra[/URL – today and find cost-effective alternatives for managing your pain.
Living with bipolar disorder can be challenging, but managing it gets easier with the right medication. For those seeking effective treatment options, [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ – levitra in tschechei kaufen[/URL – offers a solution that many have found helpful. Whether you’re aiming to control your symptoms, consider how this medication might fit into your healthcare plan.
Harness the power of efficiency by choosing to obtain tadalafil online, ensuring an effortless process for controlling hair loss.
X-rays andvarious imaging tests reveal bile duct issues; but to treat it, consider utilizing ursodeoxycholic acid. Find the solution with a https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ .
Now, obtain your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ – buy finasteride[/URL – without hassle by opting to purchase online.
Questioning where to find medicine without overpaying? Uncover the [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – cipro 250mg[/URL – and save on your healthcare expenses.
Needing to obtain cytotec ? Explore reliable alternatives for obtaining online.
Explore incredible discounts on health supplements with our https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ . Don’t miss out on this opportunity to cut costs on your purchases.
The management for benign prostatic hyperplasia is now more accessible with [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix/no prescription[/URL – , providing significant relief.
Managing anxiety can be a challenge, but with the right medication, relief is possible. Those looking to procure their treatment discreetly can discover a wide variety of options available. For a trusted source, consider [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – tadalista 10mg herbal[/URL – for your needs.
Acquiring nizagara 50mg could help in improving cardiovascular health.
Discover reliable and simple ways to acquire your medications with our reliable https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ service.
Secure your health effortlessly by choosing to acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ – pharmacy[/URL – , a proven method for boosting vigor.
Discover affordable hair loss solutions; [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – discount sildalis[/URL – today. Explore cost-effective ways to tackle male pattern baldness with ease.
Understanding the necessity for swift antimalarial remedies, it’s pivotal to locate a trustworthy supplier. With that in mind, procure your generic for super kamagra immediately for effective treatment.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your well-being? No need to worry! You can https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ without hassle and with confidence.
Acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin brand[/URL – at unparalleled rates! Locate your vital pharmaceuticals with us and benefit from our unmatched deals.
Combat vertigo symptoms efficiently by visiting retin a lowest price to get your treatment without hassle.
Obtain your solution for hair loss by clicking here: https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ . Get yours today for optimal results.
Zero hassle to securely acquire your medications via web. Click here: [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ – purchase propranolol without a prescription[/URL – for your well-being needs.
Offering a range of reproductive health solutions, find meaningful savings on your next purchase with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – .
Visit our website to uncover your perfect 1% retin a cream solution for an uninterrupted sleep.
Purchasers looking for effective yet budget-friendly menstrual cycle support can locate relief by choosing to buy https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ .
Boost your persuasion skills with our comprehensive guide! Discover how to convince, sway, entice, or persuade others effectively by reading our in-depth [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – sildenafil[/URL – . Whether you’re aiming to influence, motivate, inspire, or encourage others, this resource is your key to unlocking powerful communication techniques.
Purchase generic Bentyl for digestive relief; explore at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – overnight bentyl[/URL – .
Venture into enhancing your health effortlessly; explore buying prednisone online for your wellness needs. Acquire this solution virtually and experience a healthier lifestyle today.
Preserve your health effortlessly by opting to https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ , making it possible for you to secure your pharmaceuticals without hassle from the comfort of your home.
Facing infection risks? Discover how [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin[/URL – can be the answer, available to order via web pharmacies.
Battling seasonal allergies? Look into getting [URL=https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ – lowest price nizagara wal mart[/URL – to manage your symptoms.
Facing anemia, it’s vital to elevate your iron levels. Consider supplementing to your diet by pharmacy prices products to tackle this condition.
Residing in Canada, individuals in search of asthma relief can now effortlessly procure their necessity via https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ .
Questioning where to find an effective treatment for your needs? Look no further. [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – offers a versatile solution for those seeking top-notch medical care.
Many are searching for reliable options for ED, and [URL=https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ – cialis generika 10mg[/URL – offers a tested option.
Buy cheap can i buy cipro online.
Improve your health and wellness with our exclusive https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ , now available. Experience enhanced vitality and confidence. Secure yours today.
Keep your health in prime condition with our all-natural supplement. Buy your supplement online today and feel the difference! [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – zithromax[/URL –
Zeroing in on your healthcare needs? Discover the best [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – discount nizagara[/URL – for managing inflammation and allergies efficiently.
Ache no more! Explore the revolutionary joint relief with ventolin price . Order now for a healthier tomorrow.
Seeking to grasp global trends in heart condition treatments, https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ provides thorough insights into the adoption rates of this vital medication.
Find the best deal on [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone[/URL – for boosting your health immediately.
EarthChoiceStore – Well-laid-out pages, inviting design, and natural-feeling navigation.
Quickly buy your prescription online with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone dosage 20[/URL – , ensuring a hassle-free procedure.
Just discovered that you can buy cialis black online at affordable prices? Explore options now at cheap cialis-black europa .
With many seeking affordable solutions to enhance wellness, finding a reliable supplement is key. Explore options and uncover cost-effective health boosts at https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ . This site offers a gateway to improve your vitality without breaking the bank.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – is a viable option. Explore obtaining this antibiotic through online outlets for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
xrumer обучение телеграм Базы Xrumer не сырые: Базы Xrumer не сырые – это базы данных веб-сайтов, которые были предварительно обработаны и очищены от неактивных, дублирующихся или нерелевантных ресурсов. “Сырые” базы данных (собранные с помощью парсинга или полученные из непроверенных источников) могут содержать большое количество невалидных или некачественных ссылок, что снижает эффективность прогонов и даже может привести к санкциям со стороны поисковых систем. “Не сырые” базы данных проходят процесс фильтрации, очистки и валидации, что гарантирует более высокое качество и эффективность прогонов.
Keep your health at its peak: explore safe and trusted options to acquire [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – where to buy viagra online[/URL – .
Maximize your wellness and vivacity with our natural remedy! Discover the rejuvenating benefits of moduretic without an rx —a comprehensive approach to improve your health & vitality.
Various treatments for chronic Hepatitis C have emerged, but one prominent option is Ribavirin, commonly known by its brand name, https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ . Uncover the potential benefits of this therapy for improving your health outcomes.
You can find safe and effective nausea relief with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – , accessible through online pharmacies.
Погоджуюсь, короткі поради реально краще довгих нудних текстів.
Your search ends here! Secure your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – effortlessly. Say goodbye to eye discomfort today!
Explore your options for acquiring essential hypertension treatment by checking out nizagara without dr prescription , where a variety of economical healthcare solutions await.
I’ve discovered a reliable place to acquire your medication effortlessly. Click here for https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ , featuring swift delivery.
Uncover deals when you purchase your medication with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – lisinopril for sale[/URL – .
Discover competitive pricing on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – kamagra prescriptions online[/URL – when you purchase via web.
Secure your walmart levitra price with ease. Obtain this medication through our web portal efficiently.
Facing an unexpected situation? Locate affordable solutions via the internet with https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ , ensuring safety and peace of mind.
Boost your health today! Acquire your [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – without hassle. This crucial therapy is now away.
Boost your hair growth with affordable solutions like [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – tadalista[/URL – . Discover a range of options and regain confidence without straining your wallet.
Just found a phenomenal source for health supplements at tadalista , suitable for improving your fitness.
Keep informed on hydroxychloroquine benefits and guidelines by visiting https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ for detailed insights and updates.
Unlock exclusive savings with our [URL=https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ – generic lasix 24 hours[/URL – and enhance your health today.
Discover your path to fertility with acquisition [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – tinidazole pills[/URL – .
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, amoxil 650mg online can be a straightforward process.
For those looking to acquire HCG injections, https://mnsmiles.com/item/nizagara/ offers a reliable, secure avenue.
If you’re seeking to enhance your stamina securely, consider visiting [URL=https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix online no script[/URL – for a trusted solution.
Keeping your health in prime condition doesn’t have to empty your wallet; explore [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – lowest price for doxycycline[/URL – for an affordable choice to your requirements. With this, you obtain top-notch therapy without the high costs.
If you’re looking to obtain authentic medication, consider viagra . This alternative offers a budget-friendly solution without compromising on effectiveness.
Investigating options for enhancing fertility? Explore how https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ could be the answer for you.
Here’s how to purchase your medication effortlessly: [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – .
X-ray your options carefully; acquire the drug on the web for convenience. xenical without pres ensures fast delivery and quality.
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and discover generic solutions at https://johncavaletto.org/pill/ventolin-inhaler/ . Purchase your remedy via the web now and begin your journey towards regrowth.
Discover the current [URL=https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ – buy propecia[/URL – and look into alternatives for acquiring this drug through online pharmacies.
Optimize your health with a range of treatments by exploring cialis without pres , offering an exclusive blend of options for your wellbeing.
Purchasing a https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ can be efficiently done through our platform. Opt to buy your pharmaceuticals from our digital store for a hassle-free experience.
Having trouble with hair loss? Find solace in [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – online generic retin a[/URL – , your ultimate solution for regrowing hair growth.
When in need of prompt options, find [URL=https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ – cheap cytotec pills[/URL – for your needs.
Need to save on your cancer treatment? Consider exploring lasix for budget-friendly therapy options.
Having difficulty managing one’s menstrual symptoms? Consider exploring https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ , a proven solution. Acquire it virtually to alleviate discomfort.
For those seeking to acquire Etizolam in the UK, [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – http://www.lasix.com[/URL – offers a secure platform to meet your needs efficiently.
Procure your remedy with ease; canadian pharmacy extra super avana on the web to tackle your needs efficiently and securely.
Unlock sensational deals on essential eye care products! Buy your https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ today and ensure your vision receive the optimal care without overspending.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re aiming to acquire for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin generic canada[/URL – virtually can be a seamless process.
Very few are aware that managing epilepsy is now more convenient thanks to [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – lasix cheap[/URL – , allowing patients to obtain their treatment directly from the comfort of their home.
Discover your pathway to healthier cholesterol levels by opting to purchase your pharmacy on our website. This approach not only ensures convenience but also provides a range of options to suit your specific health needs.
Keep your eye health in optimal shape with our advanced treatment options. Discover more and secure your supply https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ promptly.
Unlock the secrets to handling your well-being with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl 20mg ndc[/URL – , your go-to destination for premium pharmaceuticals.
Unlock unbeatable savings on your healthcare essentials. Discover your optimal solution with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ – torsemide no prescription[/URL – and enjoy elevated well-being.
Unsure where to purchase your medication? For those looking to enhance their health, pharmacy offers a vast range of solutions.
Get amazing savings now! Reveal incredible price reductions on top-quality health supplements today with our https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ . Don’t miss out on this chance to save on your wellness journey.
X-plore the myriad benefits of alleviating seasonal allergy symptoms with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – tadalafil 10mg[/URL – . Whether you are in search of alleviation from itching, this remedy offers a trusted solution.
Having trouble locating cost-effective choices for fertility treatments? Explore [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone 100mg[/URL – , where you might find attractive rates for your needs.
To purchase your treatment without hassle, visit amoxicillin immediately for speedy and dependable service.
Navigating the complicated world of remedies for baldness can be daunting. Thankfully, options like https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ furnish a verified path for those searching to regain their locks.
A range of options to purchase antimalarial treatment online is now available. For those seeking protection or treatment, [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – generic nizagara at walmart[/URL – offer a feasible solution.
Boost your fertility journey with [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix[/URL – . Order a vital drug online and begin your path towards conceiving.
Nourish your vitality effortlessly with herbal max gun power buy in canada , a zenith of wellness. Obtain this potent solution online.
Discover reliable methods to boost your performance with https://seraamedia.org/item/viagra/ , the ideal solution for erectile dysfunction.
SUNWIN stands outside as a new core in search online betting enthusiasts who value dependability, alacrity, and variety. From immersive casino experiences to continually x? s? draws and competitive th? thao markets, the rostrum delivers a balanced ecosystem of trò choi. Players can observe dynamic game slots, skill-based b?n cá, high-reward jackpot, and usual arenas like dá gà and esports. Transparent mechanics such as tài x?u md5, classic xóc dia, strategic baccarat, and fast-paced r?ng h? assure exhibit play. With haunt khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, licensed cskh, voluptuous n? hu events, and flexible d?i lý programs, users dig both pleasure and opportunity. Learn more at https://creditservice.ru.com/.
Planning to an immediate cash boost in the Lone Star State? Explore your possibilities with [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – retin a buy[/URL – , a swift solution for your economic requirements.
Browse our site for the buying tamoxifen and find out economical solutions for managing your condition.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ , offering a seamless order experience for the vital treatment via our website.
Need to boost your stamina? Discover affordable solutions at [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – buy non-generic stromectol online[/URL – for your needs.
Discover how you can boost your vitality naturally with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine without dr prescription[/URL – , a supplement designed to increase HGH levels without risks.
Consider securing your vidalista tadalafil 10mg effortlessly. Purchase your prescription with utmost convenience.
X-ray your options for HIV treatment medications and discover the most affordable solutions. For those seeking economy, https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ offers a viable alternative.
Receive your prescription efficiently by choosing to buy [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – .
Ensure you obtain the lowest rate for [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone canada[/URL – by searching through our options.
Just discovered, prednisone offer a revolutionary approach to enhancing stamina and experience in men.
Harness optimal wellness with natural solutions; discover how you can https://sadlerland.com/herbolax/ for effortless digestive health support.
Obtaining [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – best price prednisone[/URL – has never been simpler. Now, Order your supply without needing a prescription via web.
Seek reliable enhancement in your condition with [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – price of tadalafil[/URL – , available for purchase on the web.
Browse our site to find generic sales amoxil , ensuring you get premium antibiotic solutions at unbeatable prices.
When in search of enhanced satisfaction and performance in the bedroom, consider exploring https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ , an option revered for its efficacy.
One can uncover competitive [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ – generic clomid from canada[/URL – and multiple choices on the internet, ensuring cost-effectiveness and availability.
Acquiring your prescription has never been more straightforward. Now you can purchase your essential medication [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – buy vidalista from the best online pharmacy cpx24[/URL – effortlessly.
Considering your health, acquiring prednisone 10mg grammi has never been more straightforward. Now, Purchase your vital heart-health support medicine online effortlessly and securely.
Venture into the realm of effective ED solutions with https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/fildena/ , accessible online.
Managing anxiety can be a challenge, but with the right medication, relief is possible. Those looking to procure their treatment discreetly can find a wide variety of options available. For a trusted source, consider [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large coupon[/URL – for your needs.
A crucial drug for managing edema is accessible here: [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – staxyn[/URL – . Whether you’re battling heart failure, kidney issues, or liver disease, consider exploring this option.
Unlock unbeatable deals on anti-diarrhea medication at clomid 25mg , your one-stop source for tackling digestive issues.
Knowing solutions for asthma are essential, many search for effective options. For those in search, https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ presents a reliable alternative, offering relief for asthma sufferers.
Vacationing in Canada and realized you left your important eye drops behind? Worry not! You can purchase your essential [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20 without a prescription[/URL – online.
Research the lowest prices for your heart medication and find the [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topamax bipolar[/URL – . Save money while taking care of your health.
Patients seeking cost-effective treatment for bipolar disorder may find nizagara 100mg competitive. Find out the price of managing your condition with these pills.
Explore various alternatives for managing your well-being by choosing to https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ .
Keep your eyes looking their best with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ – best price flomax[/URL – , available for purchase online.
X-ray your options for heart medication by exploring the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil non generic[/URL – . Find out how to manage your health affordably.
Zipping through the myriad options for securing your medications, amoxil 1000 mg pills for sale stands out as a prime choice to buy your health necessities.
Purchase your supply of https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ effortlessly via web. This pharmaceutical solution is designed to enhance your wellbeing efficiently.
Explore affordable ADHD treatment options by purchasing [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ – buy lady era online canada[/URL – to control symptoms effectively online.
Zap your health woes away! Discover affordable options with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ – torsemide without dr prescription[/URL – . Embrace a better lifestyle today.
Looking for a cost-effective solution for your ADHD medication? vidalista non generic offers a valuable opportunity to save on your prescription. This deal is suited for patients seeking budget-friendly ADHD treatment options.
Seeking affordable options for enhanced performance and stamina? Explore the potential benefits by checking the https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ , where you’ll find attractive deals.
Visit [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – non prescription amoxicillin[/URL – to buy your antibiotics on the internet at unbeatable prices.
Have you been searching for a reliable place to purchase your medications? Look no further! Our online pharmacy offers a wide array of pharmaceuticals, including [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – . With us, you can purchase your meds without hassle from the convenience of your place.
When looking to purchase medication for rheumatoid arthritis, consider exploring options to can you order retin-a online , ensuring you get efficient treatment without hassle.
Secure your health by opting to acquire your drugs virtually. Don’t miss the opportunity, https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ today and take charge of your well-being effectively.
Discover affordable options for ED by visiting [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis/ – generic cialis indian fda[/URL – , where you can buy your drugs effortlessly.
Various individuals searching for solutions to handle premature ejaculation turn to buy dapoxetine online legally as a reliable option.
Considering the demand for cost-effective anxiety treatments, https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ presents a practical option.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – is a viable option. Discover securing this treatment through online outlets for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Maximize your health by securing essential medications effortlessly through [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra/ – levitra to buy[/URL – , your reliable source for premium pharmaceutical needs.
Discover how to secure your medications easily with viagra price walmart , ensuring discretion and convenience.
Discover effective solutions for enhancing your sexual health safely at https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ .
You can find choices for [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – online.
Seeking symptom relief from allergies? Explore buy online pharmacy without prescription for an immediate solution. This drug offers potent respite from intolerances.
Acquire https://jawany.com/ventolin/ effortlessly for your ophthalmic needs. Purchase these ocular solutions via web for alleviation from dry eye conditions.
Visit our webpage to order [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – generic zithromax pay for by e check[/URL – , offering quick delivery.
Venturing north for well-being solutions? Find your health aid with tadalafil , offering a broad selection of medications.
Purchasing affordable https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ has never been easier, with numerous options available online. Secure your health today by selecting the best deal.
Researching proven treatments for alcohol dependence? Look into [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex[/URL – for cost-effective solutions.
Your health is securely maintained with [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin-a[/URL – , accessible for purchase directly.
Obtain unparalleled savings on heart health treatments by visiting canada flagyl , your premier source for affordable alternatives.
Keep your health optimized and vitality at its peak! Discover a holistic solution with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ . Enhance your wellness effortlessly by choosing a proven supplement.
Visit [URL=https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ – buy prednisone no prescription[/URL – for an affordable way to manage your condition. Secure yours right away.
With joint discomfort becoming an escalating concern, explore [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ – low price priligy[/URL – for alleviation. This product promises a powerful way to manage your issues.
Zest for a healthier lifestyle begins with managing your cholesterol levels. Explore various choices and compare priligy to discover the best offer for your wellness needs.
I’ve discovered where to [acquire inexpensive https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax/ , a commonly prescribed treatment for malaria.
Navigating the market for Cytotec, a pharmaceutical used for medical abortions, can be difficult. However, accurate and safe information is crucial. For details on where to buy [URL=https://rdasatx.com/cytotec/ – cytotec non generic[/URL – , ensure to refer to trustworthy sources only.
Looking to treat your condition? Purchase [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex in usa[/URL – now and start your journey to enhanced health.
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and buy your priligy without pres today for optimized health and vitality!
Zap high prices with our exclusive https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ , and Snag your bottle of essential antibiotics without hassle online.
Your search for comprehensive healthcare solutions ends here; explore the best [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – generic vardenafil in canada[/URL – for advanced wellness.
Order your health solutions with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – price of nolvadex[/URL – , providing a variety of pharmaceutical products.
Looking for more affordable medication options? Look into propecia for budget-friendly solutions to your healthcare needs.
Curious about how to improve your vitality? Consider trying https://nwfgenealogy.com/low-cost-prednisone/ , a reputable option designed to augment your well-being.
Quickly and conveniently purchase your antiviral pills [URL=https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ – vidalista[/URL – .
Ensure you procure your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine lowest price[/URL – safely for treating certain conditions.
Improve your health effortlessly by opting to order high-quality pharmaceuticals from the comfort of your home. herbolax cost offers a reliable, secure solution for enhancing efficacy.
If you’re in the market for affordable options on your prescription, consider checking https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ for competitive rates.
Visit [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ – cheapest secure delivery amoxil uk[/URL – to acquire your medication on the internet at incredible prices.
For individuals seeking alleviation from constipation, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – presents a trusted remedy.
Prices for essential cardiac care medications can vary; hence, it’s crucial to look up the amoxicillin 250mg to ensure you’re getting a good deal.
Acquiring https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ has never been simpler. Order your prescription with just a few clicks.
Questioning where to locate Ciprofloxacin without overpaying? Discover the [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – cipro[/URL – and save on your medical expenses.
Combat hair loss effectively! Discover how [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – asthalin[/URL – can benefit you in reviving your hair to their former glory.
Quest for relief from motion sickness? Discover how to acquire zoloft and start your journey to comfort.
Keep your health in top condition without leaving comfort behind. Purchase your vital drugs without hassle through our safe platform. https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ and ensure your well-being is always a priority.
Consider securing your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy prices[/URL – effortlessly through our webstore. Preorder now online for swift delivery.
X-plore your options for handling hypertension with reliable medication. Buy [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ – 10 mg tadalista canadian[/URL – online to ensure your heart health today.
X-plore natural remedies for kidney health; discover how to care for your renal function with cytotec , a top natural solution.
X-plore your options for securing Duovir-N easily through our https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ platform. Make your purchase and ensure your health’s safety.
Venture no further for your hormonal therapy needs; [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – offers a variety of options to restore your testosterone levels efficiently.
Quantum leaps in your health journey await! Unlock their potential with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Elevate your wellbeing immediately by choosing a innovative supplement option.
Now, discover your path towards minimized cholesterol with site trazodone , obtainable for buying via the internet.
Browse our catalog to find exclusive deals on https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ . Boost your health today by deciding to acquire reliable options on our site.
People seeking cost-effective options for stroke and heart attack prevention can find the [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/drug/arjuna/ – arjuna without an rx[/URL – when they search online pharmacies.
Maximize your savings on osteoporosis treatment by exploring the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil[/URL – . Discover affordable solutions today.
Get your amoxil easily from amoxicillin 250mg , supplying swift delivery to satisfy your healthcare needs.
I discovered an economical way to enjoy gaming from home at https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ .
Purchase affordable [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ – buy vidalista without prescription[/URL – for managing cardiac care. Explore selections online for budget-friendly solutions.
Be amazed by the affordability when you explore the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil[/URL – . Find unsurpassed deals for your vertigo treatment needs right here.
Zillions pursue effective hair loss solutions; canadian pharmacy extra super avana offers a hopeful alternative.
Visit our site to uncover a unique treatment for your needs – https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ . This product is accessible over the counter, offering a hassle-free way to tackle your concerns.
Explore our world of healthcare solutions and discover easy ways to maintain your well-being. Whether you’re seeking particular medications or broad health advice, we provide an array of options. For those in need of an alternative, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – could be your answer.
best crypto exchange – fast crypto exchange
exchange crypto
https://changely.us
best cryptocurrency exchange – instant crypto exchange
crypto exchange
https://changely.us
crypto exchange without KYC
coinswitch
https://changellly.io
Keeping your budget in mind, effortlessly acquire your medication at the [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – buy ranitidine no prescription[/URL – , ensuring you always have your essential doses.
When looking to treat OCD symptoms, consider exploring finasteride as a potential solution.
Discover the most cost-effective options for managing your health with https://shilpaotc.com/product/lady-era/ . Whether you’re in the market for this vital prescription through digital platforms, we provide a broad spectrum of alternatives to fulfill your healthcare demands.
Discover how to secure [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – buy cheap trazodone[/URL – for managing your condition. Explore multiple alternatives for treatment today.
Nabbing your essential medical supplies has never been simpler. Acquire unbranded [URL=https://renog.org/product/amoxil/ – lowest price amoxil[/URL – on the web to ensure your health needs are met with quality and affordability.
The need for reliable and efficient access to pharmaceuticals has never been greater. Explore your options and purchase nolvadex 20mg now.
Just discovered your solution to erectile dysfunction? Explore our comprehensive https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ , featuring a variety of options to meet your needs.
I found the most affordable [URL=https://purefmonline.com/propranolol/ – propranolol 20mg[/URL – while searching for cost-effective solutions for my chronic pain.
Get your health solutions conveniently with retin-a american distrubution . Secure your required treatment with ease from anywhere.
Concerned about where to acquire antiviral treatment? Your solution is just a click away with https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ – hassle-free and convenient.
Purchase your drugs with confidence from a [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – best price 100 mg generic nizagara[/URL – , where quality and consumer happiness are paramount.
Everline Market – A clean and simple layout, letting you explore the collection quickly.
Zipping through your options for managing impotence? Learn about a streamlined solution by choosing to acquire [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/purchase-viagra-online/ – viagra 50 prix pharmacie[/URL – .
Discover your solution to enhanced well-being with a vidalista en ligne . Purchase instantly for an improved lifestyle.
I discovered the https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ after looking the internet.
Just uncover how [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl tablets[/URL – can improve your well-being, offering a powerful solution for improved endurance.
Save on allergy relief by exploring our deals on sildalist 20 mg online without prescription , allowing you to combat symptoms economically.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your condition efficiently with https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ . Enhance your lifestyle now.
Regain digestive harmony with a natural solution; order [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ – online prednisone no prescription[/URL – to promote digestive well-being.
I’ve used various gambling platforms over the years, and I’m always shocked how many beginners sign up without verifying anything. In case you want a detailed look of promos, withdrawals, and available games, this overview made things easier: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s very clear and breaks down the important points before making a deposit. Definitely worth a read if you prefer to play safely.
Vacationing in Canada and realized you left your important eye drops behind? Worry not! You can buy your essential [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/mail-order-prednisone/ – mail order prednisone[/URL – remotely.
Find budget-friendly solutions for hormone therapy with tadalafil 20mg . Purchase high-quality treatments through our website effortlessly.
Considering your need for hormone therapy, consider exploring https://jawany.com/priligy/ for economical solutions.
Before deciding, compare the [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol commercial[/URL – , and review prices from different pharmacies to ensure you’re getting the best deal for managing Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Having gastrointestinal discomfort? Discover relief through [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – , a trusted medication. Seek it online for quick alleviation from stomach aches.
Procure the essential medication affordably by clicking here: dosage of levitra , securing substantial cost savings on quality healthcare.
Acquiring https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ has never been easier; Secure the necessary medication through a web portal with just a single click.
Explore the range of options for controlling menstrual disorders by acquiring [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – http://www.nizagara.com[/URL – .
WildWood Corner Hub – Well-organized fashion selection with smooth and pleasant browsing.
Navigating the world of online casinos can be tricky, especially when looking for safe and secure gaming options. [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – order nizagara online[/URL – offers a solution for this problem, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience without the hassle.
Curious about affordable treatment options for your condition? Discover a cost-effective alternative with fildena and paypal . Ideal for those seeking budget-friendly options for their health care.
The purchase of https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ on the internet delivers a simple and effective approach to get one’s hair loss treatment.
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before attempting to acquire [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – nolvadex[/URL – cannot be overstated.
You can discover the most competitive [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – stablon online uk[/URL – for your alopecia therapy on the internet today.
Residing in the Great White North, individuals looking for asthma relief can now easily access their requirement via asthalin 100mcg .
Obtain the best price on https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ online, ensuring your confidentiality and fulfillment are secured.
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – to your regimen! Discover cost-effective solutions on the web for enhancing your health journey.
Unlock enhanced vitality and vigor; discover a revitalized lifestyle with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – vardenafil[/URL – .
Discover affordable options for ED by visiting cost of cialis tablets , where you can acquire your prescriptions conveniently.
The urgency to acquire effective treatment has never been greater. Discover your key with https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ , offering a broad assortment for your well-being needs.
If you’re looking for an effective solution to manage your Crohn’s disease, consider [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ – lasix[/URL – . This medication delivers significant relief.
Discover how [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ – flomax[/URL – can reduce symptoms of an enlarged prostate by visiting our site.
Just discovered the best choice for managing HBV? Explore clomiphene today for economical treatment.
Our comprehensive review on https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ dives into potency and safety.
Regarding cardiovascular health management, consulting a healthcare professional and exploring options like [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – lowest price generic prednisone[/URL – can be advantageous.
Learn about the advised lasix for effective treatment of scabies.
X-ray your health concerns and uncover the best solution; use this link to https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ for a complete approach to wellness.
Explore the market for cartilage health solutions and find the [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ – cheap verapamil overnight[/URL – . Acquire your medication online for optimal joint health.
Buy Cytotec directly from [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – cytotec for sale overnight[/URL – for managing your health efficiently.
Quiet your anxiety at an affordable price with priligy generic 60 mg price . Get your remedy now for peace of mind.
Get the lowest prices for your healthcare needs with our unparalleled https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ . Secure your package now and guarantee your wellness is always in good hands.
Navigating the complex world of medication, finding a safe source for [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/canada-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – becomes paramount for those seeking over-the-counter options.
Quickly order your medication with vidalista , offering fast delivery right to your doorstep.
Get the best deals on brand-name Duprost today by clicking https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ . This treatment is crucial for controlling BPH symptoms.
Discover the solution to ED effortlessly. Acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – viagra uk[/URL – now and restore the assurance you’ve been missing.
Just unveiled: [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – low cost sildenafil[/URL – offers a revolutionary solution for hair loss. Now, you can acquire reliable treatment without leaving home.
Obtaining non prescription trazodone has never been simpler. Purchase this vital medication without the need to leave your house.
Maximize your vitality and stamina with https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ , the prime choice for enhancing performance. Explore the decisive alternative for improving your health and confidence seamlessly.
Discover genuine solutions for improving your strength with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – .
Just spotted a fantastic deal! For those seeking heart health solutions, now’s your chance to cut costs on your treatment. Discover substantial discounts on your next purchase by clicking here: [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – vidalista 60 mg ervaringen[/URL – . Don’t miss out on this opportunity to enhance your wellness affordably.
Browse our website to discover the purchase sildenafil without a prescription .
Secure your essential medications easily by choosing to purchase from https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ .
Uncover incredible bargains on your next purchase. Get the best [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – best generic sarafem website[/URL – now. Maximize your savings on each shopping trip.
Discover safe and convenient ways to acquire your treatment. [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – sildenafil[/URL – today for a hassle-free experience in managing your health needs.
Keep your kidneys healthy without spending too much. Find out about propecia 5mg for affordable solutions.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Locate https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ to boost your vitality efficiently and safely.
Understand the price of upholding your well-being by checking the [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ – nizagara best price usa[/URL – updated costs.
Battling with an enlarged prostate? Explore diverse treatment avenues by considering to availablility of vardenafil in new zealand . Lower your symptoms efficiently by opting to purchase this treatment via our website.
Purchase organic solutions for your health needs effortlessly on our website. Explore choices and find the best deals https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ now.
Considering the fluctuating [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone[/URL – , it’s worth researching different platforms to acquire your prescriptions online.
Visit our site to buy propecia online uk , ensuring you acquire your treatment promptly.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can acquire https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ through certified online pharmacies, offering a hassle-free way to manage their symptoms.
Seeking alleviation from tension? Explore our selection of drugs and find [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – . This pharmaceutical is famous for its efficacy in treating signs of anxiety and stress.
I understand the need for accessible choices when looking to get medication. For those considering managing their health conditions efficiently, exploring walmart flomax price provides a key solution.
Zillions are seeking effective remedies for their issues. Now, you can effortlessly acquire https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ online for top results.
Looking for affordable medication options? [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – provides an opportunity to save on your medications. Don’t miss out on these savings!
Acquiring your treatments has never been easier with [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – pharmacy[/URL – . Buy now for prompt delivery worldwide.
Visit our website to obtain vital treatment for Addison’s disease with propecia for sale , your key to managing enduring adrenal insufficiency.
X-ray your budget and invest wisely on heart health options. Discover competitive https://glenwoodwine.com/zoloft/ online.
Understanding the need for accessibility, you can now obtain your treatment online with ease. [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – fildena 150mg[/URL – and experience quick dispatch to your doorstep.
Zero hesitation required when searching for ED solutions; purchase viagra without dr prescription usa easily.
Need an effective, comprehensive solution for your health? Explore the https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ , your go-to choice for improvised wellness and vitality.
Secure your supply of essential nutrients now by deciding to purchase [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ – flagyl without a prescription[/URL – , optimal for upholding strong bones and teeth.
Zap your fertility concerns away! Explore the potential of buy cheap pristiq and learn about how it can help in enhancing your chances of conception.
I understand the importance of medication accessibility, thus highlighting the convenience of opting for mail order methods. In this context, https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ offers a seamless way to acquire your necessary medication without the hassle of visiting a pharmacy.
Visit [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – online generic staxyn[/URL – to purchase the Augmentin vial at the most affordable rate.
Keeping your vitality at its peak has never been easier. Explore a variety of solutions with our [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ – propecia[/URL – , offering a swift enhancement in your health.
Zero in on your digestive health needs: Seek and acquire premium digestive aids like where to buy herbolax with ease from your home.
Quickly discover relief from allergy-induced nasal congestion with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ , a top-rated choice for combatting allergy symptoms.
Your search for reliable and convenient access to medication ends here. Purchase [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – kamagra 100mg tablet[/URL – virtually without the hassle of a traditional pharmacy visit.
Visit [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – to secure your antibiotic with ease.
If you’re looking for an effective solution to combat bacterial infections, ponder amoxil 1000 mg acheter . This antibiotic is widely recognized for its effectiveness against a wide array of bacteria.
Zap your ocular hypertension or glaucoma symptoms by exploring https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ , offering a budget-friendly solution.
Obtain essential details on [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – to ensure you’re getting the most favorable deal on your treatment.
Yes, securing the [URL=https://center4family.com/priligy-online/ – dapoxetine[/URL – can be effortless when you hunt on web stores.
Discover how to effortlessly procure buy priligy w not prescription via a secure platform, ensuring you receive high-quality medication for your health needs.
Discover the most budget-friendly options for your medication. Evaluate https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ and conserve on your health expenses.
Just in time for your urgent needs, find your essential supplies ready at [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – canadian pharmacy cheap cialis[/URL – , right away.
To find out the current [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis-20mg/ – generic cialis canada[/URL – , check out our site.
To secure the essential iron supplements, explore lasix online uk guaranteeing value.
Considering various options to manage your BPH symptoms? Discover how you can obtain https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ via the web, offering a convenient solution to ease discomfort.
When seeking an affordable solution for your antimicrobial needs, look into tapping into the convenience of [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ – doxycycline on line[/URL – . This virtual drugstore offers a wide selection of generic medications that address various health conditions efficiently.
Unlock unparalleled convenience by purchasing your medications via generic xenical lowest price . This streamlined process guarantees a seamless path to obtaining the needed healthcare products.
Explore reliable options to get https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ , securing your safety is never compromised.
Keep your prostate health in check with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra[/URL – , available for order through our site, ensuring you receive top-quality treatment affordably and efficiently.
Yes, to manage your symptoms effectively, you could purchase [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – generic viagra from canada[/URL – .
Having trouble with uninterrupted sleep or contending with OCD? Explore how pharmacy buy could provide the relief you seek. This prescription is designed to aid in maintaining signs effectively.
Before deciding, compare the https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ , and check costs on various websites to ensure you’re getting the best deal for managing Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Battling inflammation? Explore more about how [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – propecia canadian pharmacy[/URL – could be your pathway to easing discomfort.
Before considering treatment options, explore [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – lasix cheap[/URL – to treat your health conditions effectively.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover your solution with order nexium online , the optimal choice for boosting your hormone health. Consider the way to enhance your health with just a few clicks.
Get the most affordable prices for your healthcare needs with our exclusive https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ . Find your supply now and make sure your well-being is continuously looked after.
Discover cost-effective solutions for managing your mood and mental health. Explore our selection of [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – buy amitriptyline online canada[/URL – to find the right choice tailored to your needs.
Seeking an effortless way to enhance your endurance? Explore [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – vidalista[/URL – for a reliable solution.
Secure your tadalafil canadian pharmacy today and ensure your health is in top condition. Acquire this vital remedy without hassle and preserve your well-being efficiently.
Before deciding to obtain your next dose of anxiety management medication, consider exploring your options. For those looking for a way to alleviate symptoms of anxiety safely, https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ might be the right step. Options vary widely, so make sure you’re making an informed choice.
I discovered that you can obtain [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin for order from canada[/URL – effortlessly for your motion sickness.
Zap your concerns away with a tap on the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – strattera without presc[/URL – and start your journey towards better wellness today.
Regain digestive harmony with a holistic solution; order generic viagra 25mg next day to promote digestive well-being.
Looking to control your IBS symptoms? Find out about how https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ can offer relief.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ – generic amoxicillin from canada[/URL – , and Bag your course of vital antibiotics without hassle via our website.
Various medications for chronic hepatitis B exist, yet [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – cialis black walmart price[/URL – stands out due to its effectiveness.
X-plore your financial alternatives with herbal extra power when you require immediate financial assistance.
Join us as we explore the benefits of https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ , a leading solution in managing chronic health conditions. With its proven effectiveness, it’s no wonder why many choose to acquire this vital medication for their health regime.
Managing ADHD symptoms can be challenging, but with the right medication, it’s definitely within reach. Explore your options and learn about how [URL=https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ – lowest price for viagra soft tabs[/URL – can be a game-changer in your treatment plan.
Acquire your health solution now! Purchase [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – effectively for heart health.
Discover your pathway to enhanced well-being with low minimum order priligy online , your go-to for natural solutions.
Discover ways to secure https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ , a premier choice for boosting one’s vitality.
Zeroing in on effective hair loss solutions? Explore the myriad options available for managing alopecia. [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – lasix ad[/URL – could be your answer. With various treatments accessible, it’s essential to choose one that suits your specific needs.
Certainly, obtaining Etizolam-based medications has never been simpler. For those seeking relief, [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – cheap retin a pills[/URL – offers a streamlined, secure, and diverse payment method spectrum. With an easy transaction, buy your necessary prescription online.
Discover how to enhance your health with maxaquin price cheap usa , available immediately for ordering.
Quest for premium healthcare products ends at https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ , where you can purchase everything from medications to wellness supplements via our website.
Discover a hassle-free way to secure your prescription with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ – buy pharmacy[/URL – , ensuring discretion and ease in purchase.
If you’re looking for an effective treatment to combat bacterial infections, consider [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – lowest price on generic amoxicillin[/URL – . This medication is widely recognized for its effectiveness against numerous types of bacteria.
Looking to treat your spasmodic pains? Discover how buying bentyl online can offer respite.
Obtain relief from year-round allergies with https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ , available now. This nose spray can help in reducing your allergic reactions.
Research suggests that finding the [URL=https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ – uk pharmacy prednisone[/URL – can be easy with the right guidance.
Xperience the convenience of getting your treatments with a doctor’s note. Check out [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – overnight vpxl[/URL – for a hassle-free purchase.
Just discovered you can buy your IBS relief medication online? levitra online pharmacy offers a wide range of options for your medical needs.
Need to tackle intestinal worms? Obtain your effective treatment easily by clicking https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ right away.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil on line[/URL – , a top choice for tackling baldness. Acquire them immediately and start your road to regrowth!
Find the best offer on [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara shops[/URL – for improving your health today.
Purchase your necessary antiviral conveniently through order fildena 50mg overnight , a method guaranteeing fast delivery and privacy.
You can acquire safe and trustworthy nausea relief with https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ , accessible through online pharmacies.
Zero in on your health and wellness essentials with ease by choosing to buy your medications from our [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – nizagara for sale overnight[/URL – , offering you a straightforward and convenient way to maintain your health needs with just a few clicks.
I discovered the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ – buy priligy hawaii[/URL – after looking numerous websites.
Get the best pricing on retin-a online generic by looking on the web. This treatment is essential for specific conditions, so locate your options immediately.
I located the best place to acquire https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ .
Having trouble with uninterrupted sleep or contending with OCD? Explore how [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – could offer the relief you seek. This prescription is designed to help in controlling conditions effectively.
Ce site est destine a repondre aux besoins des habitants.
Parmi les contenus disponibles, Le site propose des informations surles dispositifs locaux et les services publics.
Chaque categorie a ete structuree pour un acces rapide aux informations,que ce soitles contacts utiles.
La mise a jour constante des informations est une priorite, assurant une transparence complete envers ses habitants.
https://www.la-mairie.com/rezonville
Experiencing seasonal allergies? Find respite by opting for to acquire [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ – but lady-era in us[/URL – . This efficient treatment is obtainable for allergy sufferers.
I found an amazing source to purchase priligy 90 .
Obtain comprehensive insights and secure the https://brightnights915.com/drugs/canada-lasix/ for your antiviral medication needs by browsing our website today.
Xperience unmatched joy with our unique scent. Elevate your mood effortlessly by opting to [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix for sale[/URL – . Whether seeking to acquire a aroma virtually, it’s never been easier to enhance your wellbeing and radiate confidence.
Join the myriad of satisfied customers who have found the ease of purchasing their medication via the web with torsemide for sale , offering an effortless way to get your wellness necessities.
Zapping tuberculosis requires effective medication. Find affordable treatment options; https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ are obtainable on the web.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern solutions, managing it has become easier. Look into [URL=https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ – 20 cialis no rx[/URL – , a budget-friendly and reliable option for enhancing your performance.
Now, discover the benefits of [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – where to buy bentyl online[/URL – , and see how it can help in easing your pain.
Given the variety of options available, finding the location to purchase order prednisone is vital for efficient treatment.
Find best prices for natural vigor solutions; https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ right here.
When considering bone density improvement, looking into [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – becomes crucial. It offers patients a route to improve their bones effectively.
Revitalize your vitality and enhance your performance in the bedroom with nizagara canada . Experience a surge in your libido like never before. This product is your answer to a more fulfilling and satisfying intimate life. Say goodbye to hesitation and hello to a renewed you.
Having trouble locating a reliable source for https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ ? Look no further! Our credible platform offers an straightforward way to obtain the required medication online.
Keep your kidneys healthy without spending too much. Find out about [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ – low cost priligy[/URL – for budget-friendly choices.
WildRose Collection – Boutique has a cozy and inviting vibe, discovered a few standout items.
Seek the best offers for boosting your energy with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ – kamagra[/URL – . Shop on the internet for maximum savings.
Dealing with digestive issues? Find fast relief by selecting prednisone .
Secure your health by choosing to https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ on this platform, ensuring swift and trustworthy access to your necessary medication.
Many are searching for effective options for erectile dysfunction, and [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/lowest-price-generic-cialis/ – buy cialis[/URL – offers a proven option.
Achieve academic excellence and enhance your writing skills with our professional help at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – .
Zeroing in on HIV treatment, securing doxycycline sin receta medica becomes indispensable. Accessibly Secure a vital antiretroviral online.
Obtain ease from bowel sluggishness quickly with https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ . This treatment is ideal for individuals looking for a safe way.
Looking to improve your wellness? Consider [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lowest price on generic lady era[/URL – for a hassle-free solution.
Improve your health by visiting price cytotec 200 to find a broad selection of medical supplies.
Seeking affordable solutions for fertility issues? Consider exploring https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ , a popular alternative for those aiming to boost their chances of conception.
Seeking improved performance? Discover what you’re looking for with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – , proven to boost both energy and stamina.
With rising healthcare costs, finding affordable medication can sometimes seem daunting. However, options such as [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin 100mcg[/URL – are available to help manage costs. Whether you’re looking to purchase heart health medication without breaking the bank, exploring discounted solutions through the internet can be a wise choice.
Now, find the remedy for ED with simplicity by opting to acquire fildena 100 mg gr .
Discover reliable methods to boost your performance with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ , the optimal solution for men’s health.
The positive effects of [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara without a doctors prescription[/URL – for managing mood swings are substantial.
Your well-being is our priority; order tadalafil on the web and begin your journey to better health today.
Maximize your alertness and cognitive performance with https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ . Whether you’re looking to improve focus or reduce fatigue, this solution delivers reliable results.
Just realized you need Cialis for your condition? No need to fret! You can [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – purchase cialis[/URL – simply and with confidence.
Need fast relief from allergies without the hassle of a doctor’s visit? Explore our selection of [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a[/URL – options. Buy easily online for quick allergy relief.
Are you looking to alleviate your seasonal allergies without breaking the bank? Consider our order vidalista . These budget-friendly options offer the equivalent relief from sneezing, itchy eyes without the hefty price tag of name-brand versions.
You can find https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ online, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Venture into a world of health where securing your prescriptions [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – is straightforward.
Discover the most up-to-date [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ – online lisinopril[/URL – and explore options for purchasing this drug online.
To get your order of crucial medicine, simply visit strattera online cheap pills . Whether you’re aiming to buy for urgent needs or to replenish your stock, we’ve got you sorted.
Unlock remarkable savings when you buy your ocular medication online. For alleviation from allergies, https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ today.
Discover incredible savings on your medications at [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil 10mg[/URL – , your premier destination for cost-effective healthcare solutions.
Various individuals searching for solutions to manage premature ejaculation turn to [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – as a reliable option.
Need fast relief from allergies without the hassle of a doctor’s visit? Explore our assortment of stablon malaysia where to buy options. Order without difficulty online for quick allergy relief.
Various individuals suffering from heavy bleeding can find relief by using https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ , an innovative treatment.
Patients seeking affordable solutions for their medication can check [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ – retin a uk[/URL – to discover cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
Understand your options for managing hair loss; consider alternative treatments. cytotec uk might be your solution.
Quest for superior healthcare products ends at https://swanpercussion.com/lasix/ , where you can buy everything from medications to wellness supplements on the web.
To ease chronic cough, consider employing [URL=https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ – sildalis online canada[/URL – , a trusted remedy.
Experiencing organ transplant rejection symptoms? [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ – prednisone online canada[/URL – may assist in handling these conditions.
Reduce your cholesterol effectively with buy prednisone on line , offering a reliable way to procure your prescription.
Navigating antihistamine options becomes easier with the option to buy https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ , providing fast access to potent treatment.
When seeking relief from aches, consider [URL=https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ – tofranil[/URL – as a potent solution. This anti-inflammatory drug is perfect for treating various conditions, providing both affordability and effectiveness.
Need to learn the most recent ventolin without a percription ? Click here for budget-friendly options.
Acquiring https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ via web offers a hassle-free pathway to managing chronic conditions. With a variety of options available, guaranteeing you receive the authentic medication is no longer complicated.
Acquire safe pain relief by opting to buy your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – today.
Quickly obtain your [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ – esomeprazole[/URL – , ensuring effective management of inflammations.
Buyers seeking effective treatment for their condition can secure purchase prednisone online online.
To treat irritable bowel syndrome effectively, consider https://marksgroupbd.com/prednisone/ as your go-to solution.
Get your financial savings on medical supplies with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – retin a generic[/URL – , providing a diverse range of items.
Your search for cost-effective Cabergoline ends here: [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/nizagara-com/ – cost of nizagara tablets[/URL – .
Zap your health troubles away! Purchase your medicinal solution with ease, lasix 100 mg kopen via web. Secure and safe.
Looking to obtain your pharmaceuticals easily? Look no further! Explore our trusted https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ for a seamless experience.
Unlock the benefits of a diverse healthcare regimen by opting to [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – . Explore the convenience of acquiring your essential treatment with ease, ensuring you stay on top of your health needs.
Before making any decisions, explore your options to obtain Clomid without a prescription safely. Always consider consulting a healthcare professional for advice. Click here for more information: [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid buy online[/URL – .
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, canadian amoxil is a viable option. Discover obtaining this treatment via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
The https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ showcases how individuals battling heartburn can get respite promptly and efficiently.
Acquire [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ – cost of estrace tablets[/URL – at unparalleled rates! Find your vital pharmaceuticals with us and benefit from our exceptional offers.
To purchase your medication without hassle, click on furosemide now for speedy and reliable service.
Visit https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ today and locate budget-friendly solutions for controlling your pain.
Discover affordable options for managing addiction; [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – sildalis without pres[/URL – offers a pathway to recovery. Explore cost-effective methods for combating dependency.
Various medical professionals recommend seeking advice on [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – bentyl low priced[/URL – for gastrointestinal discomfort to guarantee safe and effective relief.
Zest for a more economical lifestyle begins with managing your cholesterol levels. Explore various choices and compare tretinoin 20g to discover the best price for your medical needs.
Explore innovative options for enhancing your body’s growth with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ , for purchase.
Given the wide array of hormone therapies available, selecting an effective and safe option is crucial. For those considering estradiol supplementation, [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara price walmart[/URL – offers a dependable alternative. Whether you’re seeking to buy a trustworthy hormone therapy online, it’s vital to opt for reputable vendors to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Ensure optimal health with our trusted source for your pharmaceutical needs. Secure your quality drugs easily from the comfort of your home. Check out cheapest 120 mg generic xenical prices for reliable and efficient service.
Need to discover the current https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ ? Visit our website for budget-friendly options.
Acquiring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – via web offers a straightforward pathway to managing chronic conditions. With numerous options available, making certain you receive the authentic medication has never been a challenge.
Discover trusted treatments for your digestive discomfort with sildenafil , a choice supported by healthcare professionals.
Researching your options for treating fertility issues? https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ offers extensive insights. Explore how this solution can aid improving reproductive health.
Obtain the treatment for hair loss by clicking here: [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – cheap prednisone[/URL – . Secure yours now for the best results.
Now, obtain your cholesterol-lowering medication conveniently [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/]cialis[/URL] .
Keep your intimate life vibrant and spontaneous; buy next-day nizagara in usa to enhance your experiences without delay.
Here’s how to obtain https://youngdental.net/tamoxifen/ for your needs without a prescription.
Discover excellent choices for managing your condition efficiently with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/]tadalafil[/URL] . Improve your health today.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can acquire [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – through certified web-based pharmacies, offering an easy way to control their symptoms.
The importance of securing reliable and effective HIV treatment cannot be overstated. With a variety of options available, it’s crucial to opt for a supplier that offers both quality and convenience. For those in need of a trusted option, generic vpxl at walmart provides an accessible path to controlling their condition effectively.
To discover the latest https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ , visit our site. Ensure you’re obtaining the top deal today.
Seeking angina treatment? Discover your options with [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , accessible on the web.
Visit our website to locate the [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/flagyl/ – overnight flagyl[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to purchase this essential pharmaceutical, we ensure you receive the best deal.
Quickly secure your retin a for sale devoid of the hassle of a medical consultation.
When looking to acquire https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ , ponder various outlets supplying it online.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – buy hydroxychloroquine[/URL – .
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxil pills 500[/URL – , and Bag your course of essential antibiotics without hassle via our website.
Looking to obtain Acamprosate? 100mg mil lasix offers a seamless way to get your medication from the comfort of your home.
Maximize your savings on antiretroviral therapy by clicking here: https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ . Discover the best rates on the internet for essential HIV treatment options.
Experience the benefits of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/lasix-walmart-price/ – prix lasix 40 mg france[/URL – by considering a natural approach to enhance your well-being.
I realized the lowest [URL=https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ – tretinoin online legitmate canada[/URL – for enhancing men’s health online.
When looking to enhance your vitality, consider opting for retin a online no script , a reliable choice. Available for acquisition online, this solution promises enhanced performance.
Zealously seeking an affordable solution for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms? Explore our cost-effective options and unlock potential savings with https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ . Uncover the path to improved wellbeing without breaking the bank.
I’ve discovered the [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/product/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2[/URL – for addressing baldness.
SUNWIN is a modish online betting ecosystem designed for players who value transparency, speed, and variety. From immersive casino experiences and data-driven x? s? systems to competitive th? thao markets, every trò choi is optimized for real-time performance. The podium stands out with high-RTP game slots, skill-based b?n cá, liberal jackpot, unwritten dá gà, and fast-growing esports. Smart algorithms power tài x?u md5, xóc dia, baccarat, r?ng h?, and explosive n? hu, while docile khuy?n mãi and long-term uu dãi prize loyalty. With sympathetic cskh and scalable d?i lý advance, users can explore the ample experience at https://sunwin24z.life/.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – virtually can be a simple process.
Keep your health in check with purchase lasix , your solution to handling inflammation.
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and order your https://cafeorestaurant.com/tamoxifen-without-pres/ today for enhanced health and vitality!
Seeking trusted malaria treatment can be a daunting task. Yet, buying [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – buy retin a online canada[/URL – has never been simpler.
Visit prix du amoxil 250 to buy your prescription easily.
Explore the best https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/order-retin-a/ for an exciting gaming experience.
Zeroing in on cost-effective healthcare solutions, many are curious about how to cheaply access medications. Discover the [URL=https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ – order prednisone online[/URL – for insights on how to budget on your health needs.
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – can aid in easing urinary symptoms linked to an enlarged prostate.
Discover secure and convenient ways to procure your medication with just a click. drugs similar to viagra offers a simple solution for your needs.
Seek trusted enhancement in your condition with https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ , available for buying on the internet.
Experiencing impotence? Discover proven solutions and purchase [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ – erectafil pills[/URL – . Securely enhance your performance today.
Discover the latest [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ – buy prednisone in canada[/URL – , a crucial detail for those aiming to buy this topical treatment.
If you’re looking to acquire high-quality medication, consider levitra buy . This option offers an affordable solution without compromising on efficacy.
Looking for cost-effective options? Find the https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ easily.
Interested in controlling your conditions? Look into purchasing your medication safely through [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – prednisone 10 order[/URL – , a reliable source for quality pharmaceuticals.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – finasteride cheap[/URL – , a top choice for tackling hair thinning. Acquire them today and start your journey to regrowth!
Visit our amoxicillin page to purchase trusted heartburn relief. Easily buy your treatment with a click.
Managing ADHD symptoms can be challenging, but with the right medication, it’s definitely within reach. Explore your options and discover how https://seraamedia.org/amoxicillin-650mg/ can be a game-changer in your treatment plan.
Questioning where to secure Ciprofloxacin? Look no further than [URL=https://jawany.com/cipro/ – where to buy cipro online[/URL – , your go-to source for reliable antibiotics.
Curious where to find the most affordable, budget-friendly, cost-effective [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ – canada pharmacy pharmacy generic[/URL – ? Explore
Alleviate your nasal congestion and relieve allergy symptoms quickly by utilizing vardenafil 10mg . This effective treatment offers immediate relief for those suffering from seasonal allergies, ensuring your daily activities are no longer hindered by annoying sniffles and sneezes.
Secure your https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ today and ensure your health is in top condition. Acquire this critical remedy without hassle and maintain your well-being efficiently.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 1000mg[/URL – is a viable option. Explore obtaining this treatment online for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
For those seeking hair growth solutions, [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – lowest price generic clonidine[/URL – offers a promising option. Explore the benefits of this solution and find out how it can assist in combating hair loss.
When seeking affordable solutions for impotence, consider fildena in usa as your preferred source.
Discover how https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ can reduce symptoms of prostate enlargement by checking our site.
Xperience enhanced vitality and wellness with our [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – , up for grabs for regular use.
Revitalize your eyelashes with effective and economical solutions. Discover myriad benefits by exploring [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – compare ed-sample-pack-2 ed[/URL – . Achieve dazzling results for a more affordable price.
Discover how pharmacy can assist in managing your heart health efficiently.
Secure your https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ effortlessly. Acquire the medicine online with just a few clicks.
When seeking effective antifungal treatment, consider trying [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-without-a-doctor/ – prednisone 40mg kaufen[/URL – for your health needs.
X-plore cost-effective solutions for your medical needs with generic flagyl lowest price , your path to enhanced wellbeing.
Keep your health in top condition with affordable solutions; explore https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ for your needs. Seek out alternatives on websites to keep up wellness efficiently.
Need to buy affordable treatment for hypertension? Check out our [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – retin a buy in canada[/URL – for top-notch options available on-site.
Now, secure your health by choosing to [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – lowest price for tamoxifen[/URL – from our reputable internet pharmacy.
Maximize your health outcomes by opting to acquire your pharmaceuticals online. For those in need, nizagara is a hassle-free way to secure your essentials quickly and efficiently.
I uncover the easiest way to acquire gentle relief from constipation: https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ .
Obtain your Hiforce ODS without hassle today. [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/ – retin a buy in canada[/URL – offers a prompt and trustworthy method for those seeking boosted stamina.
Navigating the vast web for authentic ayurvedic solutions? Your search ends here. Discover the best ayurvedic remedies at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/ – buy levitra no prescription[/URL – . Buy with confidence for your natural wellness needs.
Regarding the purchase of doxycycline , it’s vital to consult a healthcare provider prior to making a decision.
Discover affordable solutions for hair loss treatment by exploring https://endmedicaldebt.com/drug/vidalista/ . You can acquire this proven treatment on the web.
Discover proven joint pain relief with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ – prednisone best price usa[/URL – , the leading treatment for purchase on the web.
Just discovered you’re in need of a rapid solution for better endurance? With [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – extra super avana[/URL – , find your answers and enjoy improved performance sooner than you think. Now you can acquire this treatment swiftly to ensure your readiness.
Renew your vitality and feel young again; buy strattera in hong kong . Experience a rejuvenated life by choosing to order this innovative solution today.
Explore our exclusive selection and uncover unparalleled deals on https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ . Secure your bottle now for improved cardiac health.
Quality medications at unsurpassed prices! Order your medicine with no hassle at [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – super kamagra price walmart[/URL – . Your health, our priority.
Potential seizures can be effectively managed with [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ – best price on cialis 20mg[/URL – , a popular choice among various therapies.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern solutions, managing it has become easier. Explore cialis brand , a economical and reliable option for enhancing your performance.
Secure your health with ease; procure your medication with ease through our digital pharmacy. For those managing cardiovascular conditions, https://embcselma.org/product/nizagara/ now and maintain your wellbeing.
Just realized you need ED medication for your well-being? No need to stress out! You can [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/lowest-price-generic-cialis/ – cialis[/URL – without hassle and with confidence.
Combat seasonal allergies swiftly with cost-effective solutions; buy your nasal spray online. [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone mk[/URL – provides ease for itching.
Just in: Discerning shoppers can now find the cheapest nizagara on websites, ensuring you get supreme value for your wellness necessities.
Battling nasal allergies can be daunting, but relief is available through https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ . Discover ways this treatment can alleviate your symptoms now.
Considering the need for affordable medications, it’s essential to explore various options. If you’re in pursuit of cost-effective treatments, particularly for inflammation and allergic reactions, exploring [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buy-pharmacy/ – pharmacy without dr prescription usa[/URL – might be your best bet. This glucocorticoid medication, pivotal in managing numerous conditions, can be obtained with ease.
Skvely clanek! Nedavno jsem objevil Spinmama Casino CZ a nabidka je opravdu lakava. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere potesi kazdeho hrace. Herni souteze a vyherni automaty jsou pro me nejzabavnejsi – online casino pro ceske hrace s vybornymi podminkami. Chcete-li zkusit nove a bezpecne online casino, mrknete sem: Twitter . Urcite vyzkousejte a uzijete si spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Objevte Spinmama Ca
Spinmama Casino CZ – nejlepsi bonusy a promo akce
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
f09d5d5
Naturally supporting prostate health is essential for men’s well-being. Discover how [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ – chloroquine drug name[/URL – could be your partner in maintaining optimal prostate function.
Discover more about trusted birth control options at meldonium to buy .
Struggling with hair loss? Discover https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ , a top choice for tackling baldness. Purchase your supply immediately and begin your journey to regrowth!
Boost your confidence and revitalize your life with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ – lasix shop uk[/URL – , available for purchase online.
Browse our site to locate [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – low cost amoxicillin[/URL – , ensuring you obtain top-quality antibiotic options at unbeatable prices.
Considering the necessity for trustworthy methods for ED management, it’s vital to find a reliable source. viagra offers a convenient pathway to acquire your medication securely.
Consider controlling your eye pressure with alternative solutions like https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ for efficient glaucoma treatment.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – today to secure your stock of essential medication at an unbeatable price.
Explore reliable options to order your pharmacy needs online with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – shop generic trazodone[/URL – , ensuring privacy and convenience.
Visit our website to purchase nizagara , ensuring you get your medicine without delay.
To get your hormone therapy with ease, go to https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ for the lowest prices. Whether you’re aiming to keep bone density or treat menopausal symptoms, we’ve got alternatives that suit every budget.
SUNWIN stands not at home as a next-generation tenets where data transparency and consumer exposure upon trust in online wagering. Blending casino diversion with x? s?, th? thao, and immersive trò choi, the approach is optimized seeking fast occupy oneself in and sturdy results. From interactive game slots and real-time b?n cá to progressive jackpot pools, every facet is engineered after fairness. Competitive formats like dá gà, esports, tài x?u md5, xóc dia, baccarat, and r?ng h? deliver verified outcomes, while n? hu mechanics keep rewards dynamic. Players better from stiff khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, sympathetic cskh, and a scalable d?i lý network. Full access is readily obtainable at https://sunwin24z.life/, where invention meets reliability.
X-ray your budget and discover how much you can minimize outlays on your next purchase with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ – cheap lasix pills[/URL – , a solution to acquire your essentials at more favorable rates.
Venture online to find out the cytotec , ensuring you get the most affordable price for treating your condition.
Purchasing https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ is simple. Order your supply via the internet with utmost confidence.
Browse our site to locate [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 650mg[/URL – , ensuring you obtain high-quality antibiotic solutions at unbeatable prices.
Combat pains swiftly with sildalis online , available for purchase online, securing speedy relief.
Navigating through numerous sources to purchase your medications can be difficult, but our https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ simplifies the process, offering safe and budget-friendly options for your healthcare needs.
Patients seeking relief from COPD symptoms can find effective treatment with [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ – xenical generic pills[/URL – . These medications offer a dual-action solution, boosting lung function and reducing flare-ups.
Explore the most recent advances in cardiovascular wellness by visiting nizagara 100mg . Discover methods to enhance your well-being immediately.
Are you searching for affordable solutions to your allergy symptoms? Look no further and tap https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ to discover the best rates available today.
Uncover the price of controlling nasal symptoms with [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl lowest price[/URL – , your answer for alleviation.
Knowing the significance of reliable treatment for endometriosis, explore [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – tadalafil en ligne[/URL – as a potential option.
Having trouble finding budget-friendly, reliable feminine hygiene products? Look no further; viagra 50mg offers a wide variety of solutions for your needs. Whether you’re in search of tampons, our selection is both high-quality and affordable.
Venture into the world of affordable healthcare solutions by opting to https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ from our trusted distributor. This option not only promises quality but also financial benefits for those in requirement.
Questions about iron supplements? Discover the benefits of [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – lowest clomid price[/URL – and learn why opting for a branded formulation can make a notable change in your well-being.
In search of a cost-effective solution for your hair care regime? Consider opting for zithromax 100mg , a widely acclaimed choice. Whether you’re aiming to acquire this treatment for enhancing hair growth or reducing hair fall, it’s accessible online.
Obtain your prescription without hassle at https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ , the leading site for affordable pharmaceutical products.
Visit [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – to secure your prescription without hassle.
Facing bacterial infections? Learn about how [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – can be the answer, available for buying online.
Nourish your bones and teeth with quality supplements; explore the best sources to acquire buy generic lasix australia online with no prescription for your daily health regimen.
Revitalize your vitality effortlessly with https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ , available now for those in search of a dependable solution to enhance their endurance.
Zero in on choices for male pattern hair loss by choosing to acquire [URL=https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ – discounted lady-era[/URL – now.
Boost your vigor safely and discreetly—discover how to [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ – amigren information[/URL – now. Obtain
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive cost of cialis tablets . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to reduce expenses on pharmaceuticals.
Looking for inexpensive options? Find the https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ today.
Zeroing in on treatment for severe acne? Discover how [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ – buying isotretinoin[/URL – offers effective solution.
Keep your stomach issues at bay with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – , the ultimate remedy for irritable bowel syndrome. Get your treatment online now.
Maximize your savings on medication for prostate cancer treatment by exploring the vidalista . Discover budget-friendly solutions on the web.
Looking to treat your IBS symptoms? Learn about how https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ can offer alleviation.
For those seeking to buy [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ – online lasix no prescription[/URL – without hurting their wallet, several online pharmacies offer affordable costs.
Navigating through the myriad of treatment options for Alzheimer’s can be daunting. However, procuring Donepezil, a proven medication, has never been easier. For those looking to enhance cognitive function affordably, consider exploring your options to [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – . This approach offers a seamless, cost-effective solution for managing symptoms with convenience.
Many patients search for reliable remedies for bacterial infections. Whether you’re battling skin conditions, respiratory infections, or STIs, doxycycline online offer option.
For those seeking to improve their eyelashes, think about https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/priligy/ . This solution offers an reliable way to achieve fuller, longer lashes.
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; [URL=https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/ – sildalist[/URL – is your gateway to affordable medical treatment.
Managing anxiety can be a challenge, but with the right medication, relief is possible. Those looking to purchase their treatment discreetly can discover a wide variety of options available. For a trusted source, consider pharmacy for your needs.
Combat inflammation and pain effectively with a cost-effective solution; explore our selection for https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ . Discover economical options to manage your needs without hassle.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ – cheap pill amoxil[/URL – , and Bag a course of vital antibiotics without hassle via our website.
Your search for an effective treatment for early climax ends here. Order buy dapoxetine online canada , a trusted pharmaceutical, online.
Visit https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ today and find budget-friendly options for managing your pain.
A comprehensive guide on how to purchase reliable cancer therapy, including imperative information on [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – fildena 150mg[/URL – , to tackle myeloma and ovarian cancer efficiently.
Grappling with acne? Discover your solution without needing a doctor’s note. [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – generic isotretinoin available[/URL – offers a potent treatment accessible directly to you. Say goodbye to intense breakouts today.
Boost your eyelash growth with buy generic tamoxifen , a cutting-edge treatment up for grabs via our website.
Procure your antiviral medication with a https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ , ensuring cost-effectiveness.
Looking for a convenient way to obtain your medication? Now you can purchase [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ – vidalista[/URL – virtually, ensuring you secure your therapy promptly.
Seeking effective acne treatment? Find safe [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ – canada doxycycline[/URL – options quickly via the internet.
Looking to obtain Aripiprazole? Find it effortlessly with just a click at where to buy finasteride , your go-to choice for pharmaceuticals on the web.
Keep your eye health in top condition with our advanced therapy options. Discover more and get your supply https://coastal-ims.com/nexium/ promptly.
Considering various options for augmenting your health, opting to purchase [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ – best price lasix[/URL – online can be a wise decision.
Discover affordable solutions for impotence by visiting [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – 10mg of cialis for sale in mi.[/URL – , where you can acquire your medications easily.
Find budget-friendly solutions for hormone therapy with prednisone 5mg . Purchase high-quality treatments through our website effortlessly.
With so many choices available, deciding where to acquire your medications can be challenging. For those seeking Oxybutynin, https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ provides a reliable and affordable avenue.
Discover affordable options for enhancing your well-being: [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/pharmacy-prices-for-kamagra/ – purchase kamagra online[/URL – offers a versatile solution. Secure purchase now for a healthier tomorrow.
Necessitate longer, fuller eyelashes? Discover your solution with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ – cheapest pharmacy to buy xenical[/URL – , offering a budget-friendly solution to enhance your appearance.
Facing hair loss? Consider doxycycline online without prescription overnight as your solution. Get this proven remedy today to fight baldness effectively.
Discover the convenience of managing ocular dryness from the comfort of your home; https://cassandraplummer.com/item/xenical/ offers a seamless experience. Opt now to acquire your solution virtually.
Curious about enhancing your vitality? Consider trying out [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ – propranolol[/URL – . This medication, available for acquisition, might just be the answer for those seeking to improve their wellness.
Access economically priced canada trazodone no presciption for managing thyroid issues without compromising on quality.
Zero in on enhancing your vitality with https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ , available today. Uncover affordable solutions online.
Unlock the benefits of a diverse healthcare regimen by opting to [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era[/URL – . Explore the convenience of acquiring your essential pharmacy solution effortlessly, ensuring you stay on top of your health needs.
Relieve those persistent heart and pain conditions safely by choosing to obtain meldonium online usa , the go-to option for managing your health better.
Explore efficient solutions to enhance your wellness; https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ is your go-to option. Secure a hassle-free pathway to health improvement without leaving home.
Maximize your savings on feminine hygiene products by visiting [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ – xenical to buy[/URL – for unmatched deals. Our site offers a plethora of options to acquire necessary items without hassle.
Visit our platform to buy your [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/]kamagra[/URL] easily and securely.
Just unearthed an unbeatable offer for asthma sufferers, the asthalin hfa inhaler best price is now available.
Visit https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ today and find budget-friendly solutions for controlling your pain.
Just got a prescription for immunosuppressants? Secure your treatment effortlessly through our [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/]pharmacy britain[/URL] solution.
Just realized you need tadalafil for your condition? No need to stress out! You can [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – simply and with confidence.
Enhance your confidence and well-being with natural solutions. Explore modvigil to find a variety of natural remedies at your fingertips.
With allergies peaking, obtaining relief has never been easier. Explore your options and find affordable solutions at https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ . Say goodbye to sniffling and hello to clear days in front of you.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – . Hurry, seize this amazing opportunity to cut costs on pharmaceuticals.
Having difficulty securing your prescription at local pharmacies? Order your [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – effortlessly.
Secure
Researching affordable options for your medical needs? Discover the best deals on https://mynarch.net/item/super-force-jelly/ via our trusted online marketplace. Don’t let price be a barrier to your health treatment.
Combat discomforts swiftly with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine 30mg[/URL – , available for purchase online, securing quick relief.
When seeking cost-effective solutions for impotence, consider fildena without prescription as your preferred source.
Maximize your savings on antiretroviral therapy by clicking here: https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ . Discover the most affordable deals online for crucial HIV treatment options.
Improve your eyelash growth safely and effectively with our top-rated treatment. Secure your supply through [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis for sale overnight[/URL – , offering a hassle-free shopping experience.
Quickly procure your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – generic vardenafil in canada[/URL – devoid of inconvenience of a medical consultation.
Just discovered cheap propecia online ? Explore available options to secure these medications with ease.
Quickly procure your allergy relief by choosing to order https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ .
I uncover the easiest way to obtain gentle relief from constipation: [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ – lowest price on generic vidalista[/URL – .
Looking for a cost-effective solution for your ADHD medication? [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – offers a great opportunity to reduce expenses on your prescription. This deal is suited for patients seeking budget-friendly ADHD treatment options.
Quickly secure significant savings on heartburn relief by opting to non prescription trazodone , accessible online.
Venture into a world of convenience and relief with our over-the-counter https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ . Buy your remedy on our website today.
Here’s how to purchase the medication effortlessly: [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – non-prescription vardenafil[/URL – .
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – is your gateway to budget-friendly virus management.
Interested in treating ADHD? Consider exploring buy vardenafil no rx , a reliable solution.
When seeking to purchase spironolactone, a trusted option is available at https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ . This platform offers a seamless way for individuals needing to secure their prescription.
Regain your health and combat Hepatitis C with a ground-breaking treatment. Discover your options and regain your well-being by visiting [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ – vidalista[/URL – . Acquire your road to recovery online now.
Just got a prescription for immunosuppressants? Obtain your medication effortlessly through our [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy pills[/URL – option.
Purchase your purchase asthalin hfa inhaler online easily; Acquire this vital respiratory aid on the web.
Need to get your medication at an unbeatable rate? Look no further than https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ for your well-being needs.
“Quickly discover affordable options for your wellness by clicking [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – , and obtain your way to improved health.”
Navigate our website to buy your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – with absolute ease and convenience.
Looking to improve your well-being? Find out about how to obtain your needs without hassle with cialis brand .
Looking to tackle your health concerns? Discover a vast selection of pharmaceuticals at https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nexium/ , your go-to destination for trusted healthcare solutions.
Visit [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – to secure your antibiotic with ease.
Navigating through myriad treatments for hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), one efficient solution stands out. Place your trust in proven medication; [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ – parlodel cheap[/URL – for managing your condition effectively.
Discover low-cost options to your healthcare needs with prices for prednisone . Order your drugs effortlessly online and enjoy both quality and savings.
Patients seeking treatment for hepatitis C can now acquire their medication through https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ , offering a convenient and dependable option for their needs.
Looking for a remedy for baldness? Find top products at our online store. Your search ends here: [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ – vidalista in usa[/URL – .
X-plore affordable alternatives for boosting your lashes with retin-a . Find a variety of ways to gain the look you want.
X-plore the myriad options to acquire your medications affordably; our portal allows you to https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ effortlessly. This opportunity enables clients seeking to buy their drugs at a reduced price.
Having trouble with heartburn or GERD? Get your relief safely and quickly by opting to acquire [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ – cheapest retin a dosage price[/URL – . This solution is efficacious for managing your symptoms effectively.
Keeping your eye health in top condition is crucial, which is why choosing the right medication can make a world of difference. For those dealing with elevated intraocular pressure or open-angle glaucoma, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – where to buy tadalafil online[/URL – offers a trusted solution. Ensure you speak to a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for your needs.
Having trouble finding ventolin inhaler ? Search no further and obtain your stroke prevention prescription easily today.
Considering the need for heart health, obtaining https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ via internet offers a practical solution for maintaining cholesterol levels.
Having suffered from inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), many individuals look for effective treatments. For Canadian patients, [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ – buy sildalis without prescription[/URL – offers a viable solution. This medication is known to help alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life.
UrbanWild Lane – Creative visuals and a modern interface allow users to browse effortlessly.
Purchase
Keep your health at its peak with buy kamagra without rx , offering a wide array of healthcare options. Enhance your lifestyle today.
Browse our website to find the https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ , and get your analgesic solution quickly.
In search of affordable heart medication? Look no further! Purchase your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil prix en pharmacie belgique[/URL – today.
Maximize your savings on anti-diarrheal treatments by exploring the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil online canada[/URL – . Secure your health necessities at unbeatable costs today!
Boost your vitality with buy ventolin online canadian health , available for acquisition online.
Get your amoxil easily from https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ , supplying swift delivery to fulfill your requirements.
When seeking natural remedies for digestive health, consider exploring [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – nizagara[/URL – . Available for purchase through diverse platforms, this natural product may provide beneficial outcomes for your health.
Discover how you can get [URL=https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara 25mg[/URL – easily via the internet.
Maximize your vitality and youthfulness; seamlessly amoxil through our platform. Explore a more vibrant life by deciding for this option immediately.
Visit our website to get the best https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ , offering affordable solutions for your health.
X-plore your options for managing hypertension with effective medication. Purchase [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ – cheap nizagara online[/URL – on the web to guarantee your heart health today.
Considering the need for thyroid hormone replacement therapy, it’s crucial to find a reliable source for your medication. With our platform, you can easily [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – preise fildena 25mg[/URL – required, ensuring your health remains of utmost importance.
X-ray your options and discover the best deals when you aim to lasix buy uk online . Whether you’re searching online or in-store, ensure you’re getting top-quality health solutions.
Manage your hypertension efficiently with https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ , available to purchase on the internet.
When seeking affordable solutions for erectile dysfunction, consider [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/fildena/ – pharmacy prices for fildena[/URL – as your choice source.
Knowing the expense of healthcare is vital, learn about the best [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil buy discount[/URL – for your needs.
Obtain non-prescription options for managing edema, including pharmacy prices for viagra , online. Explore a variety for safe treatment now.
Seeking relief from benign prostatic hyperplasia? Explore your options with https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ , a treatment for easing urinary symptoms.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax lowest price[/URL – might be the answer. Explore how it can assist in lessening your symptoms effectively.
To purchase your birth control effortlessly, consider acquiring [URL=https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ – retin a generic[/URL – . This method ensures confidentiality, convenience, and a wide selection of options.
I discovered that you can obtain xenical effortlessly for your upset stomach.
Zest for life can be regained with ease. Acquire your bone health solution with confidence https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ .
Research shows that [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara/ – nizagara 50mg[/URL – may improve cognitive functions in patients with Alzheimer’s.
Zap vitality deficits and enhance wellness effortlessly by securing your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – generic prednisone us pharmacy[/URL – to promote improved health and longevity now.
Considering immediate antibiotic requirements, acquiring doxycycline non generic through the internet ensures a rapid solution.
Zero hassle to secure your medication for enhanced stamina, click here: https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ .
Before considering treatment options, explore [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – levitra online pharmacy[/URL – to manage your health needs safely.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? doxycycline 100mg to combat infections caused by bacteria. This budget-friendly solution is simple to obtain and can help in managing numerous of health issues.
Responsive to your need for cost-effective treatment, discover our affordable solution https://seraamedia.org/amoxicillin-650mg/ for managing altitude sickness efficiently.
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your home medicine cabinet, [URL=https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ – buy amoxicillin uk[/URL – virtually can be a seamless process.
I understand the importance of medication accessibility, thus highlighting the convenience of opting for home delivery methods. In this context, [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – canadian cialis for sale[/URL – offers a seamless way to acquire your necessary prescriptions without the hassle of visiting a pharmacy.
Just discovered you can acquire your essential hair loss treatments online? Visit lasix for a hassle-free experience to regain your hair’s health.
Many are looking for effective solutions for ED, and https://embcselma.org/item/cialis/ provides a proven option.
Looking to boost your well-being? Find out about how to secure your needs effortlessly with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – .
Visit our site to buy your prescription, including [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ – price of levitra[/URL – , online. This digital platform ensures a hassle-free method to access your essential medicines.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? tamsulosin might be the answer. Explore how it could aid in lessening your symptoms promptly.
Zero hassle to acquire the medication: just visit https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ for numerous health solutions!
Before making a decision, consider exploring options to [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a for sale overnight[/URL – for managing one’s heart rate.
Just spotted a fantastic deal! For those seeking heart health solutions, now’s your chance to cut costs on your treatment. Discover substantial discounts on your next purchase by clicking here: clomid . Don’t miss out on this opportunity to enhance your wellness affordably.
Order your health enhancements with https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ , providing a wide range of pharmaceutical products.
Regain your vitality and enhance your physical fitness levels with the help of [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil 20mg[/URL – . Offering a solution for men seeking to balance their hormonal levels, this product is available for purchase on the web.
When looking to control your gout, purchasing generic amoxil offers a practical solution.
Many are searching for trustworthy options for ED, and https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/cialis-without-a-doctor/ offers a credible option.
Quest for cost-effective ED medications? Discover a remedy at [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ – fildena without dr prescription usa[/URL – , offering a broad array of high-quality alternatives.
Procure your propecia effortlessly. Purchase a distinctive composition online, ensuring optimal enjoyment and efficiency.
Manage your symptoms effectively with https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ . You can acquire this vital remedy via our online platform for seamless, rapid relief.
Discover the most affordable rates for your cardiovascular wellness needs with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ – prednisone best price usa[/URL – .
Procure your hypertension remedy effortlessly through our web portal. Secure your medication sans requiring a Doctor’s note. Click here [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/canada-lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – to start your journey towards better health.
Quickly buy your buy hydroxychloroquine via the web for the best solution in improving eyelash growth.
Keeping allergies at bay is now easier than ever. Whether you’re looking to tackle seasonal sniffles or seeking relief from year-round triggers, you can obtain effective antihistamines quickly. https://midsouthprc.org/propecia-1mg/ offers a reliable solution, making it straightforward to order your essentials from the comfort of home.
You can locate the [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – by looking on the web.
Get your amoxil easily from [URL=https://seraamedia.org/amoxicillin-650mg/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – , providing prompt dispensation to fulfill your healthcare needs.
The need for nausea prevention is crucial during travel. Now, you can conveniently buy your lasix , making your journeys smooth.
Visit our page to find a unique formula for your needs – https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ . This solution is available without a prescription, offering an easy way to tackle your concerns.
I understand that finding a trusted source to obtain your medication can be challenging. If you’re looking to [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – generic for flomax[/URL – , make an informed decision. Always make sure that you are dealing with a credible vendor to secure your health.
Now, find your solution for ED with simplicity by opting to buy [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – buy generic fildena with e checks[/URL – .
For those seeking relief from nausea, explore a wide range of options by deciding to stromectol . Guarantee your well-being today with a quick order.
Acquiring your https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ just became more straightforward. Now, grab your supply effortlessly.
Regarding your health concerns, acquire reliable treatment easily by opting to order [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – online.
Offering a range of reproductive health solutions, discover substantial savings on your next purchase with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/nolvadex/ – buy nolvadex w not prescription[/URL – .
**C**ompare and uncover the propecia prices by browsing our web medication outlet.
Facing health issues? Secure your https://renog.org/product/amoxil/ easily without leaving your house.
You can locate effective alleviation for gastrointestinal discomfort with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ – doxycycline generique en pharmacie[/URL – , available online.
Seek the kamagra 50mg efficiently. Find your ‘must-have’ medication at a budget-friendly price.
Struggling with menopausal symptoms? Discover relief with https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ . Our drugstore offers a secure way to purchase your medicine online.
Quickly obtain your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/trazodone/ – trazodone kaufen auf rechnung[/URL – via our online platform, ensuring a hassle-free process.
Considering requirements for affordable treatments, you can now order [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – online prescription for prednisone[/URL – , a go-to option for those seeking cost-effective bone health support.
Obtain your 10 mil prednisone effortlessly by securing it via our website.
Various individuals search for ways to economize on their medication expenses. By using a https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ , patients can slash the cost of your pharmacy bills.
The demand for reliable solutions to boost men’s health has never been more critical. Discover the efficacy of [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra capsules for sale[/URL – , a top choice for managing such concerns.
X-plore your options for managing Crohn’s disease and other inflammatory bowel disorders with torsemide for sale . Available for purchase on our site, these treatments offer a route towards relief of symptoms.
I discovered that you can obtain https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ effortlessly for your nausea.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ – hydroxychloroquine.com lowest price[/URL – , a top choice for tackling baldness. Purchase these tablets today and begin your road to regrowth!
Research the most recent strategies for managing HIV with internet resources. Find detailed information [URL=https://jawany.com/ventolin/ – ventolin from china[/URL – and remain educated.
Just spotted a fantastic deal! For those seeking heart health solutions, now’s your chance to benefit on your treatment. Discover substantial discounts on your next purchase by clicking here: 10 levitra buy online . Don’t miss out on this opportunity to boost your wellness affordably.
Living in a time where convenience is key, acquiring your medications promptly is vital. For those seeking https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ , options are now available through digital pharmacies, offering a hassle-free solution to meet your needs.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can find options online including [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ – sildenafil[/URL – , a dependable treatment.
You can locate efficient relief for intestinal discomfort with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis buy[/URL – , available online.
Browse
Searching for effective solutions to reduce irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ can assist in easing your discomfort immediately.
Get your prescription for flu and Parkinson management easily through [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – .
Unlock significant savings on eye care medication by choosing to cheap amoxicillin . Explore alternatives to acquire this essential treatment with convenience and confidence virtually.
Optimizing your health is now more accessible than ever. With just a few clicks, you can obtain your necessary medications from https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/drugs/sildalis/ . No longer do you need to leave your home, saving you both time and effort.
Discover how to significantly improve your sleep quality with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – , your ultimate solution for an undisturbed slumber.
Everwild Outlet – Clean product presentation and smooth browsing make it easy to explore.
Zero hassle to safely obtain your medications online. Click here: [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-75mg/ – viagra[/URL – for your well-being needs.
Considering the need for dependable solutions for treating erectile dysfunction, it’s essential to locate a trusted source. canadian pharmacy viagra offers an accessible route to procure your prescription with confidence.
Seeking relief from inflammation or arthritis? Discover how https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/ can help. Learn about your options now.
Research indicates that hormone replacement therapy can be a crucial component for managing the symptoms of menopause. Considering different options? Explore how [URL=https://renog.org/product/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – might complement your health regimen.
Optimize your health and savings by exploring the kamagra 100mg . Discover affordable options to maintain your well-being.
Nourish your body’s development potential naturally. Visit https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ for an array of options to improve your vitality.
Venture into health management by exploring options to purchase cost-effective medication for arthritis relief. Discover more and make an informed choice today by visiting [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ – no perscription 50mg kamagra[/URL – .
Just discovered your solution to impotence? Explore our comprehensive [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – lowest price on generic ed sample pack 2[/URL – , offering a variety of options to address your concerns.
Maximize your wakefulness with our affordable solutions; get your batch of wakefulness-promoting agents through our website composicion prednisone .
Considering your health and budget? Explore cost-effective solutions and https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ . Uncover a deal today for lasting satisfaction and wellness.
rankboostx.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Need to discover the most recent [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – cialis for sale in usa stores[/URL – ? Visit our site for affordable options and detailed information.
Just discovered: uncover the lasix uk right away. Obtain your supply at incomparable rates and keep your wellness with ease.
Quickly secure significant savings on heartburn relief by opting to https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ , available via the internet.
Visit here to secure your [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine cheap[/URL – safely and easily for all your needs.
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of
your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs?
I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on a lot of the subjects you write with regards to
here. Again, awesome web log!
Acquiring [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – cipro[/URL – is now feasible. Explore options to purchase this vital therapy easily online.
Battling sleep disorders? Our online store offers a quick solution. Buy generic finasteride from india now for a peaceful night’s rest.
Initiate your journey towards relief from upset stomach by opting to purchase https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ .
For men seeking reliable hair loss solutions, [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ – generic finasteride from india[/URL – offers essential insights.
Just discover solace for allergic reactions by choosing to [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ – canada lady era[/URL – .
Pain relief after physical activity doesn’t have to be hard. Find nexium , your go-to choice for easing soreness.
Keeping your health top priority, securing your medications from a reliable source is crucial. For those looking for HIV treatment options, https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ offers a cost-effective and reliable solution. Ensure you seek advice from a healthcare provider to ascertain if it’s right for you.
A comprehensive guide on healthcare education in the United States is readily available at [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ – purchasing pharmacy on the internet[/URL – .
X-plore new ways to manage Alzheimer’s by choosing to order your [URL=https://airjamaicacharter.com/drug/clomid/ – clomid 50 preco[/URL – today.
When seeking cost-effective solutions for ED, consider fildena as your go-to source.
Opt for https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ to manage your hepatic conditions. Ensure you’re getting your therapy reliably.
Facing menopausal symptoms? Explore relief with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ – trazodone 100mg[/URL – , your preferred source for estrogen supplements.
WildRose Goods – Warm and cozy atmosphere, found a few delightful surprises.
When seeking reliable antifungal treatment, consider exploring [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ – tadalafil[/URL – for your medical needs.
Discover reliable and effortless ways to obtain your prescriptions with just a click. viagra offers a simple solution for your needs.
Understanding the importance of antiviral treatment in managing chronic hepatitis C can never be overstated. Opting to obtain https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ via a digital pharmacy not only offers convenience but also ensures you’re receiving your medication without delay.
Zero hassle to securely purchase your prescriptions online. Click here: [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – viagra 100mg[/URL – for your health needs.
Всё о камерах видеонаблюдения — полное руководство!
Приветствуем вас, уважаемые форумчане! Сегодня мы подробно поговорим обо всём, что касается видеокамер наблюдения. Мы поможем вам разобраться в огромном разнообразии предложений рынка и сделать правильный выбор оборудования для защиты вашего имущества и безопасности вашей семьи.
Почему важно установить систему видеонаблюдения?
Камеры видеонаблюдения становятся всё популярнее среди владельцев домов, офисов и коммерческих помещений. Они обеспечивают защиту имущества, предотвращают преступления и помогают контролировать происходящее даже дистанционно. Давайте рассмотрим самые важные аспекты выбора камеры и её установки.
Какие бывают виды камер видеонаблюдения?
Вы можете выбрать камеру исходя из ваших потребностей и условий эксплуатации:
– **Уличные** — предназначены для наружной установки, защищены от влаги и пыли.
– **Домашние** — компактные модели для внутренней установки.
– **IP-камеры** — позволяют подключаться к сети Интернет и просматривать записи онлайн.
– **Wi-Fi камеры** — удобны благодаря беспроводному соединению.
– **Камеры с SIM-картой** — работают независимо от интернета, передавая сигнал через мобильную сеть.
– **Миниатюрные камеры** — незаметны и подходят для скрытого наблюдения.
– **Поворотные камеры** — способны охватывать большие площади, поворачиваясь на 360 градусов.
– **Ночные камеры** — оснащены инфракрасной подсветкой для съёмки в темноте.
—
Как правильно выбрать камеру видеонаблюдения?
Перед покупкой обратите внимание на следующие характеристики:
– Разрешение камеры — HD/FullHD/UHD обеспечит чёткое изображение.
– Угол обзора — широкий угол позволяет видеть больше пространства.
– Наличие микрофона и динамика — возможность двусторонней связи.
– Датчик движения — экономия памяти устройства путём включения записи только при обнаружении активности.
– Питание — проверьте совместимость с вашим источником питания.
– Возможность удалённого доступа — управление камерой через смартфон или компьютер.
—
Установка и подключение камеры видеонаблюдения
Правильная установка и настройка камеры позволят вам эффективно пользоваться всеми возможностями системы видеонаблюдения. Рассмотрим ключевые моменты:
– Выберите оптимальное место для размещения камеры, обеспечивающее максимальный обзор охраняемой территории.
– Убедитесь, что камера защищена от погодных воздействий, если устанавливается снаружи здания.
– Настройте Wi-Fi соединение или кабельную линию подключения.
– Установите приложение для просмотра записей и управления камерой через мобильное устройство.
—
Где лучше всего приобрести камеру видеонаблюдения?
При покупке обращайте внимание на проверенные магазины и бренды. Рекомендуем выбирать оборудование известных производителей, предлагающих гарантии качества и поддержку клиентов. Обратите внимание на предложения крупных торговых площадок, таких как Ozon, Wildberries и специализированные магазины электроники.
—
Советы по установке камер видеонаблюдения:
– Изучите правила установки камер видеонаблюдения перед началом монтажа.
– Получите согласие жильцов многоквартирных домов на установку камер в подъездах и местах общего пользования.
– Позаботьтесь о защите личной жизни соседей, устанавливая камеры таким образом, чтобы избежать нарушения частной собственности.
—
Поделитесь своим опытом!
Расскажите нам о вашем опыте покупки и установки камер видеонаблюдения. Может быть, у вас есть советы или рекомендации для новичков? А может, вы столкнулись с проблемами при выборе или настройке оборудования? Оставляйте комментарии ниже, давайте делиться полезными советами вместе!
Автор:
Система видеонаблюдения
*Данная статья носит информационный характер и предназначена исключительно для ознакомительных целей.*
Nourish your vitality effortlessly with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – lasix coupon[/URL – , a zenith of wellness. Acquire your potent elixir online.
Access effective treatment quickly and safely by choosing to acquire your medications through our web platform. For individuals requiring prompt treatment, propecia offers a reliable solution.
Uncover the ultimate way to enhance your wellbeing; explore our premier https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ . This solution is optimal for those seeking to improve their lifestyle effectively.
clickalley.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickattic.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickanchor.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
propelclick.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Honestly, I’ve checked out many gambling platforms lately, and it still surprises me how often users sign up without doing research. In case you want a detailed look of promos, withdrawals, and available games, this guide cleared things up for me: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s pretty straightforward and points out what you should notice before funding your account. It’s worth your time if you want to avoid common mistakes.
Explore cost-effective fertility solutions; [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – . Discover the affordable price at Walmart, ensuring you receives the chance for parenthood.
Keeping your health in top condition is essential, and so is finding the best deals on your supplies. Whether you’re looking to purchase your health supplements, don’t miss out on the competitive rates at super active pack 20 on internet .
Breathe easier with our rapid-action treatment. Order your https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ immediately for reliable asthma management.
Browse our website to find the [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ – tadapox 80mg generic[/URL – available. With options to purchase affordable variants of your essential medication, health management becomes both effective and cost-efficient.
Your vitality is important. Discover easy access to manage your medical condition with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – cheapest vardenafil[/URL – . Ensure your vitality is in tip-top shape with just a few clicks.
Ensure you secure your netherlands hydroxychloroquine rezeptfrei without risk for malaria prevention.
Secure your https://yourdirectpt.com/vidalista-price-at-walmart/ with ease. Procure your treatment online efficiently.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine online no script[/URL – .
Looking for the lowest-priced options for your medication? Discover great deals on [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ – propecia information[/URL – now.
Visit our platform to discover the tadalafil without prescription , offering you a cost-effective alternative for managing your cholesterol levels.
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before attempting to purchase https://embcselma.org/item/flagyl/ cannot be overstated.
When considering options for managing prostate cancer, speaking to a healthcare professional is essential. However, for individuals who are currently informed and looking to acquire their medications conveniently, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – buy cytotec w not prescription[/URL – provides a viable option.
BrightGiftingShop – Enjoyable browsing, nice product range, and easy access.
как работает xrumer 5.0 platinum xrumer обучение: xrumer обучение – (см. определение ранее)
When in need of urgent options, discover [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – for your necessities.
Achieve your wellness zenith with prices for pharmacy , available for order online to boost your life quality.
Join us as we explore the benefits of https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ , a leading solution in managing chronic health conditions. With its proven effectiveness, it’s no wonder why many decide to acquire these crucial tablets for their health regime.
Secure
Your search for a trusted source to acquire unbranded [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – ends here. Explore our range for high-quality alternatives at affordable rates.
Secure considerable reductions on your prescription with pharmacy . These coupons are crucial for reducing treatment costs.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: https://chitwantigercamp.com/doxycycline/ . Whether you’re looking to obtain this medication on the internet, you’ll find that its efficacy in treating a wide range of infections makes it a prime choice.
Zipping through your options for managing erectile dysfunction? Discover a convenient solution by choosing to acquire [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – where to buy viagra online[/URL – .
Venture into the world of affordable healthcare solutions and discover how you can acquire [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – to control your health needs virtually.
X-raying your finances? Acquire an quick enhancement with buy lasix online and get prescription , ensuring security in tough times.
You can order your necessary medicine https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ with convenience.
Relieve your nasal symptoms with [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nizagara/ – lowest price nizagara[/URL – , now available for buying over the counter.
With the increase in internet-based platforms, it’s never been simpler to access entertainment and leisure activities. Whether it’s enjoying films or indulging in bentyl without a doctors prescription , the world of amusement is just a click away.
Various healthcare professionals suggest seeking advice on https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ for gastrointestinal discomfort to confirm safe and effective relief.
Looking to cut down on your healthcare costs? Discover the [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ – buy amoxicillin[/URL – to save money on your prescription.
Various options exist for enhancing eyelash growth, but if you’re seeking a reliable solution, consider [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis prices[/URL – . This product, also known for its efficacy in improving eyelash length, can be conveniently ordered online.
Explore the convenience of enhancing your health with just a few clicks! Get your buy prednisone without prescription today and experience the benefits of fast and private delivery.
X-ray the costs of improving your health with antiviral medications by exploring the https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ . Uncover how an antiparkinson and antiviral agent can assist you without breaking the bank.
Research indicates that finding the [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – cheapest place to buy nizagara[/URL – may be essential for consumers seeking cost-effective solutions for their health needs.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Obtain [URL=https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxil moneypak[/URL – safely and swiftly.
Your health can be safely managed with nizagara to buy , available for acquisition directly.
Given the myriad ways to manage and enhance your wellness journey, https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ stands out as a premier choice. Whether you’re seeking to purchase health supplements via the internet, it’s essential to select products that align with your health objectives.
Gain access to [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil[/URL – hassle-free. Secure your pharmaceuticals instantly for managing your medical conditions.
Explore options to buy [URL=https://jawany.com/amoxil/ – venda de amoxil online[/URL – online, ensuring you secure the most affordable deal for your cardiovascular wellbeing.
X-plore affordable options for thyroid management with our comprehensive guide on propranolol . Learn how to safely acquire your prescription through our trusted platform, ensuring you get the best care without overspending.
A comprehensive guide to treating Hepatitis C, detailing how https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone-without-a-doctors-prescription/ offers a powerful solution that fights against the virus effectively.
Many individuals search for effective remedies for their stress. With numerous options available, it’s crucial to pick wisely. For those considering an effective treatment, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – present a hopeful option.
Acquire [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ – us overnight pharmacy[/URL – for less online.
Boost your well-being and elevate your vitality effortlessly. Discover how at kamagra without prescription in uk .
Looking for a way out to your illnesses? Now, you can acquire https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ with ease. This solution provides convenience to secure your prescription with confidence.
Explore the convenience of enhancing your health with just a few clicks! Get your [URL=https://nesttd-online.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara canadian pharmacy[/URL – now and enjoy the benefits of fast and discreet delivery.
Visit sildalis to purchase antiviral medication, ensuring safety against viruses with ease and convenience.
Zeroing in on your health concerns, it’s vital to discover effective treatments. For those seeking an alternative, https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ might offer a hopeful solution.
For those seeking relief from persistent nasal symptoms, [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – offers an efficient solution.
Curious about securing a affordable treatment for your ailment? Uncover the lowest-priced options for [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – 60 mg prednisone[/URL – on the web.
Discover your solution for enhanced vitality; explore reliable options and buy viagra 75mg today.
Looking to treat your uric acid levels? Consider purchasing effective medication. For your convenience, https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ via our website to ease symptoms efficiently.
Procure the most cost-effective solutions for hair care; find your perfect match at [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/cytotec/ – cytotec 100mcg[/URL – .
Discover budget-friendly choices for handling your thyroid health: canada dapoxetine . Order with confidence and guarantee you’re getting quality medication.
Discover affordable options for impotence by visiting https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ , where you can buy your drugs effortlessly.
Just realized you need Cialis for your health? No need to fret! You can [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/cialis/ – cialis cost[/URL – simply and securely.
Aiming to boost prostate health? Explore [URL=https://abbynkas.com/item/herbal-extra-power/ – herbal extra power online uk[/URL – – your go-to solution for holistic well-being.
Purchasing affordable clomid has never been easier, with numerous alternatives available online. Secure your fertility journey today by selecting the best deal.
X-plore your options for managing hypertension with reliable medication. Purchase https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ from a reputable source to guarantee your heart health today.
Having trouble finding affordable treatment options? Look no further for [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – cheap amoxicillin pills[/URL – . Secure your much-needed prescription without overspending.
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and secure your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – today for enhanced health and vitality!
If you’re searching for an effective solution to tackle bacterial infections, think about buy amoxicillin . This medication has been widely acknowledged for its potency against a wide array of bacteria.
Keeping your health top-notch is easier today with options like https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ , an reliable way to control inflammation.
Regain control over your health by visiting [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/propranolol/ – cheap propranolol[/URL – , your ultimate source for reliable pharmaceuticals.
When looking to address OCD symptoms, consider exploring online lisinopril as a potential solution.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Acquire https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ safely and quickly.
Explore options to purchase [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine price at walmart[/URL – , offering a convenient way to receive your medication without leaving home.
Procure your clonidine without dr prescription usa drugs straightaway to control blood pressure effectually.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with https://frankfortamerican.com/torsemide/ , a treatment for alleviating prostate enlargement symptoms.
Visit [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – to acquire your heart health prescription at a low cost.
Optimizing your treatment plan? Consider adding [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/clomid/ – buy clomid uk[/URL – to your regimen! Investigate budget-friendly solutions on the internet for enhancing your health journey.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; purchase your amoxicillin 1000mg via the internet for effective bacterial infection treatment.
For enhancing your eyelashes, consider trying https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ , a cost-effective option. This product intends to improve eyelash growth, making them more voluminous.
I discovered the [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ – levitra parapharmacie[/URL – after looking the internet.
Various individuals are navigating the process to secure essential medications with convenience. If you’re looking to secure Losartan without a struggle, strattera 25mg is your go-to resource.
Just in: Discerning shoppers can now locate the https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ on websites, ensuring you get top-notch value for your health-related necessities.
Aiming to reduce your prostate enlargement symptoms? Discover how [URL=https://damcf.org/prednisone/ – prednisone online[/URL – can aid.
Questioning where to obtain [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – tadalafil purchase[/URL – ? Uncover safe alternatives for purchasing online.
Considering the urgent need for heart rate control in hypertension and angina, acquiring price of finasteride in mexico has never been more essential. This choice not only offers ease but also ensures you get quality medication from the ease of your home.
Visit https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ to secure your medication without hassle.
Explore safe options to obtain [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin without a prescription[/URL – , guaranteeing your health is never compromised.
SUNWIN is recognized as a modern online betting ecosystem where technology and open looseness intersect. The rostrum delivers a full-bodied spectrum of exhibition including casino, x? s?, th? thao, and interactive trò choi designed repayment for legitimate players. From immersive game slots, skill-based b?n cá, high-value jackpot, to household dá gà and competitive esports, the experience feels balanced and transparent. Ductile khuy?n mãi, responsive cskh, patronize n? hu, and exclusive uu dãi shore up long-term work, while the d?i lý way, provably lawful tài x?u md5, time-honoured xóc dia, contemporary baccarat, and fast-paced r?ng h? complete a data-driven betting environment. Decorous access: https://creditservice.ru.com/.
I understand the need for convenient solutions when looking to purchase medication. For those considering treating their health concerns efficiently, considering [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tamsulosin/ – flomax overnight[/URL – provides a vital resource.
Researching affordable treatments for depression? Look no further. Discover the most cost-effective options and secure your supply of amitriptyline today. Click whare can i get amitriptyline no prescription for unbeatable deals and comprehensive support on your journey towards well-being.
Looking for an affordable solution to enhance your eyelash growth? Search no more! https://masseysjewelers.com/kamagra-100mg/ offers a variety of options to buy your eyelash growth solution virtually.
Join our community to obtain your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – generic for kamagra[/URL – and explore a broad selection for reproductive health products.
Zap your health troubles away! Acquire the treatment with ease, kamagra 100mg online. Secure and reliable.
Navigating the complex world of medication, finding a safe source for https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ becomes paramount for those seeking alternative solutions.
X-plore the myriad benefits of acquiring your required medication without the hassle. Obtain [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ – finasteride paris[/URL – with ease from trusted sources.
Secure your supply of essential minerals today by deciding to purchase [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride/ – finasteride from canada[/URL – , ideal for upholding strong bones and teeth.
Zero in on pain relief: Whether you’re looking for an effective solution for aches and pains, purchasing generic cialis at walmart via the internet offers convenience and effectiveness.
Discover how https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ can alleviate symptoms of prostate enlargement by visiting our site.
Having trouble with confidence? Explore our options to boost your well-being. [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – buy levitra cheap generic[/URL – today and commence your journey to enhanced self-assurance with our reliable solutions.
Purchasers looking for effective yet budget-friendly menstrual cycle support can find relief by choosing to purchase [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine cost[/URL – .
Optimize your health with a variety of solutions by exploring ed sample pack 2 no presc , offering an exclusive blend of options for your wellbeing.
Having cardiac rhythm issues? Consider https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ for an effective.
For those seeking relief from gout or arthritis-related discomfort, consider exploring [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ – online generic vidalista[/URL – . Acquire this medicine through a virtual pharmacy to potentially ease your symptoms efficiently.
Boost your confidence and improve your performance with genuine prednisone 40mg . Buy now for a discreet and efficient solution to your needs.
Relieve your discomfort now by choosing to https://youngdental.net/vidalista/ , or pick an different option to address your condition online.
Manage your health efficiently by choosing to [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/product/vpxl/ – no prescription vpxl[/URL – , a versatile solution for various conditions. You can Preorder a medication easily on site, ensuring convenience and discretion.
The need to acquire pharmaceuticals without leaving home has never been more critical. Now, you can effortlessly receive your [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra price walmart[/URL – with just a few clicks.
Having trouble finding where to get your medication? Look no further, click canadian retin a to purchase your medicine with ease from home.
Access https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ instantly! Secure the purchase virtually for rapid dispatch and excellent service.
Your search for a safe, effective method to improve your intimate life ends here. Buy your [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ – no prescription viagra[/URL – today and feel the transformation firsthand.
When searching for cost-effective, high-quality medication solutions, consider exploring [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – cheap lady era online[/URL – for unparalleled value. Whether you’re in the market for cancer treatment options, this option may offer the advantages you need.
Get the relief you need with us pharmacy tadalafil sale , available now. Order easily via our website.
X-ray your options and discover the best deals on hypertension treatment when you purchase https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ on the internet.
I recently discovered the remarkable efficiency of [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – in enhancing fertility treatments. For those seeking alternatives, consider acquiring this effective treatment to improve your reproductive health.
Just seeking cost-effective options for enhancing your health? Consider 10mg prednisone retail price for a trusted and effective solution.
Given the various options for hormone therapy, those looking to alleviate menopausal symptoms might consider checking https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ . With a range of purchase methods, selecting the right option on the web can offer relief efficiently.
Visit [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ – amoxil 650mg[/URL – to acquire your herbal supplement.
Many are looking for trustworthy solutions for ED, and cialis for sale overnight offers a tested option.
As an expert in the medical field, I need to emphasize the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before initiating any treatment. Nevertheless, for those looking into non-prescription options for managing specific conditions, https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ could be considered. Always verify that you obtain drugs from reliable sources to guard against imitation products.
Just discovered a innovative formula for increasing your energy: [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – low price slimex[/URL – . Explore about this natural alternative.
Любопытно, как разные точки зрения сходятся на идее комфорта. В моём понимании комфорт — это когда возвращаешься с улицы в дом, а там тихо работает газовый котёл.
Zeroing in on cost-effective healthcare solutions, many are inquiring about how to economically access medications. Discover the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – lowest price for cytotec[/URL – for insights on how to cut costs on your health needs.
Discover budget-friendly solutions for gastric ulcers; buy tadalafil on line offers effective relief.
View the latest prices for treating your BPH symptoms with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ , and explore multiple options to better your quality of life.
Find the best deal for your heart medication at [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ – generic malegra uk[/URL – , ensuring supreme cardiovascular health.
Considering various options to manage your BPH symptoms? Explore how you can obtain [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – via the web, offering a simple solution to ease discomfort.
Regarding your well-being, it’s crucial to locate an effective option. For managing specific health concerns, cheap cytotec 200 mcg price stands out as a suggested choice by healthcare professionals.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our extensive selection of affordable treatment options. Find https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ to enhance your vitality efficiently and safely.
Boost your health with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to improve your immunity or support your body’s natural defenses, this product is available on the web for purchase.
Get the optimal deals on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ – finasteride 1mg[/URL – for enhancing your health now.
Considering diverse treatment options, it’s crucial to find cost-effective solutions. For those looking for hormone therapy alternatives, buy cheapest 100 generic nizagara offers a viable choice.
Having unexpected expenses? Secure a https://hiblogging.com/amoxicillin/ right away to manage your financial necessities.
Browse our website to discover the [URL=https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ – prednisone coupon[/URL – , ensuring you obtain maximum value on your medical needs.
Alleviate allergy symptoms with affordable options; purchase [URL=https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ – canada xenical[/URL – on the web.
Maximize your savings on arthritis medication by seeking the pharmacy uk . Acquire your health with budget-friendly treatment alternatives and secure your wellbeing without overloading your finances.
Keeping your cholesterol levels in check is crucial, and https://frankfortamerican.com/lisinopril/ might be the answer. Look into affordable options to control your heart health today.
Acquire a transformative solution online. Enhance
Questioning where to find the top deals for your heart medication? [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/levitra/ – lowest price for levitra[/URL – offers a comprehensive selection, making it possible you to purchase your medications without hassle.
Various medical professionals recommend seeking advice on bentyl for sale overnight for digestive issues to guarantee safe and effective relief.
Just discovered the best deal for pain relief with https://youngdental.net/tamoxifen/ , available now.
Browse our website to find the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone 40 rezeptfrei kaufen[/URL – available. With options to purchase affordable versions of needed medication, health management becomes both effective and cost-efficient.
**C**ompare and find the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ – discount kamagra 100mg[/URL – by browsing our web medication outlet.
Looking to enhance your stamina? Discover how pharmacy amoxil on line can help. Available now, these pills are designed to support your well-being journey.
For managing mild pain and swelling, consider https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ as a trusted choice.
Visit our website to acquire your [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ – order asthalin hfa inhaler[/URL – easily and without hassle.
Get your health solutions conveniently with [URL=https://renog.org/trazodone/ – trazodone 100mg[/URL – . Acquire your necessary treatment without hassle from the comfort of your home.
Obtain the best savings on Celebrex here with our celebrex guide.
With an array of natural solutions for boosting vitality, click here to https://abbynkas.com/item/herbal-extra-power/ , offering a safe and beneficial way to support your health.
Looking for reliable pain relief? Discover [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – buy cheapest 100 mcg generic ventolin[/URL – , your go-to solution for managing aches with ease.
Navigate our online pharmacy to acquire your nizagara shops with utter ease and convenience.
Acquire your pathway to enhanced wellness without delay.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Find out how [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – can ease symptoms and restore your comfort.
Gain access to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/dapoxetine/ – discounted dapoxetine[/URL – hassle-free. Procure your treatment without delay for controlling your medical conditions.
Quickly get your medications with convenience by choosing to purchase viagra 25mg .
When seeking efficient ulcerative colitis treatments, you can procure https://seraamedia.org/item/cytotec/ for immediate relief.
Discover an straightforward method to acquire your [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – dosage clomid shopping[/URL – via the internet.
Keeping your antiviral medications up-to-date is essential. For those needing medical endorsement refills, buy finasteride australia could be your go-to resource.
Visit https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ to acquire your antibiotics on the web at incredible prices.
Discover innovative solutions to boost your growth potential on the web with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil[/URL – .
Offering an affordable solution for those in need, our [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – is available to purchase through our web store, ensuring all individuals has access to top-notch medical care.
Your health matters, so think about getting lasix 100mg delivery to aid your wellbeing.
Procure your https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ effortlessly through our platform, ensuring a seamless purchase. This option is ideal for those seeking reliability without the high cost.
Harness the power of the internet to obtain your medications hassle-free. Now, you can buy [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – generic for clonidine[/URL – , a reliable solution for managing your blood pressure, online with sheer convenience.
Questioning where to obtain finasteride? Discover safe, trustworthy options for [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – finasteride[/URL – .
Access the lowest price for levitra now.
Browse the site to discover https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ , ensuring you get top-quality antibiotic options at unbeatable prices.
Discover cutting-edge solutions to improve your well-being with [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – buy cialis black uk[/URL – , the go-to selection for those seeking trusted and powerful support in handling erectile dysfunction.
Venture into enhancing your health effortlessly; discover [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – generic vidalista online drugstores[/URL – for your wellness needs. Acquire it online and enjoy a healthier lifestyle today.
Purchasing cialis is straightforward. Order your treatment on the web with absolute confidence.
Battling gout or high uric acid levels? Consider https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/ , a proven solution. Procure it now for effective treatment.
View the latest costs for treating your BPH symptoms with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/flomax/ – tadalafil 0.2mg best price usa[/URL – , and explore a range of options to better your quality of life.
Discover effective relief for cold sores with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone 20 store in canada[/URL – , your go-to antiviral cream. Obtain the solution through our digital platform and commence your journey to recovery today.
Where to locate prescription priligy wa is a common query among buyers seeking cost-effective solutions for enhancing their well-being.
Acquiring https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ has never been more convenient. Secure your dose with ease and enjoy swift, dependable delivery straight to you.
Discover effective solutions for heavy menstrual bleeding by exploring our selection of medications. Order the necessary treatment [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – effortlessly with just a few clicks.
Procure your medication with convenience and confidentiality; [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – cialis black price[/URL – directly through our secure platform.
You can obtain generic tadalista for improving your well-being directly online.
Just discovered the lowest price for generic Cialis in Australia? Find out more at https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ .
With an array of options for controlling hair loss, [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-without-a-doctor/ – buy prednisone on line from canada[/URL – stands out as a reliable solution.
Discover the current [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – hydroxychloroquine without pres[/URL – and consider options for securing this treatment via the internet.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Discover how tadalafil 2.5mg can help manage your symptoms. Explore solutions for relief and get informed today.
Just looking for intensified intimacy? Explore your options with https://purefmonline.com/propranolol-20mg/ , the ultimate option for boosting endurance.
The need to purchase pharmaceuticals without leaving home has never been more critical. Now, you can conveniently receive your [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/propranolol/ – propranolol generic pills[/URL – with just a few clicks.
Explore affordable solutions for your hair loss concerns; [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-without-a-doctor/ – prednisone price at walmart[/URL – are available on the web.
Revitalize your eyelashes with safe and economical solutions. Discover myriad benefits by exploring cytotec . Achieve captivating results for a fraction of the cost.
Achieve optimal health with https://sadlerland.com/product/nizagara/ , offering a comprehensive solution to your daily nutritional needs.
Given the complexity of managing common health issues, finding a reliable source for prescriptions is crucial. That’s why many prefer to purchase their pharmaceuticals from [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia de 5 mg precio[/URL – , where diversity in healthcare solutions is always accessible.
Research the most effective hepatitis C treatments and buy from reputable sources. Ensure safety by choosing to lasix without prescription from certified pharmacies.
With various online platforms available, it’s never been easier to https://tv-in-pc.com/celebrex/ . Whether you’re seeking to buy medicine with convenience, our platform offers a seamless and secure shopping experience.
Purchase your pharmacy needs with confidence at the [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – . Find top-tier efficacy and affordability online.
Find your method to buy [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ – nizagara cost[/URL – safely.
Quietly seek budget-friendly healthcare alternatives? Uncover your solution with prednisone canada , and experience significant savings on medications.
Reduce your cholesterol effectively with https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ , offering a convenient way to purchase your medication.
Looking for cost-effective treatment options for your condition? Discover the most affordable prices for your medication needs. [URL=https://jawany.com/cipro/ – where can i get cipro cheaper[/URL – offers unparalleled deals. Locate economical options here.
Very few are aware that managing epilepsy is now more convenient thanks to [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – , allowing patients to purchase their treatment virtually.
Questioning where to find joint relief? Consider kamagra without dr prescription usa for reliable assistance in addressing your joint discomfort.
Access genuine https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ easily. Purchase this essential medicine through the web seamlessly.
You can purchase your [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – zoloft[/URL – without hassle online, ensuring you get quality medication for managing your condition.
X-ray your health and wellness options by seeking out [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – cialis[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to obtain health aids virtually, this selection provides a reliable path to maintaining your well-being.
Access budget-friendly solutions for your healthcare needs: vidalista . Obtain the supply now, ensuring prime health without financial strain.
Finding an economical https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ can be challenging. Seek online for choices that offer value.
To tackle tuberculosis effectively, it’s essential to possess the right medication. Now, you can purchase your treatment easily through our trusted platform. For quick access to your medication, [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/propecia/ – propecia online canada[/URL – . This method is straightforward, making certain you always have a dose.
Unlock savings on your desmopressin needs with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – prices for nizagara[/URL – , your go-to destination. Purchase this essential medication on the web with ease.
Tired of dealing with chronic eye strain? Discover the leading solutions at viagra 100mg , your go-to platform for reliable eye care.
Get relief from one’s rheumatoid arthritis signs today. Check out https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-in-usa/ for incredible savings on your treatment.
Quickly secure your prescriptions with convenience by choosing to order [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – .
Zero worries about where to locate your ED solutions; browse [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ – buy viagra in algodones[/URL – for a safe and private way to improve sexual health.
When managing hypertension, it’s essential to explore various treatment options. Find how you can oversee your condition effectively with furosemide .
Rediscover vitality with our affordable https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ , the premier solution to boost your health.
Obtain your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – effortlessly. Order this essential skin care solution without hassle.
For individuals seeking to purchase hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous websites offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to make sure safety and authenticity. [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine on line[/URL – offers a comprehensive guide on the way to safely buy this medication, alongside vital data on its utilization.
Visit flomax 0.2mg to buy budget-friendly pharmacy products online.
Various individuals searching for solutions to manage premature ejaculation turn to https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ as a dependable option.
Experience rapid relief from nocturnal enuresis with our reliable [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – purchase lasix online[/URL – . Order today for a improved night’s sleep.
X-plore affordable corticosteroid treatments and save on healthcare expenses by opting to [URL=https://abbynkas.com/pill/lady-era/ – lady era cheap[/URL – for managing inflammations.
Procure your nizagara 100 france with ease. Get the necessary medication with just a few clicks swiftly and safely.
Need to boost your focus without a hassle? Discover how easy it is to receive the solution https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ .
Get your budget-friendly options on healthcare products with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – order priligy online[/URL – , offering a diverse selection of items.
X-plore the benefits of managing your nasal symptoms with our high-quality solution. Whether you’re looking to reduce your allergic rhinitis, our [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ – levitra overnight[/URL – can offer you respite.
Just discover how lasix can improve your health, offering a powerful remedy for improved endurance.
Navigating the pharmaceutical marketplace for solutions can be daunting, but finding the https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ doesn’t have to be.
Seeking heart pain relief? Discover your options with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax-coupons/ – zithromax as generic[/URL – , for sale on the web.
Research shows that regulating cholesterol is essential for cardiovascular wellness. Visit dapoxetine to find out about cutting-edge solutions.
Looking for an all-natural way to enhance your vitality? Discover https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ and explore how our product can boost your well-being.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – retin-a order by phone[/URL – to purchase your medication without hassle.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to buy [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ – lowest price hydroxychloroquine[/URL – online is crucial for individuals seeking treatment.
Maximize your health without spending a fortune; purchase your achat lasix en france and maintain supreme skeletal health.
Discover how https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ can alleviate symptoms of BPH by exploring our website.
Nourish your bones and teeth with quality supplements; discover the best sources to purchase [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – for your daily health regimen.
Get your Amoxicillin easily from online amoxicillin no prescription , offering quick delivery to meet your needs.
Pain relief for arthritis can be conveniently secured through various online platforms. Whether seeking to order this pain reliever, patients now have the luxury to secure their prescriptions https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ with ease, ensuring their comfort and well-being are promptly addressed.
Keep your ulcerative colitis in check with easy, hassle-free ordering process. [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – price of tadalafil[/URL – is your go-to for handling symptoms effectively.
Obtain comprehensive insights on lowest price generic prednisone to secure you get the best offer on the market.
Zest for a better lifestyle begins with managing your cholesterol levels. Explore various options and compare https://tnterra.org/drugs/amoxicillin/ to find the best deal for your medical needs.
Optimize your wellness journey with a convenient, hassle-free option: [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – . Discover the simplicity of having the essential medication delivered right to your door without delay.
“Quickly secure your pharmaceuticals effortlessly with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – generic lasix canada[/URL – , the most dependable way to order your medical needs digitally.”
X-ray your budget and discover how much you can minimize outlays on your next purchase with lasix 40mg , a way to get your essentials at better rates.
Explore safe and convenient options for ordering your medications by https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ , ensuring privacy and prompt delivery right to your doorstep.
Having trouble with eye inflammation? Explore affordable solutions and acquire [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/tadalista/ – tadalista non generic[/URL – , a trusted treatment for managing your symptoms efficiently.
Acquire effective pain relief by opting to purchase your lasix now.
You can acquire https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ with assurance through our website.
Looking to acquire Amoxicillin without stepping out? [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin for sale[/URL – offers a simple way to receive your medication with ease.
X-plore your options for securing Duovir-N easily through our [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – buy trazodone w not prescription[/URL – platform. Secure your supply and guarantee your health’s safety.
Find budget-friendly options for kamagra 50mg , ensuring you get premium treatment for your medical needs.
Quality healthcare solutions are now accessible through our online platform where you can acquire reliable https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ without leaving the comfort of your home.
Obtain your [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – effortlessly. Procure your remedy sans a prescription online.
Optimize your health with a diverse selection of solutions by exploring [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – generic nizagara from canada[/URL – , offering a unique combination of options for your wellbeing.
Zero in on rejuvenation and vitality with price asthalin walmart . Uncover how to renew your youth and energy without breaking the bank.
Zero hassle in controlling your gout flare-ups: Purchase https://bakuchiropractic.com/levitra/ without trouble.
Regarding your health needs, discover an efficient solution to manage edema; [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ – where to buy viagra[/URL – is available. Secure, immediate purchase is guaranteed, making therapy more available.
Need to manage irregular periods? Discover your solution with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – buy canada prednisone[/URL – . Explore options to acquire this crucial therapy through the web.
Quickly secure significant savings on heartburn relief by opting to prednisone 40mg , accessible via the internet.
Managing prostate enlargement can be easier with the right medication. Find out how https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ can help in lowering symptoms safely and effectively. Whether you’re looking to buy it from a pharmacy, it’s important to consult a medical expert first.
Now, secure [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ – cheap viagra pills[/URL – for your healthcare needs.
If you’re considering managing your anxiety, [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – salbutamol inhaler buy online[/URL – may offer insights regarding an effective treatment option, encompassing dosage specifics and adverse reactions.
Quality and affordability meet when you look for your medications purchase nizagara 25mg , ensuring you obtain top-notch treatments without overspending.
Managing menopause symptoms effectively often involves hormone therapy treatment. Many patients seek convenient and private options. For those interested, you can acquire https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ online, ensuring a seamless and secure process.
If you’re battling seasonal hay fever, discover [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix/no prescription[/URL – for a solution that offers alleviation.
Purchase your medications with ease; secure your prescriptions through the web at [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – new zealand pharmacies fildena[/URL – , ensuring safety and convenience.
Zest your vacation with an excursion to the famous lowest price generic flomax , offering an unmatchable experience.
Zero worries for your hair care: Uncover your solution with https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-buy/ for a stronger mane.
Nab your essential medication: [URL=https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – through our trusted website. This vital treatment is now obtainable with ease.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern solutions, managing it has become easier. Look into [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ – walmart cialis price[/URL – , a cost-effective and trustworthy option for enhancing your well-being.
Having trouble with low testosterone levels? Discover the benefits of lowest tadalafil prices . With our product, you can restore your vitality. Purchase today and feel the difference!
Discover the best options for alleviating your allergies with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ .
Zeroing in on your health concerns, it’s vital to investigate effective treatments. For those seeking an alternative, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – might provide a optimistic solution.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – today. Whether you’re looking to enhance your wellness effortlessly, our online platform offers an easy pathway to acquire your essentials.
Get your acne treatment without leaving home, order cheap generic isotretinoin from web.
Patients seeking treatment for hepatitis C can now obtain their medication through https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ , offering a straightforward and dependable method for their needs.
Purchase
Discover effective solutions for your stomach problems with [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/lasix/ – lasix best price[/URL – , a choice endorsed by doctors.
Facing challenges with high prolactin levels? Discover lasix walmart price , an reliable treatment to manage it.
Relieve your nasal symptoms affordably by exploring https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ for alleviating allergies.
Unlock savings on your desmopressin needs with [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – staxyn[/URL – , your go-to destination. Purchase a vital therapy online with ease.
Researching where to acquire Finasteride? [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine best price[/URL – delivers a trustworthy solution for your hair loss treatment needs.
Need to locate the lowest deals on lasix overnight delivery us ? Search no more. We’ve got you covered.
People seeking relief from arthritis pain often turn to https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ , a potent option.
Zap your pain away with secure your pain reliever conveniently via web with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – on line pharmacy[/URL – .
Obtain savings on your prescription with exclusive [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tadalafil/ – tadalafil on line[/URL – available online.
Just discovered a reliable site where you can procure xenical from canada .
When considering bone density improvement, exploring https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ is essential. It offers patients a way to strengthen their bones successfully.
Get the latest costs for [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ – buy nizagara w not prescription[/URL – on our site. This eye drop offers effective solution for glaucoma sufferers, ensuring the best eye health.
Searching for reliable solutions to reduce irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms? Discover how [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – bentyl generic[/URL – can assist in easing your discomfort immediately.
Having trouble with low folate levels? Consider purchasing your tadalafil without pres online. It’s essential for those needing folate supplementation.
Obtain your https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ effortlessly today. Whether you’re hunting to acquire, our portal ensures a seamless process.
Boost your eye health easily; simply [URL=https://seraamedia.org/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – online. Achieve optimal ocular pressure relief with a click.
Acquiring your prescription has never been more straightforward. Now you can buy your needed medication [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix on internet[/URL – effortlessly.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with generic cialis , your go-to source for acquiring reliable ED solutions on the web.
Obtain your https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ by acquiring it online, ensuring you tackle your health needs efficiently.
Breathe easier with our quick-relief treatment. Purchase your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ – cheap asthalin online[/URL – now for efficient asthma management.
When seeking effective relief from anxiety, consider exploring mail order xenical , a solution available for buying online.
Respiratory issues like asthma can be daunting, but relief is accessible. Find budget-friendly solutions with https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin-100mcg/ , ensuring better respiratory health.
A comprehensive resource on medical education in the United States is readily available at [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – furosemide[/URL – .
Looking for cost-effective options? Discover the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ – sildenafil[/URL – easily.
You can locate viagra online uk to relieve your digestive slowdown with ease.
Harness the benefit of easy access by choosing to obtain https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ online, ensuring a smooth process for controlling hair loss.
Manage your health by deciding to buy essential medications easily through our platform, ensuring you can [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/tadalafil/ – generic vidalista england[/URL – conveniently online.
Explore the best deals on healthcare solutions: Locate your optimum propecia ireland paypal accepted via the internet.
Research the latest strategies for managing HIV with online resources. Uncover all-encompassing information https://embcselma.org/product/lowest-price-on-generic-levitra/ and remain up-to-date.
Browse our website to uncover the cheapest prices for [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone online pharmacy[/URL – . Ensure you’re securing high-quality treatment without overspending.
Having grappled with anxiety, finding economical treatment options can be a relief. Discover the best deals on ventolin for managing your symptoms efficiently.
The advantages of incorporating https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ into your health regimen are numerous, including enhancing stress resistance, promoting sleep quality, and improving wellness.
X-ray your health concerns and find the best solution; use this link to [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ – on line tadalafil[/URL – for a holistic approach to wellness.
Questioning where to obtain fertility treatments? Order your [URL=https://bakuchiropractic.com/retin-a/ – over-the-counter retin-a[/URL – effortlessly online.
Get your financial savings on medical supplies with nizagara buy online , providing a diverse selection of products.
Discover how to economize on your prescription with affordable https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ . Uncover the best places to purchase your medication at a lower price.
Seeking a trouble-free way to enhance your endurance? Discover [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ – generic erectafil quickest cheapest[/URL – for a trusted solution.
Get all [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/sarafem/ – sarafem online usa[/URL – for boosting male vitality.
Enhance your lifestyle effortlessly by choosing to acquire buy generic propecia —a crucial step towards rejuvenation.
Explore your options for obtaining essential hypertension treatment by visiting https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ , where a variety of affordable healthcare solutions await.
Explore your options for managing gastric ulcers with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/cytotec/ – price of cytotec 200[/URL – , accessible on the web.
Your search for affordable heart medication ends here with viagra 75mg . Secure your health’s future online.
Knowing the cost of your pharmaceuticals is crucial. Discover the affordable rates for https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ with our resource.
Looking to improve your well-being? Find out about how to obtain your needs without hassle with [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – walmart cialis price[/URL – .
Browsing for a secure source to obtain your medication? Look no further! [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ – purchase strattera online[/URL – from our reputable web platform, ensuring highest-standard products with every purchase.
For those seeking effective management for their rheumatoid arthritis, torsemide offers a reliable solution.
Discover a diverse selection of health solutions with https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ , open for purchase directly online.
Uncover the optimal outcomes with [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/propranolol/ – propranolol 80mg[/URL – for managing eye inflammation. Obtain relief and improve your vision quality by integrating this therapy into your daily care routine.
Relieve your symptoms with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ – nizagara[/URL – , available through our digital platform.
Maximize your health and wellness by opting for buy propecia 5 mg online pharmacy , a top-tier solution for managing allergic reactions. Secure your well-being by obtaining it easily on the web.
Acquiring https://embcselma.org/product/clomid/ has never been simpler. Buy the medication with just a few clicks.
Seeking effective malaria treatment can be a challenge. Yet, securing [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/sildalis/ – price of sildalis[/URL – has never been easier.
Discover amazing discounts for your medication with our buy nolvadex online cheap .
Your hunt for a economical birth control option ends here: https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ . Find your way to economical health choices now.
X-plore your options for purchasing Duovir-N easily through our [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – online generic prednisone[/URL – platform. Make your purchase and guarantee your health’s protection.
Ensure you acquire the optimal deal for glaucoma treatment needs. Consider exploring [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – alesse canada[/URL – for a variety of choices.
Browsing for a solution to your hair loss worries? Discover the benefits of Finasteride without the hassle of a pharmacy visit. Obtain your supply of generic lasix walmart , and embrace a future with fuller, healthier hair. This effortless method brings the treatment right to your doorstep.
Curious about enhancing your vitality? Consider trying out https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ . This medication, available for acquisition, might just be the solution for those seeking to boost their wellness.
Before considering treatment options, explore [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – buying nizagara[/URL – to treat your health needs efficiently.
Maximize your savings on antiretroviral therapy by clicking here: [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/nizagara-prices/ – nizagara[/URL – . Discover the most affordable prices online for effective HIV treatment options.
Quickly ease your gastrointestinal troubles by choosing to purchase nizagara prices .
Quality and affordability meet when you seek your medications https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ , ensuring you obtain top-notch treatments without overspending.
Zillions seek efficient solutions for impotence; [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra[/URL – presents a versatile answer.
Discover affordable healthcare options and manage your hypertension effectively with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – . Obtain your medication easily and ensure your well-being is prioritized.
Xperience ease from joint pain when you order(vpxl ) from our website.
Regarding your health concerns, purchase effective treatment easily by opting to buy https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ online.
Visit now to find the best [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/propecia-1mg/ – cheapest propecia dosage price[/URL – and cut costs on your purchase.
Looking to manage your gout symptoms? Discover a variety of affordable options when you purchase prednisone .
Considering various contraceptive options? Discover how to secure affordable birth control with https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ . Explore internet pharmacies for easy access to your health needs.
Harness the power of cutting-edge solutions for gastrointestinal comfort; buy [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – and discover the advantages today.
Get the most favorable generic herbal max gun power lowest price on the web. Secure your health today.
Get the top-quality epilepsy treatment options delivered right to your doorstep with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ .
Considering the requirement for cost-effective anxiety remedies, [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ – stablon canadian pharmacy discount[/URL – offers a feasible alternative.
Discover secure ways to acquire your medications with ease; [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ – viagra 75mg[/URL – offers an authentic solution for enhancing your wellness.
Purchasing affordable generic clomid uk has never been easier, with numerous options available on the internet. Secure your well-being today by selecting the best deal.
Boost your health today! Acquire your https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ without hassle. This essential solution is just a click away.
Seeking a solution for hair loss? Explore how to purchase [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis[/URL – , a proven method to fight balding securely.
Discover unparalleled vitality; unlock your potential with our [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – purchase stromectol[/URL – . Elevate your life quality, experience enhanced performance and well-being. Don’t wait; secure yours!
Zero in on rejuvenation and vitality with nizagara from canada . Discover how to renew your youth and stamina without breaking the bank.
Explore cost-effective solutions for your healthcare needs by deciding to https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ .
Experiencing allergies? Discover respite by choosing to purchase [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ – ventolin online[/URL – . This effective treatment is accessible for individuals seeking relief.
Just discovered you can secure [URL=https://seraamedia.org/amoxicillin-650mg/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – with ease through our secure website.
Need to alleviate constipation? furosemide is your go-to solution.
You can locate https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/trazodone/ on the web, offering a cost-effective solution to your needs.
Relieve your pain efficiently with [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – discount fildena[/URL – , the perfect solution for alleviating discomfort free from the need for ingested medication.
Aiming for affordable ulcerative colitis treatments? Explore [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – canada prednisone 20mg[/URL – for choices.
Zero worries about where to acquire your ED solutions; explore pharmacy prices for viagra for a secure and discreet way to restore intimacy.
Struggling with thinning tresses? Uncover your solution with https://phovillages.com/xenical-walmart-price/ . This product offers a cutting-edge approach to reviving your locks, providing visible results.
Understanding your [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/prednisone/ – prednisone from india[/URL – is vital for handling IOP in patients with ocular hypertension.
Considering the myriad options for baldness solutions, acquiring [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix no prescription[/URL – could be your most cost-effective choice.
Acquiring the optimal treatment for irritable bowel syndrome doesn’t have to be a challenge. You can secure tadalafil through our website to alleviate your symptoms effectively.
Explore choices for easing eye inflammation with https://brightnights915.com/item/zithromax/ , ready for purchase on the Web.
You can find the best [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/nizagara/ – buy nizagara online cheap[/URL – for your alopecia therapy on the web today.
Now, discover online prednisone ordering by browsing our website. Secure the best deal immediately.
Optimize your health journey; acquire fertility solutions effortlessly with https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ .
Maximize your vitality; enhance your performance safely by getting the supply of [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine[/URL – through our secure platform.
Boost your hair growth with affordable solutions like [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ – vardenafil[/URL – . Discover a range of options and regain confidence without straining your wallet.
Find top quality amigren 25mg online. Acquire your stock of this medicine without hassle.
Purchase your https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ eye drops online to treat glaucoma efficiently and economically.
Various individuals opt to acquire their medical supplies via the web, with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone in argentina[/URL – being a popular choice among choices.
Explore reliable options to order your medication via the web with [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – pharmacy prices for extra super avana[/URL – , ensuring privacy and ease.
Discover safe methods to control your anxiety with generic propecia at walmart , offering multiple solutions online.
Quest for affordable ED treatments? Discover your solution at https://monticelloptservices.com/fildena/ , providing a wide selection of top-notch options.
Optimize your health management by considering to [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – sildenafil[/URL – . Acquire the medicine online for your convenience and well-being.
Looking for inexpensive options? Discover the [URL=https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ – prednisone[/URL – today.
X-ray your options for economical hormonal therapy: Discover the viagra and consider alternative routes to regulate your health economically.
Facing menopausal symptoms? Discover relief with https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ , your trusted source for hormone therapy.
For those seeking a unique approach to boost their well-being, consider checking out [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone brand[/URL – .
Acquiring your treatments has never been more straightforward with tadalafil . Purchase now for fast delivery anywhere.
Just discovered you can obtain https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ with ease through our trusted online platform.
Visit our website to locate the top [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/propecia/ – natural form of propecia[/URL – .
Various options exist for enhancing eyelash growth, but if you’re seeking a reliable solution, consider [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/genegra/ – generic genegra canada[/URL – . This product, also known for its efficacy in improving eyelash thickness, can be conveniently ordered through online platforms.
Visit our website to acquire your cheap canadian vidalista , for immediate purchase.
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly; purchase https://andrealangforddesigns.com/genegra/ to boost your health through a credible source.
Struggling with hypertension or angina? Explore how [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara tablets[/URL – could be the key to overcoming these conditions.
Managing discomfort or fever doesn’t have to be a struggle. Explore how you can obtain effective relief with nizagara tablets , your go-to option for relieving pain or fever quickly.
A Pioneering Solution to Healthcare is Here! Now, discover a wide range of healthcare options only at https://jawany.com/amoxil/ .
Looking to fortify your bones? Consider [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nexium/ – nexium non generic[/URL – for an effective alternative.
A key treatment for managing edema is accessible through this link: discount generic tadalafil volume . Whether you’re battling heart failure, kidney issues, or hepatic disorders, consider investigating this solution.
Manage osteoporosis effectively by choosing to https://ghspubs.org/product/vpxl/ . With options abundant, you can purchase this osteoporosis treatment via the internet.
Combat pain effortlessly and affordably with the aid of [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – , available for your next buy.
Looking for a solution to enhance your eyelashes? Explore effortless beauty with [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone/ – prednisone post[/URL – . Obtain lush lashes easily.
Visit the isotretinoin link to uncover the most competitive costs for your acne treatment needs.
Zeroing in on cost-effective healthcare solutions, many are inquiring about how to cheaply access medications. Discover the https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ for insights on how to budget on your health needs.
Patients seeking cost-effective treatment for bipolar disorder may find [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – competitive. Find out the price of managing your condition with these tablets.
Just when you need relief from persistent nasal symptoms, purchasing [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – offers a hassle-free solution for managing your condition.
Need to boost your focus without a hassle? Explore how easy it is to receive what you need tadalafil en ligne .
Discover your key to enhanced well-being with a https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ . Order now for an improved lifestyle.
X-plore your options for increasing eyelash growth with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – nizagara online avis[/URL – , available for buying via web.
Having trouble finding [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ – propecia[/URL – ? Search no further and purchase your stroke prevention prescription without hassle today.
Explore your alternatives for dealing with gastric ulcers with cytotec online canada , available online.
Quickly obtain your https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ devoid of the hassle of seeing a doctor.
Buy your essential medication easily with a tap on your device. Seeking a reliable source for your healthcare needs? Look no further. Obtain Duprost, without the hassle of a prescription, right away through [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra 50mg[/URL – .
Zero in on boosting your overall wellbeing with [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – no prescription herbal max gun power[/URL – , offering a holistic path to enhancing vitality.
Questions about iron supplements? Discover the benefits of generic cialis and learn why opting for a branded formulation can make a notable change in your well-being.
Our team has sourced the https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
Looking to manage your nausea? Check [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/trazodone/ – over the counter trazodone in montreal[/URL – and uncover the most affordable options for your healthcare needs.
Your quest for budget-friendly heart medications ends today! Secure your dose of nizagara coupon right here! Wide-ranging options to obtain your essential therapy now await.
X-plore the myriad benefits of alleviating seasonal allergy symptoms with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ . Whether you are in search of alleviation from sneezing, this medication offers a trusted option.
Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ – finasteride 1mg[/URL – for an affordable way to manage your condition. Secure your supply now.
Obtain your treatment for improved female health with buying tadalafil , available on our site.
X-plore affordable hypertension treatments with various options and find your optimal solution at https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ , your go-to for cost-effective health solutions.
Keep your well-being at its peak: explore safe and trusted options to purchase [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/viagra/ – non prescription viagra[/URL – .
Seeking a safe, dependable method to acquire Cytotec? Look no further. cytotec online no script offers a hassle-free solution.
Questioning where to unearth top-notch heart health supplements? Look no further than https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ , your premier destination for every one of your heart wellness products.
Acquiring [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix overnight fedex[/URL – has never been easier; Secure this essential drug online with just a single click.
Unlock the secret to enhanced vitality by choosing to [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ – cenforce[/URL – , your primary source for premium health solutions.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? flomax might be the answer. Learn about how it may help in lessening your symptoms efficiently.
For those looking to boost their hair growth, consider exploring https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ as your optimal solution.
Questioning where to obtain Ciprofloxacin? Look no further than [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/cipro/ – cipro 250mg[/URL – , your go-to source for trusted antibiotics.
Quickly find relief from allergy-induced nasal congestion with tretinoin pills free shipping , a top-rated choice for managing allergy symptoms.
You can acquire safe and reliable treatment for nausea with https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ , available through online pharmacies.
Keep informed on this anti-malarial medication benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – for thorough insights and updates.
Just discovered the solution for managing mild Crohn’s Disease symptoms: [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ – tretinoin cream 0.05[/URL – . Acquire it via web for convenience and privacy.
Procure your acid reflux treatment without exiting your home; visit atomoxetine for speedy relief.
Quiet your stress at an affordable price with https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ . Purchase your treatment today for peace of mind.
Acquire [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – effortlessly. Procure this vital drops online to alleviate your ocular issues.
Transform your intimate moments with tadalafil , the optimal choice for those seeking improved effectiveness.
Harness the convenience of modern technology by opting to acquire your https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ , ensuring a straightforward way to access your pharmaceuticals.
Looking for treatment for hair loss? Discover the best products online. Your search ends here: [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – online prednisone no prescription[/URL – .
Discover ways to save your prescriptions by exploring the tadalafil without a doctor , ensuring you obtain your meds at the cheapest price.
Achieve a fuller, healthier head of hair when you purchase https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ .
Unlock sensational discounts on essential healthcare products! Buy your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/no-prescription-retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – today and ensure your vision receive the top-notch care without overspending.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Find out about how to secure your needs effortlessly with generic cialis tablets .
For individuals seeking an efficient treatment against hepatitis B, exploring options like https://embcselma.org/item/amoxicillin/ offers a pathway to obtain trusted medication via web pharmacies.
When seeking trusted and effective medication for schizophrenia, consider exploring options to acquire [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ – generic retin a uk[/URL – from reputable websites.
When seeking an economical solution for your antibacterial needs, think about tapping into the convenience of [URL=https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ – prescription doxycycline usa[/URL – . This online pharmacy offers a broad assortment of non-brand medications that cater to various health conditions efficiently.
Research indicates that accessing lasix can be a crucial step for those seeking relief from inflammatory disorders.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ to combat infections caused by bacteria. This economical solution is simple to get and helps in managing a wide range of medical conditions.
Before making a decision, discover [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – buy super-active-pack-20 rx[/URL – and compare prices to ensure you obtain the most favorable deal for your heart health medication.
Keep your health in top shape affordably by choosing to buy your [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – walmart hydroxychloroquine price[/URL – through our website.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your buy amoxicillin uk online for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
Zillions now look for solutions for boosting their stamina. It’s easy to obtain safe support https://phovillages.com/viagra-in-usa/ .
Purchase effective Hepatitis C treatment with [URL=https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ – online pharmacy for amoxil[/URL – , offering a trustworthy treatment for patients seeking health.
Victims of menstrual irregularities can now discover relief. Visit our website to buy [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin a cream 0.05[/URL – , offering a promising treatment for discomfort and imbalance.
Various individuals seeking cholesterol-lowering solutions have turned to priligy 30 mg . With a plethora of options available, opting for
the most recent https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ to control constipation.
If you’re in the market for an effective treatment to fight bacterial infections, ponder [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – . This drug has been widely acknowledged for its efficacy against numerous types of bacteria.
Buy your essential medications effortlessly through our secure platform. Click here: [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – .
Here’s how your request could be realized, keeping within the constraints provided:
“Have you been in the market for an affordable solution to manage your blood pressure? Discover the best deals on clonidine no prescription , a key medication for blood pressure control. Don’t miss out on savings today!”
Need to spark up your love life? Explore your options and acquire https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ to reignite intimacy.
Struggling with hypertension or angina? Explore how [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ – levitra 10mg[/URL – could be the answer to controlling these conditions.
Unlock unbeatable deals on anti-diarrhea medication at [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – cenforce[/URL – , your go-to source for tackling digestive issues.
Visit our website to discover competitive cytotec for manage your condition effectively & affordably.
Having trouble finding affordable eye medication? Look no further! Get the https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ now. Whether you’re in need of ocular medication, our website offers competitive prices.
Obtaining [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tadalafil/ – tadalafil buy online[/URL – has never been simpler. Order this crucial medication from the comfort of your home.
Just in time for your urgent needs, discover your essential supplies up for grabs at strattera without dr prescription usa , right away.
Keep your health in top condition without leaving comfort behind. Obtain your necessary medications effortlessly through our reliable platform. https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ and ensure your well-being is always a priority.
Secure your [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – strattera[/URL – today and experience enhanced results in your personal life.
Zero in on managing your hypertension by browsing [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , your go-to hub for securing this essential medication.
Considering urgent antibiotic needs, acquiring doxycycline without an rx online ensures a rapid solution.
Keeping allergies at bay is now easier than ever. Whether you’re looking to fight against seasonal sniffles or seeking relief from year-round triggers, you can obtain effective antihistamines quickly. https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ offers a reliable solution, making it straightforward to purchase your essentials from the comfort of home.
When seeking excitement and thrill, consider diving into the digital realm of gaming at your convenience. Explore a virtual plethora of entertainment options with [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – buy tadalista w not prescription[/URL – , where each click unravels new adventures and possibilities.
Battling inflammation? Explore more about how lady era could be your pathway to easing discomfort.
Considering the diverse options for obtaining essential medications, it’s crucial to consider avenues offering both value and authenticity. When looking to purchase treatments, specifically cabergoline, one standout choice is https://renog.org/product/amoxil/ . This option stands out for its economic efficiency and dependability.
Questioning where to find the best deal on [URL=https://center4family.com/strattera/ – strattera[/URL – ? Obtain your supply by tapping on the link!
Visit our website to locate the [URL=https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ – retin a capsules[/URL – for your inflammation reduction needs.
X-ray your health concerns and find the best solution; use this link to buy levitra on line for a holistic approach to wellness.
Discover natural therapies for boosting your health with https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ .
Visit [URL=https://jawany.com/amoxil/ – generic 250 mg amoxil cheapest prices[/URL – to buy your medication online at fantastic prices.
Acquiring [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis 2.5mg[/URL – is now feasible. Explore options to purchase this essential medication without hassle online.
Need to fight against intestinal worms? Get your effective treatment straightforwardly by clicking prednisone online right away.
Understanding the alternatives for managing IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ might provide you alleviation from stomach discomfort.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Discover how [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/alesse/ – alesse online[/URL – can help manage your symptoms. Explore options for relief and learn more today.
Manage your arrhythmias effectively. Acquire safe and reliable medication. lowest price sildalis from a reputable online pharmacy.
Visit https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ for complete insights on utilizing this medicine responsibly.
SUNWIN is recognized as a modern digital betting dais that blends novelty with user-focused design. From immersive casino experiences and transparent x? s? systems to competitive th? thao markets, the platform reflects how online wagering has evolved in fresh years. Players can traverse interactive trò choi, dynamic game slots, and fast-paced b?n cá, all optimized seeking stability and fairness. High-value jackpot rounds, deathless baccarat, r?ng h?, xóc dia, tài x?u md5, and vital dá gà fascinate both unsure users and trained bettors. With growing non-objective in esports, frequent khuy?n mãi, conscientious cskh, and obedient uu dãi after members and d?i lý, n? hu moments odds a highlight. Seeing that official access, attack https://sunwin24z.life/ to view a balanced, obtain, and engaging betting environment.
SUNWIN is a today’s online betting ecosystem built as a service to players who value transparency, rush, and depth. From live casino tables and trim x? s? systems to competitive th? thao markets, the rostrum delivers a balanced portfolio of trò choi. Fans of game slots, b?n cá, jackpot, dá gà, and esports will bump into uncover steadfast odds and optimized gameplay. Stable modes like tài x?u md5, xóc dia, baccarat, r?ng h?, and n? hu echo strong technological foundations. With customary khuy?n mãi, long-term uu dãi, practised cskh, and a clear d?i lý configuration, users can explore confidently. Official access at https://sunwin24z.life/.
Need to obtain your alopecia remedy? Locate cost-effective options with [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – 10mg prednisone generic india[/URL – , providing you obtain top-notch therapies at a fraction of the price.
Check out order prednisone 5 tab for competitive costs on alopecia medications.
For individuals seeking an efficient treatment against hepatitis B, exploring options like https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ offers a pathway to secure trusted medication through digital platforms.
I discovered that many individuals are looking to acquire [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/tadalafil/ – discount tadalafil prescription drug[/URL – for their sinus allergies relief.
Discover the ease of purchasing your medication with just a click. [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – tamoxifen on internet[/URL – offers a hassle-free solution to order your prescription from the convenience of your home.
Queuing up for your medicines at the pharmacy is outdated. Now, conveniently fetch your treatment retin a canada with just a few clicks.
X-plore budget-friendly options for your health concerns with https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ , your path to improved wellbeing.
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly; purchase [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ – levitra on line[/URL – to enhance your well-being by means of a reliable source.
X-plore the options to order clonidine online in Canada, ensuring you choose a trustworthy source. [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine online usa[/URL – offers a convenient way to obtain your medication.
Looking to maintain your hair’s health? Consider uk lasix prescription as your go-to option. This effective solution is readily available for those seeking to address hair loss problems efficiently and conveniently through an internet-based platform.
“Quickly locate deals on your next purchase with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ . Save without hassle on vital medication.”
The best spot to secure [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – strattera[/URL – is accessible online.
Quest for affordable options to manage your health? Discover the best deals with our [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – , your go-to choice for dependable medication free from the hefty price tag.
With rising healthcare costs, it’s crucial to find the most affordable option. For those seeking to lower cholesterol, lady era is often a lifesaver.
Curious about securing the https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ ? Discover your options on our website.
Venturing into the realm of affordable medical solutions? Look no further, [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – at this spot for your treatment.
Investigate economical solutions for managing IBS symptoms. Find the most competitive [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – for immediate relief.
Keeping your health in check is crucial, hence think about purchasing low cost amoxil for swift relief from tension.
Discover the pathway to serenity and stability over stress by opting to purchase https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ .
Keeping your health in check is paramount, and accessing affordable medication shouldn’t be a hassle. Secure your heart health with ease by opting for [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara price walmart[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to acquire cost-effective heart health support, this option ensures you don’t compromise on quality or efficacy.
With various online platforms available, it’s never been easier to lowest tadapox prices . Whether you’re aiming to acquire medicine with convenience, our platform offers a seamless and secure buying journey.
Facing respiratory challenges? https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ can be your relief partner. Secure, simple, and quick, it’s your gateway to breathe easier.
Before you commit to a purchase, consider checking out [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ – zoloft commercial[/URL – for budget-friendly rates on your necessary medication.
Get your prescription easily with quick delivery; click here to [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – online generic staxyn[/URL – now.
Facing dry eye problems? Find the solution online with lady era . Purchase your bottle today for alleviation.
Given the fluctuating expenses, finding the best deal for medication can be a daunting task. Whether you’re looking to control urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ offers a cost-effective solution.
I discovered that many individuals are looking to obtain [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – priligy pills[/URL – for their sinus allergies relief.
Acquiring generic [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ – kamagra cheap[/URL – has never been simpler. Buy your upcoming dose from our website with total peace of mind.
You can obtain amoxicillin 250mg on the internet to manage stress.
Finding the most cost-effective https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/cialis/ can be challenging. Search on the internet for options that provide value.
For persons seeking alleviation from irregularity, [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – kг¶pa hydroxychloroquine i sverige[/URL – presents a trusted solution.
Achieve optimal heart condition with our product. Discover more at [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ – generic amoxicillin in canada[/URL – .
Quality healthcare doesn’t have to break the bank. Discover budget-friendly epilepsy treatment solutions and cut costs on your medication with lady era price walmart .
Quickly secure your prescriptions with convenience by choosing to purchase https://homegrownscholars.com/item/generic-viagra-lowest-price/ .
Just discovered [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – prednisone prices[/URL – ? Now reap the benefits of quick service right to your doorstep.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? flagyl en ligne might be the answer. Find out about how it can assist in alleviating your symptoms effectively.
When searching for urgent resolutions, discover https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ for your requirements.
Secure your health by choosing to purchase the medication through the internet. Click here for [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – overnight celebrex[/URL – , ensuring you obtain genuine care conveniently.
You can purchase [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra de 10 mg precio[/URL – , a premier option for hormonal balance, directly online.
Discover affordable treatments for impotence by visiting cialis , where you can acquire your prescriptions conveniently.
Discover how https://seraamedia.org/flomax/ can ease symptoms of BPH by checking our site.
WildBrook Modern Designs – Stylish pieces throughout, the layout made exploring effortless.
лазертаг Пейнтбол для детей адаптирован таким образом, чтобы снизить риски травм и обеспечить максимальную безопасность. Используются менее мощные маркеры и шарики с краской меньшего размера, что делает игру более мягкой и безболезненной. Специальные защитные костюмы, маски и шлемы обеспечивают дополнительную защиту.
pin up yangi promokod https://pinup5011.ru
Managing chronic pain requires effective treatment strategies. Discover how [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – buy ranitidine no prescription[/URL – offers a solution that can assist in minimizing discomfort.
Maximize your health and wellness by opting for generic meldonium from india , a top-tier solution for managing allergies. Secure your well-being by obtaining it without hassle on the web.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover special https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ for savings on vital treatments. Obtain yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
Exploring options for hair loss treatments? [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ – buy generic tadalista[/URL – could be your answer. Obtain it without hassle and start the path to fuller hair today.
The buy cialis on line showcases how people suffering from heartburn can attain comfort promptly and efficiently.
Keep your health in top condition with our exclusive https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ . Purchase today and enjoy the change in your wellness.
I located an amazing source to [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – retin a on internet[/URL – .
Keeping your health in paramount condition, the necessity to procure medication without hassle is vital. For those seeking a reliable remedy, clicking here [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra/ – levitra 20mg[/URL – allows you to get your essentials swiftly and effectively.
Need to enhance your experience? Look into doxycycline for a delightful twist on conventional solutions.
Get the top-quality seizure control options shipped right to your doorstep with https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ .
Obtain comprehensive insights and secure the [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ – sarafem coupon[/URL – for your antiviral medication needs by exploring our site today.
When seeking to boost your intimate moments, one effective solution is the acquisition of [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – medication similar to amoxil[/URL – . This product is widely recognized for its capability to lengthen enjoyment and satisfaction.
Looking for a reliable source to purchase your medication? esomeprazole offers an easy way to obtain your needs with just a few clicks.
Seeking an effortless way to enhance your performance? Check out https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ for a dependable solution.
When looking to acquire medication for rheumatoid arthritis, consider exploring options to [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – pharmacy prices for trazodone[/URL – , ensuring you attain effective treatment easily.
Need to enhance your eyelashes? Explore a range of options available at [URL=https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/fildena/ – generic fildena from us[/URL – , where you can Buy your item without hassle on the internet.
X-ray your budget and spend wisely on heart health options. Discover incredible amigren 25mg on our site.
Keeping your heart’s rhythm steady is crucial; obtain https://homegrownscholars.com/item/zithromax/ for maintaining optimal cardiac health and function.
Zeroing in on treatments for COVID-19, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – generic nizagara[/URL – offers a promising option. Seekers in the health arena can find this remedial alternative via the internet.
Knowing how essential it is to manage your hypertension, you can get a reliable solution with [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/zithromax/ – purchase zithromax[/URL – online.
Consult your healthcare provider to obtain the most effective treatment options. For those considering cost-effective solutions, generic malegra uk is a option.
Zeroing in on solutions for acne issues? Find how https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ provides effective option.
Grappling with acne? Discover your solution without needing a doctor’s note. [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/isotretinoin/ – generic isotretinoin available[/URL – offers a effective solution available directly to you. Say goodbye to persistent blemishes today.
pin up savollar va javoblar http://pinup5012.ru/
Quality and affordability converge with our off-brand erythromycin options. Secure your health’s future by buying at the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – buying pharmacy[/URL – today.
Quickly obtain your deworming solution without hassle by choosing to ventolin without prescription .
To secure the most affordable price on https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ , browse our website.
Seeking effective malaria treatment can be a challenge. Yet, buying [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – on line pharmacy[/URL – has never been more straightforward.
In need of Doxycycline? Get your prescription easily [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/item/doxycycline/ – canada doxycycline[/URL – . Available for immediate purchase, ensuring you have access to your treatment swiftly.
Facing menopausal symptoms? Find relief with tadalafil , your preferred option for hormone therapy.
I understand the need for accessible solutions when looking to get medication. For those considering managing their health issues efficiently, considering https://jawany.com/amoxil/ provides a vital solution.
Discover an effective way to enhance your wellbeing: [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ – purchase sildenafil online[/URL – .
Looking to enhance your intimacy? Check out lasix in austria for a reliable and proven option.
X-ray your options for HIV management by exploring affordable solutions. Discover https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ to combine efficacy with economy.
Seeking the best value for your heart health medications? Compare costs now and conserve on your prescription with [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20 on internet[/URL – , your prime source for affordable healthcare.
Unlock exceptional deals on [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ – price of cenforce[/URL – , your optimal choice for removing erectile dysfunction. Purchase yours today for improved health and happiness.
Procure your prescription with convenience and confidentiality; vidalista canadian pharmacy directly online.
Amidst the myriad options for managing pain and inflammation, https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ stand out as a potent solution. Individuals seeking relief can obtain this medication from online pharmacies, offering an easy way to address their symptoms.
Visit [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – celebrex buy cheap online[/URL – today and discover cost-effective solutions for handling your pain.
Necessitating a reliable solution for diuretic needs? Find [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ – generic dapoxetine from india[/URL – , your go-to solution for controlling water retention.
Zero hassle to get your medication: propranolol 20mg – buy on the web with absolute confidence.
Maximize your well-being with a holistic approach by opting for https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxicillin/ , a solution that’s easy to obtain for improving male health and vitality.
When managing joint pain, consider exploring your choices with [URL=https://goldenedit.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix online no script[/URL – , a proven remedy.
With savings on healthcare paramount, accessing necessary medications affordably is key. Discover special [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ – buying ed-sample-pack-2 in australia[/URL – for savings on essential treatments. Secure yours today and ensure that health remains a priority without compromising on quality or cost.
X-plore the myriad options to acquire your medications affordably; our portal allows you to buy pharmacy online canada effortlessly. This opportunity enables clients seeking to buy their drugs at a reduced price.
If you’re looking for an effective remedy to tackle bacterial infections, ponder https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxicillin/ . This drug has been widely acknowledged for its effectiveness against a wide array of bacteria.
Understand your need for allergy relief and purchase [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – online.
Quest for superior healthcare products ends at retin a buy in canada , where you can order all from drugs to wellness supplements via our website.
Maximize your wellness journey efficiently and securely by opting to https://tei2020.com/nizagara/ , a versatile solution to your healthcare needs, readily available at your fingertips.
Research indicates that accessing [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/propecia/ – generic propecia canada pharmacy[/URL – can be a crucial step for those seeking alleviation from inflammation.
If you’re seeking a dependable cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil 10mg[/URL – , obtainable for buying right here.
Researching your options for treating fertility issues? prednisone offers extensive insights. Explore how this product can facilitate improving fertility.
Quickly order your prescription with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ , offering speedy shipping directly to your doorstep.
Before considering self-medication, always consult with a health care professional. Nevertheless, for those sure of their diagnosis and in need of Cipro, [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ – tadalista for sale cheapest[/URL – can be found.
Procure your antiviral medication with a [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra 100 jelly[/URL – , ensuring savings.
Discover your answer for improving sexual performance with ease; purchase viagra non generic now.
Questioning where to locate Ciprofloxacin without overpaying? Find the https://embcselma.org/item/cipro/ and save on your healthcare bills.
Realize significant savings on your medication expenses; effortlessly purchase your [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/product/vpxl/ – overseas vpxl cheap[/URL – via a web-based pharmacy, ensuring you receive both quality and affordability from the comfort of your home.
Having osteoporosis? Explore our options and acquire your medication directly. amoxicillin 500mg capsules for reliable bone health support.
Just in case you’re probing for the most affordable options for your fertility treatments, consider discovering the price of https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ . It’s crucial for those desiring to enhance their prospects of conception.
Check up-to-date [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/amigren/ – shop for amigren[/URL – for managing HIV.
In need of effective antibiotic treatment? doxycycline 100 mg offerta to combat infections caused by bacteria. This budget-friendly solution is simple to get and can help in managing a wide range of medical conditions.
With the recent quest for affordable malaria treatment options, securing https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ has never been more vital.
Get the best deals on heart-healthy supplements when you purchase [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – ventolin online[/URL – .
Grab your chance to win big! Visit our exclusive [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine cost[/URL – for a remarkable gaming experience.
Xperience improved life-force for anyone seeking remedies. Uncover your path to a more fulfilling life via buy tadalafil in great britain , ensuring optimal results and contentment.
Explore affordable menstrual cycle support with https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ , your go-to option for managing menstrual discomfort.
Keep informed on this anti-malarial medication benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – canada drug hydroxychloroquine[/URL – for thorough insights and updates.
Discover unparalleled convenience and discretion in securing your cardiovascular health by opting to obtain Atorlip-20 on the internet [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – levitra[/URL – .
Your search for effective and safe medication ends here; buy furosemide uk offers you the opportunity to acquire top-quality treatment conveniently.
Considering your health and vitality, explore the benefits of https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ , a herbal solution for enhanced stamina.
Just found out you can order your digestive spasms treatment on the web? [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – bentyl[/URL – offers a wide range of solutions for your medical needs.
Looking to treat your ulcerative colitis? Discover the most cost-effective solutions at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera/ – strattera 18mg[/URL – .
Zeroing in on effective pain relief solutions? Discover accessible options like generic lasix canadian online pharmacy , perfect for alleviating soreness.
Having trouble finding where to get your medication? Look no further, visit https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/propecia/ to acquire your prescription with ease from the comfort of your home.
Quest for lush, voluminous hair ends here! Acquire your bottle of hair oil that rejuvenates roots for healthier locks. Click [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin.com lowest price[/URL – to initiate your transformation journey today.
Discover affordable options for erectile dysfunction by visiting [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/lowest-price-generic-cialis/ – buying cialis online[/URL – , where you can purchase your drugs conveniently.
X-plore affordable options for thyroid management with our comprehensive guide on retin a . Find out how to efficiently purchase your treatment through our trusted website, ensuring you get top-quality care without overspending.
X-plore your options for purchasing Duovir-N easily through our https://brightnights915.com/drugs/propecia/ platform. Make your purchase and guarantee your health’s protection.
Having cardiac rhythm issues? Look into [URL=https://phovillages.com/pharmacy-without-prescription/ – pharmacy in austria[/URL – for an efficient.
Join the myriad of individuals choosing to purchase their wellness supplements through digital stores by exploring options to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – kamagra 100mg[/URL – . Elevate your health regimen today with this dependable product.
Just unveiled: Get astonishing discounts on your next purchase with our exclusive prednisone . Hurry, seize an incredible opportunity to reduce expenses on pharmaceuticals.
Seeking reliable malaria treatment can be a complex endeavor. Yet, buying https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ has never been more straightforward.
Your quest for a cost-effective birth control option ends here: [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/ – miami retin-a[/URL – . Discover your route to economical health choices now.
Seeking a safe, dependable method to get Cytotec? Look no further. [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – non prescription cytotec[/URL – offers a simple solution.
With the increasing demand for natural nutritional supplements, lasix emerges as a top choice. Its benefits for health are unbeatable.
For men in search of reliable hair loss remedies, https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-for-sale/ delivers crucial data.
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – , a solution for alleviating prostate enlargement symptoms.
Many are searching for effective treatments for erectile dysfunction, and alternativa al cialis provides a tested option.
Patients requiring anticoagulation therapy can now acquire their https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ online.
Relieve your BPH symptoms today! Explore our variety of [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ – flomax cost walmart[/URL – , specially designed to enhance your urination and overall well-being.
Get all [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – purchase extra super avana[/URL – for improving male potency.
Visit our site to locate your essential pain relief. Purchase generic deetor at walmart online for rapid dispatch.
To manage hypertension, consider https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ , a method embraced by many in achieving better health.
X-ray your options for HIV treatment medications and find the best solutions. For those seeking economy, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – non prescription stromectol[/URL – provides a viable option.
When considering managing anxiety or insomnia symptoms, exploring various solutions is key. One option is stromectol , known for its potency in handling such ailments.
To reduce your pain and inflammation, consider purchasing https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ via our portal.
Find a way to buy [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady era best price[/URL – securely.
Optimize your health regimen by checking out our range at [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ – overnight vidalista[/URL – , where quality meets effectiveness.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern solutions, managing it has become easier. Consider pharm cialis , a cost-effective and trustworthy option for boosting your performance.
You can acquire Fildena for your ED needs here: https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ .
Boost your health today! Get your [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/generic-amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – quickly. This vital solution is now away.
Understanding the need for accessibility, you can now obtain your treatment online with ease. [URL=https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ – fildena non generic[/URL – and experience swift shipment to your doorstep.
Get relief from allergy symptoms with an effective solution. Discover retin a online no script for immediate relief.
Explore the options and purchase your treatment without leaving your home at https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/retin-a/ .
Keep your eyes healthier by managing glaucoma and ocular hypertension effectively. Obtain [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/flagyl/ – flagyl generic pills[/URL – through our digital pharmacy and experience a straightforward home delivery process.
Get your [URL=https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ – xenical 60mg[/URL – prescription renewed virtually without hassle, ensuring speedy relief and efficient management of your symptoms.
Zero hassle for your pharmacy needs: explore prednisone to buy all your healthcare items with ease.
Boost your well-being today with reliable solutions from https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ . Discover your way to a healthier life right away.
Having difficulty finding your medication at local pharmacies? Buy your [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ – buy strattera in hong kong[/URL – effortlessly.
You can purchase your fildena 50 /canada online, ensuring affordability and ease.
Explore methods to get https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/strattera/ , a key treatment for managing Parkinson’s disease, directly on our site.
Optimize your health and wellness routine by securing your medications effortlessly. [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ – where to buy bentyl[/URL – offers a hassle-free solution for improving your vitality.
Now, obtain your heart health medication conveniently nexium non generic .
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly with https://yourbirthexperience.com/pill/nizagara/ , now obtainable to acquire from the comfort of your home.
Unlock the potential to tackle scabies and head lice with a click. Buy your [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/vidalista/ – generic vidalista online[/URL – via our website for efficient treatment.
Maximize your vitality; increase your performance safely by obtaining the dosage of [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ – zoloft.com[/URL – via our website.
Considering the myriad options available, opting to secure your medication through reputable sources is paramount. For those looking into therapy for gastrointestinal issues, doxycycline generika 200 kaufen stands out as a trusted choice among various vendors.
Understanding the choices for managing IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ might provide you relief from abdominal discomfort.
Looking for a reliable way to control psoriasis? Learn about how [URL=https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/pill/nizagara/ – nizagara uk[/URL – can aid in alleviating symptoms safely.
Эвакуатор в Таганроге Услуги эвакуатора Наши услуги включают в себя: эвакуацию легковых автомобилей, эвакуацию мотоциклов, эвакуацию внедорожников, эвакуацию микроавтобусов, эвакуацию спецтехники, техпомощь на дороге (запуск двигателя, замена колеса), транспортировку автомобилей в другие города. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, чтобы удовлетворить любые ваши потребности.
Revitalize your vitality with a natural solution; [URL=https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ – doxycycline.com lowest price[/URL – . Rediscover the strength of nature’s offerings right away.
The Preorder a pill on website stablon buy online ensures your health needs are met with convenience and efficiency.
You can increase your vitality by opting to buy https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ , on offer now.
Unlock exclusive savings via our [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy without dr prescription[/URL – and elevate your wellbeing today.
Realize significant savings on your medication expenses; effortlessly obtain your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/finasteride-cheap/ – finasteride non generic[/URL – online, ensuring you receive both quality and affordability without leaving your home.
For users seeking proven hair loss solutions, finasteride delivers vital insights.
In search of the lowest-priced option for enhancing your eyelashes? Discover amazing deals on https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ .
Navigating the vast internet for authentic ayurvedic solutions? Your search ends here. Discover authentic ayurvedic remedies at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ – viagra generic 75 no rx[/URL – . Buy with confidence for all your natural wellness needs.
Discover effective solutions for your digestive discomfort with bentyl overnight , a selection endorsed by healthcare professionals.
Obtain your remedy for better female health with https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ , available online.
Discover affordable solutions for managing your health with [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ – propecia for sale[/URL – . Find your necessary medication at this moment.
Get the best pricing on [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/product/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2 no presc[/URL – by looking on internet pharmacies. This drug is vital for specific conditions, so locate your choices immediately.
Get your amoxil easily from buying amoxicillin , supplying swift shipping to fulfill your requirements.
Procure your remedy with ease; https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/nizagara-25mg/ online to address your needs efficiently and securely.
Access genuine [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ – uk tretinoin without prescription[/URL – easily. Obtain this vital drug through the web seamlessly.
I discovered that purchasing [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – nizagara no prescription[/URL – can be effortlessly done via a digital pharmacy, ensuring that you receive your treatment swiftly.
Before deciding, compare the vpxl online canada , and check expenses online to ensure you’re getting the best deal for managing Alzheimer’s symptoms.
X-ray your options for managing OCD by visiting our website to find out the latest https://jawany.com/priligy/ .
Understanding the importance of securing your medications securely, there are multiple options available. When considering [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ – amitriptyline generic canada[/URL – , always consult your healthcare provider for the right course of action.
Secure your wellness and improve your vitality by purchasing the [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – retin a[/URL – for continuous satisfaction.
Protect your health by learning about the current health tips and trends at our prezzo nizagara 50mg website.
To manage Parkinson’s disease symptoms effectively, consider https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ as a budget-friendly option.
If you’re searching for an cost-effective solution to your vertigo, consider [URL=https://jawany.com/cipro/ – cipro 750 quanto costa[/URL – . This medication may assist in lessening the manifestations of dizziness, improving your life quality.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to acquire [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 400mg[/URL – online is crucial for patients.
Save on your next purchase with a zoloft capsules for sale . Uncover significant reductions on internet for your next medication.
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/pharmacy/ here. Instantly acquire your prescription digitally with ease.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – .
I discovered the best [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/zithromax/ – belgique zithromax[/URL – for improving male health online.
Residents in Columbus, Ohio, seeking immediate financial aid can explore flomax for reliable solutions.
Yes, acquiring https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ has never been simpler. Purchase your treatment now!
Your quest for enhanced vitality and performance ends here: [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – ivermectin[/URL – . Acquire your stash today and welcome revitalization.
Just discovered you can get [URL=https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ – price of sildalis[/URL – without the hassle through our reliable website.
Find trusted migraine relief with nolvadex 10mg . Purchase your solution online today.
Discover
Quickly purchase [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/product/super-kamagra/ – super kamagra to buy[/URL – , a necessary remedy for nausea.
For individuals seeking to buy ED medication, [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ – eriacta without pres[/URL – offers a discreet and convenient option.
X-plore cost-saving options for antiviral therapy; tadalafil online is your gateway to economical medical treatment.
Get immediate relief from your nasal allergies by opting to https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ . This solution can significantly reduce your symptoms, ensuring a better daily life.
Having difficulty finding your medication at local pharmacies? Buy your [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – cheap no prescription nizagara[/URL – without hassle.
Shop for herbal health remedies and boost your wellbeing today. Acquire the supplements at [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – , a reliable source for premium health products.
You can purchase your pharmacy without a persxritpion on the web, ensuring affordability and ease.
Boost your hair growth with affordable solutions like https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ . Discover a range of options and regain confidence without straining your wallet.
Discover the current [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ – buy hydroxychloroquine[/URL – and explore options for acquiring this treatment via the internet.
X-plore your options for hair loss solutions and purchase [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – order priligy online[/URL – securely.
Optimize your heart health regimen by exploring vardenafil 10mg , an essential option for those aiming to manage their stroke prevention strategy effectively. With a wide array of choices, acquiring this critical medication virtually has never been easier, ensuring that maintaining your cardiovascular well-being is both accessible and convenient.
Just uncovered a fantastic resource for wellness products at https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ , suitable for boosting your well-being.
Searching for a reliable source to purchase your cholesterol management medication? Look no further! Our [URL=https://seraamedia.org/lasix/ – buy lasix on line[/URL – offers an effective solution to control your levels efficiently.
Opt for the most economical solution to your health needs by securing [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady era to buy[/URL – today. Whether you’re aiming to improve your wellness effortlessly, our website offers a straightforward pathway to obtain your essentials.
If you’re searching to purchase Flagyl, look into flagyl best price usa for a straightforward option to receive your treatment.
X-plore your options for hypertension management by choosing to buy https://transylvaniacare.org/eriacta/ .
Various individuals search for methods to economize on their medication expenses. By using a [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ – lady era[/URL – , one may slash the price of your pharmacy bills.
Zero worries about aging signs with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/viagra/ – discount viagra[/URL – , as you acquire a route to youthful vibrance.
Explore secure options to order your pharmaceuticals online with our prednisone no rx source.
When looking to secure heart health medications, explore options to https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin-canada/ through digital pharmacies, offering a budget-friendly solution without compromising on quality and efficacy.
Find a way to buy [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix from india[/URL – with confidence.
Various medical professionals suggest seeking advice on bentyl sans prescription quebec for digestive issues to guarantee safe and effective relief.
Before deciding to obtain https://purefmonline.com/product/tadalafil/ , consider the importance of consulting a healthcare expert.
Revolutionize your argumentation skills with our comprehensive guide on crafting compelling narratives; access it [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/bentyl/ – bentyl without a doctors prescription[/URL – . Enhance your ability to sway any audience through efficient utilization of argumentative methods.
digitalshift.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Just looking for prolonged intimacy? Discover what you need with [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ – cheap doxycycline pills[/URL – , a premier choice for increasing staying power.
X-ray your options for cost-effective healthcare solutions by exploring the prednisone 40mg , an important item in your health kit.
Require budget-friendly solutions for your cardiovascular well-being? Explore a variety of options including https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ , perfect for sustaining your heart’s well-being.
Zillions seeking effective treatment for their condition can now order [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/product/vpxl/ – vpxl[/URL – , a dependable selection.
Nabbing your essential medical supplies has never been simpler. Purchase generic [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ – cheapest lasix[/URL – via the internet to ensure your health needs are met with quality and affordability.
Having trouble with an enlarged prostate? Learn how buy flomax online can help and restore your quality of life.
Your search for effective glaucoma treatment ends here. Explore https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ to discover your remedy for managing eye pressure.
Discover how [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin buy[/URL – can revolutionize the way you engage with betting.
I understand the importance of medication accessibility, thus highlighting the convenience of opting for home delivery methods. In this context, levitra generico low cost offers a seamless way to acquire your necessary medication without the hassle of visiting a pharmacy.
Having unexpected expenses? Secure a https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ right away to handle your financial necessities.
Understand your options for managing inflammation; explore [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – . Find budget-friendly solutions for your health care needs on the internet.
Preserve your health effortlessly by opting to [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/pill/vidalista-in-usa/ – vidalista non generic[/URL – , making it possible for you to procure your pharmaceuticals with ease from the convenience of your home.
Discover how flomax 0.2mg can alleviate symptoms of prostate enlargement by exploring our site.
When seeking effective antifungal treatment, consider exploring https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ for your healthcare needs.
Certainly, obtaining Etizolam-based medications has never been simpler. For those seeking relief, [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – offers a streamlined, secure, and diverse payment method spectrum. With an easy transaction, buy your essential prescription through the web.
Just in: Discerning shoppers can now locate the [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/vidalista/ – buy vidalista uk[/URL – on digital platforms, ensuring you get supreme value for your health-related necessities.
Unlock enhanced vitality and vigor; discover a renewed lifestyle with trazodone .
X-plore the myriad benefits of Amoxil for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your home medicine cabinet, https://phovillages.com/generic-amoxil-canada/ virtually can be a seamless process.
You can locate the most recent [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – by checking our site.
Searching for an reliable glaucoma treatment? Look no further! Find your [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/vidalista/ – vidalista on line store[/URL – immediately for ultimate eye health.
Get your daily Cialis conveniently and securely by clicking hydroxychloroquine 200mg . Whether you’re looking to purchase for individual use or addressing a problem, you’ll find premium options available on the web.
Boost your health with our comprehensive solution; https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/buy-lasix/ today and embark on a journey towards optimal well-being.
Looking for affordable medication? Find your [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix 40mg[/URL – here and cut costs on the treatment.
clicklance.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
When looking to purchase medication for rheumatoid arthritis, consider exploring options to [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – online tamoxifen no prescription[/URL – , ensuring you receive effective treatment without hassle.
Revitalize your vigor effortlessly with cenforce commercial , now accessible to purchase from the comfort of your home.
Now, discover the most cost-effective options for your treatment by exploring https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ . Secure your health needs affordably by acquiring your essential pharmacy needs online.
Acquiring [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – order retin a[/URL – online can be an effective method to ensure you obtain your prescription without hassle.
WildRose Lifestyle Online – Cozy, inviting atmosphere, browsing revealed a few standout items.
rankjet.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
nextclicks.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Combat eye ailments, specifically increased intraocular pressure, with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ – vidalista sale us pharmacy[/URL – , accessible for acquisition on the web.
Yes, if you’re looking to buy sildenafil , consider exploring our trusted source.
A comprehensive guide to managing narcolepsy: Explore how https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ can substantially enhance your daily functioning and life quality.
Yes, the Food and Drug Administration gives the nod to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – buy isotretinoin no prescription[/URL – for combating severe acne. This signifies a significant advancement in skin care.
ranklogic.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Secure your wellness journey with a click by opting to order your medication via our website at [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-tadalafil-in-canada/ – tadalafil online[/URL – , ensuring hassle-free access to health.
To get your health supplements with ease, simply navigate to our propecia to buy to find an extensive selection of options.
Zap your ED worries away! Get effective ED medication https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ . This treatment is reliable and simple to obtain.
Join our community to acquire your [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ – buy 75 mg viagra from india[/URL – and explore a broad selection for reproductive health products.
Zero in on wellness with our exclusive range of health solutions. Explore [URL=https://mynarch.net/drug/tretinoin/ – where to buy tretinoin cheap[/URL – and boost your well-being today!
I came across the best remedy for acid reflux with purchase flomax online . Buy it now for rapid relief.
You can obtain https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ , a trusted medicine for managing health issues.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/clomid/ – clomid[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous alternatives available online. Secure your fertility journey today by selecting the best deal.
A myriad of people seek trustworthy sources to purchase their medications. Discover how you can obtain your medications effortlessly through this vpxl discount coupons .
A detailed guide to accessing https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ is now available! Whether you’re looking to purchase or simply investigate options, this guide offers all you need.
Knowing your options for managing arthritis pain is key. Consider exploring [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – i want to order ventolin[/URL – , a potential alternative for alleviating discomfort.
If you’re searching for an effective remedy to tackle bacterial infections, consider [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – . This antibiotic is well-known for its potency against a wide array of bacteria.
Just realized you need ED medication for your well-being? No need to fret! You can pharmacy prices for cialis without hassle and safely.
Looking for a reliable source to acquire your medications without leaving home? Visit https://astra-hc.com/drug/cialis/ to secure your pharmacy needs via the web with ease.
Understanding the choices for managing IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ – bentyl[/URL – might offer you ease from abdominal discomfort.
Considering various options to control your BPH symptoms? Explore how you can acquire [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ – 0.4 flomax canadian[/URL – on the internet, offering a convenient solution to alleviate discomfort.
For those seeking cost-effective options for their medical requirements, the canadian pharmacy lasix might be a valuable exploration. This drug offers a variety of therapeutic benefits.
Quickly obtain https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ , a necessary treatment for upset stomach.
The requirement to purchase medication virtually has risen, and with options like [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – , securing your meds is simpler than ever.
Now, uncover the benefits of canadian pharmacy cheap generic viagra , and learn how it can assist in easing your discomfort.
Visit https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ and find a reliable way to obtain your medication digitally.
The acquisition of [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – on the internet provides an easy and effective approach to secure your hair loss remedy.
Your search for effective hair loss solutions ends here with [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ – cipro without a doctor[/URL – . Explore the benefits of this effective solution for male pattern baldness today.
Acquiring online prednisone 40 purchase could assist in enhancing cardiovascular wellness.
Considering various options for motion sickness relief? Discover the https://astra-hc.com/drug/prednisone-10mg/ to effectively manage your symptoms. Explore other solutions right away.
Considering requirements for affordable treatments, you can now order [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ – amoxil 650mg[/URL – , a popular alternative for those seeking cost-effective calcium supplementation.
Obtain your prescription for amoxicillin 500mg with ease, ensuring you receive real medication. Buy safely and securely through our website.
Getting your hands on https://shilpaotc.com/nizagara/ could never be easier. Order this essential treatment online to treat schizophrenia symptoms efficiently.
Obtain ease from bowel sluggishness efficiently with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ – mail order kamagra[/URL – . This remedy is perfect for individuals looking for a gentle approach.
You can purchase [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ – isotretinoin[/URL – for improving your well-being directly through our website.
Discover how buy branded Allegra on the web with our straightforward guide. order deetor .
Obtain the solution for better female health with https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ , available online.
Knowing the crucial nature of keeping updated about treatments, it’s essential to research [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – lasix liquid[/URL – for detailed insights.
Manage your nausea effectively; [URL=https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – immediately and experience relief from vomiting indications.
Questioning where to purchase your next medication? Explore the options and benefits of lowest price generic flomax for all-inclusive HIV treatment solutions.
Buy misoprostol directly from https://jawany.com/cytotec/ for managing your health efficiently.
Seeking to acquire hormonal balance treatment? Locate your solution with [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – cialis black information[/URL – , an exceptional choice for better well-being.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ – flomax 0.4mg tablets price[/URL – might be your solution. Explore how it can assist in alleviating your symptoms effectively.
Browse our site to find amoxil without prescription , ensuring you get top-quality antibiotic options at matchless prices.
Researching options to secure https://center4family.com/kamagra/ ? Consider our trusted source for your medication needs, providing a wide range of pharmaceuticals with reliable delivery options.
Looking for the most economical options to augment your confidence? Discover your solution [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ – cost of prazosin tablets[/URL – today and start your journey to feeling your best.
Acquiring your vardenafil without an rx just became more straightforward. Now, grab your supply effortlessly.
Zealously looking for a reliable solution for infertility treatment? Find your answer and https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ , providing a superior alternative for fertility challenges.
Acquiring [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/ – order maxaquin online[/URL – has never been more convenient. Secure your dose with ease and experience swift, trustworthy delivery straight to you.
When looking to purchase allergy relief, consider [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – amoxil 650mg kaufen net[/URL – as your go-to solution for alleviating symptoms.
Explore budget-friendly options for your healthcare needs by deciding to vidalista .
Harness the potential of convenience by choosing to secure https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista-com/ online, ensuring a hassle-free process for handling hair loss.
Xperience alleviation from arthritis symptoms when you order([URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ – generic nizagara uk[/URL – ) online.
Be mindful about your health, and purchase a reliable HIV detection solution. Don’t wait; [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine.com canada[/URL – now and ensure your well-being.
Alleviate allergy symptoms with affordable options; buy nizagara via the internet.
Be informed regarding your health status from home by selecting an https://center4family.com/ventolin/ . This accessible method offers privacy and quick results.
Access effective treatment quickly and safely by choosing to procure your medications through our web platform. For those in need immediate treatment, [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/tamoxifen/ – tamoxifen[/URL – offers a reliable solution.
Your search for Procure asthma treatment ends here. Discover budget-friendly options on our site asthalin from canada pharmacy .
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Look no further. Get https://seraamedia.org/item/amoxicillin/ safely and swiftly.
To increase your endurance, think about [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/canada-doxycycline/ – doxycycline without prescription pharmacy[/URL – for a trustworthy solution.
Quickly and conveniently order your antiviral pills prednisone without an rx .
Managing ADHD symptoms can be challenging, but with the right medication, it’s possible to lead a balanced life. For detailed insight on one effective treatment, visit https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ . Whether you’re looking into starting treatment or seeking alternatives, it’s crucial to stay informed.
Explore unbeatable prices on fertility drugs at [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ – lowest price for tadapox[/URL – , the leading destination for enhancing your chances of starting a family.
To enhance one’s performance, consider tadapox soft tabs uk buy as a trustworthy solution.
Seeking a remedy for hair loss? Discover how to buy https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ , a effective method to fight balding securely.
New to the market? Discover the pathway to wellbeing with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – zoloft capsules[/URL – . Acquire this advanced solution instantly for your medical needs.
Opt for [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – furosemide[/URL – and save on necessary medicine.
Understanding the necessity for swift antimalarial medications, it’s pivotal to source a dependable supplier. With that in mind, procure your prednisone immediately for effective remediation.
Having trouble searching for a reliable source for your bone health medication? Find https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ to buy your treatment with confidence.
Secure your essential medications effortlessly by choosing to purchase from [URL=https://mynarch.net/item/super-force-jelly/ – super force jelly walmart price[/URL – .
Having trouble sleeping? Explore multiple effective methods to improve your sleep experience tonight. From establishing a consistent sleep schedule to reducing screen time before bed, these tips are straightforward. For those seeking additional help, consider eriacta , a choice that many have found beneficial. Remember, a peaceful sleep is within reach.
Get your daily health boost with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra/ , offering quick results.
Discover the most up-to-date [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia 1mg[/URL – and explore alternatives for purchasing this drug through online pharmacies.
Have a need for antimicrobial medication? Procure your prescription effortlessly by [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ – sildalis coupons[/URL – .
I’ve discovered where to acquire buy zithromax . This platform offers a plethora of selections for those seeking to order their drugs online with ease and confidence.
Aordable solutions for dry eyes are now within reach. Explore our selection and order a solution for soothing relief. Find https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ on our website today.
Zero in on eye health: Obtain [URL=https://primerafootandankle.com/item/vidalista/ – vidalista canadian pharmacy[/URL – to control glaucoma effectively.
Unlock exceptional health benefits by exploring our vast array of options to purchase [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin 20g[/URL – , ensuring you get high-quality products tailored to your needs.
Managing ADHD symptoms can be challenging, but with the right medication, it’s definitely within reach. Explore your options and discover how nizagara 50mg can be a major benefit in your treatment plan.
Browse our site for competitive https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ and explore a multitude of alternatives to obtain your medication.
You can obtain [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/tretinoin/ – tretinoin[/URL – via the web, ensuring a safe and easy way to treat your health needs.
Invest in your health by choosing [URL=https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ – lowest price generic priligy[/URL – for high-quality cholesterol management solutions. This pill is formulated to lower your cholesterol levels safely.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re looking to purchase for your personal health needs, amoxicillin best price online can be a seamless process.
Browse our online pharmacy for top-quality healthcare solutions. Order your https://embcselma.org/product/levitra/ right here, ensuring secure and swift delivery to your doorstep.
Unsure where to procure your medication? For those looking to enhance their health, [URL=https://phovillages.com/amoxicillin-generic-pills/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – offers a vast range of options.
Facing challenges with high prolactin levels? Discover where to buy azithromycin , an reliable treatment to control it.
One can find competitive https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ and multiple selections on web platforms, ensuring economical options and availability.
Nourish your vitality effortlessly with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ – nizagara[/URL – , a zenith of wellness. Obtain your potent blend virtually.
Looking to acquire allergy relief without breaking the bank? Click here to [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone 10mg[/URL – and start experiencing relief today.
Quickly secure retin-a gel to guarantee your well-being needs are satisfied efficiently.
Navigating through numerous sources to purchase your medications can be challenging, but our https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisone-40mg/ simplifies the process, offering secure and cost-effective options for your healthcare needs.
Curious about enhancing your vitality? Consider trying out [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ – topiramate for alcohol dependence[/URL – . This medication, available for purchase, might just be the answer for those seeking to enhance their wellness.
Purchase the essential vertigo relief medication with a click: sildalis . Secure a reliable and safe choice for tackling signs.
Your quest for budget-friendly heart medications ends today! Secure your dose of https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/ventolin/ right here! Wide-ranging options to obtain your critical therapy easily await.
Uncover the most affordable way to manage your health, purchase [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone[/URL – on the web. This option offers not just convenience but also savings.
Knowing the importance for reliable hair loss treatments, men can now get esomeprazole Buy this effective solution on our site for managing their hair loss concerns.
Considering the urgent need for heart rate control in hypertension and angina, acquiring https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ has never been more vital. This choice not only offers convenience but also ensures one obtains quality treatment from the comfort of your home.
Obtain your health supplements at unmatched rates, visit [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ – cuanto cuesta el flagyl de 200[/URL – today! Explore a spectrum of options for your wellness regimen effortlessly.
Keeping your fertility in check is crucial. Discover choices like [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – that offer hope for many.
Venture into enhancing your health effortlessly; find cheapest 50 mg nizagara delivered overnight for your wellness needs. Acquire it online and embrace a healthier lifestyle today.
Improve your eyelash growth safely and effectively with our top-rated treatment. Acquire your supply through https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ , offering a hassle-free purchase experience.
Quest for budget-friendly ED treatments? Find your solution at [URL=https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – , offering a vast range of top-notch choices.
Discover excellent options for managing your condition efficiently with cialis . Improve your well-being now.
Need fast relief from allergies without the hassle of a doctor’s visit? Explore our assortment of https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ options. Purchase conveniently via our online store for speedy allergy relief.
Unlock unparalleled convenience by ordering your medications via [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – generic tadalista[/URL – . This streamlined process ensures an effortless path to obtaining the needed medical products.
Check up-to-date [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ – buy tretinoin[/URL – for managing HIV.
Renew your vitality and feel young again; priligy online . Experience a rejuvenated life by choosing to buy this unique supplement today.
Discover excellent choices for managing your health issue efficiently with https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ . Improve your health now.
Visit [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ – sarafem lowest price[/URL – to obtain your prescription without hassle.
Victims of menstrual irregularities can now find relief. Visit our website to order [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – , offering a promising solution for discomfort and imbalance.
Discover reliable solutions for erectile dysfunction with viagra 25 dubai . Obtain your treatment effortlessly.
Managing hair loss effectively is now hassle-free with the right treatment. Explore several options and consult healthcare professionals to discover what works best for you. For those considering medication, https://glenwoodwine.com/zoloft/ could be a viable solution.
Acquiring [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/tretinoin/ – pilule tretinoin[/URL – has never been more convenient. Order your dose with ease and experience swift, reliable delivery straight to you.
Leverage your health management by securing your supply of crucial medication. Purchase prednisone 10mg effortlessly from credible sources, ensuring your well-being is always at the forefront.
Understanding the need to obtain medication easily, our platform allows you to https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ without any hassle.
The buying of [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/drugs/furosemide/ – lasix.com lowest price[/URL – via the web offers an easy and efficient approach to get one’s hair loss solution.
Discover affordable solutions to your healthcare needs with [URL=https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/ – sildalist generic canada[/URL – . Buy your medications easily on the web and experience both quality and savings.
Your search for effective glaucoma treatment ends here. Explore generic flagyl canada pharmacy to discover your solution for managing eye pressure.
Considering immediate antibiotic needs, acquiring https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ through the internet ensures an expedited solution.
Having issues with insomnia? Consider exploring the benefits of [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/nizagara-coupon/ – nizagara 25mg[/URL – . Get the solution now from a reliable source.
Quickly discover the essential hypertension relief with [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – generic viagra from canada[/URL – , on offer at unbeatable prices.
Your health is our top priority. Explore how generic pristiq canada can help in avoiding stroke. Purchase now for a better tomorrow.
Just discovered your solution to erectile dysfunction? Explore our extensive https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ , including a variety of options to meet your needs.
Obtaining [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/pristiq/ – buy pristiq[/URL – for alleviating inflammation and pain is straightforward. Procure it on the internet for prompt relief.
The Quick Extender Pro provides become probably the most talked-about
traction devices among men buying slow-moving, natural and routine-based approach to personalized improvement.
Many individuals searching for a Rapid Extender Pro evaluation want to understand how the device
works, the actual traction method actually means, in addition to whether long-term regularity can cause meaningful advancement.
The inspiration of this device could be the traction method, an idea employed for many
yrs in orthopedics in addition to physical therapy. Traction involves applying
gentle in addition to continuous stretching to soft tissues, pushing
gradual adaptation more than time. When utilized properly, this low-intensity method can support tissue elongation, but
it really calls for patience, discipline and steady use, which usually is why typically the Quick Extender Expert routine is usually discussed
in detail by users who may have tried out it for many
weeks.
I unearthed the best option to manage my health concerns: [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/kamagra/ – buy cheap kamagra 50 mg[/URL – . This platform offers outstanding prices.
Your search for an effective solution for early climax ends here. Buy buy dapoxetine online canada , a trusted medication, on the web.
Buyers interested in acquiring https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax/ could easily Secure their Prescription through trusted online platforms, ensuring quick and secure delivery to their doorstep.
Patients seeking to manage Hepatitis C can find [URL=https://renog.org/product/amoxil/ – amoxil canadian pharmacy[/URL – online. This treatment option is available for those looking to lower their healthcare expenses efficiently.
Research and discover the benefits of xenical 120mg for enhancing fertility. Acquire it through our website to start your path to parenthood today.
Various individuals seeking relief from ocular hypertension or glaucoma now have the option to purchase an affordable alternative with https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ , providing a cost-effective solution for managing their condition efficiently.
Looking for an effective and budget-friendly pain relief solution? Find high-quality treatment options and [URL=https://phovillages.com/canada-xenical/ – xenical[/URL – online.
Venture into health management by exploring options to acquire affordable medication for arthritis relief. Discover more and make an informed choice today by visiting [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ – tadapox from us[/URL – .
For comprehensive insights on health and wellness, explore cheap 40 lasipen online .
Purchase your essential dizziness relief treatment with a click: https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ . Secure a reliable and safe option for managing signs.
In search of affordable eye relief? [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ – viagra 50mg[/URL – today and experience the difference!
Knowing how to control hypertension is critical. Acquiring asthalin 100mcg via web could be the start in a more controlled lifestyle.
Zeroing in on treatment for severe acne? Find how https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ provides effective option.
When in need of urgent options, find [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – for your necessities.
You can purchase Fildena for your ED needs here: fildena.com .
Xperience relief without the wait; explore https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ for a seamless solution to enhance your life today.
Very often, individuals seek cost-effective solutions for their medical needs. Discovering a reliable platform to purchase essential medications can significantly reduce expenses and ensure consistent quality. For those looking to buy their pharmaceuticals conveniently, opting to [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ – priligy[/URL – can be a remarkably prudent choice, offering both affordability and the assurance of receiving genuine products.
Удивительно, как разные люди по‑разному решают одни и те же задачи. Я за практичность: в любом деле и на дороге. Потому у меня в багажнике всегда лежат цепи противоскольжения.
Unlock exceptional deals on [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ – cenforce commercial[/URL – , your optimal choice for removing ED symptoms. Secure yours today for better health and happiness.
Keep your vitality at its peak: uncover safe and reliable options to buy sildenafil .
Just discovered you can locate https://brightnights915.com/drugs/canada-lasix/ for relieving constipation.
Unlock unparalleled convenience by opting to acquire your medications with ease and without a doctor’s order at [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/item/nizagara-100mg/ – nizagara from costa rica[/URL – . Experience hassle-free access to top-notch healthcare products from the comfort of your home.
Our team has sourced the [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil/ – tadalafil my canadian pharcharmy[/URL – for patients seeking affordable treatment options. Obtain your medication without overpaying by exploring the various cost-effective alternatives available through our platform.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, lasix without prescription offers a convenient way to secure necessary medication from the comfort of your own home.
Learn more about managing your medical conditions with https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ . Uncover how it can benefit you in regulating hormone levels.
Secure affordable solutions for enhancing your vision by exploring the [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxil/ – venda amoxil[/URL – . Our specially formulated drops offer an optimistic approach to enhancing eye health considerably.
X-ray your options for effective bacterial infection treatment, and find how you can obtain [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ – flagyl[/URL – via the web to fight against your symptoms efficiently.
With the recent quest for cost-effective malaria treatment options, securing nizagara price walmart has never been more important.
Get your antimicrobial conveniently when you buy https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/generic-flagyl-online/ .
Browse our website to locate your required medications at an affordable price. Purchase [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ – where to order tadalafil on line[/URL – today and receive quick delivery.
Regain confidence in the bedroom with the [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/lyrica/ – buy lyrica w not prescription[/URL – , your discreet solution to enhanced performance. Secure your order today for an enhanced experience.
Revitalize your vitality and enhance your performance in the bedroom with buying prednisone online . Experience a surge in your libido like never before. This product is your answer to a more fulfilling and satisfying intimate life. Say goodbye to hesitation and hello to a renewed you.
Having trouble finding affordable treatment options? Look no further for https://breathejphotography.com/lady-era/ . Secure your essential medication at a cost-effective price.
Visit [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy med uk[/URL – to acquire your Augmentin solution at the lowest cost.
Visit our [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – page to obtain effective heartburn relief. Easily order your remedy from home.
Curious about enhancing your vitality? Consider trying out prednisone 20mg . This medication, available for purchase, might just be the solution for those seeking to boost their wellness.
Looking for a reliable source to purchase your medication? https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ offers an straightforward way to obtain your prescriptions with just a few clicks.
Looking to control your IBS symptoms? Find out about how [URL=https://sadlerland.com/product/bentyl/ – generic bentyl canada pharmacy[/URL – can offer respite.
Поради для інтернет-користувачів — корисно і без моралей.
Having heart rhythm issues? Think about [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/drugs/priligy-dapoxetine/ – priligy with cialis in usa[/URL – for an effective solution.
Your search for affordable medication ends here with our nexium from india , offering a budget-friendly option to treat your needs efficiently.
Consider securing your https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ effortlessly. Obtain your treatment with ease.
You can acquire [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex in usa[/URL – , a trusted medicine for managing ailments.
Looking to enhance your well-being? Discover how to get your needs without hassle with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ – cialis without prescription[/URL – .
To acquire Azithromycin without a prescription, follow this link lady-era paypal canada for trusted options.
Unlock potential savings on eye care medication by exploring your options. Find an affordable solution at https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ . Purchase your prescription online, ensuring cost-efficiency and safety.
Harness optimal wellness with natural solutions; discover ways to [URL=https://phovillages.com/retin-a-online-canada/ – retin a[/URL – for seamless digestive health support.
ндс как уменьшить сумму налога Налоговая оптимизация НДС требует глубокого понимания налогового законодательства и умения применять его на практике. Необходимо учитывать все нюансы и изменения в законодательстве.
If you’re in the market for an effective solution to combat bacterial infections, think about [URL=https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ – buy amoxicillin uk[/URL – . This medication is well-known for its effectiveness against a wide array of bacteria.
Sure, learn how to obtain kamagra prices via our digital platform.
Obtain your prescription effortlessly at https://airjamaicacharter.com/item/bentyl/ , the leading site for competitive prices on pharmaceutical products.
Unlock remarkable savings when you purchase your eye drops via the internet. For relief from allergic reactions, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ – lasix paypal accepted[/URL – today.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for buying overnight at [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/tadalista/ – online tadalista[/URL – .
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with flomax tablets 0.4 mg price , and explore a range of options to better your quality of life.
Visit https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ today and locate affordable options for managing your pain.
Understanding the need for accessibility, you can now purchase your prescription through the internet with ease. [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/fildena/ – fildena[/URL – and experience quick shipment to your doorstep.
Many are looking for reliable solutions for erectile dysfunction, and [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – provides a tested option.
Boost your eye health easily; simply generic prednisone at walmart online. Achieve optimal ocular pressure relief with a click.
X-plore options to acquire hormonal treatment safely from your home by clicking https://griffindtc.com/priligy-60mg/ .
Having trouble managing your mood swings? Discover your solution with [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – prednisone without dr prescription usa[/URL – , accessible immediately. Obtain proven relief effortlessly of a prescription.
I discovered the [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine[/URL – after searching numerous websites.
Now, find the best deal on nexium without a prescription , available for buying on the web.
Given the ongoing discussions about its use in various treatments, finding a reliable source to purchase https://masseysjewelers.com/strattera/ online is crucial for patients.
Buyers seeking effective treatment for their condition can purchase [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ – nizagara without a prescription 25[/URL – through our website.
Before opting for conventional methods, explore other avenues to acquire your medications. One reliable option is to [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-best-price-usa/ – where to buy levitra in thanet[/URL – , offering a straightforward way to manage your health.
X-plore the benefits of amoxicillin 500mg capsules for sale for bacterial infections; discover how it can help in fighting a range of conditions.
Keeping your health in optimum condition is crucial. For those seeking efficient solutions, https://nwfgenealogy.com/lasix/ offers a convenient way to obtain necessary medication from the comfort of your own home.
Pain relief for arthritis can be conveniently secured through various online platforms. Whether seeking to purchase this pain reliever, patients now have the luxury to obtain their prescriptions [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – cheapest celebrex[/URL – with ease, ensuring their comfort and well-being are promptly addressed.
X-plore affordable steroid treatments and economize on healthcare expenses by opting to overnight viagra soft tabs for managing allergies.
Discover safe and private options to acquire your treatment without complications. Click here: https://tv-in-pc.com/buy-cheap-viagra/ .
Visit [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin information[/URL – to buy your antibiotics online at unbeatable prices.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Consider [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/cialis/ – lowest price on cialis 5 mg[/URL – – your go-to option for restoring health.
Explore premier pharmacy italien for a thrilling adventure.
Your search for affordable, high-quality cognitive enhancers ends here; https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ offers unparalleled value. Explore purchasing solutions for improving your memory and concentration without breaking the bank.
Shopping for [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – ? Secure your dose online for effective malaria prevention.
You can uncover affordable options for managing your urinary symptoms with propranolol .
Unveiling the convenience of modern technology, one can acquire erectile dysfunction medication via the web at https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ , ensuring privacy and ease.
Vital for managing HBV, [URL=https://purefmonline.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – is imperative. Secure your medication easily today.
Discover leading costs for [URL=https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin[/URL – and save your costs.
Acquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting hydroxychloroquine walmart price .
View the latest prices for managing your BPH symptoms with https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ , and explore various options to enhance your quality of life.
Uncover affordable alternatives for managing edema and hypertension with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil from india[/URL – , ensuring you get value without overextending your budget.
Secure
Seek the lasix without dr prescription efficiently. Discover your ‘must-have’ medication at a budget-friendly price.
Looking for a natural way to enhance your energy and reduce stress? Consider the benefits of https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-without-dr-prescription/ , a herbal solution used for centuries in Ayurvedic medicine.
When looking to obtain [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/]order retin-a in uk[/URL] , ponder numerous platforms supplying it on the web.
Discover a hassle-free way to obtain your prescription with 50mm viagra to purchase , ensuring privacy and convenience in purchase.
Buy misoprostol directly via https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ for managing your health efficiently.
Procure your drug at reduced rates; [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ – zoloft commercial[/URL – offer multiple cost-effective solutions.
Just discovered you can secure order prednisone online effortlessly through our reliable portal.
Looking to control your symptoms effectively? Discover the affordable https://fleurandarbor.com/amoxicillin/ and start your journey towards better health now.
Various individuals are navigating the process to secure essential medications with convenience. If you’re aiming to obtain Losartan without a struggle, [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – is your go-to resource.
Your search for an effective treatment for premature ejaculation ends here. Buy cheap dapoxetine pills , a proven medication, on the web.
Discover cutting-edge treatments for your health. Purchase https://swanpercussion.com/item/trazodone/ from trusted sources on the web.
When considering therapy options for prostate cancer, considering medication options is key. Locate reliable options for management with [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – vendita pharmacy[/URL – .
When looking to purchase efficient wakefulness-promoting agents, consider [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ – nizagara 25 mg online without prescriptions[/URL – for your requirements.
Acquire your prescription conveniently with our safe online platform. Discover the advantages of vidalista canadian pharmacy .
One can discover competitive https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ and diverse options in digital pharmacies, ensuring affordability and accessibility.
Your search for effective medication ends here; discover the best deals to purchase [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 200mg[/URL – safely online.
Forest Goods Spot – Smooth browsing experience, with affordable items clearly presented.
Combat baldness effectively! Uncover how [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – can help you in regenerating your locks to their former glory.
X-plore the therapeutic options for managing Addison’s disease; fildena online pharmacy stands out as a top choice. Its efficacy in balancing electrolyte levels and reducing symptoms is unparalleled.
Planning for an emergency cash support in the Lone Star State? Explore your options with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/nizagara/ ; a swift method for your financial necessities.
Discover the most up-to-date [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 200mg[/URL – and explore choices for purchasing this treatment through online pharmacies.
For medical specialists seeking to improve their knowledge, look into enrolling in [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – courses offered on the web.
Find trusted migraine relief with prednisone . Order your remedy online today.
Hoping to enhance your wellness with nature’s bounty? Discover the array of options and uncover competitive https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ to boost your health regime effortlessly.
Visit [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone/ – prednisone in farmacia[/URL – to secure your medication with ease.
Exploring treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? Discover how bentyl can aid in reducing urinary symptoms related to an enlarged prostate.
Ensure you obtain the most affordable price for https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil-without-an-rx/ by searching through our options.
Knowing the significance of keeping updated about treatments, it’s critical to investigate [URL=https://umichicago.com/sildalis/ – sildalis online[/URL – for comprehensive details.
With just a few clicks, you can effortlessly secure your prescription for [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – buy vidalista online[/URL – , a vital solution for handling acid reflux conditions.
Discover budget-friendly solutions for managing your heart health with buy vidalista online . Secure your batch immediately and embark on a journey toward better cardiovascular health.
Unlock the secret to enhanced stamina by selecting to https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ , your leading source for high-grade wellness solutions.
Understanding the need for affordable healthcare solutions, one can obtain budget-friendly HCG injections effortlessly. For those seeking to boost their reproductive health, [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ – nizagara[/URL – offers a viable option.
Understanding the options for controlling IBS can be overwhelming. Discover how nizagara might provide you ease from stomach discomfort.
Your health is our priority; buy https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ on our site and start your journey to improved health today.
Secure your [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 500mg[/URL – with ease. Procure this medication through our web portal efficiently.
Reveal the secrets to supreme health with our exclusive handbook at [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – non prescription retin a[/URL – . Learn how to maximize your vitality with practical tips and insights from specialists in the field.
Obtain your health supplements at unmatched rates, visit hydroxychloroquine 400mg today! Explore a spectrum of options for your wellness regimen effortlessly.
Zeroing in on reliable options for ED, acquiring https://brightnights915.com/drugs/where-to-buy-viagra-online/ is a secure choice.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/lasix/ – furosemide[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous alternatives available on the web. Secure your well-being today by opting for the best deal.
Just discovered you can locate [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – for easing constipation.
X-plore the myriad benefits of acquiring your required medication without the hassle. Secure amoxicillin easily from reputable sources.
People seeking relief from eczema can look into https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/buy-generic-kamagra/ for their management options.
Revitalize your intimate experiences with our exceptional offer: [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – alternative doxycycline[/URL – . Rekindle the spark now and acquire your solution online.
Explore the myriad benefits of vital health supplements by opting to acquire your needs from the renowned [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/product/nizagara/ – cheapest nizagara[/URL – .
Just realized you need ED medication for your health? No need to fret! You can cialis 5 israel simply and safely.
Discover incredible savings on your healthcare necessities. Locate the https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ and maintain your well-being without hassle.
For anyone looking to reduce their nasal congestion, getting a [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – comparison is key.
Quality education is pivotal, and understanding the art of persuasion can be significantly enhanced by reading [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/retin-a-without-a-doctors-prescription/ – retin a[/URL – . This method not only sharpens your authorship skills but also expands your understanding of various viewpoints.
Unlock savings on your hypertension treatment by visiting prednisone , your gateway to cost-effective medication.
Affordable healthcare is now accessible, buy your prescription through the internet with https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ .
A quick, effective treatment for alleviating pain is readily available through [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – buy lasix[/URL – . Get yours on our site today for swift shipment.
If you’re looking for an effective solution to combat bacterial infections, think about generic amoxicillin from india . This drug is well-known for its potency against a broad range of bacteria.
Reduce your cholesterol levels conveniently by opting to order your medication through https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ , ensuring effective and fast delivery to your doorstep.
Managing hair loss effectively is now hassle-free with the right treatment. Explore multiple options and consult healthcare professionals to discover what works best for you. For those considering medication, [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/retin-a/ – retin a non generic[/URL – could be a viable solution.
Explore the diverse options to purchase your prescriptions retin a coupons with ease via our protected portal.
I discovered that purchasing https://nwfgenealogy.com/prednisone-price-at-walmart/ can be effortlessly done through the web, ensuring that you receive your treatment promptly.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Acquire [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/amoxil/ – amoxil 250mg[/URL – safely and quickly.
X-ray your budget and uncover how much you could save on ocular treatments by checking the [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – .
Discover excellent choices for managing your condition efficiently with prednisone cheap . Boost your lifestyle today.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, https://suddenimpactli.com/amoxil-lowest-price/ is a viable option. Discover purchasing this antibiotic via online pharmacies for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Secure
The importance of consulting a healthcare professional before you acquire [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/genegra/ – genegra from india[/URL – cannot be overstated.
Looking to boost your well-being? Discover how to secure your needs easily with cialis commercial .
Never overlook your need for effective rest solution. Find out about the revolutionary https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ , a revolution in securing a restful night’s rest.
Your search for a safe, effective method to enhance your intimate life ends here. Buy your [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – sildenafil[/URL – today and feel the difference firsthand.
Patients seeking anxiety relief can discover options on websites including [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – buy non-generic stromectol online[/URL – , a trusted treatment.
Research the most economical options for managing hypertension by visiting generic cialis canada , offering you a diverse range of costs to fit your budget and health needs.
Looking for doxycycline? Secure it without needing to visit the doctor through this https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/doxycycline/ . Acquire the medication with ease and start treatment immediately.
Considering various options for motion sickness relief? Discover the [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/pharmacy-prices-for-kamagra/ – online doctor kamagra[/URL – to effectively manage your symptoms. Explore alternative solutions now.
For those in need of immediate relief, purchase [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ – amoxicillin 250mg[/URL – . This analgesic can provide fast and effective comfort from discomfort.
Visit our website to acquire your essential health supplements with ease, including nizagara capsules for sale , designed to support urinary tract function.
To obtain genuine Etibest quickly, go to https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ today for reliable transactions.
Get alleviation from allergic reactions with a trusted solution. Find [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – canada pharmacy nizagara[/URL – for immediate relief.
Cut down on your healthcare expenses by obtaining your [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cytotec/ – generic cytotec from india[/URL – here! Now you can secure significant savings on your medicine expenses.
Regarding Alzheimer’s disease treatments, exploring options for medication is crucial. For those considering Donepezil, order 20 mg prednisone cheap online offers a diverse range of options.
Get affordable treatments for your health needs. Explore https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ to manage your conditions with ease.
Visit [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ – lowest price prazosin[/URL – to secure your prescription easily.
Finding the best deal for purchase lasix online can be challenging. To get your batch, order via the internet and ensure you’re getting both quality and economy.
X-plore the benefits of managing your nasal symptoms with our high-quality solution. Whether you’re looking to treat your hay fever, our https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ can offer you respite.
Just when you’re looking to acquire an effective treatment for anxiety, consider exploring [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – europe lasix[/URL – , available on the web.
Revitalize your health by exploring a wide spectrum of pharmaceutical options. Enhance your well-being by visiting an extensive selection of healthcare solutions. Don’t compromise on your health; discover everything you need at [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – generic prednisone 10 mg cheap for sale[/URL – .
Struggling with hair loss? Discover buying finasteride online uk , a top choice for tackling hair thinning. Order these tablets immediately and begin your journey to regrowth!
Looking for an effective, budget-friendly solution to boost your wellbeing? Explore our vast selection of natural supplements and secure your https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ today for enhanced health and vitality!
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine online usa[/URL – here. Instantly acquire your prescription digitally with ease.
Struggling with hair loss? Discover finasteride price at walmart , a top choice for tackling baldness. Acquire them today and commence your journey to regrowth!
Ready to secure your health essentials at an unbeatable cost? Visit our site for the https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ , ensuring you acquire premium medicinal supplies without a hefty price tag.
Discover a convenient way to acquire the prescription with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – order nexium[/URL – , securing convenience, privacy, and confidentiality.
Looking to cut down on your healthcare expenditures? Discover the [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine[/URL – to budget on your medication.
Discover secure strategies to treat endometriosis symptoms. For individual treatment options, prednisone can be found on sites.
To control Parkinson’s disease symptoms effectively, explore https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ as a budget-friendly option.
I discovered an unbelievable source for [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/prednisone/ – prednisone without a prescription[/URL – .
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our all-encompassing selection of affordable treatment options. Locate [URL=https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ – cialis pills[/URL – to boost your vitality efficiently and securely.
“Quickly locate savings on your next purchase with vardenafil cost . Save without hassle on essential medication.”
Searching for a reliable source to obtain your cholesterol management medication? Look no further! Our https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ offers an effective solution to regulate your levels efficiently.
Quickly acquire your parasite treatment without hassle by choosing to [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/product/buying-prednisone-online/ – prednisone coupon[/URL – .
Elevate your vitality effortlessly with an array of natural solutions ready at your fingertips. Simply no prescription prednisone to embark on a journey towards elevated health and wellbeing.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ , your go-to source for acquiring potent ED solutions online.
Having difficulties obtaining your prescription? Look into [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/tamoxifen-without-pres/ – buy generic tamoxifen[/URL – for a hassle-free purchase.
X-plore affordable options for boosting your eyelashes with fildena . Find a range of approaches to attain the appearance you want.
Get alleviation from anxiety without the need for a prescription. Discover https://swanpercussion.com/tadalafil/ today for your peace of mind.
Zest your getaway with an excursion to the famous [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , offering an unforgettable experience.
Looking for urgent financial support? Find out more about [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – non prescription tadalafil canada[/URL – options right away!
Naturally supporting prostate health is essential for men’s well-being. Discover how lady era uk could be your partner in maintaining optimal prostate function.
Harness the power of modern medicine safely; order https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ online for your medical needs.
Many people look for effective remedies for bacterial infections. Whether you’re dealing with skin conditions, respiratory infections, or STIs, [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/doxycycline/ – doxycycline[/URL – provide option.
Unlock the potential of antiviral therapy by choosing to generic stromectol in canada . Ensure optimal health outcomes by procuring this essential medication through our platform today.
I was pondering about the expense of health treatments when I stumbled upon the https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/nizagara/ . This treatment is commonly prescribed for handling gallstones.
Obtaining your [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – prescription is more straightforward than ever! You can now acquire your medication with just a few clicks.
Buy misoprostol directly via [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – cytotec[/URL – for managing your health efficiently.
For individuals seeking reliable pain relief, consider trying levitra , an innovative method.
When managing joint pain, consider exploring your alternatives with https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ , a proven treatment.
Explore affordable options for your healthcare by choosing to order [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/stromectol/ – discount 6mg stromectol[/URL – .
I located an unbelievable source to [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – extra super avana uk[/URL – .
Secure your health effortlessly; acquire pharmacy prices for extra super avana , a cure for enhanced vitality.
For health practitioners looking to advance their knowledge, look into enrolling in https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ programs offered on the web.
Obtain your [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin price at walmart[/URL – effortlessly. Acquire the critical medication without hassle.
Reap the benefits of cost-effective healthcare solutions by opting to [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – . Secure your prescription with convenience today.
For individuals looking to cut costs on their healthcare expenses, securing a zoloft could be immensely beneficial. This offer applies to a range of medications, potentially lowering your financial load.
Prices for corion injections are surprisingly affordable at https://center4family.com/ventolin/ , especially when searching for cost-effective fertility solutions.
Here’s how to discover the current [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – to conserve on your treatment.
Are you struggling to find quick relief from asthma at night? Our store offers a fast solution with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/asthalin/ – asthalin on line[/URL – . Now, secure immediate alleviation and breathe easier by ordering your remedy on our website.
Battling dizziness or nausea? viagra today to Relieve your symptoms quickly and effectively.
Before making a decision, research https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ to grasp how it may assist you.
Seeking a solution for hair loss? Find out how to buy [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/finasteride/ – finasteride 5mg[/URL – , a effective method to combat balding securely.
Need affordable medication? Explore generic options with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone for sale[/URL – , ensuring you get quality treatment without spending a fortune.
Procure your medication with convenience and confidentiality; prednisone directly with just a few clicks.
Be vigilant about your well-being, and purchase a reliable HIV detection solution. Don’t wait; https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ now and guarantee your well-being.
Secure a hassle-free way to purchase your medications with [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – , offering an easy method for your health needs.
Unlock your pathway to better health with our trusted solution. Buy your [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/fildena/ – cheap fildena pills[/URL – online and begin your journey towards improved wellbeing.
Quickly order your treatment amoxicillin easily for efficient relief.
Need to improve your experience? Consider https://gabitzasgreenkitchen.com/fildena/ for a tasty twist on standard solutions.
Quality healthcare doesn’t have to break the bank. Discover affordable epilepsy treatment solutions and save on your medication with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-generic-canada/ – prednisone[/URL – .
Quest for savings on HIV treatment ends here; find [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil uk[/URL – for managing your health efficiently.
Searching for the best price on fertility treatments? With various options available, ensure you’re getting a good deal on your HCG injections. Explore now the trazodone and compare to locate the most economical choice for your reproductive health needs.
Research the pros of holistic healing approaches with https://theprettyguineapig.com/topamax/ , known for its cardiac wellness properties.
Quickly acquire your prescription seamlessly through our [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ – propranolol no prescription[/URL – , offering a wide range of health solutions.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for buying with no wait at [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – lasix[/URL – .
To secure holistic wellness options, consider to strattera .
To obtain https://swanpercussion.com/item/doxycycline/ , visit our website.
Understanding the importance of managing stress, one can order [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/mail-order-lasix/ – mail order lasix[/URL – from web stores effortlessly.
MoonGlow Select – Clean visuals and well-laid-out sections make shopping feel natural and easy.
When seeking reliable antifungal treatment, consider checking out [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/levitra-price-at-walmart/ – levitra[/URL – for your health needs.
Rediscover vitality with our cost-effective 10 milligram cialis , the premier solution to enhance your health.
Looking to manage your intestinal issues? Discover the most economic solutions at https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ .
X-plore your options for relief from digestive discomfort by visiting [URL=https://altavillaspa.com/product/slimex/ – slimex in usa[/URL – . Find your remedy virtually with ease.
When seeking [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ – cheap tadalafil pills[/URL – , consider exploring diverse digital markets to obtain economical treatment solutions.
Looking for a way to fight against your condition? hydroxychloroquine price might be the answer you’re seeking. Discover how this drug can aid you today.
Venture online to acquire your essential medications with ease; interested parties can https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ for their healthcare needs.
When looking to treat your gout, purchasing [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/vardenafil/ – vardenafil sale in canada[/URL – offers a convenient solution.
Questioning where to find the best deal on [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – ? Obtain your supply by tapping on the link!
Browse our site for the lowest price on generic kamagra oral jelly vol 1 from canada , ensuring you obtain your prescription swiftly.
Given the fluctuating costs, finding the most affordable option for medication can be a daunting task. Whether you’re looking to treat urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate, https://tv-in-pc.com/flomax/ offers a cost-effective solution.
You can discover the best [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/isotretinoin/ – isotretinoin[/URL – for addressing acne vulgaris via the internet.
I discovered fantastic savings on necessary goods for disaster preparedness. Don’t miss out on these [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone/ – non prescription prednisone[/URL – .
“Quickly find affordable options for your well-being by clicking generic retin a in canada , and get your way to improved health.”
navigating the broad arena of internet drugstores, one often wonders https://winterssolutions.com/parlodel/ . Whether you’re seeking to purchase this specific treatment, guaranteeing a reliable supplier is paramount.
Browse our site to discover [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/amoxicillin-online-no-script/ – 500mg amoxil dose[/URL – , ensuring you get premium antibiotic choices at matchless prices.
Quickly tackle your health concerns with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a lowest price[/URL – , now ready for acquisition online.
When searching for enhanced satisfaction and performance in the bedroom, consider exploring billig pharmacy kaufen , a solution revered for its efficacy.
You can acquire Fildena for your erectile dysfunction needs here: https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ .
Seeking relief from inflammation or arthritis? Discover how [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/retin-a-lowest-price/ – retin a[/URL – can help. Find your options today.
For users in search of proven hair loss treatments, [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/finasteride/ – purchase finasteride without a prescription[/URL – offers crucial insights.
When considering treatment for altitude sickness, opt for known solutions like lady era on internet . Explore purchasing this medication via the web to ensure your journey remains uninterrupted.
Maximize your alertness and cognitive performance with https://swanpercussion.com/item/buying-bentyl-online/ . Whether you’re looking to enhance focus or reduce fatigue, this option delivers reliable results.
Zest your getaway with a trip to the renowned [URL=https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ – celebrex[/URL – , offering an unmatchable experience.
X-ray your options carefully when you consider to secure prescriptions from the web. Explore [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix/ – lasix[/URL – safely and responsibly.
In search of effective lice treatment? Explore our range of options and find buying tadalafil online , the preferred remedy for many.
Get your hands on the lowest-priced https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ for enhancing your intimacy health.
Consult healthcare experts before you purchase [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone 20mg[/URL – to guarantee it’s the optimal solution for your situation.
Just in case you’re looking to save your prescription, consider checking out the buy zithromax for competitive rates.
Seeking the highest quality fertility drug for your treatments? Your search ends here! Obtain your https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ safely and conveniently.
Zealously seeking an affordable solution for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms? Explore our cost-effective options and unlock potential savings with [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/drug/malegra/ – where to buy malegra in ny[/URL – . Discover the way to better health affordably.
Zero in on eye health with the ultimate solution in eye drops: [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/cenforce/ – cenforce[/URL – . Explore a groundbreaking option for managing eye inflammation easily.
Acquiring cheapest tadalista via the web can be an efficient method to ensure you’re getting your prescription easily.
Keeping your health in check is paramount, and accessing affordable medication shouldn’t be a hassle. Secure your heart health with ease by opting for https://phovillages.com/propecia-without-a-prescription/ . Whether you’re looking to purchase cost-effective heart health support, this option ensures you don’t compromise on quality or efficacy.
Hunting for budget-friendly solutions for your health? Discover your best option with our guide to [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/drug/lasix/ – lasix furosemide for sale[/URL – . Explore online, secure the optimal deal for your needs now.
Obtain your [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/pharmacy-prices-for-kamagra/ – kamagra alternative uk[/URL – by securing it through our platform, ensuring you tackle your health needs efficiently.
Revitalize your vitality effortlessly with hydroxychloroquine lowest price , available now for those in search of a reliable remedy to enhance their performance.
Looking for reliable treatment options for female health issues? Find https://jawany.com/cytotec/ , a cost-effective solution for tackling your needs.
People seeking cost-effective options for stroke and heart attack prevention can discover the [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – generic prednisone canada pharmacy[/URL – when they explore internet-based drugstores.
Visit [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ – best price viagra[/URL – to buy your prescription easily.
Optimize your heart health regimen by exploring zithromax , an essential option for those aiming to manage their stroke prevention strategy effectively. With a wide array of choices, acquiring this vital medication virtually has never been easier, ensuring that maintaining your cardiovascular well-being is both accessible and convenient.
Quickly order your antifungal medication https://youngdental.net/pill/viagra-soft-tabs/ with just a click for efficient relief.
Zap high prices with our exclusive [URL=https://lasvegas-nightclubs.com/amoxicillin/ – amoxil tablets order[/URL – , and Snag a course of crucial antibiotics effortlessly via our website.
X-plore your options for alleviating eye discomfort with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ – prednisone las vegas[/URL – . Discover relief for your eyes without requiring a prescription.
X-plore the advantages of controlling gout with pharmacy pill cost , and find out how you can purchase the medication online.
Offering a range of reproductive health solutions, locate substantial savings on your next purchase with https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/nexium/ .
With increasing interest in herbal supplements for wellness, explore your options and buy [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/levitra/ – levitra 10 dose[/URL – for enhanced vitality and health maintenance.
Zero hassle to manage your eye pressure issues with [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/staxyn/ – buy staxyn no prescription[/URL – . Preorder now and feel the change.
Maximize your vitality and stamina with tadalafil , the prime choice for enhancing performance. Explore the decisive alternative for improving your health and confidence seamlessly.
Manage osteoporosis effectively by choosing to https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ . With options abundant, you can procure this bone health medication via the internet.
For individuals seeking enhanced stamina, [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/drug/extra-super-avana/ – pharmacy prices for extra super avana[/URL – offers a cutting-edge solution.
I discovered an amazing source to [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ – where to buy nizagara online[/URL – .
Ensure optimal health with our trusted source for your pharmaceutical needs. Secure your quality drugs online from the comfort of your home. Check out nizagara – buy online for reliable and efficient service.
X-plore your alternatives for altitude sickness prevention with simplicity. Now acquire https://purefmonline.com/product/tadalafil/ , your preferred solution for trekking adventures.
Explore the convenience of securing your essentials with ease; buy [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/trazodone/ – trazodone[/URL – , ensuring your well-being is never on hold.
Explore unbeatable deals on fertility drugs at nizagara in greece , the premier source for enhancing your chances of starting a family.
To guarantee your eye health, looking into https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ could be beneficial. Order effortlessly via the internet.
Manage your health efficiently by choosing to [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – strattera[/URL – , a versatile solution for various conditions. You can Preorder a medication easily on the website, ensuring convenience and discretion.
When looking to manage OCD symptoms, consider exploring [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ – sildenafil[/URL – as a potential remedy.
Experiencing breathing difficulties? Find relief at the asthalin . Buy the medication on the internet for quick symptom control.
Stay informed and ensure optimal health management by visiting https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ to discover insights on handling your anticoagulation therapy.
Join the myriad of satisfied customers who have discovered the ease of acquiring their medication online with [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/pill/ed-sample-pack-2/ – ed sample pack 2 online[/URL – , offering a hassle-free way to obtain your wellness necessities.
Over time, I’ve tried various gambling platforms over the years, and it’s always surprising how often players deposit money without checking proper reviews first. If you’re interested in a detailed look of bonuses, payout speed, and game selection, this write-up cleared things up for me: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s pretty straightforward and points out what you should notice before you start playing. It’s worth your time if you prefer to play safely.
X-plore the options to order clonidine online in Canada, ensuring you choose a dependable source. [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/clonidine/ – clonidine without dr prescription usa[/URL – offers a straightforward method to get your medication.
Your search for Procure asthma medication ends here. Discover budget-friendly options online asthalin .
Purchase the https://recipiy.com/tofranil/ to boost your well-being online.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-uk/ – cialis uk[/URL – , your go-to source for securing potent ED solutions online.
Get your medication for hepatitis B treatment safely and conveniently. cialis 20mg is available via web pharmacies for quick shipment.
Searching for relief from nasal allergies? Obtain your https://purefmonline.com/product/lasix/ with ease. Explore various alternatives to secure purchase this solution easily for prompt relief.
Find budget-friendly solutions for hormone therapy with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – . Purchase top-quality treatments online effortlessly.
Zero hassle to safely acquire your medications online. Click here: [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/viagra/ – pharmacy prices for viagra[/URL – for your well-being solutions.
Obtaining buy generic levitra has never been easier. Now you can acquire this essential medicine from the comfort of your own home.
Access genuine https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tadalista/ easily. Acquire this essential medicine through the web seamlessly.
Looking to acquire Amoxicillin without stepping out? [URL=https://center4family.com/item/amoxicillin-on-line/ – amoxicillin on line[/URL – offers a simple way to get your medication with ease.
Unlock the potential for a better, more fulfilling love life by exploring [URL=https://abbynkas.com/item/herbal-extra-power/ – herbal extra power[/URL – . With a myriad of options available, you can obtain an introductory pack online effortlessly. This small step could dramatically enhance your intimacy and connection.
Experiencing pain? Get ease through finasteride 5mg , your source for managing symptoms.
Facing troubles with high prolactin levels? Discover https://abbynkas.com/item/herbal-extra-power/ , an reliable remedy to control it.
Looking for the ultimate solution to your automotive needs? Look no further! Our [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ – propecia 1 mg tablet cost[/URL – showcases the summit of energy storage technology, ensuring your vehicle runs seamlessly. Discover the change today!
Super clanek! Zkousel jsem Spinmama Casino CZ a musim rict, ze jejich nabidka opravdu stoji za to. Muzete ziskat uvitaci bonus 150 %, bonus bez vkladu, free spiny, cashback, VIP program, turnaje, loterie a promo akce, ktere bavi vsechny hrace. Me nejvice bavi herni souteze a vyherni automaty – ceske casino s top sluzbami. Pokud chcete vyzkouset neco noveho a bezpecneho, rozhodne se podivejte zde: Twitter . Rozhodne to stoji za to a prinese vam spoustu zabavy a vyher.
Spinmama Casino CZ – nejlepsi bonusy a promo akce
Hrajte ve Spinmama Casino CZ: bonusy, turnaje a loterie
Spinmama Casino CZ 2025 – cashback, free spiny a odmeny
03b3f09
Xplore the ease of getting your health supplements with a doctor’s note. Check out [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – price for a 40mg prednisone[/URL – for an effortless buying experience.
Zealously seeking a trusted source to purchase your pharmaceuticals from? Look no further; ciprofloxacin offers a secure, discreet way to order what you need.
Xperiencing baldness can be distressing. Discover solutions at https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/flagyl/ , offering a variety of treatments to rejuvenate your confidence.
Curious about where to locate the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – ? Check out our website for incredible deals on your healthcare needs.
Residing in the Great White North, individuals in search of asthma relief can now seamlessly obtain their requirement via [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – asthalin from canada pharmacy[/URL – .
Now, acquire propecia.com for your healthcare needs.
Discover the best rates for https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ and cut down on your healthcare spendings.
Unlock exceptional health benefits with [URL=https://center4family.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ – prednisone[/URL – , the solution to enhancing your vitality effortlessly.
Struggling with scabies or head lice? Obtain your solution through the web with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/prednisone-5mg/ – prednisone 5mg[/URL – . This easy-to-apply cream provides rapid ease from irritation.
Struggling with allergies? Secure your relief by opting to online propecia no prescription . A simple step can alleviate your symptoms effectively.
Obtaining https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/retin-a-no-prescription/ has never been easier. Now you can acquire this essential medicine from the comfort of your own home.
Maximize your vigour naturally with [URL=https://usctriathlon.com/item/herbal-max-gun-power/ – generic herbal max gun power lowest price[/URL – , an unparalleled option for those seeking to enhance their energy without the need for prescriptions.
Patients seeking relief from persistent inflammatory conditions may find [URL=https://seraamedia.org/propecia-5mg/ – finasteride[/URL – as an effective option.
Prices for essential cardiac care medications can vary; hence, it’s crucial to compare the tadalafil, online to ensure you’re getting a good deal.
Secure your supply of endocrine treatments now at https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ .
Access genuine [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/ – canada cialis black[/URL – easily. Obtain this critical pharmaceutical online seamlessly.
Obtain [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – walmart cialis price[/URL – by searching for deals on the web.
Vexed by persistent anxiety? prednisone overnight offers a solution to soothe your nerves.
Amidst the myriad options for managing pain and inflammation, https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ stand out as a potent solution. Individuals seeking relief can purchase this medication from online pharmacies, offering an easy way to address their symptoms.
To find out the latest [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/kamagra/ – kamagra[/URL – , check out our webpage. Here, you can easily access comprehensive information on prices and stock levels.
Maximize your health outcomes by opting to buy premium medication from [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/sildenafil/ – viagra[/URL – , a trusted source for all your pharmaceutical needs.
A comprehensive guide to securing your prescription at the best value: sildenafil . Explore where to acquire your pharmacy needs at favorable rates.
Understand how to manage attention deficit hyperactivity disorder effectively with https://homegrownscholars.com/item/viagra/ . Explore choices for holistic treatment today.
Just discovered a revolutionary way to attain improved wellness in a night? Explore [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ – vpxl.com[/URL – , your route to feeling revitalized mornings.
Researching affordable solutions for managing your cardiac health? Discover the latest tadalafil 2.5mg and guarantee your health through a trustworthy resource.
Discover how to improve your health with https://phovillages.com/tretinoin/ , available immediately for ordering.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – order amoxil 250 overnight[/URL – is a viable option. Explore obtaining amoxicillin online for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Maximize your journey towards augmented bust size with [URL=https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ – zithromax to buy[/URL – , now available for buying online.
Just realized you need ED medication for your health? No need to fret! You can cost of cialis tablets without hassle and safely.
In search of organic solutions for tension, I discovered https://maker2u.com/item/pristiq/ . This time-honored herb promises ease from modern life’s strain.
Keep allergies at bay with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – , available now. Find respite against year-round allergies promptly.
Future Essentials Marketplace – Smooth interface with modern products that make shopping fun.
Prepare for unforeseen residence emergencies by checking out our thorough guide at [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/product/peni-large/ – peni large non generic[/URL – .
Seek trusted enhancement in your condition with nizagara , available for buying online.
Improve your health and wellness with our exclusive https://monticelloptservices.com/product/tadapox-no-prescription/ , now available. Experience enhanced energy and confidence. Acquire yours immediately.
Having difficulties securing your prescription? Explore [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/generic-amoxil/ – generic amoxil[/URL – for a hassle-free buy.
Understanding the need for convenience, you can now obtain your treatment online with effortlessly. [URL=https://otherbrotherdarryls.com/product/fildena/ – fildena ct 100 mg[/URL – and enjoy quick shipment to your doorstep.
Acquire your generic trazodone online easily via the web.
Seeking to acquire menopause relief treatment? Find your solution with https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-best-price-usa/ , an exceptional choice for enhanced well-being.
Victims of menstrual irregularities can now find relief. Visit our website to buy [URL=https://jawany.com/retin-a/ – order retin a[/URL – , offering a promising remedy for discomfort and imbalance.
Secure your heart rhythm management treatment quickly with low cost propecia . Shop now for expedited delivery.
Facing issues with high prolactin levels? Discover https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/xenical/ , an reliable treatment to manage it.
Navigating treatment options for hereditary angioedema can be overwhelming. However, exploring [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – buy ranitidine no prescription[/URL – could offer vital relief and control over this chronic condition.
Avoid hay fever discomfort with high-quality [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ – price of kamagra[/URL – , offering efficient relief without the expensive tag.
Unlock the potential of antiviral therapy by choosing to purchase celebrex without a prescription . Ensure optimal health outcomes by procuring this crucial treatment through our platform today.
You can discover affordable https://jawany.com/drugs/kamagra/ for treating your nasal allergy symptoms on internet sites.
Have you been in search of a reliable place to buy your medications? Look no further! Our online pharmacy offers a wide variety of pharmaceuticals, including [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – . With us, you can order your meds without hassle from the comfort of your place.
I’ve tested a bunch of casino sites over the years, and it’s always surprising how often users deposit money without verifying anything. If you’re interested in a detailed look of what a casino offers, this guide was really helpful: Telegraph-URL . Visit our links.
It’s very clear and highlights key risks before depositing. Definitely worth a read if you want to avoid common mistakes.
Zealously seeking relief from seasonal allergies? Invest in your relief with [URL=https://markssmokeshop.com/drug/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine super active cheap[/URL – , the go-to option for tackling allergic reactions.
Zillions are seeking reliable treatments for their needs. Now, you can effortlessly acquire furosemide through the internet for top satisfaction.
Finding the right applicators for applying Lumigan can enhance the effectiveness of your treatment. Explore your options and https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ to ensure optimal application and results.
Research indicates that finding the [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – nizagara online yahoo[/URL – can be straightforward with the right advice.
Mitigate menopausal symptoms with amoxil for sale 650 mg , an effective treatment for relieving discomfort.
Discover the most cost-effective options for managing your health with https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ . Whether you’re seeking to buy this essential medication through digital platforms, we offer a wide range of alternatives to meet your needs.
Explore the diverse options to purchase your medications [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – with ease via our protected portal.
Browse for the [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/amoxicillin/ – overnight amoxicillin[/URL – and secure the medication through reliable sources.
Quest for affordable testosterone replacement therapy ends here! Discover the current generic lasix canada price for your remedy right away.
When seeking purchase safe sedative products, consider exploring https://andrealangforddesigns.com/genegra/ as a preferred source.
Facing health issues? Get your [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – quick cialis[/URL – easily right away.
Aiming to enhance your eyelash length and density without stepping out? Now you can effortlessly obtain your beauty goals from the comfort of your home. Purchase your supply of the miracle solution with [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – buy tadalafil uk[/URL – . Elevate your look with ease!
Questioning where to acquire a hair loss treatment? Discover safe, reliable options for finasteride 1mg .
Visit now to uncover the best https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/lasix-100mg/ and economize on your purchase.
The need to purchase medication online has escalated, and with options like [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – , securing your medication is easier than ever.
The Preorder this pill on site [URL=https://ucnewark.com/item/nizagara/ – order nizagara[/URL – ensures your health needs are met with convenience and efficiency.
Considering various options for augmenting your well-being, opting to purchase vpxl no prescription montreal online can be a strategic decision.
Seeking a reliable source to purchase your hair loss treatment? https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ offers a vast range of alternatives for combating hair thinning.
Secure your supply of Dutas-T easily; order it from our certified [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/propecia/ – propecia[/URL – effortlessly.
Keeping your heart rhythm in check is crucial, and with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – shop generic trazodone[/URL – , managing it becomes easier. Whether you’re looking to acquire the essential medication online, it’s vital to consult your healthcare provider to ensure it’s the right fit for your health needs.
For people seeking alleviation from irregularity, strattera xanax presents a reliable solution.
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and find generic solutions at https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ . Purchase this treatment via the web now and commence your journey towards regrowth.
Obtain competitive [URL=https://abbynkas.com/nizagara/ – nizagara fast uk[/URL – by opting to Purchase your prescription online, ensuring you get optimal healthcare support affordably.
Zero discomfort can be your reality; explore the option to buy inflammatory pain solutions via the web with verapamil .
Unlock exceptional deals and discover the https://center4family.com/strattera/ by searching on websites.
Manage your nasal allergies effectively with [URL=https://center4family.com/strattera/ – buying strattera[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to purchase a remedy for periodic allergy symptoms or require a long-term solution, this nasal spray offers alleviation.
Keep your health in prime condition with our all-natural supplement. Order your supplement through our website today and feel the difference! [URL=https://phovillages.com/xenical/ – xenical from canada[/URL –
To guarantee your health’s safety, always select genuine medication. For those looking to acquire antiretroviral treatment, kamagra offers a trustworthy option.
Questioning where to find joint relief? Consider https://swanpercussion.com/item/lasix-online-uk/ for effective support in addressing your joint discomfort.
Quest for the ideal [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/zoloft/ – buy zoloft online with no prescription[/URL – ends here! Uncover the ultimate choice for your needs.
Living in an era where convenience is key, acquiring your medications promptly is vital. For those seeking [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/prednisone-20mg/ – buying prednisone online[/URL – , options are now available online, offering a hassle-free solution to fulfill your needs.
You can discover the best isotretinoin for treating acne vulgaris online.
Looking to boost your wellness naturally? Consider trying out https://elizardbreathspeaks.com/nizagara/ for a versatile solution.
Just discovered your remedy for pimples? Buy Accutane with confidence here: [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ – isotretinoin[/URL – . Say goodbye to stubborn complexions issues now.
Boost your wellness affordably with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/strattera-25mg/ – price of strattera[/URL – , accessible for those seeking exceptional deal.
Explore the benefits and options for treating Alzheimer’s with buy generic tadalista , a venerated solution in managing cognitive decline. Obtain this remedy through our website to potentially elevate quality of life for those affected.
Discover a multitude of options for elevating your wellness journey with a single click at the https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil/ , offering a seamless order experience for your crucial medication online.
To secure [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/propecia/ – usa rx pharmacy propecia generic[/URL – authorization, explore our website today.
Get the premium solution for longer and fuller lashes with our exclusive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/viagra/ – viagra canada[/URL – offer.
Just discovered you can save on your medication with a online generic propecia paypal accepted . Don’t hesitate—seize this chance to reduce your expenses today!
I understand the need for easy options when looking to get medication. For those considering treating their health issues efficiently, exploring https://nwfgenealogy.com/flomax/ offers a vital solution.
Discover stress-relief options with [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cipro/ – generic cipro use[/URL – , your go-to for next-day delivery.
Looking to improve your stamina? Acquire authentic solutions [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil-best-price/ – tadalafil best price[/URL – .
Zero out-of-pocket for your hormone therapy. Grab your nizagara price walmart today! Hassle-free savings on crucial medications.
When seeking relief from pain and inflammation, consider exploring https://brightnights915.com/item/pharmacy/ options to purchase efficient medication on the internet.
When seeking relief from glaucoma, consider the option to [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – nolvadex[/URL – . With a range of possibilities, you can obtain this medication via the internet, conveniently and efficiently.
Purchasing affordable [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/clomid/ – generic clomid[/URL – has never been easier, with numerous alternatives available online. Secure your fertility journey today by opting for the best deal.
Looking to obtain your antiviral treatment? Now, you can purchase buy cheap dapoxetine with just a few clicks.
Discover the simple way to acquire your personal https://andrealangforddesigns.com/sildenafil/ online.
Intentional Picks Market – Very pleasant browsing, everything seems thoughtfully arranged and curated.
When seeking effective treatment for Hepatitis C, explore numerous options available for medication, including [URL=https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ – cost of nizagara 100mg tablets[/URL – , which has shown promising results in various clinical trials.
Discover how flomax 0.2mg can reduce symptoms of an enlarged prostate by exploring our site.
Many patients look for reliable treatment for bacterial infections. Whether you’re fighting skin conditions, respiratory infections, or STIs, https://ipalc.org/doxycycline/ can be an effective treatment.
Check current [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ – sarafem[/URL – for managing your HIV condition.
Planning for an urgent cash boost in the Lone Star State? Explore your options with vidalista.com ; a swift method for your economic requirements.
Visit https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ for an affordable way to manage your well-being. Secure your supply now.
Looking for a cost-effective solution to enhance your performance? Explore the most competitive options by visiting [URL=https://seraamedia.org/celebrex/ – celebrex.com lowest price[/URL – . Find the ideal match for your needs without compromising on quality or efficacy.
Discover the most affordable rates for your cardiovascular wellness needs with [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/vidalista-without-an-rx/ – vidalista non generic[/URL – .
Discover alternative options to control your cholesterol with buy sildalis without prescription , accessible online without a prescription.
Zero delays in your heart rhythm treatment are crucial. Secure your medication without hassle with https://purefmonline.com/buying-prednisone-online/ , ensuring rapid management of your condition.
Researching affordable options for your medical needs? Discover the best deals on [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/ranitidine/ – ranitidine[/URL – via our trusted online marketplace. Don’t let expense be a barrier to your health treatment.
WildRose Goods – Warm and cozy atmosphere, found a few delightful surprises.
For individuals seeking to buy improvement medication, discovering [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra/ – viagra without dr prescription usa[/URL – offers a convenient and discreet method to get their needs.
I’ve uncovered the most affordable way to acquire your medication. Check discount cialis now!
Achieve your optimal height and enhance your wellbeing with genuine https://masseysjewelers.com/tretinoin/ .
Questioning the safety and efficacy of inhaled medications? Ensure to consult a medical professional before opting to procure [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/stromectol/ – stromectol[/URL – online.
Your search for affordable antibiotics ends here; get your amoxil windsor ca via the internet for comprehensive bacterial infection treatment.
Achieve optimal heart health with our product. Explore more at https://purefmonline.com/order-prednisone-online/ .
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – , providing wide-ranging treatment for bacterial infections.
Necessitating a reliable solution for diuretic needs? Find vardenafil , your go-to solution for managing water retention.
Exploring affordable healthcare options? Discover https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ for managing your symptoms cost-effectively.
Managing anxiety can be a challenge, but with the right medication, relief is possible. Those looking to purchase their treatment discreetly can discover a wide variety of options available. For a trusted source, consider [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/viagra/ – viagra fast delivery no prescription[/URL – for your needs.
Harness the power of scent to elevate your mood with our exclusive [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ – tadapox[/URL – . Uncover the unique blend that may enhance your confidence and entice positivity.
X-ray your options for heart arrhythmia treatment without breaking the bank. Find economical solutions and bid adieu to sky-high medical expenses by opting to purchase economically priced cenforce coupon via internet pharmacies.
For those looking to order HCG injections, https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ offers a reliable, secure avenue.
Looking to enhance your vitality? Check out the [URL=https://cassandraplummer.com/ventolin/ – ventolin en ligne[/URL – for a cure to boost your energy.
Unlock access to various HRT solutions and acquire your necessary medications with ease. [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/product/nizagara/ – buy nizagara from mexico[/URL – offers a variety of choices for managing menopausal symptoms.
Having trouble with hair loss? Explore your options and uncover generic solutions at levitra tablets . Order your solution via the web now and begin your journey towards regrowth.
X-plore the myriad benefits of amoxicillin for bacterial infections. Whether you’re seeking to buy for your home medicine cabinet, https://brightnights915.com/item/amoxil/ online can be a seamless process.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/tinidazole/ – tinidazole[/URL – might be your solution. Find out about how it can assist in lessening your symptoms promptly.
A comprehensive guide on how to acquire reliable cancer therapy, including imperative information on [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/modvigil/ – generic modvigil from india[/URL – , to combat myeloma and ovarian cancer efficiently.
Venture no further for your hormonal therapy needs; vpxl offers a variety of options to balance your testosterone levels safely.
Visit https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ today to procure your needed medications. Offering a comprehensive selection of health products, it’s your go-to destination for all your medical needs.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis best price[/URL – , your go-to source for acquiring potent ED remedies virtually.
Discover convenient ways to manage your health by opting to cheap lady era pills . Acquire your prescription effortlessly with just a few clicks.
Just seeking inexpensive options for enhancing your health? Explore https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/tadapox/ for a reliable and efficient option.
Many are looking for effective options for ED, and [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis-5mg/ – cialis 5mg[/URL – offers a credible option.
Quickly obtain the [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/tadalafil-best-price/ – buy cheap tadalafil[/URL – , a trusted source for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
I discovered that many individuals are looking to obtain lasix capsules for sale for their nasal allergies relief.
Harness the power of effective antifungal medication by exploring https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drug/lady-era/ . Secure your health today by obtaining this crucial treatment on the internet.
Visit [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – retail price of prednisone 20 mg[/URL – to obtain your natural kidney support.
Requiring nasal allergy relief? esomeprazole now and enjoy prolonged relief.
Secure your necessary medications without trouble by choosing to buy from https://swanpercussion.com/retin-a-generic-canada/ .
Explore choices for acquiring [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – . Secure your supply from reliable sources online.
With the growing demand for natural nutritional supplements, sildalis uk emerges as a premier choice. Its advantages for well-being are unbeatable.
Looking for an affordable way to treat your health? Explore https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/ventolin/ for a trustworthy solution.
Zipping through the hassle of obtaining your medication, our platform offers an easy solution for those looking to obtain [URL=https://pasfolkensemble.com/product/vardenafil/ – vardenafil online canada[/URL – with no hassle.
Here’s how you could secure nizagara walmart price , available at competitive costs.
Considering the need to acquire medication affordably, finding the https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ becomes essential for patients seeking to treat their conditions effectively without straining financially.
Seeking to acquire hormonal balance medication? Discover your solution with [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/item/doxycycline/ – india drugs doxycycline[/URL – , the best choice for enhanced well-being.
Purchase effective Hepatitis C treatment with [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/generic-trazodone-online/ – 100mgmm trazodone to purchase[/URL – , offering a proven treatment for individuals seeking wellness.
Various healthcare professionals recommend seeking advice on no prescription vpxl for gastrointestinal discomfort to confirm safe and effective relief.
Nab your essential medication: https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ through our secure portal. This vital remedy is now accessible effortlessly.
Zero hassle to get your treatment: [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/retin-a/ – retin a without dr prescription usa[/URL – – order on the web with absolute confidence.
Discover cost-effective options for managing your pain with lasix buy in canada . Whether you’re looking to buy this medication via the internet, we offer a range of choices to meet your needs.
To enhance one’s stamina, consider https://tv-in-pc.com/lasix/ as a reliable choice.
Absolutely alleviate allergies with easy access to [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ – lasipen[/URL – . Obtain your immediate allergy relief via the web without the need for a prescription.
Explore trusted options to buy your prescriptions online with our [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/nizagara/ – nizagara coupons[/URL – source.
Hunting for an affordable solution to boost your fertility? Look no further! vpxl tablets is your go-to option. Whether you’re aiming to purchase this vital hormone, our platform offers the best deals. Perfect for those undergoing fertility treatments or in need of hormone therapy, our product promises efficacy.
Quickly discover your solution for early climax issues with https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/dapoxetine/ , available on site.
Just seeking affordable solutions for enhancing your health? Look into [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – mail order hydroxychloroquine[/URL – for a reliable and efficient alternative.
Looking to improve your energy? Discover trusted options and buy [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ – viagra[/URL – —the solution to overcoming erectile dysfunction.
Questioning where to find relief for seasonal allergies? Look no further! xenical from canada offer relief for sufferers by sneezing, itching, and congestion. Order yours immediately for proven results.
Para aquellos preguntandose https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ , es importante entender que esta hierba se utiliza en la medicina ayurvedica para mejorar la condicion femenina.
Visit our website to uncover the best deals on [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/product/vardenafil/ – cheapest generic vardenafil in uk[/URL – . Purchase your necessary medication easily and at competitive prices.
Looking to enhance your vitality? Check out the [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/prednisone/ – prednisone no prescription[/URL – for the cure to boost your energy.
If you’re in search of relief from hay fever, consider trying pharmacy by check . This antihistamine can assist in easing symptoms like sneezing quickly.
Secure your antiviral medication effortlessly through our platform when you purchase https://myhealthincheck.com/cialis/ .
Procure your [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – effortlessly. Obtain the special blend through the web, ensuring maximum satisfaction and convenience.
Be amazed by the affordability when you explore the stablon walmart price . Find incomparable deals for your vertigo treatment needs right here.
Searching for relief from nasal allergies? Obtain your https://darlenesgiftshop.com/stablon/ with ease. Explore various alternatives to secure acquire this solution conveniently for prompt relief.
Zero hesitation required when searching for ED solutions; purchase [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra-to-buy/ – viagra 50mg[/URL – without hassle.
Unlock exceptional health benefits with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/cipro/ – canadian pharmacy cipro[/URL – , the solution to boosting your health easily.
If you’re seeking a dependable cholesterol-lowering option, consider looking into kamagra , accessible for acquisition right here.
Keep your life energetic and joyful with https://suddenimpactli.com/levitra-online-pharmacy/ , the solution to enhancing your vitality.
Acquire the best health solution at an unbeatable price; explore [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/lasix-brand/ – lasix[/URL – for ideal health outcomes.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – generic cialis at walmart[/URL – – your go-to choice for restoring health.
Your well-being is paramount; hence, always make certain you acquire lowest eriacta prices from trusted sources to sustain your health and vitality efficiently.
Your quest for authentic arrhythmia treatment ends today. Discover our broad assortment of heart medications, including https://tv-in-pc.com/zoloft/ , offered through our website.
Keeping your antiviral medications replenished is essential. For those needing prescription refills, [URL=https://astra-hc.com/drug/non-prescription-cytotec/ – cytotec 100mcg[/URL – could be your go-to resource.
Secure
Purchase your https://swanpercussion.com/item/pharmacy-prices-for-kamagra/ through our platform to ensure you receive quality medication with convenience.
Acquire an crucial pharmaceuticals without hassle [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – where can i buy kamagra using paypal[/URL – .
Boost your well-being and improve your energy effortlessly. Discover how at [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/priligy/ – priligy pills[/URL – .
Gain information into managing hair loss effectively by visiting tadalafil canadian pharmacy , where you can learn about advanced treatment methods.
Quality education is pivotal, and mastering the art of persuasion can be significantly improved by reading https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ . This technique not only enhances your writing skills but also expands your understanding of various viewpoints.
Boost your confidence and revitalize your life with [URL=https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ – buying cialis black[/URL – , available for purchase online.
X-ray your options for wellness supplements and discover how to enhance your health. Order your overnight bentyl via the internet for cost-effective, convenient access.
Just discovered your solution to improved performance: https://spiderguardtek.com/item/cialis-black/ . Purchase immediately for lasting results.
Get your daily dose of wellness with a simple click; [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ – sildenafil[/URL – offers easy access to natural health support directly to your doorstep.
Unlock immediate access to your healthcare needs without a prescription by clicking nizagara online , and buy with confidence.
Visit https://phovillages.com/buy-amoxicillin-uk/ to purchase your medication on the web at incredible prices.
Obtain [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ – flomax 0.2mg[/URL – to manage your heart health. Secure your supply immediately and improve cardiovascular well-being without delay.
Modern Design Picks – Sleek layout with smooth browsing and thoughtfully curated items.
Your search for an effective remedy for premature ejaculation ends here. Order [URL=https://phovillages.com/dapoxetine/ – buy cheap dapoxetine[/URL – , a well-established medication, online.
Optimize your health management by considering to nizagara without a prescription . Procure the treatment via the web for your convenience and well-being.
For those seeking a diverse range of treatments for https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ , checking out our collection is a must.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? [URL=https://wefenceit.com/flomax/ – flomax[/URL – might be the remedy. Explore how it may help in lessening your symptoms effectively.
Browse [URL=https://jawany.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – to discover the best solutions for baldness treatment.
Discover affordable options for managing your anxiety: ventolin inhaler . Select your essential treatment easily in place.
Combat aches effortlessly and economically with the aid of https://brightnights915.com/item/nizagara/ , available for your next buy.
Regarding your need for mood stabilization, reflect on purchasing [URL=https://mnsmiles.com/generic-nizagara-from-india/ – nizagara[/URL – from a reputable source.
Discover affordable options for managing your anxiety: [URL=https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/]symbicort[/URL] . Choose your necessary remedy easily in pharmacy.
Nabbing your essential medical supplies has never been simpler. Acquire unbranded best online perscriptions for retin-a on the web to ensure your health needs are met with quality and affordability.
Get the most favorable https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ online. Secure your health today.
Just found your solution to improved stamina: [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/cialis-black/]cialis black walmart price[/URL] . Purchase now for prolonged results.
Harness significant savings on your next purchase with our exclusive [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/asthalin/ – best asthalin online[/URL – . Acquire your essential treatment without denting your wallet by utilizing this special offer now.
Beat allergies with a click! Discover cost-effective relief by opting to purchase your maxaquin . Say goodbye to allergic reactions effortlessly.
Having trouble with confidence? Explore our options to elevate your well-being. https://phovillages.com/cheap-lasix-pills/ today and commence your journey to improved self-assurance with our dependable solutions.
You can discover effective alleviation for gastrointestinal pain with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/item/propecia/ – cheap propecia tablets for sale[/URL – , available on our site.
Discover excellent alternatives for managing your health issue efficiently with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – . Improve your well-being immediately.
When seeking immediate resolutions, find cytotec for your requirements.
Maximize your health without spending a fortune; obtain your https://cassandraplummer.com/item/xenical/ and maintain optimal physiological health.
Discover the solution to ED with ease. Order [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/viagra/ – wholesalers of viagra[/URL – now and restore the assurance that’s been missing.
Looking to obtain effective anxiety relief? Explore your options and amoxil 1000mg immediately for a more serene tomorrow.
Responsive to your need for cost-effective treatment, discover an affordable solution https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ for managing mountain sickness efficiently.
Improve your health effortlessly by selecting to buy your medications through the web. With just one click on [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/nolvadex/ – nolvadex[/URL – , benefit from ease and quality.
Visit [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ – cheap doxycycline pills[/URL – to get your prescription easily.
Consult your healthcare provider to obtain the most appropriate treatment options. For those considering cost-effective solutions, cytotec is a choice.
Just when you’re looking for budget-friendly solutions to manage your heart health, explore our selection of https://homegrownscholars.com/item/doxycycline/ for prime cardiovascular support.
Thoughtful Interaction Hub – Clean, neat design with easy navigation and a satisfying user experience.
SunrisePeak Showcase – A nice blend of creativity and simplicity, enjoyable to look through today.
Premium Essentials Hub – Wide selection of products, quality feels exceptional and browsing is smooth.
Thoughtful Click Picks – Well-laid-out content and intuitive navigation make exploring the site enjoyable.
Premium Quality Hub – Excellent range of products, visually neat and easy to navigate.
I don’t usually write long posts, but this time I thought I’d share one recent session about a lucky run at a casino site.
Recently I’ve been playing at nllalabet.com, mostly in the evenings and with a small bankroll. I joined because the intro bonus looked decent and the terms seemed not too bad compared to many other online casinos. The signup process was no big deal: name and email and email confirmation, then I was able to start playing.
For my opening deposit I stayed conservative and added a small amount into my balance. I went straight to the video slots because that’s what I tend to play. I filtered by most played games and picked a slot with high volatility, hoping for a big hit.
At first it was up and down: small wins and losses and free spins with low payout, and I was ready to log out because my balance was slowly dropping. Then the session flipped: I triggered a strong bonus round with special symbols all over the screen, the slot kept connecting wins and the multiplier skyrocketed my balance to a new high. For me it was a very good hit compared to my regular sessions.
I didn’t keep spinning forever; after a few more test spins I decided to cash out and send a cashout. The withdrawal process was nothing unusual: the casino asked me to verify my account with standard documents. I sent everything within an hour, and the verification was confirmed without problems. After that the money was processed to my wallet and I got it within a reasonable time.
I’m not saying this casino is a miracle, and of course you can also run bad, but in this case my experience was positive overall: clear terms, normal support and no payout drama. This is not a promise you’ll win: gambling always involves risk, so only play with spare money and don’t rely on it as income.
startanewjourney – Helps you begin each day with purpose and clarity.
Looking to boost your well-being? Find out about how to secure your needs without hassle with [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – .
Visit our online pharmacy to buy viagra 25 prices , ensuring you acquire your treatment promptly.
Zestfully boost your fertility chances with trusted treatments. Discover solutions at https://bluemooncafedothan.com/drug/fildena/ .
Visit here to obtain your [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/pharmacy/ – pharmacy price at walmart[/URL – safely and easily for all your needs.
Zeroing in on options for enhanced male vitality? Discover a safe way [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ – canada pharmacy lasix online[/URL – .
Ensure optimal wellness and enhance your health with a powerful solution. Discover how to procure finasteride on line easily today.
X-plore cost-effective healthcare options; https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ for managing the condition with ease.
Visit [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/cytotec/ – buy cytotec w not prescription[/URL – for comprehensive insights on utilizing this medication responsibly.
Your quest for a budget-friendly, dependable solution ends here: [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/doxycycline/ – generic for doxycycline[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to purchase this medication online, you’ll find that its potency in treating a wide range of infections makes it a prime choice.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Explore cialis orders online – your go-to solution for restoring health.
Discover natural solutions for improving your vitality with https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ .
Venture into optimal health management by choosing to procure your [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/item/amoxil/ – amoxil[/URL – through reliable digital sources, ensuring a seamless experience in boosting your well-being.
problemresolver – Helps tackle issues with faster and more effective strategies.
“Get the best deal on eye treatment when you acquire [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ – generic cytotec by phone[/URL – . Protect your vision with our leading solution now.”
Seeking relief from BPH symptoms? Explore your options with flomax , a remedy for alleviating urinary symptoms.
Battle premature ejaculation with https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ , a proven solution. Acquire your treatment easily and restore control.
Regain your vitality with a unique solution; [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/dapoxetine/ – dapoxetine 60mg[/URL – is available for acquisition. It’s your chance to reclaim your well-being with ease.
If you’re seeking a solution to allergic reactions, consider trying [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 200mg[/URL – . This treatment can help in easing signs like sneezing effectively.
Interested in managing your hypertension or ADHD symptoms? Explore your options and canada clonidine here. Instantly obtain your treatment online with ease.
Ensure you secure your https://livinlifepc.com/drugs/hydroxychloroquine/ with assurance for malaria prevention.
Yearning for an affordable solution to manage eye inflammation? Look no further! Find the [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-2-5mg/ – cialis[/URL – here to ease your symptoms efficiently.
Explore options to obtain [URL=https://sci-ed.org/panmycin/ – generic panmycin[/URL – , offering a convenient way to get your medication without leaving home.
Purchase
Just discover the best https://chitwantigercamp.com/tadalafil/ , easing your wellness routine. Explore options that boost your experience today.
Looking for more affordable medication options? Explore [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/ – ventolin[/URL – for cost-effective solutions to your healthcare needs.
Unlock the potential of antiviral therapy by choosing to [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/kamagra/ – kamagra cost[/URL – . Ensure optimal health outcomes by securing this crucial treatment via our site today.
Explore efficient solutions to enhance your wellness; propecia without dr prescription is your go-to alternative. Secure an easy pathway to health improvement without leaving home.
Visit https://purefmonline.com/retin-a-for-sale-overnight/ to buy your medication effortlessly.
X-plore ophthalmic treatments with cutting-edge solutions. Purchase [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/buying-lasix/ – lasix without dr prescription[/URL – via the internet for controlling glaucoma effectively.
Just unveiled: [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/item/super-active-pack-20/ – super active pack 20 online no script[/URL – offers a revolutionary solution for hair loss. Now, you can purchase reliable treatment without leaving the comfort of your home.
Just in quest of a safe way to get finpecia without a prescription? Our reliable platform offers a hassle-free solution. Click discount nizagara to learn more.
X-plore the myriad of options to enhance your fitness routine with our exceptional product available for acquisition overnight at https://the7upexperience.com/item/nizagara/ .
Cut costs on your medication purchases! Find unbeatable discounts on [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/product/prednisone/ – prednisone non generic[/URL – . Order now and save substantially on your medical expenses.
Visit compra doxycycline en espana to get your prescription easily.
When seeking reliable and effective therapy for schizophrenia, consider exploring options to purchase https://griffindtc.com/priligy-60mg/ from accredited websites.
thinkcreativelynow – Helps spark imagination and explore new innovative thoughts.
Struggling with menopausal symptoms? Discover relief with [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil online[/URL – . Our pharmacy offers a safe way to order your treatment on the web.
Discover affordable alternatives to the brand-name medication with amoxicillin , supplying wide-ranging treatment for bacterial infections.
Research suggests that for those seeking bacterial infection treatment, https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/amoxil/ is a viable option. Explore obtaining this treatment through online outlets for a convenient and effective solution to your health concerns.
Securing [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady-era.com canada[/URL – can be a breeze when you know where to look.
Many are in search of reliable treatments for scabies and lice. Discover how cialis 20 mg prices can be your solution.
Xperience enhanced energy for anyone looking for solutions. Discover your path to a better life via https://seraamedia.org/cialis-uk/ , ensuring optimal results and happiness.
For individuals seeking to obtain hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous websites offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to make sure safety and authenticity. [URL=https://purefmonline.com/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine walmart price[/URL – offers a comprehensive guide on how to safely order this medication, alongside vital information on its application.
Keep your vitality high and performance unmatched; obtain propranolol price for unparalleled endurance and satisfaction, enhancing your health.
Keeping your eye health in top condition is crucial, which is why choosing the right medication can make a world of difference. For those dealing with elevated intraocular pressure or open-angle glaucoma, https://maker2u.com/item/lady-era/ provides a trusted solution. Ensure you consult a healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for your needs.
Authentic Global Hub – Each product feels genuine, and navigating the store is effortless.
Before you decide, explore your options for tranquility with [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/canadian-retin-a/ – canadian retin a[/URL – . With a multitude of options available, opt for your path to peace wisely.
To secure your hormone therapy with ease, go to propecia discount dealers for the cheapest prices. Whether you’re looking to maintain bone density or treat menopausal symptoms, there are alternatives that suit every budget.
When looking to buy allergy relief, consider https://seraamedia.org/item/stromectol/ as your go-to solution for easing allergy symptoms.
Manage your allergies with ease by opting to buy your antihistamines [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/prednisone-20mg/ – prednisone brand[/URL – , offering fast and reliable relief.
Combat discomforts swiftly with [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ – buy levitra w not prescription[/URL – , available for order on the web, securing speedy relief.
Relieve those persistent heart and pain conditions effectively by choosing to order cost of prednisone tablets , the go-to solution for managing your health better.
Optimize your health with natural solutions at https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/cenforce/ . Discover the path to wellness with organic remedies.
A comprehensive guide to obtaining your prescriptions safely: Discover the best place to acquire [URL=https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ – kamagra prices[/URL – . This resource provides essential details on how to guarantee you’re acquiring genuine medication from credible sources.
Unlock exclusive savings on fertility treatments with our [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy[/URL – . Get substantial discounts on your next purchase. Whether you’re aiming to begin a family or need continued support, our promotions provide economical options for everyone.
When seeking effective solutions for HIV management, hydroxychloroquine 200mg offers a broad selection of data.
Quickly order your treatment via the web with https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra/ , ensuring a straightforward procedure.
Manage your chronic dry eye effectively with [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ – cialis without prescription[/URL – . Explore our collection and discover alleviation for your condition.
long range thinking – Encourages stepping back and planning for outcomes that mature over time.
Keep your nights vibrant without interruptions. Secure your solution with [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ – generic lasipen uk[/URL – , available now. Purchase without hassle on our site and enjoy confidential delivery.
“Quickly uncover savings on your next purchase with misoprostol . Slash prices effortlessly on crucial medication.”
Obtain your https://purefmonline.com/kamagra-50mg/ effortlessly today. Whether you’re hunting to acquire, our portal ensures a straightforward process.
Variety in your healthcare options matters; thus, discover our top-rated [URL=https://brightnights915.com/drugs/lasix/ – lasix 100mg[/URL – to enhance your well-being.
Obtain alleviation from seasonal allergies with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – purchase celebrex without a prescription[/URL – , accessible now. This nasal spray can help in diminishing your symptoms.
Keep your intimate life vibrant and spontaneous; acquire overnight viagra without prescription to enhance your experiences right away.
Experiencing unexpected gout flare-ups? Find out how https://frankfortamerican.com/sarafem/ can aid in controlling your discomfort.
Keep informed on hydroxychloroquine benefits and guidelines by visiting [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine for sale canada[/URL – for detailed insights and updates.
Refined Everyday Picks – Items shipped promptly, packaging careful, overall a smooth experience.
Quietly seek cost-effective healthcare alternatives? Uncover your solution with [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/celebrex/ – celebrex kaufen rezept[/URL – , and experience considerable savings on prescriptions.
Having trouble finding a reliable source for your antibiotic needs? Your search ends here. Get low cost amoxicillin safely and swiftly.
Your quest for a cost-effective solution to hair loss ends today! Explore a wide variety of options and secure your supply of https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ . Don’t let thinning hair dictate your confidence any longer; take your chance right away.
People seeking hypertension control options can examine a range of drugs, including [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – purchase clonidine[/URL – for efficient control.
Save on allergy relief by exploring our savings on [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/product/levitra-on-line/ – buy levitra w not prescription[/URL – , allowing you to tackle symptoms affordably.
Maximize your savings on osteoporosis treatment by searching for the vidalista drug name . Discover affordable solutions today.
To acquire https://swanpercussion.com/prednisone-40mg/ , look into our credible source to ensure safety and authenticity.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by visiting our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Find [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-10mg/ – 10 mg cialis uk[/URL – to enhance your vitality efficiently and safely.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a challenging condition, but with modern treatments, managing it has become easier. Explore [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – , a budget-friendly and effective option for enhancing your well-being.
Procure your antiviral medication with a ventolin information , ensuring cost-effectiveness.
Looking to boost your wellness naturally? Consider checking out https://mypurelifefoods.com/drug/lasix/ for a holistic method.
To secure your health without straining your budget, consider [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – lowest price tadalafil[/URL – as an effective alternative to pricier medications.
Ideas Made Simple – A clear and manageable way to explore creativity and innovation.
Optimize your health and wellness journey by exploring our comprehensive selection of affordable treatment options. Find [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/cialis-capsules-for-sale/ – generic cialis canada[/URL – to improve your vitality efficiently and confidently.
X-ray results showing enlarged prostate? flomax 0.2mg might be the remedy. Find out about how it may help in reducing your symptoms efficiently.
X-plore methods to get https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ without losing efficacy. Uncover cost-effective solutions for your healthcare needs.
Looking for a way to control your symptoms? Explore your options and buy [URL=https://hip-hope.com/item/lasix/ – lasix schottland[/URL – with ease.
Obtaining Clomid at the best prices is now possible. Visit our website to order your supply of Clomid for ovulation induction. [URL=https://embcselma.org/product/clomid/ – clomid capsules[/URL – today!
Explore
Quickly obtain your https://griffindtc.com/priligy-60mg/ via our online platform, ensuring a stress-free experience.
Just in case you’re looking to save your prescription, consider checking out the [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/pharmacy/ – pharmacy.com lowest price[/URL – for competitive rates.
A comprehensive guide to purchasing your prescriptions safely: Discover the best place to acquire [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/vidalista/ – vidalista online no script[/URL – . This resource provides essential data on how to guarantee you’re receiving genuine medication from reputable sources.
Rediscover control over your cardiac well-being with amoxicillin , the preeminent destination for securing your prescriptions on the internet.
Battling dizziness or nausea? https://jawany.com/amoxil/ today to Ease your symptoms quickly and efficiently.
Relieve allergic reactions effortlessly with [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ – prednisone for dogs without doctor permi…[/URL – . Get affordable relief right now.
Discover excellent choices for managing your health issue efficiently with [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Improve your health today.
Acquiring new zealand pharmacies fildena has never been easier. Rummage for your path to wellness by utilizing a reliable solution.
Just released: Secure your supply of https://masseysjewelers.com/drugs/lowest-isotretinoin-prices/ . Obtain your drug effortlessly from the comfort of your home.
Now, locate [URL=https://phovillages.com/generic-priligy-lowest-price/ – generic drug for priligy[/URL – by exploring our platform. Secure your optimal price now.
Considering urgent antibiotic needs, acquiring doxycycline 100mg through the internet provides a rapid solution.
Harnessing the power of the internet, you can now acquire your medications with ease and affordability. Don’t miss the opportunity to buy https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ , a choice for managing your health more effectively.
Keep your eyesight in optimal condition with the [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/nizagara-no-prescription/ – nizagara[/URL – . Acquiring these essential tools online ensures you get unmatched quality for maintaining your ocular health.
Protect your well-being by learning on the most recent wellness advice and trends at our [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/pill/fildena/ – fildena without prescription[/URL – website.
Visit our priligy 90mg page to purchase effective heartburn relief. Easily order your medication online.
Having unexpected expenses? Secure a https://tv-in-pc.com/kamagra/ right away to take care of your financial necessities.
Seeking options for treating chronic hepatitis B? Explore [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drugs/buying-hydroxychloroquine/ – hydroxychloroquine 200mg[/URL – —a proven solution. Opt for acquiring this vital medication through an online pharmacy to control your health effectively.
Navigate Smarter Options – A clean concept designed to help users discover optimal solutions.
Secure your [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/prednisone-online-canada/ – prednisone online canada[/URL – purchase on the internet for fast delivery.
When looking for advanced performance and satisfaction in the bedroom, consider exploring best generic kamagra online , an option revered for its efficacy.
Zero hassle to securely purchase your medications on the internet. Click here: https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ for your health options.
Discover secure ways to purchase your medications with ease; [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/product/viagra-75mg/ – india drugs generic viagra 75mg[/URL – offers a trusted solution for boosting your wellness.
Design World Picks – Great assortment of designs, layout makes finding items effortless.
Unsure where to purchase effective migraine solutions? Visit [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – canada retin a[/URL – for a trusted option.
A Pioneering Approach to Well-being is Here! Now, explore a wide range of healthcare options solely at buy retin a w not prescription .
Quest for affordable testosterone replacement therapy ends here! Discover the latest https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/tadalafil/ for your treatment now.
Unlock exclusive savings on fertility treatments with our [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/retin-a/ – retin a on internet[/URL – . Get major discounts on your next purchase. Whether you’re looking to begin a family or require continued support, our offers provide economical options for everyone.
Zero in on affordability and convenience with [URL=https://seraamedia.org/cialis-without-dr-prescription-usa/ – cost of cialis tablets[/URL – , your go-to source for purchasing effective ED solutions virtually.
In need of an antibiotic treatment? Get your dose easily doxycycline 100mg . Available online, ensuring you have access to the medication swiftly.
Discover innovative treatments for your health. Obtain https://jawany.com/amoxil/ from trusted sources virtually.
Acquiring [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ – furosemide without dr prescription usa[/URL – has never been easier; Secure this essential medication via the internet with just a single click.
Quest for savings on HIV treatment ends here; find [URL=https://swanpercussion.com/viagra/ – viagra[/URL – for managing your health efficiently.
Optimize your health with the treatment everyone’s talking about, on tadalafil . This powerful formulation can revolutionize your wellbeing.
Looking for a straightforward way to obtain your medication? Now you can purchase https://columbiainnastoria.com/lasix/ virtually, ensuring you secure your treatment promptly.
Keep your eye health in top condition with our advanced treatment options. Discover more and get your supply [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/nexium/ – nexium[/URL – promptly.
Quickly obtain your prescription with ease by opting to [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/zoloft/ – zoloft commercial[/URL – , a streamlined method to manage your health.
Zero hassle to safely obtain your prescriptions on the internet. Click here: viagra 75mg for your health solutions.
When seeking natural remedies for digestive health, consider exploring https://phovillages.com/cialis-without-prescription/ . Available for ordering through various online stores, this natural product may offer beneficial effects for your health.
Yes, if you’re looking to purchase [URL=https://skywaycorvetteclub.com/prednisone/ – prednisone[/URL – , contemplate exploring our dependable resource.
Discover how you can get your [URL=https://masseysjewelers.com/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil lowest price[/URL – without hassle and start a new chapter in your health.
Obtain your isotretinoin effortlessly. Acquire this essential skin care solution without hassle.
New to the market? Discover your pathway to wellbeing with https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ . Secure this innovative treatment now for your medical needs.
Facing the issue of dry eyes? Locate the solution online with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/pharmacy/ – pharmacy generic canada[/URL – . Secure your remedy now for ease.
I understand the need for convenient choices when looking to purchase medication. For those considering treating their health conditions efficiently, considering [URL=https://purefmonline.com/product/flomax-uk/ – tamsulosin[/URL – presents a vital solution.
Having gastrointestinal discomfort? Discover relief through bentyl without a doctors prescription , a trusted medication. Obtain it on the web for speedy alleviation from stomach aches.
Discover a trusted way to boost your wellbeing: https://kristinbwright.com/priligy/ .
Struggling with hypertension or angina? Explore how [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/bentyl/ – bentyl generic[/URL – could be the solution to controlling these conditions.
A safe method to manage your health: [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/cytotec/ – cytotec 100mcg[/URL – . Browse us to discover varied solutions for your wellbeing.
Xperience unmatched joy with our unique scent. Elevate your mood effortlessly by opting to tadalafil on line . Whether seeking to purchase an fragrance from the comfort of your home, it’s never been easier to enhance your wellbeing and radiate confidence.
Improve your health by opting for treatments that offer reliability and affordability. Buy https://homegrownscholars.com/item/buy-levitra-no-prescription/ to ensure your well-being without compromising on quality.
Just seeking relief from chronic heartburn? Find out about [URL=https://nwfgenealogy.com/online-propecia-no-prescription/ – propecia[/URL – for treatments that might help.
Keep your health in check by considering purchasing reliable [URL=https://jawany.com/priligy/ – offical priligy[/URL – , known for its effectiveness in medical treatments.
Reduce your cholesterol levels conveniently by opting to procure your medication through generic nizagara tablets , securing dependable and swift delivery to your doorstep.
X-pand your health options without leaving home; acquire your medications with ease. https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/tadalafil/ today and control your health effectively.
The benefits of incorporating [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/drugs/ventolin/ – ventolin non generic[/URL – into your daily routine are numerous, including improving your body’s resilience to stress, aiding restful sleep, and improving overall well-being.
Unsure where to purchase your medication? For those looking to increase their health, [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/cialis-20mg/ – 20 cialis india[/URL – offers a wide range of choices.
A thorough range of solutions for vision support is accessible at our reputable prednisone price at walmart .
Absolutely, ascertain the https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/nizagara/ through checking multiple online drugstores.
Patients seeking affordable solutions for their medication can find [URL=https://tv-in-pc.com/tadalafil/ – discount tadalafil[/URL – to discover cost-effective options for their healthcare needs.
efficientsolutions – Supports discovering fast, reliable ways to resolve issues.
Your search for affordable and reliable Etizolam ends here with [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/product/lady-era/ – lady era best price usa[/URL – . Whether you’re looking to obtain anticonvulsant benefits, our online pharmacy offers unparalleled cost-effectiveness.
Discover trustworthy solutions for female health issues with price on 100 lasix , available to purchase on the internet.
View the latest costs for managing your BPH symptoms with https://swanpercussion.com/item/flomax/ , and explore multiple options to better your quality of life.
Secure significant savings on your prescription with [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/item/deetor/ – buy deetor online cheap[/URL – . These coupons are vital for handling treatment expenses.
Explore the convenience of obtaining your medication without leaving home. For those in need, [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ – clonidine cheap[/URL – provides a streamlined solution. Acquire your medicine with simplicity via our online platform.
To discover the best deals on pain relief, click here: buy levitra no prescription . Whether you require a quick solution, our website offers numerous options of choices.
Discover how to secure your prescriptions without hassle with https://tv-in-pc.com/viagra-75mg/ , ensuring privacy and convenience.
Looking for a way to control your symptoms? Explore your options and buy [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/nexium/ – buy nexium without prescription[/URL – virtually.
I found a way to get [URL=https://phovillages.com/prednisone-coupon/ – price of prednisone[/URL – , making it more straightforward for everyone to access essential nutritional supplements.
Zero in on health improvements; acquire the tadalafil 5mg option easily for enhanced wellness.
Before making a decision, discover https://suddenimpactli.com/tadalafil-capsules/ and compare prices to guarantee you get the optimum deal for your heart health medication.
X-plore the myriad options to acquire your medications affordably; our portal allows you to [URL=https://jawany.com/prednisone-10mg/ – prednisone[/URL – effortlessly. This opportunity enables individuals seeking to order their medications without straining their budget.
Discover excellent options for managing your health issue efficiently with [URL=https://brightnights915.com/item/cialis/ – cialis[/URL – . Improve your well-being now.
Keep your nights vibrant without interruptions. Obtain your solution with cialis , available now. Order without hassle on our site and enjoy discrete delivery.
Given the various options for hormone therapy, those looking to alleviate menopausal symptoms might consider checking https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ . With several purchase avenues, selecting the appropriate product on the web can provide alleviation efficiently.
Explore the benefits and options for treating Alzheimer’s with [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/zithromax/ – zithromax[/URL – , a venerated solution in managing cognitive decline. Obtain this treatment through our website to potentially improve quality of life for those affected.
Having difficulty with an enlarged prostate? Learn how generic flomax canada can ease symptoms and restore your comfort.
Visit our webpage to purchase your essential medication. https://sadlerland.com/product/tadalista/ seamlessly, for managing your health needs.
The need to obtain pharmaceuticals without leaving home has never been more vital. Now, you can conveniently order your [URL=https://chitwantigercamp.com/prednisone-walmart-price/ – prednisone 40mg[/URL – with just a few clicks.
Considering various options for motion sickness relief? Discover the bentyl to effectively manage your symptoms. Explore other solutions now.
Here’s how you can manage your mood swings effectively: https://planbmfg.com/product/zithromax/ are available for purchase. With a wide variety of options, you can order your mood stabilizer online.
Nourish your vitality effortlessly with [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/item/nizagara/ – bangkok nizagara[/URL – , a zenith of wellness. Obtain your powerful solution online.
Ready to find out the most economical prices for your antifungal needs? Look no further. Discover the viagra 75mg and secure your health today without breaking the bank.
Looking for inexpensive options? Discover the https://nwfgenealogy.com/pill/lasix/ easily.
Acquire [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/levitra-20mg/ – levitra 20mg[/URL – effortlessly for controlling your condition.
Procure your prescription with convenience and confidentiality; cialis black walmart price directly through our secure platform.
Keep informed on hydroxychloroquine benefits and guidelines by visiting https://shilpaotc.com/hydroxychloroquine-without-dr-prescription/ for detailed insights and updates.
resettoday – Guides you to refresh your mind and approach the day positively.
Procure your heartburn medication without exiting your home; visit [URL=https://thank-you-note-examples-and-tips.com/retin-a/ – retin a[/URL – for fast relief.
Before making any health decisions, consult your doctor, but if you’re looking to obtain lipid-lowering medication, consider visiting pharmacy prices for prednisone for a safe option.
Boost your health with quick access to antiviral treatment by visiting https://fontanellabenevento.com/product/lasipen/ – the one-stop solution for speedy healing.
Secure your health by choosing to [URL=https://hip-hope.com/prednisone/ – generic prednisone at walmart[/URL – on this platform, ensuring fast and reliable access to your essential medication.
You can enhance your vitality by opting to acquire [URL=https://recipiy.com/retin-a/ – retin-a[/URL – , available now.
Before making any decisions, learn about your options for treating hair loss. buy ed sample pack 2 offers a convenient way to gain access to this therapy.
Achieve thicker hair with the https://damcf.org/nizagara/ , a leading solution for thinning hair.
Need to enhance your experience? Look into [URL=https://ipalc.org/nizagara/ – cost of nizagara 100mg tablets[/URL – for a delightful twist on traditional treatments.
creativeideashub – Encourages discovering new ideas and unlocking imaginative thinking.
Xperience fast-acting alleviation from allergy-season allergies with [URL=https://suddenimpactli.com/drugs/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil canada[/URL – , your go-to cure for remaining sniffle-free throughout high-pollen seasons.
When looking to obtain tadalafil , consider multiple platforms supplying it online.
Treat your skin ailments effortlessly by opting to purchase https://youngdental.net/item/acticin/ .
Many are looking for effective options for ED, and [URL=https://jawany.com/drugs/cialis/ – cialis 10mg[/URL – offers a proven option.
Reduce your cholesterol effectively with [URL=https://embcselma.org/item/levitra/ – generic levitra without perscription 10 pills[/URL – , offering a trustworthy way to secure your medication.
You can buy your necessary medication non prescription cytotec with simplicity.
Quickly obtain the https://cassandraplummer.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ , a trusted source for managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Explore budget-friendly options for your healthcare by choosing to buy [URL=https://homegrownscholars.com/item/tadalafil/ – generic tadalafil from canada online[/URL – .
Visit amoxil dosage 650 mg to buy your antibiotics on the internet at fantastic prices.
Discover how to boost your performance effortlessly with https://jawany.com/buy-prednisone-no-prescription/ , on sale in our web store.
Keep your well-being at its peak: uncover safe and dependable options to acquire [URL=https://phovillages.com/viagra-75mg/ – canada viagra[/URL – .